Neuraminidase Inhibitor Zanamivir Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Role of NEU2/3 Inhibition in CIA and STIA
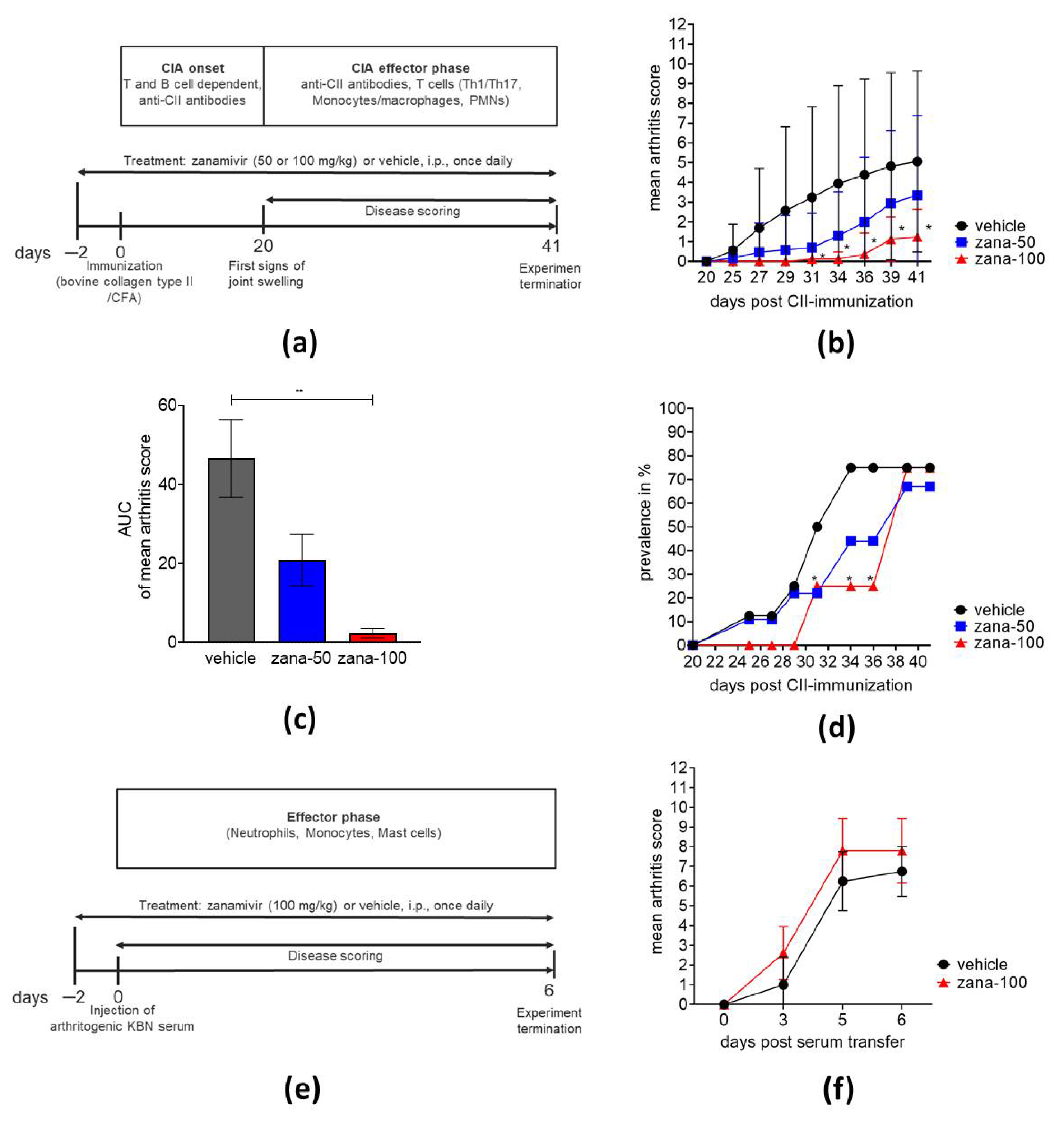
2.1.1. Zanamivir Treatment Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis But Not Serum Transfer-Induced Arthritis
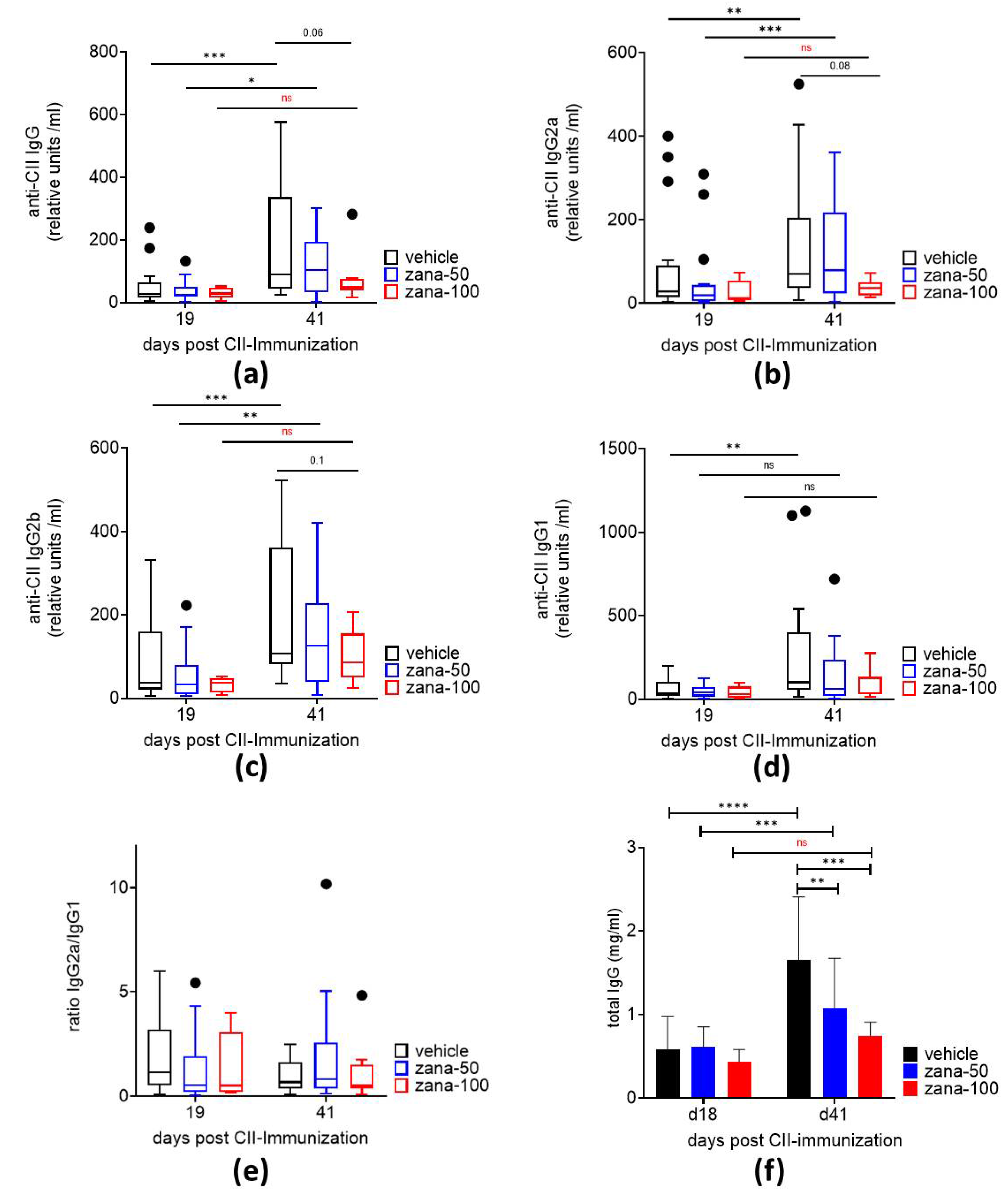
2.1.2. Zanamivir Inhibits Production of Anti-CII Autoantibodies and Total IgG in CIA
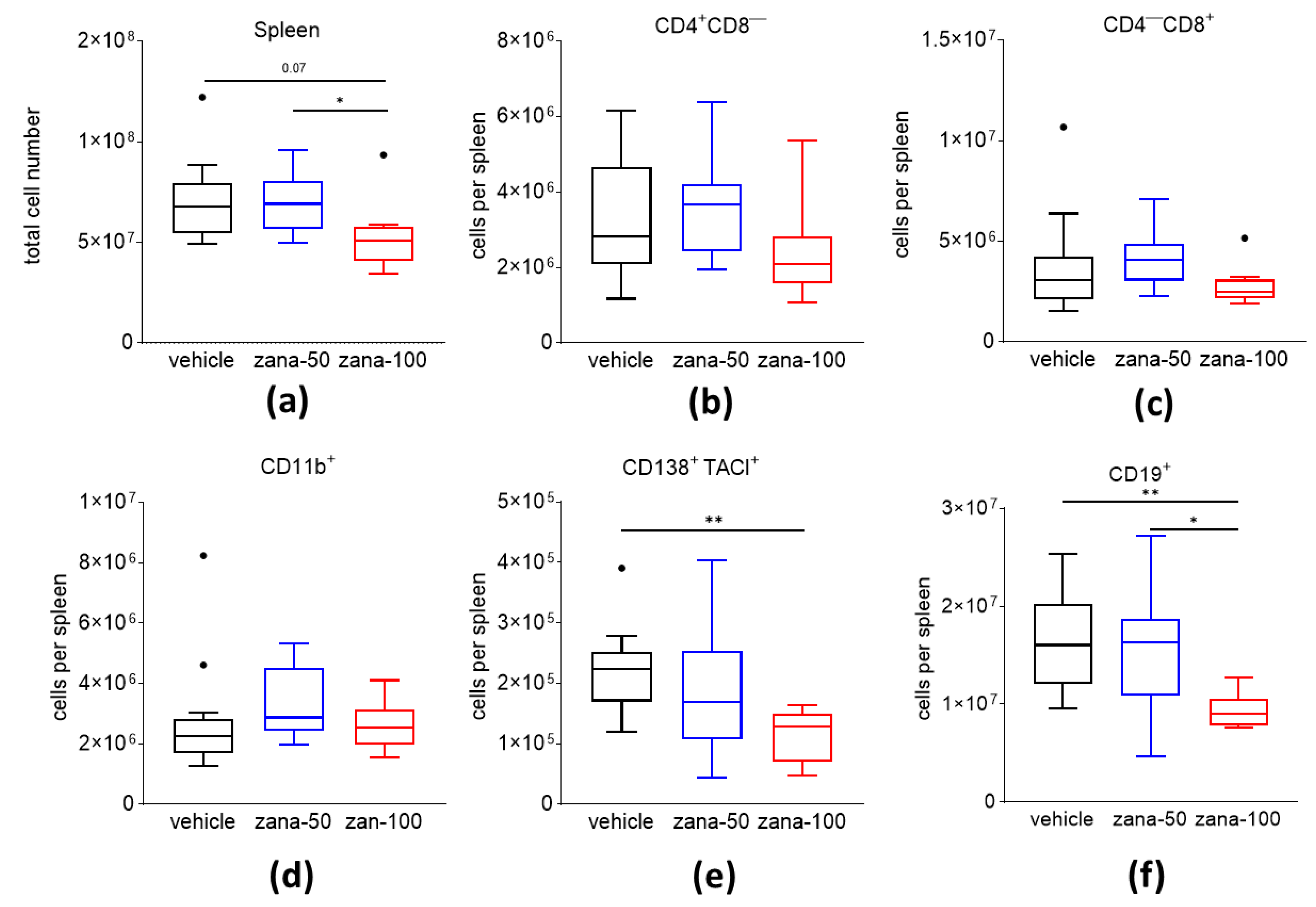
2.2. Zanamivir Treatment Decreases Absolute Numbers of CD138+/TACI+ Plasma Cells and CD19+ B Cells in CIA
2.3. Role of NEU2/3 Inhibition on Sialylation Pattern in CIA
2.3.1. Zanamivir Increases Sialic Acid Content of Circulating IgG During CIA
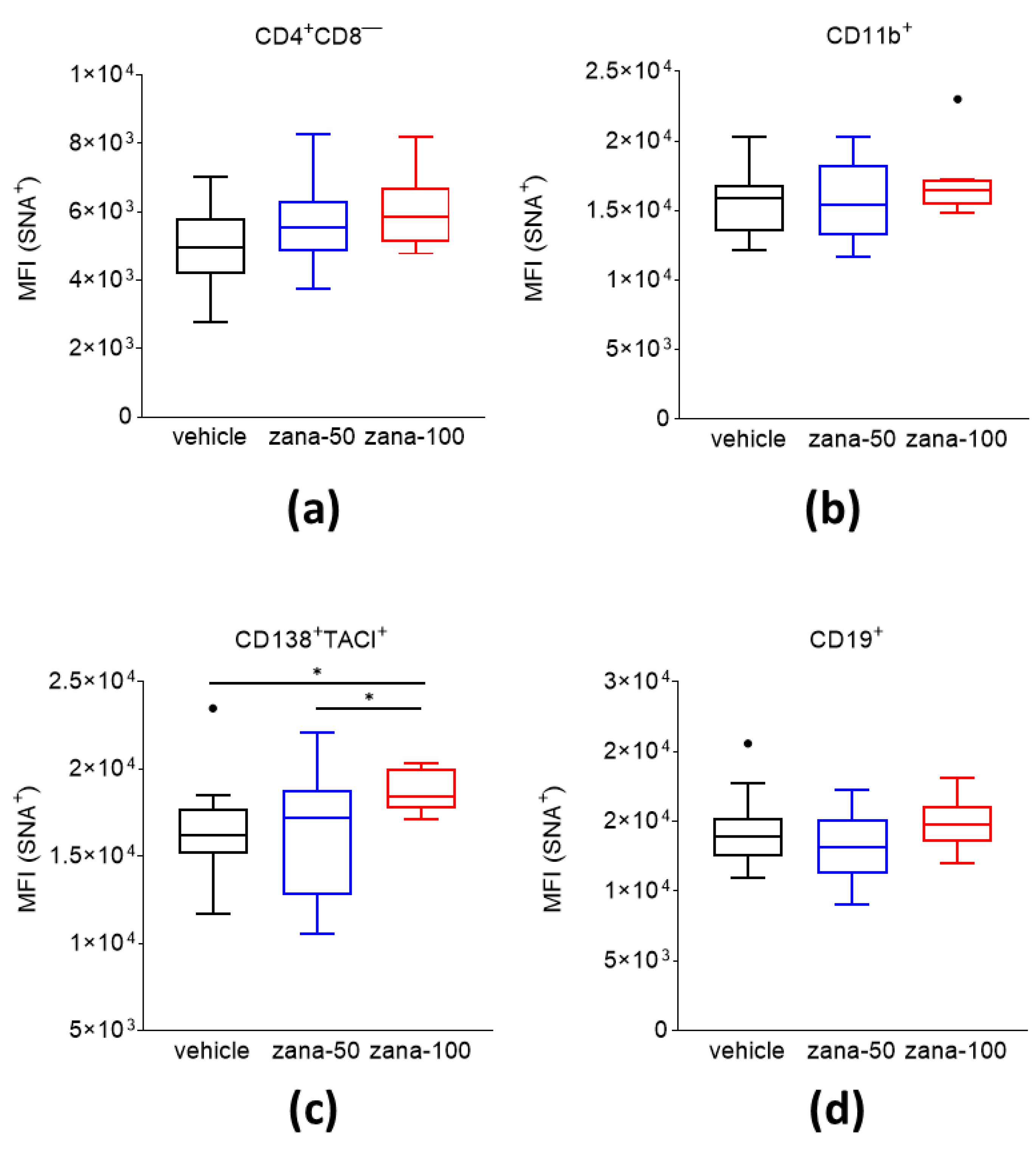
2.3.2. Zanamivir Treatment Leads to Increased Levels of (2,6)-sialic Acid Content on the Cell Surface of CD138+/TACI+ Plasma Cells
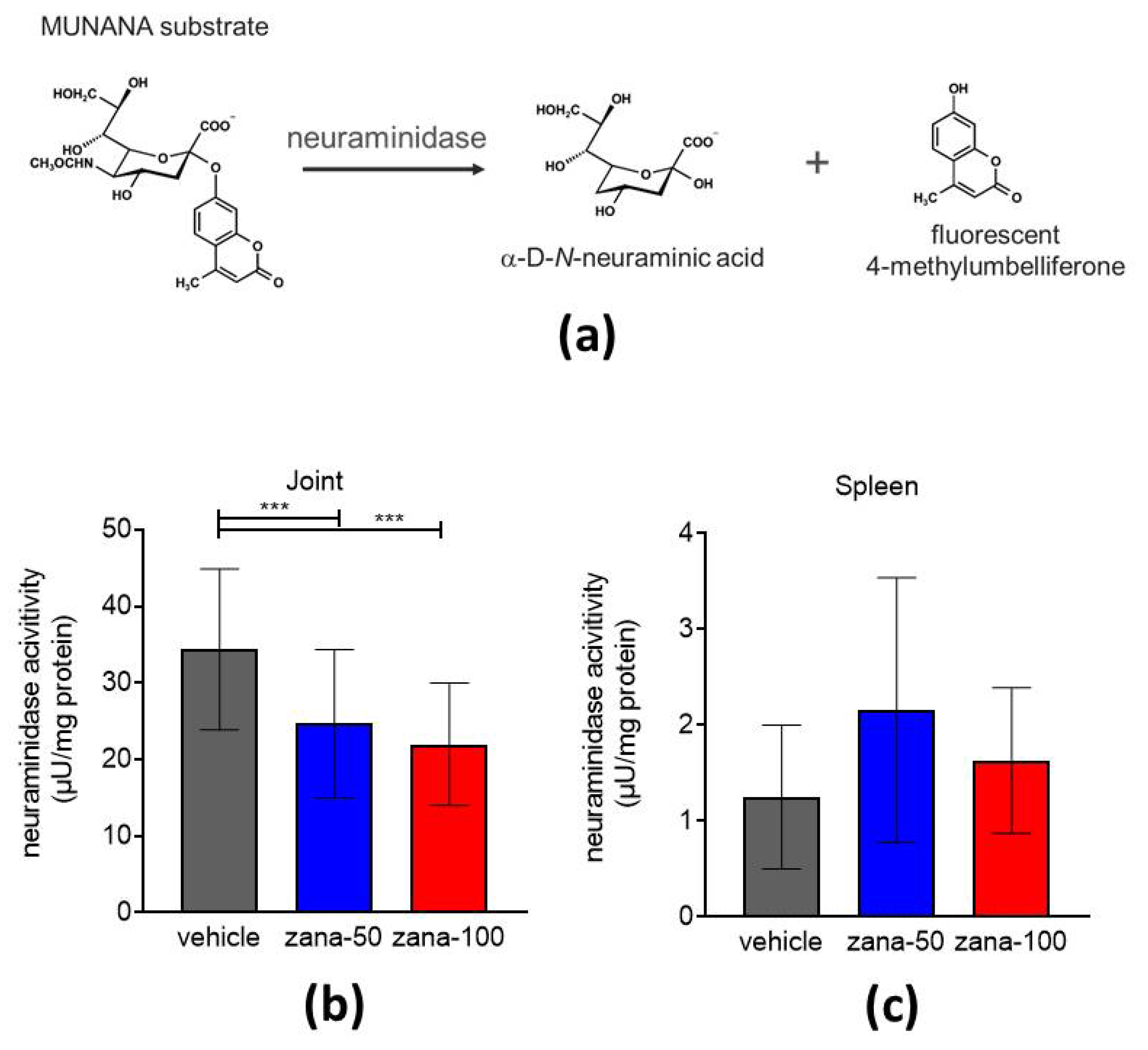
2.4. Role of NEU 2/3 Inhibition on Neuramidase Activity in CIA
Zanamivir-Treated Arthritic Mice Show Reduced Neuraminidase Activity in Arthritic Joints
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mouse Models of Arthritis and Scoring
4.2. Treatment of CIA and STIA with Zanamivir
4.3. Determination Measurement of anti-CII Autoantibodies and Total IgG
4.4. Determination of Alpha-Linked 2,6-sialic Acids on Total IgG by ELISA
4.5. Phenotyping of Splenocytes and Determination of 2,6-sialytated Cell Surface Subsets by Flow Cytometry
4.6. Preparation of Spleen and Paw Tissue Lysates
4.7. Determination of Neuraminidase Activity
