Hydroxy Pentacyclic Triterpene Acid, Kaempferol, Inhibits the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Type 3A Receptor Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
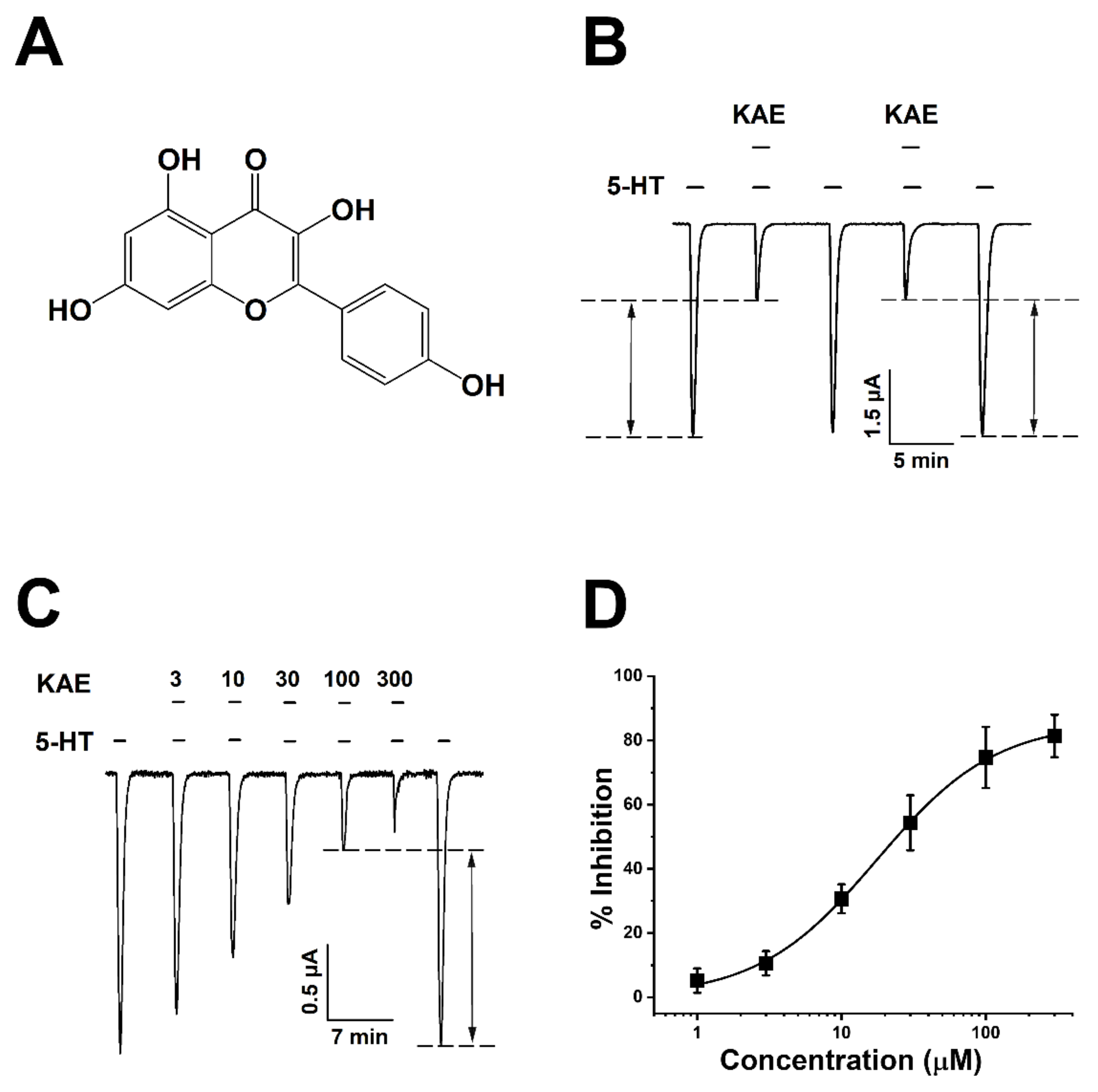
2.1. Kaempferol Inhibits Human 5-HT3A Receptor in a Reversible and Concentration-Dependent Manner
2.2. Kaempferol Inhibits Human 5-HT3A Receptor in a Voltage-Independent and Non-Competitive Manner
2.3. D Docking Modeling of Human 5-HT3A Receptor Interacting with Kaempferol
2.4. Inhibitory Effect of Kaempferol on a Double-Mutant Type Human 5-HT3A Receptor
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. In Vitro Transcription: Human 5-HT3A Receptor
4.3. Xenopus Oocytes Preparation and mRNA Microinjection
4.4. Electrophysiology Studies: Two-Electrode Voltage Clamp Data Recording
4.5. Point Mutation—Site-Directed Mutagenesis: Mutant Gene Amplification
4.6. Molecular Docking Studies: Protein-Ligand Interaction
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fakhfouri, G.; Rahimian, R.; Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J.; Zirak, M.R.; Beaulieu, J.-M. 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists in Neurologic and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: The Iceberg Still Lies beneath the Surface. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 383–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buhot, M.-C.; Martin, S.; Segu, L. Role of serotonin in memory impairment. Ann. Med. 2000, 32, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhot, M.-C. Serotonin receptors in cognitive behaviors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1997, 7, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J. Recent developments in 5-HT3 receptor pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, J.; Hoyer, D. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 195, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, C.A.; Stanford, I.M.; Ali, I.; Lin, L.; Williams, J.M.; Dubin, A.E.; Hope, A.G.; Barnes, N.M. Pharmacological comparison of human homomeric 5-HT3A receptors versus heteromeric 5-HT3A/3B receptors. Neuropharmacology 2001, 41, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faerber, L.; Drechsler, S.; Ladenburger, S.; Gschaidmeier, H.; Fischer, W. The neuronal 5-HT3 receptor network after 20 years of research—Evolving concepts in management of pain and inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 560, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Filipek, S.; Vogel, H. A Gating Mechanism of the Serotonin 5-HT 3 Receptor. Structure 2016, 24, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, A.J.; Lummis, S.C.R. The 5-HT3receptor as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krzywkowski, K.; Davies, P.A.; Feinberg-Zadek, P.L.; Brauner-Osborne, H.; Jensen, A.A. High-frequency HTR3B variant associated with major depression dramatically augments the signaling of the human 5-HT3AB receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corrie, J.; Baenziger, J.E. Gating of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels: Structural insights and ambiguities. Structure 2013, 21, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.W.