Oligomerization-Dependent Beta-Structure Formation in SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
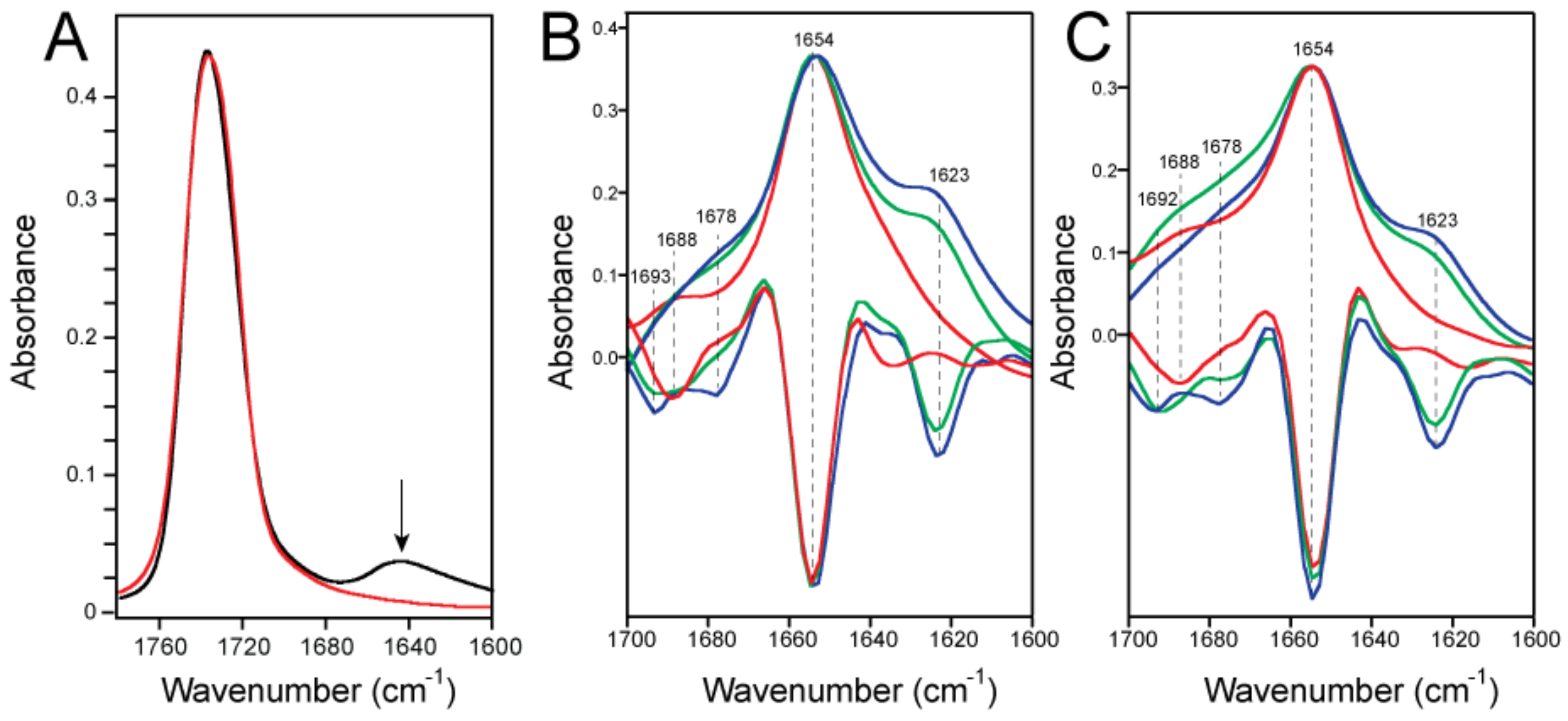
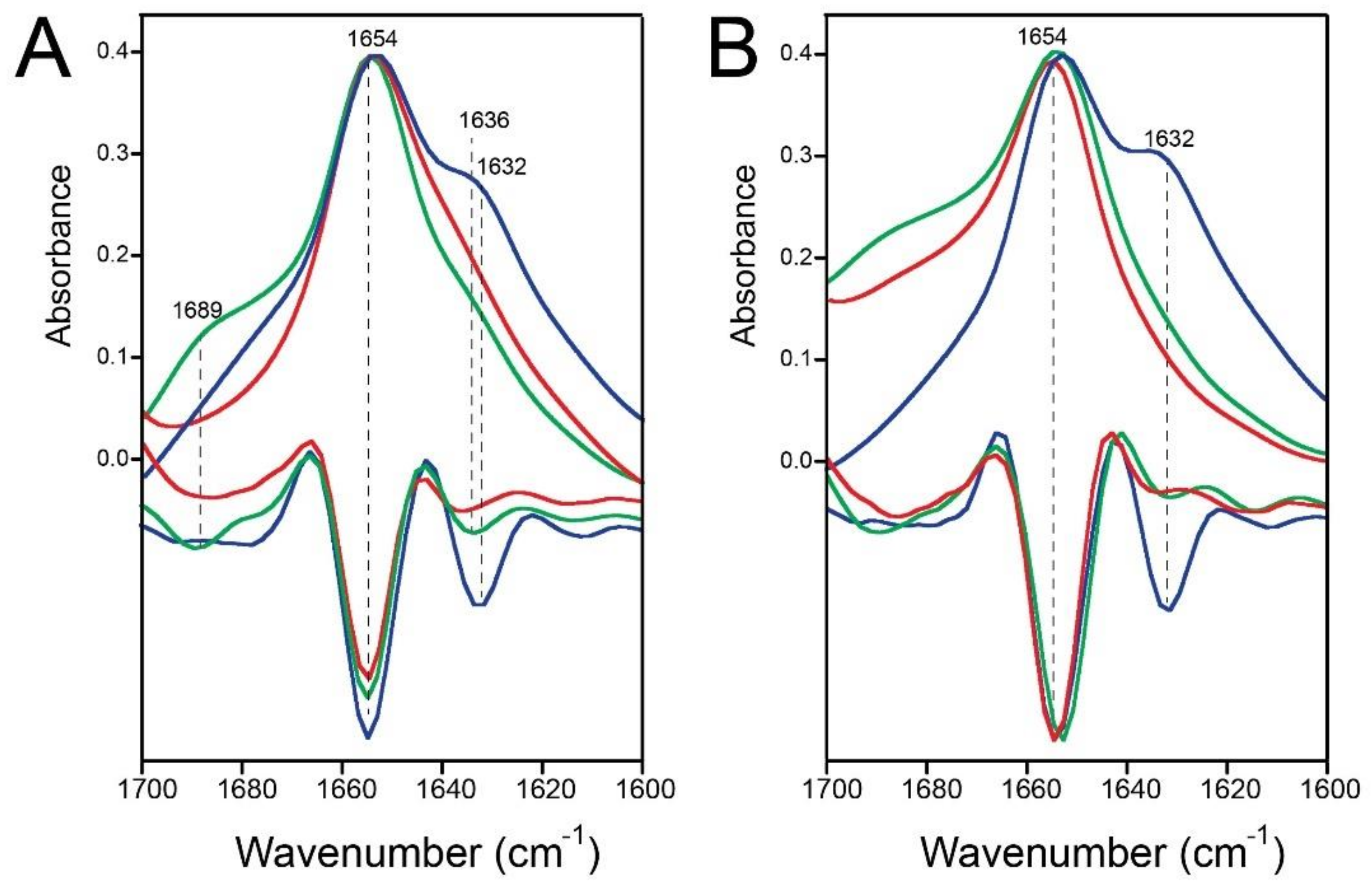
2.1. Formation of β-Structure in SARS-2 E-FL in ERGIC and PC:PG Membranes
2.2. Formation of β-Structure in E-TR in ERGIC and PC:PG Membranes
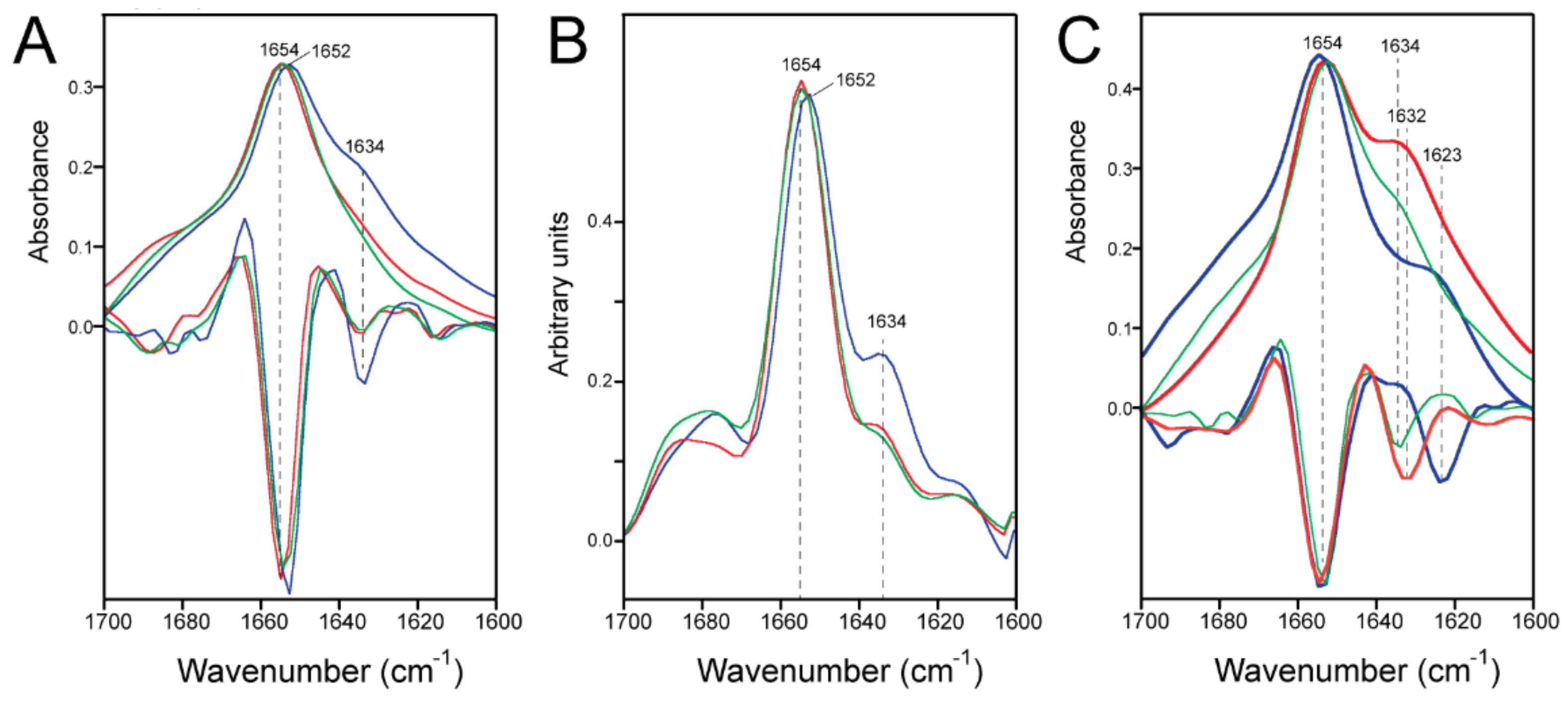
2.3. E-FL Forms Tighter Oligomers Than E-TR in Detergent
2.4. Quantification of the β-Structure Contribution
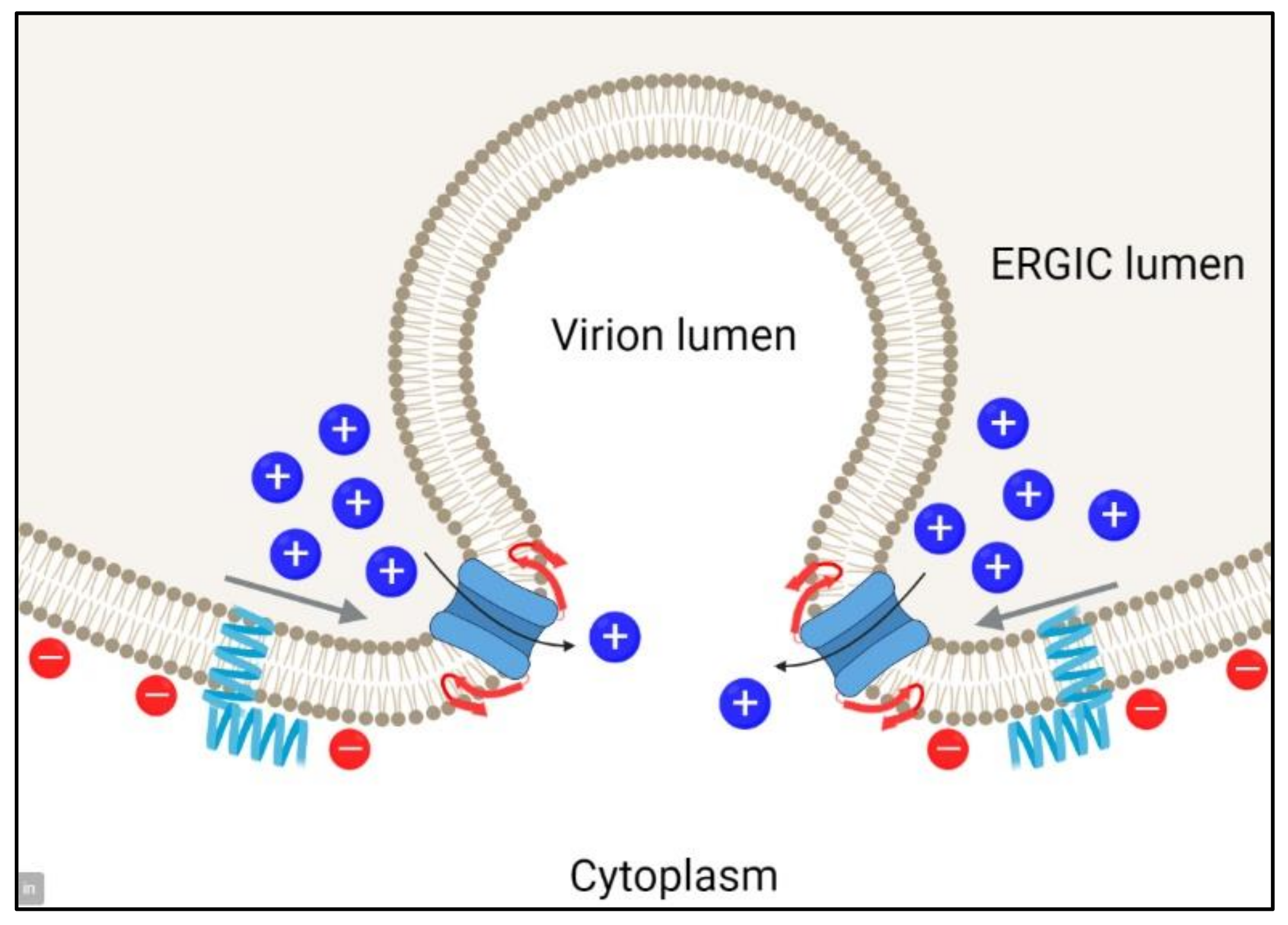
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.J.M. Prevention of the cytokine storm in COVID-19. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 21, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betton, L.; Benchetrit, D.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Oppert, J.M.; Torcivia, A.; Vaillant, J.C.; Genser, L. COVID-19 Digestive Symptoms Mimicking Internal Hernia Presentation After Roux-en-Y-Gastric Bypass; Comment on “Internal Hernia in the Times of COVID-19: To Laparoscope or Not to Laparoscope?”. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 3601–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Aguilar, R.; Osorio-Camara, J.M.; Sanjurjo-Jimenez, I.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, C.; Lopez-Carnero, J.; Perez-Moneo-Agapito, B. COVID-19: Fever syndrome and neurological symptoms in a neonate. An. Pediatr. 2020, 92, 373–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldrup, M.; Johansen, M.I.; Fjaeldstad, A.W. Anosmia and ageusia as primary symptoms of COVID-19. Ugeskr. Laeger 2020, 182, V04200205. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, N.; Yu, W.; Xia, J.; Shen, Y.; Yap, M.; Han, W. Evaluation of ocular symptoms and tropism of SARS-CoV-2 in patients confirmed with COVID-19. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, e649–e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormati, A.; Shahhamzeh, A.; Afifian, M.; Khodadust, F.; Ahmadpour, S. Can COVID-19 present unusual GI symptoms? J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi 2020, 53, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Muth, D.; Niemeyer, D.; Drosten, C. Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2018, 100, 163–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, K.V. SARS coronavirus: A new challenge for prevention and therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Pohlmann, S. A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 779–784.e775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11727–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Torres, J.L.; DeDiego, M.L.; Verdia-Baguena, C.; Jimenez-Guardeno, J.M.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Castano-Rodriguez, C.; Alcaraz, A.; Torres, J.; Aguilella, V.M.; et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein ion channel activity promotes virus fitness and pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Dediego, M.L.; Alvarez, E.; Jimenez-Guardeno, J.M.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Llorente, M.; Kremer, L.; Shuo, S.; Enjuanes, L. Subcellular location and topology of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein. Virology 2011, 415, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Maheswari, U.; Parthasarathy, K.; Ng, L.; Ding, X.L.; Gong, X. Conductance and amantadine binding of a pore formed by a lysine-flanked transmembrane domain of SARS coronavirus envelope protein. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; Gage, P.; Ewart, G. Hexamethylene amiloride blocks E protein ion channels and inhibits coronavirus replication. Virology 2006, 353, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; McKinlay, C.; Gage, P.; Ewart, G. SARS coronavirus E protein forms cation-selective ion channels. Virology 2004, 330, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Surya, W.; Claudine, S.; Torres, J. Structure of a conserved Golgi complex-targeting signal in coronavirus envelope proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12535–12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, K.; Lu, H.; Surya, W.; Vararattanavech, A.; Pervushin, K.; Torres, J. Expression and purification of coronavirus envelope proteins using a modified beta-barrel construct. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 85, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Verdia-Baguena, C.; Jimenez-Guardeno, J.M.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Castano-Rodriguez, C.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Torres, J.; Aguilella, V.M.; Enjuanes, L. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus E protein transports calcium ions and activates the NLRP3 inflammasome. Virology 2015, 485, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdia-Baguena, C.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Alcaraz, A.; Dediego, M.L.; Enjuanes, L.; Aguilella, V.M. Analysis of SARS-CoV E protein ion channel activity by tuning the protein and lipid charge. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdia-Baguena, C.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Alcaraz, A.; DeDiego, M.L.; Torres, J.; Aguilella, V.M.; Enjuanes, L. Coronavirus E protein forms ion channels with functionally and structurally-involved membrane lipids. Virology 2012, 432, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Parthasarathy, K.; Lin, X.; Saravanan, R.; Kukol, A.; Liu, D.X. Model of a putative pore: The pentameric a-helical bundle of SARS coronavirus E protein in lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Wang, J.; Parthasarathy, K.; Liu, D.X. The transmembrane oligomers of coronavirus protein E. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervushin, K.; Tan, E.; Parthasarathy, K.; Xin, L.; Jiang, F.L.; Yu, D.; Vararattanavech, A.; Soong, T.W.; Liu, D.X.; Torres, J. Structure and inhibition of the SARS coronavirus envelope protein ion channel. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, K.; Ng, L.; Lin, X.; Liu, D.X.; Pervushin, K.; Gong, X.; Torres, J. Structural flexibility of the pentameric SARS coronavirus envelope protein ion channel. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, L39–L41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Ockinger, J.; Yu, J.; Byles, V.; McColl, A.; Hofer, A.M.; Horng, T. Critical role for calcium mobilization in activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11282–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Yanagi, Y.; Ichinohe, T. Encephalomyocarditis virus viroporin 2B activates NLRP3 inflammasome. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilou, K.; Kar, S.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Triantafilou, M. Rhinovirus-induced calcium flux triggers NLRP3 and NLRC5 activation in bronchial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, V.S.; McKay, M.J.; Shcherbakov, A.A.; Dregni, A.J.; Kolocouris, A.; Hong, M. Structure and drug binding of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein transmembrane domain in lipid bilayers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, W.; Li, Y.; Torres, J. Structural model of the SARS coronavirus E channel in LMPG micelles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A.; Zscherp, C. What vibrations tell us about proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2002, 35, 369–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandekar, J.; Krimm, S. Vibrational analysis of peptides, polypeptides, and proteins: Characteristic amide bands of beta-turns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.R.; Lin, L.D.; Machamer, C.E. Identification