Mitochondria-Targeting Polymer Micelles in Stepwise Response Releasing Gemcitabine and Destroying the Mitochondria and Nucleus for Combined Antitumor Chemotherapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
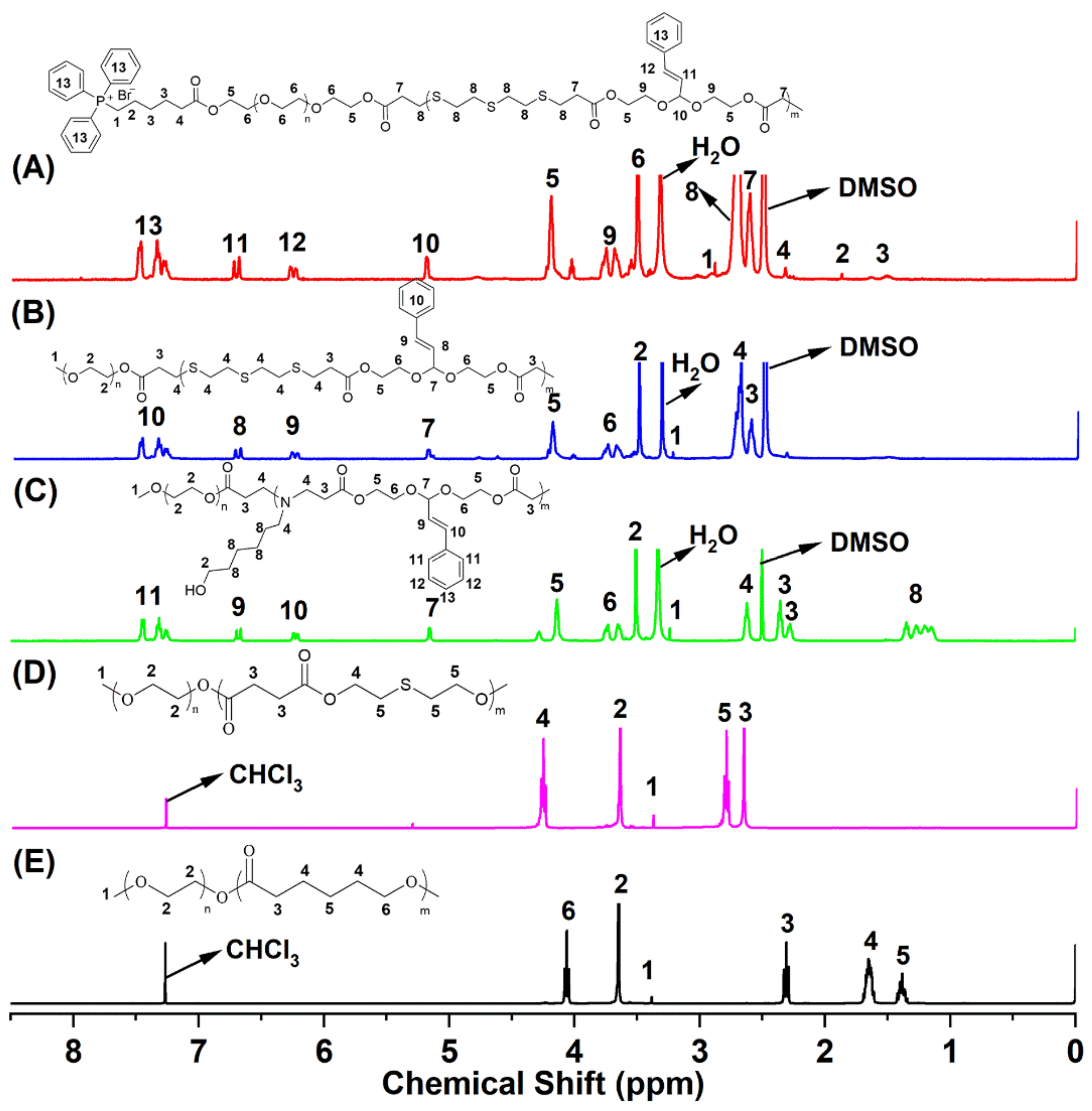
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Block Copolymer
2.2. Characterization of Blank Micelles and GEM-Loaded Micelles
2.3. pH/ROS-Responsiveness
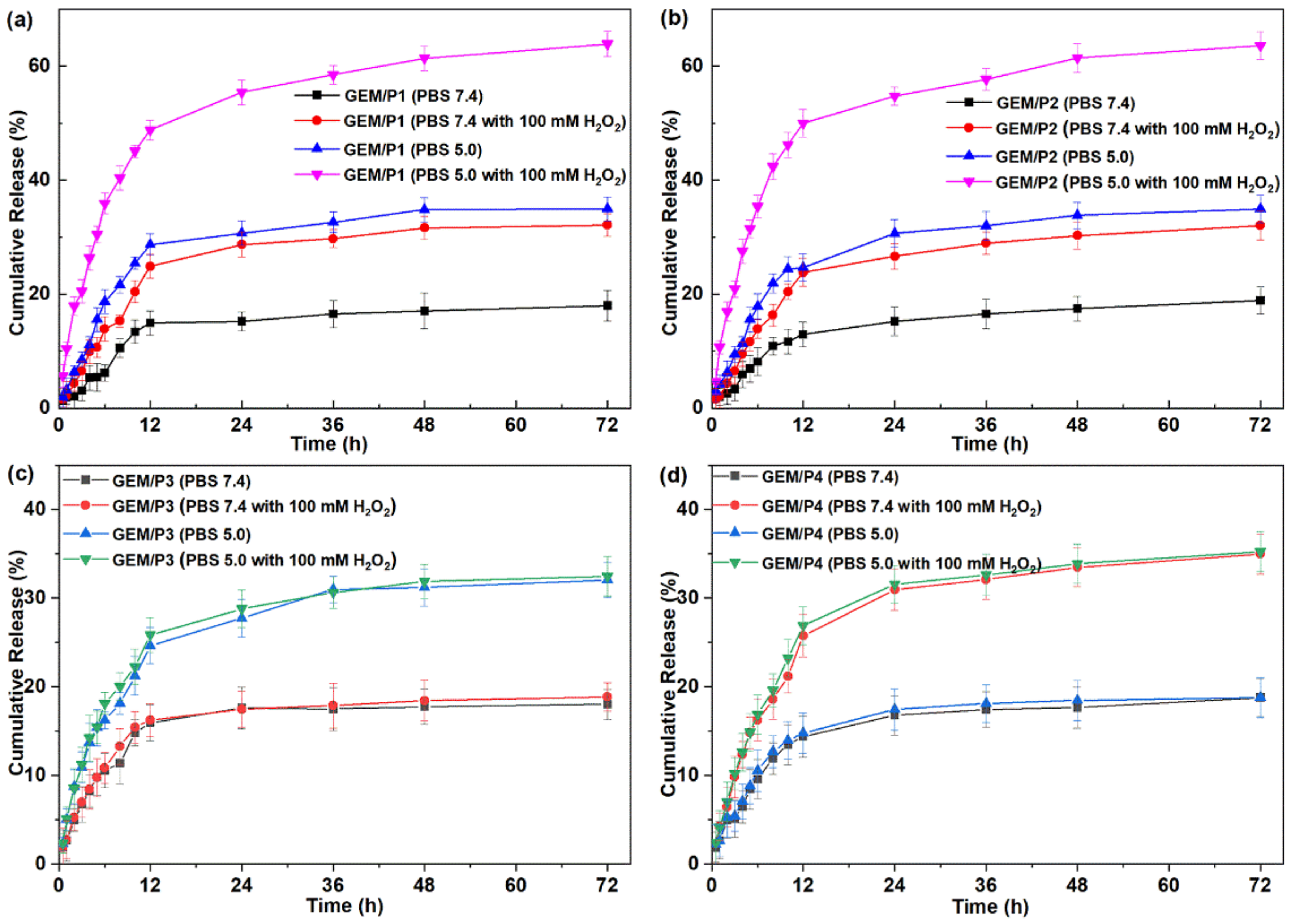
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release
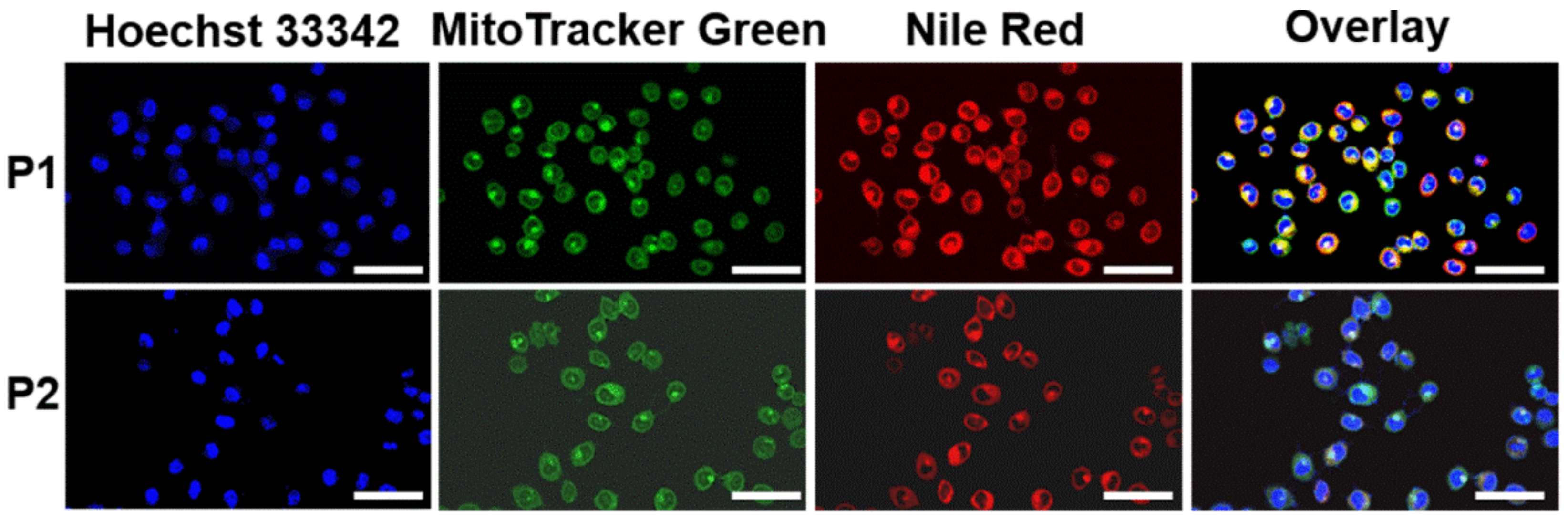
2.5. Colocalization in Mitochondria
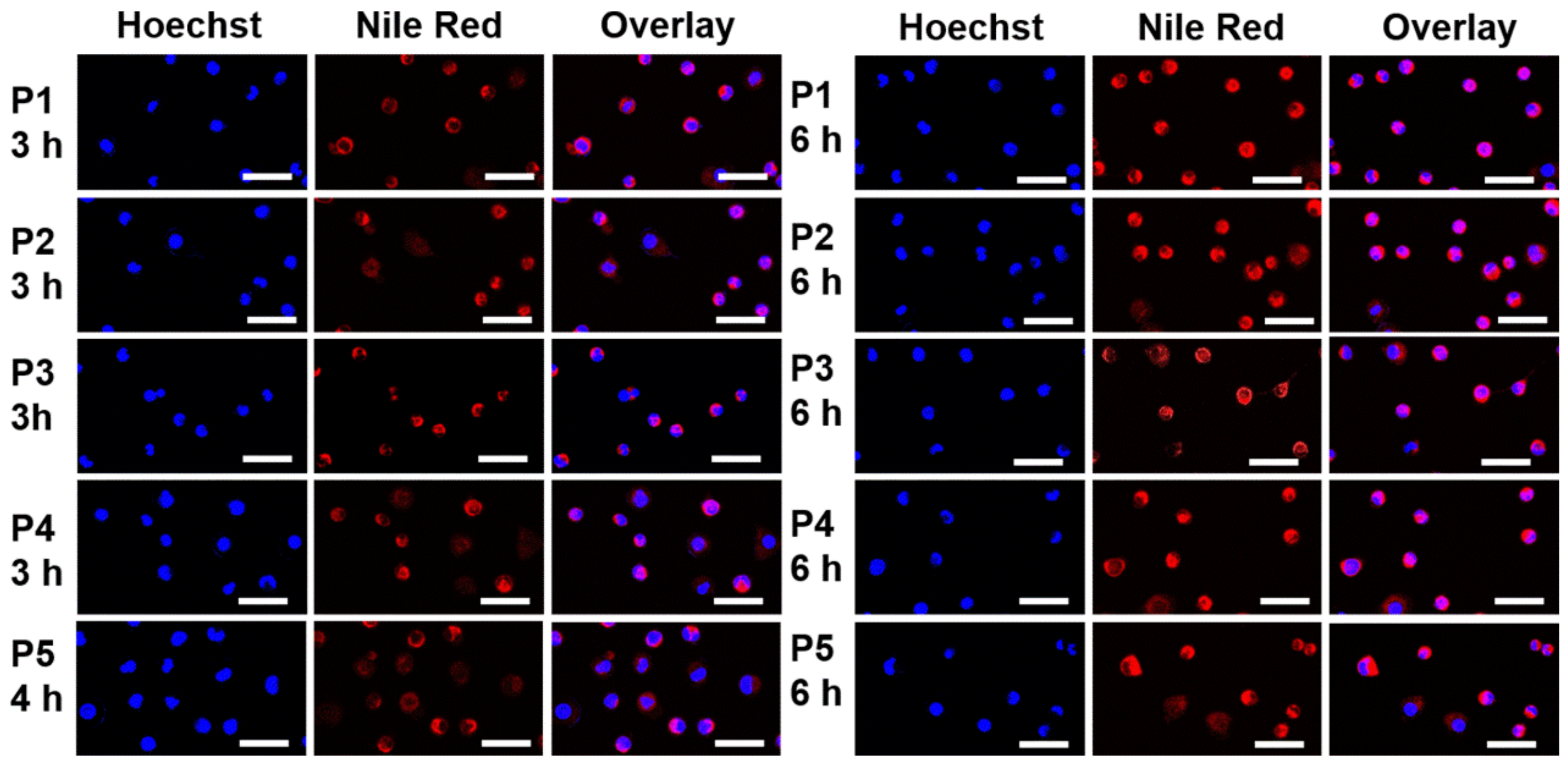
2.6. Cellular Uptake
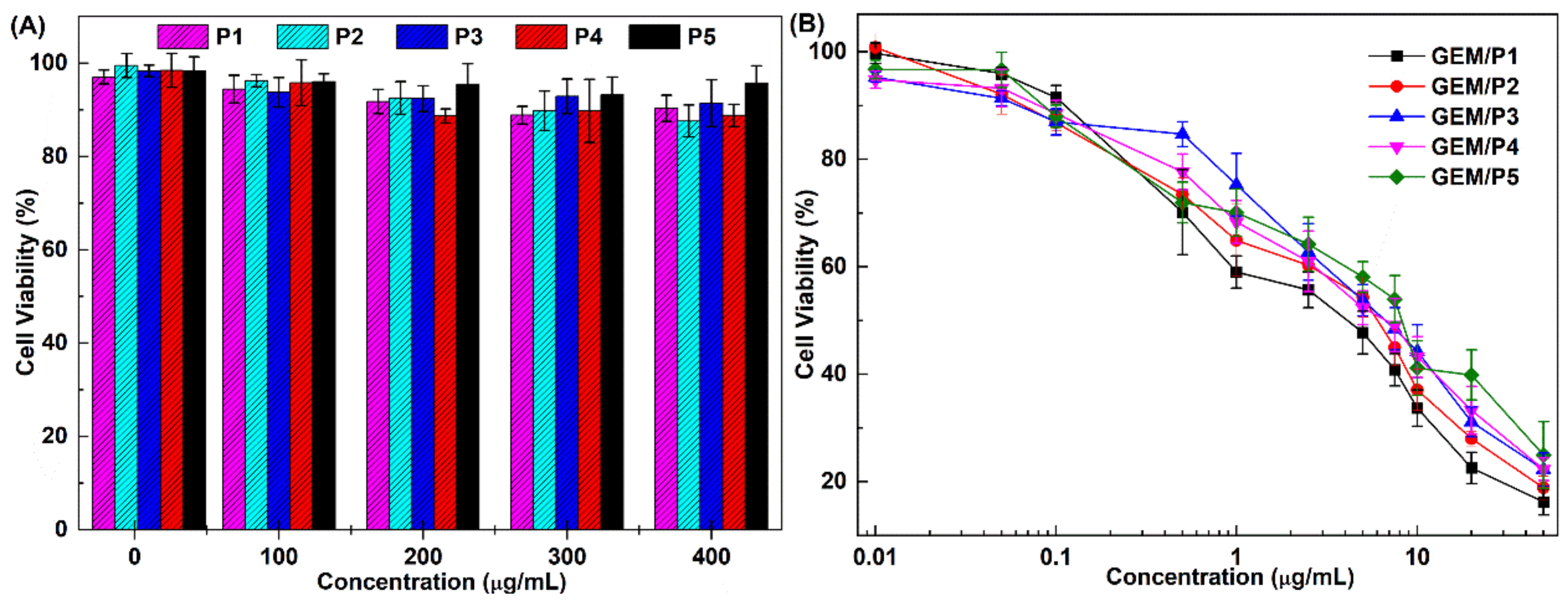
2.7. Cytotoxicity
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Materials
3.2. Characterizations
3.3. Synthesis of Double-End Alkenylated Acetal (AA)
3.4. Synthesis of Acryloyl Chloride Conjugated Methoxy Poly(ethylene glycol) (mPEG2k-AC)
3.5. Synthesis of Triphenylphosphine Conjugated Poly(ethylene glycol) (TPP-PEG2k)
3.6. Synthesis of Acryloyl Chloride Conjugated TPP-PEG2k (TPP-PEG2k-AC)
3.7. Synthesis of pH/ROS Dual-Responsive Block Copolymer Targeting Mitochondria (TPP-PEG2k-b-(BS-AA)n)
3.8. Synthesis of pH/ROS Dual-Responsive Block Copolymers (mPEG2k-b-(BS-AA)n)
3.9. Synthesis of pH-Responsive Block Copolymers (mPEG2k-b-(AH-AA)n)
3.10. Synthesis of ROS-Responsive Block Copolymers (mPEG2k-b-(SA-TG)n)
3.11. Synthesis of Non-Responsive Block Copolymers
3.12. Preparation of Blank Micelles and GEM-Loaded Micelles
3.13. Critical Micelle Concentration
3.14. Drug-Loading Content
3.15. ROS/pH-Responsiveness
3.16. In Vitro Drug Release
3.17. Cellular Uptake
3.18. Co-Localization in Mitochondria
3.19. Biocompatibility Experiment
3.20. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, N.; Liu, C.; Yao, W.; Zhou, H.; Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Qiao, W. A traceable, sequential multistage-targeting nanoparticles combining chemo/chemodynamic therapy for enhancing antitumor