MicroRNA Changes Up to 24 h following Induced Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Comparison
2.2. Acute Changes in Response to a Hypoglycemia Insult: Changes in Controls and T2D from Hypoglycemia to 4 h (Table 2)
| Control Subjects (n = 23) | T2D Subjects (n = 23) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoglycemia to 4 h After | n = 16 | Hypoglycemia to 4 h After | n = 4 | ||||
| Target Name | Rq (Fold Change) | FDR | Regulation | Target Name | Rq (Fold Change) | FDR | Regulation |
| hsa-miR-338-3p_478037_mir | 3.0 | 0.001 | Down | hsa-miR-191-5p_477952_mir | 2.5 | 0 | Down |
| hsa-miR-223-3p_477983_mir | 2.9 | 0.001 | Down | hsa-let-7b-5p_478576_mir | 3.9 | 0.001 | Down |
| hsa-miR-191-5p_477952_mir | 2.5 | 0 | Down | hsa-miR-143-3p_477912_mir | 2.2 | 0.009 | Down |
| hsa-miR-143-3p_477912_mir | 2.4 | 0.001 | Down | hsa-let-7g-5p_478580_mir | 1.7 | 0.038 | Down |
| hsa-let-7b-5p_478576_mir | 2.2 | 0.002 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-324-5p_478024_mir | 2.1 | 0.007 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-652-3p_478189_mir | 2.0 | 0.02 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-181b-5p_478583_mir | 1.9 | 0.041 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-186-5p_477940_mir | 1.9 | 0.001 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-24-3p_477992_mir | 1.8 | 0.04 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-26a-5p_477995_mir | 1.8 | 0.001 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-181a-5p_477857_mir | 1.8 | 0.044 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-339-5p_478040_mir | 1.8 | 0.004 | Down | ||||
| hsa-let-7g-5p_478580_mir | 1.7 | 0 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-126-3p_477887_mir | 1.5 | 0.042 | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-195-5p_477957_mir | 1.638 | 0.027 | Up |
2.3. Extended Effects of a Hypoglycemia Insult: Changes in Controls and T2D from Hypoglycemia to 24 h (Table 3)
| Control Subjects (n = 23) | T2D Subjects (n = 23) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoglycemia to 24 h | n = 19 | Hypoglycemia to 24 h | n = 14 | ||||
| Target Name | Rq (Fold Change) | FDR | Regulation | Target Name | Rq (Fold Change) | FDR | Regulation |
| hsa-miR-17-5p_478447_mir | 2.8 | 0.001 | Down | hsa-miR-484_478308_mir | 3.6 | 0.03 | Down |
| hsa-miR-93-5p_478210_mir | 2.6 | 0.001 | Down | hsa-miR-652-3p_478189_mir | 3.2 | 0.007 | Down |
| hsa-let-7b-5p_478576_mir | 2.5 | 0 | Down | hsa-miR-191-5p_477952_mir | 2.8 | 0.003 | Down |
| hsa-miR-191-5p_477952_mir | 2.5 | 0 | Down | hsa-miR-93-5p_478210_mir | 2.5 | 0.027 | Down |
| hsa-miR-143-3p_477912_mir | 2.4 | 0 | Down | hsa-miR-106b-5p_478412_mir | 2.3 | 0.016 | Down |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p_478586_mir | 2.2 | 0.001 | Down | hsa-let-7b-5p_478576_mir | 2.3 | 0.007 | Down |
| hsa-miR-223-3p_477983_mir | 2.2 | 0.043 | Down | hsa-miR-185-5p_477939_mir | 1.9 | 0.01 | Down |
| hsa-miR-186-5p_477940_mir | 2.2 | 0 | Down | hsa-miR-21-5p_477975_mir | 1.6 | 0.002 | Up |
| hsa-miR-338-3p_478037_mir | 2.1 | 0.031 | Down | hsa-miR-29b-3p_478369_mir | 1.7 | 0.015 | Up |
| hsa-miR-185-5p_477939_mir | 2.0 | 0.011 | Down | hsa-miR-424-5p_478092_mir | 1.7 | 0.007 | Up |
