Tumor Metabolic Reprogramming by Adipokines as a Critical Driver of Obesity-Associated Cancer Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Adipokines and Cancer
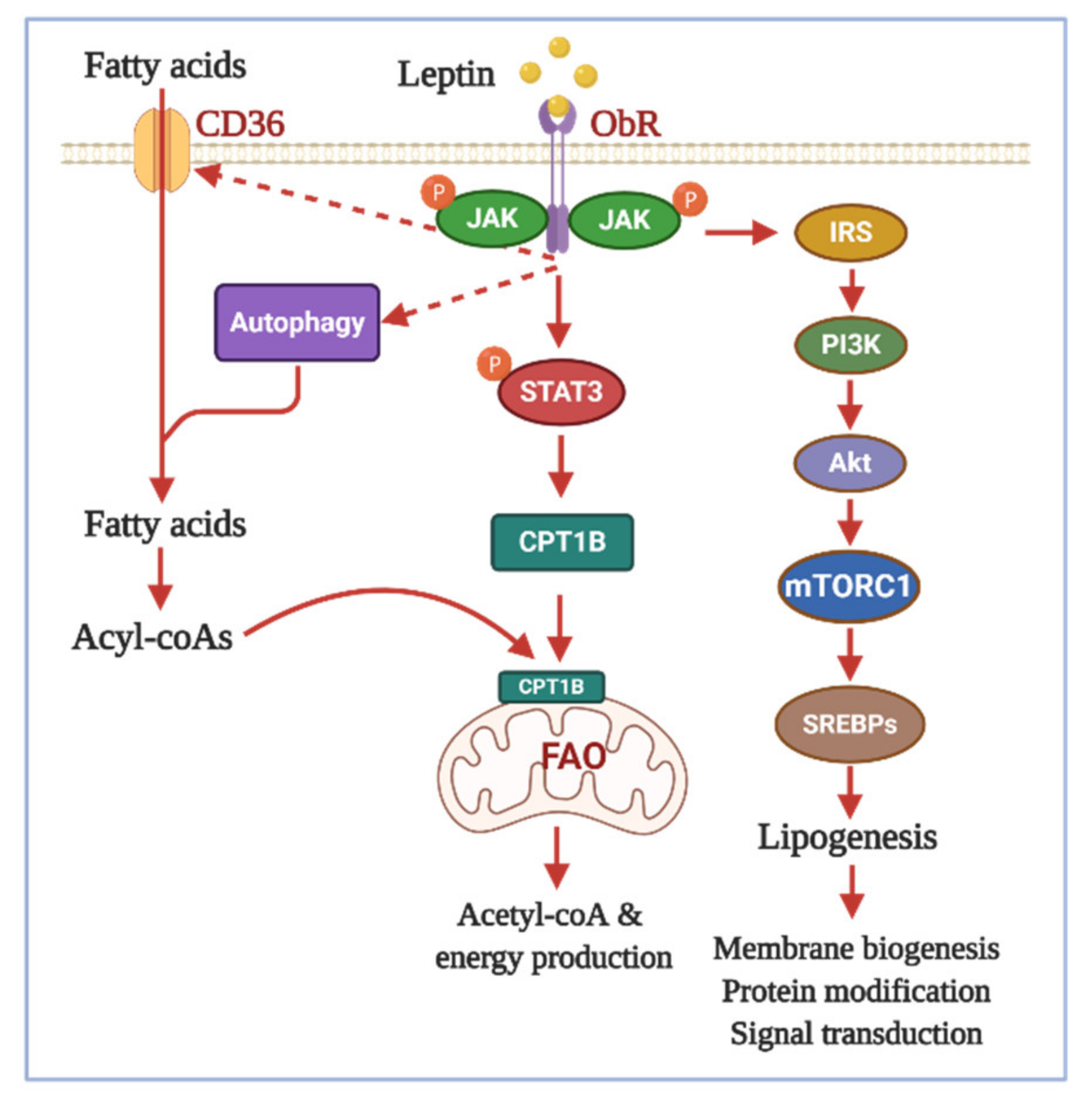
2.1. Role of Leptin in Cancer
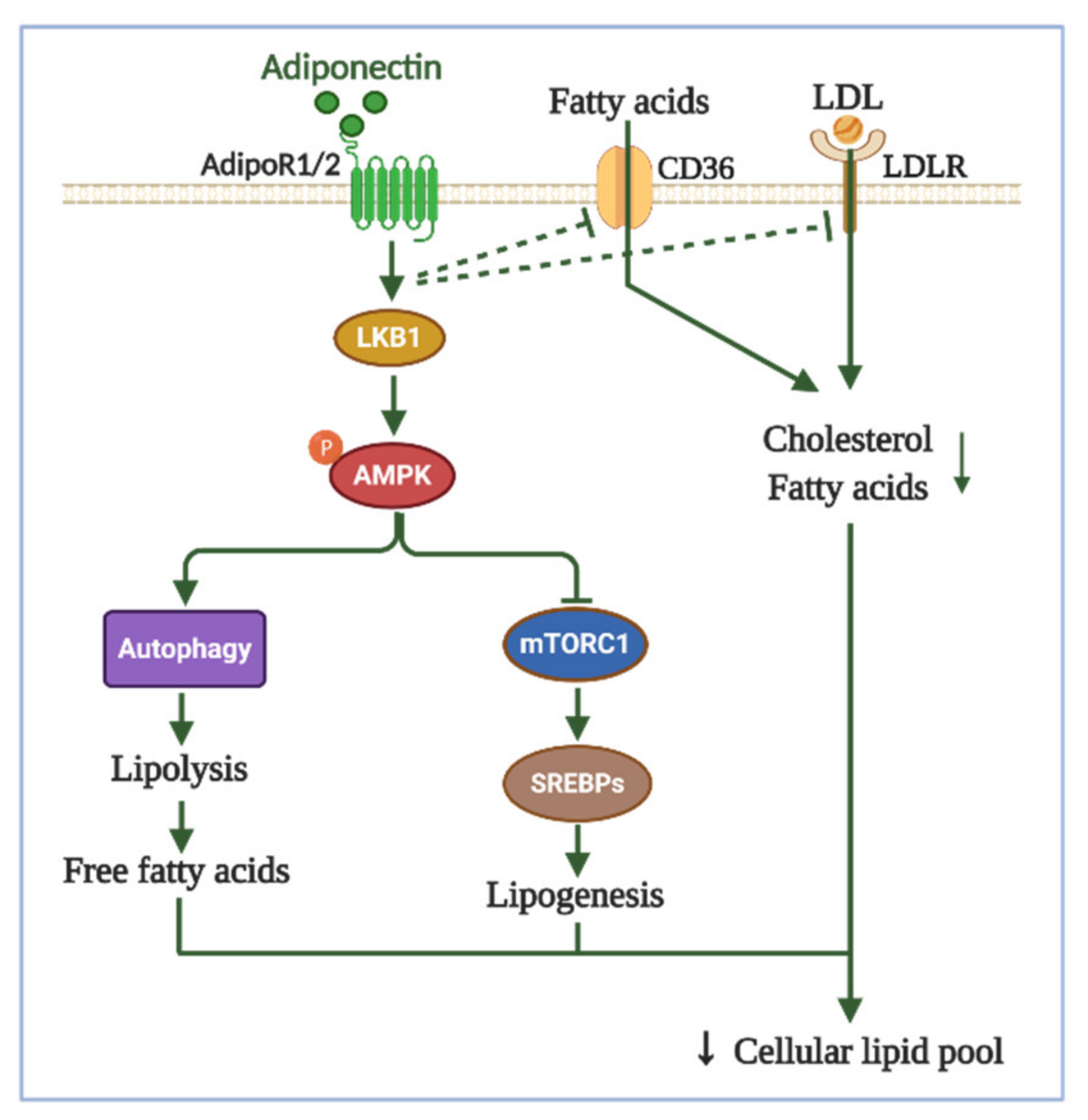
2.2. Role of Adiponectin in Cancer
2.3. Effects of Other Adipokines in Cancer
3. Effects of Adipokines on Cancer Metabolism
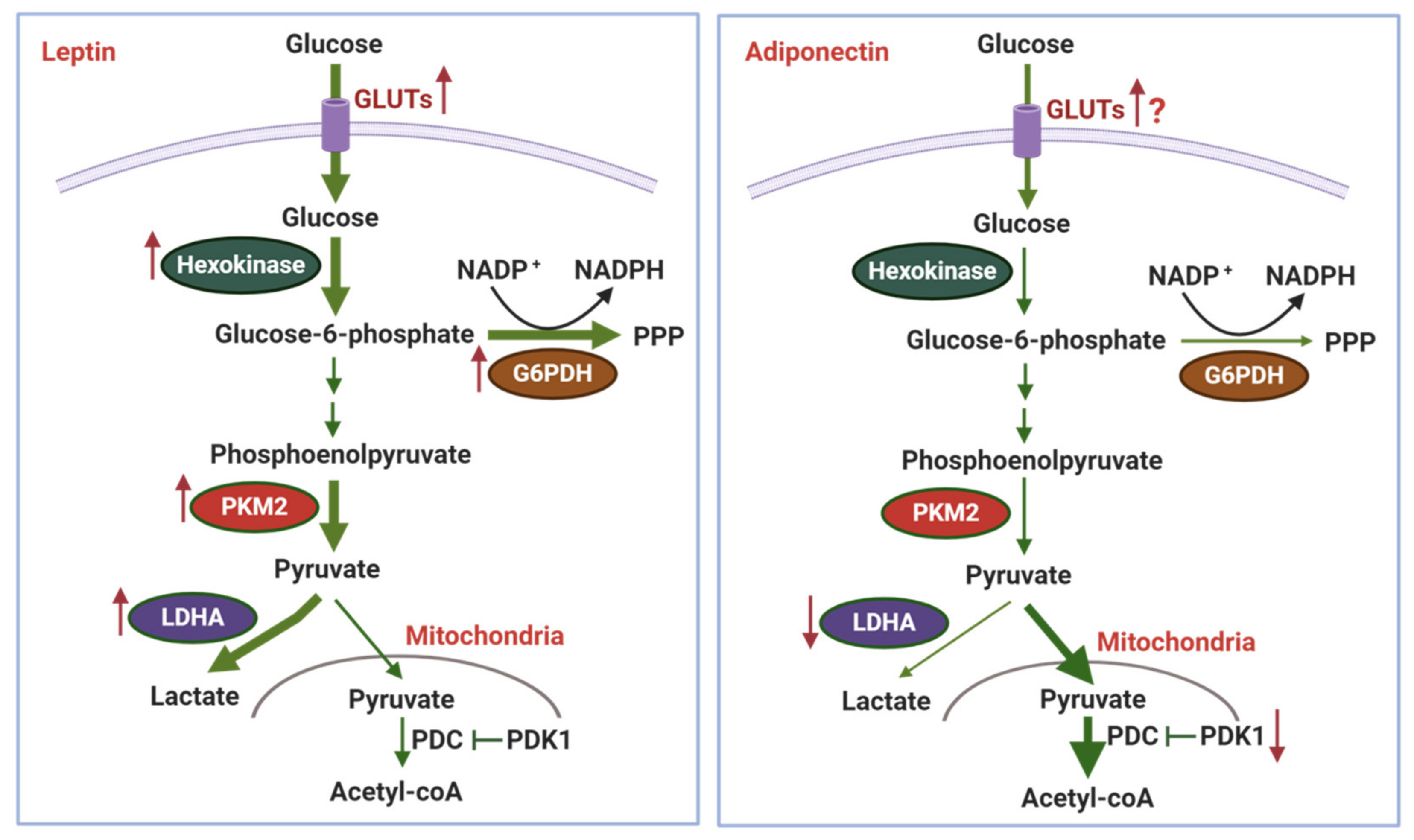
3.1. Effects of Adipokines on Glycolysis and the Warburg Effect
3.2. Effects of Adipokines on Mitochondrial Metabolism
3.3. Effects of Adipokines on Lipid Metabolism
3.4. Effects of Adipokines on Redox Balance
3.5. Effects of Adipokines on Other Metabolic Pathways
4. Autophagic Regulation: A Potential Mechanism for Cancer Cell Metabolism by Adipokines
5. Targeting Adipokines-Driven Cancer Metabolism for Counteracting Obesity-Linked Cancer
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAFs | Cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| FAO | Fatty acid β-oxidation |
| ObR | The leptin receptor |
| OXPHOS | Oxidative phosphorylation |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
References
- Bianchini, F.; Kaaks, R.; Vainio, H. Overweight, obesity, and cancer risk. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.C.; Sattar, N.; Lean, M.; McArdle, C.S. Obesity and cancer. BMJ 2006, 333, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, X. Adipocytokines and breast cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2018, 42, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, C.; Surmacz, E. Leptin and cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 207, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Hung, A.C.; Lo, S.; Yuan, S.-S.F. Adipocytokines visfatin and resistin in breast cancer: Clinical relevance, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic potential. Cancer Lett. 2020, 498, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, I.; Kelesidis, T.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin and cancer: A systematic review. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.H. Autophagy induction: A critical event for the modulation of cell death/survival and inflammatory responses by adipokines. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2018, 41, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.-V.; Park, P.-H. Recent insights on modulation of inflammasomes by adipokines: A critical event for the pathogenesis of obesity and metabolism-associated diseases. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2020, 43, 997–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Goncalves, M.D.; Cantley, L.C. Obesity and Cancer Mechanisms: Cancer Metabolism. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faubert, B.; Solmonson, A.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Metabolic reprogramming and cancer progression. Science 2020, 368, eaaw5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Chandel, N.S. Fundamentals of cancer metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, S.; Sun, S. Cancer-associated adipocytes: Key players in breast cancer progression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Torroella-Kouri, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Oncogenic role and therapeutic target of leptin signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2012, 1825, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, M.P.; Phillips, F.C.; Getzin, S.C.; Jacobson, T.L.; Jacobson, M.K.; Christensen, T.A.; Juneja, S.C.; Grande, J.P.; Maihle, N.J. Genetically obese MMTV-TGF-alpha/Lep(ob)Lep(ob) female mice do not develop mammary tumors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 77, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, M.P.; Juneja, S.C.; Phillips, F.C.; Hu, X.; Grande, J.P.; Maihle, N.J. Leptin receptor-deficient MMTV-TGF-alpha/Lepr(db)Lepr(db) female mice do not develop oncogene-induced mammary tumors. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.M.; Lu, S.; Medline, A.; Archer, M.C. Susceptibility of lean and obese Zucker rats to tumorigenesis induced by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Cancer Lett. 2001, 162, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, P.K.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, D.Y.; Jeong, G.-S.; Park, P.-H. Growth of breast cancer cells by leptin is mediated via activation of the inflammasome: Critical roles of estrogen receptor signaling and reactive oxygen species production. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 161, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.; Kim, M.J.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, S.H.; Sohn, D.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Song, K.; Choi, D.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Park, P.-H. Autophagy induction by leptin contributes to suppression of apoptosis in cancer cells and xenograft model: Involvement of p53/FoxO3A axis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7166–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Lee, H.; Li, Y.J.; Tripathi, S.C.; Yue, C.; Zhang, C.; Lifshitz, V.; Song, J.; Yuan, Y.; et al. JAK/STAT3-Regulated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation Is Critical for Breast Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Chemoresistance. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 136–150.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea-Flores, M.; Juárez-Cruz, J.C.; Mendoza-Catalán, M.A.; Padilla-Benavides, T.; Navarro-Tito, N. Signaling Pathways Induced by Leptin during Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Zazzo, E.; Polito, R.; Bartollino, S.; Nigro, E.; Porcile, C.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A.; Moncharmont, B. Adiponectin as Link Factor between Adipose Tissue and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.J.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Nagalingam, A.; Muniraj, N.; Kuppusamy, P.; Walker, A.; Woo, J.; Gyorffy, B.; Gabrielson, E.; Saxena, N.K.; et al. ADIPOQ/adiponectin induces cytotoxic autophagy in breast cancer cells through STK11/LKB1-mediated activation of the AMPK-ULK1 axis. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1386–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.-V.; Raut, P.K.; Pandit, M.; Chang, J.-H.; Katila, N.; Choi, D.-Y.; Jeong, J.-H.; Park, P.-H. Globular Adiponectin Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth through Modulation of Inflammasome Activation: Critical Role of Sestrin2 and AMPK Signaling. Cancers 2020, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Wang, J.; Fu, P.P.; Sharma, S.; Nagalingam, A.; Mells, J.; Handy, J.; Page, A.J.; Cohen, C.; Anania, F.A.; et al. Adiponectin antagonizes the oncogenic actions of leptin in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, P.K.; Park, P.-H. Globular adiponectin antagonizes leptin-induced growth of cancer cells by modulating inflammasomes activation: Critical role of HO-1 signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzel, M.S.; Hebbard, L.W.; Shostak, G.; Shapiro, L.; Cardiff, R.D.; Ranscht, B. Adiponectin deficiency limits tumor vascularization in the MMTV-PyV-mT mouse model of mammary cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3256–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbard, L.W.; Garlatti, M.; Young, L.J.T.; Cardiff, R.D.; Oshima, R.G.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin Supports Angiogenesis and Adiponectin Association with the Vasculature in a Mouse Mammary Tumor Model. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cui, S. Adiponectin Induces Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Growth Factor Expression. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk Libby, E.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Lewis, M.J.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Hurst, D.R. Globular adiponectin enhances invasion in human breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kitayama, J.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T.; Maki, T.; Miyato, H.; Yamashita, H.; Nagawa, H. Adiponectin inhibits the growth and peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer through its specific membrane receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, E.; Guo, H.; Shen, M.; Yu, H.; Gu, D.; Mao, W.; Wang, X. Adiponectin inhibits migration and invasion by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-C. The role of visfatin in cancer proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, drug resistance and clinical prognosis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3481–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Cong, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Xing, Q.; Song, N.J.A. Relationship between NAMPT/PBEF/visfatin and prognosis of patients with malignant tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, A.C.; Lo, S.; Hou, M.-F.; Lee, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.-H.; Lo, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; et al. Extracellular Visfatin-Promoted Malignant Behavior in Breast Cancer Is Mediated Through c-Abl and STAT3 Activation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lo, S.; Tseng, L.M.; Chen, D.R.; Wu, Y.C.; Hou, M.F.; Yuan, S.F. Visfatin Mediates Malignant Behaviors through Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Intermediary in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2019, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, T.Q.; Che, X.M. Nampt/PBEF/visfatin and cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Khan, S.; Ling, W.; Bam, R.; Li, X.; van Rhee, F.; Usmani, S.; Barlogie, B.; Epstein, J.; Yaccoby, S. NAMPT/PBEF1 enzymatic activity is indispensable for myeloma cell growth and osteoclast activity. Exp. Hematol. 2013, 41, 547–557.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Wang, P.J.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Lo, S.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Chiu, W.C.; Chu-Sung Hu, S.; Lu, C.W.; et al. Resistin facilitates breast cancer progression via TLR4-mediated induction of mesenchymal phenotypes and stemness properties. Oncogene 2018, 37, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, J.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Khorramdelazad, H.; Abbasloui, M.