Probing the Structure and Function of the Cytosolic Domain of the Human Zinc Transporter ZnT8 with Nickel(II) Ions
Abstract
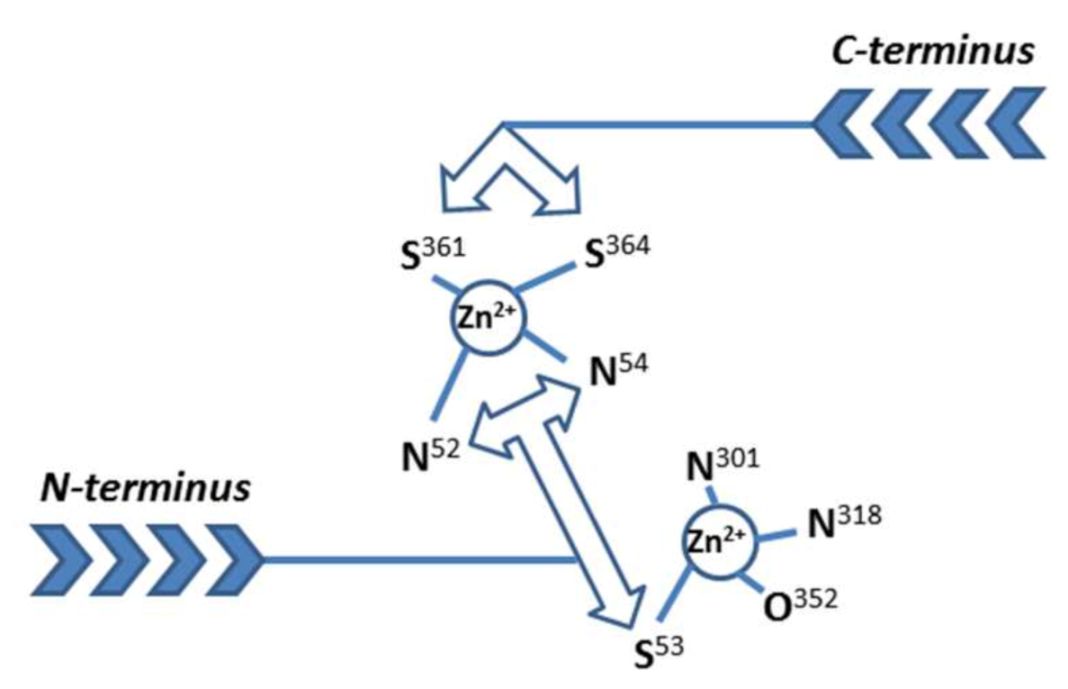
1. Introduction
2. Results
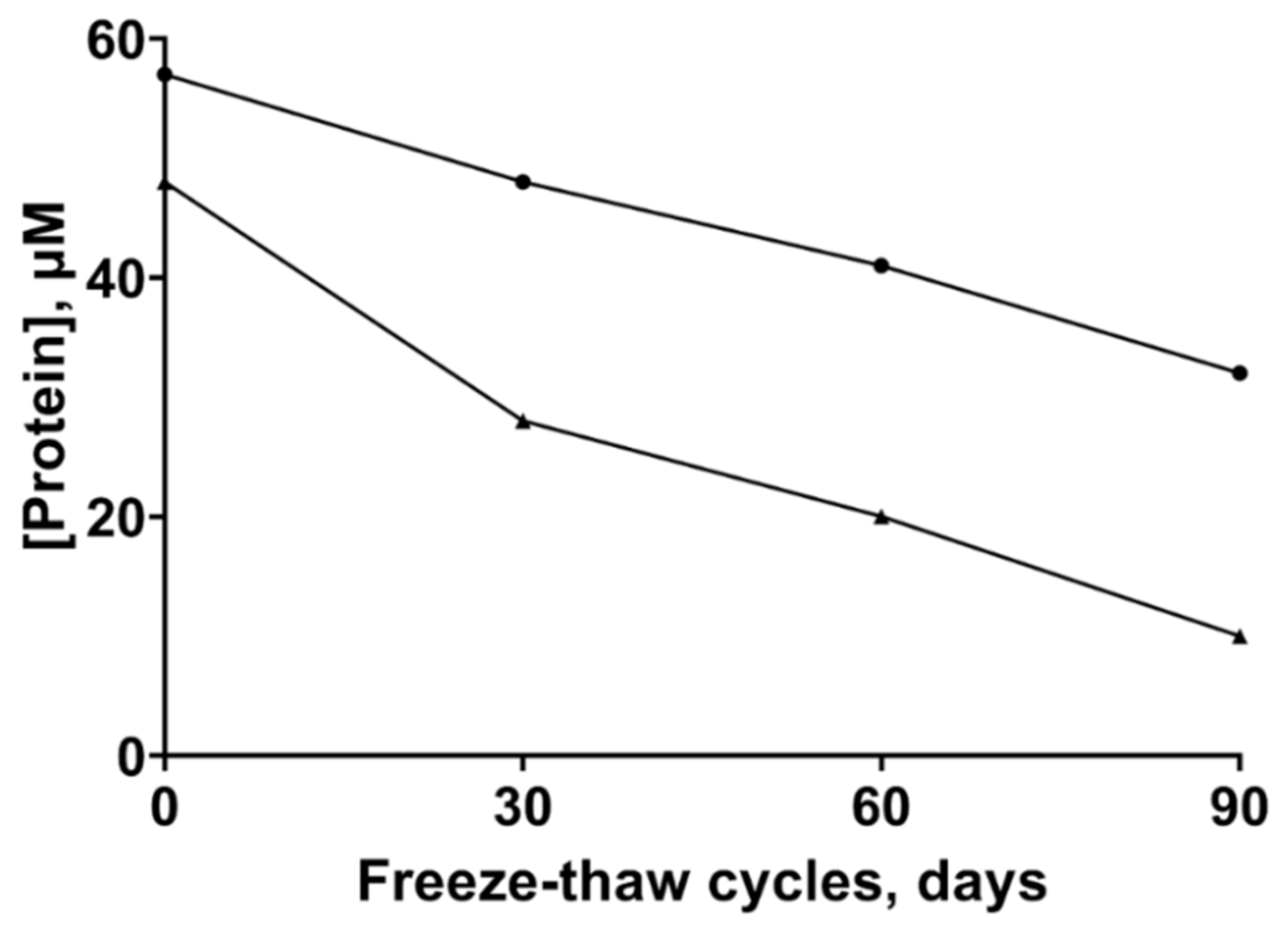
2.1. Stability of the ZnT8 CTDs
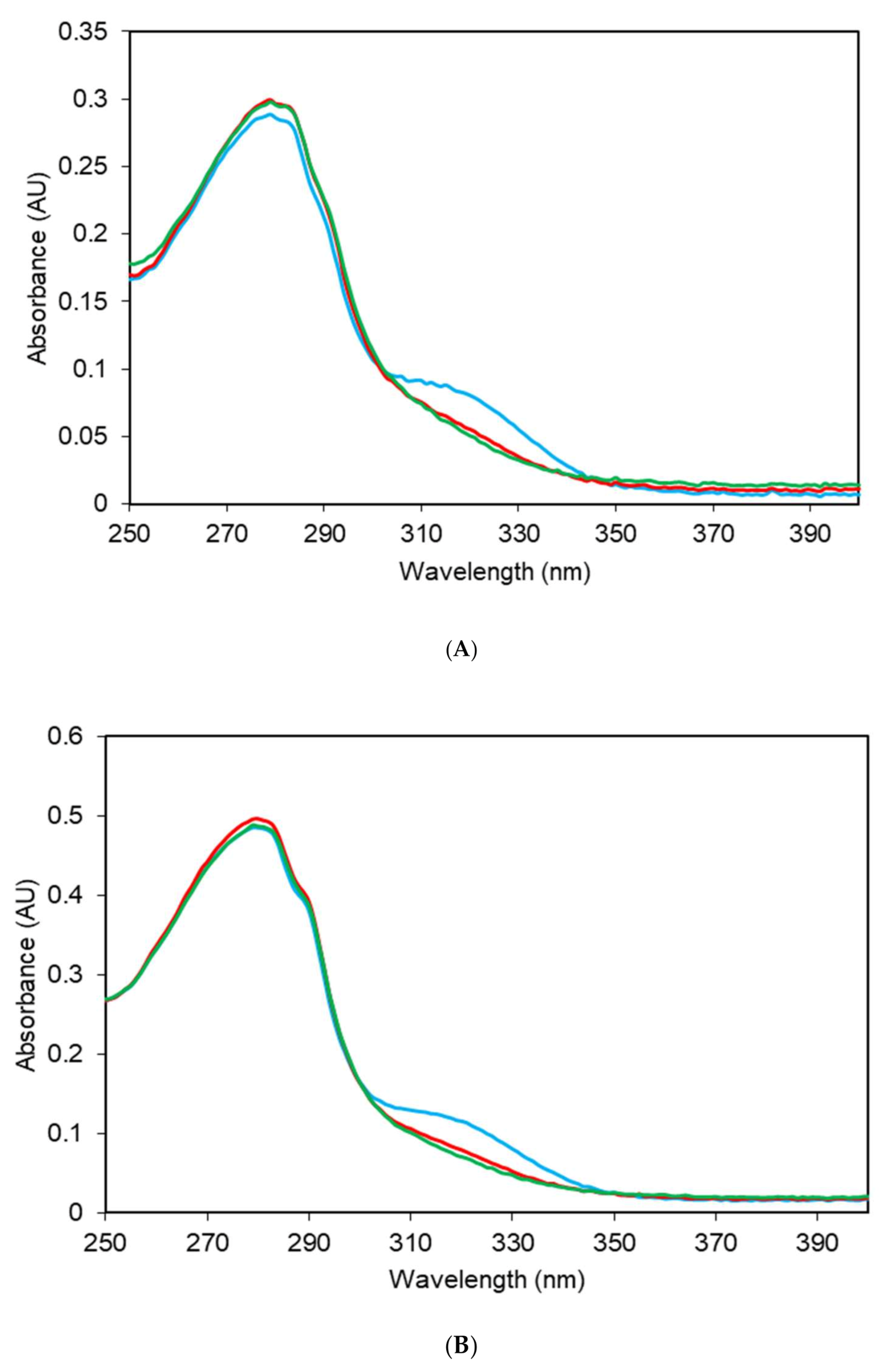
2.2. Electronic Absorption Spectra
2.3. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) and Total Reflection X-ray Fluorescence (TXRF) Metal Analyses
2.4. Thiol Assay
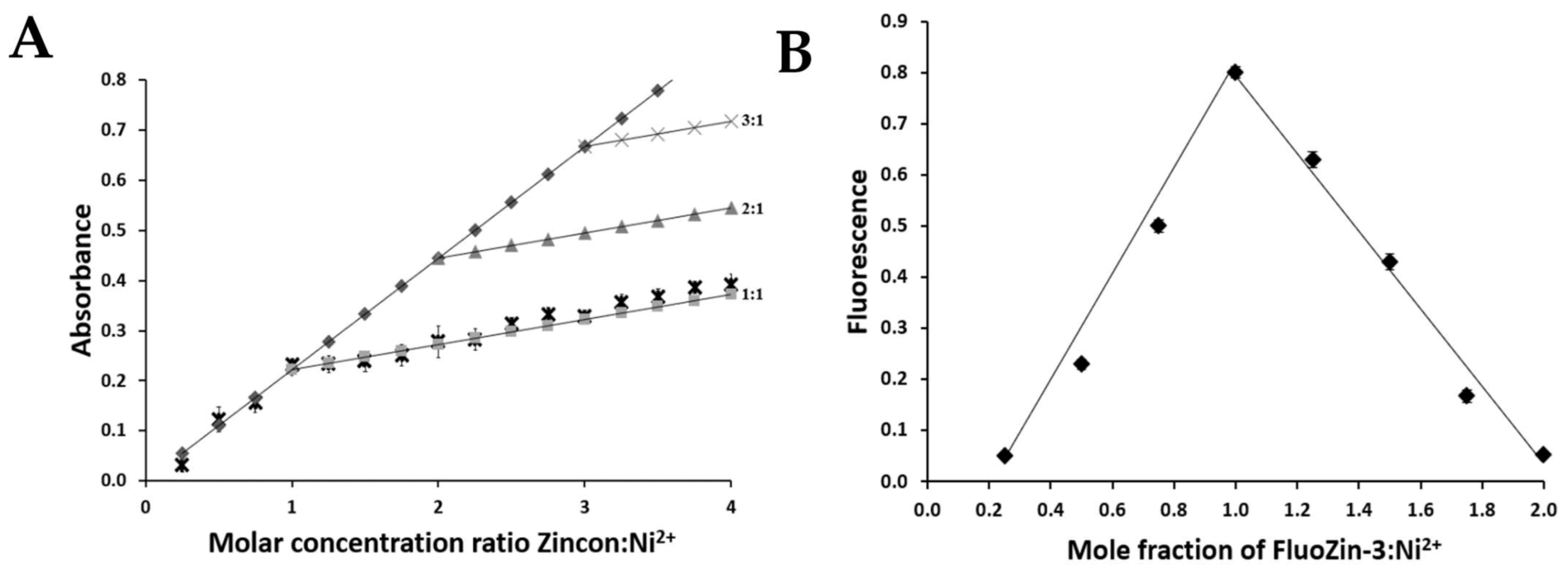
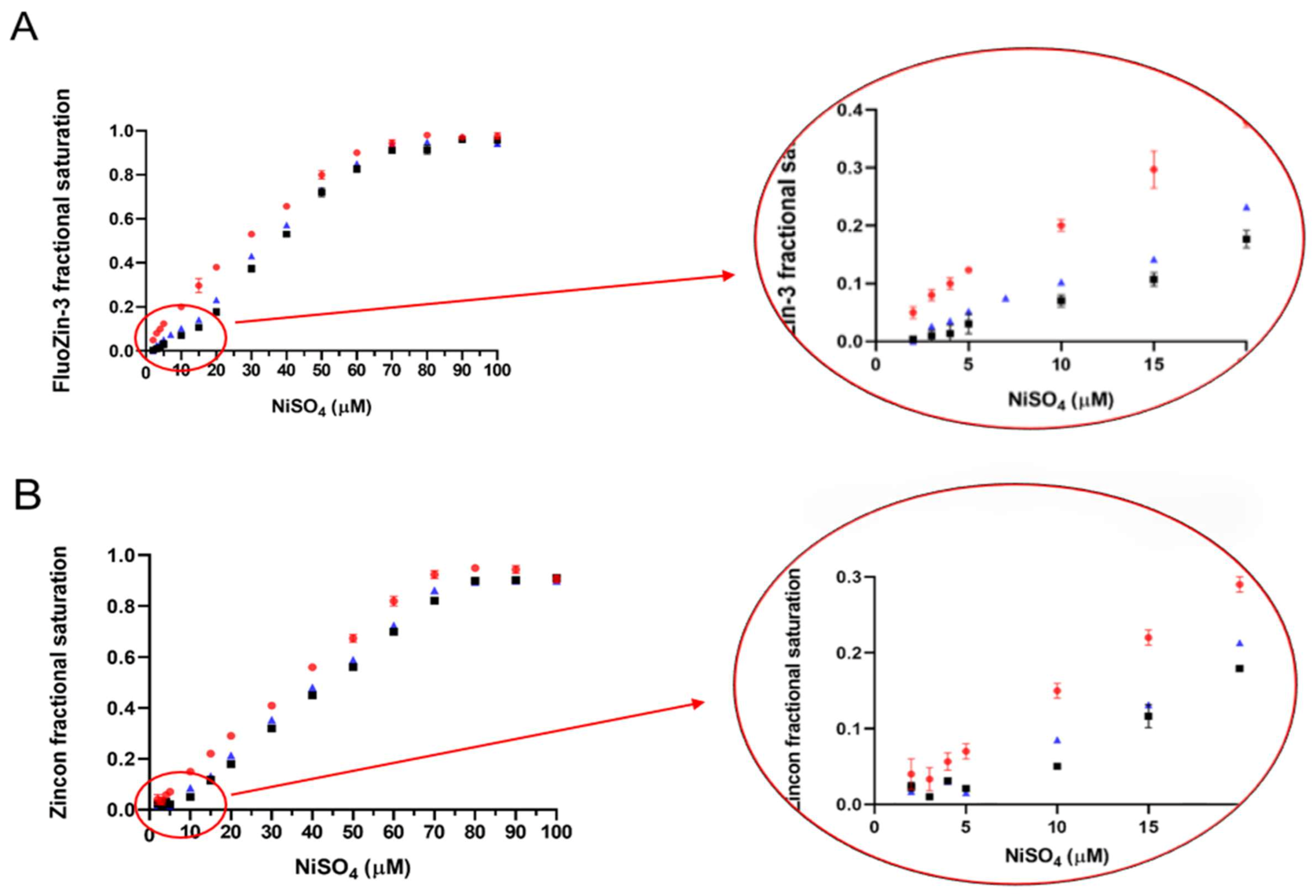
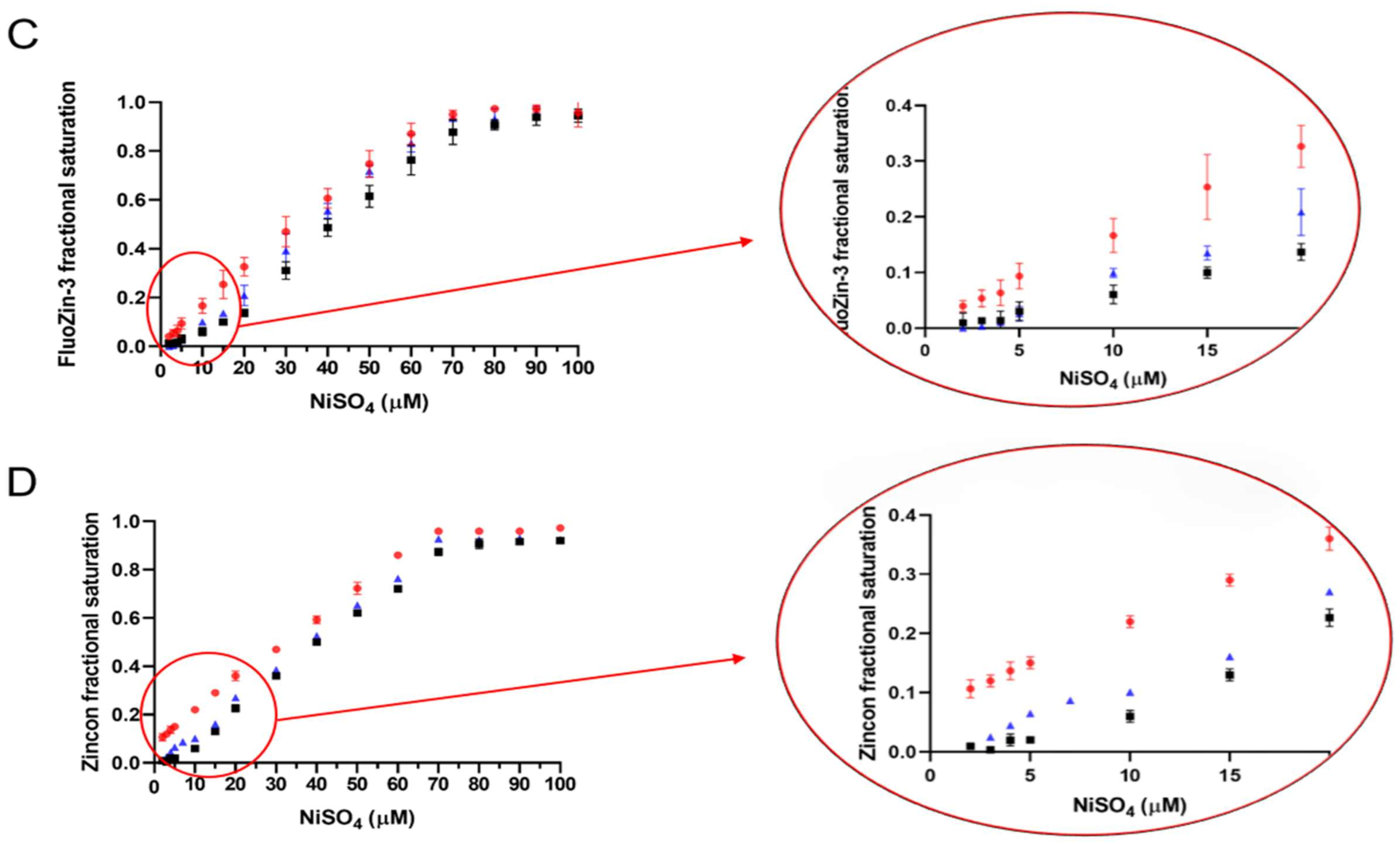
2.5. Determination of the ZnT8c Ni(II) Complex Stoichiometry with Fluorescent (Fluozin-3) and Colorimetric (Zincon) Indicators
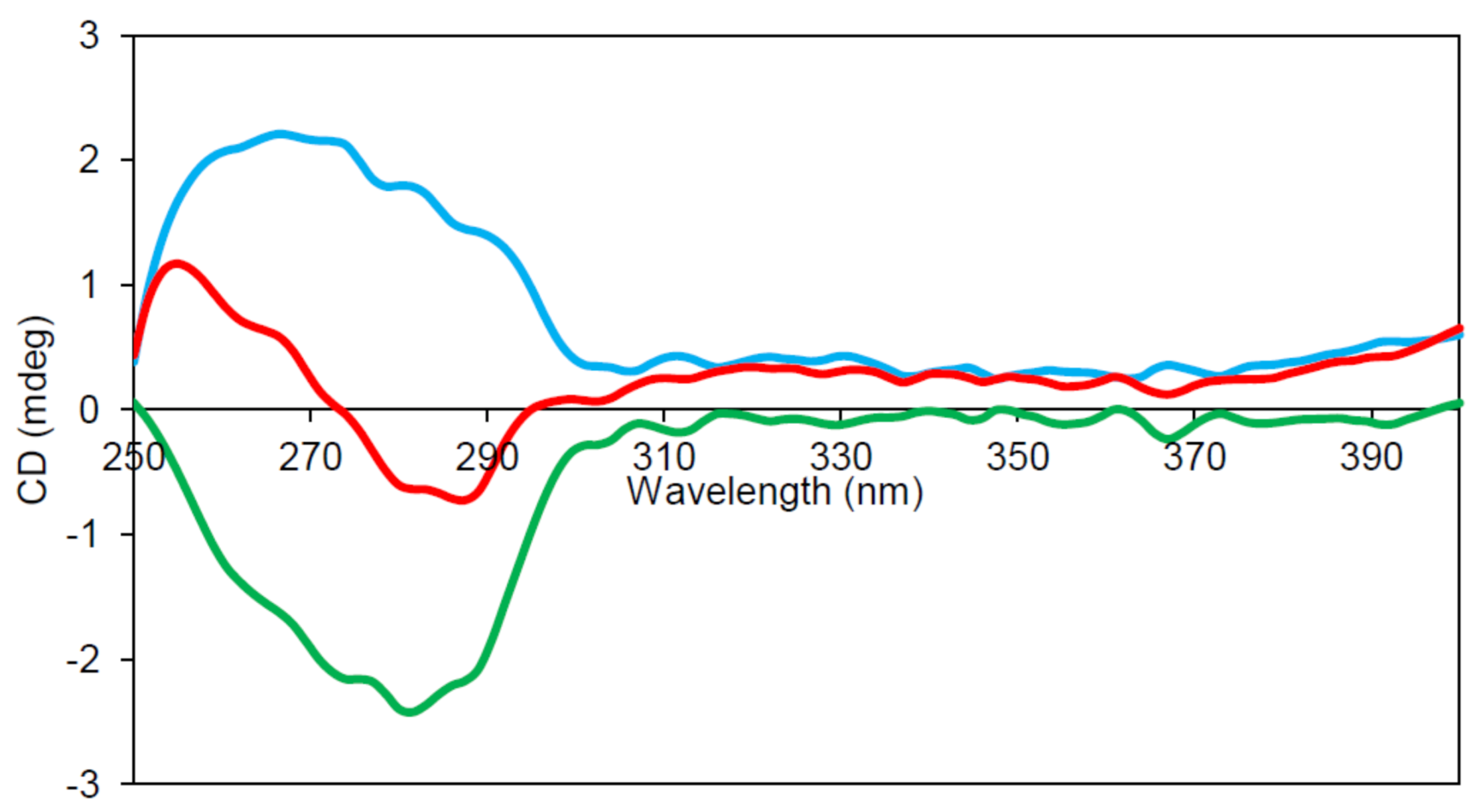
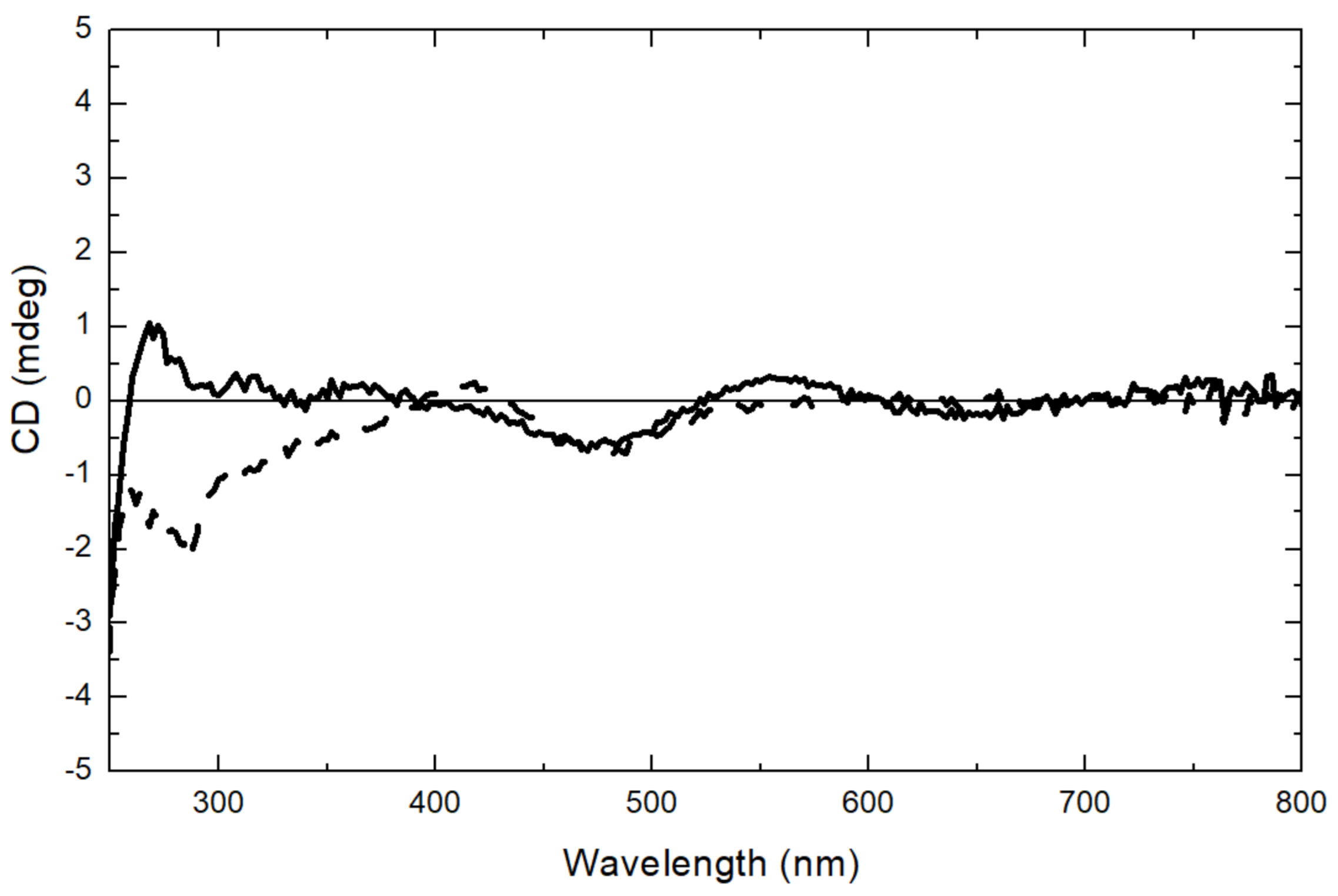
2.6. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
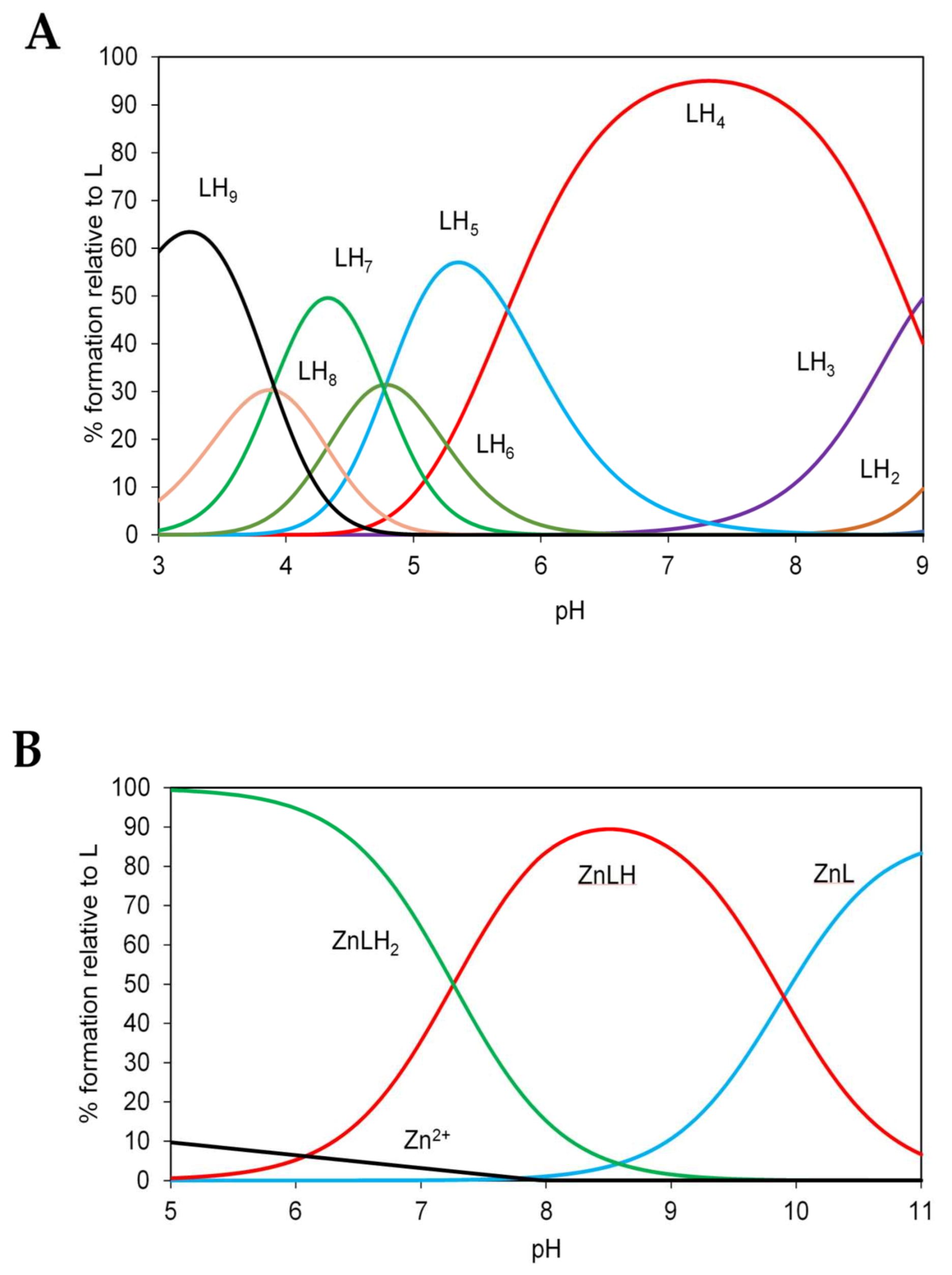
2.7. Potentiometric Characterization of Zinc Binding to N-Terminal and C-Terminal Peptides of ZnT8
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Protein Purification
4.3. Elemental Analysis by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry
4.4. Elemental Analysis by Total Reflection X-ray Fluorescence
4.5. Determination of Metal Binding with Competing Chelating Agents
4.6. Job’s Method
4.7. Complementary Approach
4.8. FluoZin-3 as a Fluorophore to Detect Nickel(II)
4.9. Zincon as a Chromophore to Detect Nickel(II)
4.10. Thiol Assays
4.11. Protein Competition Assays
4.12. Far-UV Absorbance and Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
4.13. C-Terminal and N-Terminal Peptide Syntheses
4.14. Potentiometry
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ε | extinction coefficient; |
| λmax | wavelength of maximal emission; |
| CD | circular dichroism; |
| cDNA | complementary DNA; |
| CTD | C-terminal domain; |
| CDF | cation diffusion facilitator; |
| TMD | transmembrane domain; |
| DTNB | 5,5′-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid); |
| DTT | dithiothreitol; |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid; |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate; |
| ICP-MS | inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry; |
| PAGE | polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; |
| TCEP | tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride; |
| TNB | 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoate; |