| hsa-miR-652-3p_478189_mir | 2.0 | 0.001 | Down | hsa-miR-126-5p_477888_mir | 1.8 | 0.002 | Up |
| hsa-let-7g-5p_478580_mir | 1.9 | 0.004 | Down | hsa-miR-146a-5p_478399_mir | 1.8 | 0.019 | Up |
| hsa-miR-324-5p_478024_mir | 1.7 | 0.01 | Down | hsa-miR-369-3p_478067_mir | 2.7 | 0.009 | Up |
| hsa-miR-339-5p_478040_mir | 1.5 | 0.021 | Down | hsa-miR-365a-3p_478065_mir | 6.7 | 0.019 | Up |
| hsa-miR-10a-5p_479241_mir | 1.6 | 0.019 | Up | ||||
| hsa-miR-505-3p_478145_mir | 1.9 | 0.001 | Up | ||||
| hsa-miR-99b-5p_478343_mir | 2.2 | 0.042 | Up | ||||
| hsa-miR-369-3p_478067_mir | 2.3 | 0.031 | Up | ||||
| hsa-miR-885-5p_478207_mir | 3.2 | 0.004 | Up |
2.4. Changes from Hypoglycemia Common to Both the 4 h and 24 h Timepoints in Controls (Table 2 and Table 3)
2.5. Changes from Hypoglycemia Common at Both the 4 h and 24 h Timepoints in T2D (Table 2 and Table 3)
2.6. Changes from Baseline Common at Both the 4 h and 24 h Timepoints in Controls (Supplementary Table S1)
2.7. Changes from Baseline Common at Both the 4 h and 24 h Timepoints in T2D (Supplementary Table S1)
2.8. Correlation Analyses
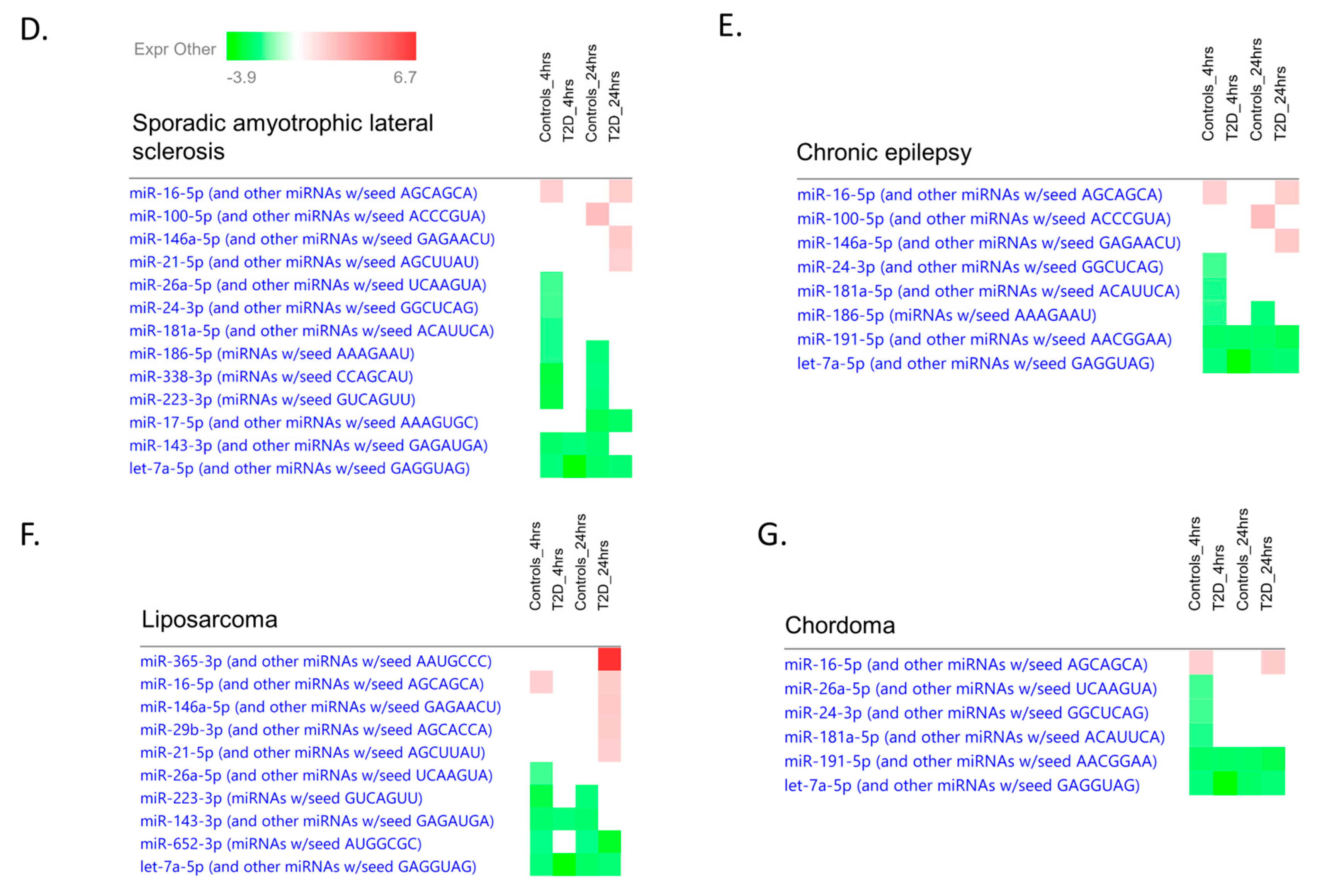
2.9. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Study Participants
4.3. Insulin Infusion
4.4. Biochemical Markers
4.5. Proteomic Analysis
4.6. RNA Extraction from Human Plasma
4.7. Expression Analysis of microRNA by TaqMan OpenArray Human Advanced MicroRNA Panel
4.8. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerstein, H.C.; Miller, M.; Byington, R.; Goff, D., Jr.; Bigger, J.T.; Buse, J.B.; Cushman, W.C.; Genuth, S.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Grimm, R.H., Jr.; et al. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group: Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2545–2559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zoungas, S.; Patel, A.; Chalmers, J.; de Galan, B.E.; Li, Q.; Billot, L.; Woodward, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Neal, B.; MacMahon, S.; et al. Severe Hypoglycemia and Risks of Vascular Events and Death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieber, T.R.; on behalf of the DEVOTE Study Group; Marso, S.P.; McGuire, D.K.; Zinman, B.; Poulter, N.R.; Emerson, S.S.; Pratley, R.E.; Woo, V.; Heller, S.; et al. DEVOTE 3: Temporal relationships between severe hypoglycaemia, cardiovascular outcomes and mortality. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The ORIGIN Trial Investigators; Mellbin, L.G.; Rydén, L.; Riddle, M.C.; Probstfield, J.; Rosenstock, J.; Díaz, R.; Yusuf, S.; Gerstein, H.C. Does hypoglycaemia increase the risk of cardiovascular events? A report from the ORIGIN trial. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaissi, A.; Papageorgiou, M.; Deshmukh, H.; Madden, L.A.; Rigby, A.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Atkin, S.L.; Sathyapalan, T. Effects of acute insulin-induced hypoglycaemia on endothelial microparticles in adults with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, A.S.; Moin, A.S.M.; Nandakumar, M.; Al-Qaissi, A.; Sathyapalan, T.; Atkin, S.L.; Butler, A.E. Impact of severe hypoglycemia on the heat shock and related protein response. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahal, H.; Aburima, A.; Spurgeon, B.; Wraith, K.S.; Rigby, A.S.; Sathyapalan, T.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Naseem, K.M.; Atkin, S.L. Platelet function following induced hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2018, 44, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halama, A.; Kahal, H.; Bhagwat, A.M.; Zierer, J.; Sathyapalan, T.; Graumann, J.; Suhre, K.; Atkin, S.L.; Grauman, J. Metabolic and proteomic signatures of hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahal, H.; Halama, A.; Aburima, A.; Bhagwat, A.M.; Butler, A.E.; Grauman, J.; Atkin, S.L. Effect of induced hypoglycemia on inflammation and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes and control subjects. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, A.S.; Moin, A.S.; Al-Qaissi, A.; Sathyapalan, T.; Atkin, S.L.; Butler, A.E. Plasma heat shock protein response to euglycemia in type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Yeom, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, V.N. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4051–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, V.N.; Han, J.; Siomi, M.C. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, S.L.; Ramachandran, V.; Yousri, N.A.; Benurwar, M.; Simper, S.C.; McKinlay, R.; Adams, T.D.; Najafi-Shoushtari, S.H.; Hunt, S.C. Changes in Blood microRNA Expression and Early Metabolic Responsiveness 21 Days Following Bariatric Surgery. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olejniczak, M.; Kotowska-Zimmer, A.; Krzyzosiak, W. Stress-induced changes in miRNA biogenesis and functioning. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Sharp, P.A. MicroRNA Functions in Stress Responses. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Weithauser, A.; Tabaraie, T.; Steffens, D.; Kränkel, N.; Stratmann, B.; Tschoepe, D.; Landmesser, U.; Rauch-Kroehnert, U. Micro–RNA-126 Reduces the Blood Thrombogenicity in Diabetes Mellitus via Targeting of Tissue Factor. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulzele, S.; El-Sherbini, A.; Ahmad, S.; Sangani, R.; Matragoon, S.; El-Remessy, A.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Liou, G.I. MicroRNA-146b-3p Regulates Retinal Inflammation by Suppressing Adenosine Deaminase-2 in Diabetes. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 846501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Sala, L.; Cattaneo, M.; De Nigris, V.; Pujadas, G.; Testa, R.; Bonfigli, A.R.; Genovese, S.; Ceriello, A. Oscillating glucose induces microRNA-185 and impairs an efficient antioxidant response in human endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, A.; Meloni, M.; Völlenkle, C.; Bonci, D.; Sala-Newby, G.B.; Addis, R.; Spinetti, G.; Losa, S.; Masson, R.; Baker, A.H.; et al. Deregulation of microRNA-503 Contributes to Diabetes Mellitus–Induced Impairment of Endothelial Function and Reparative Angiogenesis After Limb Ischemia. Circulation 2011, 123, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporali, A.; Meloni, M.; Nailor, A.; Mitic, T.; Shantikumar, S.; Riu, F.; Sala-Newby, G.B.; Rose, L.; Besnier, M.; Katare, R.; et al. p75(NTR)-dependent activation of NF-kappaB regulates microRNA-503 transcription and pericyte-endothelial crosstalk in diabetes after limb ischaemia. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanjaneya, M.; Priyanka, R.; Bensila, M.; Jerobin, J.; Pawar, K.; Sathyapalan, T.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Halabi, N.M.; Moin, A.S.M.; Atkin, S.L.; et al. MiRNA and associated inflammatory changes from baseline to hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyileten, C.; Wicik, Z.; Keshwani, D.; Aziz, F.; Aberer, F.; Pferschy, P.N.; Tripolt, N.J.; Sourij, C.; Prietl, B.; Prüller, F.; et al. Alteration of circulating platelet-related and diabetes-related microRNAs in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A stepwise hypoglycaemic clamp study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, J.E.; Arbeláez, A.M. Glucose counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2011, 9, 463–475. [Google Scholar]
- Mussa, B.M.; Taneera, J.; Mohammed, A.K.; Srivastava, A.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Sulaiman, N. Potential role of hypothalamic microRNAs in regulation of FOS and FTO expression in response to hypoglycemia. J. Physiol. Sci. 2019, 69, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Pena-Bello, L.; Manfredi-Lozano, M.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Cordido, F. Perturbation of Hypothalamic MicroRNA Expression Patterns in Male Rats After Metabolic Distress: Impact of Obesity and Conditions of Negative Energy Balance. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1838–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickels, M.R. Hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure, counterregulatory responses, and therapeutic options in type 1 diabetes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1454, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomino, G.; Lauria, F.; Russo, P.; Venezia, A.; Iannaccone, N.; Marena, P.; Ahrens, W.; de Henauw, S.; Molnár, D.; Eiben, G.; et al. The association of circulating miR-191 and miR-375 expression levels with markers of insulin resistance in overweight children: An exploratory analysis of the I. Family Study. Genes Nutr. 2021, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampetaki, A.; Kiechl, S.; Drozdov, I.; Willeit, P.; Mayr, U.; Prokopi, M.; Mayr, A.; Weger, S.; Oberhollenzer, F.; Bonora, E.; et al. Plasma MicroRNA Profiling Reveals Loss of Endothelial MiR-126 and Other MicroRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.A.E.; Schulte, C.; Barwari, T.; Phoenix, F.; Pearson, S.M.; Mayr, M.; Grant, P.J.; Storey, R.F.; Ajjan, R.A. Aspirin, clopidogrel and prasugrel monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blind randomised controlled trial of the effects on thrombotic markers and microRNA levels. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pordzik, J.; Pisarz, K.; De Rosa, S.; Jones, A.D.; Eyileten, C.; Indolfi, C.; Małek, L.; Postula, M. The Potential Role of Platelet-Related microRNAs in the Development of Cardiovascular Events in High-Risk Populations, Including Diabetic Patients: A Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangwal, S.; Stratmann, B.; Bang, C.; Lorenzen, J.M.; Kumarswamy, R.; Fiedler, J.; Falk, C.S.; Scholz, C.