Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Psoriasis: Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Identification of the Research Question
2.2. Study Selection Process
2.3. Data Extraction
3. Results and Discussion
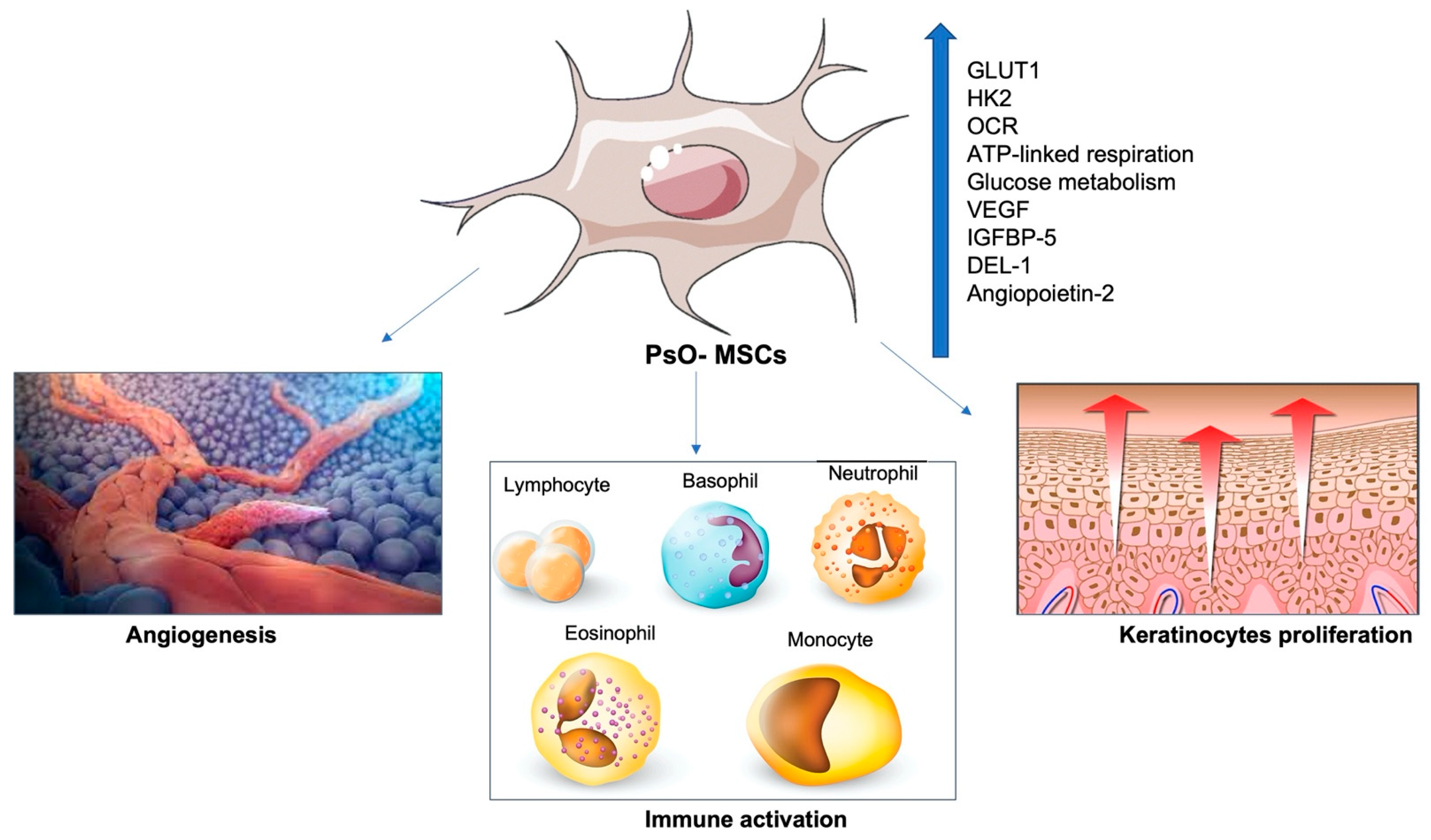
3.1. Interaction between PsO-MSCs and Inflammatory Microenvironment in Psoriasis
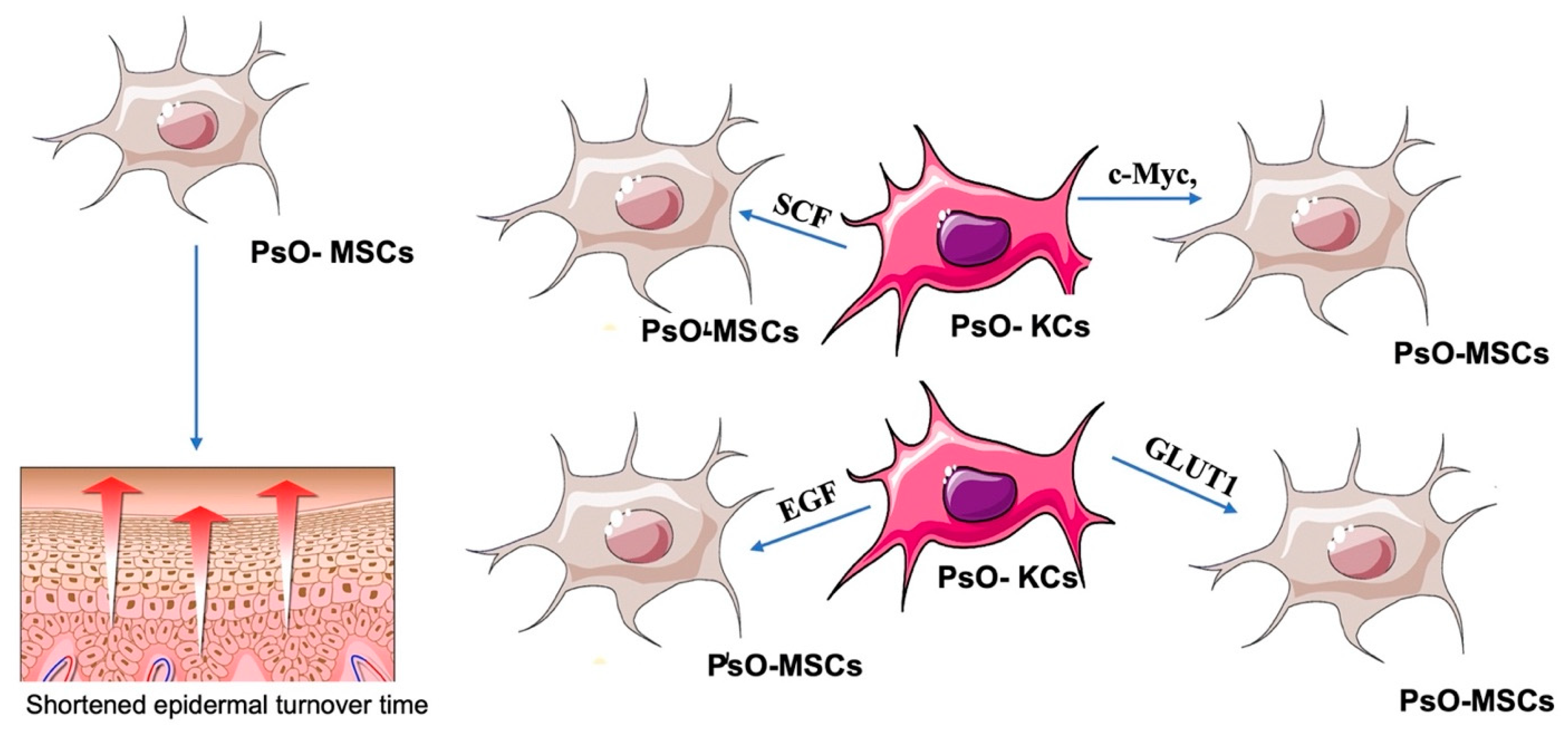
3.1.1. Relationships between PsO-MSCs and Psoriatic Keratinocytes (PsO-KCs)
3.1.2. Effects of PsO-MSCs on the Vascularization of Psoriatic Lesions
3.1.3. Relationships between PsO-MSCs and Immune Cells
3.1.4. PsO-MSCs and Micro-RNAs (miRNAs)
3.2. The Immunomodulatory Effect of “Healthy MSCs” on the Psoriasis Microenvironment
3.2.1. Effects of H-MSCs Administration in Psoriasis
3.2.2. Effects of Immunomodulatory Therapies on PsO-MSCs
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michalek, I.M.; Loring, B.; John, S.M. A systematic review of worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Derm. Venereol. 2017, 31, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackstone, B.; Patel, R.; Bewley, A. Assessing and Improving Psychological Well-Being in Psoriasis: Considerations for the Clinician. Psoriasis 2022, 12, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Robertson, A.D.; Wu, J.; Schupp, C.; Lebwohl, M.G. Undertreatment, treatment trends, and treatment dissatisfaction among patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in the United States: Findings from the National Psoriasis Foundation surveys, 2003–2011. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisondi, P.; Cazzaniga, S.; Chimenti, S.; Maccarone, M.; Picardo, M.; Girolomoni, G.; Naldi, L. Psocare Study Group. Latent tuberculosis infection in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: Evidence from the Italian Psocare Registry. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardazzi, F.; Magnano, M.; Campanati, A.; Loconsole, F.; Carpentieri, A.; Potenza, C.; Bernardini, N.; Di Lernia, V.; Carrera, C.; Raone, B.; et al. Biologic Therapies in HIV-infected Patients with Psoriasis: An Italian Experience. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 989–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Moroncini, G.; Ganzetti, G.; Pozniak, K.N.; Goteri, G.; Giuliano, A.; Martina, M.; Liberati, G.; Ricotti, F.; Gabrielli, A.; et al. Adalimumab modulates angiogenesis in psoriatic skin. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2013, 11, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, M.G.; Kavanaugh, A.; Armstrong, A.W.; Van Voorhees, A.S. US perspectives in the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Patient and physician results from the population-based multinational assessment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (MAPP) survey. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization Global Report on Psoriasis; World Health Association: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, A.; Jarvis, S.; Boehncke, W.H.; Rajagopalan, M.; Fernández-Peñas, P.; Romiti, R.; Bewley, A.; Vaid, B.; Huneault, L.; Fox, T.; et al. Patient perceptions of clear/almost clear skin in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: Results of the Clear About Psoriasis worldwide survey. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, A.; Tarentini, E.; Benassi, L.; Kaleci, S.; Magnoni, C. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of psoriasis: A comprehensive review. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaculik, C.; Schuster, C.; Bauer, W.; Iram, N.; Pfisterer, K.; Kramer, G.; Reinisch, A.; Strunk, D.; Elbe-Bürger, A. Human dermis harbors distinct mesenchymal stromal cell subsets. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132 Pt 1, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.R.; Kim, E.; Yang, J.; Lee, H.; Hong, S.H.; Woo, H.M.; Park, S.M.; Na, S.; Yang, S.R. Isolation of human dermis derived mesenchymal stem cells using explants culture method: Expansion and phenotypical characterization. Cell Tissue Bank. 2015, 16, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, T.H.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.W.; Kang, K.S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Inflammatory Skin Diseases: Clinical Potential and Mode of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orciani, M.; Campanati, A.; Salvolini, E.; Lucarini, G.; Di Benedetto, G.; Offidani, A.; Di Primio, R. The mesenchymal stem cell profile in psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanati, A.; Orciani, M.; Consales, V.; Lazzarini, R.; Ganzetti, G.; Di Benedetto, G.; Di Primio, R.; Offidani, A. Characterization and profiling of immunomodulatory genes in resident mesenchymal stem cells reflect the Th1-Th17/Th2 imbalance of psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Chang, W.; Peng, A.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, K. Dermal Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Psoriatic Lesions Stimulate HaCaT Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, and Migration via Activating the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Dermatology 2022, 238, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, K. Abnormalities in cytokine secretion from mesenchymal stem cells in psoriatic skin lesions. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2013, 23, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Liang, N.; Cao, Y.; Xing, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, X.; Hou, R.; et al. The effects of human dermal-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the keratinocyte proliferation and apoptosis in psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.F.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.C.; Zhang, K.M. Research Note Mesenchymal stem cells from skin lesions of psoriasis patients promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of HaCaT cells. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 17758–17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, R.; Li, J.; Liang, N.; Xing, J.; Jiao, J.; Chang, W.; Li, X.; et al. Expression and functional regulation of gap junction protein connexin 43 in dermal mesenchymal stem cells from psoriasis patients. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xing, J.; Lu, F.; Chang, W.; Liang, N.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Hou, R.; et al. Psoriatic Dermal-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Keratinocyte Junctions, and Increase Glycolysis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liang, N.N.; Chang, W.J.; Li, J.Q.; Jiao, J.J.; Hou, R.X.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.M. Role of psoriatic keratinocytes in the metabolic reprogramming of dermal mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xing, J.; Li, J.; Hou, R.; Niu, X.; Liu, R.; Jiao, J.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; et al. Dysregulated Dermal Mesenchymal Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation Interfered by Glucose Metabolism in Psoriasis. Int. J. Stem Cells 2021, 14, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Han, Q.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y. Del-1 in Psoriasis Induced the Expression of αvβ3 and α5β1 in Endothelial Cells. Curr. Mol. Med. 2022, 22, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Yan, H.; Niu, X.; Chang, W.; An, P.