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACPAs | anti-citrullinated protein antibodies |
| CII | collagen type II |
| CFA | complete Freund’s adjuvant |
| CIA | collagen-induced arthritis |
| DANA | 2,3-dehydro-2-deoxy-N-acetylneuraminic acid |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| FCS | fetal calf serum |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FO | follicular |
| IFN | interferon |
| Ig | immunoglobulin |
| IL | interleukin |
| IVIG | intravenous immunoglobulin G |
| MFI | mean flourescence intensity |
| MZ | marginal zone |
| 4-MUNANA | 2′-(4- Methylumbelliferyl)-α-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid |
| NEU | neuraminidase |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SA | sialic acid |
| SNA | Sambucus Nigra agglutinin |
| ST | sialyltransferases |
| STIA | serum-transfer induced arthritis |
| TH | T helper |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Scherer, H.U.; Häupl, T.; Burmester, G.R. The Etiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, T.D.; Mikuls, T.R. Recent Advances in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesharwani, D.; Paliwal, R.; Satapathy, T.; Das Paul, S. Rheumatiod Arthritis: An Updated Overview of Latest Therapy and Drug Delivery. J. Pharmacopunct. 2019, 22, 210–224. [Google Scholar]
- Rein, P.; Mueller, R.B. Treatment with Biologicals in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Rheumatol. Ther. 2017, 4, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, H.-Y.; Tee, S.Z.-Y.; Wong, M.M.-T.; Chow, S.-K.; Peh, S.-C.; Teow, S.