Involvement of Small Non-Coding RNA and Cell Antigens in Pathogenesis of Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Immunophenotypic Analysis of MM and EMD Patients
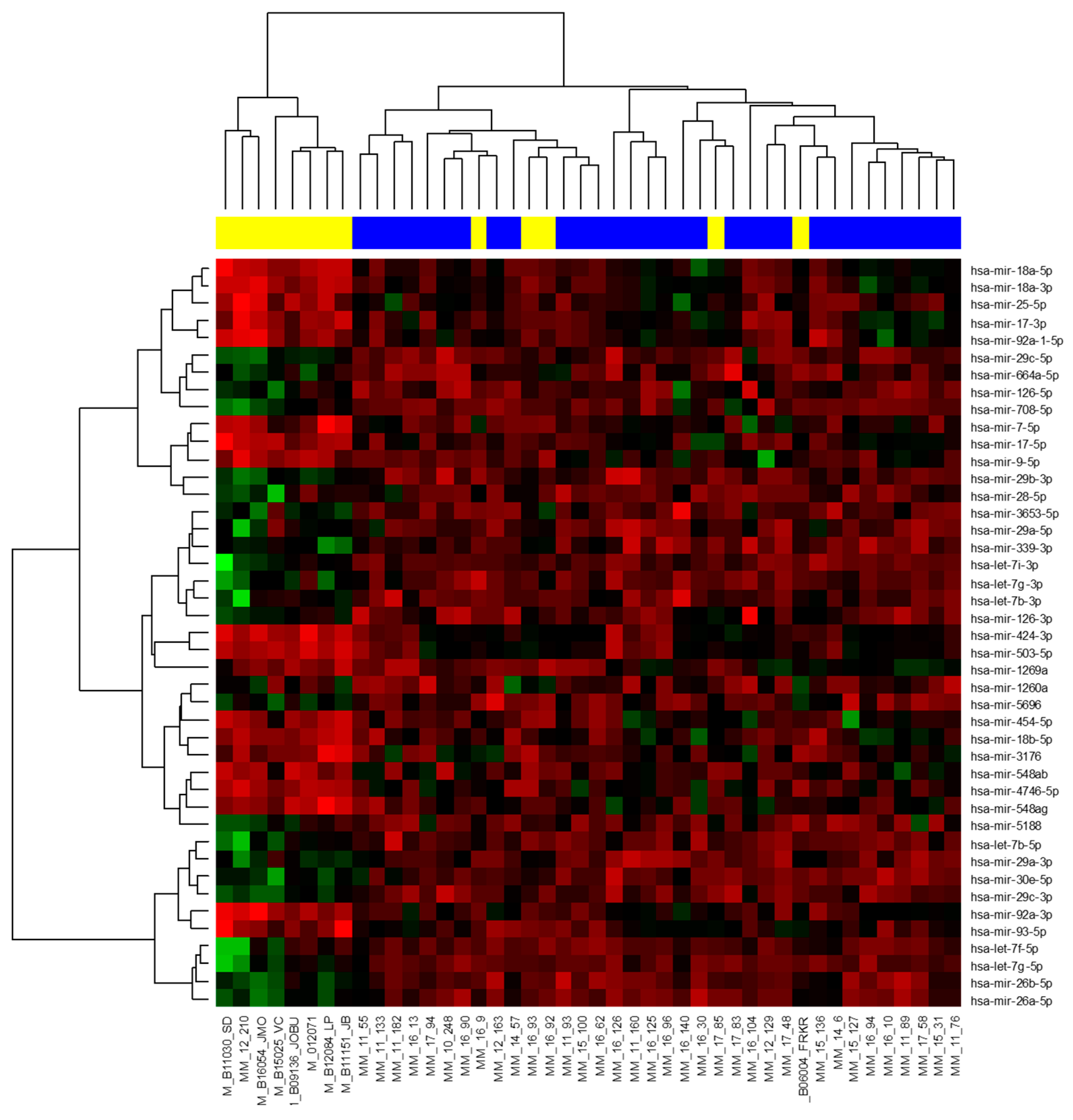
2.2. Small Non-Coding RNA Analysis
2.2.1. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.2.2. RT-qPCR Validation of MicroRNA
2.3. Association between Respective Datasets and Correlation with Clinicopathological Data
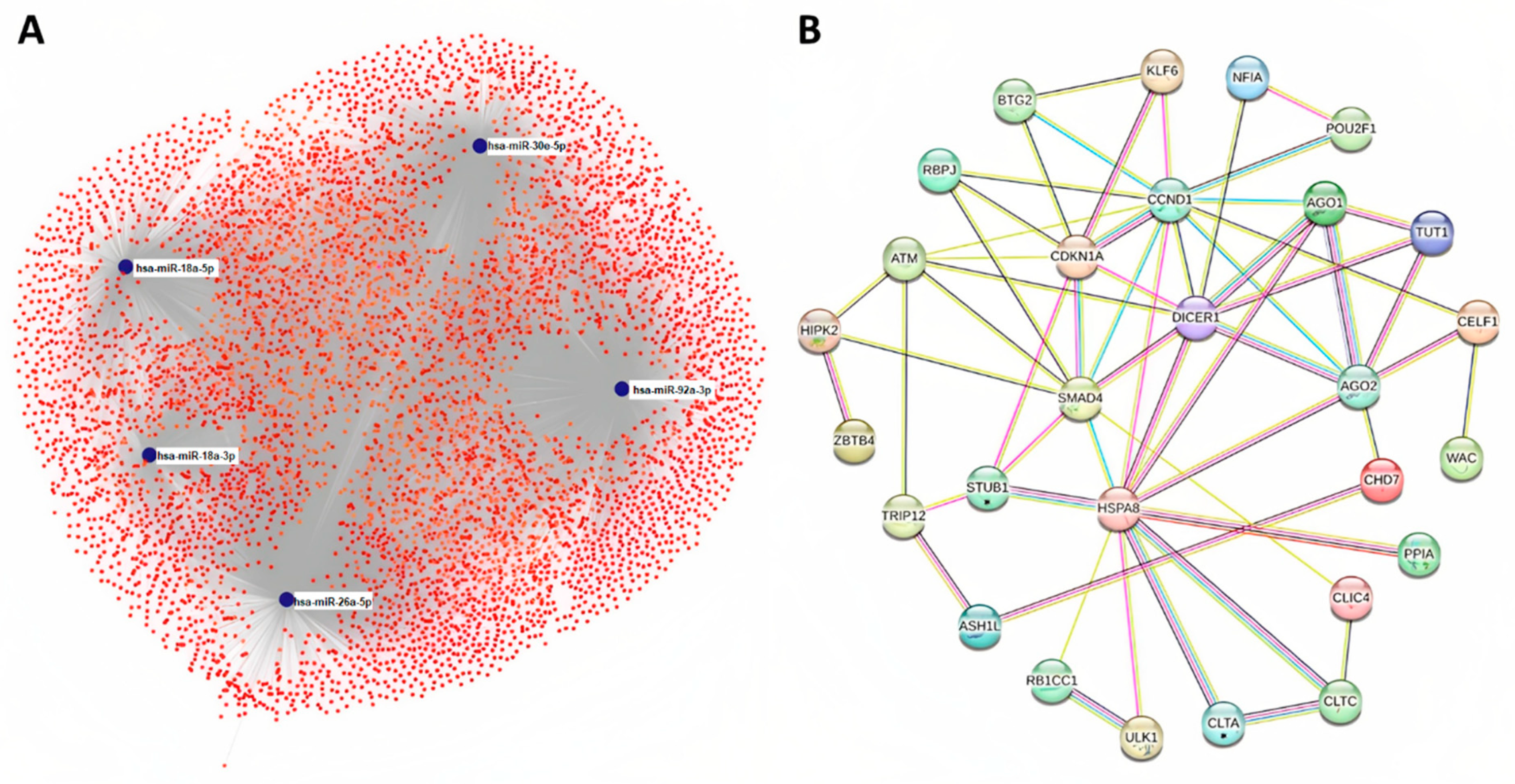
2.4. Target Prediction and Protein Association Network Analysis
2.5. Functional Annotation and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Overall Survival and Progression-Free Survival of MM and EMD Patients
2.6.1. Parameters Significantly Associated with PFS and OS of MM Patients
2.6.2. Parameters significantly Associated with PFS and OS of EMD Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients’ Characteristics
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. RNA Isolation
4.4. Next-Generation Sequencing
4.5. RT-qPCR Validation
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Prediction of miRNAs Target Genes and Protein Association Network Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajkumar, S.V. Multiple Myeloma: 2020 Update on Diagnosis, Risk-Stratification and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 548–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maluskova, D.; Svobodová, I.; Kucerova, M.; Brozova, L.; Muzik, J.; Jarkovský, J.; Hájek, R.; Maisnar, V.; Dusek, L. Epidemiology of Multiple Myeloma in the Czech Republic. Klin. Onkol. 2017, 30, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, R.A.; Child, J.A.; Anderson, K.; Barlogie, B.; Bataille, R.; Bensinger, W.; Blade, J.; Boccadoro, M.; Dalton, W.; Dimopoulos, M.; et al. Criteria for the Classification of Monoclonal Gammopathies, Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: A Report of the International Myeloma Working Group. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 749–757. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Palumbo, A.; Blade, J.; Merlini, G.; Mateos, M.-V.; Kumar, S.; Hillengass, J.; Kastritis, E.; Richardson, P.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Updated Criteria for the Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e538–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutani, M.; Foureau, D.M.; Atrash, S.; Voorhees, P.M.; Usmani, S.Z. Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, L.; Sevcikova, S.; Greslikova, H.; Kupska, R.; Majkova, P.; Zahradova, L.; Sandecka, V.; Adam, Z.; Krejci, M.; Kuglik, P.; et al. Soft-Tissue Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma Prognosis Is Significantly Worse in Comparison to Bone-Related Extramedullary Relapse. Haematologica 2014, 99, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Heuck, C.; Mitchell, A.; Szymonifka, J.; Nair, B.; Hoering, A.; Alsayed, Y.; Waheed, S.; Haider, S.; Restrepo, A.; et al. Extramedullary Disease Portends Poor Prognosis in Multiple Myeloma and Is Over-Represented in High-Risk Disease Even in the Era of Novel Agents. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varettoni, M.; Corso, A.; Pica, G.; Mangiacavalli, S.; Pascutto, C.; Lazzarino, M. Incidence, Presenting Features and Outcome of Extramedullary Disease in Multiple Myeloma: A Longitudinal Study on 1003 Consecutive Patients. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katodritou, E.; Kyrtsonis, M.-C.; Delimpasi, S.; Kyriakou, D.; Symeonidis, A.; Spanoudakis, E.; Vasilopoulos, G.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Kioumi, A.; Zikos, P.; et al. Real-World Data on Len/Dex Combination at Second-Line Therapy of Multiple Myeloma: Treatment at Biochemical Relapse Is a Significant Prognostic Factor for Progression-Free Survival. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, N.; Yeung, J.; Chang, H. P53 Nuclear Accumulation Is Associated with Extramedullary Progression of Multiple Myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevcikova, S.; Minarik, J.; Stork, M.; Jelinek, T.; Pour, L.; Hajek, R. Extramedullary Disease in Multiple Myeloma—Controversies and Future Directions. Blood Rev. 2019, 36, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.I.; Yan, K.P.; Amuthan, G.; Chendrimada, T.; Doratotaj, B.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. The Microprocessor Complex Mediates the Genesis of MicroRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Daly, S.M.; Bayraktar, R.; Anfossi, S.; Calin, G.A. The Interplay between MicroRNAs and the Components of the Tumor Microenvironment in B-Cell Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forterre, A.; Komuro, H.; Aminova, S.; Harada, M. A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Xi, Z.; Liu, R.; Yin, W.; Sui, Z.; Ren, B.; Miller, H.; Gong, Q.; Liu, C. The Function of MicroRNAs in B-Cell Development, Lymphoma, and Their Potential in Clinical Practice. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Svobodova Kovarikova, A.; Grolich, T.; Prochazka, V.; Slaba, K.; Machackova, T.; Halamkova, J.; Svoboda, M.; Kala, Z.; Kiss, I.; et al. MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathway Genes Are Deregulated in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.Y.; Ferrajoli, A.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNA Therapeutics in Cancer—An Emerging Concept. eBioMedicine 2016, 12, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, K.R.; Landgren, O.; Roccaro, A.M.; Ghobrial, I.M. Role of MicroRNAs from Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance to Multiple Myeloma. Semin. Hematol. 2011, 48, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Ballabio, E.; Chen, X.-H.; Kušec, R.; Taylor, S.; Hay, D.; Tramonti, D.; Saunders, N.J.; Littlewood, T.; Pezzella, F.; et al. MicroRNA Expression in Multiple Myeloma Is Associated with Genetic Subtype, Isotype and Survival. Biol. Direct. 2011, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, N.C.; Sarasquete, M.E.; Misiewicz-Krzeminska, I.; Delgado, M.; de Las Rivas, J.; Ticona, F.V.; Fermiñán, E.; Martín-Jiménez, P.; Chillón, C.; Risueño, A.; et al. Deregulation of MicroRNA Expression in the Different Genetic Subtypes of Multiple Myeloma and Correlation with Gene Expression Profiling. Leukemia 2010, 24, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionetti, M.; Biasiolo, M.; Agnelli, L.; Todoerti, K.; Mosca, L.; Fabris, S.; Sales, G.; Deliliers, G.L.; Bicciato, S.; Lombardi, L.; et al. Identification of MicroRNA Expression Patterns and Definition of a MicroRNA/MRNA Regulatory Network in Distinct Molecular Groups of Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2009, 114, e20–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhieddine, T.H.; Weeks, L.D.; Ghobrial, I.M. Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance. Blood 2019, 133, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichiorri, F.; Suh, S.-S.; Ladetto, M.; Kuehl, M.; Palumbo, T.; Drandi, D.; Taccioli, C.; Zanesi, N.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; et al. MicroRNAs Regulate Critical Genes Associated with Multiple Myeloma Pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12885–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P. MicroRNAs in Multiple Myeloma and Related Bone Disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rihova, L.; Vsianska, P.; Bezdekova, R.; Kralova, R.; Penka, M.; Krejci, M.; Pour, L.; Hájek, R. Minimal Residual Disease Assessment in Multiple Myeloma by Multiparametric Flow Cytometry. Klin. Onkol. 2017, 30, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorová, J.; Vrábel, D.; Radová, L.; Gablo, N.A.; Almaši, M.; Štork, M.; Slabý, O.; Pour, L.; Minařík, J.; Ševčíková, S. MicroRNA Analysis for Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma Relapse. Klin. Onkol. 2018, 31, 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Vandesompele, J.; de Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; van Roy, N.; de Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate Normalization of Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR Data by Geometric Averaging of Multiple Internal Control Genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0034.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, L.; Sedlarikova, L.; Greslikova, H.; Kupska, R.; Almasi, M.; Penka, M.; Jelinek, T.; Pour, L.; Adam, Z.; Kuglik, P.; et al. Cytogenetics in Multiple Myeloma Patients Progressing into Extramedullary Disease. Eur. J. Haematol. 2016, 97, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, L.; Sedlarikova, L.; Kryukov, F.; Nekvindova, J.; Radova, L.; Slaby, O.; Kuglik, P.; Almasi, M.; Penka, M.; Krejci, M.; et al. Circulating Serum MicroRNA-130a as a Novel Putative Marker of Extramedullary Myeloma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stork, M.; Sevcikova, S.; Minarik, J.; Krhovska, P.; Radocha, J.; Pospisilova, L.; Brozova, L.; Jarkovsky, J.; Spicka, I.; Straub, J.; et al. Identification of Patients at High Risk of Secondary Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma Development. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svachova, H.; Kryukov, F.; Kryukova, E.; Sevcikova, S.; Nemec, P.; Greslikova, H.; Rihova, L.; Kubiczkova, L.; Hajek, R. Nestin Expression throughout Multistep Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinek, T.; Bezdekova, R.; Zatopkova, M.; Burgos, L.; Simicek, M.; Sevcikova, T.; Paiva, B.; Hajek, R. Current Applications of Multiparameter Flow Cytometry in Plasma Cell Disorders. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, B.; Almeida, J.; Pérez-Andrés, M.; Mateo, G.; López, A.; Rasillo, A.; Vídriales, M.-B.; López-Berges, M.-C.; Miguel, J.F.S.; Orfao, A. Utility of Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping in Multiple Myeloma and Other Clonal Plasma Cell-Related Disorders. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2010, 78, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.E.; Gavile, C.M.; Nair, J.R.; Koorella, C.; Carlson, L.M.; Buac, D.; Utley, A.; Chesi, M.