Novel Emerging Molecular Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
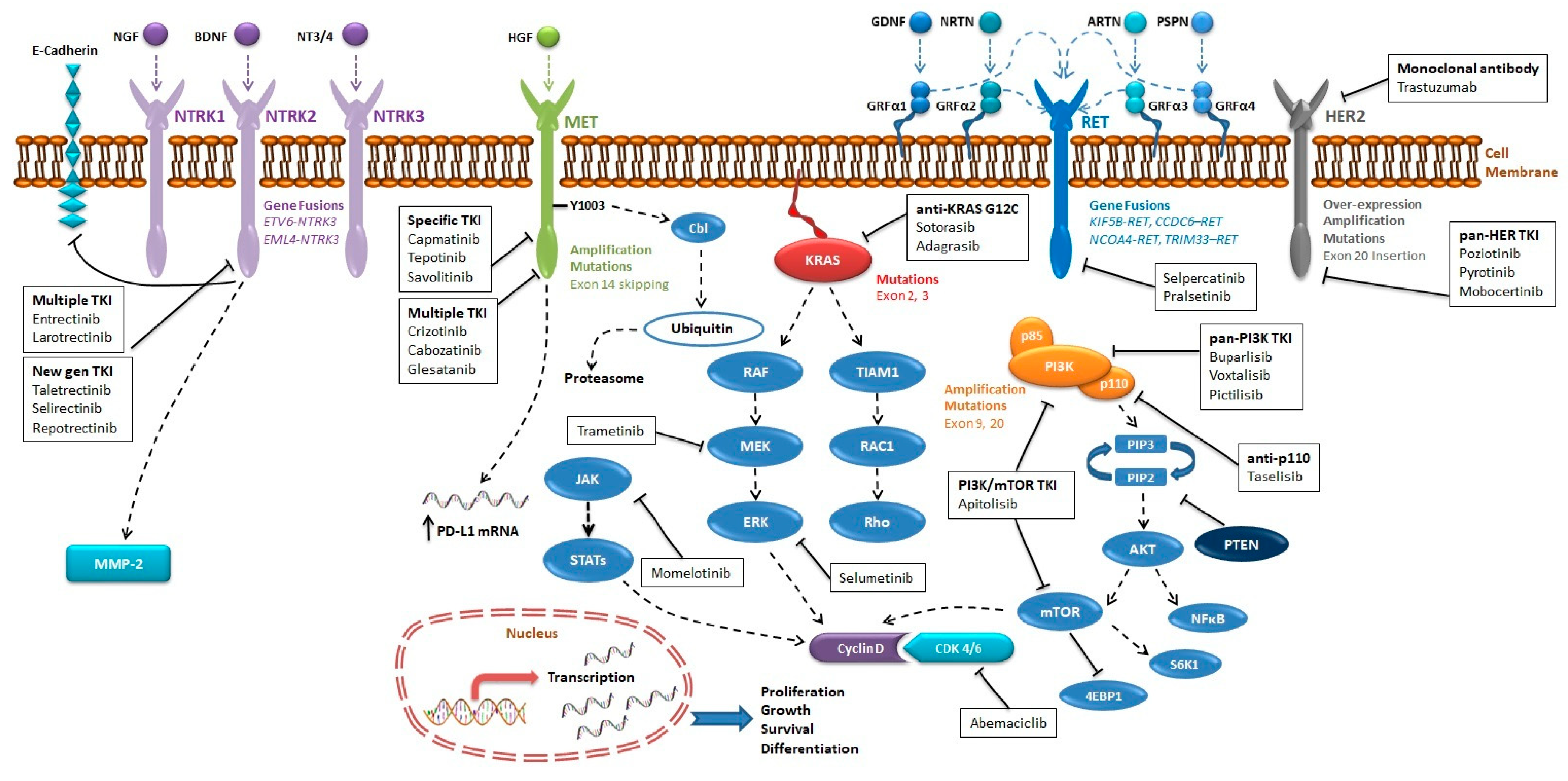
2. MET
2.1. Epidemiology
2.2. Molecular Pathway
2.3. Diagnostic Methodology
2.4. Therapeutic Implications
2.4.1. MET as Primary Oncogenic Driver
Crizotinib
Capmatinib
Tepotinib
Savolitinib
Other MET-Inhibitors
2.4.2. MET as Secondary Acquired Resistance
2.4.3. MET Alterations and Immunotherapy
3. RET
3.1. Epidemiology
3.2. Molecular Pathway
3.3. Diagnostic Methodology
3.4. Therapeutic Implications
4. NTRK
4.1. Epidemiology
4.2. Molecular Pathway
4.3. Diagnostic Methodology
4.4. Therapeutic Implications
5. KRAS
5.1. Epidemiology
5.2. Molecular Pathway
5.3. Diagnostic Methodology
5.4. Therapeutic Implications
6. PIK3CA
6.1. Epidemiology
6.2. Molecular Pathway
6.3. Diagnostic Methodology
6.4. Therapeutic Implications
7. HER2
7.1. Epidemiology
7.1.1. HER2 Mutations
7.1.2. HER2 Amplification and Protein Expression
7.2. Molecular Pathway
7.3. Diagnostic Methodology
7.4. Therapeutic Implications
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denis, M.G.; Bennouna, J. Osimertinib for Front-Line Treatment of Locally Advanced or Metastatic EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Patients: Efficacy, Acquired Resistance and Perspectives for Subsequent Treatments. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 12593–12602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbò, F.; Passiglia, F.; Novello, S. Upfront Management of ALK-Rearranged Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: One Inhibitor Fits All? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Jenkins, C.; Iyer, S.; Schoenfeld, A.; Keddy, C.; Davare, M.A. ROS1-Dependent Cancers—Biology, Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malapelle, U.; Rossi, G.; Pisapia, P.; Barberis, M.; Buttitta, F.; Castiglione, F.; Cecere, F.L.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Iaccarino, A.; Marchetti, A.; et al. BRAF as a Positive Predictive Biomarker: Focus on Lung Cancer and Melanoma Patients. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 156, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Lopes, A.R.; McCusker, M.G.; Garrigues, S.G.; Ricciardi, G.R.; Arensmeyer, K.E.; Scilla, K.A.; Mehra, R.; Rolfo, C. New Targets in Lung Cancer (Excluding EGFR, ALK, ROS1). Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, G.; Andrini, E.; Sisi, M.; Rizzo, A.; Parisi, C.; Di Federico, A.; Gelsomino, F.; Ardizzoni, A. Beyond EGFR, ALK and ROS1: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives on Newly Targetable Oncogenic Drivers in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 156, 103119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzawa, K.; Offin, M.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Odintsov, I.; Lu, D.; Lockwood, W.W.; Arcila, M.E.; Rudin, C.M.; Drilon, A.; et al. Acquired MET Exon 14 Alteration Drives Secondary Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Yoda, S.; Lennerz, J.K.; Langenbucher, A.; Lin, J.J.; Rooney, M.M.; Prutisto-Chang, K.; Oh, A.; Adams, N.A.; Yeap, B.Y.; et al. MET Alterations Are a Recurring and Actionable Resistance Mechanism in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlaender, A.; Drilon, A.; Banna, G.L.; Peters, S.; Addeo, A. The METeoric Rise of MET in Lung Cancer. Cancer 2020, 126, 4826–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Zou, Q.; Liu, H.; Qiu, B.; Li, Q.; Lin, Y.; Liang, Y. Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2020, 21, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgia, R.; Sattler, M.; Scheele, J.; Stroh, C.; Felip, E. The Promise of Selective MET Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 87, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Oxnard, G.R.; Jackman, D.M.; Savukoski, D.O.; Hall, D.; Shivdasani, P.; Heng, J.C.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Jänne, P.A.; Verma, S.; et al. MET Exon 14 Mutations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Are Associated With Advanced Age and Stage-Dependent MET Genomic Amplification and c-Met Overexpression. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.H.; Yeung, S.F.; Chan, A.W.H.; Chung, L.Y.; Chau, S.L.; Lung, R.W.M.; Tong, C.Y.; Chow, C.; Tin, E.K.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; et al. MET Amplification and Exon 14 Splice Site Mutation Define Unique Molecular Subgroups of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma with Poor Prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3048–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.D.; Lee, S.E.; Oh, D.-Y.; Yu, D.-B.; Jeong, H.M.; Kim, J.; Hong, S.; Jung, H.S.; Oh, E.; Song, J.-Y.; et al. MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Implications and Prognostic Values. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2017, 12, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digumarthy, S.R.; Mendoza, D.P.; Zhang, E.W.; Lennerz, J.K.; Heist, R.S. Clinicopathologic and Imaging Features of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. Cancers 2019, 11, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bylicki, O.; Paleiron, N.; Assié, J.-B.; Chouaïd, C. Targeting the MET-Signaling Pathway in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Evidence to Date. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5691–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, M. MET Oncogene in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Mechanism of MET Dysregulation and Agents Targeting the HGF/c-Met Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 2491–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Yu, S.; Fan, Y. Progress on Treatment of MET Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Camidge, D.R.