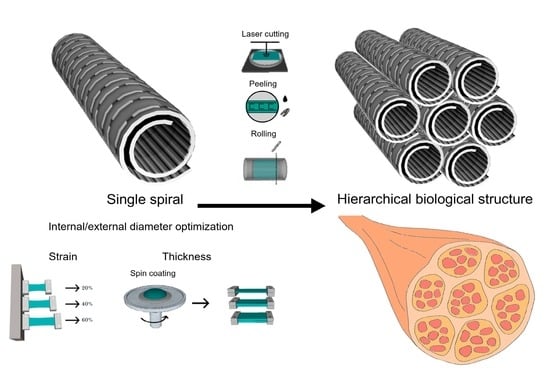
Modeling Self-Rollable Elastomeric Films for Building Bioinspired Hierarchical 3D Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
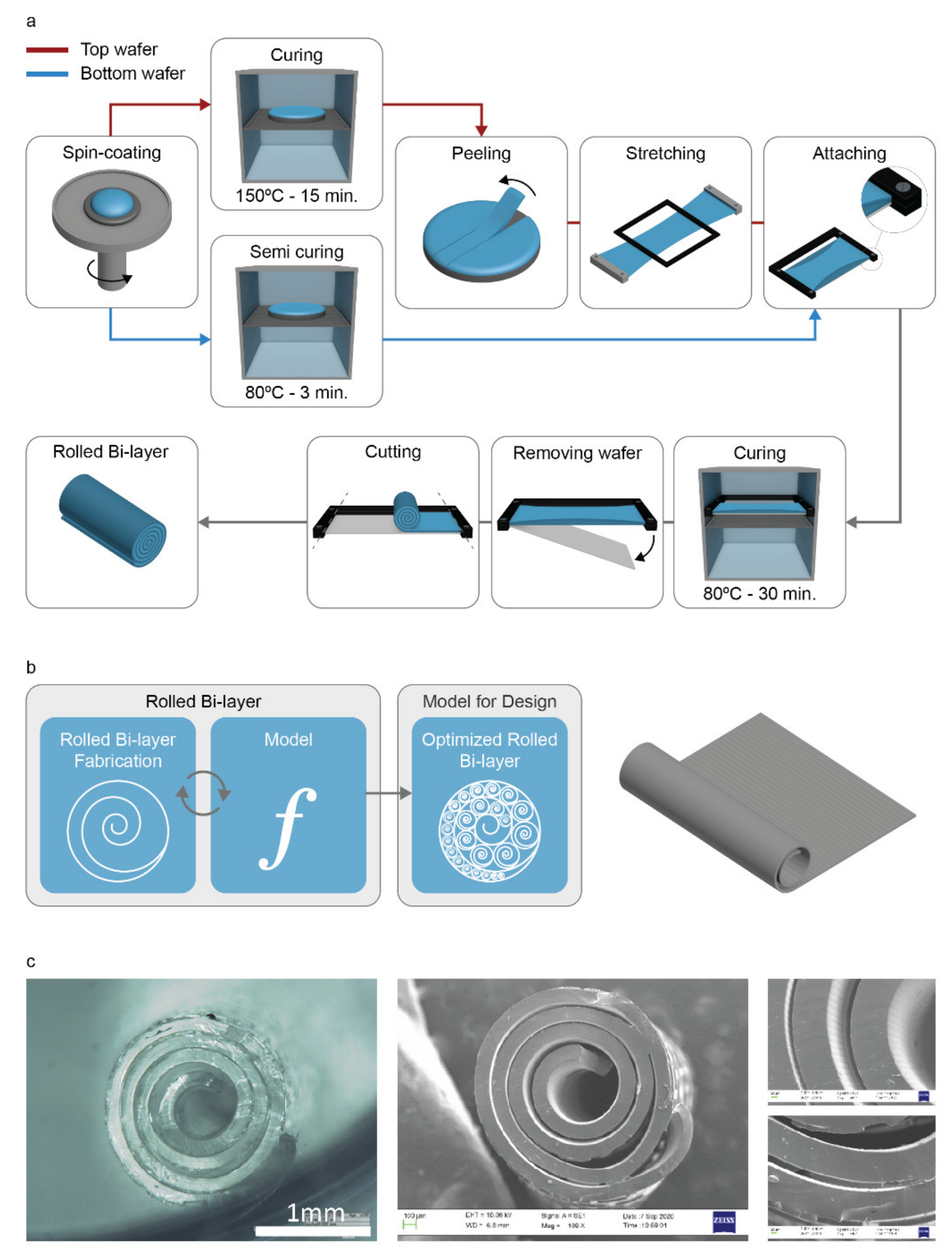
2.1. General Workflow and Fabrication of Topographical Features
2.2. Model of Rolled Bilayers
2.3. Influence of the Applied Strain on the Geometry of the Rolled Structure
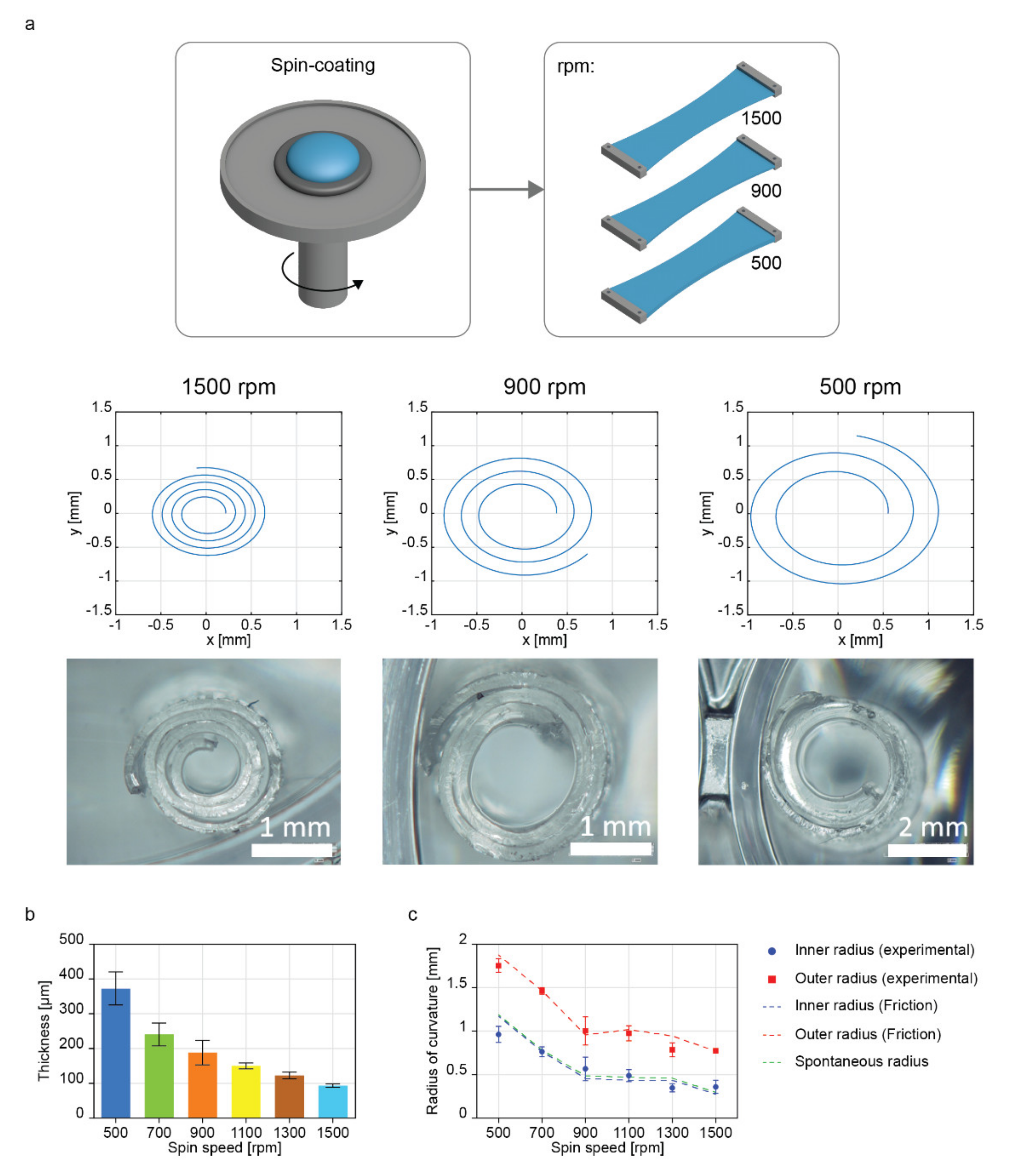
2.4. Influence of the Thickness Variation of the Bilayer on the Geometry of the Rolled Structure
2.5. Development of a Bioinspired Hierarchical Structure
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Fabrication of Rolled Structures
3.2. Fabrication of Hierarchical Rolled Structures
3.3. Morphological Characterization
3.4. Fitting of Experimental Data on Rolled Shapes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timoshenko, S. Analysis of bi-metal thermostats. JOSA 1925, 11, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracias, D.H. Stimuli responsive self-folding using thin polymer films. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Manen, T.; Janbaz, S.; Zadpoor, A.A. Programming the shape-shifting of flat soft matter. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, N.; Yuan, B.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. Stress-induced self-assembly of complex three dimensional structures by elastic membranes. Small 2013, 9, 2410–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, G.; Trase, I.; Han, X.; Mei, Y. Mechanical self-assembly of a strain-engineered flexible layer: Wrinkling, rolling, and twisting. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2016, 5, 017001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, G.; Mei, Y. Assembly and Self-Assembly of Nanomembrane Materials—From 2D to 3D. Small 2018, 14, 1703665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, J. Kirigami/origami: Unfolding the new regime of advanced 3D microfabrication/nanofabrication with “folding”. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoychev, G.; Zakharchenko, S.; Turcaud, S.; Dunlop, J.W.; Ionov, L. Shape-programmed folding of stimuli-responsive polymer bilayers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3925–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Wu, X.; Huang, G.; Mei, Y. Rolled-up Nanotechnology: Materials Issue and Geometry Capability. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, Y.; Solovev, A.A.; Sanchez, S.; Schmidt, O.G. Rolled-up nanotech on polymers: From basic perception to self-propelled catalytic microengines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Schmidt, O.G. Introducing Rolled-Up Nanotechnology for Advanced Energy Storage Devices. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños Quiñones, V.A.; Zhu, H.; Solovev, A.A.; Mei, Y.; Gracias, D.H. Origami biosystems: 3D assembly methods for biomedical applications. Adv. Biosyst. 2018, 2, 1800230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntornnond, R.; An, J.; Yeong, W.Y.; Chua, C.K. Biodegradable polymeric films and membranes processing and forming for tissue engineering. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotti, L.; Fujie, T. Thin polymeric films for building biohybrid microrobots. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2017, 12, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventre, M.; Netti, P.A. Engineering cell instructive materials to control cell fate and functions through material cues and surface patterning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14896–14908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotti, L.; Menciassi, A. Engineering stem cells for future medicine. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotti, L.; Vannozzi, L.; Dario, P.; Menciassi, A. Three-dimensional tubular self-assembling structure for bio-hybrid actuation. In Conference on Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Vannozzi, L.; Ricotti, L.; Cianchetti, M.; Bearzi, C.; Gargioli, C.; Rizzi, R.; Dario, P.; Menciassi, A. Self-assembly of polydimethylsiloxane structures from 2D to 3D for bio-hybrid actuation. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 056001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Liu, F. Modified Timoshenko formula for bending of ultrathin strained bilayer films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 021905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ionov, L. Bioinspired Microorigami by Self-Folding Polymer Films. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardinocchi, P.; Puntel, E. Finite bending solutions for layered gel beams. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 90, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naleway, S.E.; Porter, M.M.; McKittrick, J.; Meyers, M.A. Structural design elements in biological materials: Application to bioinspiration. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5455–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X. Recent advances in scaffold design and material for vascularized tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasebe, A.; Suematsu, Y.; Takeoka, S.; Mazzocchi, T.; Vannozzi, L.; Ricotti, L.; Fujie, T. Biohybrid actuators based on skeletal muscle-powered microgrooved ultrathin films consisting of poly (styrene-block-butadiene-block-styrene). ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 5734–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, I.; Logan, J.; Shi, J.; McCormick, C.; Liu, D.; Shu, W. 3D biofabrication for tubular tissue engineering. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2018, 1, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamdan, M.N.; Al-Qaisia, A.A.; Abdallah, S. Parametric study of dynamic wrinkling in a thin sheet on elastic foundation. Int. J. Mod. Nonlinear Theory Appl. 2012, 1, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Song, P.; Meng, F.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Song, J. Quantitative analysis and predictive engineering of self-rolling of nanomembranes under anisotropic mismatch strain. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 485302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannozzi, L.; Yasa, I.C.; Ceylan, H.; Menciassi, A.; Ricotti, L.; Sitti, M. Self-folded hydrogel tubes for implantable muscular tissue scaffolds. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1700377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakharchenko, S.; Puretskiy, N.; Stoychev, G.; Waurisch, C.; Hickey, S.G.; Eychmüller, A.; Sommer, J.; Ionov, L. Stimuli-responsive hierarchically self-assembled 3D porous polymer-based structures with aligned pores. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góra, A.; Pliszka, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Tubular tissues and organs of human body—Challenges in regenerative medicine. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B. A perspective on intelligent design of engineered materials and structures by interface mechanics. Mech. Res. Commun. 2022, 119, 103668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. A strategy for depositing different types of cells in three dimensions to mimic tubular structures in tissues. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Liu, N.; Xu, N.; Chen, W.; Xing, D. Engineering Complex Anisotropic Scaffolds beyond Simply Uniaxial Alignment for Tissue Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2110676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
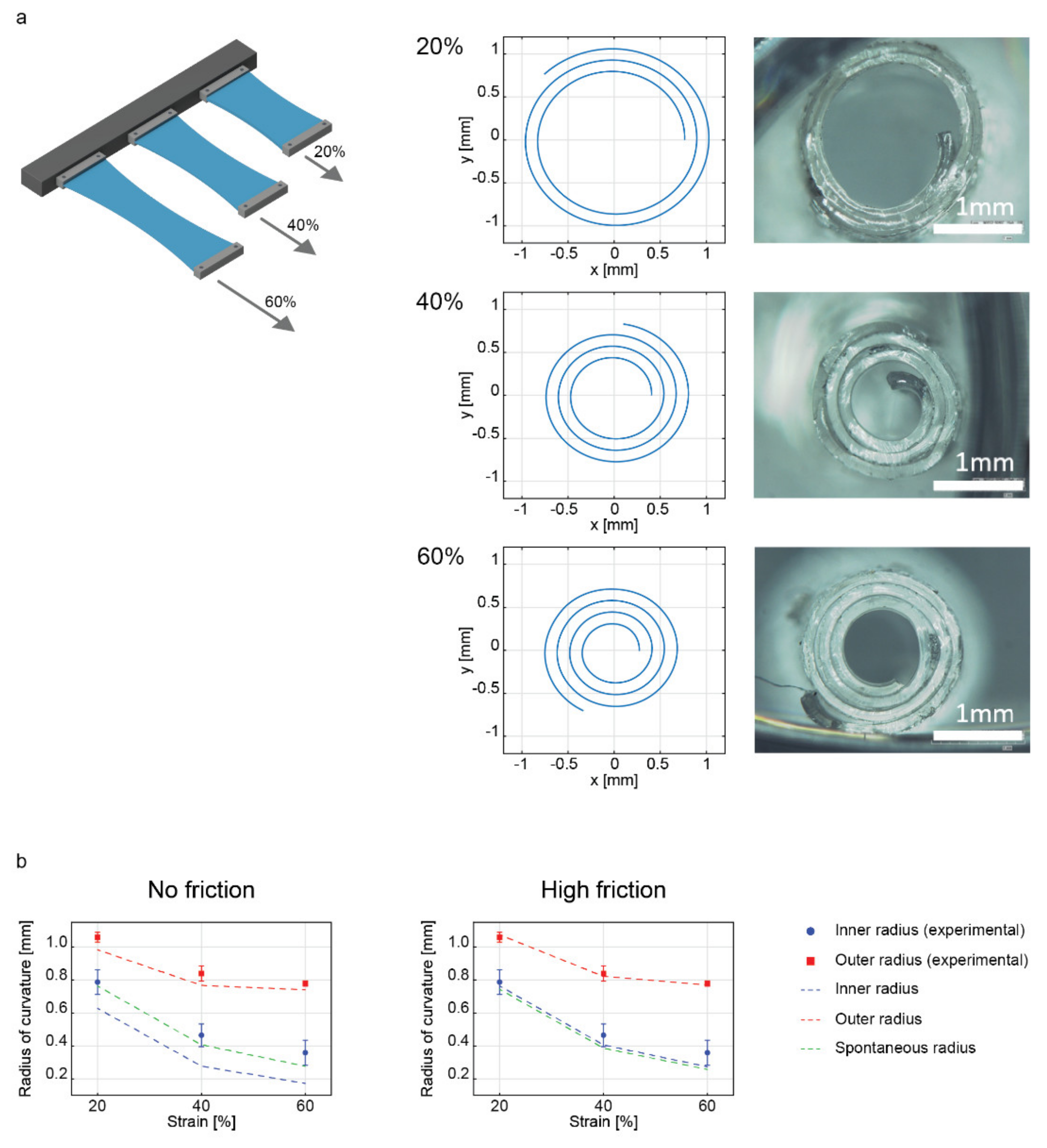

| Strain | Radius | Experiment (µm) | Spontaneous Radius (µm) | Model (No-Friction) (µm) | Model (Friction) (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | IR | 787.5 ± 74.8 | 763.7 | 626.2 (−20.5%) | 763.4 (3.1%) |
| OR | 1058.2 ± 29.1 | 982.6 (−7.1%) | 1074.0 (1.5%) | ||
| 40% | IR | 465.3 ± 68.7 | 407.3 | 277.5 (−40.4%) | 405.9 (−12.8%) |
| OR | 839.3 ± 46.2 | 767.5 (−8.5%) | 821.2 (−2.1%) | ||