| ZnT8 | member 8 of the ZnT family (SLC30A8); |
| ZnT8c | C-terminal domain of ZnT8 (residues 267–369); |
| ZnT8cR | C-terminal domain of ZnT8 expressing arginine at position 325, R325 ZnT8; |
| ZnT8cW | C-terminal domain of ZnT8 expressing tryptophan at position 325, W325 ZnT8; |
| TXRF | total reflection X-ray fluorescence |
References
- Hogstrand, C.; Fu, D. Zinc. In Binding, Transport and Storage of Metal Ions in Biological Cells; Maret, W., Wedd, A.G., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 666–694. [Google Scholar]
- Kambe, T.; Tsuji, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Itsumura, N. The Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Roles of Zinc Transporters in Zinc Homeostasis and Metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 749–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, H.W.; Wenzlau, J.M.; O’Brien, R.M. Zinc transporter 8 (ZnT8) and beta cell function. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomou, A.; Philippe, E.; Chabosseau, P.; Migrenne-Li, S.; Gaitan, J.; Lang, J.; Magnan, C.; Rutter, G.A. Over-expression of Slc30a8/ZnT8 selectively in the mouse alpha cell impairs glucagon release and responses to hypoglycemia. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Fu, D. Structure of the zinc transporter YiiP. Science 2007, 317, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Chai, J.; Fu, D. Structural basis for autoregulation of the zinc transporter YiiP. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coudray, N.; Valvo, S.; Hu, M.; Lasala, R.; Kim, C.; Vink, M.; Zhou, M.; Provasi, D.; Filizola, M.; Tao, J.; et al. Inward-facing conformation of the zinc transporter YiiP revealed by cryoelectron microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherezov, V.; Höfer, N.; Szebenyi, D.M.E.; Kolaj, O.; Wall, J.G.; Gillilan, R.; Srinivasan, V.; Jaroniec, C.P.; Caffrey, M. Insights into the mode of action of a putative zinc transporter CzrB in Thermus thermophilus. Structure 2008, 16, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Hattori, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishitani, R.; Nureki, O. Crystal structure of the cytosolic domain of the cation diffusion facilitator family protein. Proteins 2009, 76, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebe, R.; Keren-Khadmy, N.; Zeytuni, N.; Katzmann, E.; Navon, Y.; Davidov, G.; Bitton, R.; Plitzko, J.M.; Schüler, D.; Zarivach, R. The dual role of MamB in magnetosome membrane assembly and magnetite biomineralization. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 107, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeytuni, N.; Offer, T.; Davidov, G.; Zarivach, R. Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of the C-terminal domain of MamM, a magnetosome-associated protein from Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2012, 68, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udagedara, S.R.; La Porta, D.M.; Spehar, C.; Purohit, G.; Hein, M.J.A.; Fatmous, M.E.; Casas Garcia, G.P.; Ganio, K.; McDevitt, C.A.; Maher, M.J. Structural and functional characterizations of the C-terminal domains of CzcD proteins. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 208, 111087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krężel, A.; Maret, W. Zinc-buffering capacity of a eukaryotic cell at physiological pZn. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 11, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinkenborg, J.L.; Nicolson, T.J.; Bellomo, E.A.; Koay, M.S.; Rutter, G.A.; Merkx, M. Genetically encoded FRET sensors to monitor intracellular Zn2+ homeostasis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maret, W. Analyzing free zinc(II) ion concentrations in cell biology with fluorescent chelating molecules. Metallomics 2015, 7, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabosseau, P.; Woodier, J.; Cheung, R.; Rutter, G.A. Sensors for measuring subcellular zinc pools. Metallomics 2018, 10, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszałek, I.; Goch, W.; Bal, W. Ternary Zn(II) Complexes of FluoZin-3 and the Low Molecular Weight Component of the Exchangeable Cellular Zinc Pool. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 9826–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goch, W.; Bal, W. Stochastic or Not? Method to Predict and Quantify the Stochastic Effects on the Association Reaction Equilibria in Nanoscopic Systems. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, M.J.; Jagielnicki, M.; Yeager, M. Structure/Function analysis of human ZnT8 (SLC30A8): A diabetes risk factor and zinc transporter. Curr. Res. Struct. Biol. 2020, 2, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xie, T.; Zeng, W.; Jiang, Y.; Bai, X.C. Cryo-EM structures of human ZnT8 in both outward- and inward-facing conformations. eLife 2020, 9, e58823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, D.S.; Hogstrand, C.; Maret, W. The C-terminal cytosolic domain of the human zinc transporter ZnT8 and its diabetes risk variant. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesgaard, T.W.; Žilinskaitė, J.; Vänttinen, M.; Laakso, M.; Jansson, P.A.; Hammarstedt, A.; Smith, U.; Stefan, N.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.; et al. The common SLC30A8 Arg325Trp variant is associated with reduced first-phase insulin release in 846 non-diabetic offspring of type 2 diabetes patients—The EUGENE2 study. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriman, C.; Huang, Q.; Rutter, G.A.; Fu, D. Lipid-tuned Zinc Transport Activity of Human ZnT8 Protein Correlates with Risk for Type-2 Diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26950–26957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Kang, E.S.; Yim, Y.S.; Ko, S.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Rim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, C.W.; Cha, B.S.; Lee, H.C.; et al. A low-risk ZnT-8 allele (W325) for post-transplantation diabetes mellitus is protective against cyclosporin A-induced impairment of insulin secretion. Pharm. J. 2011, 11, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.; Molina-Lopez, J.; Parsons, D.; Corpe, C.; Maret, W.; Hogstrand, C. Differential cytolocation and functional assays of the two major human SLC30A8 (ZnT8) isoforms. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 44, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, D.; Giachetti, A.; Rosato, A. Insights into the Dynamics of the Human Zinc Transporter ZnT8 by MD Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzlau, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Moua, O.; Fowler, K.T.; Rangasamy, S.; Walters, J.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Davidson, H.W.; Hutton, J.C. A common nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphism in the SLC30A8 gene determines ZnT8 autoantibody specificity in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2693–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bertoglio, B.A.; Devinney, M.J., Jr.; Dineley, K.E.; Kay, A.R. The interaction of biological and noxious transition metals with the zinc probes FluoZin-3 and Newport Green. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 384, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marszałek, I.; Krężel, A.; Goch, W.; Zhukov, I.; Paczkowska, I.; Bal, W. Revised stability constant, spectroscopic properties and binding mode of Zn(II) to FluoZin-3, the most common zinc probe in life sciences. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 161, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocyła, A.; Pomorski, A.; Krężel, A. Molar absorption coefficients and stability constants of Zincon metal complexes for determination of metal ions and bioinorganic applications. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 176, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydor, A.M.; Lebrette, H.; Ariyakumaran, R.; Cavazza, C.; Zamble, D.B. Relationship between Ni(II) and Zn(II) coordination and nucleotide binding by the Helicobacter pylori [NiFe]-hydrogenase and urease maturation factor HypB. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3828–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, H.; Maret, W.; Kozlowski, H.; Zeppezauer, M. Active site-specifically reconstituted nickel(II) horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase: Optical spectra of binary and ternary complexes with coenzymes, coenzyme analogues, substrates, and inhibitors. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1981, 14, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krężel, A.; Wójcik, J.; Maciejczyk, M.; Bal, W. May GSH and L-His contribute to intracellular binding of zinc? Thermodynamic and solution structural study of a ternary complex. Chem. Commun. 2003, 704–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.P.; Harmon, J.; Tran, P.O.; Poitout, V. Beta-cell glucose toxicity, lipotoxicity, and chronic oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. 1), S119–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Árus, D.; Dancs, Á.; Nagy, N.V.; Gajda, T. A comparative study on the possible zinc binding sites of the human ZnT3 zinc transporter protein. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 12031–12040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maret, W.; Vallee, B.L. Cobalt as probe and label of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1993, 226, 52–71. [Google Scholar]
