Prognostic role of hERG1 Potassium Channels in Neuroendocrine Tumours of the Ileum and Pancreas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
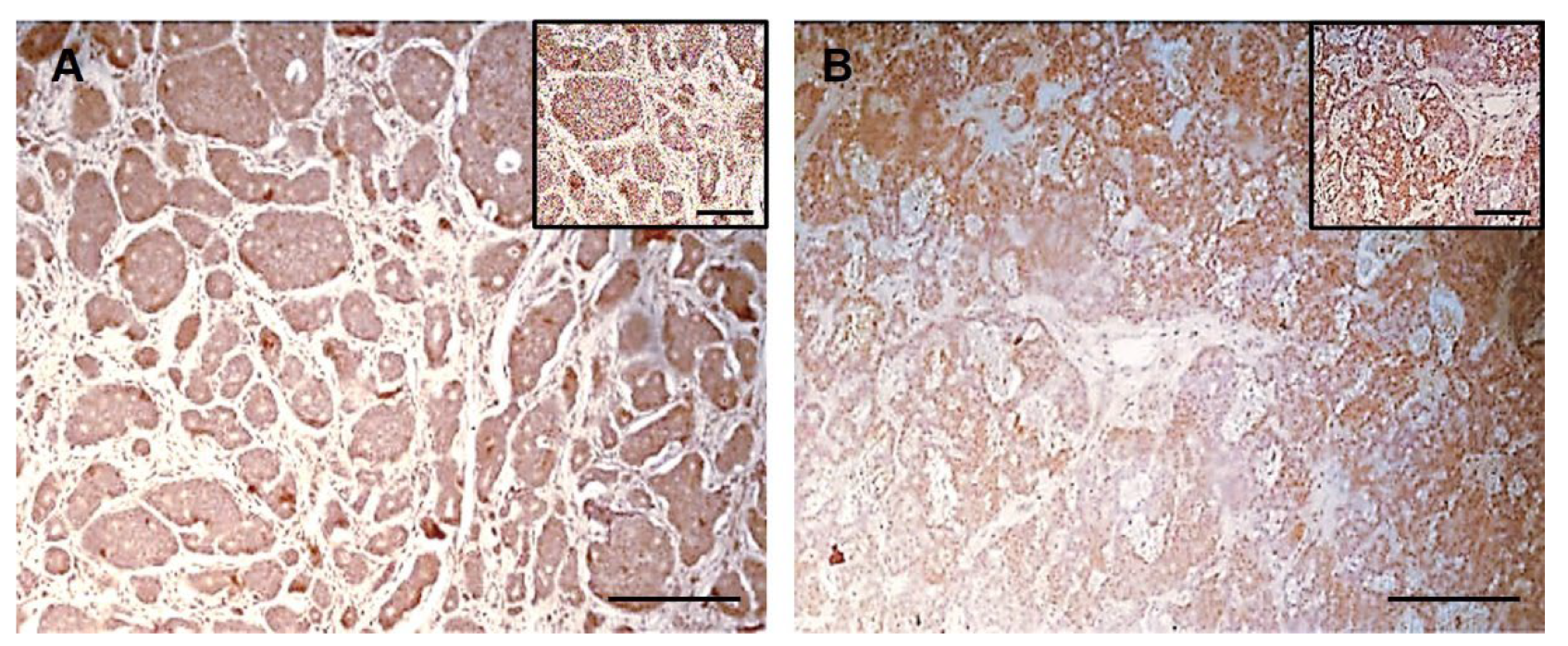
2.1. hERG1 Channel Expression in Ileal NETs
2.1.1. Association of hERG1 Expression and Clinical Features in Ileal NETs
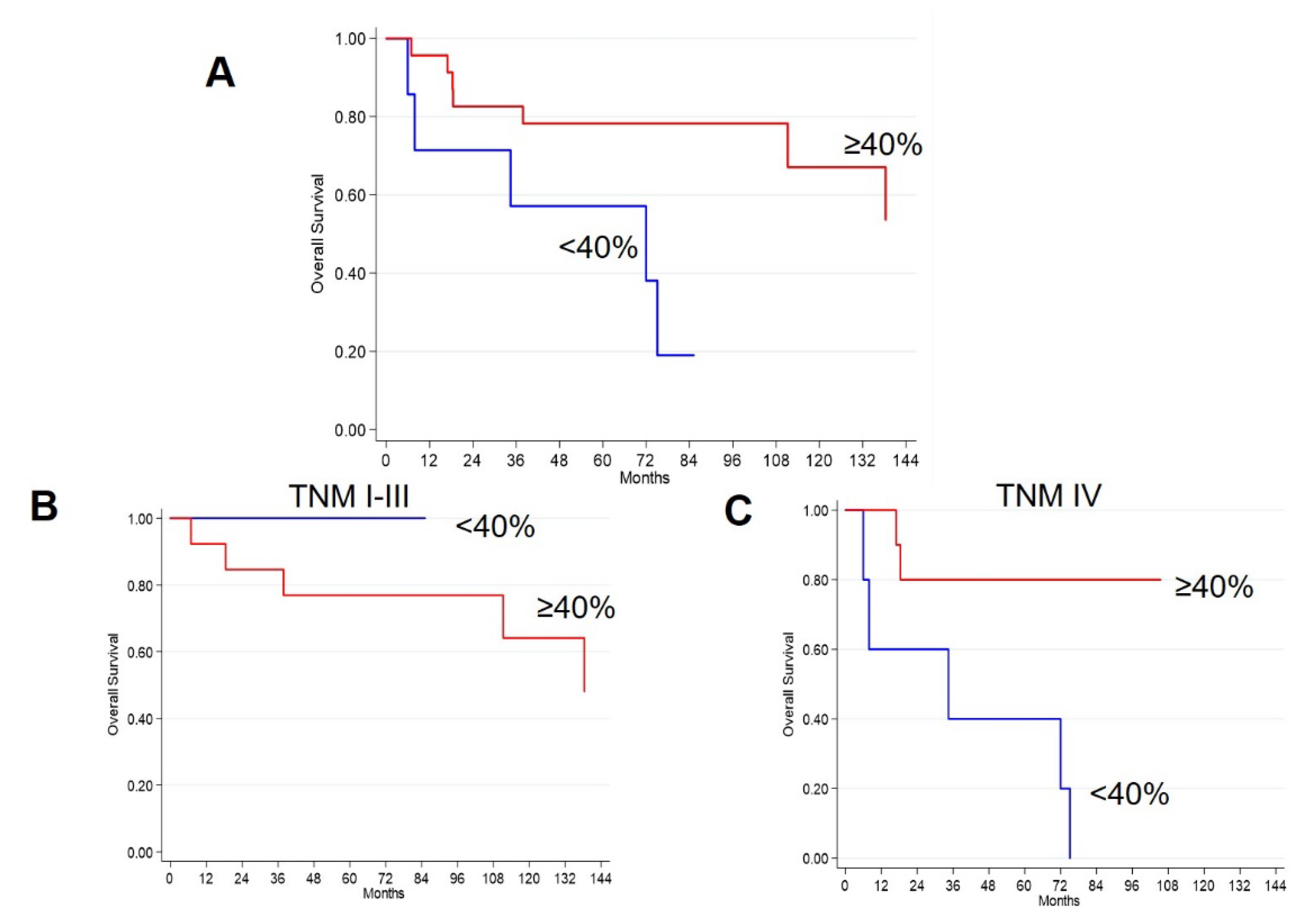
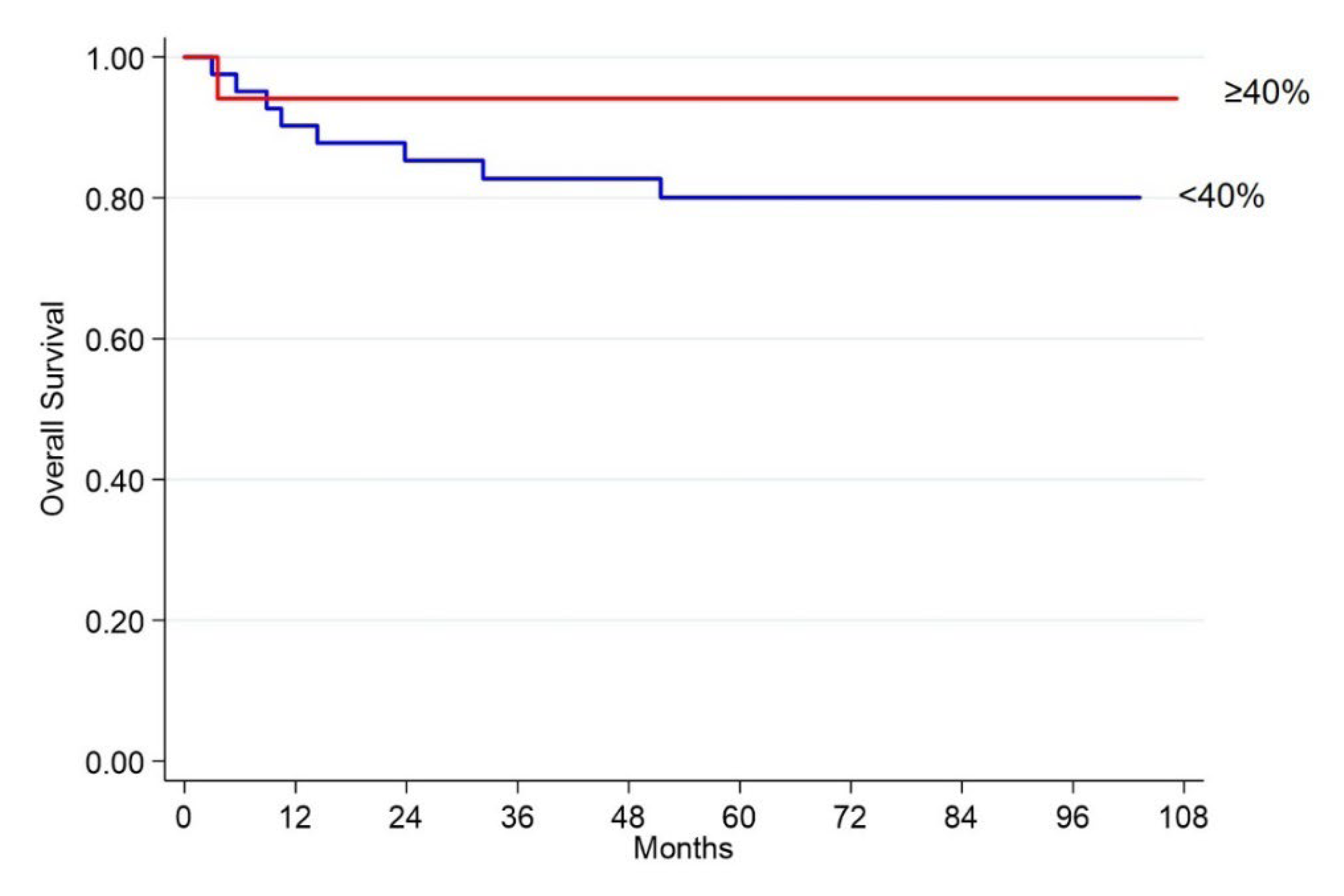
2.1.2. Survival Analyses in Ileal NETs
2.2. hERG1 Channel Expression in Pancreatic NETs
2.2.1. Association of hERG1 Expression and Clinical Features in Pancreatic NETs
2.2.2. Survival Analyses in Pancreatic NETs
2.3. Survival Analyses in the Whole Cohort
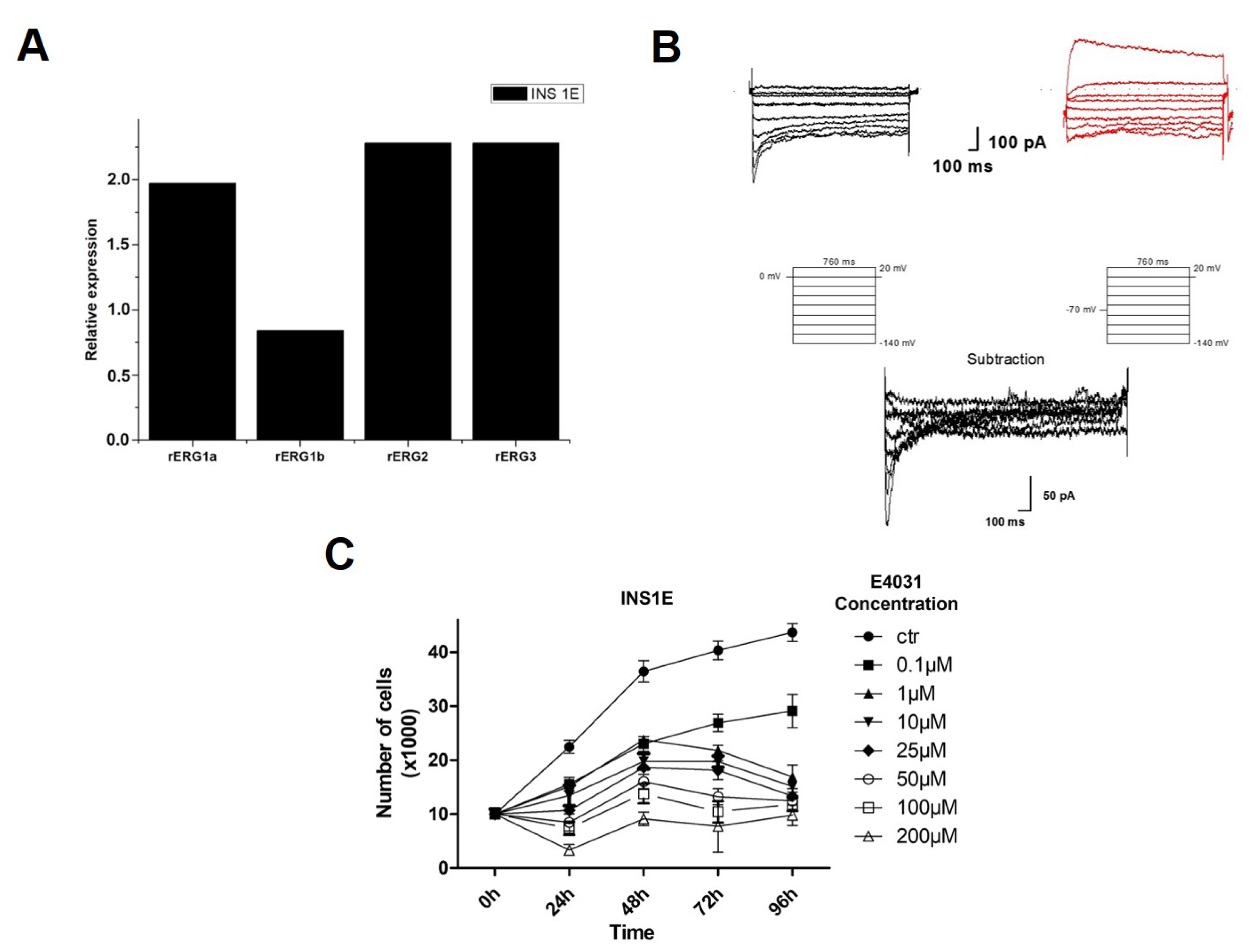
2.4. hERG1 Is Functionally Expressed in Insulinoma (INS1E) Cells and hERG1 Blockers Impair cell Proliferation In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
- rERG1a-F: 5′-TGGAGAAGGA CATGGTAGGG-3′
- rERG1a-R: 5′-GTCAGGTCCA CATCCACCAC-3′
- rERG1b-F: 5′-GGAAGGAGAG CAGGACAGG-3′
- rERG1b-R: 5′-GATGGTCCAG CGGTGTATTC-3′
- rERG2-F: 5′-AGATTGGAGT CCCGTGTGTC-3′
- rERG2-R: 5′-TCCCACCAGAA GCGTAGACT-3′
- rERG3-F: 5′-CGTCTTCCTTT ATCTCCTCC-3′
- rERG3-R: 5′-CTGTAAGATGG CCTGGATGT-3′
- GAPDH-F: 5′-AGACAGCCGCATCTTCTTGT-3′
- GAPDH-R: 5′-CTTGCCGTGGGTAGAGTCAT-3′
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duerr, E.M.; Chung, D.C. Molecular genetics of neuroendocrine tumors. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corleto, V.D.; Delle Fave, G.; Jensen, R.T. Molecular insights into gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumours: Importance and recent advances. Dig. Liver Dis. 2002, 34, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, D.C.; Jensen, R.T. Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors: Pancreatic endocrine tumors. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1469–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosai, J. The origin of neuroendocrine tumors and the neural crest saga. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24 (Suppl. S2), S53–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Leblond, C.P. Origin, differentiation and renewal of the four main epithelial cell types in the mouse small intestine. V. Unitarian Theory of the origin of the four epithelial cell types. Am. J. Anat. 1974, 141, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernman, J.; Välimäki, M.J.; Louhimo, J.; Haglund, C.; Arola, J. The Novel WHO 2010 Classification for Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumours Correlates Well with the Metastatic Potential of Rectal Neuroendocrine Tumours. Neuroendocrinology 2012, 95, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, A.; Lauretta, R.; Vottari, S.; Chiefari, A.; Barnabei, A.; Romanelli, F.; Appetecchia, M. Specific and Non-Specific Biomarkers in Neuroendocrine Gastroenteropancreatic Tumors. Cancers 2019, 11, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oronsky, B.; Ma, P.C.; Morgensztern, D.; Carter, C.A. Nothing But NET: A Review of Neuroendocrine Tumors and Carcinomas. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakis, G.; Kaltsas, G. Biochemical markers for gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (GEP-NETs). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 26, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofland, J.; Zandee, W.T.; de Herder, W.W. Role of biomarker tests for diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumours. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastraioli, E.; Iorio, J.; Arcangeli, A. Ion channel expression as promising cancer biomarker. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 2685–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Jan, L.Y. Targeting potassium channels in cancer. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 206, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crociani, O.; Guasti, L.; Balzi, M.; Becchetti, A.; Wanke, E.; Olivotto, M.; Wymore, R.; Arcangeli, A. Cell cycle-dependent expression of HERG1 and HERG1B isoforms in tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastraioli, E.; Guasti, L.; Crociani, O.; Polvani, S.; Hofmann, G.; Witchel, H.; Bencini, L.; Calistri, M.; Messerini, L.; Scatizzi, M.; et al. herg1 Gene and HERG1 Protein Are Overexpressed in Colorectal Cancers and Regulate Cell Invasion of Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.-D.; Wu, K.-C.; Guo, X.-Z.; Xie, M.-J.; Zhang, J.; Fan, D.-M. Expression and significance of HERG protein in gastric cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, A.; Becchetti, A.; Restano-Cassulini, R.; Polvani, S.; Hofmann, G.; Buccoliero, A.M.; Paglierani, M.; Pollo, B.; Taddei, G.L.; Gallina, P.; et al. hERG1 channels are overexpressed in glioblastoma multiforme and modulate VEGF secretion in glioblastoma cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, J.; Meattini, I.; Bianchi, S.; Bernini, M.; Maragna, V.; Dominici, L.; Casella, D.; Vezzosi, V.; Orzalesi, L.; Nori, J.; et al. hERG1 channel expression associates with molecular subtypes and prognosis in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, A.; Taddei, G.L.; Crociani, O.; Paglierani, M.; Buccoliero, A.M.; Fontana, L.; Noci, I.; Borri, P.; Borrani, E.; Giachi, M.; et al. HERG potassium channels are more frequently expressed in human endometrial cancer as compared to non-cancerous endometrium. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, L.; Wible, B.; Arcangeli, A.; Taglialatela, M.; Morra, F.; Castaldo, P.; Crociani, O.; Rosati, B.; Faravelli, L.; Olivotto, M.; et al. herg Encodes a K+ Current Highly Conserved in Tumors of Different Histogenesis: A Selective Advantage for Cancer Cells? Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 815–822. [Google Scholar]