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; et al. Gene expression profile of dermal mesenchymal stem cells from patients with psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Niu, X.; Hou, R.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, Y. Dermal mesenchymal stem cells promoted adhesion and migration of endothelial cells by integrin in psoriasis. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Chang, W.; Liu, R.; Hou, R.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Expression of pro-angiogenic genes in mesenchymal stem cells derived from dermis of patients with psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, e280–e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Hou, H.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, K. Psoriatic mesenchymal stem cells stimulate the angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. Microvasc. Res. 2021, 136, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Manrreza, M.E.; Bonifaz, L.; Castro-Escamilla, O.; Monroy-García, A.; Cortés-Morales, A.; Hernández-Estévez, E.; Hernández-Cristino, J.; Mayani, H.; Montesinos, J.J. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from the Epidermis and Dermis of Psoriasis Patients: Morphology, Immunophenotype, Differentiation Patterns, and Regulation of T Cell Proliferation. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 4541797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Hou, R.; Li, X.; An, P.; Yin, G.; Zhang, K. Dermal mesenchymal stem cells: A resource of migration-associated function in psoriasis? Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiao, J.; Li, X.; Hou, R.; Li, J.; Niu, X.; Liu, R.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; et al. Immunomodulatory effect of psoriasis-derived dermal mesenchymal stem cells on TH1/TH17 cells. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hou, R.; Niu, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Hao, Z.; Yin, G.; Zhang, K. Comparison of microarray and RNA-Seq analysis of mRNA expression in dermal mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chang, W.; Yang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, K. Levels of miR-31 and its target genes in dermal mesenchymal cells of patients with psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Chang, W.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Dang, E.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Mesenchymal stem cells in psoriatic lesions affect the skin microenvironment through circular RNA. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Chang, W.; Li, J.; Hou, R.; Li, J.; Yin, G.; Li, X.; et al. MiR-155 inhibits TP53INP1 expression leading to enhanced glycolysis of psoriatic mesenchymal stem cells. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2022, 105, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Blasco-Morente, G.; Cuende, N.; Arias-Santiago, S. Mesenchymal stromal cells: Properties and role in management of cutaneous diseases. J. Eur. Acad. Derm. Venereol. 2017, 31, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Li, J.; Niu, X.; Liu, R.; Chang, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Yin, G.; Zhang, K. Stem cells in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 86, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, K. Lymphocyte inhibition is compromised in mesenchymal stem cells from psoriatic skin. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2014, 24, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ren, G.; Cao, G.; Chen, Q.; Shou, P.; Zheng, C.; Du, L.; Han, X.