The Role of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives on Different Steps of Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 In Vitro Replicative Cycle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Inhibition Profile of HSV-1 by Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives
2.2. Effects of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives on Infected Cells
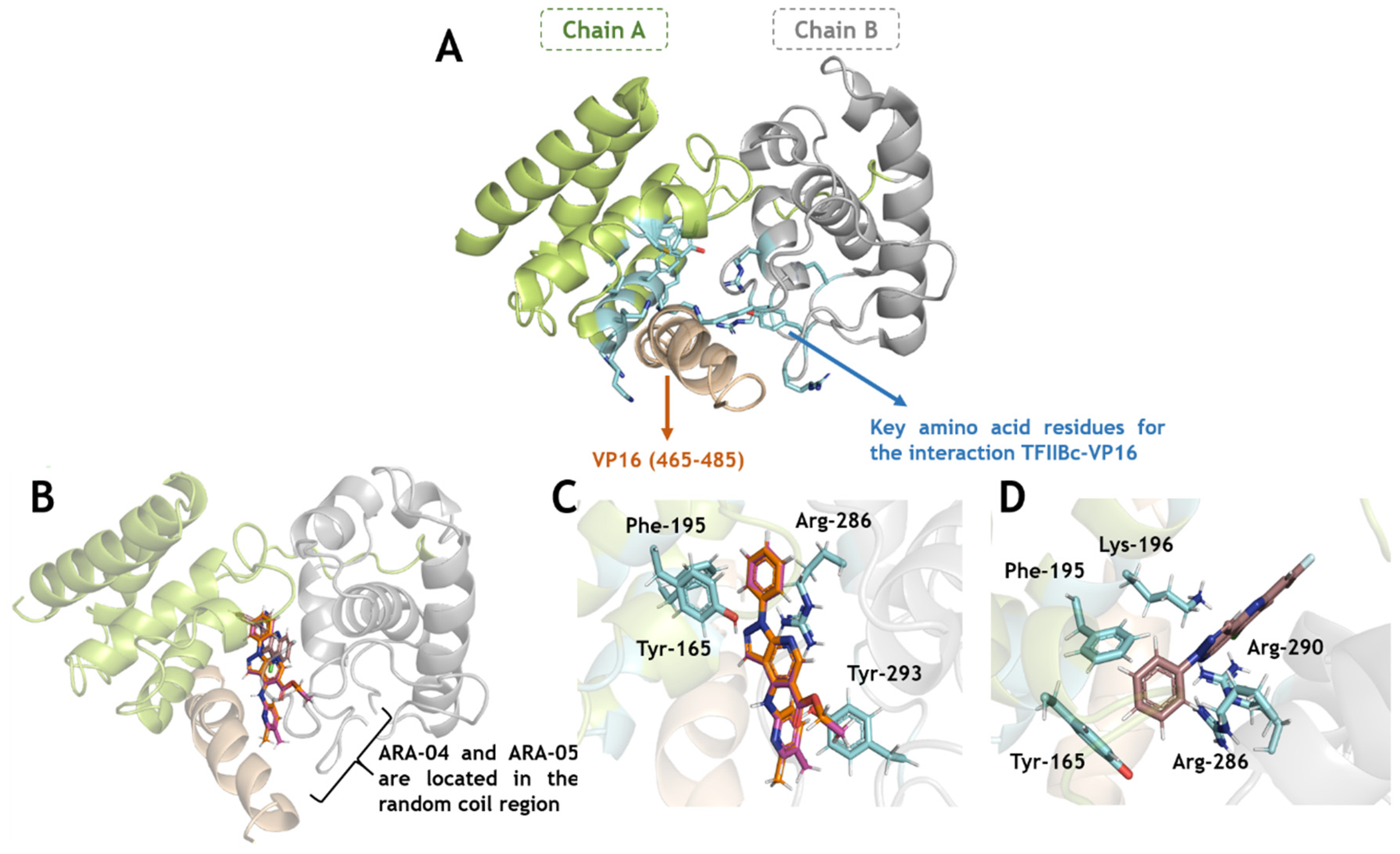
2.3. In Silico Calculations for the Main Targets of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Stock Solutions of 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine Derivatives
3.2. Cells and Virus
3.3. Cytotoxic Assays
3.4. Yield-Reduction Assays and Virus Titration
3.5. Adsorption and Penetration Inhibition Assays
3.6. Time-Of-Addition Assays
3.7. Immunoblotting
3.8. In Silico Procedure
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heldwein, E.E.; Krummenacher, C. Entry of herpesviruses into mammalian cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2008, 65, 1653–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, S.A.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. The structural basis of herpesvirus entry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Viejo-Borbolla, A. Pathogenesis and virulence of herpes simplex virus. Virulence 2021, 12, 2670–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.; Harfouche, M.; Welton, N.J.; Turner, K.M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Gottlieb, S.L.; Looker, K.J. Herpes simplex virus: Global infection prevalence and incidence estimates, 2016. Bull. World Health Organ. 2020, 98, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roizman, B.; Sears, A.E. Herpes simplex viruses and their replication. In Field’s Virology, 3rd ed.; Lippincott-Raven: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Packard, J.E.; Dembowski, J.A. HSV-1 DNA Replication-Coordinated Regulation by Viral and Cellular Factors. Viruses 2021, 13, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, C.; Chen, Z.S.; Liu, Z. Receptors and ligands for herpes simplex viruses: Novel insights for drug targeting. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 27, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, P.G. Herpes simplex virus: Receptors and ligands for cell entry. Cell. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, R.D. HSV-1 biology and life cycle. Methods Mol. Biol 2014, 1144, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madavaraju, K.; Koganti, R.; Volety, I.; Yadavalli, T.; Shukla, D. Herpes Simplex Virus Cell Entry Mechanisms: An Update. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 617578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, J.L.; Pellett, P.E.; Jenkins, F.J.; Roizman, B. Characterization and nucleotide sequence of two herpes simplex virus 1 genes whose products modulate alpha-trans-inducing factor-dependent activation of alpha genes. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri-Goldin, R.M. The many roles of the highly interactive HSV protein ICP27, a key regulator of infection. Futur. Microbiol. 2011, 6, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, P.A.; Okagaki, L.H.; Rice, S.A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 induces p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and apoptosis in HeLa cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.C.; Dybas, J.M.; Hughes, J.; Weitzman, M.D.; Boutell, C. The HSV-1 ubiquitin ligase ICP0: Modifying the cellular proteome to promote infection. Virus Res. 2020, 285, 198015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hennig, T.; Whisnant, A.W.; Erhard, F.; Prusty, B.K.; Friedel, C.C.; Forouzmand, E.; Hu, W.; Erber, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Herpes simplex virus blocks host transcription termination via the bimodal activities of ICP27. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, H.L.; Dembowski, J.A.; DeLuca, N.A. A Herpesviral Immediate Early Protein Promotes Transcription Elongation of Viral Transcripts. mBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, W.R.; Greene, C.C.; Aschman, D.P.; Schaffer, P.A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J. Virol. 1985, 55, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uprichard, S.L.; Knipe, D.M. Herpes simplex ICP27 mutant viruses exhibit reduced expression of specific DNA replication genes. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.I.; Warner, M.S.; Lum, B.J.; Spear, P.G. Herpes simplex virus-1 entry into cells mediated by a novel member of the TNF/NGF receptor family. Cell 1996, 87, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.; Liu, J.; Blaiklock, P.; Shworak, N.W.; Bai, X.; Esko, J.D.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Rosenberg, R.D.; Spear, P.G. A novel role for 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate in herpes simplex virus 1 entry. Cell 1999, 99, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagno, V.; Tseligka, E.D.; Jones, S.T.; Tapparel, C. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Viral Attachment: True Receptors or Adaptation Bias? Viruses 2019, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E. Selective anti-herpesvirus agents. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2013, 23, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eizuru, Y. Development of new antivirals for herpesviruses. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2003, 14, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kausar, S.; Said Khan, F.; Ishaq Mujeeb Ur Rehman, M.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Rasool, G.; Hamid Khan, A.; Saleem, I.; Shamim, S.; Malik, A. A review: Mechanism of action of antiviral drugs. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2021, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C. S. Pinheiro, L.; M. Feitosa, L.; O. Gandi, M.; F. Silveira, F.; Boechat, N. The Development of Novel Compounds Against Malaria: Quinolines, Triazolpyridines, Pyrazolopyridines and Pyrazolopyrimidines. Molecules 2019, 24, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, N.A.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M. New pyridone, thioxopyridine, pyrazolopyridine and pyridine derivatives that modulate inflammatory mediators in stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophage. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4547–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, B.; Afonso, I.F.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Abreu, P.A.; Garrett, R.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Azevedo, A.R.; Borges, J.C.; Vegi, P.F.; Santos, C.C.; et al. Antibacterial profile against drug-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical strain and structure-activity relationship studies of 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine and thieno[2,3-b]pyridine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 8196–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foks, H.; Pancechowska-Ksepko, D.; Kędzia, A.; Zwolska, Z.; Janowiec, M.; Augustynowicz-Kopeć, E. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyrazine and -pyridine derivatives. Farmaco 2005, 60, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.M.; Ammar, Y.A.; El-Zahaby, H.S.; Eisa, S.I.; El-Sayed Barakat, S. Synthesis of novel 1-pyrazolylpyridin-2-ones as potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Arch. Pharm. 