κ-Opioid Signaling in the Lateral Hypothalamic Area Modulates Nicotine-Induced Negative Energy Balance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. κOR Mediates Nicotine-Induced Regulation of Hypothalamic AMPK
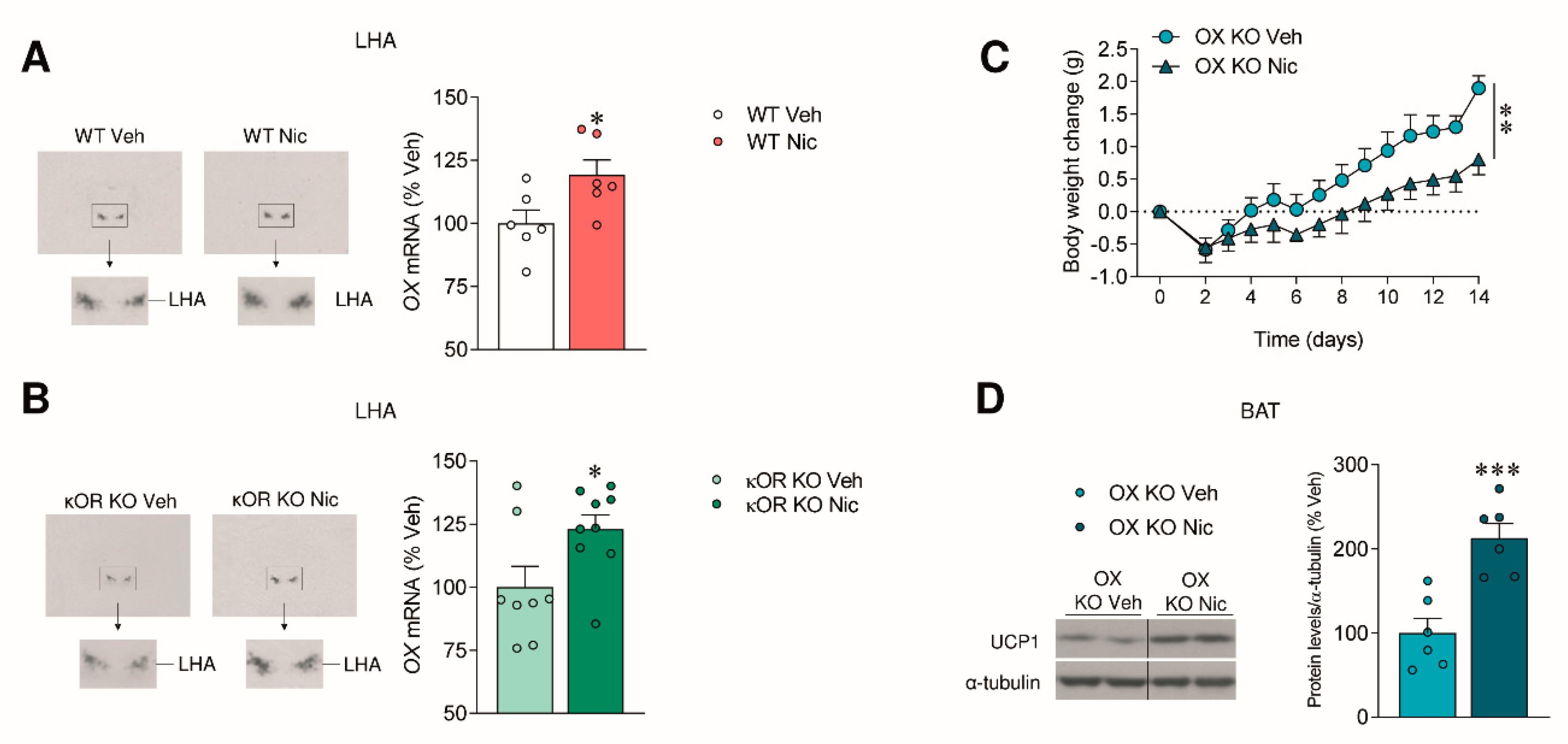
2.2. The Effect of Nicotine on Body Weight Is Independent of OX Signaling
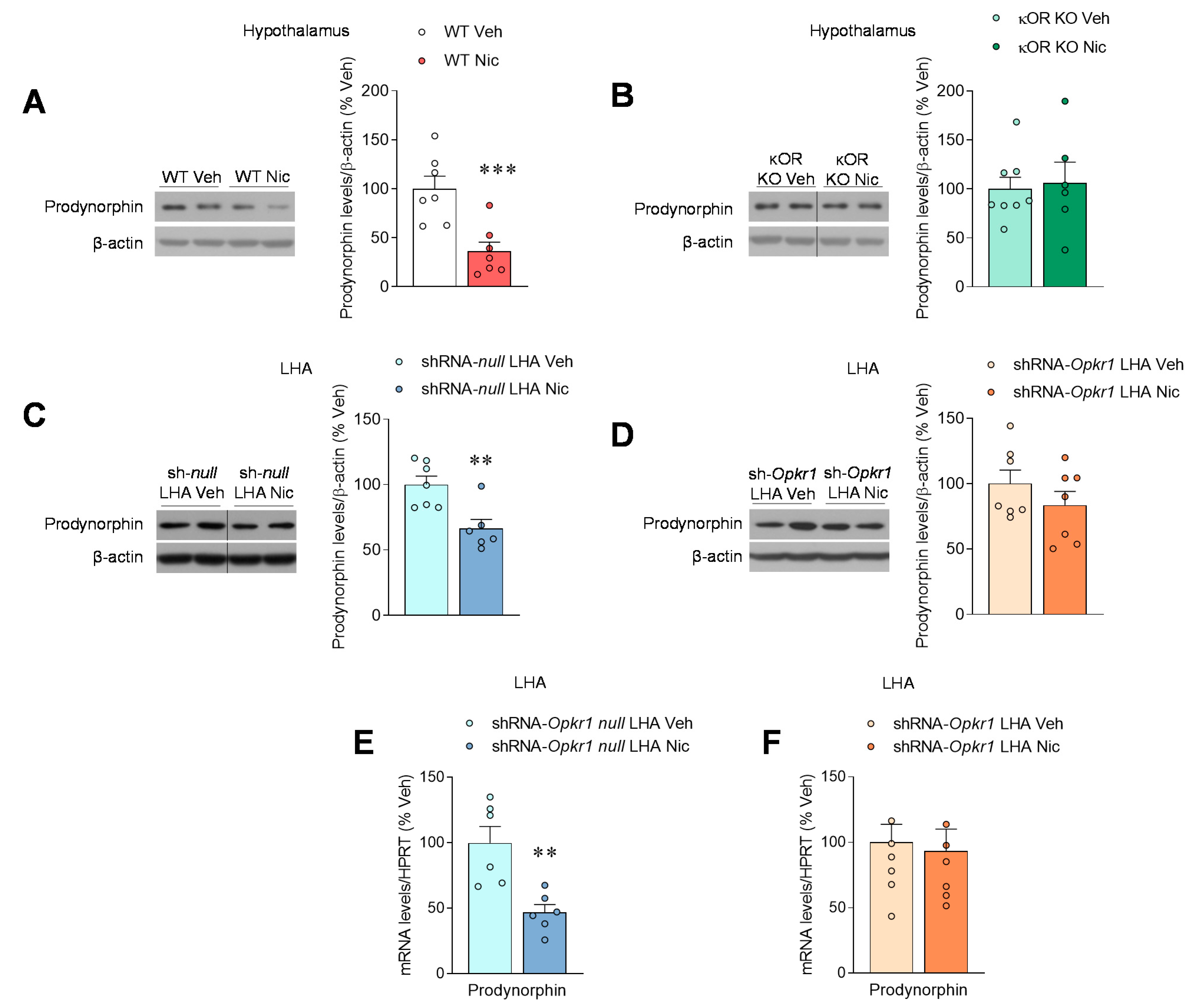
2.3. Nicotine Inhibits Prodynorphin
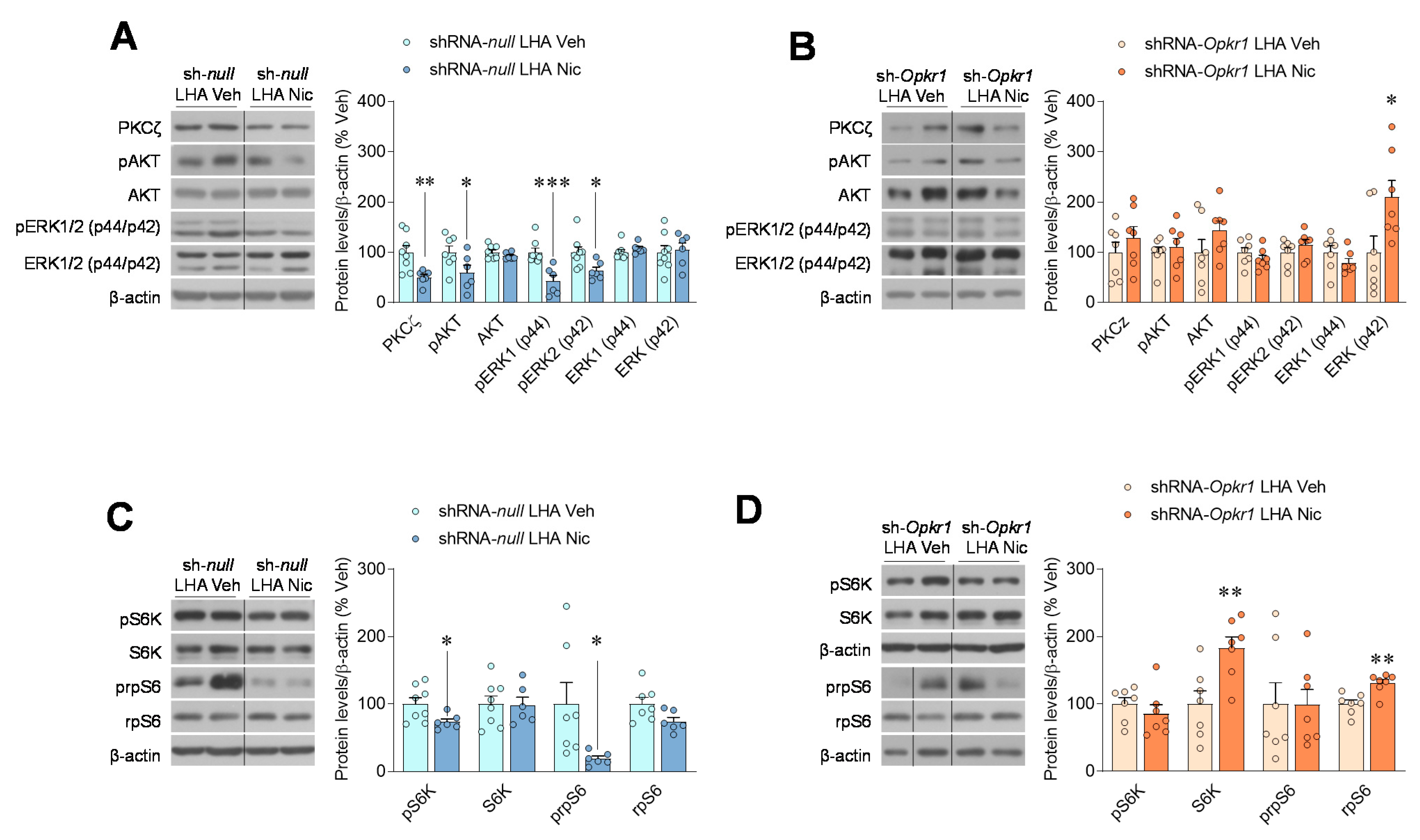
2.4. Inhibition of Opioid Signaling Mediates Nicotine Negative Energy Balance
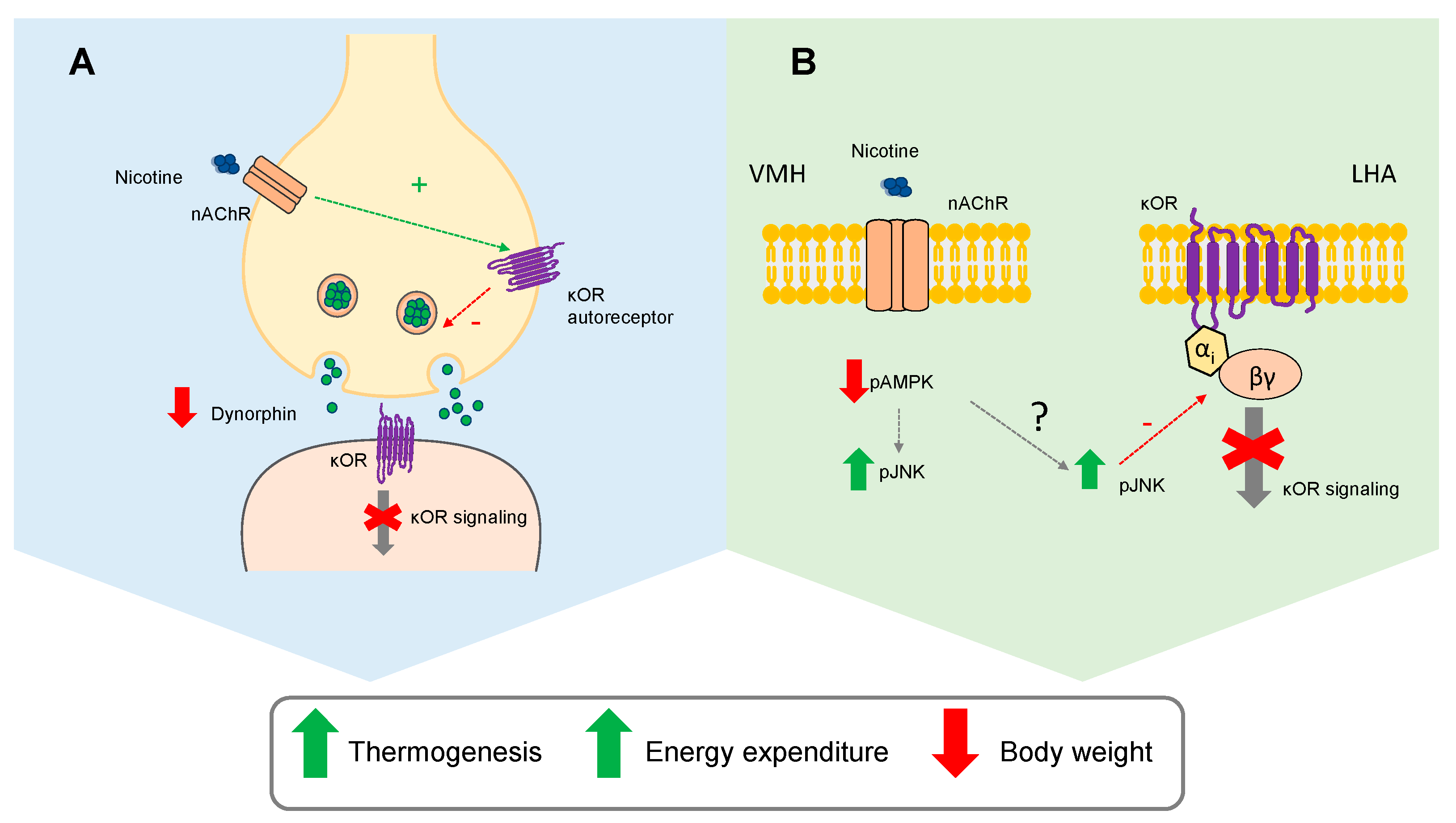
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Subcutaneous Treatment
4.3. Intracerebroventricular Treatment
4.4. Stereotaxic Microinjection of Viral Vectors
4.5. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
4.6. Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining and Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. In Situ Hybridization
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMP | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| BAT | brown adipose tissue |
| BMP8B | bone morphogenic protein 8B |
| δOR | ẟ opioid receptor |
| ERK1/2 | p44/42 MAPK |
| ICV | intracerebroventricular |
| κOR | kappa opioid receptor |
| KO | knockout |
| LHA | lateral hypothalamic area |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCH | melanin-concentrating hormone |
| nAChR | nicotinic acetylcholine receptors |
| µOR | µ opioid receptor |
| norBNI | nor-Binaltorphimine dihydrochloride |
| OX | orexin |
| OXR1 | orexin receptor 1 |
| PKCζ | protein kinase C zeta |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene difluoride membranes |
| S6K | p70S6 kinase |
| SAPK/JNK | phospho-stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| SC | subcutaneous |
| SNS | sympathetic nerve system |
| rpS6 | ribosomal protein S6 |
| UCP1 | uncoupling protein 1 |
| VMH | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus |
| WAT | white adipose tissue |
References
