E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: The Operators of the Ubiquitin Code That Regulates the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
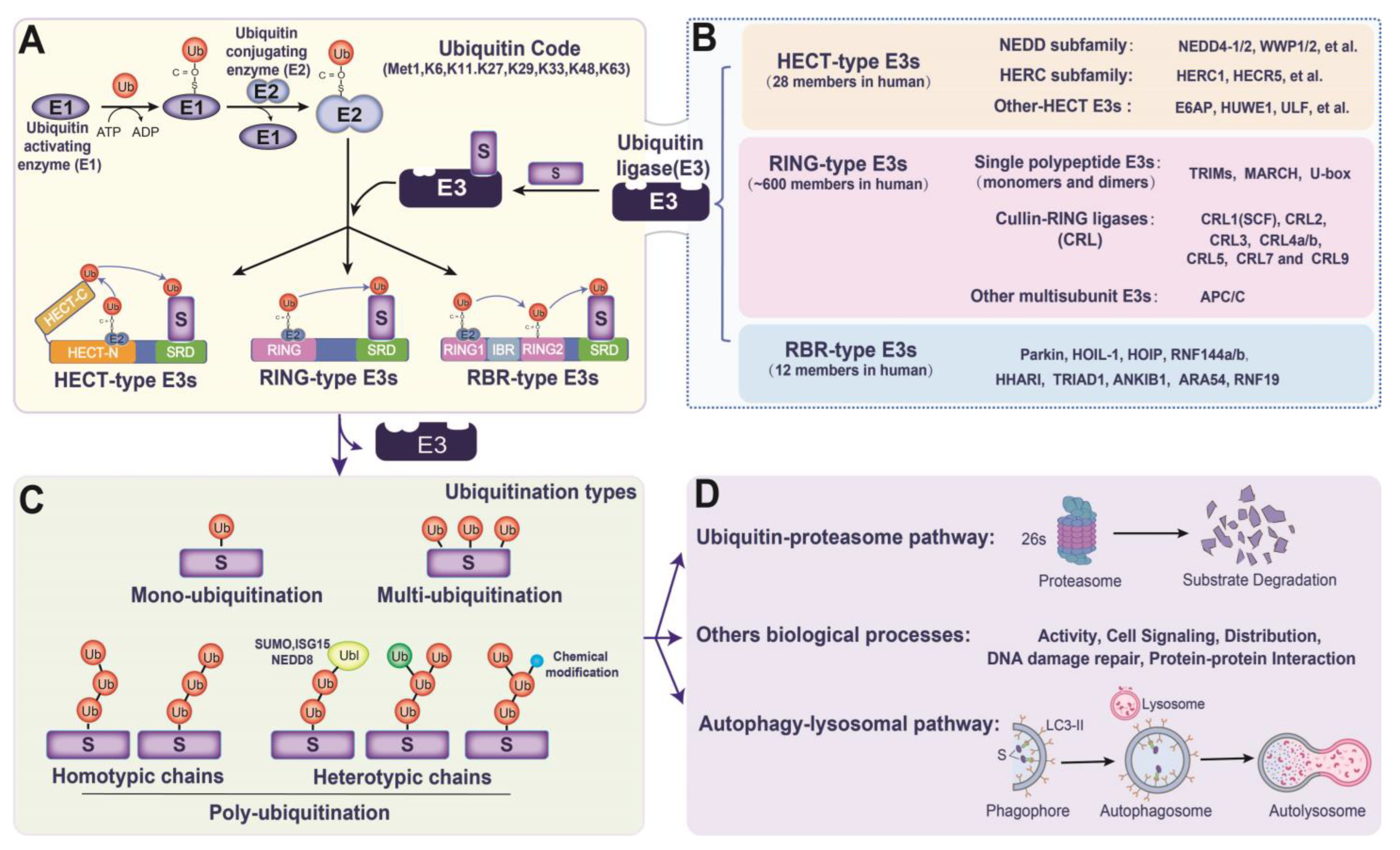
2. Overview of E3s in Ub Transformation
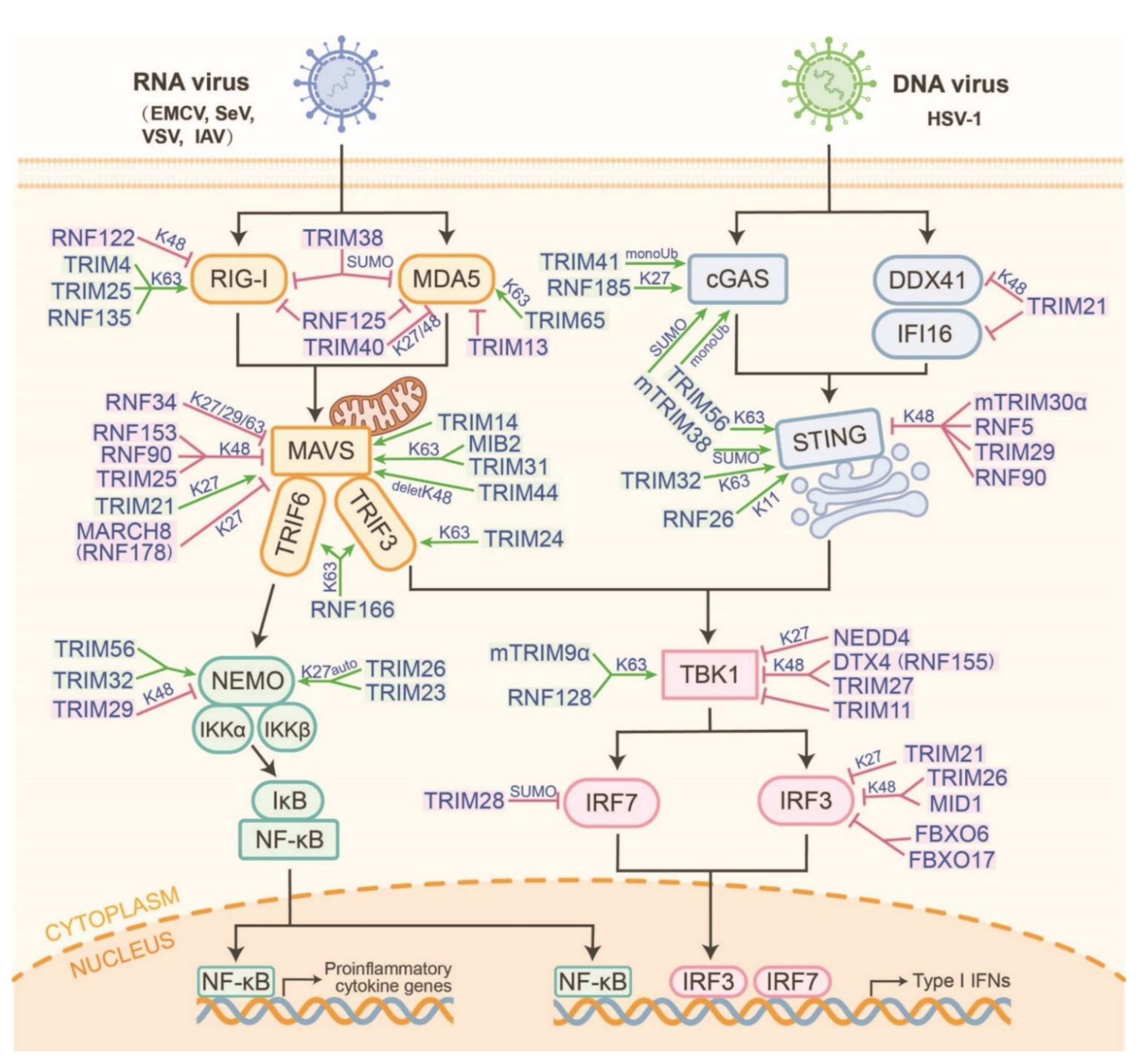
3. Manipulation of RING-Type E3s in the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways
3.1. Manipulation of RING-Type E3s That Enhances the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways
3.2. Manipulation of RING-Type E3s That Suppresses the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways
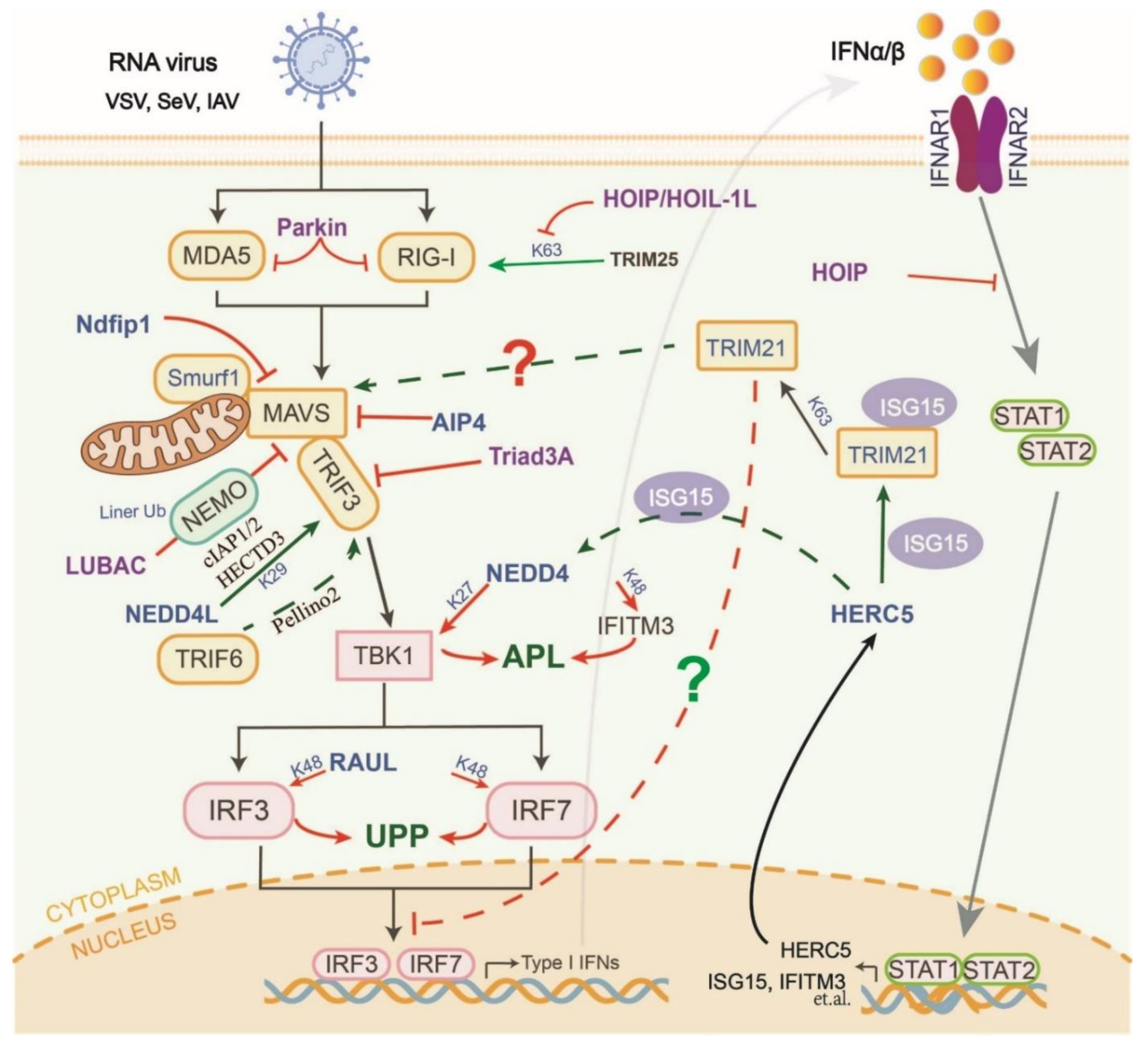
4. Manipulation of HECT-Type E3s in the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways
5. Manipulation of RBR-Type E3s in the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways
6. Manipulation of Atypical E3s in the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways
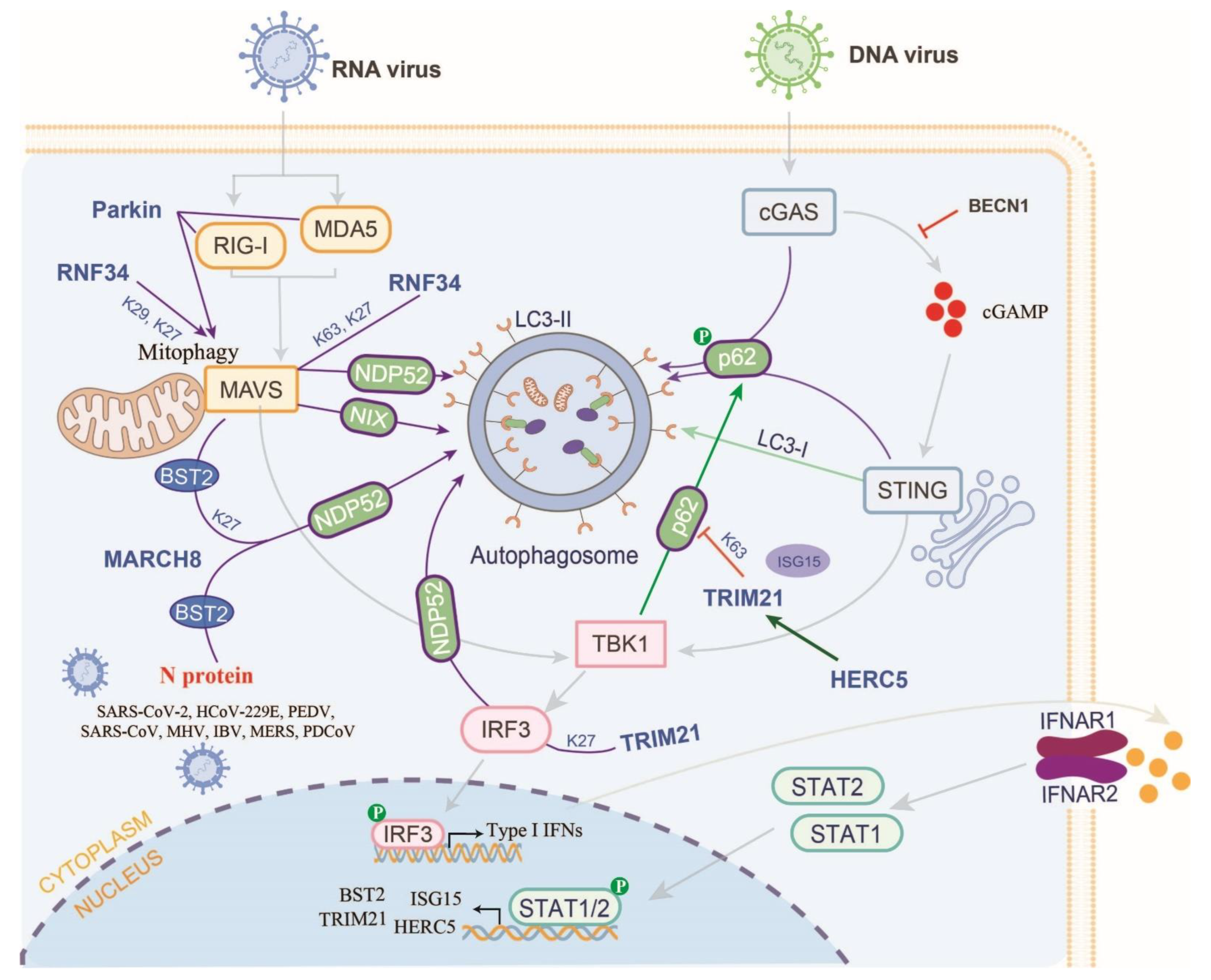
7. Manipulation of E3s-Mediated Autophagy in the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways
8. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehwinkel, J.; Gack, M.U. RIG-I-like receptors: Their regulation and roles in RNA sensing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablasser, A.; Goldeck, M.; Cavlar, T.; Deimling, T.; Witte, G.; Rohl, I.; Hopfner, K.P.; Ludwig, J.; Hornung, V. cGAS produces a 2’-5’-linked cyclic dinucleotide second messenger that activates STING. Nature 2013, 498, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diner, E.J.; Burdette, D.L.; Wilson, S.C.; Monroe, K.M.; Kellenberger, C.A.; Hyodo, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Hammond, M.C.; Vance, R.E. The Innate Immune DNA Sensor cGAS Produces a Noncanonical Cyclic Dinucleotide that Activates Human STING. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kagan, J.C. Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity. Cell 2020, 180, 1044–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechanover, A. The unravelling of the ubiquitin system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechtenberg, B.C.; Rajput, A.; Sanishvili, R.; Dobaczewska, M.K.; Ware, C.F.; Mace, P.D.; Riedl, S.J. Structure of a HOIP/E2 similar to ubiquitin complex reveals RBR E3 ligase mechanism and regulation. Nature 2016, 529, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatakeyama, S. TRIM Family Proteins: Roles in Autophagy, Immunity, and Carcinogenesis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiumi, H.; Miyashita, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. A Distinct Role of Riplet-Mediated K63-Linked Polyubiquitination of the RIG-I Repressor Domain in Human Antiviral Innate Immune Responses. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadena, C.; Ahmad, S.; Xavier, A.; Willemsen, J.; Park, S.; Park, J.W.; Oh, S.W.; Fujita, T.; Hou, F.J.; Binder, M.; et al. Ubiquitin-Dependent and-Independent Roles of E3 Ligase RIPLET in Innate Immunity. Cell 2019, 177, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gack, M.U.; Shin, Y.C.; Joo, C.H.; Urano, T.; Liang, C.; Sun, L.J.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Chen, Z.J.; Inoue, S.S.; et al. TRIM25 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for RIG-I-mediated antiviral activity. Nature 2007, 446, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Sun, L.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Hou, F.; Adhikari, A.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.J. Reconstitution of the RIG-I pathway reveals a signaling role of unanchored polyubiquitin chains in innate immunity. Cell 2010, 141, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Li, Q.; Mao, A.P.; Hu, M.M.; Shu, H.B. TRIM4 modulates type I interferon induction and cellular antiviral response by targeting RIG-I for K63-linked ubiquitination. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 6, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuniyoshi, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Pandey, S.; Satoh, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Akira, S.; Kawai, T. Pivotal role of RNA-binding E3 ubiquitin ligase MEX3C in RIG-I-mediated antiviral innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5646–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.H.; Yuan, B.F.; Zhu, W.T.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Hao, X.J.; Chen, S.; Hou, F.J. Ube2D3 and Ube2N are essential for RIG-I-mediated MAVS aggregation in antiviral innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lang, X.T.; Tang, T.T.; Jin, T.C.; Ding, C.; Zhou, R.B.; Jiang, W. TRIM65-catalized ubiquitination is essential for MDA5-mediated antiviral innate immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.M.; Sun, L.J.; Liu, H.H.; Chen, X.; Seth, R.B.; Forman, J.; Chen, Z.J.J. The specific and essential role of MAVS in antiviral innate immune responses. Immunity 2006, 24, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawai, T.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, S.; Coban, C.; Kumar, H.; Kato, H.; Ishii, K.J.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, M.; Chu, H.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Wu, H.F.; Song, G.H.; Wang, P.; Zhao, K.; Hou, J.X.; Wang, X.; et al. The ubiquitin E3 ligase TRIM31 promotes aggregation and activation of the signaling adaptor MAVS through Lys63-linked polyubiquitination. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Li, H.; Guo, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zou, X.; Deng, R.; Li, G.; Zhu, H. TRIM21 Promotes Innate Immune Response to RNA Viral Infection through Lys27-Linked Polyubiquitination of MAVS. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00321-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Jia, X.; Xue, Q.; Dou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, Z.; He, B.; Jin, Q.; Wang, J. TRIM14 is a mitochondrial adaptor that facilitates retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptor-mediated innate immune response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E245–E254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.C.; Yu, T.; Gan, S.C.; Wang, Y.; Pei, Y.F.; Zhao, Q.F.; Pei, S.Y.; Hao, S.M.; Yuan, J.; Xu, J.; et al. TRIM24 facilitates antiviral immunity through mediating K63-linked TRAF3 ubiquitination. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20192083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhou, H.Y.; Wu, X.D.; Tian, Z.G.; Sun, B. Novel Function of Trim44 Promotes an Antiviral Response by Stabilizing VISA. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3613–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quicke, K.M.; Kim, K.Y.; Horvath, C.M.; Suthar, M.S. RNA Helicase LGP2 Negatively Regulates RIG-I Signaling by Preventing TRIM25-Mediated Caspase Activation and Recruitment Domain Ubiquitination. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenoir, J.J.; Parisien, J.P.; Horvath, C.M. Immune regulator LGP2 targets Ubc13/UBE2N to mediate widespread interference with K63 polyubiquitination and NF-kappaB activation. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 110175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisien, J.P.; Lenoir, J.J.; Mandhana, R.; Rodriguez, K.R.; Qian, K.; Bruns, A.M.; Horvath, C.M. RNA sensor LGP2 inhibits TRAF ubiquitin ligase to negatively regulate innate immune signaling. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e45176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, A.M.; Horvath, C.M. LGP2 synergy with MDA5 in RLR-mediated RNA recognition and antiviral signaling. Cytokine 2015, 74, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duic, I.; Tadakuma, H.; Harada, Y.; Yamaue, R.; Deguchi, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshimura, S.H.; Kato, H.; Takeyasu, K.; Fujita, T. Viral RNA recognition by LGP2 and MDA5, and activation of signaling through step-by-step conformational changes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 11664–11674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.H.; Liu, B.