2007, 340, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.R.; Santos, M.B.; Albuquerque, S.; Castro, H.C.; de Souza, A.M.; Freitas, A.C.; DiVaio, M.A.; Cabral, L.M.; Rodrigues, C.R. Synthesis, in vitro evaluation, and SAR studies of a potential antichagasic 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine series. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, A.A.; Shaban, A.K.F.; Nassar, I.F.; El-Kady, D.S.; Ismail, N.S.M.; Mahmoud, S.F.; Awad, H.M.; El-Sayed, W.A. Discovery of New Pyrazolopyridine, Furopyridine, and Pyridine Derivatives as CDK2 Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Docking Studies, and Anti-Proliferative Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadurai, N.; Agrawal, K.; Dzubak, P.; Hajduch, M.; Das, V. Microtubule affinity-regulating kinases are potential druggable targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2017, 74, 4159–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.S.; Lim, J.J.; Tinney, E.; Tucker, T.J.; Saggar, S.; Sisko, J.T.; Wan, B.L.; Young, M.B.; Anderson, K.D.; Rudd, D.; et al. Biaryl ethers as potent allosteric inhibitors of reverse transcriptase and its key mutant viruses: Aryl substituted pyrazole as a surrogate for the pyrazolopyridine motif. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4328–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardino, A.M.R.; Ferreira, V.F.; Fontoura, G.A.T.; Frugulhetti, I.C.P.P.; Lee, M.Y.; Romeiro, G.A.; Souza, M.C.B.; Sá, P.M. Synthesis of 4-anilino-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine derivatives and their in vitro antiviral activities. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 1996, 7, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.R.; Ferreira, V.F.; de Mello, H.; Leão-Ferreirab, L.R.; Jabor, A.V.; Frugulhetti, I.C.; Pereira, H.S.; Moussatche, N.; Bernardino, A.M.R. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylic Acids Againt Vaccínia Vírus. Heterocycl. Commun. 2002, 8, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardino, A.M.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Ferreira, V.F.; Azevedo, A.R. Synthesis and Antiviral Activity of new 4-(phenylamino)thieno[2,3-b]pyridine derivatives. Heterocycl. Commun. 