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.-T.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, W.S.; Jeong, T.-S.; Park, K.H. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of xanthones from Cudrania tricuspidata. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 5548–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, R.; Mehta, C.M. Bauhinia variegata: A comprehensive review on bioactive compounds, health benefits and utilization. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2020, 21, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Gondal, T.A.; Saeed, F.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Arshad, M.U.; Khan, H.; et al. Kaempferol: A Key Emphasis to Its Anticancer Potential. Molecules 2019, 24, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calderon-Montano, J.M.; Burgos-Moron, E.; Perez-Guerrero, C.; Lopez-Lazaro, M. A Review on the Dietary Flavonoid Kaempferol. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 298–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, H.; Spencer, J.P.; Rice-Evans, C.; Williams, R.J. Flavonoids protect neurons from oxidized low-density-lipoprotein-induced apoptosis involving c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), c-Jun and caspase-3. Biochem. J. 2001, 358, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuk, M.; Kulma, A.; Dymińska, L.; Szołtysek, K.; Prescha, A.; Hanuza, J.; Szopa, J. Flavonoid engineering of flax potentiate its biotechnological application. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Tu, Y.-C.; Lian, T.-W.; Hung, J.-T.; Yen, J.-H.; Wu, M.-J. Distinctive Antioxidant and Antiinflammatory Effects of Flavonols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9798–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pu, X.-P. Neuroprotective Effect of Kaempferol against a 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sloley, B.D.; Urichuk, L.J.; Morley, P.; Durkin, J.; Shan, J.J.; Pang, P.K.T.; Coutts, R.T. Identification of Kaempferol as a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor and Potential Neuroprotectant in Extracts of Ginkgo Biloba Leaves. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 52, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, S.; Bananej, M.; Zarei, M.; Komaki, A.; Hajikhani, R. Possible Involvement of Serotonergic Mechanism(s) in the Antinociceptive Effects of kaempferol. Avicenna J. Neuro. Psycho. Physiol. 2020, 8, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochner, M.; Thompson, A.J. The muscarinic antagonists scopolamine and atropine are competitive antagonists at 5-HT 3 receptors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 108, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, A.; Lummis, S. Discriminating between 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kannan, K.; Jain, S.K. Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 2000, 7, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh Loh, K.; Hong Huang, S.; De Silva, R.; Tan, H.; Benny, K.; Zhun Zhu, Y. Oxidative Stress: Apoptosis in Neuronal Injury. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2006, 3, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mao, J.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Wu, B.; Yuan, Y. Kaempferol Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Through Intervening Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress Induced Apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holford, N.; Sheiner, L.B. Understanding the Dose-Effect Relationship. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1981, 6, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, G.M. Pharmacology, Part 1: Introduction to Pharmacology and Pharmacodynamics. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2018, 46, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebich, B.L.; Akundi, R.S.; Seidel, M.; Geyer, V.; Haus, U.; Müller, W.; Stratz, T.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Expression of 5-HT3A receptors in cells of the immune system. Scand. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2004, 119, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesters, D.; Thompson, A.J.; Brams, M.; van Elk, R.; Spurny, R.; Geitmann, M.; Villalgordo, J.M.; Guskov, A.; Danielson, H.; Lummis, S.C.R.; et al. Structural basis of ligand recognition in 5-HT 3 receptors. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Dang, H.; Zhu, Q.-M.; Schnegelsberg, B.; Rozengurt, N.; Cain, G.; Prantil, R.; Vorp, D.A.; Guy, N.; Julius, D.; et al. Uropathic Observations in Mice Expressing a Constitutively Active Point Mutation in the 5-HT3A Receptor Subunit. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 5537–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eom, S.; Lee, J.; Baek, Y.-B.; Yeom, H.D.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Park, Y.; Park, S.-I.; Lee, C.-M.; Lee, J.H. Identification and molecular study on the interaction of Schisandrin C with human 5-HT3A receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 906, 174220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, M.C.; Emerit, M.B.; Nosjean, A.; Simon, A.; Rumajogee, P.; Brisorgueil, M.J.; Doucet, E.; Hamon, M.; Verge, D. Differential subcellular localization of the 5-HT3-As receptor subunit in the rat central nervous system. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maura, G.; Andrioli, G.C.; Cavazzani, P.; Raiteri, M. 5-Hydroxytryptamine3Receptors Sited on Cholinergic Axon Terminals of Human Cerebral Cortex Mediate Inhibition of Acetylcholine Release. J. Neurochem. 1992, 58, 2334–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, N.H.; Lester, H.A.; Dougherty, D.A. Ondansetron and Granisetron Binding Orientation in the 5-HT3 Receptor Determined by Unnatural Amino Acid Mutagenesis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papke, R.; Papke, J.K.P.; Rose, G. Activity of α7-selective agonists at nicotinic and serotonin 5HT3 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 1849–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammes, G.; Eisensamer, B.; Ferrari, U.; Shapa, M.; Gimpl, G.; Gilling, K.; Parsons, C.; Riering, K.; Hapfelmeier, G.; Bondy, B.; et al. Antipsychotic drugs antagonize human serotonin type 3 receptor currents in a noncompetitive manner. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fakhfouri, G.; Rahimian, R.; Ghia, J.-E.; Khan, W.I.; Dehpour, A.R. Impact of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists on peripheral and central diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dremencov, E.; Weizmann, Y.; Kinor, N.; Gispan-Herman, I.; Yadid, G. Modulation of Dopamine Transmission by 5HT2C and 5HT3 Receptors: A Role in the Antidepressant Response. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolving inflammation: Dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niesler, B.; Frank, B.; Kapeller, J.; Rappold, G.A. Cloning, physical mapping and expression analysis of the human 5-HT3 serotonin receptor-like genes HTR3C, HTR3D and HTR3E. Gene 2003, 310, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


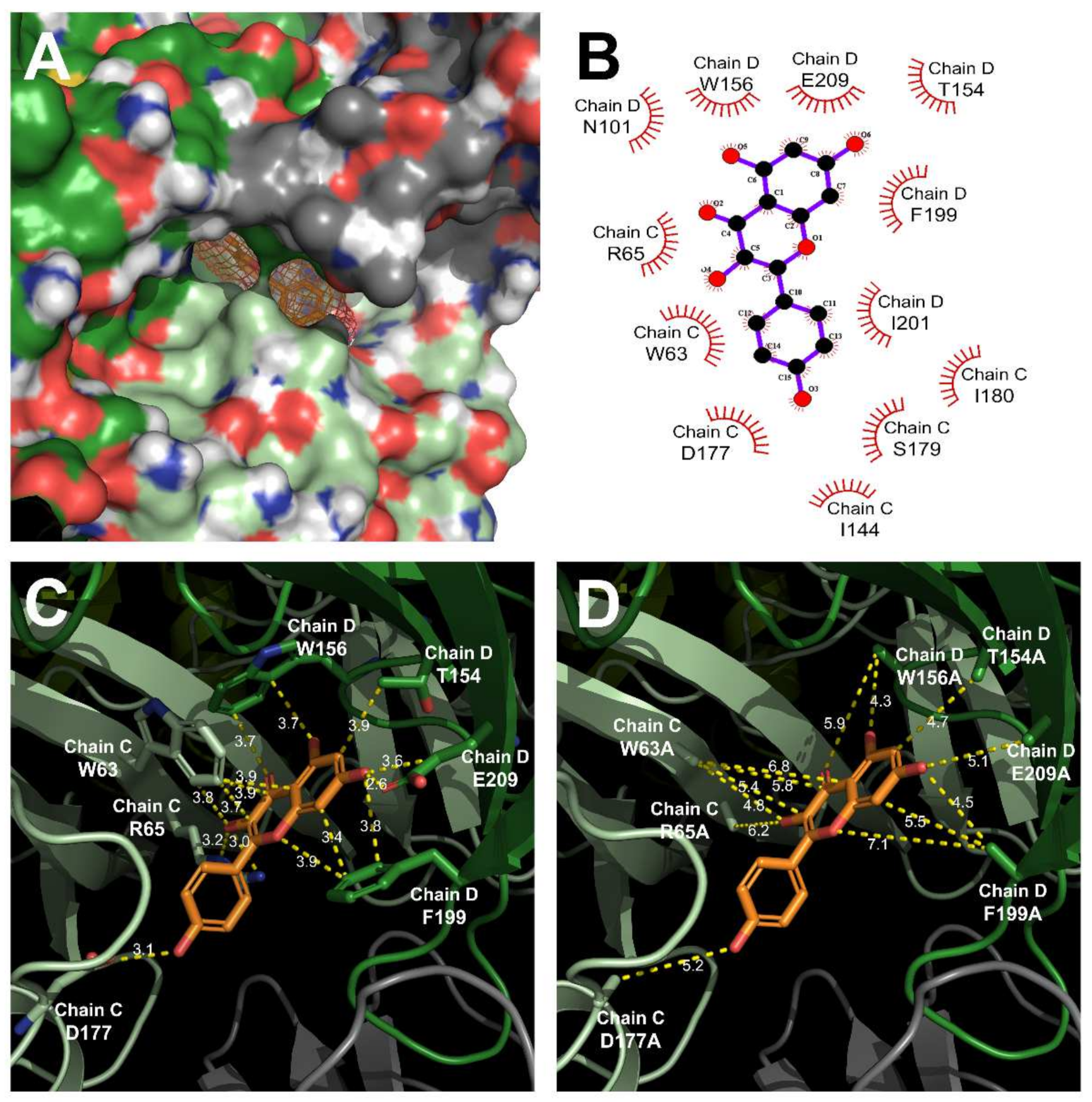

| Mutant Type | Vmax | IC50 | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild type | 79.3 ± 4.6 | 23.4 ± 8.3 | 1.2 ± 0.3 |
| R65A | 82.6 ± 7.4 | 44.7 ± 9.1 | 1.8 ± 0.7 |
| W63A | 76.3 ± 10.7 | 33.7 ± 5.7 | 1.3 ± 0.5 |
| N101A | 83.7 ± 8.6 | 56.4 ± 9.7 | 1.1 ± 0.6 |
| I144A | 71.6 ± 11.8 | 34.9 ± 11.2 | 1.5 ± 0.4 |
| T154A | 73.5 ± 9.4 | 33.4 ± 7.9 | 1.1 ± 0.4 |
| D177A | 23.3 ± 13.4 | 13.9 ± 4.2 | 1.3 ± 0.2 |
| I180A | 89.5 ± 12.1 | 45.5 ± 12.9 | 1.8 ± 0.6 |
| F199A | 53.3 ± 10.4 | 21.5 ± 5.7 | 1.4 ± 0.4 |
| E209A | 81.1 ± 9.7 | 55.1 ± 5.8 | 1.7 ± 0.6 |
| I210A | 78.4 ± 11.4 | 35.4 ± 9.7 | 1.8 ± 0.5 |
| D177A+F199A | 11.9 ± 1.2 | 42.9 ± 10.2 | 1.3 ± 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Seol, H.-S.; Eom, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, J.H. Hydroxy Pentacyclic Triterpene Acid, Kaempferol, Inhibits the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Type 3A Receptor Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010544
Lee S, Seol H-S, Eom S, Lee J, Kim C, Park J-H, Kim T-H, Lee JH. Hydroxy Pentacyclic Triterpene Acid, Kaempferol, Inhibits the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Type 3A Receptor Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010544
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Shinhui, Hee-Soo Seol, Sanung Eom, Jaeeun Lee, Chaelin Kim, Jong-Hwan Park, Tae-Hwan Kim, and Junho H. Lee. 2022. "Hydroxy Pentacyclic Triterpene Acid, Kaempferol, Inhibits the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Type 3A Receptor Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010544
APA StyleLee, S., Seol, H.-S., Eom, S., Lee, J., Kim, C., Park, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., & Lee, J. H. (2022). Hydroxy Pentacyclic Triterpene Acid, Kaempferol, Inhibits the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Type 3A Receptor Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010544