- Lastraioli, E.; Pillozzi, S.; Mari, A.; Tellini, R.; Duranti, C.; Baldazzi, V.; Venturini, S.; Minervini, A.; Lapini, A.; Nesi, G.; et al. hERG1 and CA IX expression are associated with disease recurrence in surgically resected clear cell renal carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 46, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastraioli, E.; Perrone, G.; Sette, A.; Fiore, A.; Crociani, O.; Manoli, S.; D’Amico, M.; Masselli, M.; Iorio, J.; Callea, M.; et al. HERG1 channels drive tumour malignancy and may serve as prognostic factor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanguinetti, M.; Jiang, C.; Curran, M.; Keating, M. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell 1995, 81, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.K.; Schwarz, J.R. Ether-à-go-go K + channels: Effective modulators of neuronal excitability. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mewe, M.; Wulfsen, I.; Schuster, A.M.E.; Middendorff, R.; Glassmeier, G.; Schwarz, J.R.; Bauer, C.K. Erg K+ channels modulate contractile activity in the bovine epididymal duct. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R895–R904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.K.; Schäfer, R.; Schiemann, D.; Reid, G.; Hanganu, I.; Schwarz, J.R. A functional role of the erg-like inward-rectifying K+ current in prolactin secretion from rat lactotrophs. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1999, 148, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, F.; Ales, E.; Rosati, B.; Lecchi, M.; Masi, A.; Guasti, L.; Cano-Abad, M.F.; Arcangeli, A.; Lopez, M.G.; Wanke, E. ERG K+ channel blockade enhances firing and epinephrine secretion in rat chromaffin cells: The missing link to LQT2-related sudden death? FASEB J. 2003, 17, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binggeli, R.; Weinstein, R. Membrane potentials and sodium channels: Hypotheses for growth regulation and cancer formation based on changes in sodium channels and gap junctions. J. Theor. Biol. 1986, 123, 377–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becchetti, A.; Duranti, C.; Arcangeli, A. Dynamics and physiological meaning of complexes between ion channels and integrin receptors: The case of Kv11.1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 322, C1138–C1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becchetti, A.; Crescioli, S.; Zanieri, F.; Petroni, G.; Mercatelli, R.; Coppola, S.; Gasparoli, L.; D’Amico, M.; Pillozzi, S.; Crociani, O.; et al. The conformational state of hERG1 channels determines integrin association, downstream signaling, and cancer progression. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaaf3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Luo, H.; Luo, B.; Xu, D.; Gao, S. Overexpression of hERG1 in resected esophageal squamous cell carcinomas: A marker for poor prognosis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 97, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, J.; Lastraioli, E.; Tofani, L.; Petroni, G.; Antonuzzo, L.; Messerini, L.; Perrone, G.; Caputo, D.; Francesconi, M.; Amato, M.M.; et al. hERG1 and HIF-2α Behave as Biomarkers of Positive Response to Bevacizumab in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.J.; Cormier, R.T.; Scott, P.M. Role of ion channels in