2004, 10, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardino, A.M.R.; Azevedo, A.R.; Pinheiro, L.C.d.S.; Borges, J.C.; Carvalho, V.C.L.; Miranda, M.D.; Meneses, M.D.O.F.; Nascimento, M.; Ferreira, D.; Rebello, M.A.; et al. Synthesis and antiviral activity of new 4-(phenylamino)/4-[(methylpyridin-2-yl)amino]-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-4-carboxylic acids derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2007, 16, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardino, A.M.; Azevedo, A.R.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Borges, J.C.; Paixão, I.C.; Mesquita, M.; Souza, T.M.; Dos Santos, M.S. Synthesis and anti-HSV-1 evaluation of new 3H-benzo[b]pyrazolo[3,4-h]-1,6-naphthyridines and 3H-pyrido[2,3-b]pyrazolo[3,4-h]-1,6-naphthyridines. Org. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.C.; Ferreira, V.F.; Vaz, M.G.F.; Cassaro, R.A.A.; Resende, J.; Sacramento, C.Q.; Costa, J.; Abrantes, J.L.; Souza, T.M.L.; Jordão, A.K. Chemistry and anti-herpes simplex virus type 1 evaluation of 4-substituted-1H-1,2,3-triazole-nitroxyl-linked hybrids. Mol. Divers. 2020, 25, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, T.J.; Sisko, J.T.; Tynebor, R.M.; Williams, T.M.; Felock, P.J.; Flynn, J.A.; Lai, M.T.; Liang, Y.; McGaughey, G.; Liu, M.; et al. Discovery of 3-{5-[(6-amino-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-yl)methoxy]-2-chlorophenoxy}-5-chloro benzonitrile (MK-4965): A potent, orally bioavailable HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with improved potency against key mutant viruses. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 6503–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisco, A.; Vanpouille, C.; Margolis, L. War and peace between microbes: HIV-1 interactions with coinfecting viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bender, F.C.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Lou, H.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B binds to cell surfaces independently of heparan sulfate and blocks virus entry. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11588–11597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouyan, P.; Nie, C.; Bhatia, S.; Wedepohl, S.; Achazi, K.; Osterrieder, N.; Haag, R. Inhibition of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Attachment and Infection by Sulfated Polyglycerols with Different Architectures. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, C.D.; Barreiro, E.J.; Fraga, C.A. Privileged structures: A useful concept for the rational design of new lead drug candidates. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.D.; Robinson, P.C.; Uldrick, T.S.; Ljungman, P. COVID-19 in immunocompromised populations: Implications for prognosis and repurposing of immunotherapies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Wilson, D.W. HSV-1 Cytoplasmic Envelopment and Egress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, I.; Vajeeha, A.; Younas, S.; Afzal, S.; Shahid, M.; Nawaz, R.; Khan, M.U.; Idrees, M. HSV-1 Infection: Role of Viral Proteins and Cellular Receptors. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2019, 29, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri-Goldin, R.M. The many roles of the regulatory protein ICP27 during herpes simplex virus infection. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5241–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, M.K.; Panagiotidis, C.A. High-mobility group protein A1 binds herpes simplex virus gene regulatory sequences and affects their expression. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, W.; Huang, C.C.; Herr, W.; Cheng, X. Crystal structure of the conserved core of the herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein VP16. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1692–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, H.R.; Wechselberger, R.W.; Boelens, R.; Folkers, G.E.; Kaptein, R. Structural properties of the promiscuous VP16 activation domain. Biochemistry 2004, 44, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), G. Protein Ligand Docking Software. Available online: https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/solutions/csd-discovery/components/gold/ (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Di Giovine, P.; Settembre, E.C.; Bhargava, A.K.; Luftig, M.A.; Lou, H.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Krummenacher, C.; Carfi, A. Structure of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D bound to the human receptor nectin-1. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozikowski, B.A.; Burt, T.M.; Tirey, D.A.; Williams, L.E.; Kuzmak, B.R.; Stanton, D.T.; Morand, K.L.; Nelson, S.L. The effect of freeze/thaw cycles on the stability of compounds in DMSO. J. Biomol. Screen 2003, 8, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dludla, P.V.; Jack, B.; Viraragavan, A.; Pheiffer, C.; Johnson, R.; Louw, J.; Muller, C.J.F. A dose-dependent effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on lipid content, cell viability and oxidative stress in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Nguyen, H.T.L.; Truong, K.D. Comparative cytotoxic effects of methanol, ethanol and DMSO on human cancer cell lines. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2020, 7, 3855–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquenazi, D.; Wigg, M.D.; Miranda, M.M.; Rodrigues, H.M.; Tostes, J.B.; Rozental, S.; da Silva, A.J.; Alviano, C.S. Antimicrobial and antiviral activities of polyphenolics from Cocos nucifera Linn. (Palmae) husk fiber extract. Res. Microbiol. 2002, 153, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Tsai, W.J.; Ho, Y.H. Regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 replication in Vero cells by Psychotria serpens: Relationship to gene expression, DNA replication, and protein synthesis. Antivir. Res. 2001, 51, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizot, F.; Lang, R. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 89, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Logu, A.; Loy, G.; Pellerano, M.L.; Bonsignore, L.; Schivo, M.L. Inactivation of HSV-1 and HSV-2 and prevention of cell-to-cell virus spread by Santolina insularis essential oil. Antivir. Res. 2000, 48, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Matthews, B.; Cheung, D.; Tam, T.; Gadawski, I.; Leung, D.; Holan, G.; Raff, J.; Sacks, S. Evidence of dual sites of action of dendrimers: SPL-2999 inhibits both virus entry and late stages of herpes simplex virus replication. Antivir. Res. 2002, 55, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.M.; Abrantes, J.L.; Epifanio, R.D.A.; Leite Fontes, C.F.; Frugulhetti, I.C. The alkaloid 4-methylaaptamine isolated from the sponge Aaptos aaptos impairs Herpes simplex virus type 1 penetration and immediate-early protein synthesis. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.M.; De Souza, M.C.; Ferreira, V.F.; Canuto, C.V.; Marques, I.P.; Fontes, C.F.; Frugulhetti, I.C. The chloroxoquinolinic derivative 6-chloro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl) quinoline-3-carboxylic acid inhibits HSV-1 adsorption by impairing its adsorption on HVEM. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, S.S.G.; Soares, V.C.; Ferreira, A.C.; Sacramento, C.Q.; Fintelman-Rodrigues, N.; Temerozo, J.R.; Teixeira, L.; Nunes da Silva, M.A.; Barreto, E.; Mattos, M.; et al. Lipid droplets fuel SARS-CoV-2 replication and production of inflammatory mediators. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