efficacy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, C.; Yao, W.; Zhou, H.; Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Qiao, W. Endogenous reactive oxygen species burst induced and spatiotemporally controlled multiple drug release by traceable nanoparticles for enhancing antitumor efficacy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4968–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, L.; Han, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. Blood circulation stable doxorubicin prodrug nanoparticles containing hydrazone and thioketal moieties for antitumor chemotherapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 201, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Gao, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; He, B.; Pu, Y. A reactive oxygen species-responsive prodrug micelle with efficient cellular uptake and excellent bioavailability. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Han, R.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L. Construction of polymeric micelles for improving cancer chemotherapy by promoting the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species and self-accelerating drug release. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkooli, F.M.; Soltani, M.; Souri, M. Controlled anti-cancer drug release through advanced nano-drug delivery systems: Static and dynamic targeting strategies. J. Control Release 2020, 327, 316–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, G.; Zhao, J.; Yang, G.; Zhou, S. Stepwise dual targeting and dual responsive polymer micelles for mitochondrion therapy. J. Control Release 2020, 322, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L. Tumor microenvironment-responsive intelligent nanoplatforms for cancer theranostics. Nano Today 2020, 32, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, Y.J.; Yang, X.L.; Wu, W.X.; Zhang, M.Q.; Li, M.Y.; Hu, Z.E.