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Clark, J.W.; Socinski, M.; Riely, G.J.; Winter, M.; Wang, S.; Monti, K.; Wilner, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of crizotinib in patients (pts) with advanced MET exon 14-altered non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer’s XALKORI® (Crizotinib) Receives FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation in Two New Indications/Pfizer. Available online: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer_s_xalkori_crizotinib_receives_fda_breakthrough_therapy_designation_in_two_new_indications-0 (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Drilon, A.; Clark, J.W.; Weiss, J.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.J.; Otterson, G.A.; Villaruz, L.C.; Riely, G.J.; Heist, R.S.; et al. Antitumor Activity of Crizotinib in Lung Cancers Harboring a MET Exon 14 Alteration. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, L.; Chiari, R.; Tiseo, M.; D’Incà, F.; Dazzi, C.; Chella, A.; Delmonte, A.; Bonanno, L.; Giannarelli, D.; Cortinovis, D.L.; et al. Crizotinib in MET-Deregulated or ROS1-Rearranged Pretreated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (METROS): A Phase II, Prospective, Multicenter, Two-Arms Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7312–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro-Sibilot, D.; Cozic, N.; Pérol, M.; Mazières, J.; Otto, J.; Souquet, P.J.; Bahleda, R.; Wislez, M.; Zalcman, G.; Guibert, S.D.; et al. Crizotinib in C-MET- or ROS1-Positive NSCLC: Results of the AcSé Phase II Trial. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Leonardi, G.C.; Kravets, S.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Drilon, A.; Noonan, S.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Costa, D.B.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Impact of MET Inhibitors on Survival among Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring MET Exon 14 Mutations: A Retrospective Analysis. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2019, 133, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines). Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Version 3.2021—February 19 2021. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl_blocks.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Capmatinib for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. (FDA website); FDA; 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-capmatinib-metastatic-non-small-cell-lung-cancer#:~:text=On%20May%206%2C%202020%2C%20the,by%20an%20FDA%2Dapproved%20test (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.-Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Hida, T.; de Jonge, M.; Orlov, S.V.; et al. Capmatinib in MET Exon 14-Mutated or MET-Amplified Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, P.K.; Veillon, R.; Cortot, A.B.; Felip, E.; Sakai, H.; Mazieres, J.; Griesinger, F.; Horn, L.; Senellart, H.; Meerbeeck, J.P.V.; et al. Phase II Study of Tepotinib in NSCLC Patients with METex14 Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Felip, E.; Veillon, R.; Sakai, H.; Cortot, A.B.; Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Viteri, S.; Senellart, H.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; et al. Tepotinib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepotinib Breakthrough Therapy—News—Merck Global. Available online: https://www.merckgroup.com/en/news/tepotinib-breakthrough-therapy-designation-11-09-2019.html (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Lu, S.; Fang, J.; Cao, L.; Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Abstract CT031: Preliminary Efficacy and Safety Results of Savolitinib Treating Patients with Pulmonary Sarcomatoid Carcinoma (PSC) and Other Types of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, CT031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, R.A.; Neves, N.M.; Amaral, G.A.; Lippo, E.G.; Castelo-Branco, P.; Pozza, D.H.; Tajima, C.C.; Antoniou, G. The Role of MET Inhibitor Therapies in the Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, K.; Inoue, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Karayama, M.; Yamada, H.; Iwashita, Y.; Kawase, A.; Tanahashi, M.; Ogawa, H.; Inui, N.; et al. Elucidation of the Relationships of MET Protein Expression and Gene Copy Number Status with PD-L1 Expression and the Immune Microenvironment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2020, 141, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazieres, J.; Drilon, A.; Lusque, A.; Mhanna, L.; Cortot, A.B.; Mezquita, L.; Thai, A.A.; Mascaux, C.; Couraud, S.; Veillon, R.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer and Oncogenic Driver Alterations: Results from the IMMUNOTARGET Registry. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, J.K.; Leonardi, G.C.; Shu, C.A.; Umeton, R.; Montecalvo, J.; Ni, A.; Chen, R.; Dienstag, J.; Mrad, C.; Bergagnini, I.; et al. PD-L1 Expression, Tumor Mutational Burden, and Response to Immunotherapy in Patients with MET Exon 14 Altered Lung Cancers. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayenga, M.; Assié, J.-B.; Monnet, I.; Massiani, M.-A.; Tabeze, L.; Friard, S.; Fraboulet, S.; Métivier, A.-C.; Chouaïd, C.; Zemoura, L.; et al. Durable Responses to Immunotherapy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers Harboring MET Exon-14-Skipping Mutation: A Series of 6 Cases. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2020, 150, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisier, F.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; Viñas, F.; Doubre, H.; Ricordel, C.; Ropert, S.; Janicot, H.; Bernardi, M.; Fournel, P.; Lamy, R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Patients With Advanced NSCLC With BRAF, HER2, or MET Mutations or RET Translocation: GFPC 01-2018. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2020, 15, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, A.; Morten, J.; Ji, Q.; Elvin, P.; Womack, C.; Su, X.; Donald, E.; Gray, N.; Read, J.; Bigley, G.; et al. A Retrospective Analysis of RET Translocation, Gene Copy Number Gain and Expression in NSCLC Patients Treated with Vandetanib in Four Randomized Phase III Studies. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, H.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, T.; Li, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. RET Fusions Define a Unique Molecular and Clinicopathologic Subtype of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4352–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, S.; Scheel, A.H.; Scheffler, M.; Schultheis, A.M.; Gautschi, O.; Aebersold, F.; Diebold, J.; Pall, G.; Rothschild, S.; Bubendorf, L.; et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics of RET Rearranged Lung Cancer in European Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Clinicopathologic Characteristics, Genetic Variability and Therapeutic Options of RET Rearrangements Patients in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2016, 101, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, A.K.; Sidorova, Y.A. RET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: Role in Neurodegeneration, Obesity, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzbauer, P.T.; Lampe, P.A.; Heuckeroth, R.O.; Golden, J.P.; Creedon, D.J.; Johnson, E.M.; Milbrandt, J. Neurturin, a Relative of Glial-Cell-Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Nature 1996, 384, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, M.L.; Molliver, D.C.; Osborne, P.A.; Vejsada, R.; Golden, J.P.; Lampe, P.A.; Kato, A.C.; Milbrandt, J.; Johnson, E.M. Analysis of the Retrograde Transport of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF), Neurturin, and Persephin Suggests That in Vivo Signaling for the GDNF Family Is GFRalpha Coreceptor-Specific. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 9322–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloh, R.H.; Tansey, M.G.; Lampe, P.A.; Fahrner, T.J.; Enomoto, H.; Simburger, K.S.; Leitner, M.L.; Araki, T.; Johnson, E.M.; Milbrandt, J. Artemin, a Novel Member of the GDNF Ligand Family, Supports Peripheral and Central Neurons and Signals through the GFRalpha3-RET Receptor Complex. Neuron 1998, 21, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Chai, S.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Si, J.; Huang, F.; et al. KIF5B-RET Fusion Kinase Promotes Cell Growth by Multilevel Activation of STAT3 in Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, W.; Hutchinson, K.E. Chipping Away at the Lung Cancer Genome. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipson, D.; Capelletti, M.; Yelensky, R.; Otto, G.; Parker, A.; Jarosz, M.; Curran, J.A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Bloom, T.; Brennan, K.W.; et al. Identification of New ALK and RET Gene Fusions from Colorectal and Lung Cancer Biopsies. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, H.; Jung, Y.J.; Kang, H.W.; Park, I.-K.; Kang, C.-H.; Lee, J.W.; Ju, Y.S.; Seo, J.-S.; Chung, D.H.; Kim, Y.T. Diagnostic Method for the Detection of KIF5B-RET Transformation in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2013, 82, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukami, T.; Shiraishi, K.; Shimada, Y.; Ogiwara, H.; Tsuta, K.; Ichikawa, H.; Sakamoto, H.; Kato, M.; Shibata, T.; Nakano, T.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Oncogenic RET Fusion in Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2014, 9, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuta, K.; Kohno, T.; Yoshida, A.; Shimada, Y.; Asamura, H.; Furuta, K.; Kushima, R. RET-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Clinicopathological and Molecular Analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoh, K.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Nishio, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, H.; Nogami, N.; Matsumoto, S.; Kohno, T.; Tsuta, K.; et al. Vandetanib in Patients with Previously Treated RET-Rearranged Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (LURET): An Open-Label, Multicentre Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Velcheti, V.; Reckamp, K.L.; Nokihara, H.; Sachdev, P.; Kubota, T.; Nakada, T.; Dutcus, C.E.; Ren, M.; Tamura, T. A Phase 2 Study of Lenvatinib in Patients with RET Fusion-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2019, 138, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiike, A.; Takeuchi, K.; Uenami, T.; Kawano, Y.; Tanimoto, A.; Kaburaki, K.; Tambo, Y.; Kudo, K.; Yanagitani, N.; Ohyanagi, F.; et al. Sorafenib Treatment for Patients with RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2016, 93, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Rekhtman, N.; Arcila, M.; Wang, L.; Ni, A.; Albano, M.; Van Voorthuysen, M.; Somwar, R.; Smith, R.S.; Montecalvo, J.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced RET-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Single-Centre, Phase 2, Single-Arm Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.W.; Loong, H.H.F.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ESMO FDA Approves Pralsetinib for Lung Cancer with RET Gene Fusions. Available online: https://www.esmo.org/oncology-news/fda-approves-pralsetinib-for-lung-cancer-with-ret-gene-fusions (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- Elfving, H.; Broström, E.; Moens, L.N.J.; Almlöf, J.; Cerjan, D.; Lauter, G.; Nord, H.; Mattsson, J.S.M.; Ullenhag, G.J.; Strell, C.; et al. Evaluation of NTRK Immunohistochemistry as a Screening Method for NTRK Gene Fusion Detection in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2021, 151, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farago, A.F.; Taylor, M.S.; Doebele, R.C.; Zhu, V.W.; Kummar, S.; Spira, A.I.; Boyle, T.A.; Haura, E.B.; Arcila, M.E.; Benayed, R.; et al. Clinicopathologic Features of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring an NTRK Gene Fusion. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozono, K.; Ohishi, Y.; Onishi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Motoshita, J.; Kato, M.; Nakanishi, R.; Nakamura, M.; Oda, Y. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor/Tropomyosin-Related Kinase B Signaling Pathway Contributes to the Aggressive Behavior of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2017, 97, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, K.; Harada, T.; Wang, S.; Ijichi, K.; Furuyama, K.; Koga, T.; Okamoto, T.; Takayama, K.; Yano, T.; Nakanishi, Y. Expression of TrkB and BDNF Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2012, 78, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatalica, Z.; Xiu, J.; Swensen, J.; Vranic, S. Molecular Characterization of Cancers with NTRK Gene Fusions. Mod. Pathol. Off. J. US Can. Acad. Pathol. Inc. 2019, 32, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haratake, N.; Seto, T. NTRK Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The Diagnosis and Targeted Therapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Offin, M.; Harnicar, S.; Li, B.T.; Drilon, A. Entrectinib: An Orally Available, Selective Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of NTRK, ROS1, and ALK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummar, S.; Lassen, U.N. TRK Inhibition: A New Tumor-Agnostic Treatment Strategy. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiò, C.; Scaltriti, M.; Ladanyi, M.; Iafrate, A.J.; Bibeau, F.; Dietel, M.; Hechtman, J.F.; Troiani, T.; López-Rios, F.; Douillard, J.-Y.; et al. ESMO Recommendations on the Standard Methods to Detect NTRK Fusions in Daily Practice and Clinical Research. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, S.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; Ahn, M.-J. Evaluating Entrectinib as a Treatment Option for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Pizzutilo, E.G.; Marrapese, G.; Tosi, F.; Cerea, G.; Siena, S. Entrectinib for the Treatment of Metastatic NSCLC: Safety and Efficacy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2020, 20, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Siena, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Farago, A.F.; Blakely, C.M.; Seto, T.; Cho, B.C.; Tosi, D.; et al. Entrectinib in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic NTRK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumours: Integrated Analysis of Three Phase 1-2 Trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; DuBois, S.G.; Kummar, S.; Farago, A.F.; Albert, C.M.; Rohrberg, K.S.; van Tilburg, C.M.; Nagasubramanian, R.; Berlin, J.D.; Federman, N.; et al. Larotrectinib in Patients with TRK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumours: A Pooled Analysis of Three Phase 1/2 Clinical Trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slebos, R.J.; Kibbelaar, R.E.; Dalesio, O.; Kooistra, A.; Stam, J.; Meijer, C.J.; Wagenaar, S.S.; Vanderschueren, R.G.; van Zandwijk, N.; Mooi, W.J. K-Ras Oncogene Activation as a Prognostic Marker in Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, S.; Stevens, J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Blowers, D. Mutation Incidence and Coincidence in Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Meta-Analyses by Ethnicity and Histology (MutMap). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, S.; Shen, R.; Ang, D.C.; Johnson, M.L.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Paik, P.K.; Brzostowski, E.B.; Riely, G.J.; Kris, M.G.; Zakowski, M.F.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of EGFR and KRAS Mutations in 3,026 Lung Adenocarcinomas: Higher Susceptibility of Women to Smoking-Related KRAS-Mutant Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6169–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.; Baraibar, I.; López, I.; Nadal, E.; Rolfo, C.; Vicent, S.; Gil-Bazo, I. KRAS Oncogene in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Clinical Perspectives on the Treatment of an Old Target. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitin, N.; Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J. Signaling Interplay in Ras Superfamily Function. Curr. Biol. CB 2005, 15, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackelford, R.E.; Whitling, N.A.; McNab, P.; Japa, S.; Coppola, D. KRAS Testing: A Tool for the Implementation of Personalized Medicine. Genes Cancer 2012, 3, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralvo, J.; Friedlaender, A.; Achard, V.; Addeo, A. The Activity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in KRAS Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single Centre Experience. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2019, 16, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, B.J. Prognostic Value of KRAS Mutation in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis and Review. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 48248–48252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-Y.; Zhong, W.-Z.; Zhang, X.-C.; Su, J.; Xie, Z.; Liu, S.-Y.; Tu, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-J.; Sun, Y.-L.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Potential Predictive Value of TP53 and KRAS Mutation Status for Response to PD-1 Blockade Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Goldberg, M.E.; Greenawalt, D.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Awad, M.M.; Gainor, J.F.; Schrock, A.B.; Hartmaier, R.J.; Trabucco, S.E.; Gay, L.; et al. STK11/LKB1 Mutations and PD-1 Inhibitor Resistance in KRAS-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.S.; Fakih, M.G.; Strickler, J.H.; Desai, J.; Durm, G.