Targeting GRK5 for Treating Chronic Degenerative Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
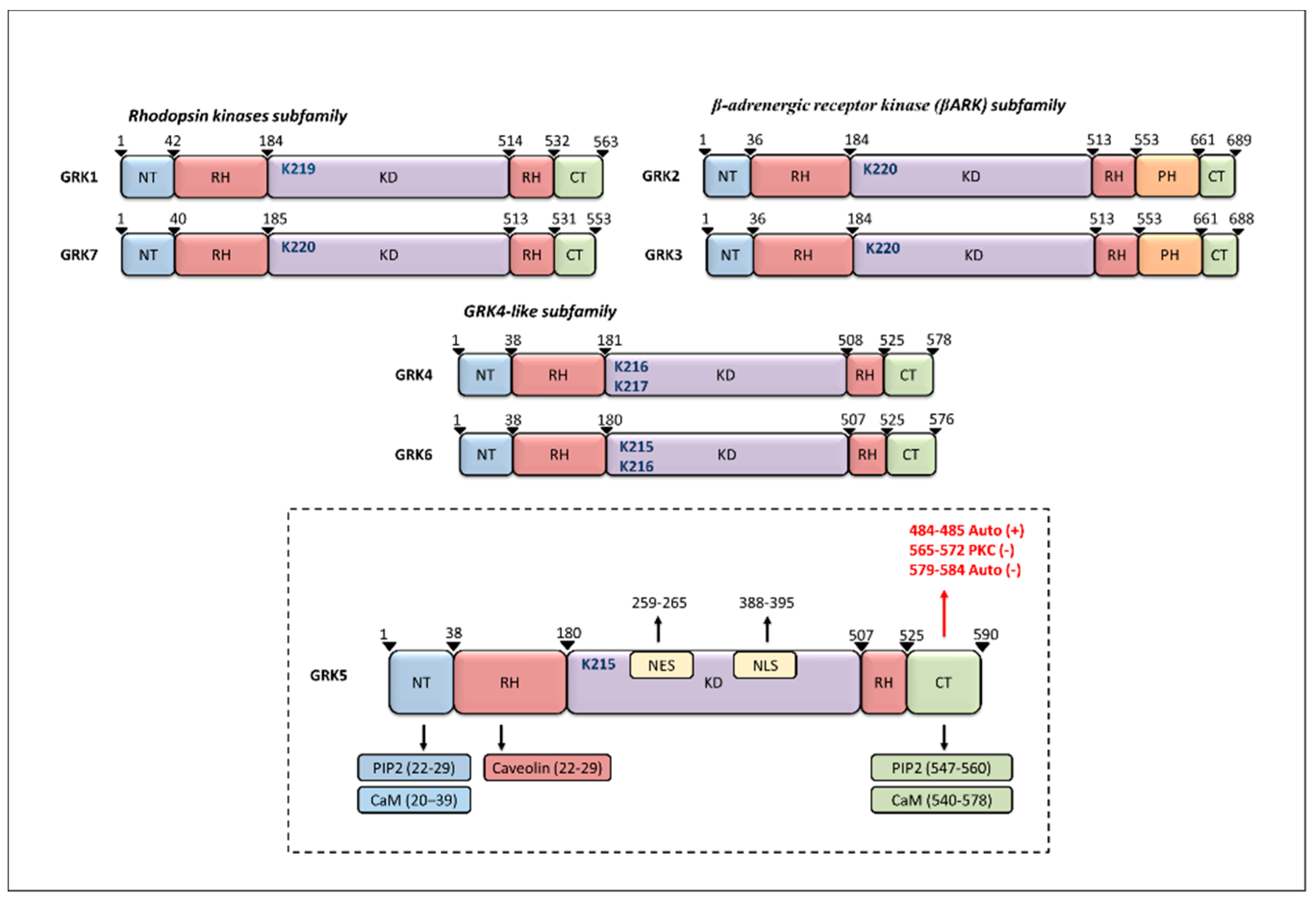
2. GRK5 Structure
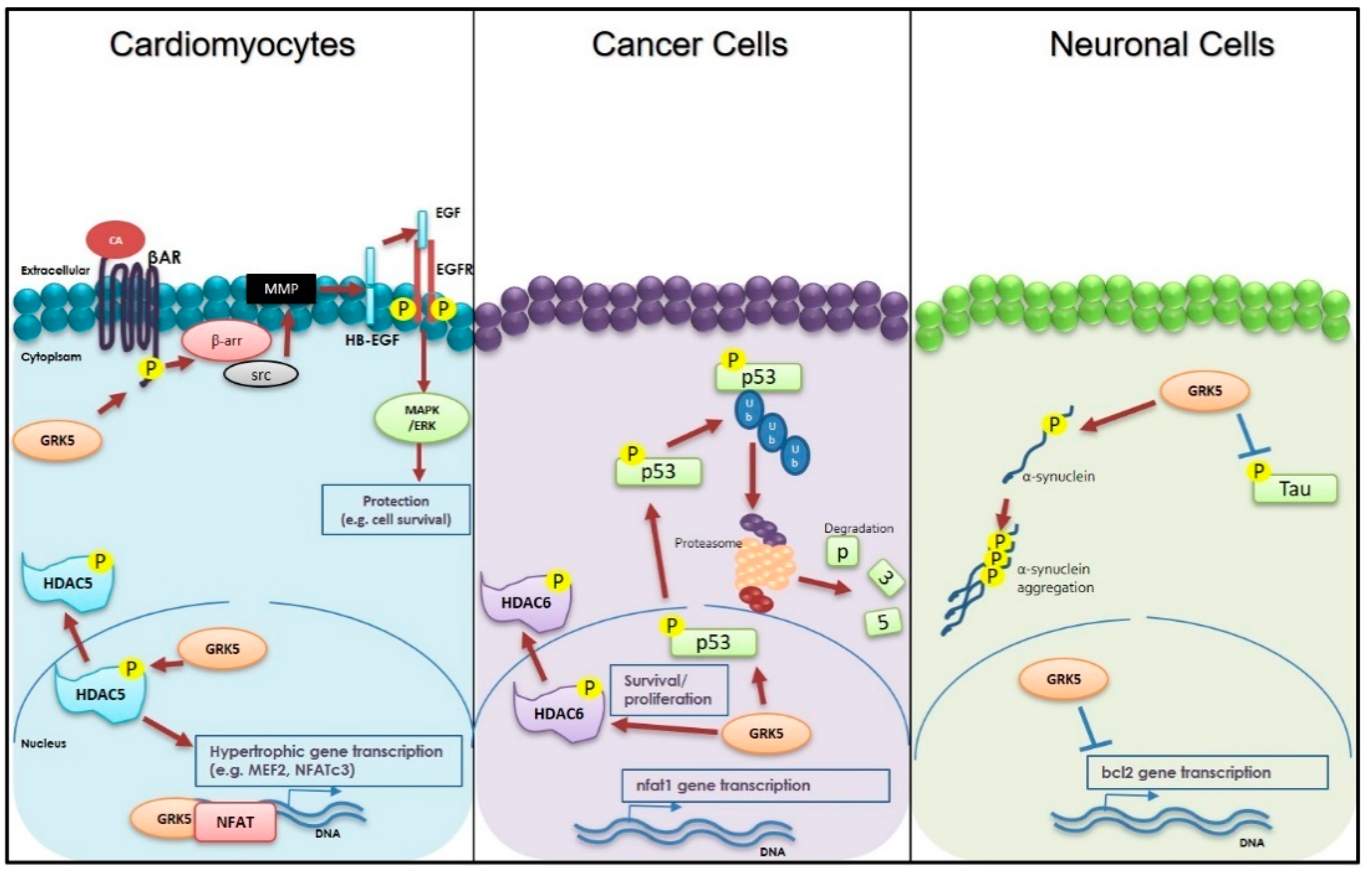
3. Cardiac Roles of GRK5
4. GRK5 and Neurodegenerative Diseases
5. GRK5 and Cancer
6. Targeting GRK5 as a Therapeutic Strategy for Chronic-Degenerative Disease
7. Conclusive Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferguson, S.S. Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: The role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierce, K.L.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Classical and new roles of β-arrestins in the regulation of G-PROTEIN-COUPLED receptors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, K.; Nakaya, M.; Kurose, H. Multiple functions of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J. Mol. Signal. 2014, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavo, A.; Komici, K.; Bencivenga, L.; D’Amico, M.L.; Gambino, G.; Liccardo, D.; Ferrara, N.; Rengo, G. GRK2 as a therapeutic target for heart failure. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premont, R.T.; Inglese, J.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Protein kinases that phosphorylate activated G protein-coupled receptors. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, P.Y.; Chuprun, J.K.; Schwartz, M.; Koch, W.J. The Evolving Impact of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinases in Cardiac Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 377–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, S.M.; Koch, W.J. Noncanonical Roles of G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinases in Cardiovascular Signaling. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 70, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.R.; Raman, D.; Shirakawa, S.; Ducceschi, M.H.; Bertram, P.T.; Wong, F.; Kraft, T.W.; Osawa, S. The cloning of GRK7, a candidate cone opsin kinase, from cone- and rod-dominant mammalian retinas. Mol. Vis. 1998, 4, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, E.R.; Ducceschi, M.H.; Horner, T.J.; Li, A.; Craft, C.M.; Osawa, S. Species-Specific Differences in Expression of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase (GRK) 7 and GRK1 in Mammalian Cone Photoreceptor Cells: Implications for Cone Cell Phototransduction. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9175–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premont, R.T.; Macrae, A.D.; Stoffel, R.H.; Chung, N.; Pitcher, J.A.; Ambrose, C.; Inglese, J.; Macdonald, M.E.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Characterization of the G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase GRK4. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 6403–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virlon, B.; Firsov, D.; Cheval, L.; Reiter, E.; Troispoux, C.; Guillou, F.; Elalouf, J.-M. Rat G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase GRK4: Identification, Functional Expression, and Differential Tissue Distribution of Two Splice Variants. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallese, M.; Salvatore, L.; D’Urbano, E.; Sala, G.; Storto, M.; Launey, T.; de Blasi, A.; Nicoletti, F.; Knopfel, T. The G-protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK4 mediates homologous desensitization of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, R.A.; Sanada, H.; Xu, J.; Yu, P.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Watanabe, H.; Asico, L.D.; Wang, W.; Zheng, S.; Yamaguchi, I.; et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 gene variants in human essential hypertension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3872–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenninkmeijer, C.B.; Price, S.A.; Bernal, A.L.; Phaneuf, S. Expression of G-protein-coupled receptor kinases in pregnant term and non-pregnant human myometrium. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 162, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunapuli, P.; Benovic, J.L. Cloning and expression of GRK5: A member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5588–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.R.; Robinson, J.D.; Lester, K.N.; Pitcher, J.A. Distinct Structural Features of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 (GRK5) Regulate Its Nuclear Localization and DNA-Binding Ability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesmer, V.M.; Kawano, T.; Shankaranarayanan, A.; Kozasa, T.; Tesmer, J.J.G. Snapshot of Activated G Proteins at the Membrane: The G q-GRK2-G Complex. Science 2005, 310, 1686–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglese, J.; Freedman, N.; Koch, W.; Lefkowitz, R. Structure and mechanism of the G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23735–23738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, A.; Santulli, G.; Sorriento, D.; Cipolletta, E.; Garbi, C.; Dorn, G.W.; Trimarco, B.; Feliciello, A.; Iaccarino, G. Mitochondrial localization unveils a novel role for GRK2 in organelle biogenesis. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Sato, P.Y.; Chuprun, J.K.; Peroutka, R.J.; Otis, N.J.; Ibetti, J.; Pan, S.; Sheu, S.-S.; Gao, E.; Koch, W.J.; et al. Prodeath signaling of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in cardiac myocytes after ischemic stress occurs via extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent heat shock protein 90-mediated mitochondrial targeting. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siderovski, D.P.; Hessel, A.; Chung, S.; Mak, T.W.; Tyers, M. A new family of regulators of G-protein-coupled receptors? Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, C.; Penela, P.; Murga, C.; Salcedo, A.; García-Hoz, C.; Jurado-Pueyo, M.; Aymerich, I.; Mayor, F. The G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) interactome: Role of GRKs in GPCR regulation and signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglese, J.; Koch, W.J.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Isoprenylation in regulation of signal transduction by G-protein-coupled receptor kinases. Nat. Cell Biol. 1992, 359, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, J.A.; Inglese, J.; Higgins, J.B.; Arriza, J.L.; Casey, P.J.; Kim, C.; Benovic, J.L.; Kwatra, M.M.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Role of beta gamma subunits of G proteins in targeting the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase to membrane-bound receptors. Science 1992, 257, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, W.; Inglese, J.; Stone, W.; Lefkowitz, R. The binding site for the beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins on the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8256–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb-Burman, S.K.; Ptasienski, J.; Benovic, J.L.; Hosey, M.M. G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase GRK2 Is a Phospholipid-dependent Enzyme That Can Be Conditionally Activated by G Protein βγ Subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22552–22562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, R.H.; Randall, R.R.; Premont, R.T.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Inglese, J. Palmitoylation of G protein-coupled receptor kinase, GRK6. Lipid modification diversity in the GRK family. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27791–27794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Benovic, J.L.; Wedegaertner, P.B. Plasma Membrane and Nuclear Localization of G Protein–coupled Receptor Kinase 6A. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2960–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiyagarajan, M.M.; Stracquatanio, R.P.; Pronin, A.N.; Evanko, D.S.; Benovic, J.L.; Wedegaertner, P.B. A Predicted Amphipathic Helix Mediates Plasma Membrane Localization of GRK5. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17989–17995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunapuli, P.; Gurevich, V.; Benovic, J. Phospholipid-stimulated autophosphorylation activates the G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK5. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10209–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Glukhova, A.; Sobczyk-Kojiro, K.; Mosberg, H.I.; Tesmer, J.J.G.; Chen, Z. Unveiling the Membrane-Binding Properties of N-Terminal and C-Terminal Regions of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 by Combined Optical Spectroscopies. Langmuir 2014, 30, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Glukhova, A.; Tesmer, J.J.G.; Chen, Z. Membrane Orientation and Binding Determinants of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 as Assessed by Combined Vibrational Spectroscopic Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pronin, A.N.; Satpaev, D.K.; Slepak, V.Z.; Benovic, J.L. Regulation of G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinases by Calmodulin and Localization of the Calmodulin Binding Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18273–18280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penela, P.; Ribas, C.; Mayor, F. Mechanisms of regulation of the expression and function of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Cell. Signal. 