gastrointestinal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5732–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, C.; Iorio, J.; Lottini, T.; Lastraioli, E.; Crescioli, S.; Bagni, G.; Lulli, M.; Capitani, C.; Bouazzi, R.; Stefanini, M.; et al. Harnessing the hERG1/β1 Integrin Complex via a Novel Bispecific Single-chain Antibody: An Effective Strategy against Solid Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modlin, I.M.; Bodei, L.; Kidd, M. Neuroendocrine tumor biomarkers: From monoanalytes to transcripts and algorithms. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 30, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocchini, M.; Nicolini, F.; Severi, S.; Bongiovanni, A.; Ibrahim, T.; Simonetti, G.; Grassi, I.; Mazza, M. Biomarkers for Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms (PanNENs) Management-An Updated Review. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorio Pla, A.; Gkika, D. Ca2+ Channel Toolkit in Neuroendocrine Tumors. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Chikazawa, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Imaizumi, Y.; Yamamura, H. Involvement of the γ1 subunit of the large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel in the proliferation of human somatostatinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcangeli, A.; Romoli, M.R.; Boni, L.; Gerlini, G.; Tofani, L.; Urso, C.; Borgognoni, L. High hERG1 expression in advanced melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastraioli, E.; Lottini, T.; Iorio, J.; Freschi, G.; Fazi, M.; Duranti, C.; Carraresi, L.; Messerini, L.; Taddei, A.; Ringressi, M.N.; et al. hERG1 behaves as biomarker of progression to adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus and can be exploited for a novel endoscopic surveillance. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59535–59547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yang, W.; Gao, S.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Luo, H. Prognostic significance of hERG1 expression in gastric cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointer, K.B.; Clark, P.A.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Salamat, M.S.; Robertson, G.A.; Kuo, J.S. Administration of Non-Torsadogenic human Ether-à-go-go-Related Gene Inhibitors Is Associated with Better Survival for High hERG-Expressing Glioblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muratori, L.; Petroni, G.; Antonuzzo, L.; Boni, L.; Iorio, J.; Lastraioli, E.; Bartoli, G.; Messerini, L.; Di Costanzo, F.; Arcangeli, A. HERG1 positivity and Glut-1 negativity identifies high-risk TNM stage I and II colorectal cancer patients, regardless of adjuvant chemotherapy. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2016, 9, 6325–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández–Valle, Á.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Rodríguez–Santamarta, T.; Villaronga, M.