-Y. Pathogenic Role of Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications in Clinical Treatment and Biomarker Development. Cells 2018, 7, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetland, M.L.; Christensen, I.J.; Tarp, U.; Dreyer, L.; Hansen, A.; Hansen, I.T.; Kollerup, G.; Linde, L.; Lindegaard, H.M.; Poulsen, U.E.; et al. All Departments of Rheumatology in, D., Direct Comparison of Treatment Responses, Remission Rates, and Drug Adherence in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Adalimumab, Etanercept, or Infliximab: Results from Eight Years of Surveillance of Clinical Practice in the Nationwide Danish DANBIO Registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kalden, J.R.; Schulze-Koops, H. Immunogenicity and Loss of Response to TNF Inhibitors: Implications for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, H.; Koller, T.; Engström, Å.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Turnay, J.; Kraetsch, H.G.; Kalden, J.R.; Holmdahl, R. Epitope-Specific Recognition of Type II Collagen by Rheumatoid Arthritis Antibodies Is Shared with Recognition by Antibodies That Are Arthritogenic in Collagen-Induced Arthritis in the Mouse. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delft, v.M.A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J. An Overview of Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, S.; Nimmerjahn, F. The Role of FC Receptors and Complement in Autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, S.; Schwab, I.; Lux, A.; Nimmerjahn, F. The Role of Sialic Acid as a Modulator of the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of IgG. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, H.; Collin, M.; Dudziak, D.; Ravetch, J.V.; Nimmerjahn, F. In Vivo Enzymatic Modulation of IgG Glycosylation Inhibits Autoimmune Disease in an IgH Subclass-Dependent Manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15005–15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Immunoglobulin G Resulting from Fc Sialylation. Science 2006, 313, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwedler, C.; Häupl, T.; Kalus, U.; Blanchard, V.; Burmester, G.-R.; Poddubnyy, D.; Hoppe, B. Hypogalactosylation of Immunoglobulin G in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Relationship to HLA-DRB1 Shared Epitope, Anticitrullinated Protein Antibodies, Rheumatoid Factor, and Correlation with Inflammatory Activity. Arthritis Res. 2018, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Wormald, M.R.; Rudd, P.M.; Fischer, P.B.; Dwek, R.A.; Sim, R.B. Glycosylation Changes of IgG Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Can Activate Complement via the Mannose-Binding Protein. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmi, Y.; Ise, W.; Harazono, A.; Takakura, D.; Fukuyama, H.; Baba, Y.; Narazaki, M.; Shoda, H.; Takahashi, N.; Ohkawa, Y.; et al. Si-Alylation Converts Arthritogenic IgG into Inhibitors of Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ashline, D.J.; Reinhold, V.N.; Paulson, J.C.; Ravetch, J.V. Recapitulation of IVIG Anti-Inflammatory Activity with a Recombinant IgG Fc. Science 2008, 320, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontyev, D.; Katsman, Y.; Ma, X.