Strategic Modification of Gut Microbiota through Oral Bacteriotherapy Influences Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α: Therapeutic Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
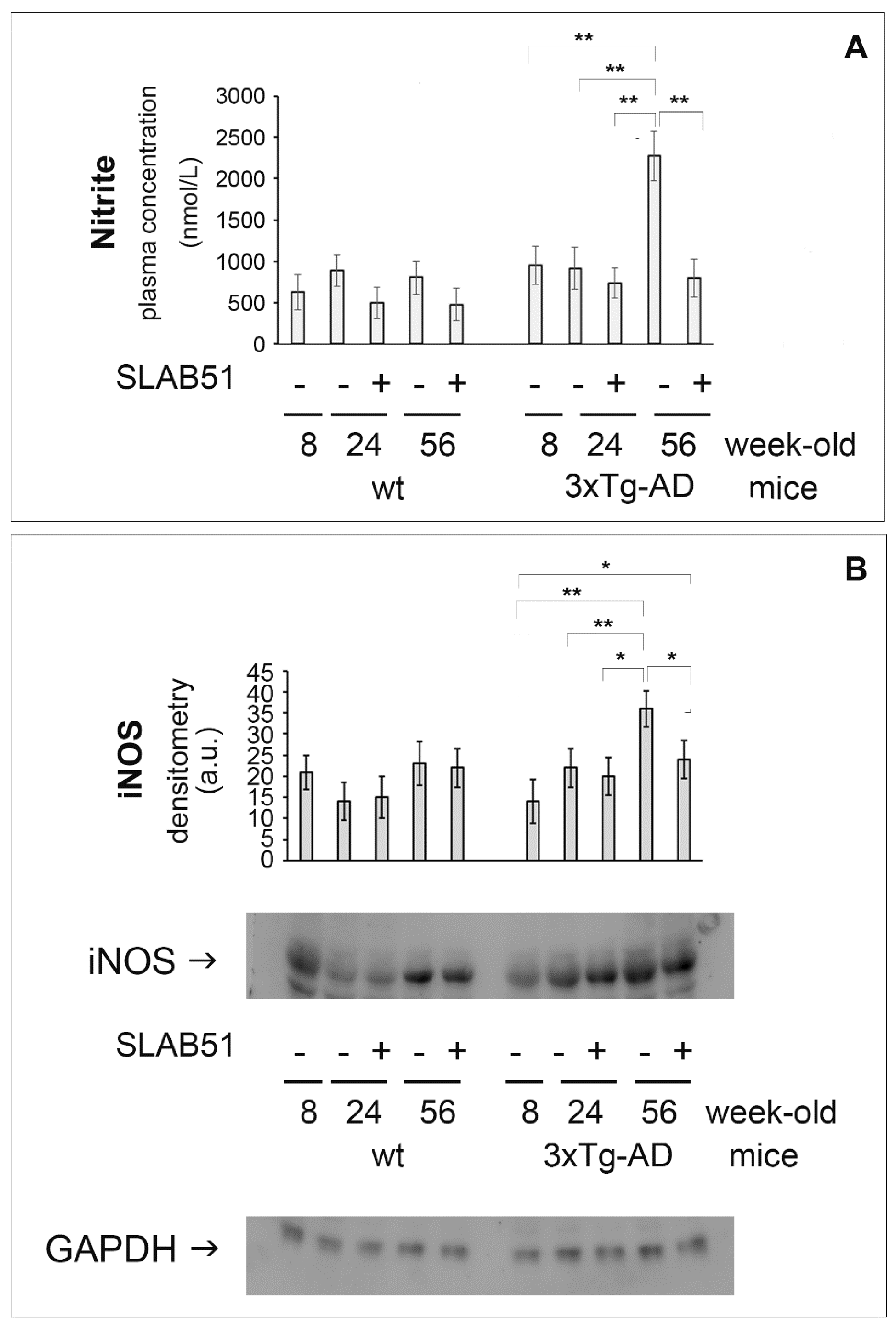
2.1. SLAB51 Affected Nitric Oxide Related Pathways
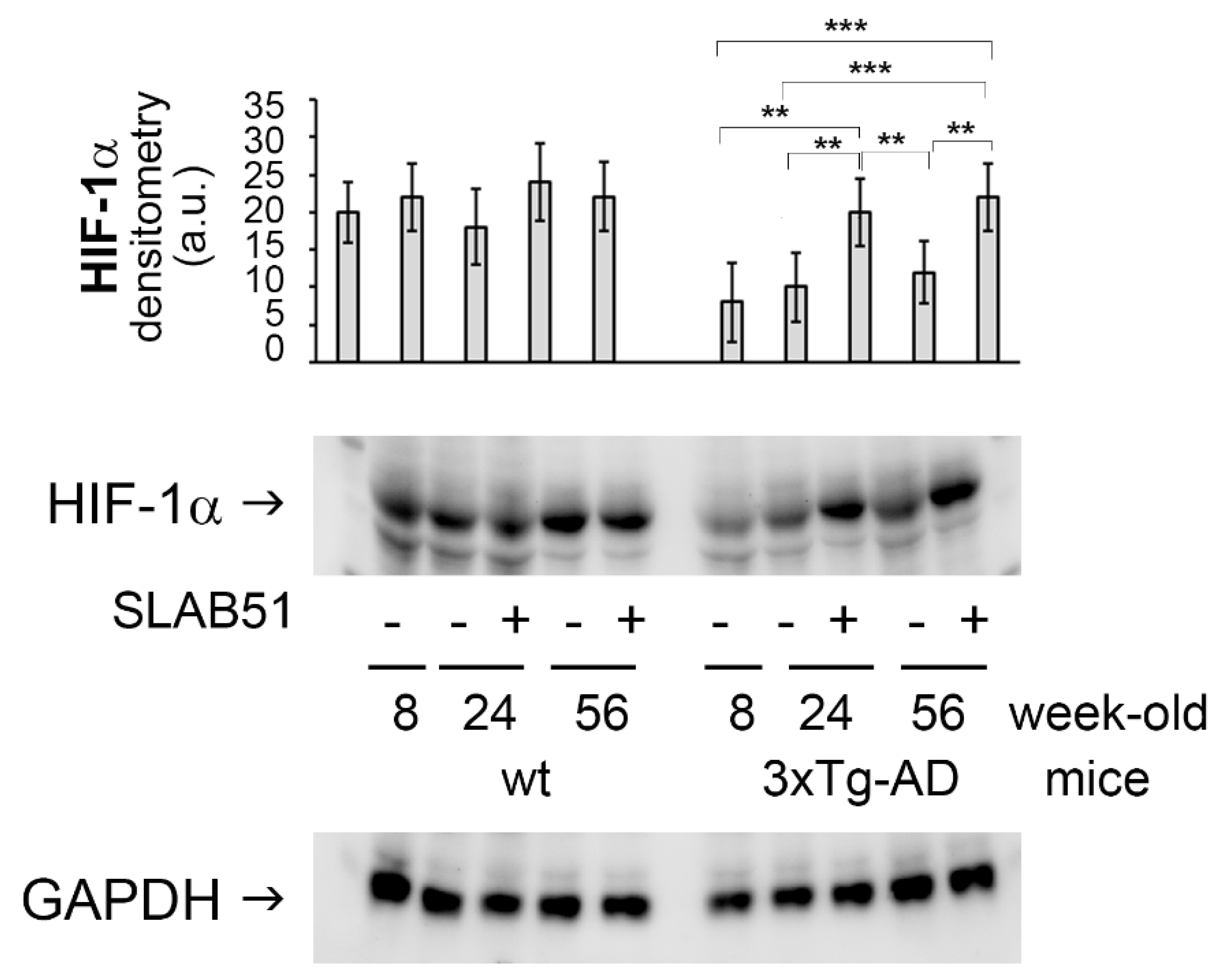
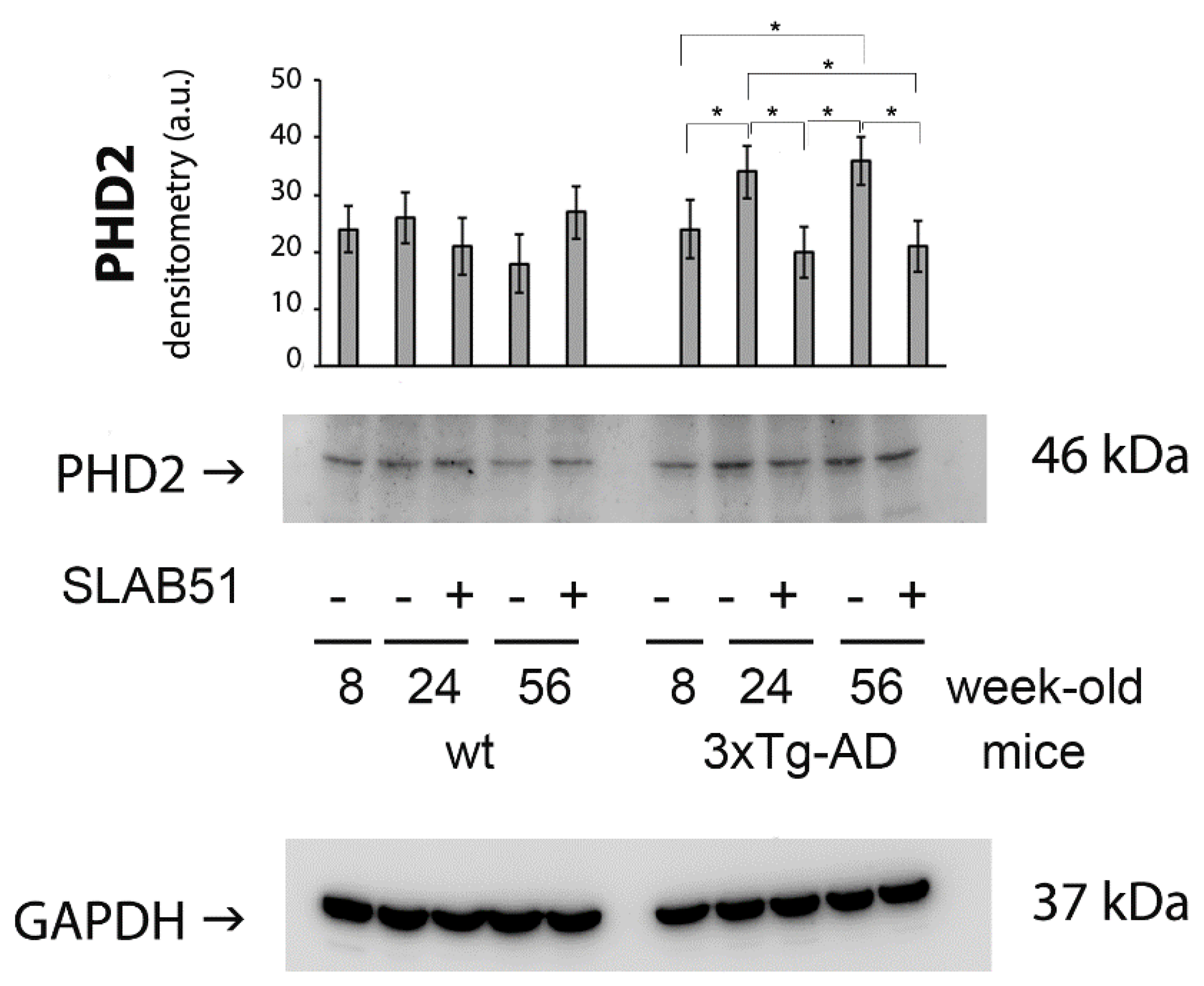
2.2. SLAB51 Restored HIF-1α Cerebral Expression in AD Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Studies
4.2. Preparation of Brain Homogenates
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Nitrite Level Assay
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shabbir, U.; Arshad, M.S.; Sameen, A.; Oh, D.H. Crosstalk between Gut and Brain in Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of Gut Microbiota Modulation Strategies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Gogoi, O.; Gong, C.; Cuccioloni, M.; Angeletti, M.; Rossi, G.; Eleuteri, A.M. Microbiota modulation as preventative and therapeutic approach in Alzheimer’s disease. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2836–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunshola, O.O.; Antoniou, X. Contribution of hypoxia to Alzheimer’s disease: Is HIF-1alpha a mediator of neurodegeneration? Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3555–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitic, M.; Lazarevic-Pasti, T. Does the application of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease lead to depression? Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Berardi, S.; Scarpona, S.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Nasuti, C.; Fiorini, D.; Boarelli, M.C.; Rossi, G.; Eleuteri, A.M. Microbiota modulation counteracts Alzheimer’s disease progression influencing neuronal proteolysis and gut hormones plasma levels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Cuccioloni, M.; Angeletti, M.; Berardi, S.; Scarpona, S.; Rossi, G.; Eleuteri, A.M. SLAB51 