Á.; Álvarez–Teijeiro, S.; García–Pedrero, J.M.; Suárez–Fernández, L.; Lequerica–Fernández, P.; de Vicente, J.C. HERG1 potassium channel expression in potentially malignant disorders of the oral mucosa and prognostic relevance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2016, 38, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastraioli, E.; Bencini, L.; Bianchini, E.; Romoli, M.R.; Crociani, O.; Giommoni, E.; Messerini, L.; Gasperoni, S.; Moretti, R.; di Costanzo, F.; et al. hERG1 channels and Glut-1 as independent prognostic indicators of worse outcome in stage I and II colorectal cancer: A pilot study. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 5, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, B.; Marchetti, P.; Crociani, O.; Lecchi, M.; Lupi, R.; Arcangeli, A.; Olivotto, M.; Wanke, E. Glucose- and arginine-induced insulin secretion by human pancreatic beta-cells: The role of HERG K(+) channels in firing and release. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crociani, O.; Lastraioli, E.; Boni, L.; Pillozzi, S.; Romoli, M.R.; D’Amico, M.; Stefanini, M.; Crescioli, S.; Taddei, A.; Bencini, L.; et al. HERG1 channels regulate VEGF-A secretion in human gastric cancer: Clinicopathological correlations and therapeutical implications. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polvani, S.; Masi, A.; Pillozzi, S.; Gragnani, L.; Crociani, O.; Olivotto, M.; Becchetti, A.; Wanke, E.; Arcangeli, A. Developmentally regulated expression of the mouse homologues of the potassium channel encoding genes m-erg1, m-erg2 and m-erg3. Gene Expr. Patterns 2003, 3, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, M.P.; Aránega, A.; Franco, D. Protein distribution of Kcnq1, Kcnh2, and Kcne3 potassium channel subunits during mouse embryonic development. Anat. Rec. Part A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2006, 288, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcangeli, A.; Rosati, B.; Cherubini, A.; Crociani, O.; Fontana, L.; Ziller, C.; Wanke, E.; Olivotto, M. HERG- and IRK-like inward rectifier currents are sequentially expressed during neuronal development of neural crest cells and their derivatives. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 2596–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcangeli, A.; Becchetti, A.; Mannini, A.; Mugnai, G.; De Filippi, P.; Tarone, G.; Del Bene, M.; Barletta, E.; Wanke, E.; Olivotto, M. Integrin-mediated neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells depends on the activation of potassium channels. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcangeli, A.; Bianchi, L.; Becchetti, A.; Faravelli, L.; Coronnello, M.; Mini, E.; Olivotto, M.; Wanke, E. A novel inward-rectifying K+ current with a cell-cycle dependence governs the resting potential of mammalian neuroblastoma cells. J. Physiol. 1995, 489, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, C.; Lastraioli, E.; Iorio, J.; Capitani, C.; Carraresi, L.; Gonnelli, L.; Arcangeli, A. Expression and purification of a novel single-chain diabody (scDb-hERG1/β1) from Pichia pastoris transformants. Protein Expr. Purif. 