- Seoane-Collazo, P.; Dieguez, C.; Nogueiras, R.; Rahmouni, K.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Lopez, M. Nicotine’ actions on energy balance: Friend or foe? Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineur, Y.S.; Abizaid, A.; Rao, Y.; Salas, R.; DiLeone, R.J.; Gundisch, D.; Diano, S.; De Biasi, M.; Horvath, T.L.; Gao, X.B.; et al. Nicotine decreases food intake through activation of POMC neurons. Science 2011, 332, 1330–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez de Morentin, P.B.; Whittle, A.J.; Ferno, J.; Nogueiras, R.; Dieguez, C.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Lopez, M. Nicotine induces negative energy balance through hypothalamic AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes 2012, 61, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Kim, K.; Kaneko, K.; Iketani, M.; Otagiri, A.; Yamauchi, N.; Shibasaki, T. Nicotine infusion alters leptin and uncoupling protein 1 mRNA expression in adipose tissues of rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E867–E876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mano-Otagiri, A.; Iwasaki-Sekino, A.; Ohata, H.; Arai, K.; Shibasaki, T. Nicotine suppresses energy storage through activation of sympathetic outflow to brown adipose tissue via corticotropin-releasing factor type 1 receptor. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 455, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane-Collazo, P.; Linares-Pose, L.; Rial-Pensado, E.; Romero-Pico, A.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Iglesias-Rey, R.; Morgan, D.A.; Tomasini, N.; et al. Central nicotine induces browning through hypothalamic kappa opioid receptor. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.; Varela, L.; Vazquez, M.J.; Rodriguez-Cuenca, S.; Gonzalez, C.R.; Velagapudi, V.R.; Morgan, D.A.; Schoenmakers, E.; Agassandian, K.; Lage, R.; et al. Hypothalamic AMPK and fatty acid metabolism mediate thyroid regulation of energy balance. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanida, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Shibamoto, T.; Rahmouni, K. Involvement of hypothalamic AMP-activated protein kinase in leptin-induced sympathetic nerve activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, A.J.; Carobbio, S.; Martins, L.; Slawik, M.; Hondares, E.; Vazquez, M.J.; Morgan, D.; Csikasz, R.I.; Gallego, R.; Rodriguez-Cuenca, S.; et al. BMP8B increases brown adipose tissue thermogenesis through both central and peripheral actions. Cell 2012, 149, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiroa, D.; Imbernon, M.; Gallego, R.; Senra, A.; Herranz, D.; Villarroya, F.; Serrano, M.; Ferno, J.; Salvador, J.; Escalada, J.; et al. GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez de Morentin, P.B.; Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Martins, L.; Lage, R.; Fernandez-Mallo, D.; Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Liu, J.; Morgan, D.A.; Pinilla, L.; et al. Estradiol regulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis via hypothalamic AMPK. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.; Seoane-Collazo, P.; Contreras, C.; Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Gonzalez, F.; Zalvide, J.; Gallego, R.; Dieguez, C.; Nogueiras, R.; et al. A Functional link between AMPK and orexin mediates the effect of BMP8B on energy balance. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2231–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Seoane-Collazo, P.; Contreras, C.; Varela, L.; Villarroya, J.; Rial-Pensado, E.; Buque, X.; Aurrekoetxea, I.; Delgado, T.C.; Vazquez-Martinez, R.; et al. Hypothalamic AMPK-ER stress-JNK1 axis mediates the central actions of thyroid hormones on energy balance. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 212–229.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane-Collazo, P.; Martinez de Morentin, P.B.; Ferno, J.; Dieguez, C.; Nogueiras, R.; Lopez, M. Nicotine improves obesity and hepatic steatosis and ER stress in diet-induced obese male rats. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmensen, C.; Jall, S.; Kleinert, M.; Quarta, C.; Gruber, T.; Reber, J.; Sachs, S.; Fischer, K.; Feuchtinger, A.; Karlas, A.; et al. Coordinated targeting of cold and nicotinic receptors synergistically improves obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavkin, C.; James, I.F.; Goldstein, A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science 1982, 215, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyzyk, T.A.; Nogueiras, R.; Lockwood, J.F.; McKinzie, J.H.; Coskun, T.; Pintar, J.E.; Hammond, C.; Tschop, M.H.; Statnick, M.A. Kappa-opioid receptors control the metabolic response to a high-energy diet in mice. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Pico, A.; Vazquez, M.J.; Gonzalez-Touceda, D.; Folgueira, C.; Skibicka, K.P.; Alvarez-Crespo, M.; Van Gestel, M.A.; Velasquez, D.A.; Schwarzer, C.; Herzog, H.; et al. Hypothalamic kappa-opioid receptor modulates the orexigenic effect of ghrelin. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.K.; Price, D.J.; Kyriakis, J.M.; Pelech, S.; Sanghera, J.; Avruch, J. An array of insulin-activated, proline-directed serine/threonine protein kinases phosphorylate the p70 S6 kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 3325–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lim, M.S.; Park, J.H.; Park, C.H.; Koh, H.C. PTEN promotes dopaminergic neuronal differentiation through regulation of ERK-dependent inhibition of S6K signaling in human neural stem cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouet, C.; Ono, H.; Schwartz, G.J. Mediobasal hypothalamic p70 S6 kinase 1 modulates the control of energy homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Martinez de Morentin, P.B.; Estevez-Salguero, A.; Contreras, C.; Romero-Pico, A.; Ferno, J.; Nogueiras, R.; Dieguez, C.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Tovar, S.; et al. mTOR signaling in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus mediates the anorectic action of estradiol. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 238, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folgueira, C.; Beiroa, D.; Porteiro, B.; Duquenne, M.; Puighermanal, E.; Fondevila, M.F.; Barja-Fernandez, S.; Gallego, R.; Hernandez-Bautista, R.; Castelao, C.; et al. Hypothalamic dopamine signaling regulates brown fat thermogenesis. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Pico, A.; Sanchez-Rebordelo, E.; Imbernon, M.; Gonzalez-Touceda, D.; Folgueira, C.; Senra, A.; Ferno, J.; Blouet, C.; Cabrera, R.; van Gestel, M.; et al. Melanin-concentrating hormone acts through hypothalamic kappa opioid system and p70S6K to stimulate acute food intake. Neuropharmacology 2018, 130, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintron-Colon, R.; Johnson, C.W.; Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Guijas, C.; Faulhaber, L.