-J.; Thum, T.; Tschoepe, D. Impairment of Wound Healing in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Influences Circulating MicroRNA Patterns via Inflammatory Cytokines. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berillo, O.; Huo, K.-G.; Fraulob-Aquino, J.C.; Richer, C.; Briet, M.; Boutouyrie, P.; Lipman, M.L.; Sinnett, D.; Paradis, P.; Schiffrin, E.L. Circulating let-7g-5p and miR-191-5p Are Independent Predictors of Chronic Kidney Disease in Hypertensive Patients. Am. J. Hypertens. 2020, 33, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xihua, L.; Shengjie, T.; Weiwei, G.; Matro, E.; Tingting, T.; Lin, L.; Fang, W.; Jiaqiang, Z.; Fenping, Z.; Hong, L. Circulating miR-143-3p inhibition protects against insulin resistance in Metabolic Syndrome via targeting of the insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor. Transl. Res. 2019, 205, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, R.; Gong, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, N.; Li, J. Altered microRNA expression in inflamed and non-inflamed terminal ileal mucosa of adult patients with active Crohn’s disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Han, J.; Chen, S.; Xie, R.; Yang, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, R. MicroLet-7b Regulates Neutrophil Function and Dampens Neutrophilic Inflammation by Suppressing the Canonical TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, C.; Doubi-Kadmiri, S.; Benigni, X.; Crepin, D.; Riffault, L.; Poizat, G.; Vacher, C.-M.; Taouis, M.; Baroin-Tourancheau, A.; Amar, L. miRNA Long-Term Response to Early Metabolic Environmental Challenge in Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Mudher, A. Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: A Critical Assessment of the Shared Pathological Traits. Front Neurosci. 2018, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Guo, Y.; Chao, L. Protective Role of Endogenous Kallistatin in Vascular Injury and Senescence by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4138560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Xiao, F.; Wang, P.; Hu, Y.-X. lncRNA H19 sponging miR-93 to regulate inflammation in retinal epithelial cells under hyperglycemia via XBP1s. Agents Actions 2020, 69, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Rong, J.; Wang, K. LncRNA HCP5 knockdown inhibits high glucose-induced excessive proliferation, fibrosis and inflammation of human glomerular mesangial cells by regulating the miR-93-5p/HMGA2 axis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Qin, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, D. Circ_WBSCR17 aggravates inflammatory responses and fibrosis by targeting miR-185-5p/SOX6 regulatory axis in high glucose-induced human kidney tubular cells. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, J.; Steel, D.H.W.; Schlingemann, R.O.; Koss, M.J.; Hammes, H.-P.; Krenning, G.; Klaassen, I. microRNA Expression Profile in the Vitreous of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Patients and Differences from Patients Treated with Anti-VEGF Therapy. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeløv Vestergaard, A.; Heiner Bang-Berthelsen, C.; Fløyel, T.; Lucien Stahl, J.; Christen, L.; Taheri Sotudeh, F. MicroRNAs and histone deacetylase inhibition-mediated protection against inflammatory β-cell damage. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalavino, V.; Liso, M.; Cavalcanti, E.; Gigante, I.; Lippolis, A.; Mastronardi, M.; Chieppa, M.; Serino, G. miR-369-3p modulates inducible nitric oxide synthase and is involved in regulation of chronic inflammatory response. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mu, Y.; Ji, Q.; Huang, Q.; Kuang, H.; Ji, L.; Yang, X. Hypoglycaemia, Abnormal Lipids, and Cardiovascular Disease among Chinese with Type 2 Diabetes. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 862896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, A.S.; Al-Qaissi, A.; Sathyapalan, T.; Atkin, S.L.; Butler, A.E. Hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes exacerbates amyloid-related proteins associated with dementia. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, M.A.; Day, S.J. Internal pilot studies for estimating sample size. Stat. Med. 1994, 13, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Baseline | Type 2 Diabetes (n = 23) | Controls (n = 23) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64 ± 8 (66) | 60 ± 10 (63) | 0.15 |
| Sex (M/F) | 12/11 | 11/12 | 0.77 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32 ± 4 (32) | 28 ± 3(27) | 0.001 |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | 4.5 ± 2.2 (5.0) | N/A | |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 51.2 ± 11.4 (50.0) | 37.2 ± 2.2 (37.0) | <0.0001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.8 ± 1.0 (6.7) | 5.6 ± 0.2 (5.5) | <0.0001 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.2 ± 1.0 (4.1) | 4.8 ± 0.67 (4.9) | 0.02 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.7 ± 0.7 (1.5) | 1.34 ± 0.6 (1.3) | 0.06 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.1 ± 0.3 (1.1) | 1.5 ± 0.4 (1.4) | 0.002 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.27 ± 0.8 (2.1) | 2.7 ± 0.7 (2.8) | 0.06 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 3.0 ± 2.7 (1.9) | 5.1 ± 10.3 (2.1) | 0.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramanjaneya, M.; Bettahi, I.; Pawar, K.; Halabi, N.M.; Moin, A.S.M.; Sathyapalan, T.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Atkin, S.L.; Butler, A.E. MicroRNA Changes Up to 24 h following Induced Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314696
Ramanjaneya M, Bettahi I, Pawar K, Halabi NM, Moin ASM, Sathyapalan T, Abou-Samra AB, Atkin SL, Butler AE. MicroRNA Changes Up to 24 h following Induced Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314696
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamanjaneya, Manjunath, Ilham Bettahi, Krunal Pawar, Najeeb M. Halabi, Abu Saleh Md Moin, Thozhukat Sathyapalan, Abdul Badi Abou-Samra, Stephen L. Atkin, and Alexandra E. Butler. 2022. "MicroRNA Changes Up to 24 h following Induced Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314696
APA StyleRamanjaneya, M., Bettahi, I., Pawar, K., Halabi, N. M., Moin, A. S. M., Sathyapalan, T., Abou-Samra, A. B., Atkin, S. L., & Butler, A. E. (2022). MicroRNA Changes Up to 24 h following Induced Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314696