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Jamali, N. Role of Apelin/APJ axis in cancer development and progression. Adv. Med. Sci. 2020, 65, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treeck, O.; Buechler, C.; Ortmann, O. Chemerin and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppenol, W.H.; Bounds, P.L.; Dang, C.V. Otto Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. The Emerging Hallmarks of Cancer Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Attané, C.; Milhas, D.; Dirat, B.; Dauvillier, S.; Guerard, A.; Gilhodes, J.; Lazar, I.; Alet, N.; Laurent, V.; et al. Mammary adipocytes stimulate breast cancer invasion through metabolic remodeling of tumor cells. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e87489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, P.; Rodriguez-Vita, J.; Etzerodt, A.; Masse, M.; Rastoin, O.; Gouirand, V.; Ulas, T.; Papantonopoulou, O.; Van Eck, M.; Auphan-Anezin, N.; et al. Membrane Cholesterol Efflux Drives Tumor-Associated Macrophage Reprogramming and Tumor Progression. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1376–1389.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekola, K.; Rosen, S.T.; Shanmugam, M. Glucose transporters in cancer metabolism. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancey, P.B.; Contat, C.; Meylan, E. Glucose transporters in cancer-from tumor cells to the tumor microenvironment. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2926–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Koyama, K.; Shimabukuro, M.; Mangelsdorf, D.; Newgard, C.B.; Unger, R.H. Overexpression of leptin receptors in pancreatic islets of Zucker diabetic fatty rats restores GLUT-2, glucokinase, and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11921–11926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tan, M.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Sheng, H. Leptin receptor mediates the proliferation and glucose metabolism of pancreatic cancer cells via AKT pathway activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.-J.; Xu, H.-Z.; Li, J.-S.; Geng, L.-Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhou, X.-X.; Wang, X. Leptin and its receptor in glucose metabolism of T-cell lymphoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5838–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.A.; Rasti, M.; Bauer, P.V.; Lam, T.K.T. Leptin enhances hypothalamic lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA)-dependent glucose sensing to lower glucose production in high-fat-fed rats. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 4159–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Li, K.; Pang, X.; Guo, B.; Su, M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, N.; Ji, F.; Zhong, C.; Yang, J.; et al. Leptin promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer via the upregulation of pyruvate kinase M2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, H.; Subbaramaiah, K.; Iyengar, N.M.; Zhou, X.K.; Chen, I.C.; Bhardwaj, P.; Gucalp, A.; Morrow, M.; Hudis, C.A.; Dannenberg, A.J.; et al. Leptin regulation of the p53-HIF1α/PKM2-aromatase axis in breast adipose stromal cells: A novel mechanism for the obesity-breast cancer link. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2018, 42, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Sun, Z.; Li, O.; Guo, C.; Yi, W.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, B. Leptin stimulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pro-angiogenic capability of cholangiocarcinoma cells through the miR-122/PKM2 axis. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Huang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Y.; Tian, S.; et al. Leptin enhances glycolysis via OPA1-mediated mitochondrial fusion to promote mesenchymal stem cell survival. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Q.; Tian, Q.; Li, D.; He, S.-Q.; Hu, M.; Liu, S.-Y.; Zou, W.; Chen, Y.-J.; Zhang, P.; Tang, X.-Q. Leptin mediates protection of hydrogen sulfide against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson’s disease: Involving enhancement in Warburg effect. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 135, 104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquer-Rosselló, M.d.M.; Oliver, J.; Sastre-Serra, J.; Valle, A.; Roca, P. Leptin regulates energy metabolism in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 72, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Sakuma, H.; Kojima, T.; Maruyama, T.; Jamali, M.; Cooper, D.R.; Yasuda, K. Leptin and high glucose stimulate cell proliferation in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: Reciprocal involvement of PKC-α and PPAR expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2002, 1592, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlob, K.; Majewski, N.; Kennedy, S.; Kandel, E.; Robey, R.B.; Hay, N. Inhibition of early apoptotic events by Akt/PKB is dependent on the first committed step of glycolysis and mitochondrial hexokinase. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieman, H.L.; Wofford, J.A.; Rathmell, J.C. Cytokine stimulation promotes glucose uptake via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt regulation of Glut1 activity and trafficking. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabral, S.; Muecke, C.; Valasarajan, C.; Schmoranzer, M.; Wietelmann, A.; Semenza, G.L.; Meister, M.; Muley, T.; Seeger-Nukpezah, T.; Samakovlis, C.; et al. A RASSF1A-HIF1α loop drives Warburg effect in cancer and pulmonary hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calgani, A.; Delle Monache, S.; Cesare, P.; Vicentini, C.; Bologna, M.; Angelucci, A. Leptin contributes to long-term stabilization of HIF-1α in cancer cells subjected to oxygen limiting conditions. Cancer Lett. 2016, 376, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T. Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, R.B.; Somwar, R.; Maida, A.; Fang, X.; Bikopoulos, G.; Sweeney, G. Globular adiponectin increases GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, F.; Santos, E.D.; Poidatz, D.; Sérazin, V.; Gronier, H.; Vialard, F.; Dieudonné, M.-N. Adiponectin Inhibits Nutrient Transporters and Promotes Apoptosis in Human Villous Cytotrophoblasts: Involvement in the Control of Fetal Growth1. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 94, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, M.P.; Sweeney, G. The role of adiponectin signaling in metabolic syndrome and cancer. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendar, J.; Frohberger, S.J.; Karunakaran, I.; Schmitt, V.; Stamminger, W.; Neumann, A.-L.; Wilhelm, C.; Hoerauf, A.; Hübner, M.P. Adiponectin Limits IFN-γ and IL-17 Producing CD4 T Cells in Obesity by Restraining Cell Intrinsic Glycolysis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T. Adiponectin Receptor Signaling: A New Layer to the Current Model. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardé, T.; Perrier, S.; Vasson, M.P.; Caldefie-Chézet, F. Molecular mechanisms of leptin and adiponectin in breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faubert, B.; Boily, G.; Izreig, S.; Griss, T.; Samborska, B.; Dong, Z.; Dupuy, F.; Chambers, C.; Fuerth, B.J.; Viollet, B.; et al. AMPK is a negative regulator of the Warburg effect and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Kridel, S. Visfatin/Nampt: A potential regulator of prostate tumor cell proliferation, metabolism, and survival. Cancer Res. 2008, 68 (Suppl. 9), 4362. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.K.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, B.K.; Park, Y.G.; Ko, G.J.; Kang, Y.S.; Han, J.Y.; Han, S.Y.; Han, K.H.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Visfatin: A new player in mesangial cell physiology and diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2008, 295, F1485–F1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Young, D.A.; Lu, Z.H.; Wang, T.; Meier, T.I.; Shepard, R.L.; Roth, K.; Zhai, Y.; Huss, K.; Kuo, M.S.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT), an enzyme essential for NAD+ biosynthesis, in human cancer cells: Metabolic basis and potential clinical implications. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3500–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porporato, P.E.; Filigheddu, N.; Pedro, J.M.B.-S.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.P.; Attardi, G. Human cells lacking mtDNA: Repopulation with exogenous mitochondria by complementation. Science 1989, 246, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaini, G.; Sgarbi, G.; Baracca, A. Oxidative phosphorylation in cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2011, 1807, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathupala, S.P.; Ko, Y.H.; Pedersen, P.L. The pivotal roles of mitochondria in cancer: Warburg and beyond and encouraging prospects for effective therapies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2010, 1797, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Blanquer-Rosselló, M.M.; Santandreu, F.M.; Oliver, J.; Roca, P.; Valle, A. Leptin Modulates Mitochondrial Function, Dynamics and Biogenesis in MCF-7 Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Fei, Z.; Yang, Z.; Duan, K.; Zi, J.; Cui, Q.; Yu, M.; Xiong, W. Leptin promotes fatty acid oxidation and OXPHOS via the c-Myc/PGC-1 pathway in cancer cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kusminski, C.M.; Chua, S.C.; Scherer, P.E. Leptin receptor signaling supports cancer cell metabolism through suppression of mitochondrial respiration in vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 3133–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehuda-Shnaidman, E.; Nimri, L.; Tarnovscki, T.; Kirshtein, B.; Rudich, A.; Schwartz, B. Secreted human adipose leptin decreases mitochondrial respiration in HCT116 colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, E.M. The Adiponectin-Mitochondria Connection. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ec136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snaebjornsson, M.T.; Janaki-Raman, S.; Schulze, A. Greasing the Wheels of the Cancer Machine: The Role of Lipid Metabolism in Cancer. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chajès, V.; Cambot, M.; Moreau, K.; Lenoir, G.M.; Joulin, V. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha is essential to breast cancer cell survival. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5287–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.R.; Schulze, A. Lipid metabolism in cancer. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Temkin, S.M.; Hawkridge, A.M.; Guo, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.Y.; Fang, X. Fatty acid oxidation: An emerging facet of metabolic transformation in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 435, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Yang, H. The role of cholesterol metabolism in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Fazolini, N.P.B.; Cruz, A.L.S.; Werneck, M.B.F.; Viola, J.P.B.