2021, 184, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillozzi, S.; Brizzi, M.F.; Bernabei, P.A.; Bartolozzi, B.; Caporale, R.; Basile, V.; Boddi, V.; Pegoraro, L.; Becchetti, A.; Arcangeli, A. VEGFR-1 (FLT-1), beta1 integrin, and hERG K+ channel for a macromolecular signaling complex in acute myeloid leukemia: Role in cell migration and clinical outcome. Blood 2007, 110, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lottini, T.; Iorio, J.; Lastraioli, E.; Carraresi, L.; Duranti, C.; Sala, C.; Armenio, M.; Noci, I.; Pillozzi, S.; Arcangeli, A. Transgenic mice overexpressing the LH receptor in the female reproductive system spontaneously develop endometrial tumour masses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N. (%) | |
|---|---|
| Age, years: median value (range, IQR) | 63 (40–86, 54–74) |
| <70 | 22 (71.0) |
| ≥70 | 9 (29.0) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 16 (51.6) |
| Male | 15 (48.4) |
| TNM at diagnosis | |
| I | 0 (0.0) |
| II | 5 (16.1) |
| III | 11 (35.5) |
| IV | 15 (48.4) |
| Metastases at diagnosis | |
| No | 16 (51.6) |
| Yes | 15 (48.4) |
| Radical surgery | |
| No | 13 (41.9) |
| Yes | 18 (48.1) |
| Metastatic sites | |
| 0 | 16 (51.7) |
| 1 | 25 (80.6) |
| >1 | 6 (19.4) |
| Ki67 (%) | |
| <3 | 15 (48.4) |
| 3–20 | 14 (45.2) |
| >20 | 2 (6.4) |
| Relapse | |
| No | 20 (64.5) |
| Yes | 11 (35.5) |
| Liver | 4 |
| Lung | 1 |
| Limphnodes | 2 |
| Peritoneum | 2 |
| Other | 1 |
| Unknown/missing | 1 |
| SSA 2 Receptors | |
| No | 11 (35.5) |
| Yes | 20 (64.5) |
| PET-FDG 3 | |
| No | 20 (76.9) |
| Yes | 6 (23.1) |
| Unknown/missing | 5 |
| First line therapy | |
| None | 8 (25.8) |
| Somatostatin | 14 (45.2) |
| Chemotherapy | 5 (16.2) |
| Biological therapy and somatostatin | 1 (3.2) |
| Best supportive care | 1 (3.2) |
| Local therapy | 2 (6.4) |
| Progression after first line therapy | |
| No | 11 (35.5) |
| Yes | 20 (58.1) |
| Grading | |
| G1 | 15 (48.4) |
| G2 | 14 (45.2) |
| G3 | 2 (6.4) |
| N. (%) | |
|---|---|
| Age, years: median value (range, IQR) | 63 (25–79, 49–69) |
| <70 | 46 (78.0) |
| ≥70 | 13 (22.0) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 29 (49.1) |
| Male | 30 (50.9) |
| TNM at diagnosis | |
| I | 6 (10.2) |
| II | 17 (28.8) |
| III | 17 (28.8) |
| IV | 19 (32.2) |
| Metastases at diagnosis | |
| No | 40 (67.8) |
| Yes | 19 (32.2) |
| Radical surgery | |
| No | 17 (28.8) |
| Yes | 42 (71.2) |
| Metastatic sites | |
| None | 40 (67.8) |
| Liver | 15 (25.4) |
| Lymphnodes | 2 (3.4) |
| Peritoneum | 1 (1.7) |
| Other | 1 (1.7) |
| Ki67 (%) | |
| <3 | 31 (52.5) |
| 3–20 | 21 (35.6) |
| >20 | 7 (11.9) |
| Relapse | |
| No | 31 (52.5) |
| Yes | 11 (18.6) |
| Liver | 7 (63.6) |
| Lymphnodes | 2 (18.2) |
| Other | 2 (18.2) |
| Unknown/missing | 17 (28.8) |
| SSA Receptors2 | |
| No | 1 (1.7) |
| Yes | 21 (35.6) |
| Unknown/missing | 37 (62.7) |
| PET-FDG3 | |
| No | 8 (13.6) |
| Yes | 12 (20.3) |
| Unknown/missing | 39 (66.1) |
| Grading | |
| G1 | 36 (61.0) |
| G2 | 17 (28.8) |
| G3 | 6 (10.2) |
| First line therapy | |
| None | 29 (49.1) |
| Chemotherapy | 10 (17.0) |
| Everolimus | 2 (3.4) |
| Radiometabolic therapy | 3 (5.1) |