| 60% | IR | 359.2 ± 75.7 | 277.5 | 172.9 (−51.9%) | 274.1 (−23.7%) |
| OR | 778.4 ± 15.8 | 742.4 (−4.6%) | 770.7 (−1.0%) |
| Spin Speed | Radius | Experiment (µm) | Spontaneous Radius (µm) | Model (Friction) (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 rpm | IR | 963.1 ± 92.9 | 1170.3 | 1173.2 (21.8%) |
| OR | 1754.3 ± 78.3 | 1875.2 (6.9%) | ||
| 700 rpm | IR | 764.8 ± 55.9 | 765.5 | 767.9 (0.4%) |
| OR | 1463.7 ± 37.3 | 1466.2 (0.2%) | ||
| 900 rpm | IR | 566.7 ± 134.4 | 468.6 | 456.1 (−19.4%) |
| OR | 1004.5 ± 162.1 | 958.3 (−4.6%) | ||
| 1100 rpm | IR | 489.3 ± 67.9 | 450.8 | 434.3 (−11.2%) |
| OR | 976.6 ± 86.6 | 1020.3 (4.5%) | ||
| 1300 rpm | IR | 348.2 ± 45.6 | 441.1 | 434.0 (24.6%) |
| OR | 786.2 ± 79.1 | 945.6 (20.3%) | ||
| 1500 rpm | IR | 359.2 ± 75.7 | 277.5 | 274.1 (−23.7%) |
| OR | 778.4 ± 15.8 | 770.7 (−1.0%) |
| Mean Value for Inner Spirals | Experiment (µm) | Model (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| IR | 193.3 ± 14.7 | 237.4 (18.56%) |
| OR | 430.5 ± 42.0 | 424.1 (−1.01%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vannozzi, L.; Lucantonio, A.; Castillo, A.; De Simone, A.; Ricotti, L. Modeling Self-Rollable Elastomeric Films for Building Bioinspired Hierarchical 3D Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158467
Vannozzi L, Lucantonio A, Castillo A, De Simone A, Ricotti L. Modeling Self-Rollable Elastomeric Films for Building Bioinspired Hierarchical 3D Structures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158467
Chicago/Turabian StyleVannozzi, Lorenzo, Alessandro Lucantonio, Arturo Castillo, Antonio De Simone, and Leonardo Ricotti. 2022. "Modeling Self-Rollable Elastomeric Films for Building Bioinspired Hierarchical 3D Structures" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158467
APA StyleVannozzi, L., Lucantonio, A., Castillo, A., De Simone, A., & Ricotti, L. (2022). Modeling Self-Rollable Elastomeric Films for Building Bioinspired Hierarchical 3D Structures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158467