-Z.; Miescher, S.; Käsermann, F.; Branch, D.R. Sialylation-Independent Mechanism Involved in the Amelioration of Murine Immune Thrombocytopenia Using Intravenous Gammaglobulin. Transfusion 2012, 52, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorczyca, W.; Wieczorek, Z.; Lisowski, J. Cell Surface Sialic Acid Affects Immunoglobulin Binding to Macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1989, 259, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Takasaki, S. Suppressive Role of Sialylated N-Glycans in Fc Receptor-Mediated Phagocytosis by Macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 192, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, J.; Kerst, G.; Handgretinger, R.; Müller, I. Increased α2,6-Sialylation of Surface Proteins on Tolerogenic, Immature Dendritic Cells and Regulatory T Cells. Exp. Hematol. 2006, 34, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, X.-L. Sialyltransferase Inhibition and Recent Advances. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2016, 1864, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, T.; Yamaguchi, K. Mammalian Sialidases: Physiological and Pathological Roles in Cellular Functions. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 880–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, K.; Koseki, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Moriya, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Yingsakmongkon, S.; Hirai, G.; Sodeoka, M.; Von Itzstein, M.; Miyagi, T. Limited Inhibitory Effects of Oseltamivir and Zanamivir on Human Sialidases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3484–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, J.; Gilbertson, B.P.; Trifkovic, S.; Brown, L.E.