Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Roles of Fascial Hyaluronan in Obesity-Related Myofascial Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hyaluronan Biochemistry, Cellular Synthesis, and Homeostasis
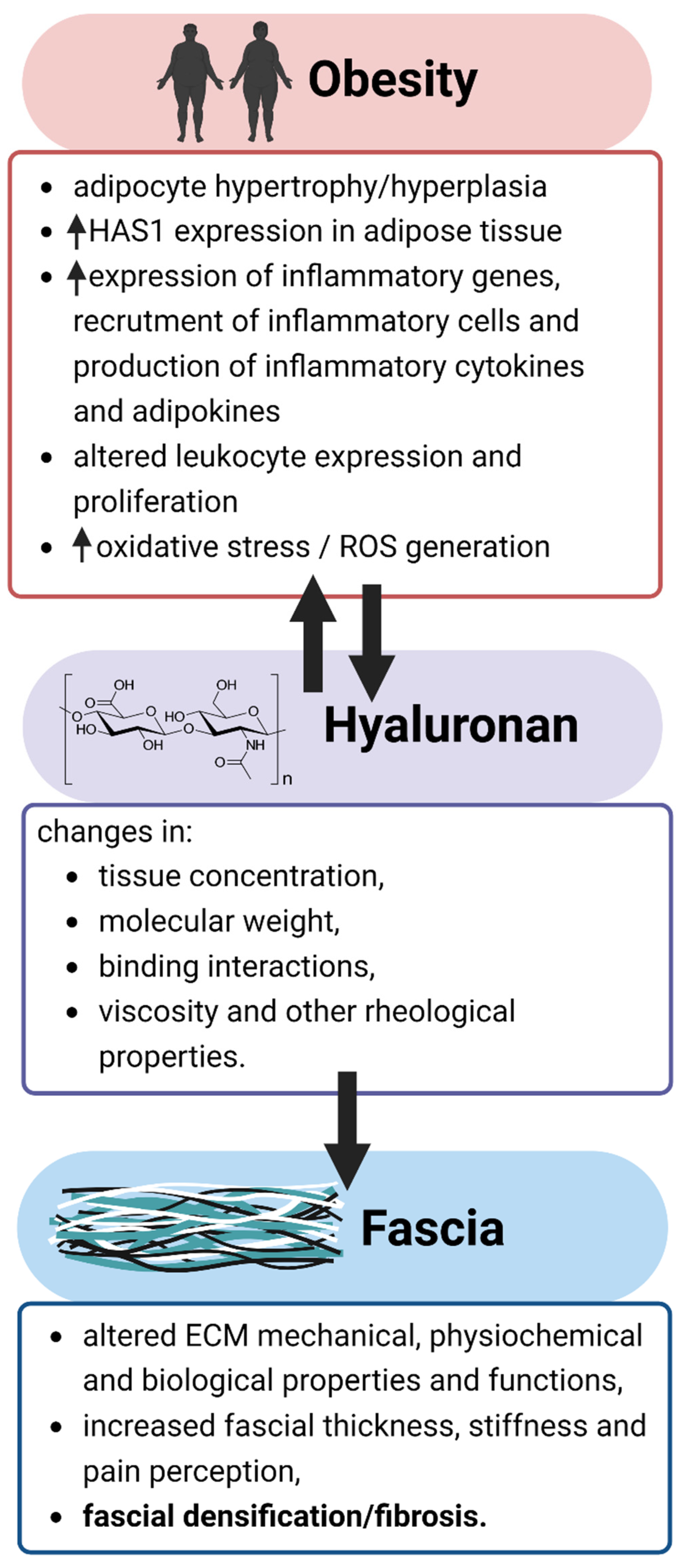
3. Obesity and Myofascial Disease
4. Pathophysiological Importance and Associated Alterations of Hyaluronan in Obesity
5. The Etiological Significance of Changes in Hyaluronan Properties in Myofascial Disease
6. Therapeutic Considerations of Hyaluronan in Myofascial Disease
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adstrum, S.; Hedley, G.; Schleip, R.; Stecco, C.; Yucesoy, C.A. Defining the Fascial System. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2017, 21, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, B.; Escher, A.R.; Tobbi, F.; Pianese, L.; Ciardo, A.; Yamahata, J.; Hernandez, S.; Sanchez, O. Fascial Nomenclature: Update 2022. Cureus 2022, 14, e25904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleip, R.; Hedley, G.; Yucesoy, C.A. Fascial Nomenclature: Update on Related Consensus Process. Clin. Anat. 2019, 32, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fede, C.; Pirri, C.; Fan, C.; Petrelli, L.; Guidolin, D.; de Caro, R.; Stecco, C. A Closer Look at the Cellular and Molecular Components of the Deep/Muscular Fasciae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, B.; Varacallo, M. Anatomy, Fascia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pirri, C.; Fede, C.; Pirri, N.; Petrelli, L.; Fan, C.; de Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Diabetic Foot: The Role of Fasciae, a Narrative Review. Biology 2021, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, S.; Teo, E.C.; Fekete, G.; Gu, Y. The Influence of Heel Height on Strain Variation of Plantar Fascia During High Heel Shoes Walking-Combined Musculoskeletal Modeling and Finite Element Analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 791238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleip, R.; Klingler, W. Active Contractile Properties of Fascia. Clin. Anat. 2019, 32, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Abbott, H.; Masi, A.T.; Henderson, J.; Nair, K. Biomechanical Properties of Low Back Myofascial Tissue in Younger Adult Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients and Matched Healthy Control Subjects. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 57, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleip, R.; Gabbiani, G.; Wilke, J.; Naylor, I.; Hinz, B.; Zorn, A.; Jäger, H.; Breul, R.; Schreiner, S.; Klingler, W. Fascia Is Able to Actively Contract and May Thereby Influence Musculoskeletal Dynamics: A Histochemical and Mechanographic Investigation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stecco, C.; Corradin, M.; Macchi, V.; Morra, A.; Porzionato, A.; Biz, C.; de Caro, R. Plantar Fascia Anatomy and Its Relationship with Achilles Tendon and Paratenon. J. Anat. 2013, 223, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, R.L. Hyaluronan and the Fascial Frontier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Palmer, J.W. The Polysaccharide of the Vitreous Humor. J. Biol. Chem. 1934, 107, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwowska, N.M.; Bebenek, K.A.; Żądło, D.A.; Wcisło-Dziadecka, D.L. Physiochemical Properties and Application of Hyaluronic Acid: A Systematic Review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, E.A.; Laurent, T.C.; Jeanloz, R.W. Nomenclature of Hyaluronic Acid. Biochem. J. 1986, 235, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, M.A. Hyaluronic Acid in Dermatology. Skinmed 2017, 15, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.R.E.; Laurent, T.C.; Laurent, U.B.G. Hyaluronan: Its Nature, Distribution, Functions and Turnover. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 242, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fakhari, A.; Berkland, C. Applications and Emerging Trends of Hyaluronic Acid in Tissue Engineering, as a Dermal Filler and in Osteoarthritis Treatment. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7081–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruckmani, K.; Shaikh, S.Z.; Khalil, P.; Muneera, M.S.; Thusleem, O.A. Determination of Sodium Hyaluronate in Pharmaceutical Formulations by HPLC–UV. J. Pharm. Anal. 2013, 3, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobetz, M.A.; Chan, D.S.; Neesse, A.; Bapiro, T.E.; Cook, N.; Frese, K.K.; Feig, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Caldwell, M.E.; Zecchini, H.I.; et al. Hyaluronan Impairs Vascular Function and Drug Delivery in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Gut 2013, 62, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.M.; Park, S.J.; Noh, I.; Kim, C.H. The Effects of the Molecular Weights of Hyaluronic Acid on the Immune Responses. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavianatou, A.G.; Caon, I.; Franchi, M.; Piperigkou, Z.; Galesso, D.; Karamanos, N.K. Hyaluronan: Molecular Size-Dependent Signaling and Biological Functions in Inflammation and Cancer. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2883–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Entwistle, J.; Hall, C.L.; Turley, E.A. HA Receptors: Regulators of Signalling to the Cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biochem. 1996, 61, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Qian, K.; Cho, W.C.; Duan, L. NcRNA-Mediated High Expression of HMMR as a Prognostic Biomarker Correlated with Cell Proliferation and Cell Migration in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecco, A.; Cowman, M.; Pirri, N.; Raghavan, P.; Pirri, C. Densification: Hyaluronan Aggregation in Different Human Organs. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecco, C.; Fede, C.; Macchi, V.; Porzionato, A.; Petrelli, L.; Biz, C.; Stern, R.; de Caro, R. The Fasciacytes: A New Cell Devoted to Fascial Gliding Regulation. Clin. Anat. 2018, 31, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartok, B.; Firestein, G.S. Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes: Key Effector Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCombe, D.; Brown, T.; Slavin, J.; Morrison, W.A. The Histochemical Structure of the Deep Fascia and Its Structural Response to Surgery. J. Hand Surg. Br. 2001, 26, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecco, C.; Stern, R.; Porzionato, A.; MacChi, V.; Masiero, S.; Stecco, A.; de Caro, R. Hyaluronan within Fascia in the Etiology of Myofascial Pain. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2011, 33, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman, M.K.; Schmidt, T.A.; Raghavan, P.; Stecco, A. Viscoelastic Properties of Hyaluronan in Physiological Conditions. F1000Research 2015, 4, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piehl-Aulin, K.; Laurent, C.; Engstrom-Laurent, A.; Hellstrom, S.; Henriksson, J. Hyaluronan in Human Skeletal Muscle of Lower Extremity: Concentration, Distribution, and Effect of Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 71, 2493–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Ji, B.; Gao, H. Modeling Active Mechanosensing in Cell-Matrix Interactions. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2015, 44, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zügel, M.; Maganaris, C.N.; Wilke, J.; Jurkat-Rott, K.; Klingler, W.; Wearing, S.C.; Findley, T.; Barbe, M.F.; Steinacker, J.M.; Vleeming, A.; et al. Fascial Tissue Research in Sports Medicine: From Molecules to Tissue Adaptation, Injury and Diagnostics: Consensus Statement. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolf, K.J.; Kumar, S. Hyaluronic Acid: Incorporating the Bio into the Material. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3753–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csoka, A.B.; Stern, R. Hypotheses on the Evolution of Hyaluronan: A Highly Ironic Acid. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fede, C.; Angelini, A.; Stern, R.; Macchi, V.; Porzionato, A.; Ruggieri, P.; de Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Quantification of Hyaluronan in Human Fasciae: Variations with Function and Anatomical Site. J. Anat. 2018, 233, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentham, J.; di Cesare, M.; Bilano, V.; Bixby, H.; Zhou, B.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Taddei, C.; Hajifathalian, K.; Lu, Y.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reilly, J.J.; El-Hamdouchi, A.; Diouf, A.; Monyeki, A.; Somda, S.A. Determining the Worldwide Prevalence of Obesity. Lancet 2018, 391, 1773–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovski, J.A. Obesity: Trends in Underweight and Obesity—Scale of the Problem. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- Okunogbe, A.; Nugent, R.; Spencer, G.; Ralston, J.; Wilding, J. Economic Impacts of Overweight and Obesity: Current and Future Estimates for Eight Countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulis, W.D.; Silva, S.; Koes, B.W.; van Middelkoop, M. Overweight and Obesity Are Associated with Musculoskeletal Complaints as Early as Childhood: A Systematic Review. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannini, S.N.; Doŕia-Filho, U.; Damiani, D.; Silva, C.A.A. Musculoskeletal Pain in Obese Adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2011, 87, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weller, J.L.; Comeau, D.; Otis, J.A.D. Myofascial Pain. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecco, A.; Gesi, M.; Stecco, C.; Stern, R. Fascial Components of the Myofascial Pain Syndrome. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddle, D.L.; Schappert, S.M. Volume of Ambulatory Care Visits and Patterns of Care for Patients Diagnosed with Plantar Fasciitis: A National Study of Medical Doctors. Foot Ankle Int. 2004, 25, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, K.; Ravarian, B.; Saberi, A.; Salari, A.; Reyhanian, Z.; Khakpour, M.; Chabok, S.Y. Prevalence of Cervical Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Its Correlation with the Severity of Pain and Disability in Patients with Chronic Non-Specific Neck Pain. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2021, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezo-Téllez, E.; Torres-Lacomba, M.; Mayoral-del Moral, O.; Sánchez-Sánchez, B.; Dommerholt, J.; Gutiérrez-Ortega, C. Prevalence of Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Chronic Non-Specific Neck Pain: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 2369–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bron, C.; Dommerholt, J.; Stegenga, B.; Wensing, M.; Oostendorp, R.A. High Prevalence of Shoulder Girdle Muscles with Myofascial Trigger Points in Patients with Shoulder Pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.K.; Nizar, A.J. Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Chronic Back Pain Patients. Korean J. Pain 2011, 24, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.J.; Saini, V.; Saini, S. Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A Treatment Review. Pain Ther. 2013, 2, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.B.; Furia, J. Economic Burden of Plantar Fasciitis Treatment in the United States. Am. J. Orthop. 2010, 39, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.A.; Jones, G.; Cook, J.; Squibb, K.; Wills, K.; Lahham, A.; Winzenberg, T. Chronic Plantar Heel Pain Modifies Associations of Ankle Plantarflexor Strength and Body Mass Index with Calcaneal Bone Density and Microarchitecture. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamstra-Wright, K.L.; Huxel Bliven, K.C.; Bay, R.C.; Aydemir, B. Risk Factors for Plantar Fasciitis in Physically Active Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Health 2021, 13, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, R.; Kunal, K. Modifiable Risk Factors of Plantar Fasciitis in Non-Athletic Patients and Proposal of a New Objective Assessment System—RKISP. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2021, 56, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, D.L.; Pulisic, M.; Pidcoe, P.; Johnson, R.E. Risk Factors for Plantar Fasciitis: A Matched Case-Control Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. A 2003, 85, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irving, D.B.; Cook, J.L.; Young, M.A.; Menz, H.B. Obesity and Pronated Foot Type May Increase the Risk of Chronic Plantar Heel Pain: A Matched Case-Control Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2007, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mickle, K.J.; Steele, J.R. Obese Older Adults Suffer Foot Pain and Foot-Related Functional Limitation. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gimenez-Donoso, C.; Bosque, M.; Vila, A.; Vilalta, G.; Santafe, M.M. Effects of a Fat-Rich Diet on the Spontaneous Release of Acetylcholine in the Neuromuscular Junction of Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, K.D.B.; Rogers, J.; Winzenberg, T.; van Middelkoop, M. Higher Body Mass Index Is Associated with Plantar Fasciopathy/’plantar Fasciitis’: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Various Clinical and Imaging Risk Factors. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, M.; Schiavone, C.; di Carlo, L.; Salini, V. Achilles Tendon and Plantar Fascia in Recently Diagnosed Type II Diabetes: Role of Body Mass Index. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.E.; Cusumano, J.; Duffin, A.C.; Hing, S.; Gallego, P.H.; Donaghue, K.C.; Lam, A. Plantar Fascia Thickness, a Measure of Tissue Glycation, Predicts the Development of Complications in Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benitez-Aguirre, P.Z.; Craig, M.E.; Jenkins, A.J.; Gallego, P.H.; Cusumano, J.; Dufin, A.C.; Hing, S.; Donaghue, K.C. Plantar Fascia Thickness Is Longitudinally Associated with Retinopathy and Renal Dysfunction: A Prospective Study from Adolescence to Adulthood. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ursini, F.; Arturi, F.; Nicolosi, K.; Ammendolia, A.; D’Angelo, S.; Russo, E.; Naty, S.; Bruno, C.; de Sarro, G.; Olivieri, I.; et al. Plantar Fascia Enthesopathy Is Highly Prevalent in Diabetic Patients without Peripheral Neuropathy and Correlates with Retinopathy and Impaired Kidney Function. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, B.Y.C.; Woodburn, J.; Newcombe, L.; Barn, R. Plantar Soft Tissues and Achilles Tendon Thickness and Stiffness in People with Diabetes: A Systematic Review. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2021, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, C.K.; Cvetko, E.; Umek, N. Skeletal Muscle Microvascular Dysfunction in Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Skeletal Muscle Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Money, S. Pathophysiology of Trigger Points in Myofascial Pain Syndrome. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2017, 31, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, M.J.; Kaber, G.; Demirdjian, S.; Cai, P.C.; Burgener, E.B.; Nagy, N.; Barlow, G.L.; Popescu, M.; Nicolls, M.R.; Ozawa, M.G.; et al. Biochemical, Biophysical, and Immunological Characterization of Respiratory Secretions in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infections. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e152629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, A.; Short, W.D.; Wang, X.; Keswani, S.G. Hyaluronidases in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, N.; Kuipers, H.F.; Marshall, P.L.; Wang, E.; Kaber, G.; Bollyky, P.L. Hyaluronan in Immune Dysregulation and Autoimmune Diseases. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78–79, 292–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karousou, E.; Misra, S.; Ghatak, S.; Dobra, K.; Götte, M.; Vigetti, D.; Passi, A.; Karamanos, N.K.; Skandalis, S.S. Roles and Targeting of the HAS/Hyaluronan/CD44 Molecular System in Cancer. Matrix Biol. 2017, 59, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, P.; Kolliopoulos, C.; Lin, C.Y.; Heldin, C.H. Involvement of Hyaluronan and CD44 in Cancer and Viral Infections. Cell. Signal. 2020, 65, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homann, S.; Grandoch, M.; Kiene, L.S.; Podsvyadek, Y.; Feldmann, K.; Rabausch, B.; Nagy, N.; Lehr, S.; Kretschmer, I.; Oberhuber, A.; et al. Hyaluronan Synthase 3 Promotes Plaque Inflammation and Atheroprogression. Matrix Biol. 2018, 66, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; Sunkari, V.G.; Kaber, G.; Hasbun, S.; Lam, D.N.; Speake, C.; Sanda, S.; McLaughlin, T.L.; Wight, T.N.; Long, S.R.; et al. Hyaluronan Levels Are Increased Systemically in Human Type 2 but Not Type 1 Diabetes Independently of Glycemic Control. Matrix Biol. 2019, 80, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Angulo, P.; Lymp, J.; Li, D.; Satomura, S.; Lindor, K. Hyaluronic Acid, an Accurate Serum Marker for Severe Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, H.; Hashimoto, E.; Yatsuji, S.; Tokushige, K.; Shiratori, K. Hyaluronic Acid Levels Can Predict Severe Fibrosis and Platelet Counts Can Predict Cirrhosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Lantier, L.; Kennedy, A.; Bonner, J.S.; Mayes, W.H.; Bracy, D.P.; Bookbinder, L.H.; Hasty, A.H.; Thompson, C.B.; Wasserman, D.H. Hyaluronan Accumulates with High-Fat Feeding and Contributes to Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morita, M.; Yano, S.; Ishibashi, Y.; Nakata, N.; Kurioka, S.; Sugimoto, T. Close Relationship between Serum Hyaluronan Levels and Vascular Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Biomarkers 2014, 19, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kruglikov, I.L.; Akgul, Y.; Scherer, P.E. Hyaluronan in Adipogenesis, Adipose Tissue Physiology and Systemic Metabolism. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78–79, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, M.; López-Vicario, C.; Pérez-Romero, N.; Casulleras, M.; Martínez-Puchol, A.I.; Sánchez, B.; Flores-Costa, R.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Duran-Güell, M.; Ibarzábal, A.; et al. Small Fragments of Hyaluronan Are Increased in Individuals with Obesity and Contribute to Low-Grade Inflammation through TLR-Mediated Activation of Innate Immune Cells. Int. J. Obes. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogelstrand, P.; Borén, J. Treatment of Hyaluronan Accumulation Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance in Mice. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1816–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasib, A.; Hennayake, C.K.; Bracy, D.P.; Bugler-Lamb, A.R.; Lantier, L.; Khan, F.; Ashford, M.L.J.; McCrimmon, R.J.; Wasserman, D.H.; Kang, L. CD44 Contributes to Hyaluronan-Mediated Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle of High-Fat-Fed C57BL/6 Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E973–E983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, E.; Jung, M.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.; Seo, C.R.; Park, K.W.; Lee, E.K.; Yeom, C.H.; Lee, S. Inhibition of Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells and Suppression of Abdominal Fat Accumulation in High-Fat Diet-Feeding C57BL/6J Mice after Downregulation of Hyaluronic Acid. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Toda, K.; Yamada, S.; Hara, K.; Irie, J.; Sirota, M.; Morgan, A.A.; Chen, R.; Ohtsu, H.; et al. Expression-Based Genome-Wide Association Study Links the Receptor CD44 in Adipose Tissue with Type 2 Diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7049–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avenoso, A.; Bruschetta, G.; D`Ascola, A.; Scuruchi, M.; Mandraffino, G.; Saitta, A.; Campo, S.; Campo, G.M. Hyaluronan Fragmentation During Inflammatory Pathologies: A Signal That Empowers Tissue Damage. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brecht, M.; Mayer, U.; Schlosser, E.; Prehm, P. Increased Hyaluronate Synthesis Is Required for Fibroblast Detachment and Mitosis. Biochem. J. 1986, 239, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Byers, H.R.; Vink, J.; Stamenkovic, I. CD44H Regulates Tumor Cell Migration on Hyaluronate-Coated Substrate. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 118, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, C.L.; Turley, E.A. Hyaluronan: RHAMM Mediated Cell Locomotion and Signaling in Tumorigenesis. J. Neurooncol. 1995, 26, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdin, B.; Hällgren, R. Dynamic Role of Hyaluronan (HYA) in Connective Tissue Activation and Inflammation. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 242, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garantziotis, S.; Savani, R.C. Proteoglycans in Toll-like Receptor Responses and Innate Immunity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C202–C214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamadzadeh, M.; DeGrendele, H.; Arizpe, H.; Estess, P.; Siegelman, M. Proinflammatory Stimuli Regulate Endothelial Hyaluronan Expression and CD44/HA-Dependent Primary Adhesion. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, H.; Terao, T. Hyaluronic Acid-Specific Regulation of Cytokines by Human Uterine Fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, C1151–C1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranova, N.S.; Nilebäck, E.; Haller, F.M.; Briggs, D.C.; Svedhem, S.; Day, A.J.; Richter, R.P. The Inflammation-Associated Protein TSG-6 Cross-Links Hyaluronan via Hyaluronan-Induced TSG-6 Oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25675–25686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lui, P.P.Y.; Yung, P.S.H. Inflammatory Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Tendinopathy. J. Orthop. Translat. 2021, 31, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacChi, M.; Spezia, M.; Elli, S.; Schiaffini, G.; Chisari, E. Obesity Increases the Risk of Tendinopathy, Tendon Tear and Rupture, and Postoperative Complications: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Yu, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Ma, Y.; Li, S. Causal Associations of Obesity with Achilles Tendinopathy: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 902142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, G.; Kwan, C.K.; Fu, S.C.; Ling, S.K.K.; Chan, K.M.; Yung, P.S.H.; Rolf, C. A Systematic Review of Inflammatory Cells and Markers in Human Tendinopathy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chisari, E.; Rehak, L.; Khan, W.S.; Maffulli, N. Tendon Healing in Presence of Chronic Low-Level Inflammation: A Systematic Review. Br. Med. Bull. 2019, 132, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, G.D.; Bonanno, A.; Cavalieri, L.; Ingrassia, E.; di Sano, C.; Siena, L.; Riccobono, L.; Gagliardo, R.; Profita, M. Effect of High, Medium, and Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronan on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in an In Vitro Model of Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8727289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhuri, O.; Cooper-White, J.; Janmey, P.A.; Mooney, D.J.; Shenoy, V.B. Effects of Extracellular Matrix Viscoelasticity on Cellular Behaviour. Nature 2020, 584, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grolma, J.M.; Weinand, P.; Moone, D.J. Extracellular Matrix Plasticity as a Driver of Cell Spreading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25999–26007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastardot, F.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Vollenweider, P. Association of Body Temperature with Obesity. The CoLaus Study. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 43, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smilek, J.; Jarábková, S.; Velcer, T.; Pekař, M. Compositional and Temperature Effects on the Rheological Properties of Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Hydrogels. Polymers 2019, 11, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matteini, P.; Dei, L.; Carretti, E.; Volpi, N.; Goti, A.; Pini, R. Structural Behavior of Highly Concentrated Hyaluronan. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatej, I.; Popa, M.; Rinaudo, M. Role of the PH on Hyaluronan Behavior in Aqueous Solution. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.N.J.; Liao, Y.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Yu, J.X.; Li, Z.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, G.J.; Lin, C.H.; Wong, A.M.K. Diet-Induced Obesity Accelerates Blood Lactate Accumulation of Rats in Response to Incremental Exercise to Maximum. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 313, R601–R607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maleki, A.; Kjøniksen, A.L.; Nyström, B. Effect of PH on the Behavior of Hyaluronic Acid in Dilute and Semidilute Aqueous Solutions. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 274, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisárčik, M.; Bakoš, D.; Čeppan, M. Non-Newtonian Properties of Hyaluronic Acid Aqueous Solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 97, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, I.A.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Alexander, K.; Melzer, D. Obesity, Physical Function, and Mortality in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, H.K.; Vincent, K.R.; Lamb, K.M. Obesity and Mobility Disability in the Older Adult. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, E.J.; McDermott, K.; Funk, M.F. Evaluation of Hyaluronan Content in Areas of Densification Compared to Adjacent Areas of Fascia. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2019, 23, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, P.G.; Stecco, A.; Stern, R.; Stecco, C. Painful Connections: Densification versus Fibrosis of Fascia. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2014, 18, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, J.; Macchi, V.; de Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Fascia Thickness, Aging and Flexibility: Is There an Association? J. Anat. 2019, 234, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stecco, A.; Meneghini, A.; Stern, R.; Stecco, C.; Imamura, M. Ultrasonography in Myofascial Neck Pain: Randomized Clinical Trial for Diagnosis and Follow-Up. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2014, 36, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelin, G.; Silveira, A.L.M.; Martins, L.B.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Clément, K. Deciphering the Cellular Interplays Underlying Obesity-Induced Adipose Tissue Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4032–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fede, C.; Petrelli, L.; Guidolin, D.; Porzionato, A.; Pirri, C.; Fan, C.; de Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Evidence of a New Hidden Neural Network into Deep Fasciae. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Rodriguez, V.; Fede, C.; Pirri, C.; Petrelli, L.; Loro-Ferrer, J.F.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, D.; de Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Fascial Innervation: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, D.; Hudgins, T.; MacNaughton, J.; Newman, E.; Tan, J.; Wigger, M. A Systematic Review of Manual Therapy Techniques, Dry Cupping and Dry Needling in the Reduction of Myofascial Pain and Myofascial Trigger Points. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2019, 23, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, M.; Schneebeli, A.; Koetsier, E.; Maino, P. Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Trigger Points: Evaluation and Treatment in Patients with Musculoskeletal Pain. Curr. Opin. Support Palliat. Care 2019, 13, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galasso, A.; Urits, I.; An, D.; Nguyen, D.; Borchart, M.; Yazdi, C.; Manchikanti, L.; Kaye, R.J.; Kaye, A.D.; Mancuso, K.F.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of the Treatment and Management of Myofascial Pain Syndrome. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2020, 24, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thottungal, A.; Kumar, P.; Bhaskar, A. Interventions for Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Cancer Pain: Recent Advances: Why, When, Where and How. Curr. Opin. Support Palliat. Care. 2019, 13, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urits, I.; Charipova, K.; Gress, K.; Schaaf, A.L.; Gupta, S.; Kiernan, H.C.; Choi, P.E.; Jung, J.W.; Cornett, E.; Kaye, A.D.; et al. Treatment and Management of Myofascial Pain Syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2020, 34, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatangelo, G.; Vindigni, V.; Avruscio, G.; Pandis, L.; Brun, P. Hyaluronic Acid: Redefining Its Role. Cells 2020, 9, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, M.; Azadi, A.; Rafiei, P. Hydrogel Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serban, M.A.; Skardal, A. Hyaluronan Chemistries for Three-Dimensional Matrix Applications. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78–79, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, D.W.; Alam, M.; Kim, J.Y.S. Injectable Fillers for Facial Rejuvenation: A Review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2009, 62, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.H. Use of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers for the Treatment of the Aging Face. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.F.; Chou, Y.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, W.L. Hyaluronic Acid as a Treatment for Ankle Osteoarthritis. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2009, 2, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urits, I.; Hasegawa, M.; Orhurhu, V.; Peck, J.; Kelly, A.C.; Kaye, R.J.; Orhurhu, M.S.; Brinkman, J.; Giacomazzi, S.; Foster, L.; et al. Minimally Invasive Treatment of Chronic Ankle Instability: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2020, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalia, R.; Albo, E.; Russo, F.; Tecame, A.; Torre, G.; Sterzi, S.; Bressi, F.; Denaro, V. The Use of Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Ankle Osteoarthritis: A Review of the Evidence. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, H.; Gotoh, M.; Kanazawa, T.; Ohzono, H.; Nakamura, H.; Ohta, K.; Nakamura, K.I.; Fukuda, K.; Teramura, T.; Hashimoto, T.; et al. Hyaluronic Acid Accelerates Tendon-to-Bone Healing After Rotator Cuff Repair. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 3322–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osti, L.; Berardocco, M.; di Giacomo, V.; di Bernardo, G.; Oliva, F.; Berardi, A.C. Hyaluronic Acid Increases Tendon Derived Cell Viability and Collagen Type i Expression in Vitro: Comparative Study of Four Different Hyaluronic Acid Preparations by Molecular Weight. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crimaldi, S.; Liguori, S.; Tamburrino, P.; Moretti, A.; Paoletta, M.; Toro, G.; Iolascon, G. The Role of Hyaluronic Acid in Sport-Related Tendinopathies: A Narrative Review. Medicina 2021, 57, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogan, G.; Šoltés, L.; Stern, R.; Gemeiner, P. Hyaluronic Acid: A Natural Biopolymer with a Broad Range of Biomedical and Industrial Applications. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, M.; Schiavone, C.; Salini, V. The Use of Hyaluronic Acid after Tendon Surgery and in Tendinopathies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 783632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaux, J.-F.; Samson, A.; Crielaard, J.-M. Hyaluronic Acid and Tendon Lesions. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2015, 5, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giordan, N.; Giordan, N.; Mazzoni, G. Efficacy and Safety of Hyaluronic Acid (500-730kDa) Ultrasound-Guided Injections on Painful Tendinopathies: A Prospective, Open Label, Clinical Study. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2017, 7, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, F.; Marsilio, E.; Asparago, G.; Frizziero, A.; Berardi, A.C.; Maffulli, N. The Impact of Hyaluronic Acid on Tendon Physiology and Its Clinical Application in Tendinopathies. Cells 2021, 10, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fede, C.; Pirri, C.; Petrelli, L.; Guidolin, D.; Fan, C.; de Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Sensitivity of the Fasciae to the Endocannabinoid System: Production of Hyaluronan-Rich Vesicles and Potential Peripheral Effects of Cannabinoids in Fascial Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeissadat, S.A.; Nouri, F.; Darvish, M.; Esmaily, H.; Ghazihosseini, P. Ultrasound-Guided Injection of High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid versus Corticosteroid in Management of Plantar Fasciitis: A 24-Week Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumai, T.; Muneta, T.; Tsuchiya, A.; Shiraishi, M.; Ishizaki, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Samoto, N.; Isomoto, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Takakura, Y. The Short-Term Effect after a Single Injection of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid in Patients with Enthesopathies (Lateral Epicondylitis, Patellar Tendinopathy, Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy, and Plantar Fasciitis): A Preliminary Study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2014, 19, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, G.F.; Sevilla, D.; Oliveira, C.N.; Junior, L.C.N.; Arliani, G.G.; Oliveira, V.O.; Filho, M.V.P. Comparison of the Effect of Hyaluronic Acid Injection versus Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Chronic Plantar Fasciitis: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozo, M.A.; Balazs, E.A.; Belmonte, C. Reduction of Sensory Responses to Passive Movements of Inflamed Knee Joints by Hylan, a Hyaluronan Derivative. Exp. Brain Res. 1997, 116, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreland, L.W. Intra-Articular Hyaluronan (Hyaluronic Acid) and Hylans for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: Mechanisms of Action. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eymard, F.; Chevalier, X.; Conrozier, T. Obesity and Radiological Severity Are Associated with Viscosupplementation Failure in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 2269–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conrozier, T.; Eymard, F.; Chouk, M.; Chevalier, X. Impact of Obesity, Structural Severity and Their Combination on the Efficacy of Viscosupplementation in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coombes, B.K.; Bisset, L.; Vicenzino, B. Efficacy and Safety of Corticosteroid Injections and Other Injections for Management of Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1751–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumai, T.; Samoto, N.; Hasegawa, A.; Noguchi, H.; Shiranita, A.; Shiraishi, M.; Ikeda, S.; Sugimoto, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Takakura, Y. Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of Hyaluronic Acid Injection for Plantar Fasciopathy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynen, N.; de Vroey, T.; Spiegel, I.; van Ongeval, F.; Hendrickx, N.J.; Stassijns, G. Comparison of Peritendinous Hyaluronan Injections Versus Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in the Treatment of Painful Achilles’ Tendinopathy: A Randomized Clinical Efficacy and Safety Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebbi, R.; Rezasoltani, Z.; Mir, M.; Mohebbi, M.; Vatandoost, S.; Esmaily, H. High- Versus Low-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid for the Treatment of Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Triple-Blind Randomized Comparative Trial. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, M.H.; Raeissadat, S.A.; Cheraghi, M.; Rahimi-Dehgolan, S.; Ebrahimpour, A. Efficacy of Single High-Molecular-Weight versus Triple Low-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid Intra-Articular Injection among Knee Osteoarthritis Patients. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrey, A.C.; de la Motte, C.A. Hyaluronan, a Crucial Regulator of Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Noble, P.W. Hyaluronan as an Immune Regulator in Human Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 221–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chin, L.; Calabro, A.; Walker, E.; Derwin, K.A. Mechanical Properties of Tyramine Substituted-Hyaluronan Enriched Fascia Extracellular Matrix. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinho, A.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Hyaluronic Acid: A Key Ingredient in the Therapy of Inflammation. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fede, C.; Albertin, G.; Petrelli, L.; Sfriso, M.M.; Biz, C.; de Caro, R.; Stecco, C. Expression of the Endocannabinoid Receptors in Human Fascial Tissue. Eur. J. Histochem. 2016, 60, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghasemi, M.; Mosaffa, F.; Hoseini, B.; Behnaz, F. Comparison of the Effect of Bicarbonate, Hyaluronidase, and Lidocaine Injection on Myofascial Pain Syndrome. Anesth. Pain Med. 2020, 10, e101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, P.; Lu, Y.; Mirchandani, M.; Stecco, A. Human Recombinant Hyaluronidase Injections for Upper Limb Muscle Stiffness in Individuals with Cerebral Injury: A Case Series. eBioMedicine 2016, 9, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ugwoke, C.K.; Cvetko, E.; Umek, N. Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Roles of Fascial Hyaluronan in Obesity-Related Myofascial Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911843
Ugwoke CK, Cvetko E, Umek N. Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Roles of Fascial Hyaluronan in Obesity-Related Myofascial Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911843
Chicago/Turabian StyleUgwoke, Chiedozie Kenneth, Erika Cvetko, and Nejc Umek. 2022. "Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Roles of Fascial Hyaluronan in Obesity-Related Myofascial Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911843
APA StyleUgwoke, C. K., Cvetko, E., & Umek, N. (2022). Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Roles of Fascial Hyaluronan in Obesity-Related Myofascial Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911843






