The L-Type Lectin-like Receptor Kinase Gene TaLecRK-IV.1 Regulates the Plant Height in Wheat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
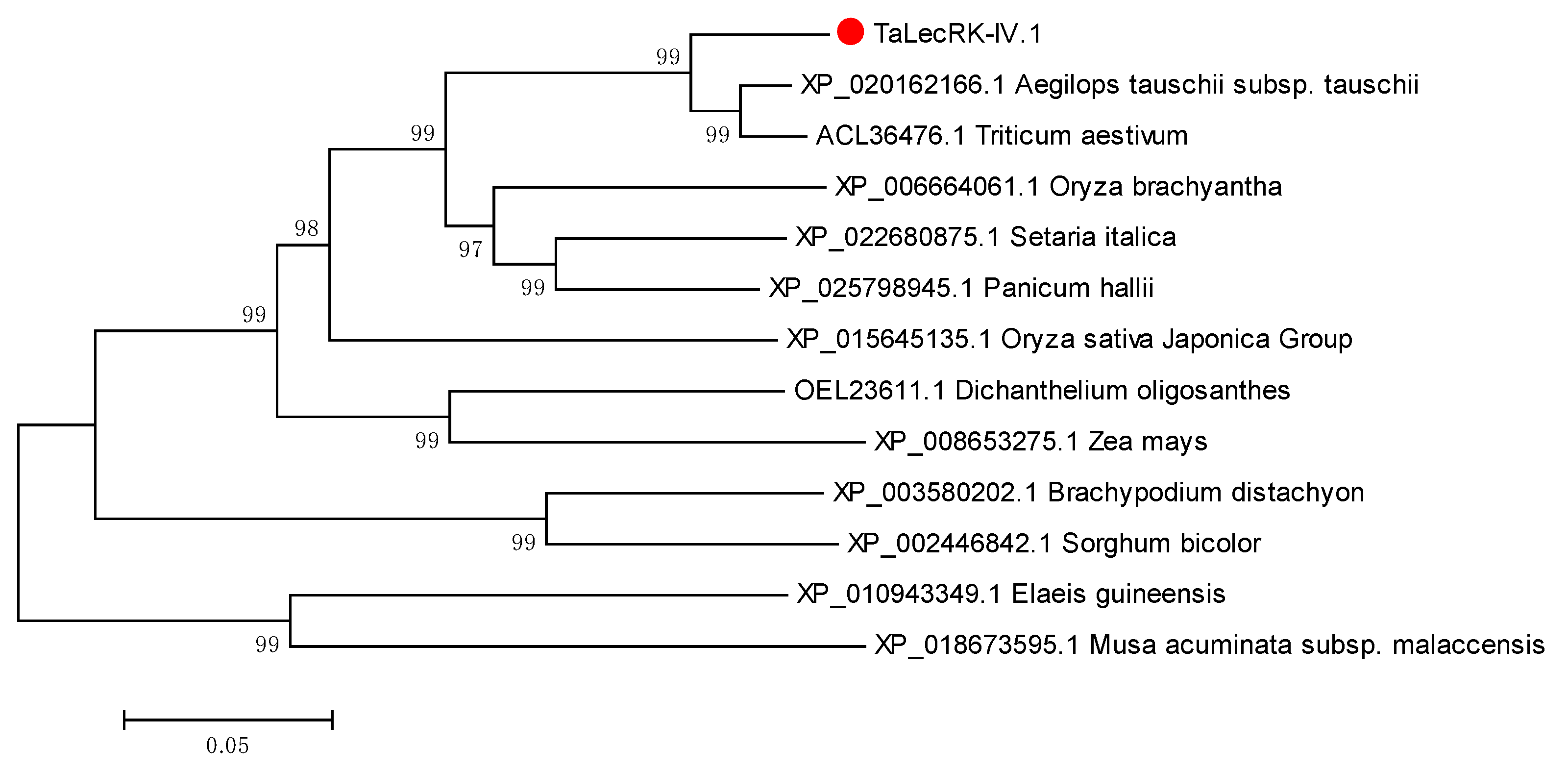
2.1. Cloning of TaLecRK-IV.1 Gene Encoding an L-Type Lectin Domain Containing Receptor Kinase IV.1
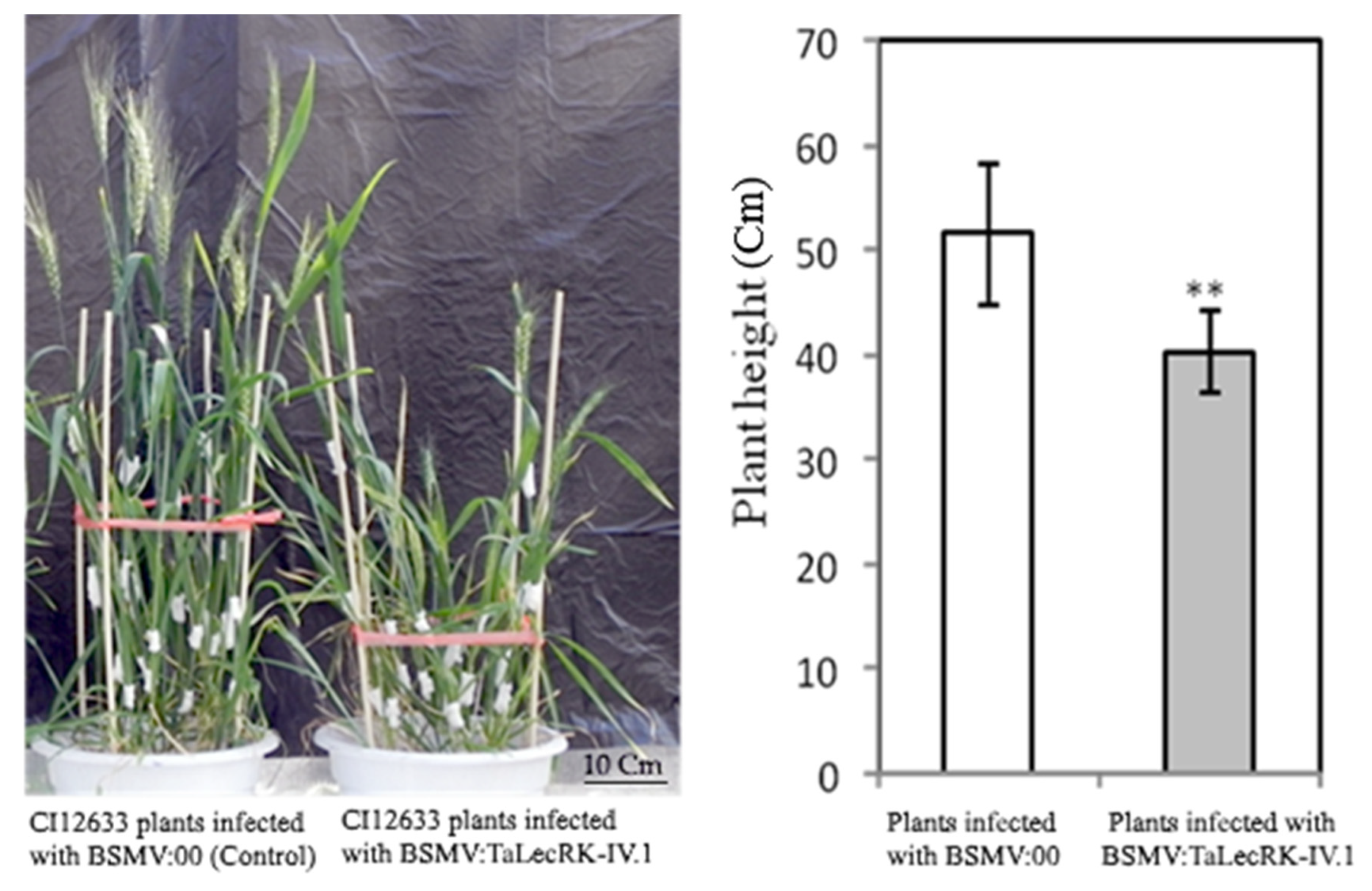
2.2. Silencing of TaLecRK-IV.1 Leads to Dwarf Plants
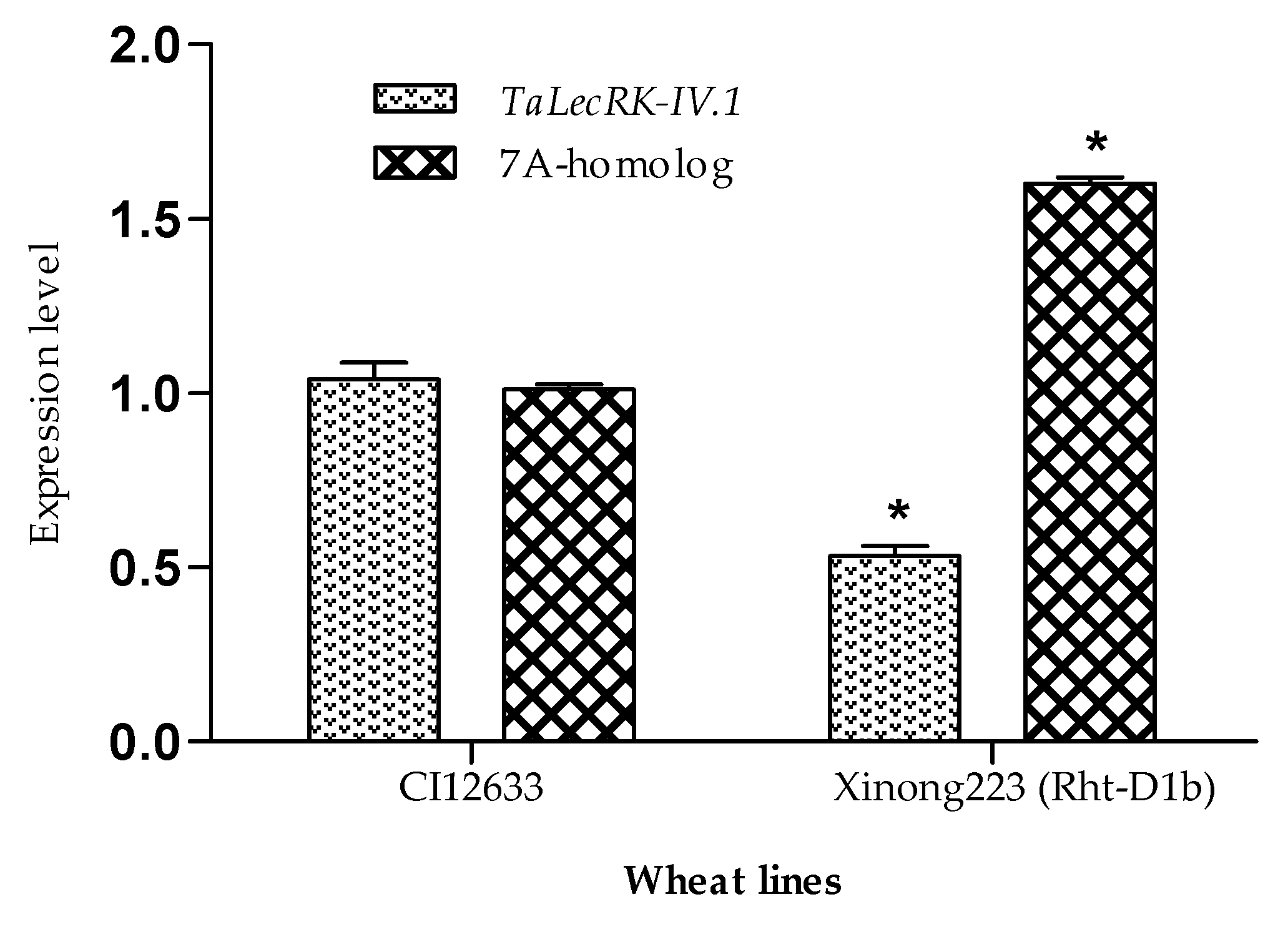
2.3. The Expression of TaLecRK-IV.1 in the Wheat Line with Rht-D1b Gene
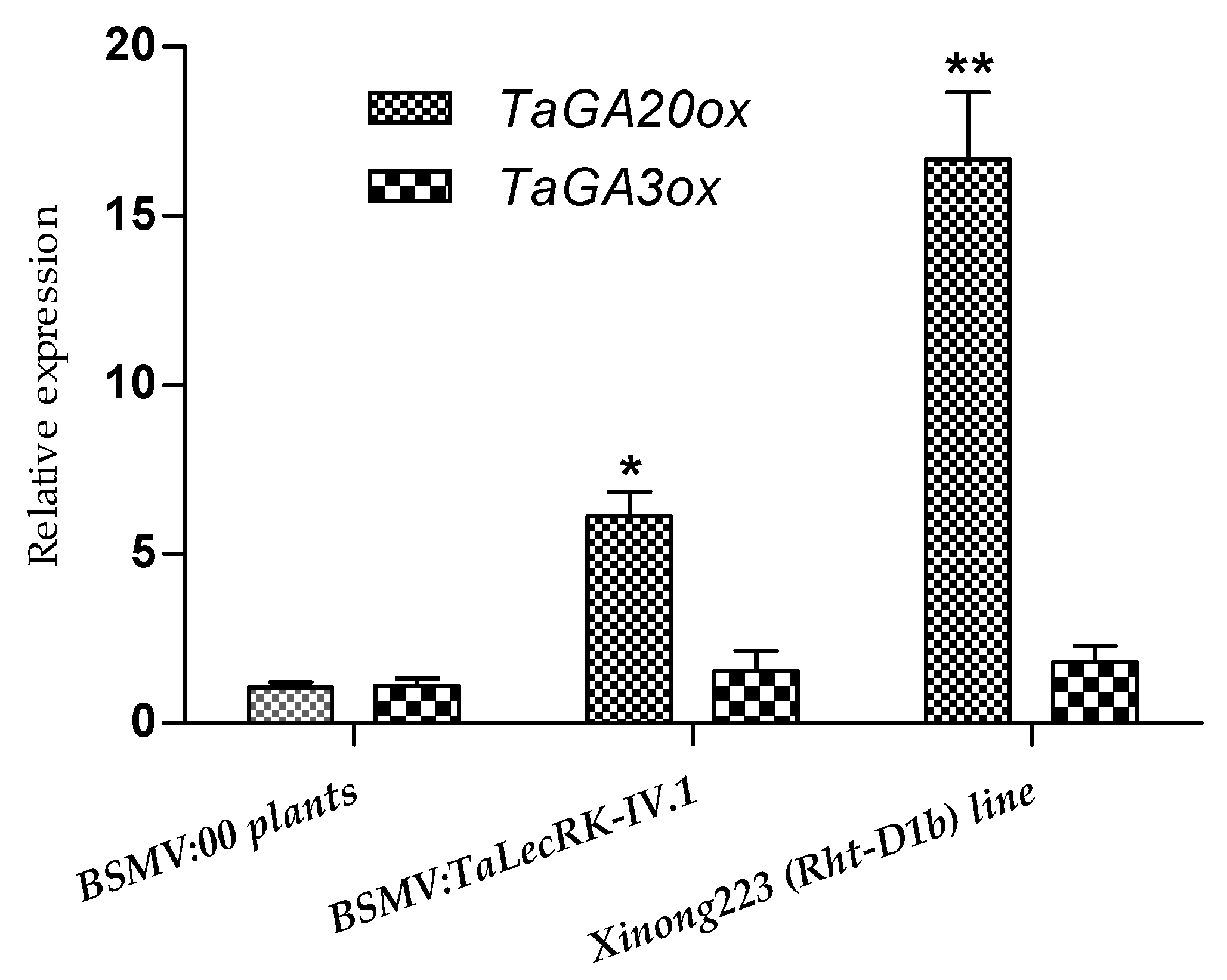
2.4. Relative Expression of GA Biosynthetic Enzymes TaGA20ox and TaGA3ox in Rht-D1b-Carring Wheat Line and TaLecRK-IV.1-Silenced CI12633 Plants
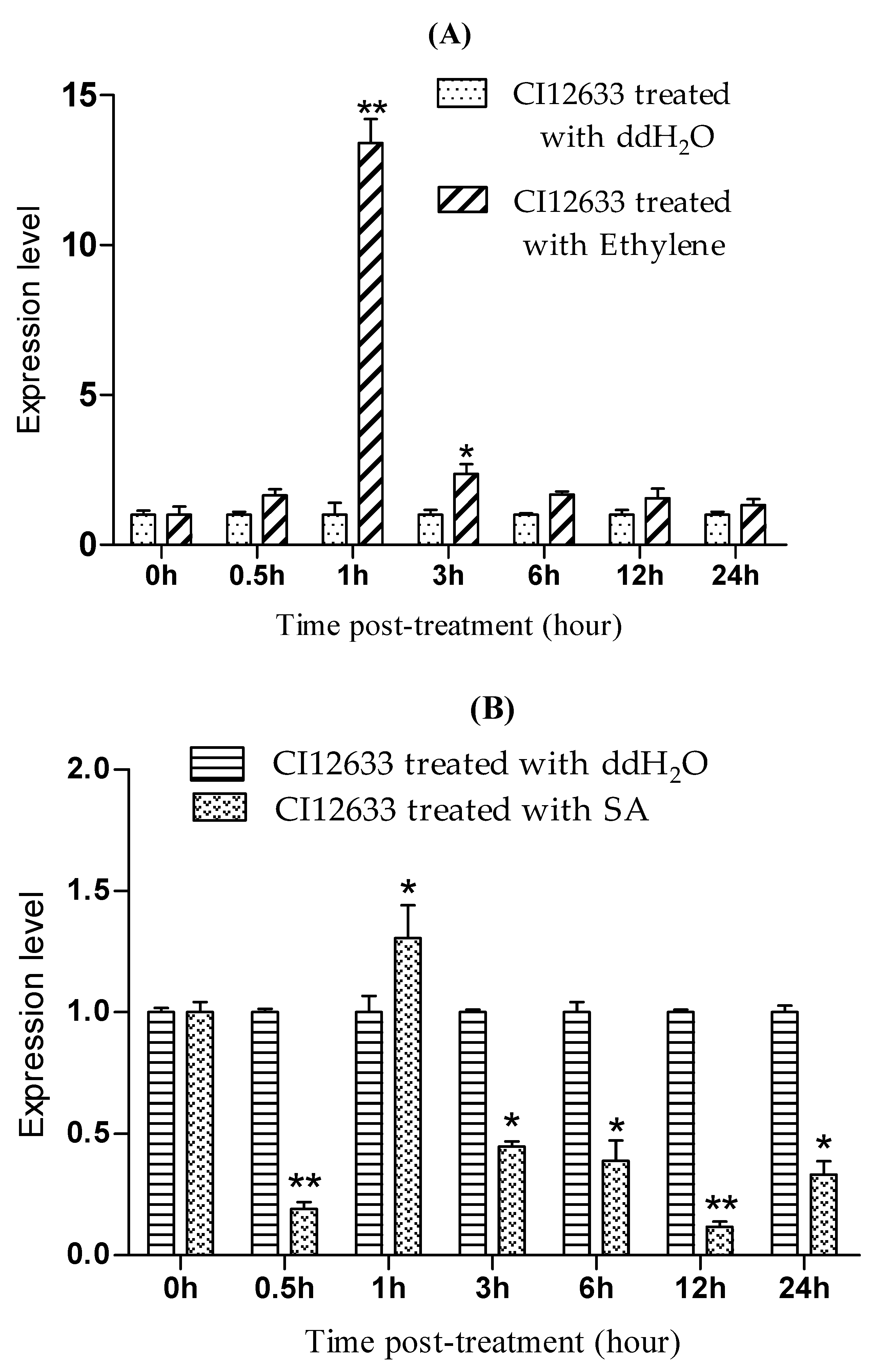
2.5. TaLecRK-IV.1 Is Expressed in Response to Exogenous GA and Auxin Treatments
2.6. Resistance Responses to Sharp Eyespot of the Plants Subjected to the VIGS Experiment
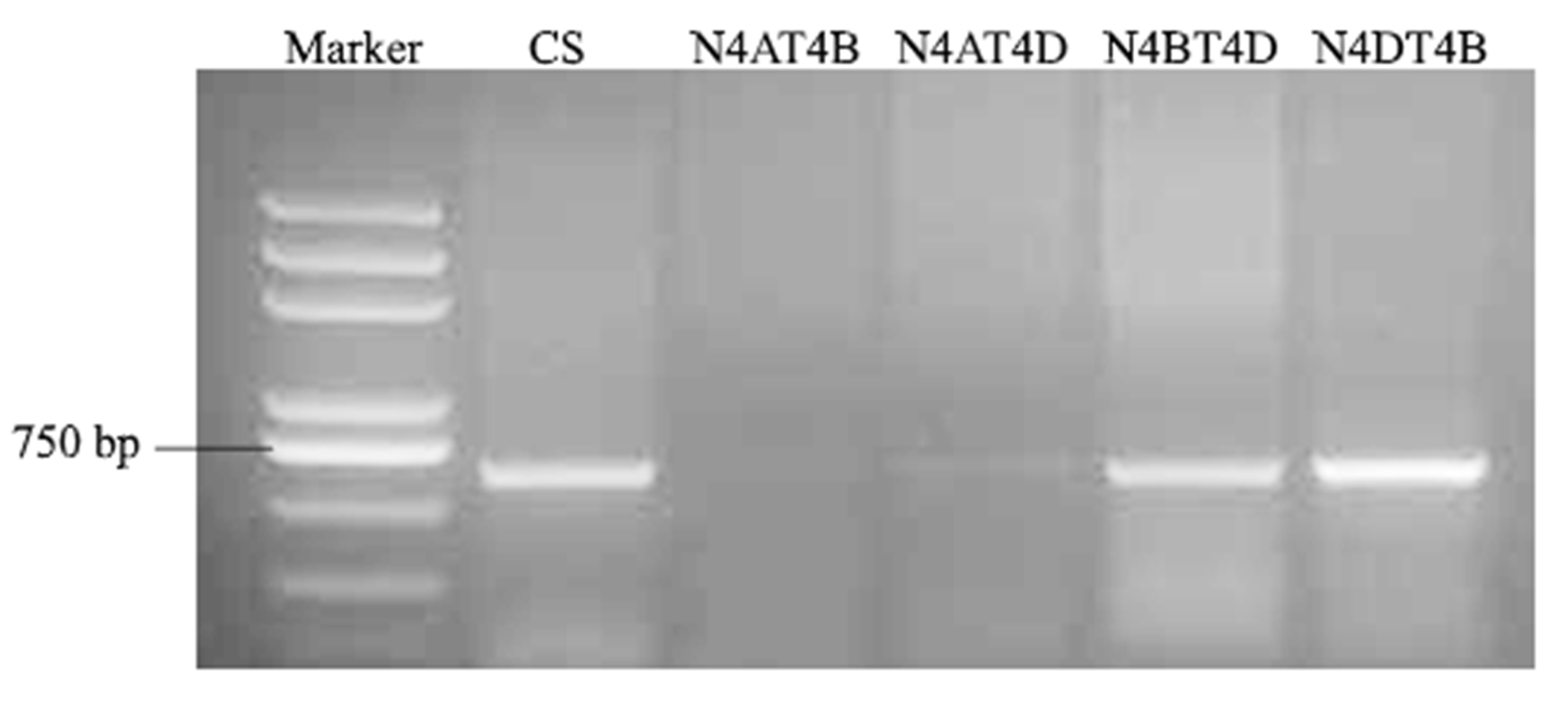
2.7. TaLecRK-IV.1 Is Assigned to Chromosome 4A
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions and Treatments
4.2. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of TaLecRK-IV.1
4.4. Virus-Induced Gene Silencing of TaLecRK-IV.1
4.5. Real Time PCR Analysis
4.6. Test for Susceptibility to Sharp Eyespot
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaid, N.; Macovei, A.; Tuteja, N. Knights in action: Lectin Receptor-like kinases in plant development and stress responses. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouwmeester, K.; Govers, F. Arabidopsis L-type lectin receptor kinases: Phylogeny, classification, and expression profile. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 4383–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.; Ju, H.; Min, J.; Zhang, X.; Kim, S.; Yang, K.; Kim, C. Overexpression of L-type lectin-like protein kinase 1 confers pathogen resistance and regulates salinity response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 2013, 203–204, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannoo, N.; Van Damme, J.M. Lectin domains at the frontiers of plant defense. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barre, A.; Herye, C.; Lescure, B.; Rouge, P. Lectin receptor kinases in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2002, 21, 379–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kuo, Y.C.; Mishra, S.; Tsai, C.H.; Chien, C.C.; Chen, C.W.; Desclos-Theveniau, M.; Chu, P.W.; Schulze, B.; Chinchilla, D.; et al. The lectin-receptor kinase-VI.2 is required for priming and positively regulates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1256–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouwmeester, K.; De Sain, M.; Weide, R.; Gouget, A.; Klamer, S.; Canut, H.; Govers, F. The lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.9 is a novel Phytophthora resistance component and a potential host target for a RXLR effector. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fan, A.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Muhammad, F.; Wang, H.; et al. LecRK-V, an L-type lectin receptor kinase in Haynaldia villosa, plays positive role in resistance to wheat powdery mildew. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishiguchi, M.; Yoshida, K.; Sumizono, T.; Tazaki, K. A receptor-like protein kinase with a lectin-like domain from Lombardy poplar: Gene expression in response to wounding and characterization of phosphorylation activity. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2002, 267, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riou, C.; Hervé, C.; Pacquit, V.; Dabos, P.; Lescure, B. Expression of an Arabidopsis lectin kinase receptor gene, lecRK-a1, is induced during senescence, wounding and in response to oligogalacturonic acids. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 40, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, S.R.; Huang, L.; Brandt, A.S.; Gill, B.S. Development of a virus-induced gene-silencing system for hexaploid wheat and its use in functional analysis of the Lr21-mediated leaf rust resistance pathway. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 2165–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.W.; Herrera-Foessel, S.; Lan, C.; Schnippenkoetter, W.; Ayliffe, M.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Lillemo, M.; Viccars, L.; Milne, R.; Periyannan, S.; et al. A recently evolved hexose transporter variant confers resistance to multiple pathogens in wheat. Nat. Genet. 2011, 47, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.; Saville, R.; Vaughan, S.P.; Chandler, P.M.; Wilhelm, E.P.; Sparks, C.A.; Al-Kaff, N.; Korolev, A.; Boulton, M.I.; Phillips, A.L.; et al. Molecular characterization of Rht-1 dwarfing genes in hexaploid wheat. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, L.T. Feeding the Ten Billion: Plants and Population Growth; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Richards, D.E.; Hartley, N.M.; Murphy, G.P.; Devos, K.M.; Flintham, J.E.; Beales, J.; Fish, L.J.; Worland, A.J.; Pelica, F.; et al. ‘Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 1999, 400, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S. Gibberellin metabolism and its regulation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davière, J.M.; Achard, P. A pivotal role of DELLAs in regulating multiple hormone signals. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Achard, P.; Genschik, P. Releasing the brakes of plant growth: How GAs shutdown DELLA proteins. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appleford, N.E.; Evans, D.J.; Lenton, J.R.; Gaskin, P.; Croker, S.J.; Devos, K.M.; Phillips, A.M.; Hedden, P. Function and transcript analysis of gibberellin-biosynthetic enzymes in wheat. Planta 2006, 223, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedden, P. The genes of the green revolution. Trends Genet. 2003, 19, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, G.H.; Du, Z.Y.; Quan, W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Che, M.Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.J. Mapping of QTL Conferring resistance to sharp eyespot (Rhizoctoniacerealis) in bread wheat at the adult plant growth stage. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 2865–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBeath, J.H.; McBeath, J. Plant diseases, pests and food security. In Environmental Change and Food Security in China; Martin, B., Ed.; Springer Technology and Engineering; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, M.S.; Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, Z. The escalating threat of Rhizoctonia cerealis, the causal agent of sharp eyespot in wheat. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, K.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Q.; Rong, W.; Du, L.; Ye, X.; Qi, L.; Zhang, Z. The wheat AGC kinase TaAGC1 is a positive contributor to host resistance to the necrotrophic pathogen Rhizoctoniacerealis. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6591–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Cheng, K.; Zhao, R.; Zang, S.; Bie, T.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, R.; Gao, D.; Zhang, B. Quantitative trait loci responsible for sharp eyespot resistance in common wheat CI12633. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holzberg, S.; Brosio, P.; Gross, C.; Pogue, G.P. Barley stripe mosaic virus-induced gene silencing in a monocot plant. Plant J. 2002, 30, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Rong, W.; Qi, L.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Z. Isolation and characterization of a novel wheat cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene induced by Rhizoctonia cerealis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Qi, L.; Liu, X.; Cai, S.; Xu, H.; Huang, R.; Li, J.R.