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Aguirre, C.A.; Shankar, K.; Singh, M.; Galmozzi, A.; et al. Activation of kappa opioid receptor regulates the hypothermic response to calorie restriction and limits body weight loss. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 4291–4299.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueiras, R.; Sabio, G. Brain JNK and metabolic disease. Diabetologia 2020, 64, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinones, M.; Al-Massadi, O.; Folgueira, C.; Bremser, S.; Gallego, R.; Torres-Leal, L.; Haddad-Tovolli, R.; Garcia-Caceres, C.; Hernandez-Bautista, R.; Lam, B.Y.H.; et al. p53 in AgRP neurons is required for protection against diet-induced obesity via JNK1. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.D.; McDonald, P.H. The orexin 1 receptor modulates kappa opioid receptor function via a JNK-dependent mechanism. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Lee, C.E.; Lu, J.; Elmquist, J.K.; Hara, J.; Willie, J.T.; Beuckmann, C.T.; Chemelli, R.M.; Sakurai, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; et al. Orexin (hypocretin) neurons contain dynorphin. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, RC168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romualdi, P.; Donatini, A.; Izenwasser, S.; Cox, B.M.; Ferri, S. Chronic intracerebroventricular cocaine differentially affects prodynorphin gene expression in rat hypothalamus and caudate-putamen. Mol. Brain Res. 1996, 40, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romualdi, P.; D’Addario, C.; Ferri, S.; Cox, B.M.; Izenwasser, S. Chronic GBR 12909 administration differentially alters prodynorphin gene expression compared to cocaine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 413, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, A.; Dreisbach, V.C.; Blenis, J. Characterization of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent phosphorylation of the hydrophobic motif site Thr(389) in p70 S6 kinase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 40281–40289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.; Nogueiras, R.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Dieguez, C. Hypothalamic AMPK: A canonical regulator of whole-body energy balance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferno, J.; Senaris, R.; Dieguez, C.