A Regulatory Axis between Epithelial Splicing Regulatory Proteins and Estrogen Receptor α Modulates the Alternative Transcriptome of Luminal Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
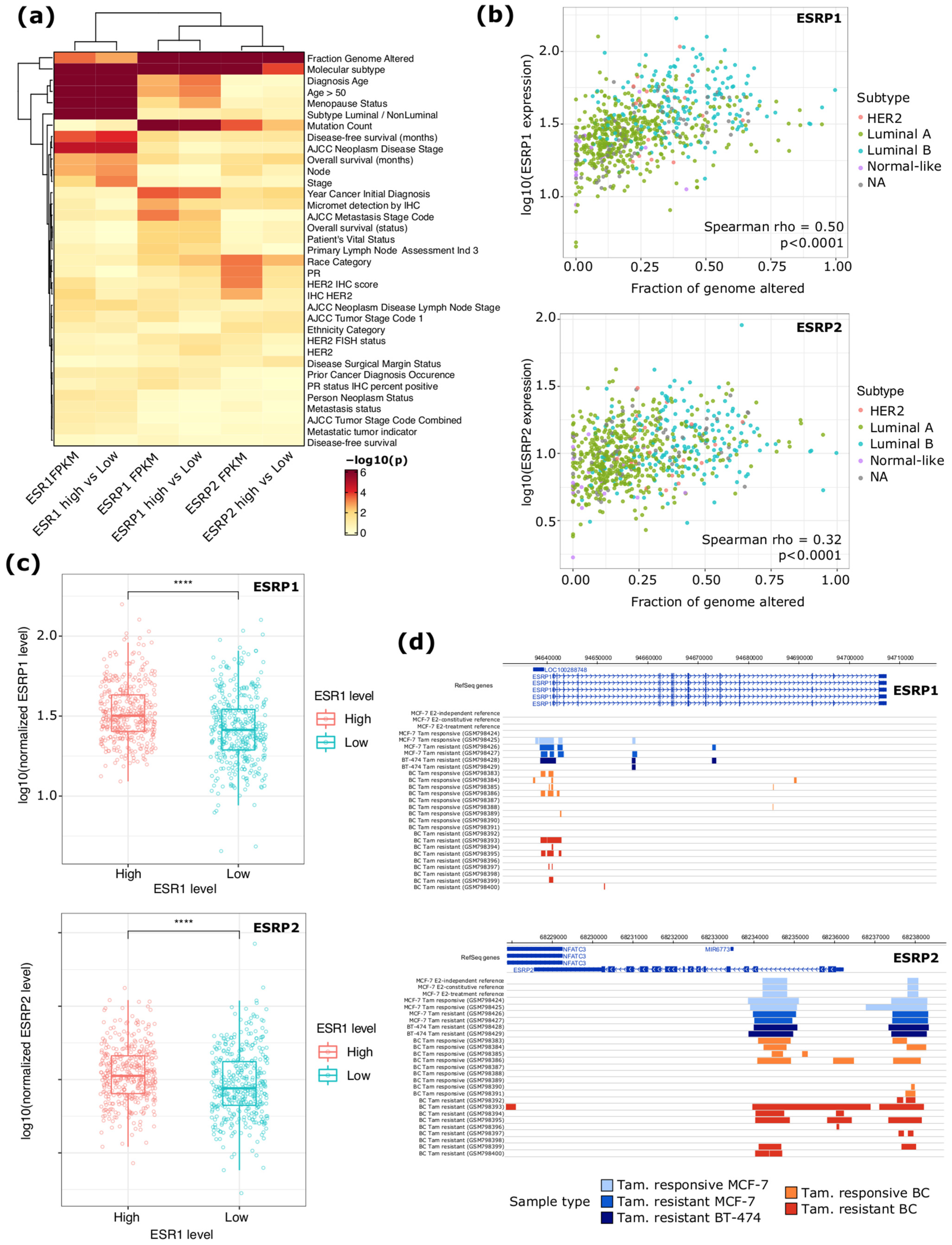
2.1. ESRP1 and ESRP2 Expression Is Altered in ERα+ BC and It Is Regulated by ERα
2.2. Effects of ESRP1 and ESRP2 Knock-Down in MCF-7 Cells
2.3. Validation of ASEs Regulated by ESRP1 and ESRP2
2.4. Isoform-Switching Analysis Confirms the Observed ESRPs Modulation of AS in MCF-7 Cells
2.5. Network-Based Functional Prediction of ASEs upon ESRP1/ESRP2 Silencing
2.6. ESRP1/2-Regulated ASEs Occur upon ERα Silencing in Hormone-Deprived MCF-7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Analysis of ESRP1, ESRP2, and ESR1 Expression in TCGA Clinical Data
4.2. Overlap with ERα ChIP-Seq Data
4.3. Cell Culture and siRNA Transfection
4.4. RNA Isolation, RT-PCR, RNA-Seq Libraries Preparation and Sequencing
| Gene | Target ASE | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAC1 | ES_03_04_05 | 5′-GACAGATTACGCCCCCTATCC-3 | 5′-CAGGACTCACAAGGGAAAAGC-3′ |
| SCRIB | ES_16_17_18 | 5′-CATCCGCAAGGACACACCT-3′ | 5′-CCTTATAGGGTGTGGAGCCCT-3′ |
| MYOF | ES_16_17_18 | 5′-CTCTGGTGGGGAAGTGGAAG-3′ | 5′-CGTGTACTCTCTGGGGCTTC-3′ |
| USO1 | ES_13_14_15 | 5′-TGCTCAGGGTTCAACTTGCT-3′ | 5′-GGGACAATTGCTTAGCCAGG-3′ |
4.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
4.6. Differential Expression and Differential Alternative Splicing Analysis
4.7. Differential Expression Analysis
4.8. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
4.9. Isoform Switching Analysis
4.10. Differential Alternative Splicing Analysis
4.11. RBP Binding Motif Enrichment Analysis
4.12. Overlap with ASEs in Primary Tumor Data
4.13. Definition of Domain–Domain Network for ASE Functional Prediction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESRP | Epithelial splicing regulatory protein |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| ASE | Alternative splicing event |
| ES | Exon skipping |
| MXE | Mutually exclusive exon |
| A5′SS | Alternative A5′ splice site |
| A3′SS | Alternative 3′ splice site |
| RI | Intron retention |
| AS | Alternative splicing |
| UTR | Untranslated region |
| dPSI | Delta percent spliced-in index |
| RBP | RNA-binding protein |
| SR | Serine/arginine rich |
| hnRNP | Heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles |
References
- Rahman, M.A.; Krainer, A.R.; Abdel-Wahab, O. SnapShot: Splicing Alterations in Cancer. Cell 2020, 180, 208–208.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desterro, J.; Bak-Gordon, P.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Targeting mRNA Processing as an Anticancer Strategy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanski, L.M.; Leclair, N.; Anczuków, O. Alternative-Splicing Defects in Cancer: Splicing Regulators and Their Downstream Targets, Guiding the Way to Novel Cancer Therapeutics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2018, 9, e1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankiw, L.; Baltimore, D.; Li, G. Alternative mRNA Splicing in Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahles, A.; Lehmann, K.-V.; Toussaint, N.C.; Hüser, M.; Stark, S.G.; Sachsenberg, T.; Stegle, O.; Kohlbacher, O.; Sander, C.; Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Alternative Splicing across Tumors from 8705 Patients. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 211–224.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trincado, J.L.; Sebestyén, E.; Pagés, A.; Eyras, E. The Prognostic Potential of Alternative Transcript Isoforms across Human Tumors. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reis-Filho, J.S.; Pusztai, L. Gene Expression Profiling in Breast Cancer: Classification, Prognostication, and Prediction. Lancet 2011, 378, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzier, R.; Perou, C.M.; Symmans, W.F.; Ibrahim, N.; Cristofanilli, M.; Anderson, K.; Hess, K.R.; Stec, J.; Ayers, M.; Wagner, P.; et al. Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes Respond Differently to Preoperative Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5678–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y. Aberrant Alternative Splicing in Breast Cancer. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.J.; Manley, J.L. Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing Regulation in Cancer: Pathways and Programs Unhinged. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2343–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, B.; Yu, P.; He, J.; Meng, L.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhou, K.; Xue, Y.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Analysis and Modelling of Prognostic Alternative Splicing Signatures in Invasive Breast Cancer: A Prospective Clinical Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blijlevens, M.; Li, J.; van Beusechem, V.W. Biology of the mRNA Splicing Machinery and Its Dysregulation in Cancer Providing Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, I.M.; Cheng, A.W.; Flytzanis, N.C.; Balsamo, M.; Condeelis, J.S.; Oktay, M.H.; Burge, C.B.; Gertler, F.B. An EMT-Driven Alternative Splicing Program Occurs in Human Breast Cancer and Modulates Cellular Phenotype. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warzecha, C.C.; Shen, S.; Xing, Y.; Carstens, R.P. The Epithelial Splicing Factors ESRP1 and ESRP2 Positively and Negatively Regulate Diverse Types of Alternative Splicing Events. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Park, J.W.; Bebee, T.W.; Warzecha, C.C.; Guo, Y.; Shang, X.; Xing, Y.; Carstens, R.P. Determination of a Comprehensive Alternative Splicing Regulatory Network and Combinatorial Regulation by Key Factors during the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 1704–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizutani, A.; Koinuma, D.; Seimiya, H.; Miyazono, K. The Arkadia-ESRP2 Axis Suppresses Tumor Progression: Analyses in Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3514–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gökmen-Polar, Y.; Neelamraju, Y.; Goswami, C.P.; Gu, Y.; Gu, X.; Nallamothu, G.; Vieth, E.; Janga, S.C.; Ryan, M.; Badve, S.S. Splicing Factor Controls ER-Positive Breast Cancer by Altering Metabolic Pathways. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e46078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caizzi, L.; Ferrero, G.; Cutrupi, S.; Cordero, F.; Ballaré, C.; Miano, V.; Reineri, S.; Ricci, L.; Friard, O.; Testori, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Activity of Unliganded Estrogen Receptor-α in Breast Cancer Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4892–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miano, V.; Ferrero, G.; Rosti, V.; Manitta, E.; Elhasnaoui, J.; Basile, G.; De Bortoli, M. Luminal lncRNAs Regulation by ERα-Controlled Enhancers in a Ligand-Independent Manner in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elhasnaoui, J.; Miano, V.; Ferrero, G.; Doria, E.; Leon, A.E.; Fabricio, A.S.C.; Annaratone, L.; Castellano, I.; Sapino, A.; De Bortoli, M. DSCAM-AS1-Driven Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells Involves Regulation of Alternative Exon Splicing and 3’-End Usage. Cancers 2020, 12, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhasnaoui, J.; Ferrero, G.; Miano, V.; Cutrupi, S.; De Bortoli, M. The Estrogen Receptor α Signaling Pathway Controls Alternative Splicing in the Absence of Ligands in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, G.; Miano, V.; Beccuti, M.; Balbo, G.; De Bortoli, M.; Cordero, F. Dissecting the Genomic Activity of a Transcriptional Regulator by the Integrative Analysis of Omics Data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross-Innes, C.S.; Stark, R.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Holmes, K.A.; Ali, H.R.; Dunning, M.J.; Brown, G.D.; Gojis, O.; Ellis, I.O.; Green, A.R.; et al. Differential Oestrogen Receptor Binding Is Associated with Clinical Outcome in Breast Cancer. Nature 2012, 481, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, S.; Park, J.W.; Lu, Z.