- Krężel, A.; Szczepanik, W.; Sokołowska, M.; Jeżowska-Bojczuk, M.; Bal, W. Correlations between complexation modes and redox activities of Ni(II)-GSH complexes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieba, L.; Nieba-Axmann, S.E.; Persson, A.; Hamalainen, M.; Edebratt, F.; Hansson, A.; Lidholm, J.; Magnusson, K.; Karlsson, A.F.; Pluckthun, A. BIACORE analysis of histidine-tagged proteins using a chelating NTA sensor chip. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 252, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, R.; Shehzad, A.; Shah, M.A.; De March, M.; Ismat, F.; Iqbal, M.; Onesti, S.; Rahman, M.; McPherson, M.J. C-Terminal Domain of the Human Zinc Transporter hZnT8 Is Structurally Indistinguishable from Its Disease Risk Variant (R325W). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubillas, C.; Vinuesa, P.; Tabche, M.L.; Garcia-de los Santos, A. Phylogenomic analysis of Cation Diffusion Facilitator proteins uncovers Ni2+/Co2+ transporters. Metallomics 2013, 5, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.P.; Allen, N.B.; Meyers, M.S.; Link, E.O.; Zhang, X.; MacRenaris, K.W.; El Muayed, M. Exploring the Association Between Demographics, SLC30A8 Genotype, and Human Islet Content of Zinc, Cadmium, Copper, Iron, Manganese and Nickel. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoch, E.; Lin, W.; Chai, J.; Hershfinkel, M.; Fu, D.; Sekler, I. Histidine pairing at the metal transport site of mammalian ZnT transporters controls Zn2+ over Cd2+ selectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7202–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Muayed, M.; Raja, M.R.; Zhang, X.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Bhatt, S.; Chen, X.; Urbanek, M.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Lowe, W.L., Jr. Accumulation of cadmium in insulin-producing beta cells. Islets 2012, 4, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, P. Recherches sur la formation des complexes minéraux en solution, et sur leur stabilité. Ann. Chim. 1928, 9, 113–203. [Google Scholar]
- Filipsky, T.; Riha, M.; Hrdina, R.; Vavrova, K.; Mladěnka, P. Mathematical calculations of iron complex stoichiometry by direct UV-Vis spectrophotometry. Bioorganic Chem. 2013, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabel, C.E.; Neureuther, J.M.; Siemann, S. A spectrophotometric method for the determination of zinc, copper, and cobalt ions in metalloproteins using Zincon. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 397, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, G.B. Introduction to peptide synthesis. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2001, 26, 18.1.1–18.1.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gans, P.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs. Talanta 1996, 43, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mol. Equiv. Zn2+ Added | ZnT8cR | Metal:Monomer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn (μM) | Ni (μM) | Total Metal (μM) | ||