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, N.; Yu, X.Q. Rational construction of a mitochondrial targeting, fluorescent self-reporting drug-delivery platform for combined enhancement of endogenous ros responsiveness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 32432–32445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ma, H.; Lin, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, N.; Feng, X. Nucleus-selective codelivery of proteins and drugs for synergistic antitumor therapy. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 10342–10348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.G.; Leshuk, T.; Gu, F.X. Emerging nanomaterials for targeting subcellular organelles. Nano Today 2011, 6, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, H. Intracellular condensates of oligopeptide for targeting lysosome and addressing multiple drug resistance of cancer. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jia, F.; Chen, X.; Jin, Q.; Ji, J. Atp suppression by ph-activated mitochondria-targeted delivery of nitric oxide nanoplatform for drug resistance reversal and metastasis inhibition. Small 2020, 16, e2001747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Fan, H.; Guo, C.; Cui, L.; Zhang, P.; Mu, H.; Xu, H.; Zhao, F.; Chen, D. Novel mitochondrial targeting multifunctional surface charge-reversal polymeric nanoparticles for cancer treatment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 2151–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, S.S.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Yao, S.Q. Co-delivery of proteins and small molecule drugs for mitochondria-targeted combination therapy. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 3215–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroudi, S.A.K.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Aljaghwani, A.; Rahmani, M.E.-K.A.A.H.; Khan, A.A. Novel strategies for disrupting cancer-cell functions with mitochondria-targeted antitumor drug-loaded nanoformulations. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3907–3936. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Shen, Q.; Xing, D. Mitochondria-specific drug release and reactive oxygen species burst induced by polyprodrug nanoreactors can enhance chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Alfranca, G.; Cheng, S.