| Somatostatin analogues | 15 (25.4) |
| Progression after first line therapy | |
| No | 39 (66.1) |
| Yes | 20 (33.9) |
| N. Patients | N. Deaths | Median OS 1 (Months) (95% CI) | HR 2 (95% CI 3) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 31 | 12 | 138 (72-nr) | - | - |
| Age (continuous variable) | 31 | 12 | - | 1.051 (0.99–1.107) | 0.055 |
| <70 | 22 | 8 | 138 (75-nr) | 1.00 | |
| ≥70 | 9 | 4 | nr | 2.24 (0.63–8.00) | 0.215 |
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 16 | 5 | nr | 1.00 | |
| Male | 15 | 7 | 138 (17-nr) | 1.46 (0.44–4.83) | 0.530 |
| Stage at diagnosis | |||||
| II | 5 | 2 | 138 (38-nr) | 1.00 | |
| III | 11 | 3 | nr | 0.96 (0.16–5.81) | |
| IV | 15 | 7 | nr | 1.98 (0.39–10.14) | 0.505 |
| Metastases at diagnosis | |||||
| No | 16 | 5 | nr | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 15 | 7 | nr | 2.03 (0.62–6.69) | 0.242 |
| Radical Surgery | |||||
| No | 13 | 7 | 111 (18-nr) | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 18 | 5 | nr | 0.35 (0.10–1.22) | 0.100 |
| Ki67 (%) | |||||
| <3 | 15 | 4 | nr | 1.00 | |
| 3–20 | 14 | 6 | 111 (18-nr) | 2.16 (0.59–7.86) | |
| >20 | 2 | 2 | 21 (8-nr) | 11.58 (1.79–74.73) | 0.036 |
| SSA Receptors 4 | |||||
| No | 11 | 5 | nr | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 20 | 7 | 138 (75-nr) | 0.65 (0.20–2.10) | 0.472 |
| PET-FDG 5 | |||||
| No | 20 | 8 | 138 (34-nr) | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 6 | 1 | nr | 0.64 (0.08–5.36) | 0.682 |
| % hERG1 positive cells | |||||
| Negative (<40) | 7 | 5 | 72 (6-nr) | 1.00 | |
| Positive (≥40) | 24 | 7 | nr | 0.23 (0.07–0.80) | 0.020 |
| % hERG1 Positive Tumour Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| Median Value (Range) | p | |
| Overall | 13 (0–90) | - |
| Age | ||
| <70 | 14 (0–90) | |
| ≥70 | 8 (0–80) | 0.808 |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 25 (0–80) | |
| Male | 9 (0–90) | 0.053 |
| TNM at diagnosis | ||
| I | 7 (0–80) | |
| II | 40 (0–90) | |
| III | 0 (0–80) | |
| IV | 8 (0–90) | 0.011 |
| Metastases at diagnosis | ||
| No | 15 (0–90) | |
| Yes | 8 (0–90) | 0.196 |
| Radical Surgery | ||
| No | 8 (0–90) | |
| Yes | 15 (0–90) | 0.439 |
| Ki67 (%) | ||
| <3 | 20 (0–90) | |
| 3–20 | 12 (0–80) | |
| >20 | 0 (0–90) | 0.292 |
| SSA Receptors 1 | ||
| No | 0 (-) | |
| Yes | 12 (0–60) | 0.317 |
| PET-FDG 2 | ||
| No | 5 (0–15) | |
| Yes | 0 (0–80) | 0.374 |
| Grading | ||
| G1 | 20 (0–90) | |
| G2 | 12 (0–80) | |
| G3 | 0 (0–90) | 0.128 |
| N. pts | N. Deaths | Median OS 1 (Months) (95% CI 2) | P (Logrank) | HR 3 (95% CI) | P (Cox) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 59 | 10 | nr | - | - | - |
| Age (continuous variable) | 59 | 10 | - | - | 0.977 (0.937–1.019) | 0.271 |
| <70 | 46 | 10 | nr | 1.00 | ||
| ≥70 | 13 | 0 | nr | 0.076 | Ne | - |
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 29 | 2 | nr | 1.00 | ||
| Male | 30 | 8 | nr | 0.040 | 4.43 (0.94–20.93) | 0.060 |
| Stage at diagnosis | ||||||
| I | 6 | 0 | nr | Ne | ||
| II | 17 | 0 | nr | 1.00 | ||