Probiotic Formulation Activates SIRT1 Pathway Promoting Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Effects in an AD Mouse Model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 7987–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Gogoi, O.; Berardi, S.; Scarpona, S.; Angeletti, M.; Rossi, G.; Eleuteri, A.M. Gut microbiota manipulation through probiotics oral administration restores glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 87, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, R.; Mohammed, R.; Ojha, U. What are the links between hypoxia and Alzheimer’s disease? Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarember, K.A.; Malech, H.L. HIF-1alpha: A master regulator of innate host defenses? J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1702–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidenko, Z.N.; Blagosklonny, M.V. The purpose of the HIF-1/PHD feedback loop: To limit mTOR-induced HIF-1alpha. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, H.; Chen, R. Hypoxia in Alzheimer’s disease: Effects of hypoxia inducible factors. Neural Regen Res. 2021, 16, 310–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaw, K.; Bell, L.; Boyd, K.; Grijseels, D.M.; Clarke, D.; Bonnar, O.; Crombag, H.S.; Hall, C.N. Neurovascular coupling and oxygenation are decreased in hippocampus compared to neocortex because of microvascular differences. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillieul, S.; Chacaroun, S.; Doutreleau, S.; Detante, O.; Pepin, J.L.; Verges, S. Hypoxic conditioning and the central nervous system: A new therapeutic opportunity for brain and spinal cord injuries? Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verges, S.; Chacaroun, S.; Godin-Ribuot, D.; Baillieul, S. Hypoxic Conditioning as a New Therapeutic Modality. Front. Pediatr. 