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Wu, H.F.; Wang, P.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C.J. E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF128 promotes innate antiviral immunity through K63-linked ubiquitination of TBK1. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, T.Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, M.J.; Li, N.; Xu, X.F.; Cao, X.T. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1 ‘preferentially’ promotes TLR-mediated production of type I interferon. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jiang, M.H.; Wang, W.D.; Liu, W.; Song, X.Q.; Ma, Z.F.; Zhang, S.K.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X.T. Nuclear RNF2 inhibits interferon function by promoting K33-linked STAT1 disassociation from DNA. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Yang, Y.K.; Xu, H.; Yang, W.W.; Zhai, Z.H.; Chen, D.Y. Ring finger protein 166 potentiates RNA virus-induced interferon-beta production via enhancing the ubiquitination of TRAF3 and TRAF6. Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 14770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, G.J.; Kim, C.; Shin, W.J.; Sklan, E.H.; Eoh, H.; Jung, J.U. TRIM56-mediated monoubiquitination of cGAS for cytosolic DNA sensing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.F.; Chen, Y.F. Ubiquitination of cGAS by TRAF6 regulates anti-DNA viral innate immune responses. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 514, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Cai, H.; Zhao, M.; Mao, J.; Dai, J.; Xia, T.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, T. RINCK-mediated monoubiquitination of cGAS promotes antiviral innate immune responses. Cell Biosci. 2018, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.X.; Meng, Q.C.; Qin, Y.F.; Liang, P.P.; Tan, P.; He, L.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, Y.J.; Huang, J.J.; Wang, R.F.; et al. TRIM14 Inhibits cGAS Degradation Mediated by Selective Autophagy Receptor p62 to Promote Innate Immune Responses. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuchida, T.; Zou, J.A.; Saitoh, T.; Kumar, H.; Abe, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM56 Regulates Innate Immune Responses to Intracellular Double-Stranded DNA. Immunity 2010, 33, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, M.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shu, H.B. TRIM32 Protein Modulates Type I Interferon Induction and Cellular Antiviral Response by Targeting MITA/STING Protein for K63-linked Ubiquitination. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28646–28655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, R.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Lv, M.; Gao, P.; Yu, X.; Mu, P.; Zhang, R.; Bi, S.; Feng, J.; et al. NEMO-IKKβ Are Essential for IRF3 and NF-κB Activation in the cGAS-STING Pathway. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3222–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Shang, G.; Gui, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.C.; Chen, Z.J. Structural basis of STING binding with and phosphorylation by TBK1. Nature 2019, 567, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, K.; Funami, K.; Saeki, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Okawa, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Murakami, Y.; Shimotohno, K. Polyubiquitin conjugation to NEMO by triparite motif protein 23 (TRIM23) is critical in antiviral defense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15856–15861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, L.; Hong, Z.; Lv, Z.; Mao, Z.; Tang, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF185 facilitates the cGAS-mediated innate immune response. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, B.; Zhang, L.; Lei, C.; Li, Y.; Mao, A.P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Shu, H.B. The ubiquitin ligase RNF5 regulates antiviral responses by mediating degradation of the adaptor protein MITA. Immunity 2009, 30, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Zhou, M.T.; Hu, M.M.; Hu, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; Zhong, B.; Shu, H.B. RNF26 temporally regulates virus-triggered type I interferon induction by two distinct mechanisms. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.S.; Kim, N.; Lee, K.J.; Nam, Y.R.; Lee, U.; Joo, C.H. Lysine 63-Linked TANK-Binding Kinase 1 Ubiquitination by Mindbomb E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 2 Is Mediated by the Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12765–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.F.; Liu, Q.X.; Tian, S.; Xie, W.H.; Cui, J.; Wang, R.F. TRIM9 short isoform preferentially promotes DNA and RNA virus-induced production of type I interferon by recruiting GSK3 beta to TBK1. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.L.; Pan, Z.Y.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.Y. Autoubiquitination of TRIM26 links TBK1 to NEMO in RLR-mediated innate antiviral immune response. J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 8, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Han, C.; Xie, B.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q.; Shi, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Zheng, P.; et al. Induction of Siglec-G by RNA viruses inhibits the innate immune response by promoting RIG-I degradation. Cell 2013, 152, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arimoto, K.; Takahashi, H.; Hishiki, T.; Konishi, H.; Fujita, T.; Shimotohno, K. Negative regulation of the RIG-I signaling by the ubiquitin ligase RNF125. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7500–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X. RNF122 suppresses antiviral type I interferon production by targeting RIG-I CARDs to mediate RIG-I degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9581–9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Jia, M.T.; Song, H.; Yu, Z.X.; Wang, W.W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhao, W.; Cao, X.T. The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM40 Attenuates Antiviral Immune Responses by Targeting MDA5 and RIG-I. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.J.; Lai, L.H.; Chong, Z.L.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xue, Y.; Xie, Y.W.; Chen, S.C.; Dong, P.; Chen, L.Q.; et al. E3 ligase FBXW7 is critical for RIG-I stabilization during antiviral responses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.F.; Shi, H.Y.; Ji, Z.Y.N.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, J.B.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.B.; et al. Innate Immune Evasion of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus through Degradation of the FBXW7 Protein via the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0088921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, G.; Qin, X.; Huang, Y.; Ren, X.; Sun, J.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y.; Song, D.; Liu, Y.; et al. Negative Regulation of RNF90 on RNA Virus-Triggered Antiviral Immune Responses Targeting MAVS. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Song, D.; Zhang, G.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, H.; et al. RNF90 negatively regulates cellular antiviral responses by targeting MITA for degradation. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.J.; Lin, L.B.; Tong, Y.L.; Liu, Y.T.; Mou, J.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, X.X.; Gong, Y.