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhi, X.; Ni, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Ros-responsive mitochondria-targeting blended nanoparticles: Chemo- and photodynamic synergistic therapy for lung cancer with on-demand drug release upon irradiation with a single light source. Theranostics 2016, 6, 2352–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Yu, Y.; Han, R.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Hu, D.; Qian, Z. Polymeric nanoparticles with ros-responsive prodrug and platinum nanozyme for enhanced chemophotodynamic therapy of colon cancer. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, C.; Ma, T.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Kong, L. Hypericin-functionalized graphene oxide for enhanced mitochondria-targeting and synergistic anticancer effect. Acta Biomater. 2018, 77, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Cao, X.; Jia, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, W.; Dai, F.; Zhang, S. Mitochondria-targeted supramolecular coordination container encapsulated with exogenous itaconate for synergistic therapy of joint inflammation. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3251–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, R.; Mu, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Guo, L.; Hai, L.; Wu, Y. Multiple targeted doxorubicin-lonidamine liposomes modified with p-hydroxybenzoic acid and triphenylphosphonium to synergistically treat glioma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 230, 114093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, K.; Diao, J.; Cai, X.; Feng, F.; Wang, S. Gsh and H2O2 co-activatable mitochondria-targeted photodynamic therapy under normoxia and hypoxia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 12122–12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, M.; Ren, L.; Tang, B.Z. Mitochondria- and lysosomes-targeted synergistic chemo-photodynamic therapy associated with self-monitoring by dual light-up fluorescence. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Wang, Z.; Hao, S.; He, H.; Wan, Y.; Zhu, C.; Sun, L.P.; Cheng, G.; Zheng, S.Y. Mitochondria-targeting polydopamine nanoparticles to deliver doxorubicin for overcoming drug resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16793–16802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Q.; Ye, W.L.; Huan, M.L.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, D.Z.; Cui, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, B.L.; Mei, Q.B.; Zhou, S.Y. Mitochondria and nucleus delivery of active form of 10-hydroxycamptothecin with dual shell to precisely treat colorectal cancer. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1011–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Wen, H.; Shi, W.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, P.; Chen, J.; Qin, L.; et al. Tumor- and mitochondria-targeted nanoparticles eradicate drug resistant lung cancer through mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. J. Nanobiotech. 2020, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrache, S.; Dhar, S. Engineering of blended nanoparticle platform for delivery of mitochondria-acting therapeutics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16288–16293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Wu, J.Y.; Xiang, D.X.; Luo, S.L.; Hu, X.B.; Tang, T.T.; Sun, T.L.; Liu, X.Y. Micelles loaded with puerarin and modified with triphenylphosphonium cation possess mitochondrial targeting and demonstrate enhanced protective effect against isoprenaline-induced h9c2 cells apoptosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8345–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, R.; Shi, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hai, L.; Wu, Y. Ph-redox responsive cascade-targeted liposomes to intelligently deliver doxorubicin prodrugs and lonidamine for glioma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 235, 114281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Im, B.N.; Hwang, H.S.; Na, K. Gemcitabine-loaded dspe-peg-pheoa liposome as a photomediated immune modulator for