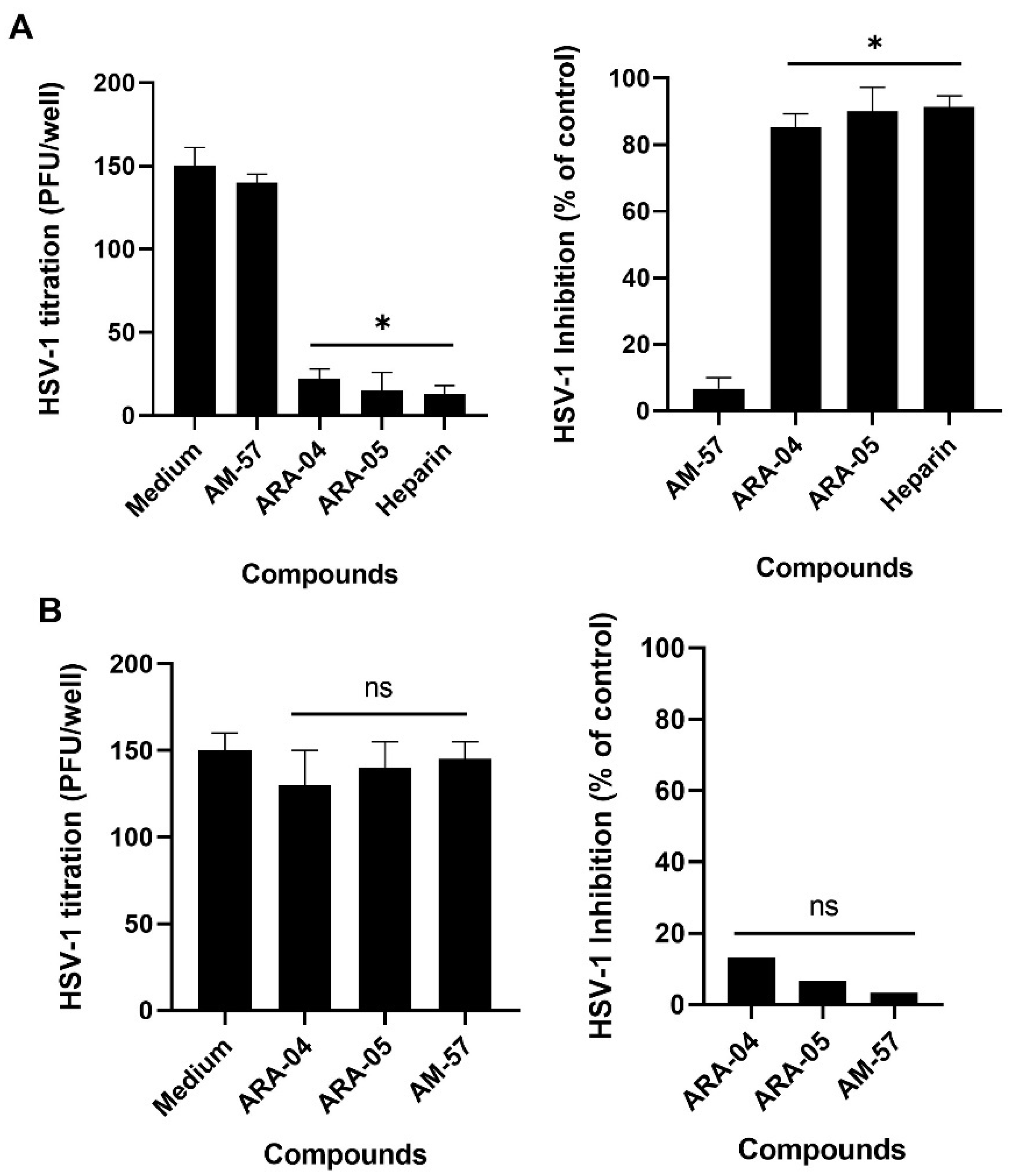
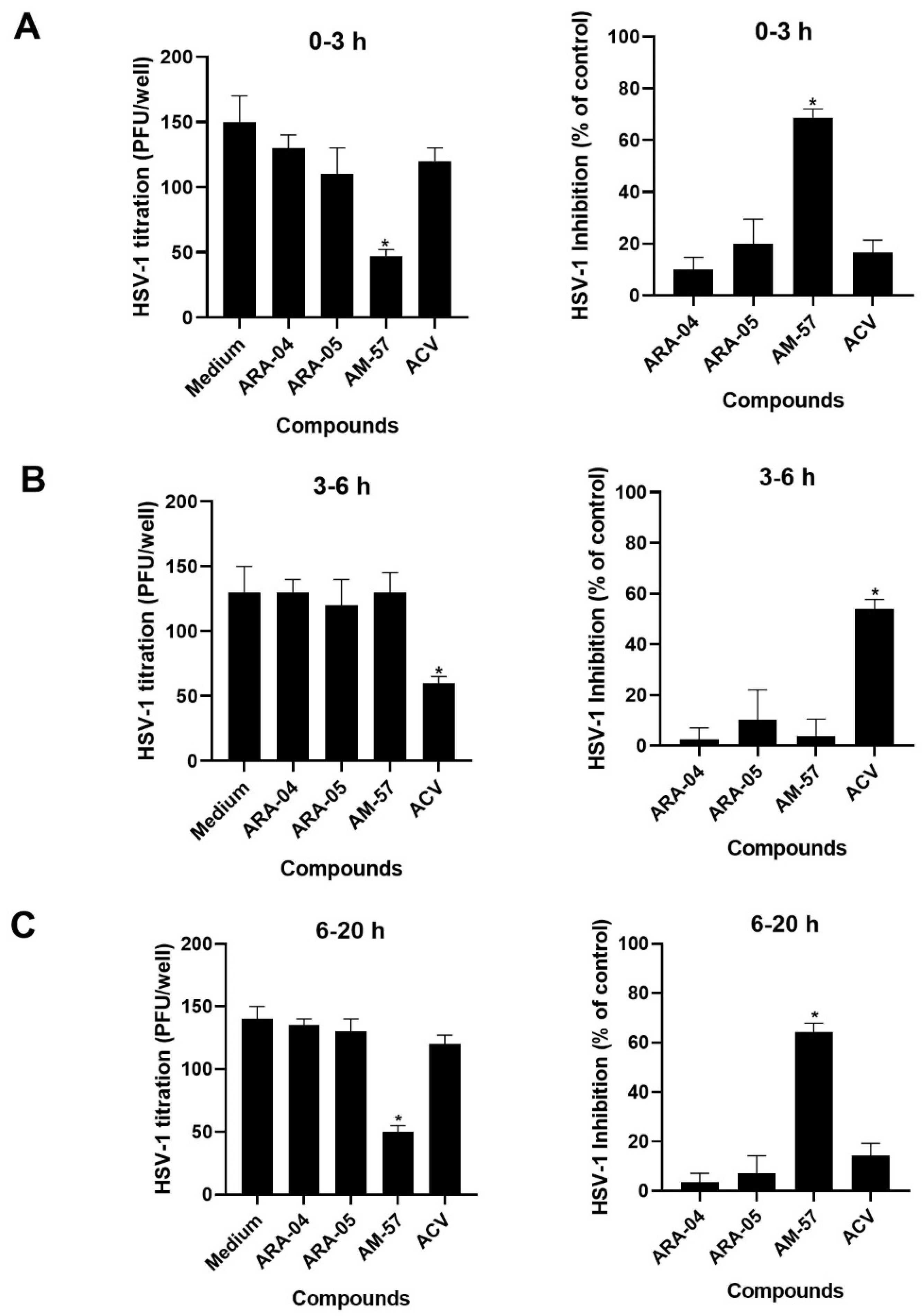
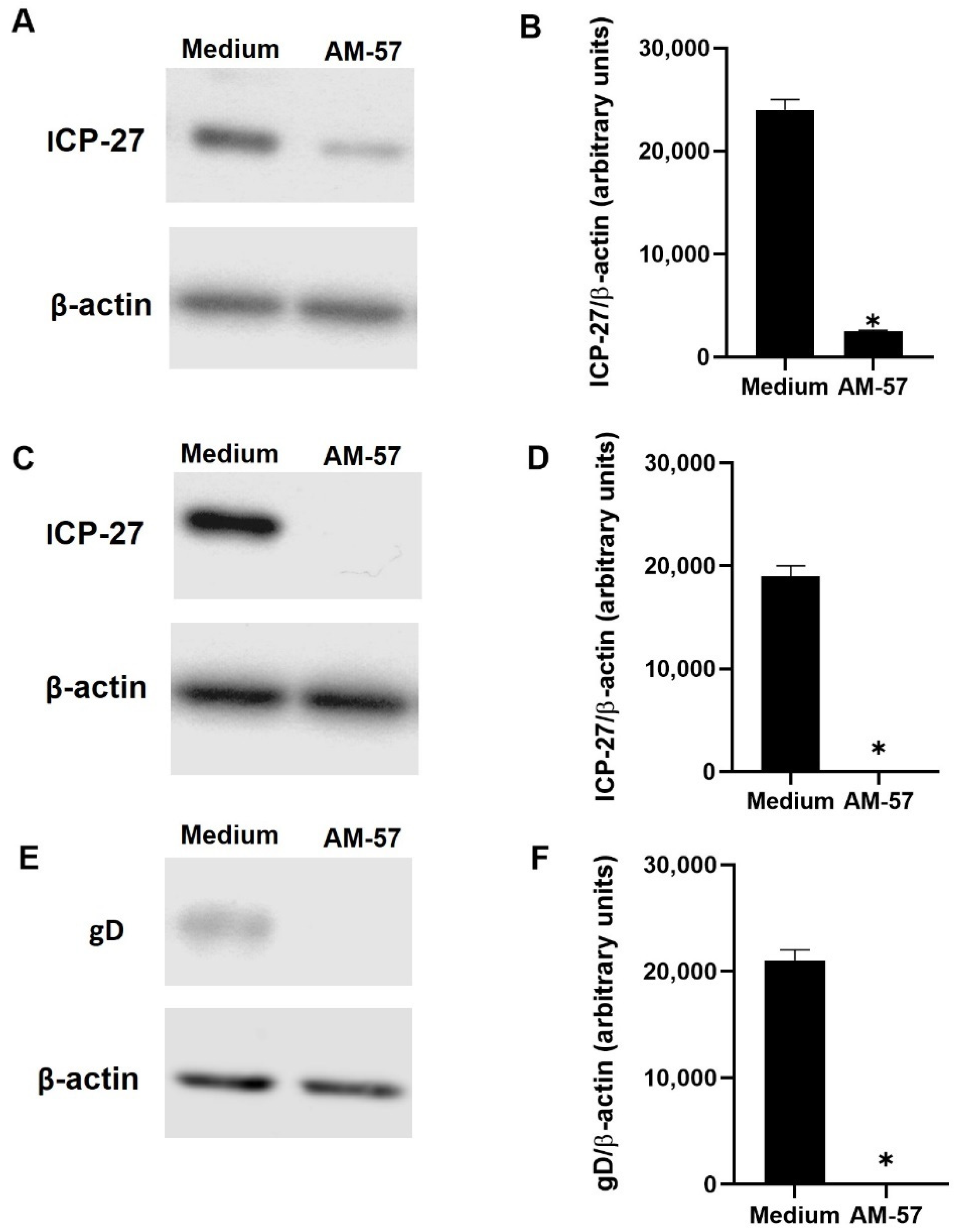
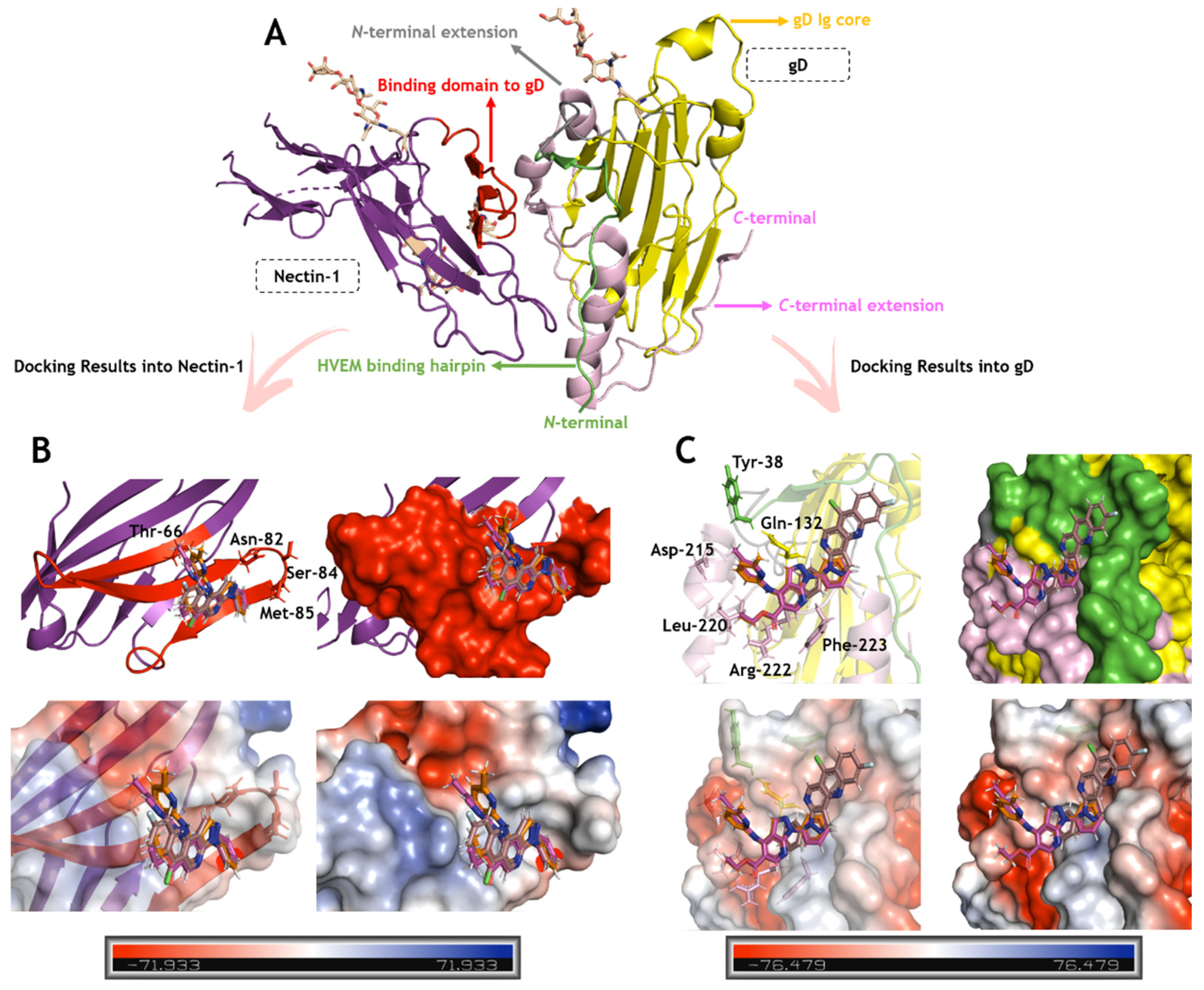
| Compound | CC50 (μM) | EC50 (μM) | SI a |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARA-04 | 1000 ± 100 | 1.00 ± 0.10 | 1000 |
| ARA-05 | 1000 ± 80 | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 1000 |
| AM-57 | 600 ± 50 | 0.70 ± 0.10 | 857 |
| ACV | 960 ± 156 | 1.10 ± 0.25 | 880 |
| Compound | gD | Nectin-1 | TFIIBc-VP16 | TFIIBc | VP16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARA-04 | 55.8 | 46.8 | 8.39 | 42.7 | 39.9 |
| ARA-05 | 55.9 | 41.1 | 5.84 | 43.2 | 42.5 |
| AM-57 | 44.9 | 30.2 | 25.5 | 56.0 | 50.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda, M.D.; Chaves, O.A.; Rosa, A.S.; Azevedo, A.R.; Pinheiro, L.C.d.S.; Soares, V.C.; Dias, S.S.G.; Abrantes, J.L.; Bernardino, A.M.R.; Paixão, I.C.P.; et al. The Role of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives on Different Steps of Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 In Vitro Replicative Cycle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158135
Miranda MD, Chaves OA, Rosa AS, Azevedo AR, Pinheiro LCdS, Soares VC, Dias SSG, Abrantes JL, Bernardino AMR, Paixão ICP, et al. The Role of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives on Different Steps of Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 In Vitro Replicative Cycle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158135
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda, Milene D., Otávio Augusto Chaves, Alice S. Rosa, Alexandre R. Azevedo, Luiz Carlos da Silva Pinheiro, Vinicius C. Soares, Suelen S. G. Dias, Juliana L. Abrantes, Alice Maria R. Bernardino, Izabel C. P. Paixão, and et al. 2022. "The Role of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives on Different Steps of Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 In Vitro Replicative Cycle" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158135
APA StyleMiranda, M. D., Chaves, O. A., Rosa, A. S., Azevedo, A. R., Pinheiro, L. C. d. S., Soares, V. C., Dias, S. S. G., Abrantes, J. L., Bernardino, A. M. R., Paixão, I. C. P., Souza, T. M. L., & Fontes, C. F. L. (2022). The Role of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives on Different Steps of Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 In Vitro Replicative Cycle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158135








