Screening and Molecular Mechanisms of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. ACE-Inhibitory Activity and Antihypertensive Effect of GLP
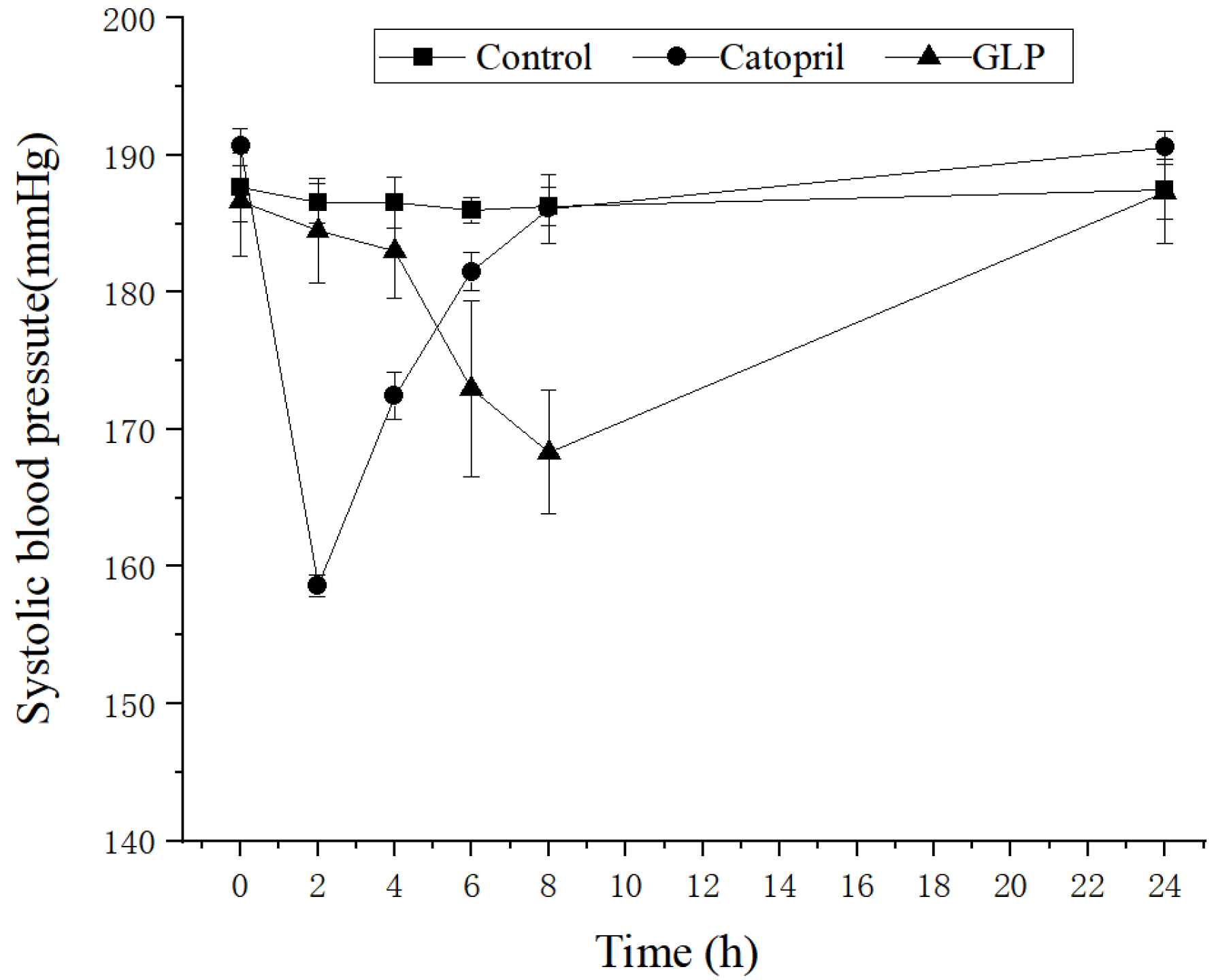
2.2. Antihypertensive Activity of the GLP in SHR
2.3. Identification and Virtual Screening of the ACE-Inhibitory Peptide from GLP
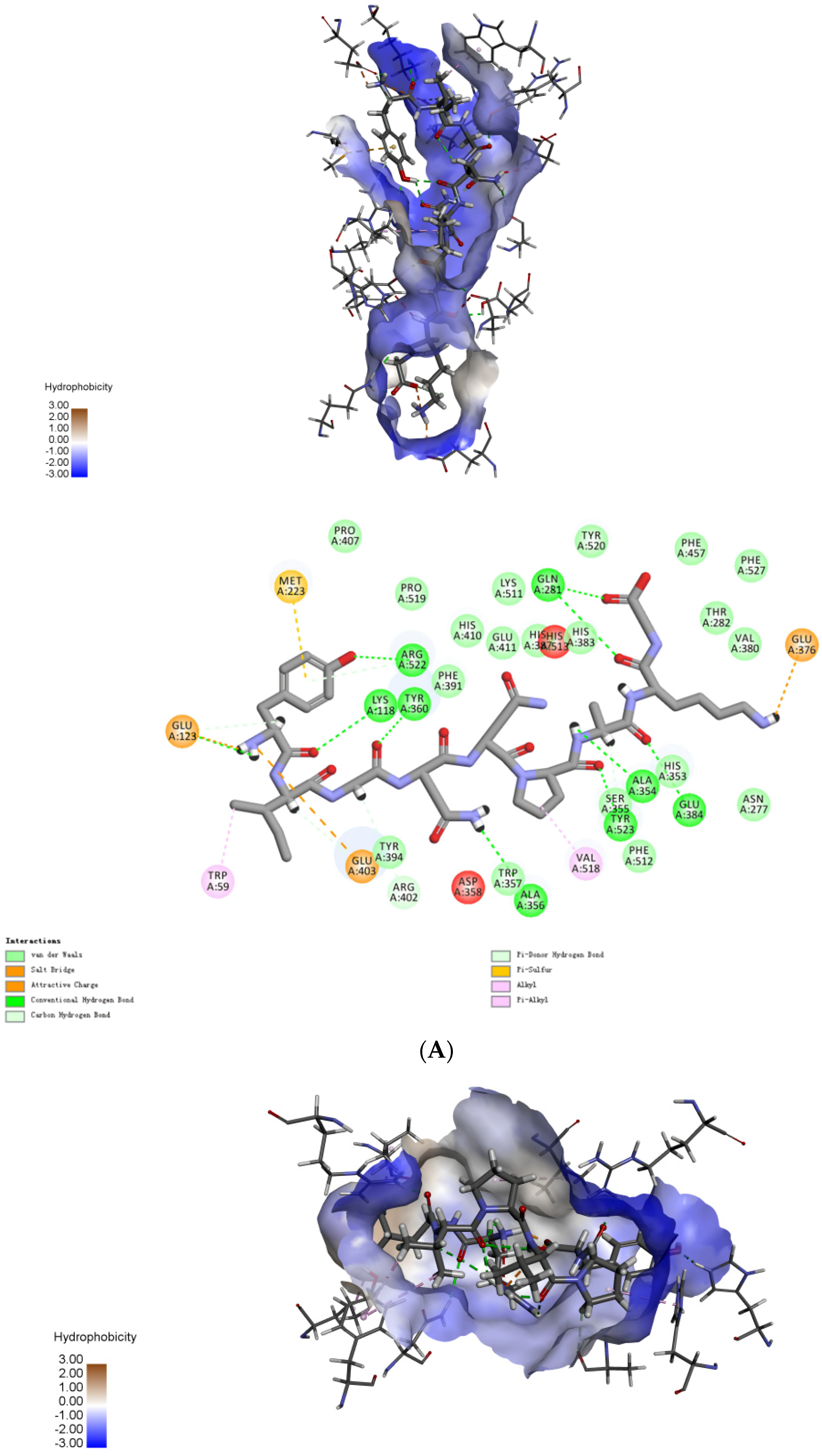
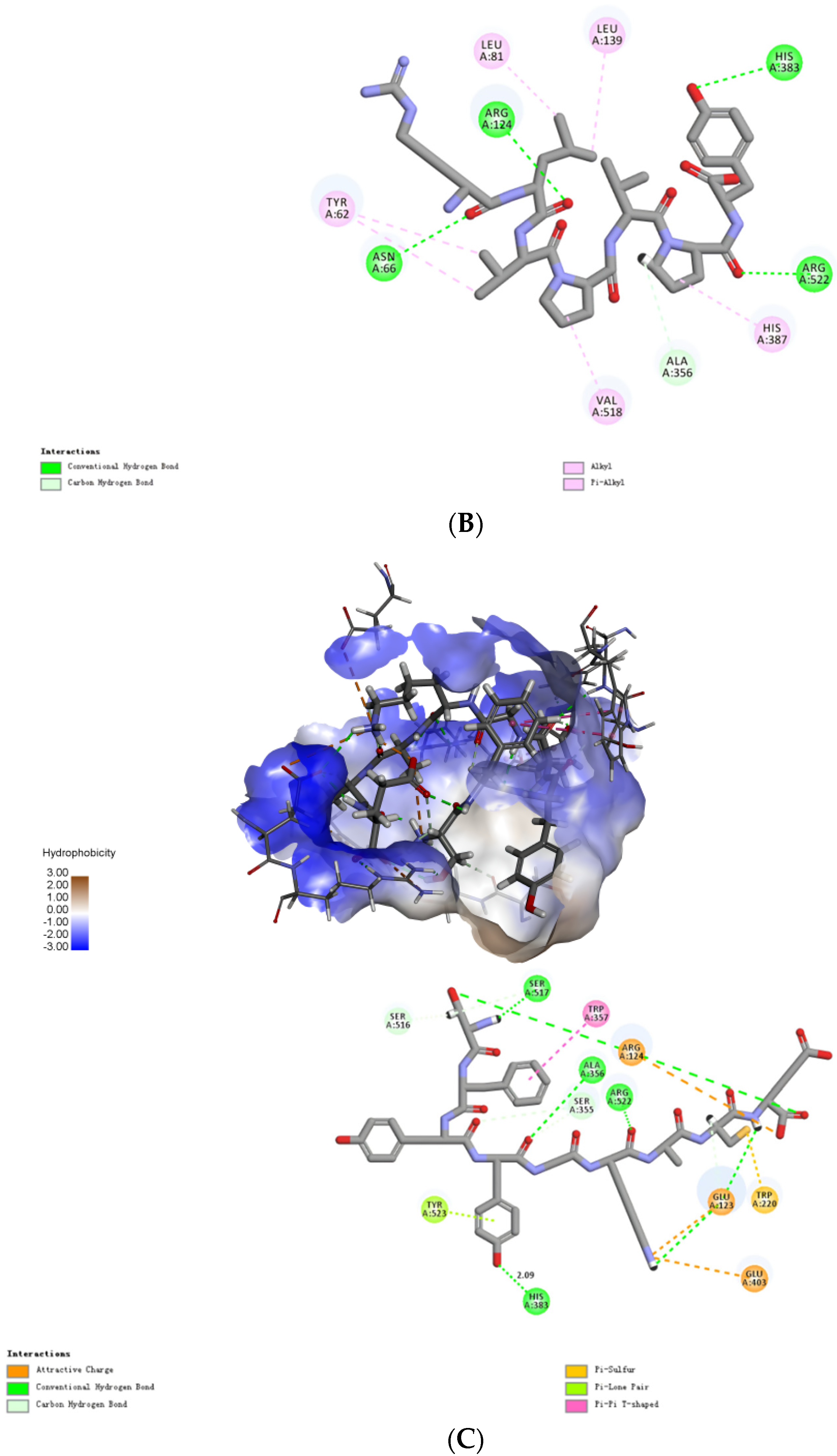
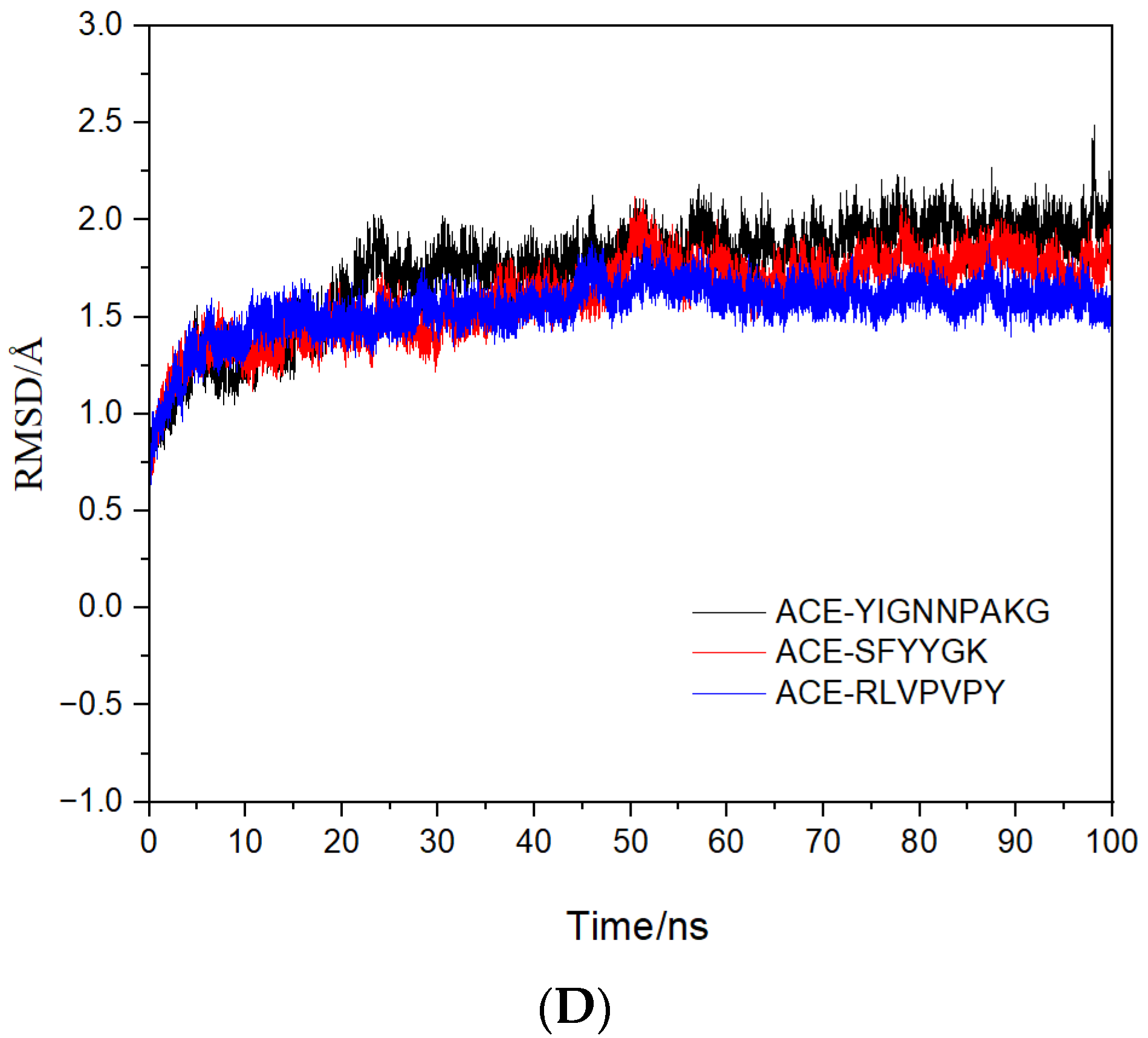
2.4. Molecular Mechanisms of the Interactions between Peptides and ACE
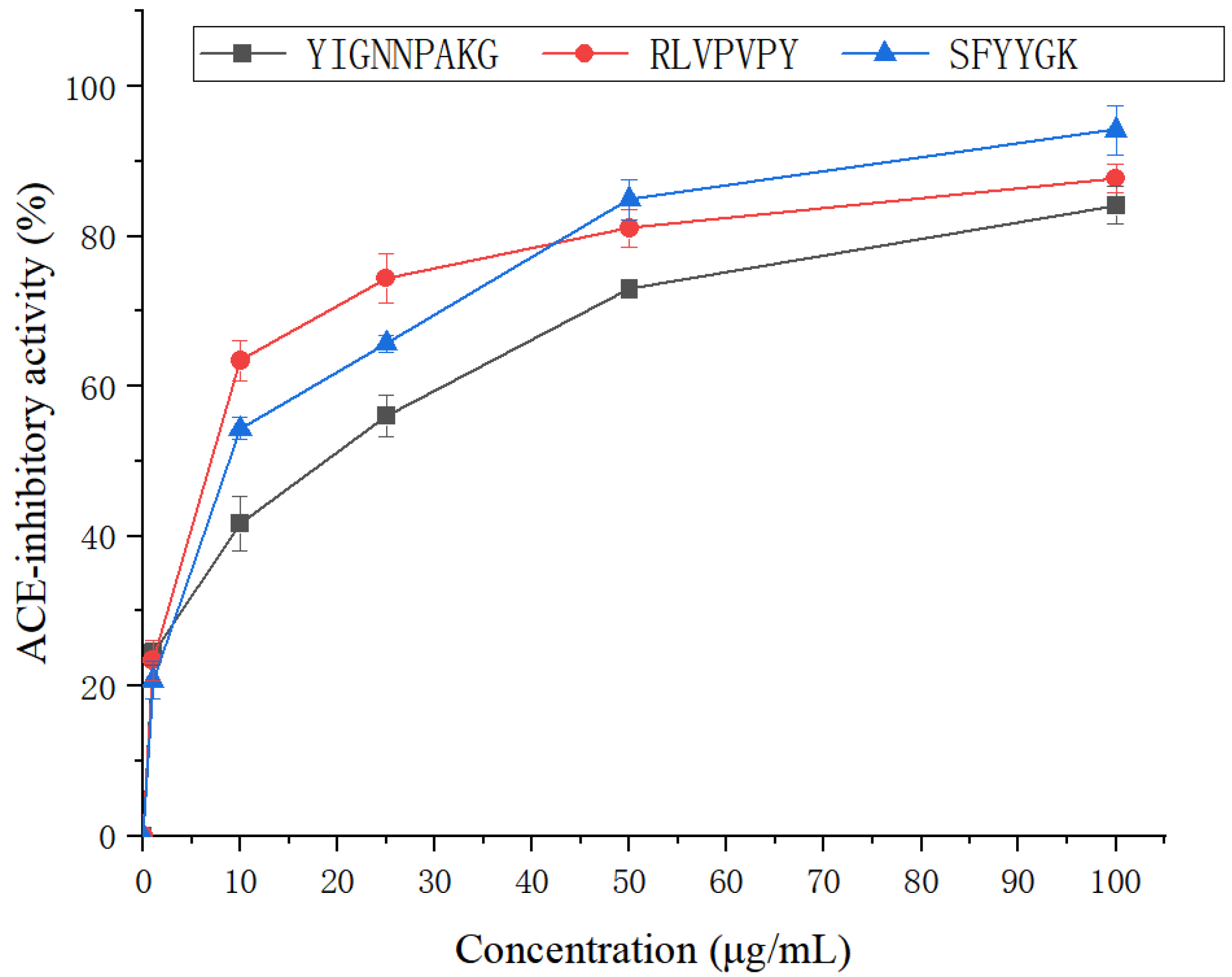
2.5. Antihypertensive Activity of SFYYGK, RLVPVPY and YIGNNPAKG
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of G. lemaneiformis Peptides (GLP)
3.3. Assay of ACE-Inhibitory Activity
3.4. Antihypertensive Effect of GLP
3.5. Identification and Virtual Screening of the ACE-Inhibitory Peptide
3.6. Peptide Synthesis and Individual Bioactivity Assays
3.7. Molecular Mechanisms
3.8. Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Volpe, M.; Battistoni, A.; Chin, D.; Rubattu, S.; Tocci, G. Renin as a biomarker of cardiovascular disease in clinical practice. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagoor Meeran, M.F.; Goyal, S.N.; Suchal, K.; Sharma, C.; Patil, C.R.; Ojha, S.K. Pharmacological Properties, Molecular Mechanisms, and Pharmaceutical Development of Asiatic Acid: A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid of Therapeutic Promise. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.; Mao, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L. Angiotensin-converting enzymes and drug discovery in cardiovascular diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, A.; Kehinde, B.A.