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Q.; et al. miR-155 regulates immune modulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells by targeting TAK1-binding protein 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11074–11079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Orciani, M.; Sorgentoni, G.; Consales, V.; Mattioli Belmonte, M.; Di Primio, R.; Offidani, A. Indirect co-cultures of healthy mesenchymal stem cells restore the physiological phenotypical profile of psoriatic mesenchymal stem cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 193, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Kruszewska, A.; Placek, W.; Maksymowicz, W.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Stem Cells as Potential Candidates for Psoriasis Cell-Replacement Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Costa, L.; Esparza, P.; Landin, M.; Diaz-Rodriguez, P.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Homeostasis and Systemic Diseases: Hypothesis, Evidences, and Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Shi, Y. Current Research and Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Therapy of Autoimmune Diseases. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 14, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Lim, C.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.C.; Ahn, J.Y.; Lee, E.J. Human Embryonic Stem Cells-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce the Symptom of Psoriasis in Imiquimod-Induced Skin Model. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 16, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Peng, J.; Xie, Q.; Xiao, N.; Su, X.; Mei, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dai, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis by Reducing the Production of Type I Interferon (IFN-I) by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells (pDCs). Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 6961052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lai, R.C.; Sim, W.K.; Choo, A.B.H.; Lane, E.B.; Lim, S.K. Topical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Alleviates the Imiquimod Induced Psoriasis-Like Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Shi, P.; Su, D.; Cheng, X.; Yi, W.; Yan, J.; Chen, H.; Cheng, F. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from MSCs Have Immunomodulatory Effects to Enhance Delivery of ASO-210 for Psoriasis Treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 842813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Niu, J.W.; Ning, H.M.; Pan, X.; Li, X.B.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.H.; Hu, L.D.; Sheng, H.X.; Xu, M.; et al. Treatment of Psoriasis with Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, e13–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus, M.M.; Santiago, J.S.; Trinidad, C.V.; See, M.E.; Semon, K.R.; Fernandez, M.O., Jr.; Chung, F.S. Autologous Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for the Treatment of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Case Report. Cell Transplant 2016, 25, 2063–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.G.; Hsu, N.C.; Wang, S.M.; Wang, F.N. Successful Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis with Allogeneic Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Case Study. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2020, 2020, 4617520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Caffarini, M.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Lucarini, G.; Di Vincenzo, M.; Orciani, M.; Offidani, A. The efficacy of in vivo administration of Apremilast on mesenchymal stem cells derived from psoriatic patients. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Orciani, M.; Lazzarini, R.; Ganzetti, G.; Consales, V.; Sorgentoni, G.; Di Primio, R.; Offidani, A. TNF-α inhibitors reduce the pathological Th1 -Th17 /Th2 imbalance in cutaneous mesenchymal stem cells of psoriasis patients. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennie, S.; Soeiro, I.; Dyson, P.J.; Lam, E.W.; Dazzi, F. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T Cells. Blood 2005, 105, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, K.; Ryan, J.M.; Tobin, L.; Murphy, M.J.; Barry, F.P.; Mahon, B.P. Cell contact, prostaglandin E2 and transforming growth factor β1 play non-redundant roles in human mesenchymal stem cell induction of CD4+CD25high forkhead box p3+ regulatory T Cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 156, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nicola, M.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Magni, M.; Milanesi, M.; Longoni, P.D.; Matteucci, P.; Grisanti, S.; Gianni, A.M. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood 2002, 99, 3838–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Pittenger, M.F. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood 2005, 105, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orciani, M.; Campanati, A.; Caffarini, M.; Ganzetti, G.; Consales, V.; Lucarini, G.; Offidani, A.; Di Primio, R. T helper (Th)1, Th17 and Th2 imbalance in mesenchymal stem cells of adult patients with atopic dermatitis: At the origin of the problem. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Jung, W.J.; Pi, J.; Lee, K.H. Psoriasis treatment using minimally manipulated umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 6798–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, G.; Lorenz, M.; Pösel, C.; Maria Riegelsberger, U.; Störbeck, V.; Kamprad, M.; Kranz, A.; Wagner, D.C.; Boltze, J. Transplantation of cryopreserved human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells does not induce sustained recovery after experimental stroke in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antebi, B.; Asher, A.M.; Rodriguez, L.A., 2nd; Moore, R.K.; Mohammadipoor, A.; Cancio, L.C. Cryopreserved mesenchymal stem cells regain functional potency following a 24-h acclimation period. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukomska, B.; Stanaszek, L.; Zuba-Surma, E.; Legosz, P.; Sarzynska, S.; Drela, K. Challenges and Controversies in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9628536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, P.W. Clear Evidence of Safety and Efficacy Is Needed for Stromal Vascular Fraction Products: Commentary on “Arguments for a Different Regulatory Categorization and Framework for Stromal Vascular Fraction”. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diotallevi, F.; Di Vincenzo, M.; Martina, E.; Radi, G.; Lariccia, V.; Offidani, A.; Orciani, M.; Campanati, A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Psoriasis: Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315080
Diotallevi F, Di Vincenzo M, Martina E, Radi G, Lariccia V, Offidani A, Orciani M, Campanati A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Psoriasis: Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):15080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315080
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiotallevi, Federico, Mariangela Di Vincenzo, Emanuela Martina, Giulia Radi, Vincenzo Lariccia, Annamaria Offidani, Monia Orciani, and Anna Campanati. 2022. "Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Psoriasis: Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 15080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315080
APA StyleDiotallevi, F., Di Vincenzo, M., Martina, E., Radi, G., Lariccia, V., Offidani, A., Orciani, M., & Campanati, A. (2022). Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Psoriasis: Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 15080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315080