-X.; Lin, L.; Henry, M.D.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhou, Q.; Xing, Y. rMATS: Robust and Flexible Detection of Differential Alternative Splicing from Replicate RNA-Seq Data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5593–E5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.W.; Tokheim, C.; Shen, S.; Xing, Y. Identifying Differential Alternative Splicing Events from RNA Sequencing Data Using RNASeq-MATS. In Deep Sequencing Data Analysis; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Warzecha, C.C.; Jiang, P.; Amirikian, K.; Dittmar, K.A.; Lu, H.; Shen, S.; Guo, W.; Xing, Y.; Carstens, R.P. An ESRP-Regulated Splicing Programme Is Abrogated during the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3286–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.C.; Cleland, J.; Kim, R.; Wong, W.C.; Weinstein, J.N. SpliceSeq: A Resource for Analysis and Visualization of RNA-Seq Data on Alternative Splicing and Its Functional Impacts. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2385–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitting-Seerup, K.; Sandelin, A. IsoformSwitchAnalyzeR: Analysis of Changes in Genome-Wide Patterns of Alternative Splicing and Its Functional Consequences. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4469–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.W.; Pan, Y.; Tsai, B.L.; Xie, Z.; Demirdjian, L.; Xiao, W.; Yang, H.T.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.H.; Cheng, D.; et al. Pathway-Guided Analysis Identifies Myc-Dependent Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing in Aggressive Prostate Cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5269–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebestyén, E.; Singh, B.; Miñana, B.; Pagès, A.; Mateo, F.; Pujana, M.A.; Valcárcel, J.; Eyras, E. Large-Scale Analysis of Genome and Transcriptome Alterations in Multiple Tumors Unveils Novel Cancer-Relevant Splicing Networks. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehár, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia Enables Predictive Modelling of Anticancer Drug Sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.E.M.; Smid, M.; Nagelkerke, A.; Martens, J.W.M.; Bussink, J.; Sweep, F.C.G.J.; Span, P.N. Interferon-Stimulated Genes Are Involved in Cross-Resistance to Radiotherapy in Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cervantes-Badillo, M.G.; Paredes-Villa, A.; Gómez-Romero, V.; Cervantes-Roldán, R.; Arias-Romero, L.E.; Villamar-Cruz, O.; González-Montiel, M.; Barrios-García, T.; Cabrera-Quintero, A.J.; Rodríguez-Gómez, G.; et al. IFI27/ISG12 Downregulates Estrogen Receptor α Transactivation by Facilitating Its Interaction with CRM1/XPO1 in Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 568375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheriyath, V.; Kaur, J.; Davenport, A.; Khalel, A.; Chowdhury, N.; Gaddipati, L. G1P3 (IFI6), a Mitochondrial Localised Antiapoptotic Protein, Promotes Metastatic Potential of Breast Cancer Cells through mtROS. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, C.C.; Sato, T.K.; Nabet, B.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Carstens, R.P. ESRP1 and ESRP2 Are Epithelial Cell-Type-Specific Regulators of FGFR2 Splicing. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munkley, J.; Li, L.; Krishnan, S.R.G.; Hysenaj, G.; Scott, E.; Dalgliesh, C.; Oo, H.Z.; Maia, T.M.; Cheung, K.; Ehrmann, I.; et al. Androgen-Regulated Transcription of Drives Alternative Splicing Patterns in Prostate Cancer. eLife 2019, 8, e47678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, S.E.; Xu, Y.; Lin, X.; Gao, X.D.; Qiu, Y.; Ahn, J.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, C. Coregulation of Alternative Splicing by hnRNPM and ESRP1 during EMT. RNA 2018, 24, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villemin, J.-P.; Lorenzi, C.; Cabrillac, M.-S.; Oldfield, A.; Ritchie, W.; Luco, R.F. A Cell-to-Patient Machine Learning Transfer Approach Uncovers Novel Basal-like Breast Cancer Prognostic Markers amongst Alternative Splice Variants. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnelzer, A.; Prechtel, D.; Knaus, U.; Dehne, K.; Gerhard, M.; Graeff, H.; Harbeck, N.; Schmitt, M.; Lengyel, E. Rac1 in Human Breast Cancer: Overexpression, Mutation Analysis, and Characterization of a New Isoform, Rac1b. Oncogene 2000, 19, 3013–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, V.; Henriques, A.F.A.; Pereira, J.F.S.; Neves Costa, A.; Moyer, M.P.; Moita, L.F.; Gama-Carvalho, M.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Phosphorylation of SRSF1 by SRPK1 Regulates Alternative Splicing of Tumor-Related Rac1b in Colorectal Cells. RNA 2014, 20, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Licciulli, S.; Avila, J.L.; Cho, M.; Troutman, S.; Jiang, P.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Showe, L.C.; Liu, Q.; Vachani, A.; et al. The Rac1 Splice Form Rac1b Promotes K-Ras-Induced Lung Tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinn, R.; Otterbein, H.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. RAC1B: A Guardian of the Epithelial Phenotype and Protector Against Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cells 2019, 8, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eiden, C.; Ungefroren, H. The Ratio of RAC1B to RAC1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines as a Determinant of Epithelial/Mesenchymal Differentiation and Migratory Potential. Cells 2021, 10, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, C.; Hass, R.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. RAC1B: A Rho GTPase with Versatile Functions in Malignant Transformation and Tumor Progression. Cells 2019, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melzer, C.; Hass, R.; von der Ohe, J.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. The Role of TGF-β and Its Crosstalk with RAC1/RAC1b Signaling in Breast and Pancreas Carcinoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pradella, D.; Naro, C.; Sette, C.; Ghigna, C. EMT and Stemness: Flexible Processes Tuned by Alternative Splicing in Development and Cancer Progression. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, Y.-I.; Meyer, E.J.; Kroesen, A.; McKinney, S.A.; Gibson, M.C. Epithelial Junctions Maintain Tissue Architecture by Directing Planar Spindle Orientation. Nature 2013, 500, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metodieva, G.; Adoki, S.; Lausen, B.; Metodiev, M.V. Decreased Usage of Specific Scrib Exons Defines a More Malignant Phenotype of Breast Cancer with Worsened Survival. EBioMedicine 2016, 8, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, L.C.; Hartig, N.; Muñoz-Alegre, M.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Durdu, S.; Bender, S.; Vijayakumar, V.; Vietri Rudan, M.; Gewinner, C.; Henderson, S.; et al. An MRAS, SHOC2, and SCRIB Complex Coordinates ERK Pathway Activation with Polarity and Tumorigenic Growth. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heo, Y.; Yoon, H.-J.; Ko, H.; Jang, S.; Lee, H.H. Crystal Structures of Uso1 Membrane Tether Reveal an Alternative Conformation in the Globular Head Domain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howley, B.V.; Link, L.A.; Grelet, S.; El-Sabban, M.; Howe, P.H. A CREB3-Regulated ER-Golgi Trafficking Signature Promotes Metastatic Progression in Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1308–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailor, P.D.; Kodeboyina, S.K.; Bai, S.; Patel, N.; Sharma, S.; Ratnani, A.; Copland, J.A.; She, J.-X.; Sharma, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker Potential of Kallikrein Family Genes in Different Cancer Types. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17876–17888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grossman, R.L.; Heath, A.P.; Ferretti, V.; Varmus, H.E.; Lowy, D.R.; Kibbe, W.A.; Staudt, L.M. Toward a Shared Vision for Cancer Genomic Data. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ala, U.; Manco, M.; Mandili, G.; Tolosano, E.; Novelli, F.; Provero, P.; Altruda, F.; Fagoonee, S. Proteomics-Based Evidence for a Pro-Oncogenic Role of ESRP1 in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate Transcript Quantification from RNA-Seq Data with or without a Reference Genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soneson, C.; Love, M.I.; Robinson, M.D. Differential Analyses for RNA-Seq: Transcript-Level Estimates Improve Gene-Level Inferences. F1000Research 2015, 4, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, L. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis by WICKHAM, H. Biometrics 2011, 67, 678–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape Provides a Biologist-Oriented Resource for the Analysis of Systems-Level Datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 Improves Signal Peptide Predictions Using Deep Neural Networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Yang, D.-C.; Kong, L.; Hou, M.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC2: A Fast and Accurate Coding Potential Calculator Based on Sequence Intrinsic Features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W12–W16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam Protein Families Database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Park, J.W.; Huang, J.; Dittmar, K.A.; Lu, Z.-X.; Zhou, Q.; Carstens, R.P.; Xing, Y. MATS: A Bayesian Framework for Flexible Detection of Differential Alternative Splicing from RNA-Seq Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, D.; Ha, K.C.H.; Nie, K.; Zheng, H.; Hughes, T.R.; Morris, Q.D. RNAcompete Methodology and Application to Determine Sequence Preferences of Unconventional RNA-Binding Proteins. Methods 2017, 118–119, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, C.E.; Bailey, T.L.; Noble, W.S. FIMO: Scanning for Occurrences of a given Motif. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1017–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oughtred, R.; Rust, J.; Chang, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Stark, C.; Willems, A.; Boucher, L.; Leung, G.; Kolas, N.; Zhang, F.; et al. The BioGRID database: A comprehensive biomedical resource of curated protein, genetic, and chemical interactions. Protein Sci. 2021, 1, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, R.; Ceol, A.; Stein, A.; Olivella, R.; Aloy, P. 3did: A catalog of domain-based interactions of known three-dimensional structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D374–D379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 11, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elhasnaoui, J.; Ferrero, G.; Miano, V.; Franchitti, L.; Tarulli, I.; Coscujuela Tarrero, L.; Cutrupi, S.; De Bortoli, M. A Regulatory Axis between Epithelial Splicing Regulatory Proteins and Estrogen Receptor α Modulates the Alternative Transcriptome of Luminal Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147835
Elhasnaoui J, Ferrero G, Miano V, Franchitti L, Tarulli I, Coscujuela Tarrero L, Cutrupi S, De Bortoli M. A Regulatory Axis between Epithelial Splicing Regulatory Proteins and Estrogen Receptor α Modulates the Alternative Transcriptome of Luminal Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(14):7835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147835
Chicago/Turabian StyleElhasnaoui, Jamal, Giulio Ferrero, Valentina Miano, Lorenzo Franchitti, Isabella Tarulli, Lucia Coscujuela Tarrero, Santina Cutrupi, and Michele De Bortoli. 2022. "A Regulatory Axis between Epithelial Splicing Regulatory Proteins and Estrogen Receptor α Modulates the Alternative Transcriptome of Luminal Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 14: 7835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147835
APA StyleElhasnaoui, J., Ferrero, G., Miano, V., Franchitti, L., Tarulli, I., Coscujuela Tarrero, L., Cutrupi, S., & De Bortoli, M. (2022). A Regulatory Axis between Epithelial Splicing Regulatory Proteins and Estrogen Receptor α Modulates the Alternative Transcriptome of Luminal Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(14), 7835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147835