| 0 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.15 |
| 1 | 2.80 ± 0.07 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 3.03 | 1.52 |
| 2 | 5.28 ± 0.39 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 5.52 | 2.76 |
| 4 | 6.65 ± 0.09 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 6.77 | 3.39 |
| 10 | 5.99 ± 0.30 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 6.00 | 3.00 |
| Mol. Equiv. Zn2+ Added | ZnT8cW | Metal:Monomer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn (μM) | Ni (μM) | Total Metal (μM) | ||
| 0 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.37 | 0.19 |
| 1 | 2.48 ± 0.15 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 2.76 | 1.38 |
| 2 | 5.06 ± 0.21 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 5.30 | 2.65 |
| 4 | 6.51 ± 0.38 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 6.63 | 3.32 |
| 10 | 6.23 ± 0.25 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 6.31 | 3.16 |
| TXRF | ICP-MS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni:Monomer | Zn:Monomer | Ni:Monomer | Zn:Monomer | |
| ZnT8cW | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.05 | 0.1 ± 0.06 |
| ZnT8cR | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.10 | 0.2 ± 0.10 |
| Variant | A412 | TNB, µM | ZnT8c, µM | Free Thiol/Monomer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ZnT8cR | 0.989 ± 0.01 | 5.59 ± 0.01 | 2 ± 0.001 | 2.79 ± 0.02 |
| ZnT8cW | 0.960 ± 0.01 | 5.42 ± 0.01 | 2 ± 0.001 | 2.71 ± 0.01 | |
| B | ZnT8cR | 0.500 ± 0.005 | 0.62 ± 0.02 | 2 ± 0.005 | 0.31 ± 0.02 |
| ZnT8cW | 0.512 ± 0.002 | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 2 ± 0.002 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | |
| C | ZnT8cR | 0.450 ± 0.003 | 0.550 ± 0.005 | 2 ± 0.005 | 0.27 ± 0.04 |
| ZnT8cW | 0.420 ± 0.002 | 0.520 ± 0.008 | 2 ± 0.003 | 0.26 ± 0.05 |
| Proteins as Isolated (ICP-MS) | Proteins with Free Cysteines (ICP-MS) | Proteins with Blocked Cysteines (ICP-MS) | Proteins with Free Cysteines (Competition Assay) | Proteins with Blocked Cysteines (Competition Assay) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel:Monomer | Nickel:Monomer | Nickel:Monomer | Nickel:Monomer | Nickel:Monomer | |