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Boise, L.H.; et al. CD28-Mediated pro-Survival Signaling Induces Chemotherapeutic Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2014, 123, 3770–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wu, C.; Han, W.; Zhao, S.; Wu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Qu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L. Clinical Significance of CD200 Expression in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma Patients and Dynamic Changing during Treatment. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, S.; Azmy, E.; El-Gilany, A.H. Upregulation of CD200 Is Associated with Regulatory T Cell Expansion and Disease Progression in Multiple Myeloma. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, H.; Fang, C.; Li, C.; Xhyliu, F.; Dysert, H.; Bodo, J.; Habermehl, G.; Russell, B.E.; Li, W.; et al. Targeting of CD38 by the Tumor Suppressor MiR-26a Serves as a Novel Potential Therapeutic Agent in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2031–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-H.; Lee, S.-E.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Yim, S.-H.; Kim, T.W.; Min, C.-K.; Chung, Y.-J. Circulating MicroRNA Expressions Can Predict the Outcome of Lenalidomide plus Low-Dose Dexamethasone Treatment in Patients with Refractory/Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2017, 102, e456–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Fang, B. Comparative Analysis of MiRNA Expression Profiles of Multiple Myeloma with 1q21 Gains and Normal FISH. Acta Haematol. 2018, 139, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manier, S.; Liu, C.-J.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Park, J.; Shi, J.; Campigotto, F.; Salem, K.Z.; Huynh, D.; Glavey, S.V.; Rivotto, B.; et al. Prognostic Role of Circulating Exosomal MiRNAs in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2017, 129, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Gao, X.; Qu, X.; Zhao, M.; Qiao, C.; Xu, J.; Li, J. MiR-17-92 Cluster MicroRNAs Confers Tumorigenicity in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Lett. 2011, 309, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A.; Young, A.G.; Winslow, M.M.; Lintault, L.; Meissner, A.; Erkeland, S.J.; Newman, J.; Bronson, R.T.; Crowley, D.; Stone, J.R.; et al. Targeted Deletion Reveals Essential and Overlapping Functions of the MiR-17 through 92 Family of MiRNA Clusters. Cell 2008, 132, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blimark, C.; Holmberg, E.; Mellqvist, U.-H.; Landgren, O.; Björkholm, M.; Hultcrantz, M.; Kjellander, C.; Turesson, I.; Kristinsson, S.Y. Multiple Myeloma and Infections: A Population-Based Study on 9253 Multiple Myeloma Patients. Haematologica 2015, 100, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Kyle, R.A. Neurological Aspects of Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2005, 18, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grufferman, S.; Cohen, H.J.; Delzell, E.S.; Morrison, M.C.; Schold, S.C.; Moore, J.O. Familial Aggregation of Multiple Myeloma and Central Nervous System Diseases. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1989, 37, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, M.; Karaahmet, F.; Tezcan, M.E.; Bulut, N.; Altundag, K. Estrogen or Testosterone May Be Effective Agents in the Management of Both Multiple Myeloma and Alzheimer’s Disease. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 68, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liang, L.; Zhang, X.-F.; Jia, H.-L.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, X.-C.; Gao, X.-M.; Qiao, P.; Zheng, Y.; Sheng, Y.-Y.; et al. MicroRNA-26a Suppresses Tumor Growth and Metastasis of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting Interleukin-6-Stat3 Pathway. Hepatology 2013, 58, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhatia, H.S.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Fiebich, B.L. MicroRNA-26a Modulates Inflammatory Response Induced by Toll-like Receptor 4 Stimulation in Microglia. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Li, L.-F.; Yang, G.-D.; Xia, S.-S.; Wang, R.; Leng, Z.-W.; Liu, Z.-L.; Tian, H.-P.; He, Y.; Meng, C.-Y.; et al. MiR-92a Promotes Stem Cell-like Properties by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101760–101770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, M.; Trenkmann, M.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S.; Speich, R.; Huber, L.C. MicroRNA-18a Enhances the Interleukin-6-Mediated Production of the Acute-Phase Proteins Fibrinogen and Haptoglobin in Human Hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 40142–40150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, M.C.; Gironelli, L.; Bonuccelli, U.; Cei, G.; Meucci, G.; Giraldi, C. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with multiple myeloma. Riv. Neurol. 1990, 60, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koc, F.; Paydas, S.; Yerdelen, D.; Demirkiran, M. Motor Neuron Disease Associated with Multiple Myeloma. Int. J. Neurosci. 2008, 118, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terré, A.; Colombat, M.; Cez, A.; Martin, C.; Diet, C.; Brechignac, S.; Oghina, S.; Bodez, D.; Faguer, S.; Savey, L.; et al. AA Amyloidosis Complicating Monoclonal Gammopathies, an Unusual Feature Validating the Concept of “Monoclonal Gammopathy of Inflammatory Significance”? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocanières, P.; Lamure, S.; Geny, C.; Hillaire-Buys, D.; Faillie, J.-L.; Bres, V. Parkinsonian Patients Requiring Proteasome Inhibitors for Multiple Myeloma: Exceptional Circumstances Call for Extra Caution. J. Park. Dis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Wu, F.; Gao, H.; Wang, G.; Zheng, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, C. Overexpression of MiR-92a Promotes the Tumor Growth of Osteosarcoma by Suppressing F-Box and WD Repeat-Containing Protein 7. Gene 2017, 606, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Dou, C.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, X.; Tu, K. MicroRNA-92a Contributes to Tumor Growth of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting FBXW7. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Cai, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Hu, R.; Ding, F. MicroRNA-30e-5p Suppresses Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumorigenesis by Regulating USP22-Mediated Sirt1/JAK/STAT3 Signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 362, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Chu, H.; Wang, C.; Shi, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Z. Targeting USP22 with MiR-30-5p to Inhibit the Hypoxia-induced Expression of PD-L1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohami, T.; Drucker, L.; Shapiro, H.; Radnay, J.; Lishner, M. Overexpression of Tetraspanins Affects Multiple Myeloma Cell Survival and Invasive Potential. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zismanov, V.; Drucker, L.; Attar-Schneider, O.; Matalon, S.T.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Lishner, M. Tetraspanins Stimulate Protein Synthesis in Myeloma Cell Lines. J. Cell Biochem. 2012, 113, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Expression of CD81 and CD117 in Plasma Cell Myeloma and the Relationship to Prognosis. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 5920–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Xia, T.; Ling, Y.; Chen, B. MiRNAs with Prognostic Significance in Multiple Myeloma. Medicine 2019, 98, e16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, Y.; Sakai, A.; Oue, N.; Asaoku, H.; Otsuki, T.; Shiomomura, T.; Masuda, R.; Hino, N.; Takimoto, Y.; Imanaka, F.; et al. A Possible Role for the Loss of CD27-CD70 Interaction in Myelomagenesis. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 120, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guikema, J.E.J.; Hovenga, S.; Vellenga, E.; Conradie, J.J.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Bekkema, R.; Smit, J.W.; Zhan, F.; Shaughnessy, J.; Bos, N.A. CD27 Is Heterogeneously Expressed in Multiple Myeloma: Low CD27 Expression in Patients with High-Risk Disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbanjo, L.T.; Chellaiah, M.A. CD44: A Multifunctional Cell Surface Adhesion Receptor Is a Regulator of Progression and Metastasis of Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, J.-J.; Simicek, M.; Vicari, M.; Brozova, L.; Burgos, L.; Bezdekova, R.; Alignani, D.; Calasanz, M.-J.; Growkova, K.; Goicoechea, I.; et al. Transcriptional Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells in Multiple Myeloma: A New Model to Understand Disease Dissemination. Leukemia 2020, 34, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Yin, K.; Lan, J. MicroRNA-29a-3p Enhances Dental Implant Osseointegration of Hyperlipidemic Rats via Suppressing Dishevelled 2 and Frizzled 4. Cell Biosci. 2018, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, D.; Li, S.; Le, W. MiR-29 Regulates Tet1 Expression and Contributes to Early Differentiation of Mouse ESCs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64932–64941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.Y.; Psathas, J.N.; Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Weiss, M.J.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A. CD19 Is a Major B Cell Receptor-Independent Activator of MYC-Driven B-Lymphomagenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2257–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-M.; Hong, S. Astaxanthin Suppresses the Metastasis of Colon Cancer by Inhibiting the MYC-Mediated Downregulation of MicroRNA-29a-3p and MicroRNA-200a. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yan, L.; Zheng, P.; Li, J. MiR-29a-3p Directly Targets Smad Nuclear Interacting Protein 1 and Inhibits the Migration and Proliferation of Cervical Cancer HeLa Cells. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Orfao, A.; Beksac, M.; Bezdickova, L.; Brooimans, R.A.; Bumbea, H.; Dalva, K.; Fuhler, G.; Gratama, J.; Hose, D.; et al. Report of the European Myeloma Network on Multiparametric Flow Cytometry in Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders. Haematologica 2008, 93, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, G.; Montalbán, M.A.; Vidriales, M.-B.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Mateos, M.V.; Gutiérrez, N.; Rosiñol, L.; Montejano, L.; Bladé, J.; Martínez, R.; et al. Prognostic Value of Immunophenotyping in Multiple Myeloma: A Study by the PETHEMA/GEM Cooperative Study Groups on Patients Uniformly Treated with High-Dose Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2737–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhou, G.; Soufan, O.; Xia, J. MiRNet 2.0: Network-Based Visual Analytics for MiRNA Functional Analysis and Systems Biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W244–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING Database in 2021: Customizable Protein-Protein Networks, and Functional Characterization of User-Uploaded Gene/Measurement Sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Qu, H.; Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, R.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhong, W.-D.; Jia, Z. GDCRNATools: An R/Bioconductor Package for Integrative Analysis of LncRNA, MiRNA and MRNA Data in GDC. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2515–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Plasma Cells Phenotype | MM (n = 70) | EMD (n = 31) | p 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Median (Min–Max) | n | Median (Min–Max) | ||
| % PC—peripheral blood | n = 70 | 0.1 (0.0–13.2) | n = 31 | 0.1 (0.0–7.0) | 0.074 |
| % PC—bone marrow | n = 70 | 21.0 (1.2–64.5) | n = 31 | 17.6 (0.9–72.5) | 0.222 |
| CD19 A-PC | n = 70 | 0.0 (0.0–55.6) | n = 31 | 0.0 (0.0–8.0) | 0.221 |
| CD56 A-PC | n = 70 | 99.1 (0.0–100.0) | n = 31 | 99.6 (0.0–100.0) | 0.660 |
| CD20 A-PC | n = 39 | 0.0 (0.0–91.7) | n = 20 | 0.0 (0.0–22.6) | 0.965 |
| CD27 A-PC | n = 69 | 2.3 (0.0–99.0) | n = 31 | 3.8 (0.0–98.0) | 0.994 |
| CD28 A-PC | n = 67 | 0.0 (0.0–99.5) | n = 26 | 0.1 (0.0–99.7) | 0.219 |
| CD44 A-PC | n = 65 | 66.7 (0.0–100.0) | n = 25 | 92.5 (0.9–100.0) | 0.290 |
| CD81 A-PC | n = 61 | 2.0 (0.0–98.5) | n = 27 | 2.0 (0.0–99.2) | 0.914 |
| CD117 A-PC | n = 68 | 3.4 (0.0–99.7) | n = 28 | 0.1 (0.0–99.3) | 0.082 |
| CD200 A-PC | n = 54 | 97.5 (0.0–100.0) | n = 20 | 85.2 (0.0–100.0) | 0.184 |
| nestin A-PC | n = 61 | 0.9 (0.0–100.0) | n = 22 | 9.8 (0.0–98.2) | 0.204 |
| aPC | n = 67 | 99.9 (98.0–100.0) | n = 31 | 99.6 (72.7–100.0) | 0.011 |
| miRNA | logFC | Average Expression | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-4746-5p | 1.891 | 0.467 | 2.432 · 10−6 | 1.185 · 10−3 |
| miR-26a-5p | −1.157 | 16.334 | 3.751 · 10−6 | 1.185 · 10−3 |
| miR-92a-3p | 1.693 | 13.075 | 9.052 · 10−6 | 1.328 · 10−3 |
| miR-548ag | 2.029 | 0.789 | 1.155 · 10−5 | 1.328 · 10−3 |
| miR-18a-3p | 1.759 | 5.093 | 1.700 · 10−5 | 1.328 · 10−3 |
| miR-339-3p | −1.403 | 5.490 | 1.723 · 10−5 | 1.328 · 10−3 |
| miR-3653-5p | −1.717 | 4.819 | 1.806 · 10−5 | 1.328 · 10−3 |
| miR-30e-5p | −1.096 | 12.501 | 2.003 · 10−5 | 1.328 · 10−3 |
| miR-29a-3p | −1.367 | 12.986 | 2.100 · 10−5 | 1.328 · 10−3 |
| miR-18a-5p | 1.872 | 5.292 | 2.101 · 10−5 | 1.328 · 10−3 |
| miRNA | MM (n = 39) | EMD (n = 20) | p1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Median (Min–Max) | n | Median (Min–Max) | ||