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Bozza, P.T. Leptin activation of mTOR pathway in intestinal epithelial cell triggers lipid droplet formation, cytokine production and increased cell proliferation. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Su, M.; Ji, F.; Wang, N.; Zhong, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; et al. Leptin promotes the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by upregulating ACAT2. Cell. Oncol. 2017, 40, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.-V.; Tilija Pun, N.; Park, P.-H. Autophagy activation and SREBP-1 induction contribute to fatty acid metabolic reprogramming by leptin in breast cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogalska, A.; Sucajtys-Szulc, E.; Swierczynski, J. Leptin decreases lipogenic enzyme gene expression through modification of SREBP-1c gene expression in white adipose tissue of aging rats. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2005, 54, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuma, T.; Lee, Y.; Higa, M.; Wang, Z.-w.; Pan, W.; Shimomura, I.; Unger, R.H. Leptin, troglitazone, and the expression of sterol regulatory element binding proteins in liver and pancreatic islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momken, I.; Chabowski, A.; Dirkx, E.; Nabben, M.; Jain, S.S.; McFarlan, J.T.; Glatz, J.F.; Luiken, J.J.; Bonen, A. A new leptin-mediated mechanism for stimulating fatty acid oxidation: A pivotal role for sarcolemmal FAT/CD36. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Han, H.; Liu, L.; Duan, Y.; Yang, X.; Ma, C.; Zhu, Y.; Han, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. CD36 plays a critical role in proliferation, migration and tamoxifen-inhibited growth of ER-positive breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.W.; Wilkins, O.; Bang, S.; Ung, M.; Li, J.; An, J.; Del Genio, C.; Canfield, K.; DiRenzo, J.; Wells, W.; et al. CD36-Mediated Metabolic Rewiring of Breast Cancer Cells Promotes Resistance to HER2-Targeted Therapies. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 3405–3420.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Garcia, M.; Steinbauer, B.; Srivastava, K.; Singhal, M.; Mattijssen, F.; Maida, A.; Christian, S.; Hess-Stumpp, H.; Augustin, H.G.; Müller-Decker, K.; et al. Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 1-Dependent Protein Acetylation Controls Breast Cancer Metastasis and Recurrence. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 842–855.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, C.; Pinto, A.; Martherus, R.; Santiago de Jesus, J.P.; Polet, F.; Feron, O. Acidosis Drives the Reprogramming of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Cancer Cells through Changes in Mitochondrial and Histone Acetylation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awazawa, M.; Ueki, K.; Inabe, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Kaneko, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Bardeesy, N.; Ohnishi, S.; Nagai, R.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin suppresses hepatic SREBP1c expression in an AdipoR1/LKB1/AMPK dependent pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbard, L.; Ranscht, B. Multifaceted roles of Adiponectin in cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Takahashi, H.; Hosono, K.; Endo, H.; Kato, S.; Yoneda, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; Wada, K.; et al. Adiponectin inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth through the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Zheng, J.; Yao, X.; Peng, B. Adiponectin inhibits VEGF-A in prostate cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 4287–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, J.-J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.B. Adiponectin Increases Fatty Acid Oxidation in Skeletal Muscle Cells by Sequential Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase, p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, and Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor α. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.; Godlewski, G.; Earley, B.J.; Zhou, L.; Jourdan, T.; Szanda, G.; Cinar, R.; Kunos, G. Role of adiponectin in the metabolic effects of cannabinoid type 1 receptor blockade in mice with diet-induced obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E457–E468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S.-L.; Wong, N.-S.; Chen, J.; Shepherd, P.R.; Wang, Y. Cholesterol-induced mammary tumorigenesis is enhanced by adiponectin deficiency: Role of LDL receptor upregulation. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 1804–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, S.R.; Collins, J.M.; Cheng, W.-C.; Haider, S.; Wigfield, S.; Gaude, E.; Fielding, B.A.; Pinnick, K.E.; Harjes, U.; Segaran, A.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of human primary breast cancer identifies fatty acid oxidation as a target for metformin. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miethe, C.; Zamora, M.; Torres, L.; Raign, K.G.; Groll, C.J.; Price, R.S. Characterizing the differential physiological effects of adipocytokines visfatin and resistin in liver cancer cells. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2019, 38, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yu, L.; Zhou, W.; Luo, M. Resistin increases lipid accumulation and CD36 expression in human macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, B.; Di Donato, M.; Pezone, A.; Di Zazzo, E.; Giovannelli, P.; Galasso, G.; Castoria, G.; Migliaccio, A. ROS in cancer therapy: The bright side of the moon. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.S.; Tuveson, D.A. The promise and perils of antioxidants for cancer patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroyen, B.; Guimarães, E.L.; Dollé, L.; Coulon, S.; Empsen, C.; Nyssen, M.; Geerts, A.; Colle, I.; Geerts, A.; van Grunsven, L.A. Leptin-mediated reactive oxygen species production does not significantly affect primary mouse hepatocyte functions in vitro. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 24, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbouli, S.; Der Vartanian, A.; Ortega, S.; Rougé, S.; Vasson, M.-P.; Rossary, A. Leptin induces ROS via NOX5 in healthy and neoplastic mammary epithelial cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3254–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal-Serrano, M.; Sastre-Serra, J.; Valle, A.; Roca, P.; Oliver, J. Chronic-Leptin Attenuates Cisplatin Cytotoxicity in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bułdak, R.J.; Pilc-Gumuła, K.; Bułdak, Ł.; Witkowska, D.; Kukla, M.; Polaniak, R.; Zwirska-Korczala, K. Effects of ghrelin, leptin and melatonin on the levels of reactive oxygen species, antioxidant enzyme activity and viability of the HCT 116 human colorectal carcinoma cell line. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2275–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahbouli, S.; Talvas, J.; der Vartanian, A.; Ortega, S.; Rougé, S.; Vasson, M.-P.; Rossary, A. Activation of antioxidant defences of human mammary epithelial cells under leptin depend on neoplastic state. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzy, R.D.; Hoyos, B.; Robin, E.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Mansfield, K.D.; Simon, M.C.; Hammerling, U.; Schumacker, P.T. Mitochondrial complex III is required for hypoxia-induced ROS production and cellular oxygen sensing. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bułdak, R.J.; Bułdak, Ł.; Polaniak, R.; Kukla, M.; Birkner, E.; Kubina, R.; Kabała-Dzik, A.; Duława-Bułdak, A.; Żwirska-Korczala, K. Visfatin affects redox adaptative responses and proliferation in Me45 human malignant melanoma cells: An in vitro study. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronis, K.N.; Siatis, K.E.; Giannopoulou, E.; Kalofonos, P.H. Adiponectin Promotes Autophagy and Apoptosis in Endometrial Cancer Cell Lines. Clincs Oncol. 2019, 4, 1660. [Google Scholar]
- Nigro, E.; Schettino, P.; Polito, R.; Scudiero, O.; Monaco, M.L.; De Palma, G.D.; Daniele, A. Adiponectin and colon cancer: Evidence for inhibitory effects on viability and migration of human colorectal cell lines. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 448, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yu, C.-H.; Jen, C.-Y.; Cheng, C.-F.; Chou, Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Juan, S.-H. Adiponectin-Mediated Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction Protects Against Iron-Induced Liver Injury via a PPARα-Dependent Mechanism. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Nagy, L.E.; Park, P.-H. Globular adiponectin inhibits ethanol-induced reactive oxygen species production through modulation of NADPH oxidase in macrophages: Involvement of liver kinase B1/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 86, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Ma, M.; Zhou, D.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.; Jia, L.; et al. Adiponectin modulates oxidative stress-induced mitophagy and protects C2C12 myoblasts against apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanand, S.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Emerging Roles for Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, E.L.; Nguyen, T.; Rhyne, S.; Kim, J. Amino acids in cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettore, L.; Westbrook, R.L.; Tennant, D.A. New aspects of amino acid metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, D.R.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Mancuso, A.; Sayed, N.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Pfeiffer, H.K.; Nissim, I.; Daikhin, E.; Yudkoff, M.; McMahon, S.B.; et al. Myc regulates a transcriptional program that stimulates mitochondrial glutaminolysis and leads to glutamine addiction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chang, Y.C.; Liu, C.L.; Chang, K.J.; Guo, I.C. Leptin-induced growth of human ZR-75-1 breast cancer cells is associated with up-regulation of cyclin D1 and c-Myc and down-regulation of tumor suppressor p53 and p21WAF1/CIP1. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 98, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.N.; Higashi, R.M.; Fan, T.W.M. Metabolic reprogramming in tumors: Contributions of the tumor microenvironment. Genes Dis. 2020, 7, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.S.; Kang, C.W.; Kang, S.; Jang, Y.; Chae, Y.C.; Kim, B.G.; Cho, N.H. ITGB4-mediated metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncogene 2020, 39, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.M.; O’Connell, J.T.; Vo, A.P.; Cain, M.P.; Tampe, D.; Bizarro, L.; Sugimoto, H.; McGow, A.K.; Asara, J.M.; Lovisa, S.; et al. Epigenetic Reprogramming of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Deregulates Glucose Metabolism and Facilitates Progression of Breast Cancer. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazeides, C.; Le, A. Metabolic Relationship between Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Cancer Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1063, 149–165. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, I.; Catalano, S.; Gelsomino, L.; Marsico, S.; Giordano, C.; Panza, S.; Bonofiglio, D.; Bossi, G.; Covington, K.R.; Fuqua, S.A.W.; et al. Leptin Mediates Tumor–Stromal Interactions That Promote the Invasive Growth of Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, S.; Chen, F.; Fu, Z.; Yin, H.; Lu, X.; Yu, J.; Lu, C. Mammary fat of breast cancer: Gene expression profiling and functional characterization. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Cha, Y.J.; Koo, J.S. Adipocyte biology in breast cancer: From silent bystander to active facilitator. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 69, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V.; White, E. Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewirtz, D.A. The four faces of autophagy: Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.; Mehnert, J.M.; Chan, C.S. Autophagy, Metabolism, and Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5037–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.-X.; Yin, X.-M. Mitophagy: Mechanisms, pathophysiological roles, and analysis. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kaushik, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Novak, I.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, K.; Cuervo, A.M.; Czaja, M.J. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halama, A.; Kulinski, M.; Dib, S.S.; Zaghlool, S.B.; Siveen, K.S.; Iskandarani, A.; Zierer, J.; Prabhu, K.S.; Satheesh, N.J.; Bhagwat, A.M.; et al. Accelerated lipid catabolism and autophagy are cancer survival mechanisms under inhibited glutaminolysis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 430, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosc, C.; Broin, N.; Fanjul, M.; Saland, E.; Farge, T.; Courdy, C.; Batut, A.; Masoud, R.; Larrue, C.; Skuli, S.; et al. Autophagy regulates fatty acid availability for oxidative phosphorylation through mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum contact sites. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Qian, W.; Li, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Duan, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. High glucose microenvironment accelerates tumor growth via SREBP1-autophagy axis in pancreatic cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, F.; Servais, S.; Besson, P.; Roger, S.; Dumas, J.-F.; Brisson, L. Autophagy and mitophagy in cancer metabolic remodelling. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 98, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, M.; Marusawa, H.; Wang, H.Q.; Iwai, A.; Ikeuchi, K.; Imai, Y.; Kataoka, A.; Nukina, N.; Takahashi, R.; Chiba, T. Parkin as a tumor suppressor gene for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6002–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, P.; Wang, W.; Kim, S.H.; Wang, S.; Burns, T.F.; Sax, J.K.; Buzzai, M.; Dicker, D.T.; McKenna, W.G.; Bernhard, E.J.; et al. Bnip3L is induced by p53 under hypoxia, and its knockdown promotes tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourasia, A.H.; Boland, M.L.; Macleod, K.F. Mitophagy and cancer. Cancer Metab. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Overholtzer, M.; Thompson, C.B. Autophagy in cellular metabolism and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, D.R.; Thompson, C.B. Glutamine addiction: A new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geldermalsen, M.; Wang, Q.; Nagarajah, R.; Marshall, A.D.; Thoeng, A.; Gao, D.; Ritchie, W.; Feng, Y.; Bailey, C.G.; Deng, N.; et al. ASCT2/SLC1A5 controls glutamine uptake and tumour growth in triple-negative basal-like breast cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. Cancer cell metabolism: The essential role of the nonessential amino acid, glutamine. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Xuan, Z.; Xu, P.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Sun, G.; Xu, J.; Xu, Z. Novel role of miR-133a-3p in repressing gastric cancer growth and metastasis via blocking autophagy-mediated glutaminolysis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, V.H.; Merhi, F.; Djavaheri-Mergny, M.; Durán, R.V. Glutaminolysis and autophagy in cancer. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, R.V.; Hall, M.N. Glutaminolysis feeds mTORC1. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 4107–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, W.H.; Chang, T.M.; Lee, W.J.; Ou, H.C.; Wu, C.M.; Tseng, L.N.; Lang, H.F.; Wu, C.S.; Wan, C.J.; Lee, I.T. Effect of weight loss on proinflammatory state of mononuclear cells in obese women. Obesity 2008, 16, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Conde, R.; Perez Castrillon, J.L. Effects of lifestyle modification on adipocytokine levels in obese patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 12, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Bellioo, D.; Conde, R. Effects of a low-fat versus a low-carbohydrate diet on adipocytokines in obese adults. Horm. Res. 2007, 67, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.M.; Newcomer, A.D.; Moertel, C.G.; Go, V.L.; Dimagno, E.P. Assessment of weight loss, food intake, fat metabolism, malabsorption, and treatment of pancreatic insufficiency in pancreatic cancer. Cancer 1983, 52, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebowski, R.T.; Blackburn, G.L.; Thomson, C.A.; Nixon, D.W.; Shapiro, A.; Hoy, M.K.; Goodman, M.T.; Giuliano, A.E.; Karanja, N.; McAndrew, P.; et al. Dietary fat reduction and breast cancer outcome: Interim efficacy results from the Women’s Intervention Nutrition Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zacher, J.H.; Neil, E.S.; McGinley, J.N.; Thompson, H.J. Effects of energy restriction and wheel running on mammary carcinogenesis and host systemic factors in a rat model. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otvos, L., Jr.; Kovalszky, I.; Riolfi, M.; Ferla, R.; Olah, J.; Sztodola, A.; Nama, K.; Molino, A.; Piubello, Q.; Wade, J.D.; et al. Efficacy of a leptin receptor antagonist peptide in a mouse model of triple-negative breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otvos, L., Jr.; Kovalszky, I.; Scolaro, L.; Sztodola, A.; Olah, J.; Cassone, M.; Knappe, D.; Hoffmann, R.; Lovas, S.; Hatfield, M.P.; et al. Peptide-based leptin receptor antagonists for cancer treatment and appetite regulation. Biopolymers 2011, 96, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malih, S.; Najafi, R. AdipoRon: A possible drug for colorectal cancer prevention? Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 6673–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, M.; Maruyama, R.; Kawabata, Y.; Tajima, Y.; Takenaga, K. Antidiabetic adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon suppresses tumour growth of pancreatic cancer by inducing RIPK1/ERK-dependent necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramzan, A.A.; Bitler, B.G.; Hicks, D.; Barner, K.; Qamar, L.; Behbakht, K.; Powell, T.; Jansson, T.; Wilson, H. Adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon induces apoptotic cell death and suppresses proliferation in human ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 461, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: Rationale and promise. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxhaj, G.; Manning, B.D. The PI3K–AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Pauli, C.; Du, X.; Wang, D.G.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Amadiume, S.C.; Goncalves, M.D.; Hodakoski, C.; Lundquist, M.R.; et al. Suppression of insulin feedback enhances the efficacy of PI3K inhibitors. Nature 2018, 560, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leo, V.; la Marca, A.; Orvieto, R.; Morgante, G. Effect of Metformin on Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) I and IGF-Binding Protein I in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1598–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, T.; da Silva Xavier, G.; Leclerc, I.; Rutter, G.A. 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase controls insulin-containing secretory vesicle dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52042–52051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, G.A.; Da Silva Xavier, G.; Leclerc, I. Roles of 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in mammalian glucose homoeostasis. Biochem. J. 2003, 375 Pt 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Hildebrandt, I.J.; Prins, R.M.; Soto, H.; Mazzotta, M.M.; Dang, J.; Czernin, J.; Shyy, J.Y.J.; Watson, A.D.; Phelps, M.; et al. The AMPK agonist AICAR inhibits the growth of EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastomas by inhibiting lipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Saha, A.K.; Wen, R.; Ruderman, N.B.; Luo, Z. AMP-activated protein kinase activators can inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells by multiple mechanisms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham, D.-V.; Park, P.-H. Tumor Metabolic Reprogramming by Adipokines as a Critical Driver of Obesity-Associated Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031444
Pham D-V, Park P-H. Tumor Metabolic Reprogramming by Adipokines as a Critical Driver of Obesity-Associated Cancer Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031444
Chicago/Turabian StylePham, Duc-Vinh, and Pil-Hoon Park. 2021. "Tumor Metabolic Reprogramming by Adipokines as a Critical Driver of Obesity-Associated Cancer Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031444
APA StylePham, D.-V., & Park, P.-H. (2021). Tumor Metabolic Reprogramming by Adipokines as a Critical Driver of Obesity-Associated Cancer Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031444