| ZnT8cW | 0.50 ± 0.05 | 2.00 ± 0.01 | 1.26 ± 0.05 | 1.98 ± 0.02 | 1.25 ± 0.07 |
| ZnT8cR | 0.60 ± 0.01 | 1.97 ± 0.01 | 0.97 ± 0.03 | 2.00 ± 0.03 | 1.00 ± 0.02 |
| (Znp)LqHr | log β | log K | Predicted Protonated Residue |
|---|---|---|---|
| LH | 10.58 ± 0.02 | 10.58 | Tyrosine side chain |
| LH2 | 19.84 ± 0.02 | 9.27 | Cysteine sulfhydryl |
| LH3 | 26.89 ± 0.02 | 7.05 | Histidine side chain |
| LH4 | 32.71 ± 0.02 | 5.82 | Histidine side chain |
| ZnLH | 18.85 ± 0.02 | ||
| ZnL | 9.58 ± 0.02 |
| LqHr | log β | log K | Predicted Protonated Residue |
|---|---|---|---|
| LH | 11.29 | 11.29 | Proline α-amino |
| LH2 | 21.43 | 10.14 | Cysteine sulfhydryl |
| LH3 | 31.14 | 9.71 | Cysteine sulfhydryl |
| LH4 | 40.05 | 8.91 | Cysteine sulfhydryl |
| LH5 | 45.79 | 5.74 | Glutamic acid side chain |
| LH6 | 50.57 | 4.78 | Aspartic acid side chain |
| LH7 | 55.33 | 4.76 | Aspartic acid side chain |
| LH8 | 59.22 | 3.89 | Aspartic acid side chain |
| LH9 | 63.14 | 3.92 | Aspartic acid α-COOH |
| ZnpLqHr | log β | log K |
|---|---|---|
| ZnL | 15.98 | 15.98 |
| ZnLH | 25.88 | 9.9 |
| ZnLH2 | 33.14 | 7.26 |
| ZnL2 | 23.33 | 7.35 |
| ZnL2H | 33.85 | 10.52 |
| ZnL2H2 | 44.20 | 10.35 |
| ZnL2H3 | 53.43 | 9.23 |
| ZnL2H4 | 63.01 | 9.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Catapano, M.C.; Parsons, D.S.; Kotuniak, R.; Mladěnka, P.; Bal, W.; Maret, W. Probing the Structure and Function of the Cytosolic Domain of the Human Zinc Transporter ZnT8 with Nickel(II) Ions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062940
Catapano MC, Parsons DS, Kotuniak R, Mladěnka P, Bal W, Maret W. Probing the Structure and Function of the Cytosolic Domain of the Human Zinc Transporter ZnT8 with Nickel(II) Ions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062940
Chicago/Turabian StyleCatapano, Maria Carmen, Douglas S. Parsons, Radosław Kotuniak, Přemysl Mladěnka, Wojciech Bal, and Wolfgang Maret. 2021. "Probing the Structure and Function of the Cytosolic Domain of the Human Zinc Transporter ZnT8 with Nickel(II) Ions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062940
APA StyleCatapano, M. C., Parsons, D. S., Kotuniak, R., Mladěnka, P., Bal, W., & Maret, W. (2021). Probing the Structure and Function of the Cytosolic Domain of the Human Zinc Transporter ZnT8 with Nickel(II) Ions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062940