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, D.; Kaur, S. Recently isolated food-derived antihypertensive hydrolysates and peptides: A review. Food Chem. 2020, 346, 128719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, A.; Michaud, A.; Chauvet, M.T.; Lenfant, M.; Corvol, P. The hemoregulatory peptide N-acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro is a natural and specificsubstrate of the N-terminal active site of human angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3656–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Maqueda, D.; Miralles, B.; Recio, I.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins: A review. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Abidin, N.B.Z.; Auwal, S.M.; Chay, S.Y.; Haiyee, Z.A.; Sikin, A.; Saari, N. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Peptide Interactions: Inhibition Kinetics, In Silico Molecular Docking and Stability Study of Three Novel Peptides Generated from Palm Kernel Cake Proteins. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aluko, R.E. Antihypertensive Peptides from Food Proteins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.T.; Ross, R.P.; Bolton, D.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Bioactive Peptides from Muscle Sources: Meat and Fish. Nutrients 2011, 3, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shangguan, W.; Bao, C.; Shu, G.; Chen, H. Collaborative optimization and molecular docking exploration of novel ACE-inhibitory peptides from bovine milk by complex proteases hydrolysis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 48, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abachi, S.; Bazinet, L.; Beaulieu, L. Antihypertensive and Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from Fish as Potential Cardioprotective Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aluko, R.E. Structure and function of plant protein-derived antihypertensive peptides. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 4, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, M.S.; Croft, A.K.; Hayes, M. A review of antihypertensive and antioxidant activities in macroalgae. Bot. Mar. 2010, 53, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsuna, K.; Chen, J.-R. Identification of Antihypertensive Peptides from Peptic Digest of Two Microalgae, Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2001, 3, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, N. Preparation and Identification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from the Marine Macroalga Ulva intestinalis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.L.; Zheng, G.Q.; You, L.J.; Wen, L.R.; Li, C.; Fu, X.; Zhou, L. Structural characterization and macrophage im-munomodulatory activity of a polysaccharide isolated from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.-M.; Yang, Y.; Maleki, S.J.; Alcocer, M.; Xu, S.-S.; Shi, C.-L.; Cao, M.-J.; Liu, G.-M. Anti-Food Allergic Activity of Sulfated Polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis is Dependent on Immunosuppression and Inhibition of p38 MAPK. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4536–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-Y.; Huang, X.; Cheong, K.-L. Recent Advances in Marine Algae Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structure, and Activities. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Pan, C.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Qi, B.; Yang, X. Insights on preparation, structure and activities of Gracilaria lemaneiformis polysaccharide. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, D.; Sun, X.; Sun, S.; Xu, N. Preparation and identification of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of marine alga Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 31, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Lv, X.; Xu, X.; Yu, H.; Sun, X.; Xu, N. Purification and identification of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from marine alga Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis protein hydrolysate. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisuthiphaet, N.; Kongruang, S.; Chamcheun, C. Production of Fish Protein Hydrolysates by Acid and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. J. Med. Bioeng. 2015, 4, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasri, M. Protein hydrolysates and biopeptides: Production, biological activities, and applications in foods and health benefits. A Review. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 81, 109–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sirtori, C.R.; Galli, C.; Anderson, J.W.; Arnoldi, A. Nutritional and nutraceutical approaches to dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis prevention: Focus on dietary proteins. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, A.; Mora, L.; Aristoy, M.-C.; Hashemi, M.; Safari, M.; Toldrá, F. ACE-Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activities of Peptide Fragments Obtained from Tomato Processing By-Products Fermented Using Bacillus subtilis: Effect of Amino Acid Composition and Peptides Molecular Mass Distribution. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 181, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pujiastuti, D.Y.; Amin, M.N.G.; Alamsjah, M.A.; Hsu, J.-L. Marine Organisms as Potential Sources of Bioactive Peptides that Inhibit the Activity of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme: A Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mas-Capdevila, A.; Iglesias-Carres, L.; Arola-Arnal, A.; Aragonès, G.; Muguerza, B.; Bravo, F.I. Implication of Opioid Receptors in the Antihypertensive Effect of a Novel Chicken Foot-Derived Peptide. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Chaput, L.; Villoutreix, B.O. Virtual screening web servers: Designing chemical probes and drug candidates in the cyberspace. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 22, 1790–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, L.-W.; Han, X.; Cheng, D.-Y. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protease hy-drolysates of Qula casein: Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling and molecular docking study. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Shiuan, D.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Identification and the molecular mechanism of a novel myosin-derived ACE inhibitory peptide. Food Funct. 2017, 9, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.F.D.S.; Olanda, C.G.; Fokoue, H.H.; Sant’Anna, C.M. Virtual Screening Techniques in Drug Discovery: Review and Recent Applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1751–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheeree, N.; Sangtanoo, P.; Srimongkol, P.; Saisavoey, T.; Reamtong, O.; Choowongkomon, K.; Karnchanatat, A. ACE inhibitory peptides derived from de-fatted lemon basil seeds: Optimization, purification, identification, structure-activity relationship and molecular docking analysis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8161–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Alashi, A.M.; Young, J.F.; Therkildsen, M.; Aluko, R.E. Enzyme inhibition kinetics and molecular interactions of patatin peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme and renin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.D.; Yang, R.; Leng, C.J. Truncation, modification, and optimization of MIG6(segment 2) peptide to target lung cancer-related EGFR. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 61, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.-F.; Wang, H.; Wei, C.-K.; Thakur, K.; Wei, Z.-J.; Jiang, L. Three Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides Isolated From Ginkgo biloba Seeds: Purification, Inhibitory Kinetic and Mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tu, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Lu, W.; Jiang, L.; Du, M. Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.T.; Brozell, S.R.; Mukherjee, S.; Pettersen, E.F.; Meng, E.C.; Thomas, V.; Rizzo, R.C.; Case, D.A.; James, T.L.; Kuntz, I.D.; et al. DOCK 6: Combining techniques to model RNA–small molecule complexes. RNA 2009, 15, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.; Balius, T.E.; Rizzo, R.C. Docking Validation Resources: Protein Family and Ligand Flexibility Experiments. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 1986–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Xue, S.; Yu, Z.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Novel ACE inhibitors derived from soybean proteins using in silico and in vitro studies. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Fang, M.; Xie, J.; Wei, D. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme in-hibitory peptides from Sipuncula (Phascolosoma esculenta): Purification, identification, molecular docking and antihypertensive effects on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Process Biochem. 2017, 63, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| No | Peptide Sequence | Length | Mass (Da) | −10lgP | Grid Score (kJ/mol.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | YDYIGNNPAKG | 11 | 1210.562 | 38.32 | −187.632 |
| 2 | YIGNNPAKGGLF | 12 | 1249.646 | 41.35 | −186.059 |