| III | 17 | 2 | nr | Ne | ||
| IV | 19 | 8 | 112 (14-nr) | 0.001 | Ne | - |
| Metastases at diagnosis | ||||||
| No | 40 | 2 | nr | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 19 | 8 | 112 (14-nr) | 0.0001 | 11.27 (2.38–53.32) | 0.002 |
| Radical Surgery | ||||||
| No | 17 | 7 | nr | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 42 | 3 | nr | 0.0003 | 0.12 (0.03–0.48) | 0.002 |
| Ki67 (%) | ||||||
| <3 | 31 | 2 | nr | 1.00 | ||
| 3–20 | 21 | 3 | nr | 2.63 (0.44–15.82) | ||
| >20 | 7 | 5 | 7 (3-nr) | <0.0001 | 51.17 (8.64–303.09) | <0.0001 |
| SSA Receptors 4 | ||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 3 (-) | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 21 | 5 | nr | <0.0001 | Ne | - |
| PET-FDG 5 | ||||||
| No | 8 | 3 | 112 (14-nr) | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 12 | 4 | nr | 0.975 | 1.02 (0.23–4.58) | 0.975 |
| % hERG1 positive cells | ||||||
| Negative (<40) | 41 | 9 | nr | 1.00 | ||
| Positive (≥40) | 18 | 1 | nr | 0.134 | 0.23 (0.03–1.85) | 0.169 |
| N. Patients | N. Deaths | Median OS 1 (Months) (95% CI 2) | HR (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OVERALL | |||||
| % hERG1 positive cells | |||||
| Negative (<40) | 48 | 14 | nr | 1.00 | |
| Positive (≥40) | 42 | 8 | nr | 0.60 (0.25–1.43) | 0.248 |
| TNM IV | |||||
| % hERG1 positive cells | |||||
| Negative (<40) | 21 | 13 | 72 (10-nr) | 1.00 | |
| Positive (≥40) | 13 | 2 | nr | 0.22 (0.05–0.97) | 0.046 |
| TNM I-III | |||||
| % hERG1 positive cells | |||||
| Negative (<40) | 27 | 1 | 96 (88–100) | 1.00 | |
| Positive (≥40) | 29 | 6 | 86 (73–99) | 5.18 (0.62–43.36) | 0.129 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iorio, J.; Antonuzzo, L.; Scarpi, E.; D’Amico, M.; Duranti, C.; Messerini, L.; Sparano, C.; Caputo, D.; Lavacchi, D.; Borzomati, D.; et al. Prognostic role of hERG1 Potassium Channels in Neuroendocrine Tumours of the Ileum and Pancreas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810623
Iorio J, Antonuzzo L, Scarpi E, D’Amico M, Duranti C, Messerini L, Sparano C, Caputo D, Lavacchi D, Borzomati D, et al. Prognostic role of hERG1 Potassium Channels in Neuroendocrine Tumours of the Ileum and Pancreas. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810623
Chicago/Turabian StyleIorio, Jessica, Lorenzo Antonuzzo, Emanuela Scarpi, Massimo D’Amico, Claudia Duranti, Luca Messerini, Clotilde Sparano, Damiano Caputo, Daniele Lavacchi, Domenico Borzomati, and et al. 2022. "Prognostic role of hERG1 Potassium Channels in Neuroendocrine Tumours of the Ileum and Pancreas" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810623
APA StyleIorio, J., Antonuzzo, L., Scarpi, E., D’Amico, M., Duranti, C., Messerini, L., Sparano, C., Caputo, D., Lavacchi, D., Borzomati, D., Antonelli, A., Nibid, L., Perrone, G., Coppola, A., Coppola, R., di Costanzo, F., Lastraioli, E., & Arcangeli, A. (2022). Prognostic role of hERG1 Potassium Channels in Neuroendocrine Tumours of the Ileum and Pancreas. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810623