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Z. The wheat ethylene response factor transcription factor pathogen-induced ERF1 mediated host responses to both the necrotrophic pathogen Rhizoctonia cerealis and freezing stresses. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rong, W.; Luo, M.; Shan, T.; Wei, X.; Du, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z. A Wheat cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase TaCAD12 contributes to host resistance to the sharp eyespot disease. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Shen, F.; Hong, Y.; Rong, W.; Du, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z. The wheat calcium-dependent protein kinase TaDPK7-D positively regulates host resistance to sharp eyespot disease. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Lu, C.; Du, L.; Ye, X.; Liu, X.; Coules, A.; Zhang, Z. The wheat NB-LRR gene TaRCR1 is required for host defence response to the necrotrophic fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia cerealis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ford, B.A.; Foo, E.; Sharwood, R.; Karafiatova, M.; Vrána, J.; MacMillan, C.; Nichols, D.S.; Steuernagel, B.; Uauy, C.; Dolozel, J.; et al. Rht18 semidwarfism in wheat is due to increased GA 2-oxidaseA9 expression and reduced GA content. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Shan, Q.; Ye, X.; Wang, D.; Yu, K.; Lu, W.; Xin, P.; Pei, Z.; et al. A wheat dominant dwarfing line with Rht12, which reduces stem cell length and affects gibberellic acid synthesis, is a 5AL terminal deletion line. Plant J. 2019, 97, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleford, N.E.; Wilkinson, M.D.; Ma, Q.; Evans, D.J.; Stone, M.C.; Pearce, S.P.; Powers, S.J.; Thomas, S.G.; Jones, H.D.; Phillips, A.L.; et al. Decreased shoot stature and grain α-amylase activity following ectopic expression of a gibberellin 2-oxidase gene in transgenic wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 3213–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Itoh, H.; Tagiri, A.; Kayano, T.; Tanaka, H.; Iwahori, S.; Matsuoka, M. Expression of a gibberellin 2-oxidase gene around the shoot apex is related to phase transition in rice. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakai, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Saito, T.; Matsuoka, M.; Tanaka, H.; Kobayashi, M. Expression of novel rice gibberellin 2-oxidase gene is under homeostatic regulation by biologically active gibberellins. J. Plant Res. 2003, 116, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.F.; Yang, S.Y.; Chen, K.T.; Hsing, Y.I.; Zeevaart, J.A.; Chen, L.J.; Yu, S.M. A novel class of gibberellin 2-oxidases control semidwarfism, tillering, and root development in rice. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2603–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Tang, D.; Shen, Y.; Qin, B.; Hong, L.; You, A.