2003, 15, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronin, A.N.; Carman, C.V.; Benovic, J.L. Structure-Function Analysis of G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase-5. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31510–31518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, C.V.; Lisanti, M.P.; Benovic, J.L. Regulation of G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinases by Caveolin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8858–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.R.; Scott, M.G.H.; Pitcher, J.A. G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 Contains a DNA-Binding Nuclear Localization Sequence. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 10169–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynham, C.J.; Hullmann, J.; Koch, W.J. Canonical and non-canonical actions of GRK5 in the heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 92, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambardella, J.; Franco, A.; del Giudice, C.; Fiordelisi, A.; Cipolletta, E.; Ciccarelli, M.; Trimarco, B.; Iaccarino, G.; Sorriento, D. Dual role of GRK5 in cancer development and progression. Transl. Med. UniSa 2016, 14, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickx, J.O.; van Gastel, J.; Leysen, H.; Santos-Otte, P.; Premont, R.T.; Martin, B.; Maudsley, S. GRK5—A Functional Bridge Between Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavo, A.; Liccardo, D.; Koch, W.J. Targeting cardiac β-adrenergic signaling via GRK2 inhibition for heart failure therapy. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockman, H.A.; Choi, D.J.; Rahman, N.U.; Akhter, S.A.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Koch, W.J. Receptor-specific in vivo desensitization by the G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9954–9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaccarino, G.; Barbato, E.; Cipolletta, E.; de Amicis, V.; Margulies, K.B.; Leosco, D.; Trimarco, B.; Koch, W.J. Elevated myocardial and lymphocyte GRK2 expression and activity in human heart failure. Eur. Hear. J. 2005, 26, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüero, J.; Almenar, L.; Montó, F.; Oliver, E.; Sánchez-Lázaro, I.; Vicente, D.; Martínez-Dolz, L.; D’Ocon, P.; Rueda, J.; Salvador, A. Myocardial G Protein Receptor–Coupled Kinase Expression Correlates With Functional Parameters and Clinical Severity in Advanced Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2012, 18, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimiri, N.; Muiya, P.; Andres, E.; Al-Halees, Z. Differential functional expression of human myocardial G protein receptor kinases in left ventricular cardiac diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 489, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzimiri, N.; Basco, C.; Moorji, A.; Afrane, B.; Al-Halees, Z. Characterization of Lymphocyte beta2-Adrenoceptor Signalling In Patients With Left Ventricular Volume Overload Disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, J.S.; Raake, P.; Vinge, L.E.; DeGeorge, B.R.; Chuprun, J.K.; Harris, D.M.; Gao, E.; Eckhart, A.D.; Pitcher, J.A.; Koch, W.J. Uncovering G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 as a histone deacetylase kinase in the nucleus of cardiomyocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12457–12462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.I.; Gao, E.; Shang, X.; Premont, R.T.; Koch, W.J. Determining the Absolute Requirement of G Protein–Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 for Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggett, S.B.; Cresci, S.; Kelly, R.J.; Syed, F.M.; Matkovich, S.J.; Hahn, H.S.; Diwan, A.; Martini, J.S.; Sparks, L.; Parekh, R.R.; et al. A GRK5 polymorphism that inhibits β-adrenergic receptor signaling is protective in heart failure. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noma, T.; Lemaire, A.; Prasad, S.V.N.; Barki-Harrington, L.; Tilley, D.G.; Chen, J.; Le Corvoisier, P.; Violin, J.D.; Wei, H.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; et al. β-Arrestin–mediated β1-adrenergic receptor transactivation of the EGFR confers cardioprotection. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, E.V.; Tesmer, J.J.G.; Mushegian, A.; Gurevich, V.V. G protein-coupled receptor kinases: More than just kinases and not only for GPCRs. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 40–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullmann, J.; Traynham, C.J.; Coleman, R.C.; Koch, W.J. The expanding GRK interactome: Implications in cardiovascular disease and potential for therapeutic development. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 110, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynham, C.J.; Cannavo, A.; Zhou, Y.; Vouga, A.G.; Woodall, B.P.; Hullmann, J.; Ibetti, J.; Gold, J.I.; Chuprun, J.K.; Gao, E.; et al. Differential Role of G Protein–Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 in Physiological Versus Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.I.; Martini, J.S.; Hullmann, J.; Gao, E.; Chuprun, J.K.; Lee, L.; Tilley, D.G.; Rabinowitz, J.E.; Bossuyt, J.; Bers, D.M.; et al. Nuclear Translocation of Cardiac G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 Downstream of Select Gq-Activating Hypertrophic Ligands Is a Calmodulin-Dependent Process. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hullmann, J.E.; Grisanti, L.A.; Makarewich, C.A.; Gao, E.; Gold, J.I.; Chuprun, J.K.; Tilley, D.G.; Houser, S.R.; Koch, W.J. GRK5-Mediated Exacerbation of Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy Involves Facilitation of Nuclear NFAT Activity. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maning, J.; McCrink, K.A.; Pollard, C.M.; Desimine, V.L.; Ghandour, J.; Perez, A.; Cora, N.; Ferraino, K.E.; Parker, B.M.; Brill, A.R.; et al. Antagonistic Roles of GRK2 and GRK5 in Cardiac Aldosterone Signaling Reveal GRK5-Mediated Cardioprotection via Mineralocorticoid Receptor Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavo, A.; Liccardo, D.; Eguchi, A.; Elliott, K.J.; Traynham, C.J.; Ibetti, J.; Eguchi, S.; Leosco, D.; Ferrara, N.; Rengo, D.L.N.F.G.; et al. Myocardial pathology induced by aldosterone is dependent on non-canonical activities of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kato, T.; Uchinoumi, H.; Fukui, G.; Hamada, Y.; Nanno, T.; Ishiguchi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; et al. Nuclear translocation of calmodulin in pathological cardiac hypertrophy originates from ryanodine receptor bound calmodulin. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 125, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.-T.; Zambrano, C.M.; Koch, W.J.; Purcell, N.H. PH domain leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase 2 (PHLPP2) regulates G-protein–coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5)-induced cardiac hypertrophy in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 8056–8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premont, R.T.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Physiological Roles of G Protein–Coupled Receptor Kinases and Arrestins. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdtmann-Vourliotis, M.; Mayer, P.; Ammon, S.; Riechert, U.; Höllt, V. Distribution of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) isoforms 2, 3, 5 and 6 mRNA in the rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 95, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Long, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ma, L. GRK5 promotes F-actin bundling and targets bundles to membrane structures to control neuronal morphogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunapuli, P.; Onorato, J.; Hosey, M.; Benovic, J. Expression, purification, and characterization of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK5. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubser, M.; Byun, N.; Wood, M.R.; Jones, C.K. Muscarinic Receptor Pharmacology and Circuitry for the Modulation of Cognition. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 121–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainetdinov, R.R.; Bohn, L.M.; Walker, J.K.; Laporte, S.A.; Macrae, A.D.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Premont, R.T. Muscarinic Supersensitivity and Impaired Receptor Desensitization in G Protein–Coupled Receptor Kinase 5–Deficient Mice. Neuron 1999, 24, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Liu, P.; Shen, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Ma, L. GRK5 Regulates Social Behavior Via Suppression of mTORC1 Signaling in Medial Prefrontal Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 28, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Peng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Suo, W.Z. GRK5 deficiency leads to susceptibility to intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive impairment. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 302, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Z.; Wu, M.; Citron, B.A.; Wong, G.T.; Festoff, B.W. Abnormality of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinases at Prodromal and Early Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Association with Early -Amyloid Accumulation. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3444–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, Z.; Cox, A.A.; Bartelli, N.; Rasul, I.; Festoff, B.W.; Premont, R.T.; Arendash, G.W. GRK5 deficiency leads to early Alzheimer-like pathology and working memory impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1873–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 459–509. [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Staging of Alzheimer’s disease-related neurofibrillary changes. Neurobiol. Aging. 1995, 16, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liccardo, D.; Marzano, F.; Carraturo, F.; Guida, M.; Femminella, G.D.; Bencivenga, L.; Agrimi, J.; Addonizio, A.; Melino, I.; Valletta, A.; et al. Potential Bidirectional Relationship between Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakaski, M.; Kalman, J. Interactions between the amyloid and cholinergic mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 53, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossner, S.; Ueberham, U.; Schliebs, R.; Perez-Polo, J.R.; Bigl, V.; Roßner, S. The regulation of amyloid precursor protein metabolism by cholinergic mechanisms and neurotrophin receptor signaling. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 541–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Suo, W.Z. GRK5 deficiency exaggerates inflammatory changes in TgAPPsw mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2008, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Rasul, I.; Liu, J.; Zhao, B.; Tang, R.; Premont, R.T.; Suo, W.Z. Augmented axonal defects and synaptic degenerative changes in female GRK5 deficient mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 78, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Rasul, I.; Sun, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, L.; Premont, R.T.; Suo, W.Z. GRK5 Deficiency Leads to Reduced Hippocampal Acetylcholine Level via Impaired Presynaptic M2/M4 Autoreceptor Desensitization. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19564–19571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Li, L.; He, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; He, M.; Grasing, K.; Premont, R.T.; Suo, W.Z. GRK5 Deficiency Accelerates β-Amyloid Accumulation in Tg2576 Mice via Impaired Cholinergic Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 41541–41548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Singh, P.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, W.; Ding, X.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Premont, R.T.; Morgan, D.; et al. GRK5 Deficiency Leads to Selective Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neuronal Vulnerability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Shen, G.; Zhao, Q.; Shangguan, L.; He, M. GRK5 dysfunction accelerates tau hyperphosphorylation in APP (swe) mice through impaired cholinergic activity. NeuroReport 2014, 25, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Mai, H.; Yang, J.; Fan, W.; Tang, P.; et al. GRK5 influences the phosphorylation of tau via GSK3β and contributes to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 10411–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yin, M.; Cai, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, H.; Chen, T.; Huang, P.; et al. The influence of two functional genetic variants of GRK5 on tau phosphorylation and their association with Alzheimer’s disease risk. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 72714–72726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arawaka, S.; Wada, M.; Goto, S.; Karube, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Ren, C.-H.; Koyama, S.; Nagasawa, H.; Kimura, H.; Kawanami, T.; et al. The Role of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 in Pathogenesis of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 9227–9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, E.; Gurevich, V.; Joyce, J.; Benovic, J. Arrestins and two receptor kinases are upregulated in Parkinson’s disease with dementia. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhyre, T.R.; Boyd, J.T.; Hamill, R.W.; Maguire-Zeiss, K.A. Parkinson’s Disease. Cholesterol Binding and Cholesterol Transport. Proteins 2012, 65, 389–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Nakajo, S.; Tu, P.H.; Tomita, T.; Nakaya, K.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Iwatsubo, T. Aggregation of Al-pha-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Gao, N.; Zhu, H.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, C.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Qin, C. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5, overexpressed in the α-synuclein up-regulation model of Parkinson’s disease, regulates bcl-2 expression. Brain Res. 2010, 1307, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, G.; de Luca, V.; Tarantino, P.; Gagliardi, M.; Iannello, G.; Novellino, F.; Morelli, M.; Annesi, G.; Quattrone, A. Role of G-protein coupled receptor kinase 5 gene in cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 230, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, P.; de Marco, E.V.; Annesi, G.; Rocca, F.E.; Annesi, F.; Civitelli, D.; Provenzano, G.; Scornaienchi, V.; Greco, V.; Colica, C.; et al. Lack of association between G-protein coupled receptor kinase 5 gene and Parkinson’s disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2010, 156, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsam, R.T.; Gutkind, J.S. G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappano, R.; Maggiolini, M. G protein-coupled receptors: Novel targets for drug discovery in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 10, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michal, A.M.; So, C.H.; Beeharry, N.; Shankar, H.; Mashayekhi, R.; Yen, T.J.; Benovic, J.L. G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 5 Is Localized to Centrosomes and Regulates Cell Cycle Progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6928–6940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, C.H.; Michal, A.M.; Mashayekhi, R.; Benovic, J.L. G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 5 Phosphorylates Nucleophosmin and Regulates Cell Sensitivity to Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 17088–17099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, F.; Wahl, G.M. Regulating the p53 pathway: In vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorriento, D.; del Giudice, C.; Bertamino, A.; Ciccarelli, M.; Gomez-Monterrey, I.; Campiglia, P.; Novellino, E.; Illario, M.; Trimarco, B.; de Luca, N.; et al. New small molecules, ISA27 and SM13, inhibit tumour growth inducing mitochondrial effects of p53. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 112, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, M.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, L. G-protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 5 Phosphorylates p53 and Inhibits DNA Damage-induced Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12823–12830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, M.; Nishimura, Y. Extended String Binding Mode of the Phosphorylated Transactivation Domain of Tumor Suppressor p53. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14143–14152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.I.; Chakraborty, P.; Wang, Z.; Daaka, Y. G-Protein Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 Regulates Prostate Tumor Growth. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Coomes, A.S.; Kim, W.-J.; Stupay, R.; Lynch, L.D.; Atkinson, T.; Kim, J.I.; Nie, Z.; Daaka, Y. G Protein–Coupled Receptor Kinase GRK5 Phosphorylates Moesin and Regulates Metastasis in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3489–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Kim, J.; Kaur, R.; Tan, I.; Bloch, O.; Sun, M.Z.; Safaee, M.; Oh, M.C.; Sughrue, M.; Phillips, J.; et al. G-protein coupled receptor kinase (GRK)-5 regulates proliferation of glioblastoma-derived stem cells. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-P.; Fan, S.-Q.; Xiong, Q.-X.; Zhou, Y.-C.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Li, G.-F.; Huang, Y.-C.; Wu, M.-G.; Shen, Q.-S.; Liu, K.; et al. GRK5 functions as an oncogenic factor in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagman, J.; Sayegh, P.; Lee, C.S.; Sulon, S.M.; Jacinto, A.Z.; Sok, V.; Peng, N.; Alp, D.; Benovic, J.L.; So, C.H. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 modifies cancer cell resistance to paclitaxel. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 461, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.L.; Gan, X.X.; Bao, Y.; Wang, W.P.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.H. GRK5 promotes tumor progression in renal cell carcinoma. Neoplasma 2019, 66, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Robinson, K.; Vleeshouwer-Neumann, T.; Annis, J.E.; Chen, E.Y. Characterization of GRK5 as a novel regulator of rhabdomyosarcoma tumor cell growth and self-renewal. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1448–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Tsai, F.-M.; Shyu, R.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-M.; Wang, C.-H.; Jiang, S.-Y. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 mediates Tazarotene-induced gene 1-induced growth suppression of human colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.-M.; Wu, C.-C.; Shyu, R.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Jiang, S.-Y. Tazarotene-induced gene 1 inhibits prostaglandin E2-stimulated HCT116 colon cancer cell growth. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 18, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Métayé, T.; Menet, E.; Guilhot, J.; Kraimps, J.-L. Expression and Activity of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinases in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3279–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geras-Raaka, E.; Arvanitakis, L.; Bais, C.; Cesarman, E.; Mesri, E.A.; Gershengorn, M.C. Inhibition of Constitutive Signaling of Kaposi’s Sarcoma–associated Herpesvirus G Protein–Coupled Receptor by Protein Kinases in Mammalian Cells in Culture. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Leach, M.W.; Manfra, D.; Homey, B.; Wiekowski, M.; Sullivan, L.; Jenh, C.-H.; Narula, S.K.; Chensue, S.W.; et al. Transgenic Expression of the Chemokine Receptor Encoded by Human Herpesvirus 8 Induces an Angioproliferative Disease Resembling Kaposi’s Sarcoma. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Kobilka, B.K. The Structure and Function of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. Nature 2009, 459, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. GPCR Signaling Regulation: The Role of GRKs and Arrestins. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfleger, J.; Gresham, K.; Koch, W.J. G protein-coupled receptor kinases as therapeutic targets in the heart. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, L.M.; Pistner, A.R.; Belmonte, S.L.; Migdalovich, D.; Stolpnik, O.; Nwakanma, F.E.; Vorobiof, G.; Dunaevsky, O.; Matavel, A.; Lopes, C.M.; et al. Small Molecule Disruption of Gβγ Signaling Inhibits the Progression of Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, D.M.; Homan, K.T.; Chen, J.; Wu, E.K.; Hinkle, P.M.; Huang, Z.M.; Chuprun, J.K.; Song, J.; Gao, E.; Cheung, J.Y.; et al. Paroxetine Is a Direct Inhibitor of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 and Increases Myocardial Contractility. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, R.A.; Cato, M.C.; Waldschmidt, H.V.; Bouley, R.A.; Chen, Q.; Avramova, L.; Larsen, S.D.; Tesmer, J.J.G.; White, A.D. Structure-Based Design of Selective, Covalent G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1628–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorriento, D.; Ciccarelli, M.; Santulli, G.; Campanile, A.; Altobelli, G.G.; Cimini, V.; Galasso, G.; Astone, D.; Piscione, F.; Pastore, L.; et al. The G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 inhibits NFκB transcriptional activity by inducing nuclear accumulation of IκBα. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17818–17823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorriento, D.; Santulli, G.; Fusco, A.; Anastasio, A.; Trimarco, B.; Iaccarino, G. Intracardiac Injection of AdGRK5-NT Reduces Left Ventricular Hypertrophy by Inhibiting NF-κB–Dependent Hypertrophic Gene Expression. Hypertension 2010, 56, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorriento, D.; Santulli, G.; Ciccarelli, M.; Maione, A.S.; Illario, M.; Trimarco, B.; Iaccarino, G. The Amino-Terminal Domain of GRK5 Inhibits Cardiac Hypertrophy through the Regulation of Calcium-Calmodulin Dependent Transcription Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyett, T.S.; Fraley, A.E.; LaBudde, E.; Patra, D.; Coleman, R.C.; Eguchi, A.; Glukhova, A.; Chen, Q.; Williams, R.M.; Koch, W.J.; et al. Perturbation of the interactions of calmodulin with GRK5 using a natural product chemical probe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15895–15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Seo, H.W.; Ryu, J.Y.; Lim, C.J.; Yi, K.Y.; Oh, K.