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Falchook, G.S.; Price, T.J.; Sacher, A.; Denlinger, C.S.; et al. KRASG12C Inhibition with Sotorasib in Advanced Solid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.L.; Ou, S.H.I.; Barve, M.; Rybkin, I.I.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Leal, T.A.; Velastegui, K.; Christensen, J.G.; Kheoh, T.; Chao, R.C.; et al. KRYSTAL-1: Activity and Safety of Adagrasib (MRTX849) in Patients with Colorectal Cancer (CRC) and Other Solid Tumors Harboring a KRAS G12C Mutation. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 138, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puyol, M.; Martín, A.; Dubus, P.; Mulero, F.; Pizcueta, P.; Khan, G.; Guerra, C.; Santamaría, D.; Barbacid, M. A Synthetic Lethal Interaction between K-Ras Oncogenes and Cdk4 Unveils a Therapeutic Strategy for Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.W.; Mazieres, J.; Barlesi, F.; Dragnev, K.H.; Koczywas, M.; Göskel, T.; Cortot, A.B.; Girard, N.; Wesseler, C.; Bischoff, H.; et al. A Randomized Phase III Study of Abemaciclib Versus Erlotinib in Patients with Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer With a Detectable KRAS Mutation Who Failed Prior Platinum-Based Therapy: JUNIPER. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 578756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, Y. High Frequency of Mutations of the PIK3CA Gene in Human Cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffler, M.; Bos, M.; Gardizi, M.; König, K.; Michels, S.; Fassunke, J.; Heydt, C.; Künstlinger, H.; Ihle, M.; Ueckeroth, F.; et al. PIK3CA Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Genetic Heterogeneity, Prognostic Impact and Incidence of Prior Malignancies. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Cai, D.; Sun, Y.; et al. PIK3CA Mutations Frequently Coexist with EGFR/KRAS Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Suggest Poor Prognosis in EGFR/KRAS Wildtype Subgroup. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Che, G. Clinical Significance of PIK3CA Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, J.; Damianovich, M.; Hout Siloni, G.; Dar, E.; Cohen, Y.; Perelman, M.; Ben Nun, A.; Simansky, D.; Yellin, A.; Urban, D.; et al. Genetic Mutation Screen in Early Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Specimens. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.; Ayesh, H.S.K.; Halawani, H. PIK3CA Gene Mutations in Solid Malignancies: Association with Clinicopathological Parameters and Prognosis. Cancers 2019, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarris, E.G.; Saif, M.W.; Syrigos, K.N. The Biological Role of PI3K Pathway in Lung Cancer. Pharm. Basel Switz. 2012, 5, 1236–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Shcherba, M.; Pendurti, G.; Liang, Y.; Piperdi, B.; Perez-Soler, R. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway: Potential for Lung Cancer Treatment. Lung Cancer Manag. 2014, 3, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The Evolution of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinases as Regulators of Growth and Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Canon, J.-L.; De Braud, F.; Grossi, F.; De Pas, T.; Gray, J.E.; Su, W.-C.; Felip, E.; Yoshioka, H.; Gridelli, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Buparlisib (BKM120) in Patients with PI3K Pathway-Activated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results from the Phase II BASALT-1 Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2015, 10, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in Cancer: Mechanisms and Advances in Clinical Trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.C. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/MTOR Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schram, A.M.; Gandhi, L.; Mita, M.M.; Damstrup, L.; Campana, F.; Hidalgo, M.; Grande, E.; Hyman, D.M.; Heist, R.S. A Phase Ib Dose-Escalation and Expansion Study of the Oral MEK Inhibitor Pimasertib and PI3K/MTOR Inhibitor Voxtalisib in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Cohen, R.B.; Laird, A.D.; Macé, S.; Engelman, J.A.; Ruiz-Soto, R.; Rockich, K.; Xu, J.; Shapiro, G.I.; Martinez, P.; et al. Phase I Safety and Pharmacokinetic Study of the PI3K/MTOR Inhibitor SAR245409 (XL765) in Combination with Erlotinib in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Adjei, A.A.; Bahleda, R.; Besse, B.; Ferte, C.; Planchard, D.; Zhou, J.; Ware, J.; Morrissey, K.; Shankar, G.; et al. A Phase IB Dose-Escalation Study of the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Pictilisib in Combination with Either Paclitaxel and Carboplatin (with or without Bevacizumab) or Pemetrexed and Cisplatin (with or without Bevacizumab) in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 1990 2017, 86, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.; Spira, A.; Becker, D.; Evans, T.; Schnadig, I.; Camidge, D.R.; Bauman, J.E.; Hausman, D.; Walker, L.; Nemunaitis, J.; et al. A Randomized, Phase 2 Trial of Docetaxel with or without PX-866, an Irreversible Oral Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Relapsed or Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2014, 9, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, G.I.; Rodon, J.; Bedell, C.; Kwak, E.L.; Baselga, J.; Braña, I.; Pandya, S.S.; Scheffold, C.; Laird, A.D.; Nguyen, L.T.; et al. Phase I Safety, Pharmacokinetic, and Pharmacodynamic Study of SAR245408 (XL147), an Oral Pan-Class I PI3K Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; LoRusso, P.; Bahleda, R.; Lager, J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, J.; Martini, J.-F.; Macé, S.; Burris, H. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Pilaralisib (SAR245408, XL147), a Pan-Class I PI3K Inhibitor, in Combination with Erlotinib in Patients with Solid Tumors. The Oncologist 2015, 20, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, E.; Boni, V.; Heist, R.S.; Matulonis, U.; Janne, P.A.; Hamid, O.; Holgado, E.; Ordoñez, J.M.; Nunez, J.; Ugrenovic, M.; et al. 1230PD—Phase 1B Study of Oral Dual-Pi3K/Mtor Inhibitor Gdc-0980 in Combination with Carboplatin (Carbo)/Paclitaxel (Pac) ± Bevacizumab (Bev) and Cisplatin (Cis)/Pemetrexed (Pem) in Patients (Pts) with Advanced Solid Tumors and Nsclc. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iv429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Langer, C.J.; Redman, M.W.; Wade, J.L.; Aggarwal, C.; Bradley, J.D.; Crawford, J.; Stella, P.J.; Knapp, M.H.; Miao, J.; Minichiello, K.; et al. SWOG S1400B (NCT02785913), a Phase II Study of GDC-0032 (Taselisib) for Previously Treated PI3K-Positive Patients with Stage IV Squamous Cell Lung Cancer (Lung-MAP Sub-Study). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Chaft, J.E.; Nafa, K.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S.; Lau, C.; Zaidinski, M.; Paik, P.K.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. Prevalence, Clinicopathologic Associations, and Molecular Spectrum of ERBB2 (HER2) Tyrosine Kinase Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4910–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Shiraishi, K.; Yoshida, A.; Shimada, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Asamura, H.; Furuta, K.; Kohno, T.; Tsuta, K. HER2 Gene Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas: Concurrence with Her2 Gene Amplification and Her2 Protein Expression and Phosphorylation. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2015, 87, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Vijayan, R.S.K.; Nilsson, M.B.; Hu, L.; He, J.; Zhang, F.; Pisegna, M.; Poteete, A.; Sun, H.; et al. Pan-Cancer Landscape and Analysis of ERBB2 Mutations Identifies Poziotinib as a Clinically Active Inhibitor and Enhancer of T-DM1 Activity. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris, M.G.; Johnson, B.E.; Berry, L.D.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Iafrate, A.J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Franklin, W.A.; Aronson, S.L.; Su, P.-F.; et al. Using Multiplexed Assays of Oncogenic Drivers in Lung Cancers to Select Targeted Drugs. JAMA 2014, 311, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Ross, D.S.; Aisner, D.L.; Chaft, J.E.; Hsu, M.; Kako, S.L.; Kris, M.G.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Arcila, M.E. HER2 Amplification and HER2 Mutation Are Distinct Molecular Targets in Lung Cancers. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Nafa, K.; Chaft, J.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Lau, C.; Reva, B.A.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, Molecular Heterogeneity, and Clinicopathologic Characteristics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Meng, Z.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Guan, D.; Liang, C.; Zhou, J.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G. Molecular Mechanisms and Translational Therapies for Human Epidermal Receptor 2 Positive Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.-W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.-C.; Yang, J.-J.; Chen, Z.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Zhou, Q. Mutational Landscape and Characteristics of ERBB2 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.S.; Zehir, A.; Cheng, D.T.; Benayed, R.; Nafa, K.; Hechtman, J.F.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Weigelt, B.; Razavi, P.; Hyman, D.M.; et al. Next-Generation Assessment of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (ERBB2) Amplification Status: Clinical Validation in the Context of a Hybrid Capture-Based, Comprehensive Solid Tumor Genomic Profiling Assay. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budiarto, B.R. Desriani Dataset Reporting Detection of Breast Cancer-Related HER2I655V Polymorphism Using Allele-Specific Polymerase Chain Reaction. Data Brief 2016, 9, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imyanitov, E.N.; Iyevleva, A.G.; Levchenko, E.V. Molecular Testing and Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Vijver, M. Emerging Technologies for HER2 Testing. Oncology 2002, 63 (Suppl. 1), 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, G.; Evers, K.; Papadopoulos, S.; Ebert, A.; Bühler, H. Current Use of HER2 Tests. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2001, 12, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Mao, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, K.; Ma, R.; Wu, J.; Cao, H. Next-generation Sequencing-based Detection of EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, PIK3CA, Her-2 and TP53 Mutations in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2191–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, E.F.; Nakagawa, K.; Nagasaka, M.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Li, B.T.; Murakami, H.; Barlesi, F.; Saltos, A.; Perol, M.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (T-DXd; DS-8201) in Patients With HER2-Mutated Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Interim Results of DESTINY-Lung0. 5. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, K.; Bang, Y.-J.; Iwasa, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Ryu, M.-H.; Sakai, D.; Chung, H.-C.; Kawakami, H.; Yabusaki, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Cornelissen, R.; Garassino, M.C.; Clarke, J.; Tchekmedyian, N.; Molina, J.; Goldman, J.W.; Bhat, G.; Lebel, F.; Le, X. LBA60 ZENITH20, a Multinational, Multi-Cohort Phase II Study of Poziotinib in NSCLC Patients with EGFR or HER2 Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prelaj, A.; Bottiglieri, A.; Proto, C.; Lo Russo, G.; Signorelli, D.; Ferrara, R.; Galli, G.; Toma, A.; Viscardi, G.; Brambilla, M.; et al. 1388P Poziotinib in Advanced NSCLC with EGFR or HER2 Exon 20 Insertion Mutation: Initial Results from a Single Site Expanded Access Program. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Qin, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Rivard, C.; Gao, G.; Ng, T.L.; Tu, M.M.; et al. HER2 Exon 20 Insertions in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Are Sensitive to the Irreversible Pan-HER Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Pyrotinib. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fang, J.; Chen, G.; et al. Single-Arm, Phase II Study of Pyrotinib in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients with HER2 Exon 20 Mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Neal, J.W.; Camidge, D.R.; Spira, A.I.; Piotrowska, Z.; Horn, L.; Costa, D.B.; Tsao, A.S.; Patel, J.D.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Antitumor Activity of TAK-788 in NSCLC with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadziuszko, R.; Smit, E.F.; Dafni, U.; Wolf, J.; Wasąg, B.; Biernat, W.; Finn, S.P.; Kammler, R.; Tsourti, Z.; Rabaglio, M.; et al. Afatinib in NSCLC With HER2 Mutations: Results of the Prospective, Open-Label Phase II NICHE Trial of European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP). J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2019, 14, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Aoe, K.; Kozuki, T.; Ohashi, K.; Ninomiya, K.; Ichihara, E.; Kubo, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Chikamori, K.; Harada, D.; et al. A Phase II Study of Trastuzumab Emtansine in HER2-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, I.; Goda, T.; Watanabe, K.; Maemondo, M.; Oizumi, S.; Amano, T.; Hatanaka, Y.; Matsuno, Y.; Nishihara, H.; Asahina, H.; et al. A Phase II Study of Trastuzumab Monotherapy in Pretreated Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers (NSCLCs) Harboring HER2 Alterations: HOT1303-B Trial. Ann Oncol 2018, 29, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Velden, D.L.; van Herpen, C.M.L.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Willems, S.M.; Nederlof, P.M.; Langenberg, M.H.G.; Cuppen, E.; Sleijfer, S.; et al. Molecular Tumor Boards: Current Practice and Future Needs. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, 3070–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Drug | Trial | Phase | Therapy Line * | N pts | Main Results | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multikinase inhibitors | ||||||
| Crizotinib | PROFILE-1001 (NCT00585195) | I | 1L ≥2L | Tot 69 26 in 1L 43 in ≥2L | ORR tot = 32% ORR 1L = 25% ORR 2L = 37% mDOR = 9.1 mo mPFS = 7.3 mo mOS = 20.5 mo | Closed FDA-Approved |
| AcSé trial (NCT02034981) | II | ≥1L | 25 | ORR = 40% mDOR = 2.4 mo mPFS = 3.6 mo mOS = 9.5 mo | Closed | |
| METROS (NCT02499614) | II | ≥2L | 9 | ORR = 20% mDOR = NE mPFS = 2.6 mo mOS = 3.8 mo | Closed | |
| MET-specific TKI | ||||||
| Capmatinib | GEOMETRY-mono-1 (NCT02414139) | II | 1L 2L,3L | 28 in 1L | ORR = 68% mDOR = 12.6 mo mPFS = 12.4 mo | Ongoing FDA-Approved |
| 69 in 2L,3L | ORR = 41% mDOR = 9.7 mo mPFS = 5.4 mo | |||||
| Tepotinib | VISION (NCT02864992) | II | 1L,2L,3L | 66 diagnosed with LBx | ORR = 48% mDOR = 9.9 mo mPFS = 8.5 mo | Ongoing (preliminary data) FDA breakthrough designation |
| 60 diagnosed with TBx | ORR = 50% mDOR = 15.7 mo mPFS = 11.0 mo | |||||
| 99 diagnosed with LBx + TBx | ORR = 46% mDOR = 11.1 mo mPFS = 8.5 mo | |||||
| Savolitinib | NCT02897479 | II | ≥2L | 70 | ORR = 47.5% mDOR = NR mPFS = 6.8 mo | Ongoing |
| Drug | Trial | Phase | Therapy Line * | Prior Treatment | Treatment Arm | N pts | Main Results | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single agent | ||||||||
| Capmatinib | GEOMETRY -mono-1 (NCT02414139) | II | ≥2L | NA | Capmatinib | 69 | ORR = 29% mDOR = 8.3 mo mPFS = 4.1 mo | Ongoing |
| Combinations | ||||||||
| Tepotinib | INSIGH (NCT01982955) | Ib/II | 2L | 1G-2G EGFR-TKIs | Tepotinib + Gefitinib vs. Platinum-based CT | 19 | ORR = 67% vs. 43% mPFS = 16.6 vs. 4.2 mo mOS = 37.3 vs. 13.1 mo | Closed |
| Capmatinib | NCT01610336 | II | 2L | Gefitinib/ Erlotinib | Capmatinib + Gefitinib | 100 | ORR = 47% | Closed |
| Cabozantinib | NCI 9303 II (NCT01866410) | II | ≥2L | 1G, 2G, 3G EGFR-TKIs | Cabozantinib + Erlotinib | 37 | ORR = 10.8% mPFS = 3.6 mo mOS = 13.1 mo | Closed |
| Drug | Trial | Phase | Therapy Line * | N pts | Main Results | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selpercatinib | LIBRETTO-001 (NCT03157128) | II | ≥1L | 39 in 1L | ORR = 85% 1y-PFS = 75% | Closed FDA approved |
| 105 in ≥2L | ORR = 64% mDOR = 17.5 mo mPFS = 16.5 mo 1yPFS = 66% | |||||
| Pralsetinib | ARROW (NCT03037385) | I/II | ≥1L | 79 | ORR = 56% | Ongoing FDA approved |
| Vandetanib | LURET (UMIN000010095 **) | II | ≥2L | 19 | ORR = 53% | Ongoing (preliminary data) |
| Lenvatinib | NCT01877083 | II | ≥1L | 25 | ORR = 16% | Ongoing (preliminary data) |
| Sorafenib | 000007515 ** | II | ≥2L | 3 | ORR = 0% | Closed |
| Cabozantinib | NCT01639508 | II | ≥1L | 26 | ORR = 28% mDOR = 7 mo mPFS = 5.5 mo mOS = 9.9 mo | Closed |
| Drug | Trial | Phase | Therapy Line * | N pts | Main Results | Status *** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entrectinib | ALKA-372-001 (EudraCT2012–000148–88) | I | Any | 10 ** | ORR = 70% mDOR = 12.9 mo mPFS = 14.9 mo mOS = 23.9 mo | Closed |
| STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) | I | Any | Closed | |||
| STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267) | II | Any | Ongoing | |||
| Larotrectinib | LOXO-TRK-14001 (NCT02122913) | I | Any | 12 ** | ORR = 75% mDOR = NE mPFS = 28.3 mo mOS = 44.4 mo | Closed |
| LOXO-TRK-15003 (NCT02637687) | I/II | Any | Ongoing | |||
| NAVIGATE (NCT02576431) | II | Any | Ongoing |