| 3 | RELIIGDR | 8 | 970.556 | 30.57 | −162.231 |
| 4 | YIGNNPAKG | 9 | 932.472 | 25.92 | −160.014 |
| 5 | SYPGIKF | 7 | 810.428 | 27.52 | −154.084 |
| 6 | RLVPVPY | 7 | 842.501 | 24.24 | −149.115 |
| 7 | NYPAWGY | 7 | 869.371 | 27.91 | −147.764 |
| 8 | TGDSNNN | 7 | 720.268 | 28.5 | −144.587 |
| 9 | SFYYGK | 6 | 763.354 | 25.63 | −141.493 |
| 10 | APTHPIRL | 8 | 903.529 | 30.66 | −141.45 |
| 11 | FFFK | 4 | 587.311 | 25.43 | −139.879 |
| 12 | SIYVSLPF | 8 | 924.496 | 24.61 | −139.56 |
| 13 | AYPGDVF | 7 | 767.349 | 25.54 | −137.737 |
| 14 | FQEPNPI | 7 | 843.413 | 30.31 | −132.76 |
| 15 | WEK | 3 | 461.2274 | 30.09 | −126.44 |
| 16 | WWK | 3 | 518.2642 | 39.07 | −125.302 |
| 17 | KWW | 3 | 518.2642 | 36.8 | −123.22 |
| 18 | LLVR | 4 | 499.3482 | 24.75 | −123.037 |
| 19 | WKPW | 4 | 615.3169 | 25.49 | −122.007 |
| 20 | KIYP | 4 | 519.3057 | 23.97 | −121.024 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Shen, J.; Yi, Z.; Liu, S.; Cai, S.; Pan, N.; Qiao, K.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; et al. Screening and Molecular Mechanisms of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314850
Su Y, Chen S, Shen J, Yi Z, Liu S, Cai S, Pan N, Qiao K, Chen X, Chen B, et al. Screening and Molecular Mechanisms of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314850
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yongchang, Shicheng Chen, Jiashen Shen, Zhiwei Yi, Shuji Liu, Shuilin Cai, Nan Pan, Kun Qiao, Xiaoting Chen, Bei Chen, and et al. 2022. "Screening and Molecular Mechanisms of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314850
APA StyleSu, Y., Chen, S., Shen, J., Yi, Z., Liu, S., Cai, S., Pan, N., Qiao, K., Chen, X., Chen, B., Xu, M., Yang, S., & Liu, Z. (2022). Screening and Molecular Mechanisms of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314850








