Study on Biogenic Spindle-Shaped Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles by Pseudostaurosira trainorii in Field of Laser Desorption/Ionization Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Diatom Mediated Biofabrication of IONPs
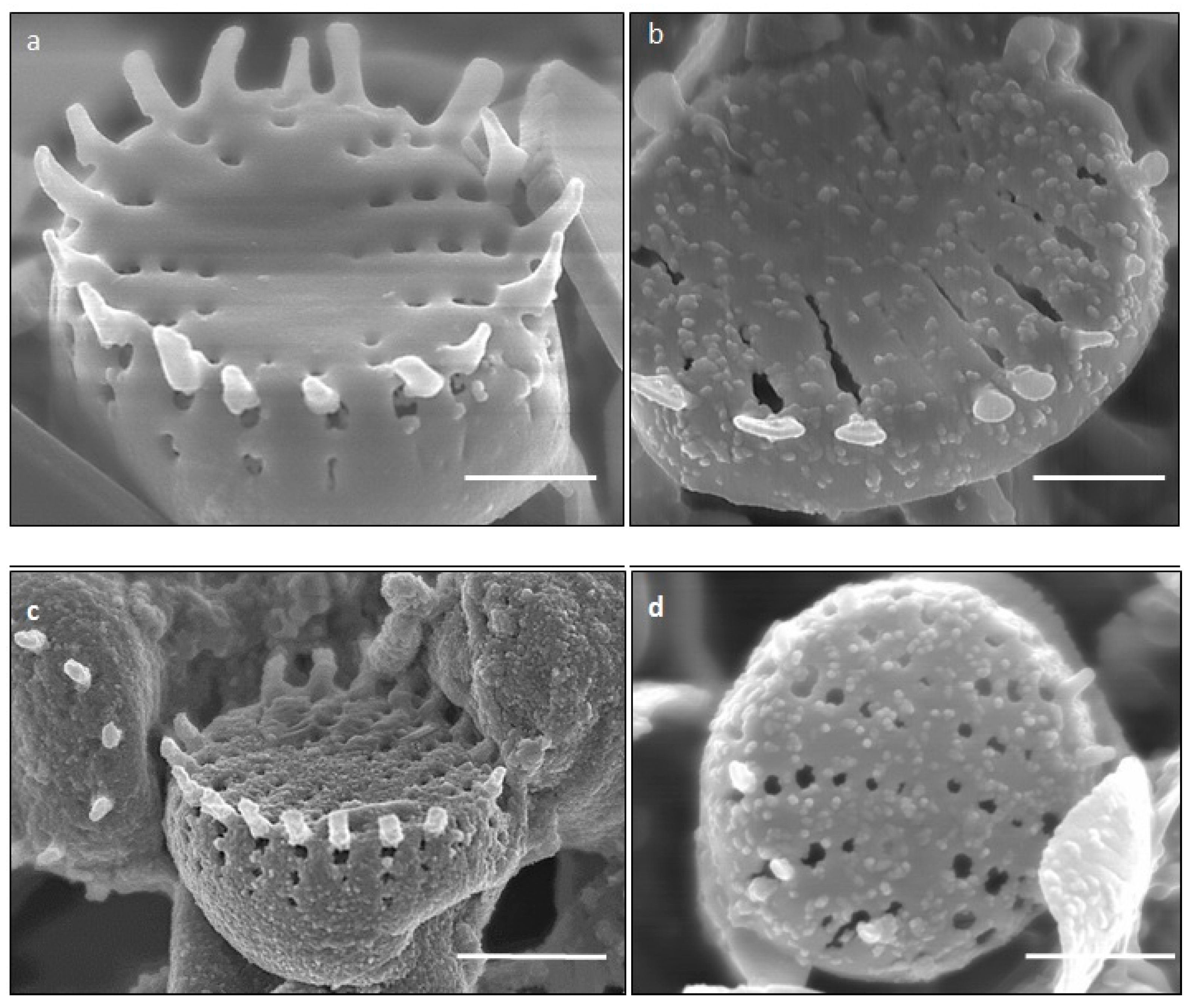
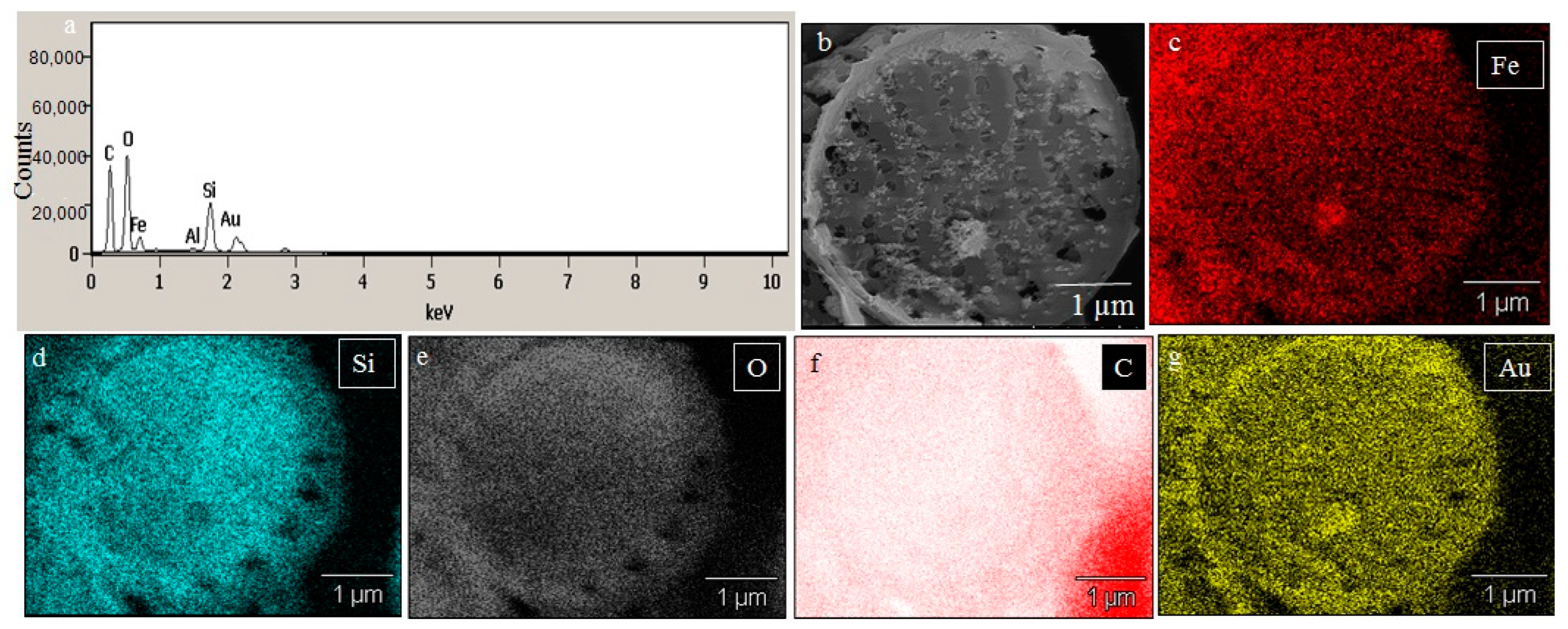
2.2. SEM Analysis of Fe3+ Treated P. trainorii with EDAX and Elemental Mapping
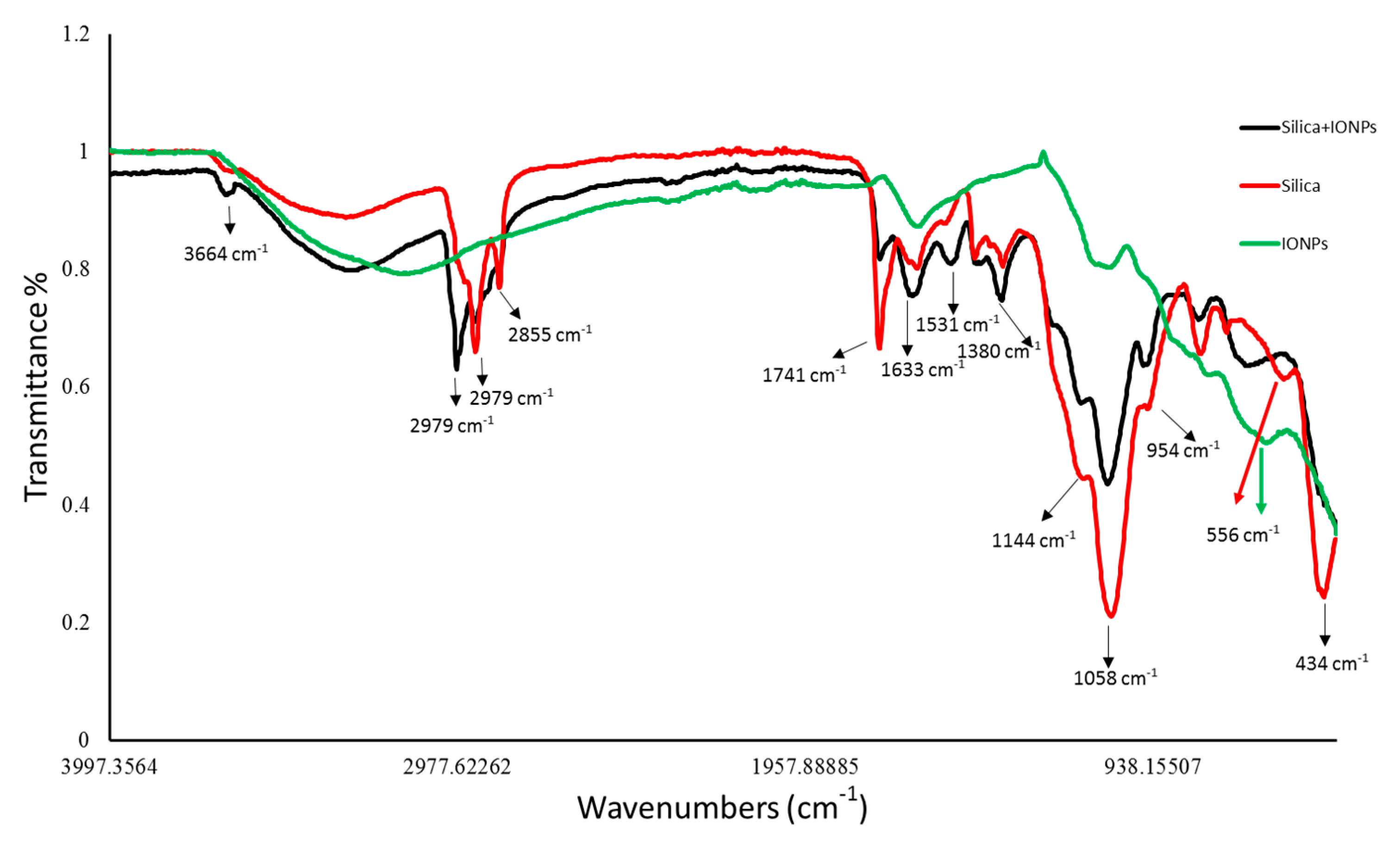
2.3. UV-Vis and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
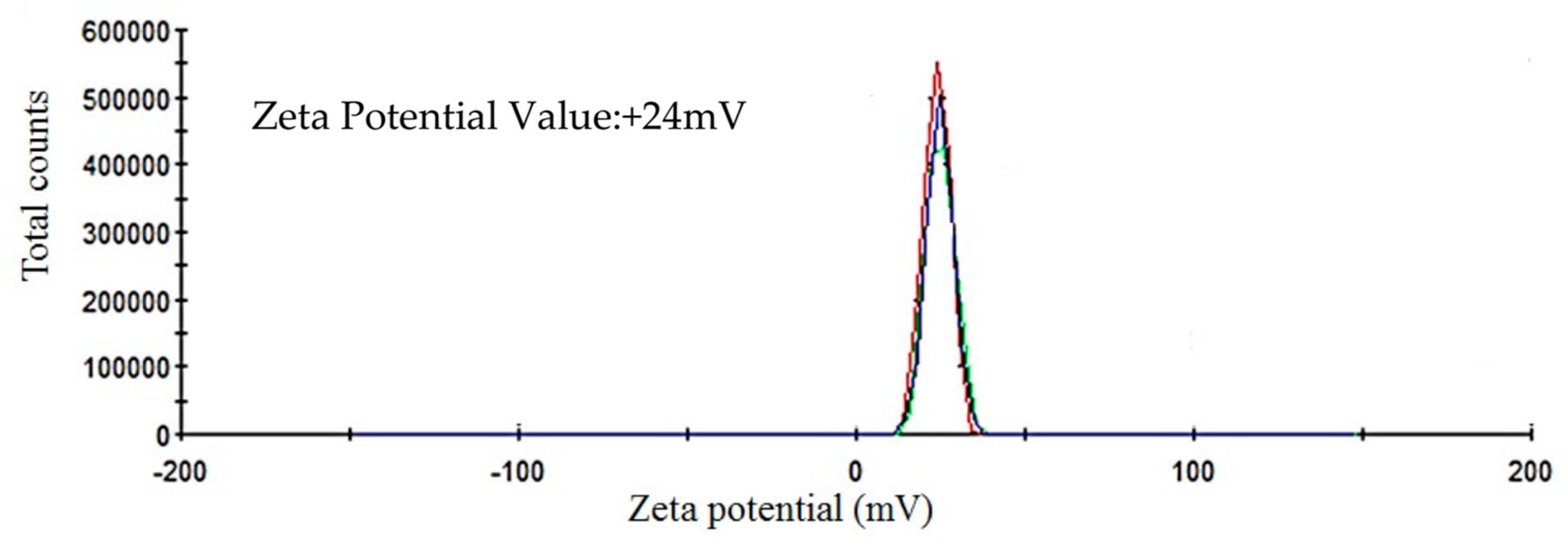
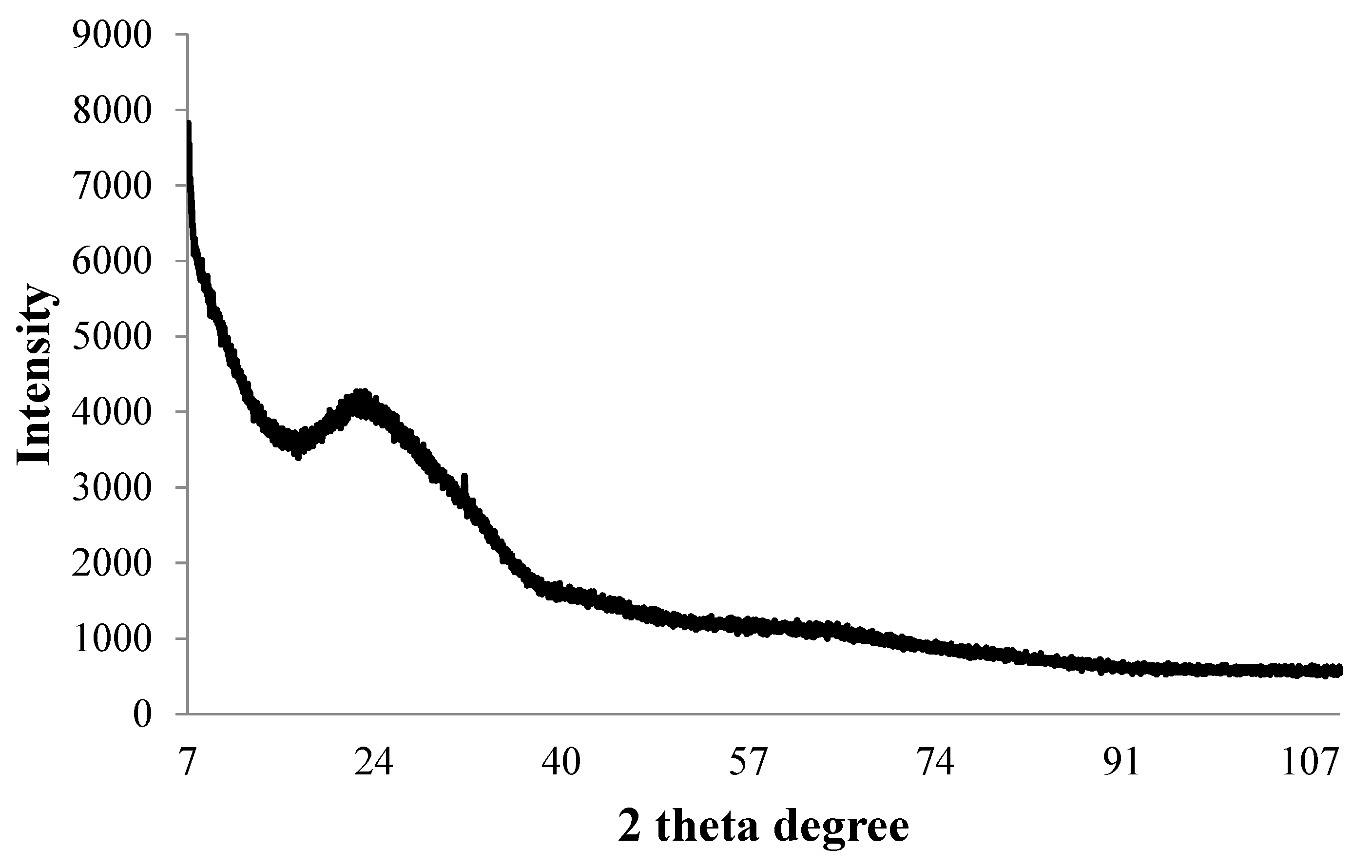
2.4. ICP-MS, Zeta Potential and X-ray Diffraction
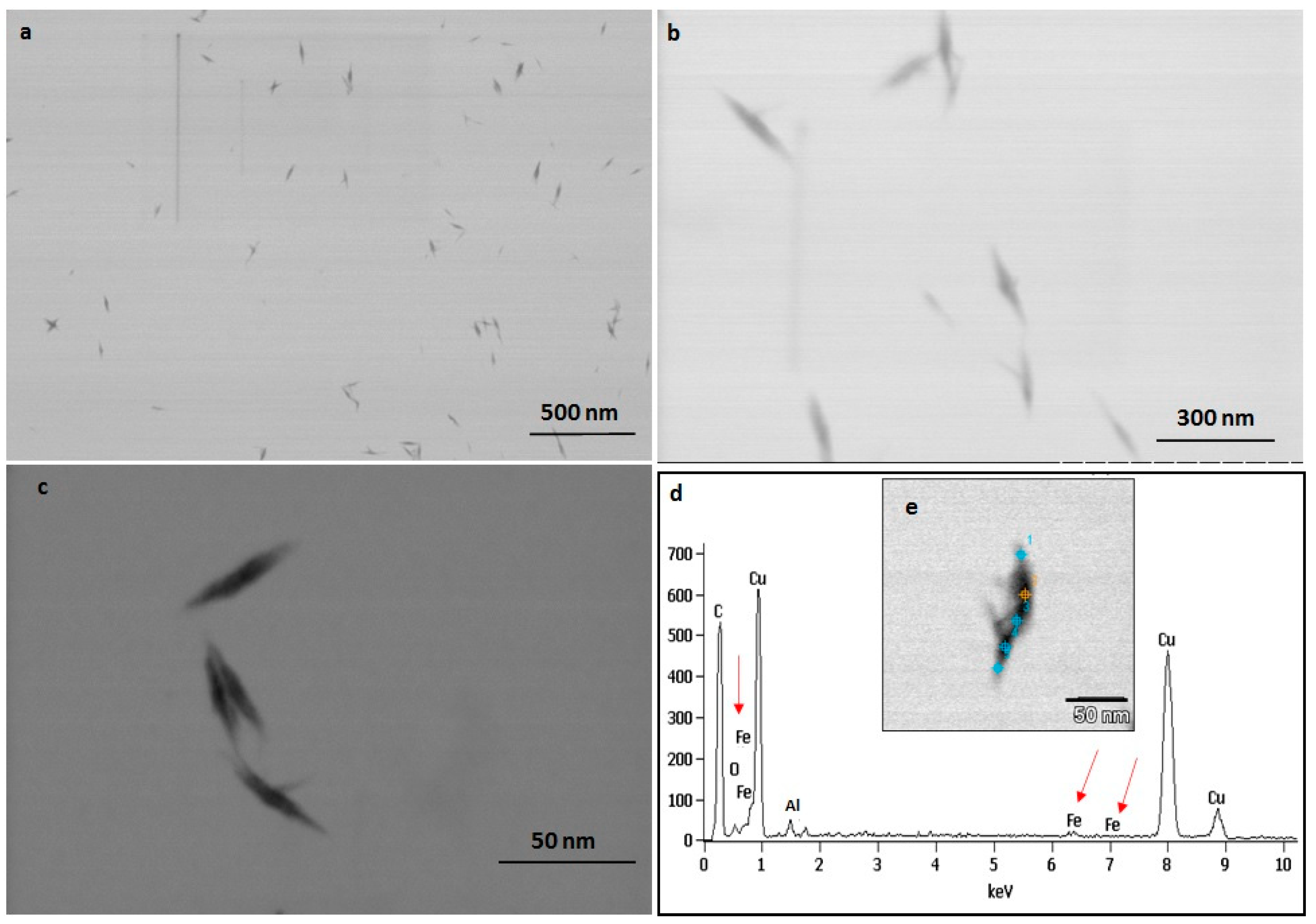
2.5. TEM and EDAX
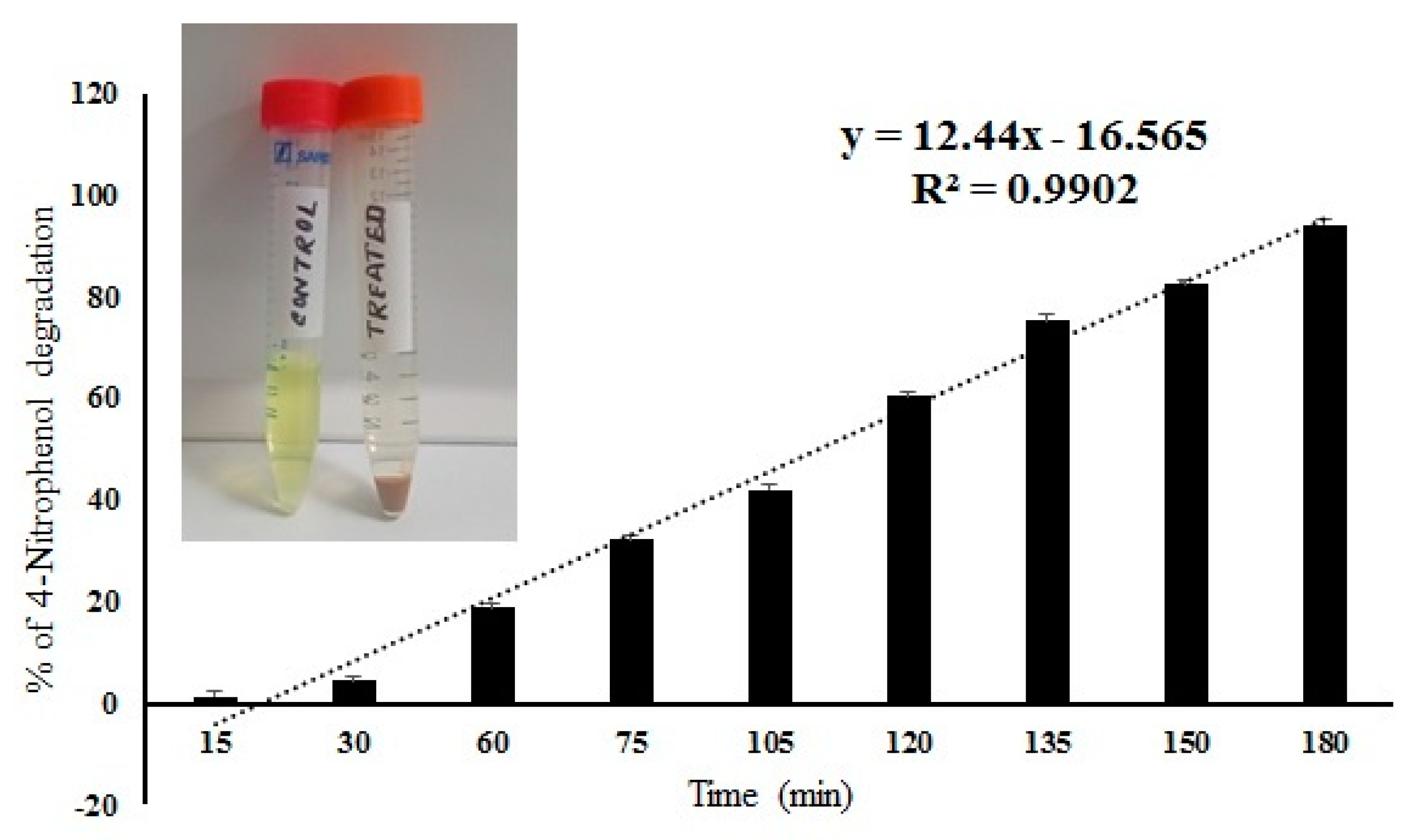
2.6. 4-Nitrophenol Degradation by IONPs Decorated Frustules
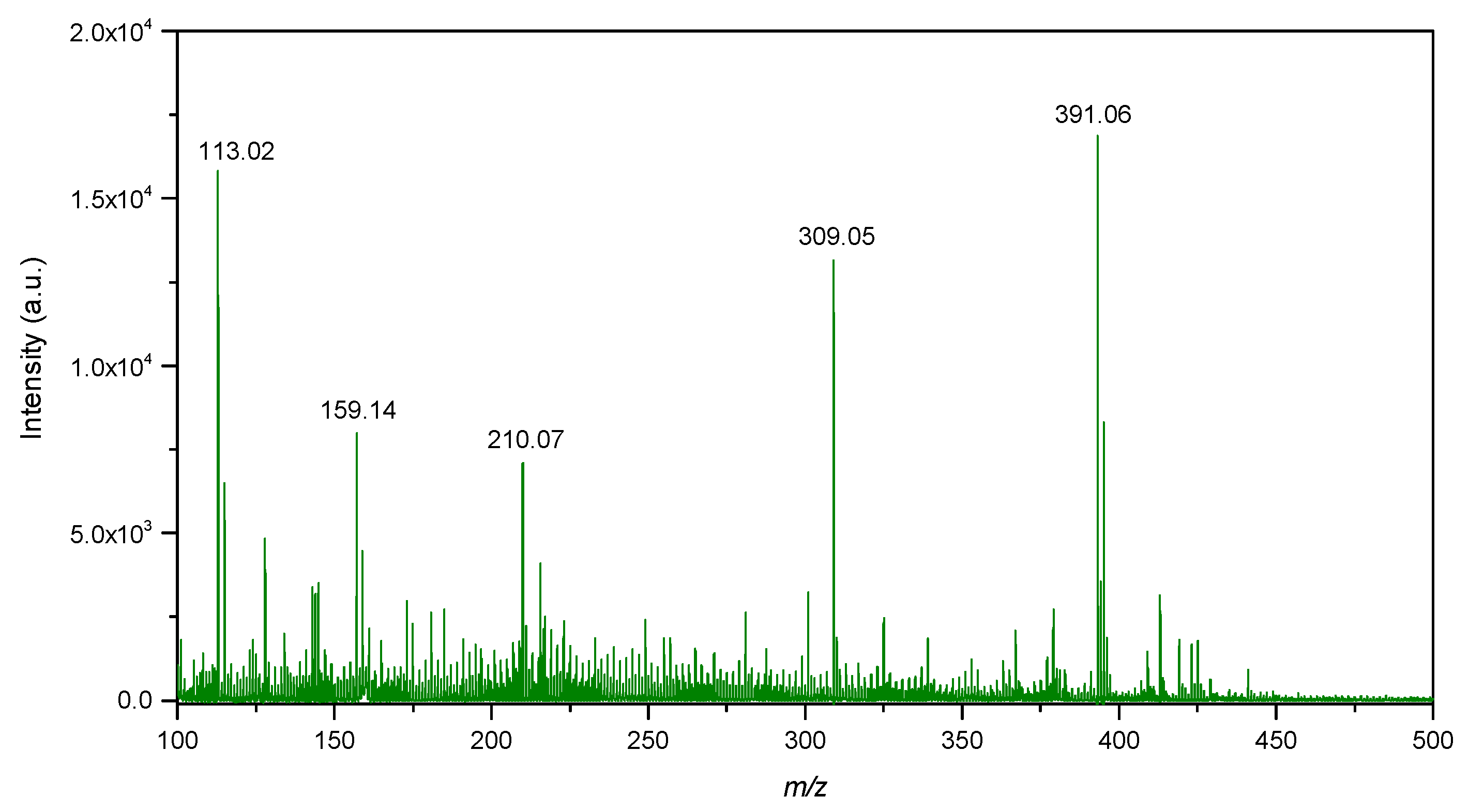
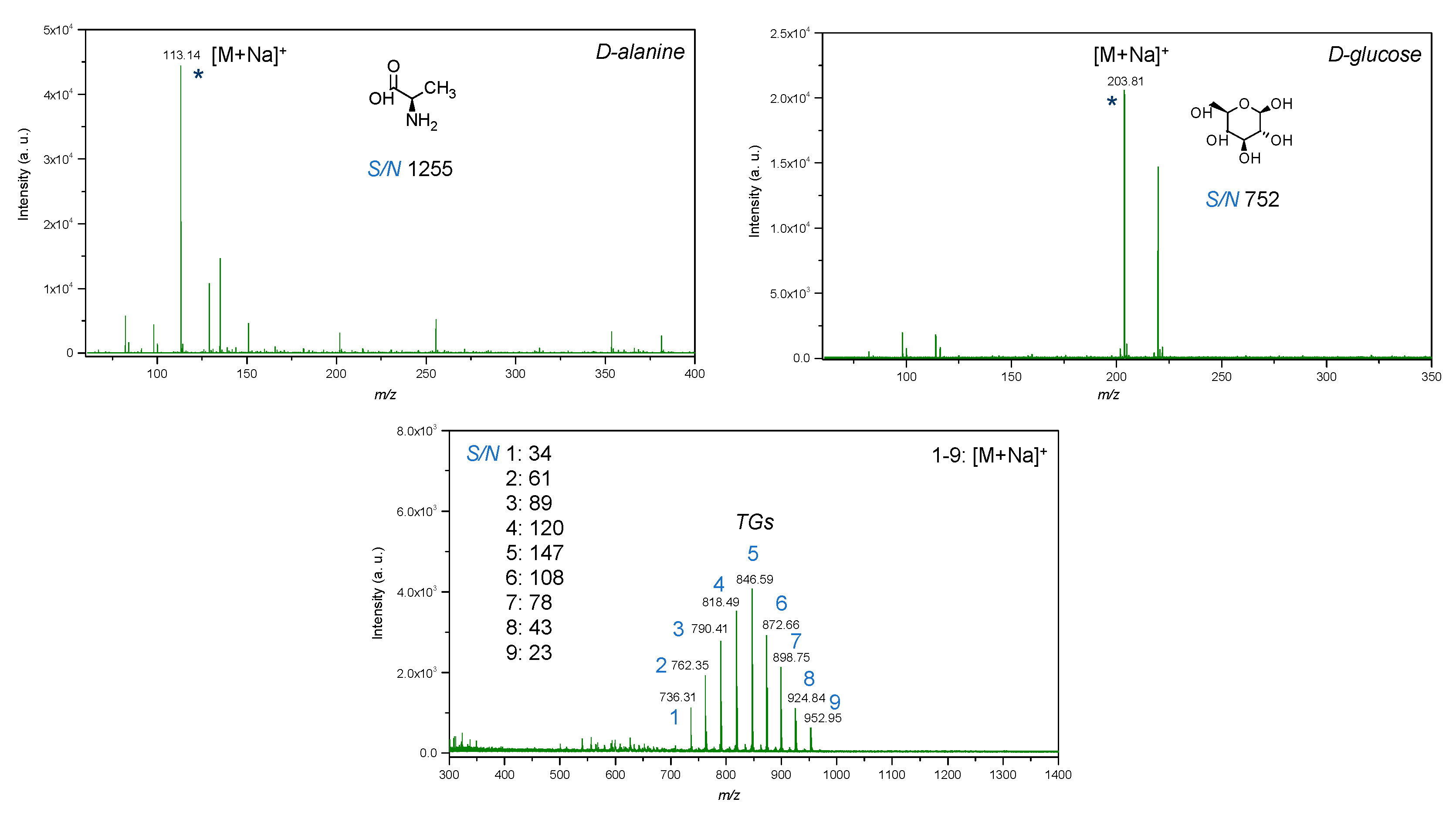
2.7. LDI-Mass Spectrometry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Diatom Mediated Biosynthesis of IONPs
4.2.1. Cultivation of Diatom
4.2.2. Biofabrication of Spindle-Shaped IONPs
4.2.3. Purification of Diatom Based Biosynthesized IONPs
4.3. Microscopic Analysis of Fe3+ Treated P. trainorii with EDAX and Elemental Mapping
4.4. Characterizations of Frustule Associated and External Biogenic IONPs
4.4.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.4.2. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry, Zeta Potential and X-ray Diffraction
4.4.3. TEM and EDAX
4.5. Photocatalytic Degradation of 4-Nitrophenol by IONPs Decorated Frustules
4.6. LDI-MS Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estelrich, J.; Busquets, M.A. Iron oxide nanoparticles in photothermal therapy. Molecules 2018, 23, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangijzegem, T.; Stanicki, D.; Laurent, S. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery: Applications and characteristics. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofanidis, S.A.; Galvita, V.V.; Konstantopoulos, C.; Poelman, H.; Marin, G.B. Fe-Based Nano-Materials in Catalysis. Materials. 2018, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseem, M.; Ghaffar, F.A.; Farooqui, M.F.; Shamim, A. Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Based Magnetic Ink Development for Fully Printed Tunable Radio-Frequency Devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakha, M.; Pal, S.; Samantarrai, D.; Panigrahi, T.K.; Mallick, B.C.; Pramanik, K.; Mallick, B.; Jha, S. Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kläser, K.; Graeser, M.; Steinhagen, D.; Luedtke-Buzug, K. Construction of a device for magnetic separation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 1, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.S.U.; Qureshi, M.T.; Sultana, K.; Rehman, W.; Khan, M.Y.; Asif, M.H.; Farooq, M.; Sultana, N. Single step growth of iron oxide nanoparticles and their use as glucose biosensor. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 4451–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Xu, C.; Wu, H. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles mediated gene therapy for breast cancer--an in vitro study. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2006, 26, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Lien, H.L.; Koel, B.E.; Zhang, W.X. Iron nanoparticles for environmental clean-up: Recent developments and future outlook. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabler, M.; Zhu, W.; Hedayati, M.; Attaluri, A.; Zhou, H.; Mihalic, J.; Geyh, A.; DeWeese, T.L.; Ivkov, R.; Artemov, D. Magnetic resonance imaging contrast of iron oxide nanoparticles developed for hyperthermia is dominated by iron content. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufschmid, R.; Teeman, E.; Mehdi, B.L.; Krishnan, K.M.; Browning, N.D. Observing the colloidal stability of iron oxide nanoparticles in situ. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 13098–13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusoff, A.H.M.; Salimi, M.N.; Jamlos, M.F. A review: Synthetic strategy control of magnetite nanoparticles production. Adv. Nano Res. 2018, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shasha, C.; Krishnan, K.M. Nonequilibrium dynamics of magnetic nanoparticles with applications in biomedicine. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 1904131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahmandjou, M.; Soflaee, F. Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles using Borohydride Reduction. Int. J. Bio Inorg. Hybrid Nanomater. 2014, 3, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Pravallika, P.L.; Mohan, G.K.; Rao, K.V.; Shanker, K. Biosynthesis, characterization and acute oral toxicity studies of synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using ethanolic extract of Centella asiatica plant. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshtkhoo, N.; Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Savardashtaki, A.; Amani, A.M.; Taghizadeh, S. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by aqueous leaf extract of Daphne mezereum as a novel dye removing material. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, M.; Sabry, S.; Ghozlan, H.; El-Gendy, A.A.; Carpenter, E.E. Microbial-physical Synthesis of Fe and Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles Using Aspergillus niger YESM1 and Supercritical Condition of Ethanol. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Mahanty, S.; Das, P.; Chaudhuri, P.; Das, S. Biofabrication of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Manglicolous Fungus Aspergillus niger BSC-1 and Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, P.A.; Augustine, R.; Kannan, M. Extracellular Biosynthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Bacillus Subtilis Strains Isolated from Rhizosphere Soil. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2012, 17, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubran, A.S.; Al-Zamely, O.M.; Al-Ammar, M.H. A Study of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesis by Using Bacteria. Int. J. Pharm. Qual. Assur. 2020, 11, 01–08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashjoor, S.; Yousefzadi, M.; Zolgharnain, H.; Kamrani, E.; Alishahi, M. Organic and inorganic nano-Fe3O4: Alga Ulva flexuosa-based synthesis, antimicrobial effects and acute toxicity to briny water rotifer Brachionus rotundiformis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kassas, H.Y.; Aly-Eldeen, M.A.; Gharib, S.M. Green synthesis of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using two selected brown seaweeds: Characterization and application for lead bioremediation. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhashini, G.; Ruban, P.; Daniel, T. Biosynthesis and characterization of magnetic (Fe3O4) iron oxide nanoparticles from a red seaweed gracilaria edulis and its antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Adv. 2018, 3, 184–189. [Google Scholar]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Kuwano, N.; Bt Ahmad Khairudin, N.B.; Bt Mohamad, S.E.; Lee, K.X. Green synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleelullah, M.M.S.I.; Murugan, M.; Radha, K.V.; Thiyagarajan, D.; Shimura, Y.; Hayakawa, Y. Synthesis of super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles assisted by brown seaweed Turbinaria decurrens for removal of reactive navy-blue dye. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, W.; Sprynskyy, M.; Wojtczak, I.; Dąbek, P.; Witkowski, A.; Buszewski, B. “Outsourcing” diatoms in fabrication of metal-doped 3D biosilica. Materials 2020, 13, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, P.; Nandi, C.; Pal, R. Diatom-based biosynthesis of gold-silica nanocomposite and their DNA binding affinity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, R.; Roychoudhury, P.; Pal, R. In-situ green synthesis of fluorescent silica–silver conjugate nanodendrites using nanoporous frustules of diatoms: An unprecedented approach. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantschke, A.; Herrmann, A.K.; Lesnyak, V.; Eychmüller, A.; Brunner, E. Decoration of diatom biosilica with noble metal and semiconductor nanoparticles (<10 nm): Assembly, characterization, and applications. Asian J. Chem. 2021, 7, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Monte, F.D.; Rodriguez, B.J.; Dockery, P.; Finn, D.P.; Pandit, A. Integration of TiO2 into the diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii during frustule synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffryes, C.; Gutu, T.; Jiao, J.; Rorrer, G.L. Two-stage photobioreactor process for the metabolic insertion of nanostructured germanium into the silica microstructure of the diatom Pinnularia sp. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 28, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Szczyglewska, P.; Wojtczak, I.; Nowak, I.; Witkowski, A.; Buszewski, B.; Feliczak-Guzik, A. Diatom biosilica doped with palladium (II) chloride nanoparticles as new efficient photocatalysts for methyl orange degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, S.; Singh, J.; Koduru, J.R. Effect of ultrasonic waves on degradation of phenol and para-nitrophenol by iron nanoparticles synthesized from Jatropha leaf extract. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiza, A.J.; Pandian, K.; Gopinath, S.C.B. Biosynthesis of zerovalent iron nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and decoloration of textile dyes. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhu, K.; Liu, B.; Wang, N.; Liu, H.; Chen, R. Comprehensive Effect of P-Nitrophenol Degradation in the Iron Oxide/Oxalate Suspension. Water. Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahy, J.G.; Tasseroul, L.; Herlitschke, M.; Hermann, R.P.; Lambert, S.D. Fe3+/iron oxide/SiO2 xerogel catalysts for p-nitrophenol degradation by photo-Fenton effects: Influence of thermal treatment on catalysts texture. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, L.P.; Songca, S.P.; Ajibade, P.A. Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayner, R.; Yéprémian, C.; Djediat, C.; Coradin, T.; Herbst, F.; Livage, J.; Fernand, F.; Couté, A. Photosynthetic microorganism-mediated synthesis of akaganeite (β-FeOOH) nanorods. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10062–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Roychoudhury, P.; Dasgupta, A.K.; Dutta, M.; Pal, R. Arthrospira platensis (Cyanobacteria)–a potential biofactory for fluoromagnetic nanoiron production. Phycologia 2021, 60, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Banerjee, I.; Dutta, M.; Pal, R. Fabrication of iron nanoparticles using Leptolyngbya valderiana and investigation of its Cr (VI) removal potential in the free and biomass associated forms. Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomastowski, P.; Buszewski, B. Complementarity of matrix-and nanostructure-assisted laser desorption/ionization approaches. Nanomater 2019, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.L.; Tseng, W.L. Gold nanoparticles as assisted matrix for determining neutral small carbohydrates through laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez, R.C.; Castellani, E.T.; Russell, D.H. Sol-Gel-derived silver-nanoparticle-embedded thin film for mass spectrometry-based biosensing. Langmuir 2013, 29, 6502–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Yonezawa, T.; Arakawa, R. Surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (SALDI-MS) of low molecular weight organic compounds and synthetic polymers using zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Ozawa, T.; Hisatomi, H.; Arakawa, R. Platinum vapor deposition surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization for imaging mass spectrometry of small molecules. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antone, A.J.; Liang, Q.; Sherwood, J.A.; Weiss, J.C.; Wilson, J.M.; Deb, S.; Cassady, C.J.; Bao, Y. Surface Effects of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on the MALDI In-Source Decay Analysis of Glycans and Peptides. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3999–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Sherwood, J.; Macher, T.; Wilson, J.M.; Bao, Y.; Cassady, C.J. Citric acid capped iron oxide nanoparticles as an effective MALDI matrix for polymers. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 28, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.C.; Obena, R.; Lu, Y.W.; Lin, P.C.; Lin, P.Y.; Yen, Y.S.; Lin, J.T.; Huang, L.D.; Lu, K.L.; Lai, L.L.; et al. Dihydrobenzoic acid modified nanoparticle as a MALDI-TOF MS matrix for soft ionization and structure determination of small molecules with diverse structures. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, E.A. Morphological studies in selected fragilarioid diatoms (Bacillariophyceae) from Connecticut waters (U.S.A.). Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 2001, 151, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, H.S.; Boda, M.A.; Shah, M.A.; Parveen, S.; Wani, A.H. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Platanus orientalis leaf extract for antifungal activity. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, P.; Golubeva, A.; Dąbek, P.; Gloc, M.; Dobrucka, R.; Kurzydłowski, K.; Witkowski, A. Diatom Mediated Production of Fluorescent Flower Shaped Silver-Silica Nanohybrid. Materials 2021, 14, 7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Lu, Z.; Cao, D.; Chen, Z. Effects of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide on the morphology of green synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles used to remove phosphate. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 82, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Jézéquel, V.; Hildebrand, M.; Brzezinski, M.A. Silicon metabolism in diatoms: Implications for growth. J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 821–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lin, D.Y.; Chen, B.H. Metasilicate-based catalyst prepared from natural diatomaceous earth for biodiesel production. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tommasi, E.; De Luca, A.C. Diatom biosilica in plasmonics: Applications in sensing, diagnostics and therapeutics. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 3080–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, I.; Terracciano, M.; Martucci, N.M.; De Stefano, L.; Migliaccio, N.; Tatè, R.; Rendina, I.; Arcari, P.; Lamberti, A.; Rea, I. Diatomite silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tang, J.; Zeng, G.; Yang, G.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiong, W. Rapid reductive degradation of aqueous p-nitrophenol using nanoscale zero-valent iron particles immobilized on mesoporous silica with enhanced antioxidation effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 333, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.Z.; Ma, X.; Chen, T.; Ren, W.; Xiang, L.; Wu, A. Silica-coated super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONPs): A new type contrast agent of T 1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5172–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, F.; Nasr, M.; Ahmed, Y. Preparation and evaluation of iron oxide nanoparticles for treatment of iron deficiency anemia. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 10, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madivoli, E.S.; Kareru, P.G.; Maina, E.G.; Nyabola, A.O.; Wanakai, S.I.; Nyang’au, J.O. Biosynthesis of iron nanoparticles using Ageratum conyzoides extracts, their antimicrobial and photocatalytic activity. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, S.; Tahir, A.; Asim, T.; Chen, Y.; Adil, S.F. Polymeric nanocomposites of iron–oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) synthesized using Terminalia chebula leaf extract for enhanced adsorption of arsenic (V) from water. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Srivastava, M.; Alhazmi, A.; Mohammad, A.; Khan, S.; Pal, D.B.; Haque, S.; Singh, R.; Mishra, P.K.; Gupta, V.K. Sustainable green approach to synthesize Fe3O4/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposite using waste pulp of Syzygium cumini and its application in functional stability of microbial cellulases. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbalagan, G.; Prabakaran, A.R.; Gunasekaran, S. Spectroscopic characterization of Indian standard sand. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2010, 77, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupiasih, N.N.; Suharta, W.G.; Sumadiyasa, M.; Islami, M.N. The Current-Voltage Properties of Ch/AgNP Composite Membranes: A Study on the Effect of AgNP Content. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 515, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamnev, A.A.; Dyatlova, Y.A.; Kenzhegulov, O.A.; Vladimirova, A.A.; Mamchenkova, P.V.; Tugarova, A.V. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic analyses of microbiological samples and biogenic selenium nanoparticles of microbial origin: Sample preparation effects. Molecules 2021, 26, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Salih, E.; Reicha, F.M. Green synthesis of densely dispersed and stable silver nanoparticles using myrrh extract and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2013, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabaharan, D.M.D.M.; Sadaiyandi, K.; Mahendran, M.; Sagadevan, S. Structural, optical, morphological and dielectric properties of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Ali, D.; Khan, S.H.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Choudhary, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Thai, V.N.; Hussain, S.A.; Manhrdas, S. Synthesis and characterization of amorphous iron oxide nanoparticles by the sonochemical method and their application for the remediation of heavy metals from wastewater. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Urban, P.L. Coffee-ring effects in laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagandykova, G.; Piszczek, P.; Radtke, A.; Mametov, R.; Pryshchepa, O.; Gabryś, D.; Kolankowski, M.; Pomastowski, P. Silver Nanostructured Substrates in LDI-MS of Low Molecular Weight Compounds. Materials 2022, 15, 4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, P.; Dąbek, P.; Gloc, M.; Golubeva, A.; Dobrucka, R.; Kurzydłowski, K.; Witkowski, A. Reducing Efficiency of Fucoxanthin in Diatom Mediated Biofabrication of Gold Nanoparticles. Materials 2021, 14, 4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillard, R.R.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms.1. Cyclotella nana hustedt, and detonula confervacea (cleve) gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roychoudhury, P.; Golubeva, A.; Dąbek, P.; Pryshchepa, O.; Sagandykova, G.; Pomastowski, P.; Gloc, M.; Dobrucka, R.; Kurzydłowski, K.; Buszewski, B.; et al. Study on Biogenic Spindle-Shaped Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles by Pseudostaurosira trainorii in Field of Laser Desorption/Ionization Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911713
Roychoudhury P, Golubeva A, Dąbek P, Pryshchepa O, Sagandykova G, Pomastowski P, Gloc M, Dobrucka R, Kurzydłowski K, Buszewski B, et al. Study on Biogenic Spindle-Shaped Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles by Pseudostaurosira trainorii in Field of Laser Desorption/Ionization Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911713
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoychoudhury, Piya, Aleksandra Golubeva, Przemysław Dąbek, Oleksandra Pryshchepa, Gulyaim Sagandykova, Paweł Pomastowski, Michał Gloc, Renata Dobrucka, Krzysztof Kurzydłowski, Bogusław Buszewski, and et al. 2022. "Study on Biogenic Spindle-Shaped Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles by Pseudostaurosira trainorii in Field of Laser Desorption/Ionization Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911713
APA StyleRoychoudhury, P., Golubeva, A., Dąbek, P., Pryshchepa, O., Sagandykova, G., Pomastowski, P., Gloc, M., Dobrucka, R., Kurzydłowski, K., Buszewski, B., & Witkowski, A. (2022). Study on Biogenic Spindle-Shaped Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles by Pseudostaurosira trainorii in Field of Laser Desorption/Ionization Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911713