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Gu, M.; et al. Activation of gibberellin 2-oxidase 6 decreases active gibberellin levels and creates a dominant semi-dwarf phenotype in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Genet. Genom. 2010, 37, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, V.; McCallum, B.; Bakkeren, G. Host-induced gene silencing of wheat leaf rust fungus Puccinia triticina pathogenicity genes mediated by the Barley stripe mosaic virus. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 81, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Categories | Mean Disease Index | Student’s t-Test |
|---|---|---|
| Control plants | 27.43 | 0.848 |
| TaLecRK-IV.1-silenced plants | 25.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saidou, M.; Zhang, Z. The L-Type Lectin-like Receptor Kinase Gene TaLecRK-IV.1 Regulates the Plant Height in Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158208
Saidou M, Zhang Z. The L-Type Lectin-like Receptor Kinase Gene TaLecRK-IV.1 Regulates the Plant Height in Wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158208
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaidou, Mamoudou, and Zengyan Zhang. 2022. "The L-Type Lectin-like Receptor Kinase Gene TaLecRK-IV.1 Regulates the Plant Height in Wheat" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158208
APA StyleSaidou, M., & Zhang, Z. (2022). The L-Type Lectin-like Receptor Kinase Gene TaLecRK-IV.1 Regulates the Plant Height in Wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158208