| Drug | Trial | Phase | Therapy Line * | Treatment Arm | N pts | Main Results | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targeting KRAS pathway | |||||||
| Selumetinib (MAPK inhibitor) | SELECT-1 (NCT01933932) | III | 2L | Selumetinib + Docetaxel vs. Placebo + Docetaxel | 510 | mPFS = 3.9 vs. 2.8 mo mOS = 8.7 vs. 7.9 mo ORR = 20.1% vs. 13.7% mDOR = 2.9 vs. 4.5 mo | Closed |
| IND.219 (NCT02337530) | II | 1L | ARM A: Salumetinib intermittent + Pemetrexed/Platinum | 20 | ORR = 35% mPFS = 7.5 mo | Closed | |
| ARM B: Salumetinib continuous + Pemetrexed/Platinum | 21 | ORR = 62% mPFS = 6.7 mo | |||||
| ARM C: Pemetrexed/Platinum | 21 | ORR = 24% mPFS = 4.0 mo | |||||
| Trametinib (MEK 1-2 inhibitor) | NCT01362296 | II | ≥2L | Trametinib vs. Docetaxel | 134 | mPFS = 12 vs. 11 weeks mOS = 8 mo vs. NR ORR = 12% vs. 12% | Closed |
| Momelotinib (JAK1-2 inhibitor) | NCT02258607 | Ib | ≥2L | Momelotinib + Trametinib | 21 | ORR = NR DCR = 57.1% mPFS = 3.6 mo mOS = 7.4 mo | Closed |
| Defactinib (FAK inhibitor) | NCT01951690 | II | ≥2L | Defactinib | 55 | 12wks-PFS = 28% | Closed |
| Targeting KRAS G12C | |||||||
| Sotorasib (AMG510) | CODEBREAK 100 (NCT03600883) | I/II | ≥2L | Sotorasib | 129 (59 NSCLC) | ORR = 32.2% DCR = 88.1% mPFS = 6.3 mo | Ongoing |
| Adagrasib (MRTX849) | KRYSTAL-1 (NCT03785249) | I/II | ≥1L | Adagrasib | 110 (79 NSCLC) | ORR = 45% DCR = 96% | Ongoing |
| Targeting CDK 4/6 | |||||||
| Abemaciclib (LY2835219) | JUNIPER (NCT02152631) | III | ≥2L | Abemaciclib vs Erlotinib | 453 | mOS = 7.4 vs. 7.8 mo mPFS = 3.6 vs. 1.9 mo ORR = 8.9% vs. 2.7% DCR = 54.5% vs. 31.7% | Ongoing |
| Drug | Trial | Phase | Therapy Line | Treatment Arms *** | N pts | Main Results | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selective PI3K inhibitor (anti p110α) | |||||||
| GDC-0032 (Taselisib) | Lung-MAP sub-study (NCT02785913) | II | ≥2L * | Taselisib | 26 Sq | ORR = 4.8% mPFS = 2.9 mo mOS = 5.9 mo | Closed at futility analysis |
| Pan-PI3K inhibitor | |||||||
| BKM120 (Buparlisib) | BASALT-1 (NCT01297491) | II | ≥2L * | Buparlisib | 30 Sq 33 Nsq | 12 wks PFS = Sq 23.3%, Nsq 20.0% mOS = Sq 7.98 mo, Nsq 7.2 mo ORR = 3.3% Sq, 3.0% Nsq | Closed at futility analysis |
| BASALT-2 (NCT01820325) | Ib/II | 1L | Buparlisib + CBDCA + paclitaxel | 6 Sq | ORR = 16.7% | Early study termination | |
| BASALT-3 (NCT01911325) | Ib/II | ≥2L * | Buparlisib + docetaxel | 27 Sq | ORR 80 mg/daily = 6% ORR 100 mg/daily = 18% | Early study termination | |
| NCT01487265 | II | ≥2L ** | Buparlisib + erlotinib | 37 | 3 mo PFS = 50.4% mOS = 12.2 ORR = 5.4% | Completed | |
| XL765 (SAR245409, Voxtalisib) | NCT01390818 | Ib | Any line | Voxtalisib + pimasertib (MEK inhibitor) | Advanced solid tumors (33 NSCLC) | ORR = 5% | Completed |
| NCT00777699 | I | ≥2L ** | Voxtalisib + erlotinib | Advanced solid tumors (37 NSCLC) | SD as best response | Completed | |
| PX-866 | NCT01204099 | II | 2L-3L | Docetaxel + PX-866 vs. docetaxel | 95 | ORR = 6% vs. 0%, p = 0.12 mPFS = 2.0 vs. 2.9 mo, p = 0.65 mOS = 7.9 vs. 9.4 mo, p = 0.9 | Completed |
| XL147 (SAR245408) | NCT01392924 | I | Further lines | XL147 | Advanced solid tumors (24 NSCLC) | ORR = 16.7% | Completed |
| NCT00692640 | I | ≥2L ** | XL147 + erlotinib | Advanced solid tumors (20 NSCLC) | ORR = 3.7% DCR = 51.9% | Completed | |
| GDC-0941 (Pictilisib) | NCT01458067 | Ib | 1L | Arm A: pictilisib + CBDCA + paclitaxel Arm B: CBDCA + paclitaxel + bevacizumab Arm C: CDDP + pemetrexed + bevacizumab Arm D: CDDP + pemetrexed | 66 | ORR = 43.9% | Completed |
| Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor | |||||||
| GDC-0980 (Apitolisib) | NCT01301716 | Ib | 1L | Arm A: apitolisib + CBDCA + paclitaxel ARM B: CBDCA + paclitaxel + bevacizumab Arm C: CDDP + pemetrexed | Advanced solid tumors (39 NSCLC) | ORR = 64% | Completed |
| Drug | Trial | Phase | Therapy Line * | N pts | Main Results | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) | DESTINY-Lung01 (NCT03505710) | II | ≥2L | 42 (HER2exp, HER2mut) | ORR = 61.9% mPFS = 14 mo | Ongoing |
| Poziotinib | ZENITH20-2 (NCT03318939) | II | ≥2L | 90 (HER2mut) | ORR = 27.8% mPFS = 5.5 mo | Ongoing |
| Afatinib | NICHE (NCT02369484) | II | ≥2L | 13 (HER2mut) | ORR = 7.7% mPFS = 15.9 wks mOS = 56 wks | Completed |
| Pyrotinib | NCT02834936 | II | ≥2L | 60 (HER2mut) | ORR = 31.7% mPFS = 6.8 mo mOS = NA | Unknown |
| Mobocertinib (TAK-788) | NCT02716116 | I/II | ≥1L | 57 (EGFR exon20ins = 39 HER2 mut = 13) | NA | Ongoing |
| Trastuzumab Emtansine | NCT02675829 | II | ≥1L | 18 (HER2 mut) | ORR = 44% mPFS = 5 mo | Ongoing |
| Trastuzumab | HOT1303-B (UMIN000012551) | II | ≥2L | 10 (HER2exp, HER2mut) | ORR = 0% mPFS = 5.2 mo | Completed |
| Dacomitinib | NCT00818441 | II | ≥2L | 26 | ORR = 12% mPFS = 3 mo mOS = 9 mo | Completed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebuzzi, S.E.; Zullo, L.; Rossi, G.; Grassi, M.; Murianni, V.; Tagliamento, M.; Prelaj, A.; Coco, S.; Longo, L.; Dal Bello, M.G.; et al. Novel Emerging Molecular Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052625
Rebuzzi SE, Zullo L, Rossi G, Grassi M, Murianni V, Tagliamento M, Prelaj A, Coco S, Longo L, Dal Bello MG, et al. Novel Emerging Molecular Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052625
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebuzzi, Sara Elena, Lodovica Zullo, Giovanni Rossi, Massimiliano Grassi, Veronica Murianni, Marco Tagliamento, Arsela Prelaj, Simona Coco, Luca Longo, Maria Giovanna Dal Bello, and et al. 2021. "Novel Emerging Molecular Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052625
APA StyleRebuzzi, S. E., Zullo, L., Rossi, G., Grassi, M., Murianni, V., Tagliamento, M., Prelaj, A., Coco, S., Longo, L., Dal Bello, M. G., Alama, A., Dellepiane, C., Bennicelli, E., Malapelle, U., & Genova, C. (2021). Novel Emerging Molecular Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052625