| miR-18a-5p | n = 39 | 0.76 (0.02–12.37) | n = 20 | 0.72 (0.00–3.50) | 0.706 |
| miR-18a-3p | n = 39 | 0.00 (0.00–0.39) | n = 20 | 0.01 (0.00–1.29) | 0.318 |
| miR-30e-5p | n = 39 | 11.08 (1.23–72.24) | n = 20 | 4.06 (0.84–35.96) | 0.009 |
| miR-92a-3p | n = 39 | 8.27 (0.97–91.61) | n = 20 | 5.10 (1.04–34.61) | 0.163 |
| miR-26a-5p | n = 39 | 56.81 (2.64–476.74) | n = 20 | 17.61 (0.25–741.21) | 0.003 |
| miR-29a-3p | n = 26 | 20.93 (4.20–161.13) | n = 10 | 34.38 (8.45–176.17) | 0.741 |
| miR-424-3p | n = 26 | 0.03 (0.00–3.90) | n = 10 | 0.07 (0.00–28.35) | 0.539 |
| miR-126-3p | n = 26 | 3.01 (0.03–29.64) | n = 10 | 1.09 (0.01–22.50) | 0.189 |
| miR-339-3p | n = 26 | 0.43 (0.15–3.83) | n = 10 | 0.59 (0.00–4.19) | 0.475 |
| miR-708-5p | n = 26 | 0.11 (0.00–2.59) | n = 10 | 0.14 (0.00–3.19) | 0.590 |
| miRNA | Flow-Cytometry | n | rS | p1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-18a-5p | % PC—peripheral blood | 59 | 0.278 | 0.033 |
| nestin A-PC | 53 | 0.347 | 0.011 | |
| miR-339-3p | CD27 A-PC | 35 | 0.303 | 0.077 |
| miR-18a-3p | % PC—peripheral blood | 59 | 0.267 | 0.041 |
| CD81 A-PC | 54 | −0.278 | 0.042 | |
| CD200 A-PC | 52 | −0.254 | 0.069 | |
| miR-30e-5p | CD20 A-PC | 59 | 0.221 | 0.092 |
| CD27 A-PC | 58 | 0.226 | 0.088 | |
| CD81 A-PC | 54 | 0.362 | 0.007 | |
| miR-92a-3p | CD81 A-PC | 54 | 0.351 | 0.009 |
| miR-26a-5p | CD27 A-PC | 58 | 0.312 | 0.017 |
| CD81 A-PC | 54 | 0.384 | 0.004 | |
| aPC | 59 | 0.218 | 0.097 | |
| miR-29a-3p | % PC—bone marrow | 36 | −0.295 | 0.081 |
| CD19 A-PC | 36 | −0.381 | 0.022 | |
| CD44 A-PC | 33 | 0.407 | 0.019 | |
| CD117 A-PC | 32 | 0.310 | 0.084 | |
| miR-424-3p | CD20 A-PC | 36 | −0.422 | 0.010 |
| CD81 A-PC | 32 | 0.342 | 0.056 | |
| aPC | 36 | −0.293 | 0.082 | |
| miR-126-3p | CD117 A-PC | 32 | 0.440 | 0.012 |
| miR-339-3p | CD27 A-PC | 35 | 0.303 | 0.077 |
| miR-708-5p | CD20 A-PC | 36 | −0.282 | 0.096 |
| CD44 A-PC | 33 | 0.330 | 0.061 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlachová, M.; Gregorová, J.; Vychytilová-Faltejsková, P.; Gabło, N.A.; Radová, L.; Pospíšilová, L.; Almáši, M.; Štork, M.; Knechtová, Z.; Minařík, J.; et al. Involvement of Small Non-Coding RNA and Cell Antigens in Pathogenesis of Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314765
Vlachová M, Gregorová J, Vychytilová-Faltejsková P, Gabło NA, Radová L, Pospíšilová L, Almáši M, Štork M, Knechtová Z, Minařík J, et al. Involvement of Small Non-Coding RNA and Cell Antigens in Pathogenesis of Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314765
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlachová, Monika, Jana Gregorová, Petra Vychytilová-Faltejsková, Natalia Anna Gabło, Lenka Radová, Lenka Pospíšilová, Martina Almáši, Martin Štork, Zdeňka Knechtová, Jiří Minařík, and et al. 2022. "Involvement of Small Non-Coding RNA and Cell Antigens in Pathogenesis of Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314765
APA StyleVlachová, M., Gregorová, J., Vychytilová-Faltejsková, P., Gabło, N. A., Radová, L., Pospíšilová, L., Almáši, M., Štork, M., Knechtová, Z., Minařík, J., Popková, T., Jelínek, T., Hájek, R., Pour, L., Říhová, L., & Ševčíková, S. (2022). Involvement of Small Non-Coding RNA and Cell Antigens in Pathogenesis of Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314765