-S.; Lee, B.H. KR-39038, a Novel GRK5 Inhibitor, Attenuates Cardiac Hypertrophy and Improves Cardiac Function in Heart Failure. Biomol. Ther. 2020, 28, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, K.T.; Wu, E.; Cannavo, A.; Koch, W.J.; Tesmer, J.J.G. Identification and Characterization of Amlexanox as a G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 Inhibitor. Molecules 2014, 19, 16937–16949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.-K.; Falcenberg, M.; Ljepoja, B.; Fröhlich, T.; Arnold, G.J.; Wagner, E.; Roidl, A. Downregulation of GRK5 hampers the migration of breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-H.; Zhang, L.; Fanaroff, A.C.; Cai, X.; Sharma, K.C.; Brian, L.; Exum, S.T.; Shenoy, S.K.; Peppel, K.; Freedman, N.J. G Protein–Coupled Receptor Kinase-5 Attenuates Atherosclerosis by Regulating Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and 7-Transmembrane Receptors. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Shen, M.; Ma, L. GRK5 deficiency decreases diet-induced obesity and adipogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, M.; Wang, F.; Ma, L. GRK5 ablation contributes to insulin resistance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 429, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Dong, J.; Liang, C. GRK5 Intronic (CA)n Polymorphisms Associated with Type 2 Diabetes in Chinese Hainan Island. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lutz, S.Z.; Falcenberg, M.; Machicao, F.; Peter, A.; Kächele, M.; Randrianarisoa, E.; Lehn-Stefan, A.; Wagner, R.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the G-Protein Coupled Receptor Kinase 5 (GRK5) Gene are associated with Plasma LDL-Cholesterol Levels in Humans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.M.; Carrasco, G.A.; Qin, B.; Gao, B.; Yu, J.; Yuan, J.; Lou, Z. G-protein Receptor Kinase 5 Regulates the Cannabinoid Receptor 2-induced Up-regulation of Serotonin 2A Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 15712–15724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-C.; Chung, R.-H.; Kuo, H.-W.; Liu, T.-H.; Fang, C.-P.; Liu, S.C.; Liu, C.-C.; Tsou, H.-H.; Chen, A.C.H.; Liu, Y.-L. GRK5 Is Associated with the Regulation of Methadone Dosage in Heroin Dependence. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Hu, W.; Feng, Z. The Regulation of Ferroptosis by Tumor Suppressor p53 and its Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Comish, P.B.; Tang, D.; Kang, R. Characteristics and Biomarkers of Ferroptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 637162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| GRK5 Inhibitors | Type of Study | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Compound 5 | In vitro (Rowlands et al., 2019) | 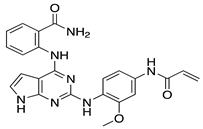 |
| Compound 16d | In vitro (Rowlands et al., 2019) | 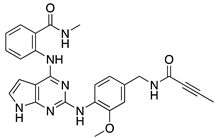 |
| Malbrancheamide | In vitro (Beyett et al., 2019) |  |
| KR-39038 | In vitro/In vivo (Lee et al., 2020) | 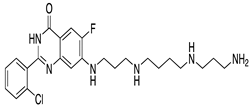 |
| Amlexanox | In vitro (Homan et al., 2014) |  |
| CCG-215022 | In vitro/In vivo (Pham et al., 2020) | 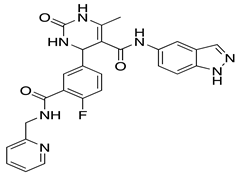 |
| Sunitinib | In vitro (Sommer et al., 2019) | 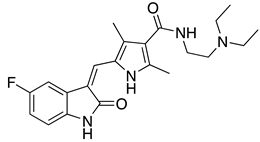 |
| Adenovirus (Ad) GRK5-NT | In vitro/In vivo (Sorriento et al., 2010) |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marzano, F.; Rapacciuolo, A.; Ferrara, N.; Rengo, G.; Koch, W.J.; Cannavo, A. Targeting GRK5 for Treating Chronic Degenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041920
Marzano F, Rapacciuolo A, Ferrara N, Rengo G, Koch WJ, Cannavo A. Targeting GRK5 for Treating Chronic Degenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041920
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarzano, Federica, Antonio Rapacciuolo, Nicola Ferrara, Giuseppe Rengo, Walter J. Koch, and Alessandro Cannavo. 2021. "Targeting GRK5 for Treating Chronic Degenerative Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041920
APA StyleMarzano, F., Rapacciuolo, A., Ferrara, N., Rengo, G., Koch, W. J., & Cannavo, A. (2021). Targeting GRK5 for Treating Chronic Degenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041920