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Lopez, M. Orexins (hypocretins) and energy balance: More than feeding. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 418, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milbank, E.; Lopez, M. Orexins/hypocretins: Key regulators of energy homeostasis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolarakis, K.E.; Almeida, O.F.; Yassouridis, A.; Herz, A. Presynaptic auto- and allelo-receptor regulation of hypothalamic opioid peptide release. Neuroscience 1989, 31, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, R.L.; Terrian, D.M. U-50,488H inhibits dynorphin and glutamate release from guinea pig hippocampal mossy fiber terminals. Brain Res. 1991, 548, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Yang, T.; Schreiber, S.; Defino, M.; Kwan, S.C.; Li, S.; Chavkin, C. Long-acting kappa opioid antagonists disrupt receptor signaling and produce noncompetitive effects by activating c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29803–29811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattauer, S.S.; Land, B.B.; Reichard, K.L.; Abraham, A.D.; Burgeno, L.M.; Kuhar, J.R.; Phillips, P.E.M.; Ong, S.E.; Chavkin, C. Peroxiredoxin 6 mediates Galphai protein-coupled receptor inactivation by cJun kinase. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcheva, M.M.; Vogel, Z.; Ignatova, E.; Avidor-Reiss, T.; Zippel, R.; Levy, R.; Young, E.C.; Barg, J.; Coscia, C.J. Opioid modulation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase activity is ras-dependent and involves Gbetagamma subunits. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcheva, M.M.; Clark, A.L.; Haas, P.D.; Serna, J.S.; Hahn, J.W.; Kiss, A.; Coscia, C.J. Mu and kappa opioid receptors activate ERK/MAPK via different protein kinase C isoforms and secondary messengers in astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27662–27669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hasani, R.; Bruchas, M.R. Molecular mechanisms of opioid receptor-dependent signaling and behavior. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Contreras, C.; Estevez-Salguero, A.