cholangiocarcinoma treatment. Biomaterials 2018, 183, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, Y.; Dalgic, A.D.; Gerekci, S.; Gulec, E.A.; Tezcaner, A.; Ozen, C.; Keskin, D. A new therapeutic combination for osteosarcoma: Gemcitabine and Clofazimine co-loaded liposomal formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 557, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fang, Z.; Song, M.; Liu, K. Mitochondrial targeted hierarchical drug delivery system based on ha-modified liposomes for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 241, 114648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Walker, G.C. Mechanisms of DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Ding, X.; Shan, T.; Liu, Q.; Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Xia, M.; He, Y.; Huang, Z.; et al. Reactive oxygen species-activatable self-amplifying watson-crick base pairing-inspired supramolecular nanoprodrug for tumor-specific therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Cao, J.; Pu, Y.; He, B. Cinnamaldehyde-Based Poly(ester-thioacetal) To Generate Reactive Oxygen Species for Fabricating Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 4658–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Song, W.; Xu, Y.; Si, X.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. Rationally designed polymer conjugate for tumor-specific amplification of oxidative stress and boosting antitumor immunity. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2514–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Q.; Wang, K.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, M.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J. Amplification of tumor oxidative stresses by poly(disulfide acetal) for multidrug resistance reversal. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ge, Z. Dual-targeting polymeric nanocarriers to deliver ros-responsive prodrugs and combat multidrug resistance of cancer cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, e2100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, M.; Gao, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pu, Y.; He, B. Polymeric nanoparticles responsive to intracellular ros for anticancer drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Teng, W.; Jin, Q.; Ji, J. One-step preparation of reduction-responsive cross-linked gemcitabine prodrug micelles for intracellular drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Vakili, M.R.; Abyaneh, H.S.; Molavi, O.; Lai, R.; Lavasanifar, A. Mitochondrial delivery of doxorubicin via triphenylphosphine modification for overcoming drug resistance in mda-mb-435/dox cells. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2640–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zheng, F.; Liu, K.; Liu, S.; Xiao, T.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L. Mitochondria-Targeting Polymer Micelles in Stepwise Response Releasing Gemcitabine and Destroying the Mitochondria and Nucleus for Combined Antitumor Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012624
Zhang S, Zheng F, Liu K, Liu S, Xiao T, Zhu Y, Xu L. Mitochondria-Targeting Polymer Micelles in Stepwise Response Releasing Gemcitabine and Destroying the Mitochondria and Nucleus for Combined Antitumor Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(20):12624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012624
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shanming, Fen Zheng, Kaige Liu, Shengke Liu, Tonghu Xiao, Yabin Zhu, and Long Xu. 2022. "Mitochondria-Targeting Polymer Micelles in Stepwise Response Releasing Gemcitabine and Destroying the Mitochondria and Nucleus for Combined Antitumor Chemotherapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 20: 12624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012624
APA StyleZhang, S., Zheng, F., Liu, K., Liu, S., Xiao, T., Zhu, Y., & Xu, L. (2022). Mitochondria-Targeting Polymer Micelles in Stepwise Response Releasing Gemcitabine and Destroying the Mitochondria and Nucleus for Combined Antitumor Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(20), 12624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012624