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. TRIM29 negatively controls antiviral immune response through targeting STING for degradation (vol 4, 13, 2018). Cell Discov. 2018, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.J.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, X.C.; Zeng, M.S.; Zhang, Z.Q. TRIM29 promotes DNA virus infections by inhibiting innate immune response. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.J.; Weng, L.Y.; Yuan, B.; Wang, Z.; Jia, L.; Jin, R.; Lu, H.B.; Li, X.C.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Identification of a role for TRIM29 in the control of innate immunity in the respiratory tract (vol 17, pg 1373, 2016). Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lian, Q.; Yang, B.; Yan, S.; Zhou, H.; He, L.; Lin, G.; Lian, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, B. TRIM30α Is a Negative-Feedback Regulator of the Intracellular DNA and DNA Virus-Triggered Response by Targeting STING. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Bao, M.S.; Lu, N.; Weng, L.Y.; Yuan, B.; Liu, Y.J. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 negatively regulates the innate immune response to intracellular double-stranded DNA. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.P.; Wu, R.S.; Guo, W.; Xie, L.F.; Qiao, Z.G.; Chen, S.C.; Zhu, J.F.; Huang, C.H.; Huang, J.; Chen, B.C.; et al. STING-Mediated IFI16 Degradation Negatively Controls Type I Interferon Production. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Song, B.; Park, C.; Kwon, K.S. TRIM11 Negatively Regulates IFN beta Production and Antiviral Activity by Targeting TBK1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63255. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C.J. TRIM26 Negatively Regulates Interferon-beta Production and Antiviral Response through Polyubiquitination and Degradation of Nuclear IRF3. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Q.L.; Hou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Xie, B.; Cao, X.T. Siglec1 suppresses antiviral innate immune response by inducing TBK1 degradation via the ubiquitin ligase TRIM27. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1121–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Peng, S.J.; Meng, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, X.P.; Sun, X.Y.; Pang, X.W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. USP7-TRIM27 axis negatively modulates antiviral type I IFN signaling. Faseb. J. 2018, 32, 5238–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.J.; Xu, Y.; Tu, W.H.; Huang, F.; Zuo, Y.B.; Zhang, H.G.; Jin, L.C.; Feng, Q.; Ren, T.F.; He, J.Y.; et al. Ubiquitin E3 ligase MID1 inhibits the innate immune response by ubiquitinating IRF3. Immunology 2021, 163, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.H.; Meng, F.; Peng, D.; Wang, Z.N.; Ouyang, W.; Hang, Y.; Gu, Y.Y.; Fan, L.B.; Wu, F.; Jiang, X.D.; et al. Noncanonical Role of FBXO6 in Regulating Antiviral Immunity. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Wang, Z.N.; Huang, A.F.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, F.X.F. A Novel Function of F-Box Protein FBXO17 in Negative Regulation of Type I IFN Signaling by Recruiting PP2A for IFN Regulatory Factor 3 Deactivation. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Fan, S.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Liao, Q.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, G.; Cao, H.; Xiao, W.H. Zebrafish F-box Protein fbxo3 Negatively Regulates Antiviral Response through Promoting K27-Linked Polyubiquitination of the Transcription Factors irf3 and irf7. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Dai, T.; Jin, K.; Zhang, Z.K.; Wang, S.; Xie, F.; Fang, P.F.; Yang, B.; Huang, H.Z.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes antagonize innate antiviral immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Kumar, S. Nedd4 and Nedd4-2: Closely related ubiquitin-protein ligases with distinct physiological functions. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.H.; Jin, S.H.; Zhang, C.Q.; Yang, S.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.; Songyang, Z.; Cui, J. Selective autophagy controls the stability of TBK1 via NEDD4 to balance host defense. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesarino, N.M.; McMichael, T.M.; Yount, J.S. E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4 Promotes Influenza Virus Infection by Decreasing Levels of the Antiviral Protein IFITM3. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bieniasz, P.D. Late budding domains and host proteins in enveloped virus release. Virology 2006, 344, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novelli, G.; Liu, J.; Biancolella, M.; Alonzi, T.; Novelli, A.; Patten, J.J.; Cocciadiferro, D.; Agolini, E.; Colona, V.L.; Rizzacasa, B.; et al. Inhibition of HECT E3 ligases as potential therapy for COVID-19. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Tong, X.M.; Ye, X. Ndfip1 Negatively Regulates RIG-I-Dependent Immune Signaling by Enhancing E3 Ligase Smurf1-Mediated MAVS Degradation. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5304–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, F.P.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Sun, W.X.; Liang, S.M.; Zhai, Z.H.; Jiang, Z.F. PCBP2 mediates degradation of the adaptor MAVS via the HECT ubiquitin ligase AIP4. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.S.; Qi, H.Y.; Boularan, C.; Huang, N.N.; Abu-Asab, M.; Shelhamer, J.H.; Kehrl, J.H. SARS-Coronavirus Open Reading Frame-9b Suppresses Innate Immunity by Targeting Mitochondria and the MAVS/TRAF3/TRAF6 Signalosome. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3080–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.X.; Hayward, G.S. The Ubiquitin E3 Ligase RAUL Negatively Regulates Type I Interferon through Ubiquitination of the Transcription Factors IRF7 and IRF3. Immunity 2010, 33, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, P.; Ma, X.W.; Yuan, M.; Yi, Y.L.; Liu, G.K.; Wen, M.Y.; Jiang, W.; Ji, R.H.; Zhu, L.X.; Tang, Z.; et al. E3 ligase Nedd4l promotes antiviral innate immunity by catalyzing K29-linked cysteine ubiquitination of TRAF3. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Green, Y.S.; Xie, Y.Y.; Christian, J.L. Tril dampens Nodal signaling through Pellino2-and Traf6-mediated activation of Nedd4l. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104661118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inn, K.S.; Gack, M.U.; Tokunaga, F.; Shi, M.D.; Wong, L.Y.; Iwai, K.; Jung, J.U. Linear Ubiquitin Assembly Complex Negatively Regulates RIG-I- and TRIM25-Mediated Type I Interferon Induction. Mol. Cell 2011, 41, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgnaoui, S.M.; Paz, S.; Samuel, S.; Goulet, M.L.; Sun, Q.; Kikkert, M.; Iwai, K.; Dikic, I.; Hiscott, J.; Lin, R.T. Linear Ubiquitination of NEMO Negatively Regulates the Interferon Antiviral Response through Disruption of the MAVS-TRAF3 Complex. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakhaei, P.; Mesplede, T.; Solis, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, T.J.; Yang, L.; Chuang, T.H.; Ware, C.F.; Lin, R.T.; Hiscott, J. The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Triad3A Negatively Regulates the RIG-I/MAVS Signaling Pathway by Targeting TRAF3 for Degradation. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuo, Y.B.; Feng, Q.; Jin, L.C.; Huang, F.; Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, H.G.; Guo, T.T.; et al. Regulation of the linear ubiquitination of STAT1 controls antiviral interferon signaling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Q.M.; Deng, H.Y.; Li, X.J.; Wu, X.F.; Tang, Q.Y.; Chang, T.H.; Peng, H.Z.; Rauscher, F.J.; Ozato, K.; Zhu, F.X. Tripartite Motif-Containing Protein 28 Is a Small Ubiquitin-Related Modifier E3 Ligase and Negative Regulator of IFN Regulatory Factor 7. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4754–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.M.; Liao, C.Y.; Yang, Q.; Xie, X.Q.; Shu, H.B. Innate immunity to RNA virus is regulated by temporal and reversible sumoylation of RIG-I and MDA5. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.M.; Yang, Q.; Xie, X.Q.; Liao, C.Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, T.T.; Yin, L.; Shu, H.B. Sumoylation Promotes the Stability of the DNA Sensor cGAS and the Adaptor STING to Regulate the Kinetics of Response to DNA Virus. Immunity 2016, 45, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Meng, X.; Huo, Y.; Deng, H. Induced TRIM21 ISGylation by IFN-β enhances p62 ubiquitination to prevent its autophagosome targeting. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, H.; Yang, S.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J. LRRC59 modulates type I interferon signaling by restraining the SQSTM1/p62-mediated autophagic degradation of pattern recognition receptor DDX58/RIG-I. Autophagy 2020, 16, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Duan, T.H.; Feng, Y.C.; Liu, Q.X.; Lin, M.; Cui, J.; Wang, R.F. LRRC25 inhibits type I IFN signaling by targeting ISG15-associated RIG-I for autophagic degradation. EMBO J. 2018, 37, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakhova, O.A.; Zhang, D.E. ISG15 inhibits Nedd4 ubiquitin E3 activity and enhances the innate antiviral response. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 8783–8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deretic, V. Autophagy in inflammation, infection, and immunometabolism. Immunity 2021, 54, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.R.; Ban, J.; Lee, N.J.; Yi, C.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.K.; Seong, J.; Cho, N.H.; Jung, J.U.; et al. Activation of RIG-I-Mediated Antiviral Signaling Triggers Autophagy Through the MAVS-TRAF6-Beclin-1 Signaling Axis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, P.P.; Guo, S.T.; He, M.; Xiao, J.S.; Li, P.; Zhong, Y.H.; Jia, P.H.; Cao, Y.Y.; et al. The Ubiquitin E3 Ligase Parkin Inhibits Innate Antiviral Immunity Through K48-Linked Polyubiquitination of RIG-I and MDA5. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.H.; Wu, J.; Zhong, T.S.; Zhu, W.T.; She, G.L.; Tang, H.; Du, W.; Ye, B.C.; Qi, N. Upstream ORFs Prevent MAVS Spontaneous Aggregation and Regulate Innate Immune Homeostasis. Iscience 2020, 23, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Geng, Y.Q.; Gong, J.; Geng, J.; Zhang, P.P.; Zhang, X.T.; Liu, N.; Peng, Y.M.; et al. RNF34 functions in immunity and selective mitophagy by targeting MAVS for autophagic degradation. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.H.; Tian, S.; Luo, M.; Xie, W.H.; Liu, T.; Duan, T.H.; Wu, Y.X.; Cui, J. Tetherin Suppresses Type I Interferon Signaling by Targeting MAVS for NDP52-Mediated Selective Autophagic Degradation in Human Cells. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, Y.J.; Kong, N.; Wang, H.; Sun, D.G.; Dong, S.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Zheng, H.; Tong, W.; Yu, H.; Yu, L.X.; et al. PABPC4 Broadly Inhibits Coronavirus Replication by Degrading Nucleocapsid Protein through Selective Autophagy. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00908-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kong, N.; Jiao, Y.J.; Dong, S.J.; Sun, D.G.; Chen, X.Y.; Zheng, H.; Tong, W.; Yu, H.; Yu, L.X.; et al. EGR1 Suppresses Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication by Regulating IRAV To Degrade Viral Nucleocapsid Protein. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00645-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, T.; Bodda, C.; Krapp, C.; Zhang, B.C.; Christensen, M.H.; Sun, C.L.; Reinert, L.; Cai, Y.J.; Jensen, S.B.; Skouboe, M.K.; et al. Attenuation of cGAS-STING signaling is mediated by a p62/SQSTM1-dependent autophagy pathway activated by TBK1. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gui, X.; Yang, H.; Li, T.; Tan, X.J.; Shi, P.Q.; Li, M.H.; Du, F.H.; Chen, Z.J.J. Autophagy induction via STING trafficking is a primordial function of the cGAS pathway. Nature 2019, 567, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.M.; Seo, G.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kwak, M.J.; Ge, J.N.; Rodgers, M.A.; Shi, M.D.; Leslie, B.J.; Hopfner, K.P.; Ha, T.; et al. Crosstalk between the cGAS DNA Sensor and Beclin-1 Autophagy Protein Shapes Innate Antimicrobial Immune Responses. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sparrer, K.M.J.; Gableske, S.; Zurenski, M.A.; Parker, Z.M.; Full, F.; Baumgart, G.J.; Kato, J.; Pacheco-Rodriguez, G.; Liang, C.Y.; Pornillos, O.; et al. TRIM23 mediates virus-induced autophagy via activation of TBK1. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.X.; Jin, S.H.; Liu, Q.X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.P.; Cui, J. Selective autophagy controls the stability of transcription factor IRF3 to balance type I interferon production and immune suppression. Autophagy 2021, 17, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.H.; Zhang, L.L.; Qian, D.; Cheng, M.X.; Hu, H.Y.; Hong, Z.; Cui, Y.; Yu, H.S.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhu, J.J.; et al. RNF111-facilitated neddylation potentiates cGAS-mediated antiviral innate immune response. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, D.L.; Park, M.; Murphy, K.A.; Beachboard, D.C.; Horner, S.M. Signaling from the RNA sensor RIG-I is regulated by ufmylation. Prco. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119531119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Jin, J.Y.; Shen, Z.; Feng, X.Y.; Zou, T.; Deng, L.J.; Cheng, D.H.; Zhang, X.T.; et al. Myeloid neddylation targets IRF7 and promotes host innate immunity against RNA viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Calderon-Villalobos, L.I.A.; Sharon, M.; Zheng, C.X.; Robinson, C.V.; Estelle, M.; Zheng, N. Mechanism of auxin perception by the TIR1 ubiquitin ligase. Nature 2007, 446, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.L.; Shen, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Shen, J.Y.; Xiao, X.; Bai, H.Q.; Feng, T.; Ye, A.Y.; Li, L.; et al. Generation of a live attenuated influenza A vaccine by proteolysis targeting. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhou, H.L.; Wu, C.; Wu, Q.K.; Ma, S.C.; Wei, C.W.; Cao, Y.; Song, J.D.; Zhong, H.; Zhou, Z.; et al. The Ubiquitin Ligase RNF125 Targets Innate Immune Adaptor Protein TRIM14 for Ubiquitination and Degradation. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4652–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lu, J.; Bao, S.; Shen, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: The Operators of the Ubiquitin Code That Regulates the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314601
Ji L, Wang Y, Zhou L, Lu J, Bao S, Shen Q, Wang X, Liu Y, Zhang W. E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: The Operators of the Ubiquitin Code That Regulates the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314601
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Likai, Yan Wang, Liying Zhou, Juan Lu, Siwen Bao, Quan Shen, Xiaochun Wang, Yuwei Liu, and Wen Zhang. 2022. "E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: The Operators of the Ubiquitin Code That Regulates the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314601
APA StyleJi, L., Wang, Y., Zhou, L., Lu, J., Bao, S., Shen, Q., Wang, X., Liu, Y., & Zhang, W. (2022). E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: The Operators of the Ubiquitin Code That Regulates the RLR and cGAS-STING Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314601