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Colsh, B.; Pensado, I.; Linares-Pose, L.; Rial-Pensado, E.; Martinez de Morentin, P.B.; Ferno, J.; et al. Estradiol regulates energy balance by ameliorating hypothalamic ceramide-induced ER stress. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 413–423.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Crespo, M.; Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Garcia-Lavandeira, M.; Alvarez, C.V.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Nogueiras, R.; Dieguez, C.; Lopez, M. The orexigenic effect of orexin-A revisited: Dependence of an intact growth hormone axis. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3589–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.; Lage, R.; Tung, Y.C.; Challis, B.G.; Varela, L.; Virtue, S.; O’Rahilly, S.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Dieguez, C.; Coll, A.P. Orexin expression is regulated by alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2007, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seoane-Collazo, P.; Romero-Picó, A.; Rial-Pensado, E.; Liñares-Pose, L.; Estévez-Salguero, Á.; Fernø, J.; Nogueiras, R.; Diéguez, C.; López, M. κ-Opioid Signaling in the Lateral Hypothalamic Area Modulates Nicotine-Induced Negative Energy Balance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041515
Seoane-Collazo P, Romero-Picó A, Rial-Pensado E, Liñares-Pose L, Estévez-Salguero Á, Fernø J, Nogueiras R, Diéguez C, López M. κ-Opioid Signaling in the Lateral Hypothalamic Area Modulates Nicotine-Induced Negative Energy Balance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041515
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeoane-Collazo, Patricia, Amparo Romero-Picó, Eva Rial-Pensado, Laura Liñares-Pose, Ánxela Estévez-Salguero, Johan Fernø, Rubén Nogueiras, Carlos Diéguez, and Miguel López. 2021. "κ-Opioid Signaling in the Lateral Hypothalamic Area Modulates Nicotine-Induced Negative Energy Balance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041515
APA StyleSeoane-Collazo, P., Romero-Picó, A., Rial-Pensado, E., Liñares-Pose, L., Estévez-Salguero, Á., Fernø, J., Nogueiras, R., Diéguez, C., & López, M. (2021). κ-Opioid Signaling in the Lateral Hypothalamic Area Modulates Nicotine-Induced Negative Energy Balance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041515