of a Golgi complex-targeting signal in the cytoplasmic tail of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5794–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, W.; Samsó, M.; Torres, J. Structural and Functional Aspects of Viroporins in Human Respiratory Viruses: Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Coronaviruses. In Respiratory Disease and Infection—A New Insight; Vats, M., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; pp. 47–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmin, A.; Orekhov, P.; Astashkin, R.; Gordeliy, V.; Gushchin, I. Structure and dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein monomer. Proteins 2022, 90, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, J.S.; Jing, X.; Leser, G.P.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 protein mediates ESCRT-independent membrane scission. Cell 2010, 142, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, F.; Hunt, C.A.; Szoka, F.C.; Vail, W.J.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Preparation of liposomes of defined size distribution by extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. BBA Biomembr. 1979, 557, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.; Li, C.; Eremina, N.; Goormaghtigh, E.; Barth, A. Simultaneous Fitting of Absorption Spectra and Their Second Derivatives for an Improved Analysis of Protein Infrared Spectra. Molecules 2015, 20, 12599–12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyr, M.J. Fityk: A General-Purpose Peak Fitting Program. Appl. Cryst. 2010, 43, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuck, P.; Perugini, M.A.; Gonzales, N.R.; Howlett, G.J.; Schubert, D. Size-distribution analysis of proteins by analytical ultracentrifugation: Strategies and application to model systems. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 1096–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brautigam, C.A. Calculations and Publication-Quality Illustrations for Analytical Ultracentrifugation Data. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 562, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laue, T.M.; Shah, B.; Ridgeway, T.M.; Pelletier, S.L. Computer-aided Interpretation of Sedimentation Data for Proteins. In Analytical Ultracentrifugation in Biochemistry and Polymer Science; Harding, S.E., Horton, J.C., Rowe, A.J., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1992; pp. 90–125. [Google Scholar]
- Schuck, P. On the analysis of protein self-association by sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 320, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | f/f0 1 | MC (Da) 2 | δD 3 | νC (mL/g) 4 | Mb (Da) 5 | Diam. (nm) 6 | S 7 | S-Range 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| His-E-TR monomer | 2.2 | 9081 + 30,179 = 39,260 | 0.000 | 0.754 | 1989 | 2.8 | 0.52 | 0.44–0.52 |
| His-E-TR pentamer | 1.7 | 45,405 + 30,179 = 75,584 | 0.000 | 0.754 | 9947 | 4.8 | 1.97 | 1.89–1.97 |
| E-FL monomer | 2.2 | 8542 + 30,179 = 38,721 | 0.000 | 0.765 | 1777 | 2.8 | 0.47 | 0.40–0.47 |
| E-FL pentamer | 1.7 | 42,710 + 30,179 = 72,889 | 0.000 | 0.765 | 8883 | 4.7 | 1.78 | 1.71–1.78 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Surya, W.; Torres, J. Oligomerization-Dependent Beta-Structure Formation in SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113285
Surya W, Torres J. Oligomerization-Dependent Beta-Structure Formation in SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113285
Chicago/Turabian StyleSurya, Wahyu, and Jaume Torres. 2022. "Oligomerization-Dependent Beta-Structure Formation in SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113285
APA StyleSurya, W., & Torres, J. (2022). Oligomerization-Dependent Beta-Structure Formation in SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113285