2015, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Marazzato, M.; Celani, L.; Lombardi, F.; Piccirilli, A.; Mancone, M.; Trinchieri, V.; Pugliese, F.; Mastroianni, C.M.; d’Ettorre, G. Oxygen Sparing Effect of Bacteriotherapy in COVID-19. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohgi, H.; Abe, T.; Yamazaki, K.; Murata, T.; Isobe, C.; Ishizaki, E. The cerebrospinal fluid oxidized NO metabolites, nitrite and nitrate, in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia of Binswanger type and multiple small infarct type. J. Neural Transm. 1998, 105, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Sakata, M.; Takeda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Sawada, K.; Kimura, A.; Minekawa, R.; Tahara, M.; Tasaka, K.; et al. Induction of glucose transporter 1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha under hypoxic conditions in trophoblast-derived cells. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 183, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Gong, C.X. Decreased glucose transporters correlate to abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer disease. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, M.C.; Holt-Martyn, J.P.; Schofield, C.J.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Pharmacological targeting of the HIF hydroxylases—A new field in medicine development. Mol. Aspects Med. 2016, 47–48, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cong, L.; Jaber, V.; Lukiw, W.J. Microbiome-Derived Lipopolysaccharide Enriched in the Perinuclear Region of Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeh, S.H.; Hung, J.J.; Gean, P.W.; Chang, W.C. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protects cultured cortical neurons from lipopolysaccharide-induced cell death via regulation of NR1 expression. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14259–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagao, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Koyasu, S.; Chow, C.C.T.; Harada, H. HIF-1-Dependent Reprogramming of Glucose Metabolic Pathway of Cancer Cells and Its Therapeutic Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Mansfield, K.D.; Bertozzi, C.C.; Rudenko, V.; Chan, D.A.; Giaccia, A.J.; Simon, M.C. Multiple factors affecting cellular redox status and energy metabolism modulate hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase activity in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metzen, E.; Zhou, J.; Jelkmann, W.; Fandrey, J.; Brune, B. Nitric oxide impairs normoxic degradation of HIF-1alpha by inhibition of prolyl hydroxylases. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3470–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.; Grotsch, B.; Luo, Y.; Knaup, K.X.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chen, X.X.; Jantsch, J.; Fillatreau, S.; Schett, G.; Bozec, A. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is a critical transcription factor for IL-10-producing B cells in autoimmune disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berra, E.; Benizri, E.; Ginouves, A.; Volmat, V.; Roux, D.; Pouyssegur, J. HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4082–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luth, H.J.; Holzer, M.; Gartner, U.; Staufenbiel, M.; Arendt, T. Expression of endothelial and inducible NOS-isoforms is increased in Alzheimer’s disease, in APP23 transgenic mice and after experimental brain lesion in rat: Evidence for an induction by amyloid pathology. Brain. Res. 2001, 913, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luth, H.J.; Munch, G.; Arendt, T. Aberrant expression of NOS isoforms in Alzheimer’s disease is structurally related to nitrotyrosine formation. Brain. Res. 2002, 953, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.C.; Rehman, A.; Yu, S.; Andino, N.M. Brain fogginess, gas and bloating: A link between SIBO, probiotics and metabolic acidosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, M.; D’Urso, F.; Piccininni, C.; Montagna, M.; Sardone, R.; Resta, E.; Dibello, V.; Daniele, A.; Giannelli, G.; Bellomo, A.; et al. The relationship between epigenetics and microbiota in neuropsychiatric diseases. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A.; Shepherd, J.D.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E.; Kayed, R.; Metherate, R.; Mattson, M.P.; Akbari, Y.; LaFerla, F.M. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles: Intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 2003, 39, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawford, J.D.; Terry, M.E.; Rourke, G.M. Simplification of drug dosage calculation by application of the surface area principle. Pediatrics 1950, 5, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonfili, L.; Gong, C.; Lombardi, F.; Cifone, M.G.; Eleuteri, A.M. Strategic Modification of Gut Microbiota through Oral Bacteriotherapy Influences Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α: Therapeutic Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010357
Bonfili L, Gong C, Lombardi F, Cifone MG, Eleuteri AM. Strategic Modification of Gut Microbiota through Oral Bacteriotherapy Influences Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α: Therapeutic Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010357
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonfili, Laura, Chunmei Gong, Francesca Lombardi, Maria Grazia Cifone, and Anna Maria Eleuteri. 2022. "Strategic Modification of Gut Microbiota through Oral Bacteriotherapy Influences Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α: Therapeutic Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010357
APA StyleBonfili, L., Gong, C., Lombardi, F., Cifone, M. G., & Eleuteri, A. M. (2022). Strategic Modification of Gut Microbiota through Oral Bacteriotherapy Influences Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α: Therapeutic Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010357