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Structure and Functions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubareva, L.V.; Kaiser, L.; Hayden, F.G. Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Inhibitors. Lancet 2000, 355, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, O.; Kessler, N.; Lina, B. Sensitivity of Influenza Viruses to Zanamivir and Oseltamivir: A Study Performed on Viruses Circulating in France Prior to the Introduction of Neuraminidase Inhibitors in Clinical Practice. Antivir. Res. 2005, 68, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, L.-B.; Huang, C.-C. Sialyltransferase and Neuraminidase Levels/Ratios and Sialic Acid Levels in Peripheral Blood B Cells Correlate with Measures of Disease Activity in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtenay, J.S.; Dallman, M.J.; Dayan, A.D.; Martin, A.; Mosedale, B. Immunisation against Heterologous Type II Collagen Induces Arthritis in Mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 1980, 283, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentham, E.D.; Townes, A.S.; Kang, A.H. Autoimmunity to Type II Collagen an Experimental Model of Arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 1977, 146, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, M.-L.; Bonnefoy, J.-Y.; Accart, N.; Cochin, S.; Pohle, S.; Haegel, H.; De Meyer, M.; Zemmour, C.; Preville, X.; Guillen, C.; et al. Bone- and Cartilage-Protective Effects of a Monoclonal Antibody Against Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor in Experimental Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2989–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, F.; Nomura, M.; Nakamura, K. Arthritis in Mice Induced by a Single Immunisation with Collagen. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1996, 55, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alunno, A.; Carubbi, F.; Giacomelli, R.; Gerli, R. Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: New Players and Therapeutic Targets. BMC Rheumatol. 2017, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, M.J.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. The Role of Collagen Antibodies in Mediating Arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2008, 18, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Itzstein, M.; Wu, W.-Y.; Kok, G.B.; Pegg, M.S.; Dyason, J.C.; Jin, B.; Van Phan, T.; Smythe, M.L.; White, H.F.; Oliver, S.W.; et al. Rational Design of Potent Sialidase-Based Inhibitors of Influenza Virus Replication. Nat. Cell Biol. 1993, 363, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.D.; Haase, C.; Cook, A.D.; Hamilton, J.A. K/BxN Serum-Transfer Arthritis as a Model for Human Inflammatory Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, K.; Clauder, A.-K.; Manz, R.A. Targeting B Cells and Plasma Cells in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, Y.C.; Rahmöller, J.; Mertes, M.M.M.; Eiglmeier, S.; Lorenz, F.K.M.; Stoehr, A.D.; Braumann, D.; Lorenz, A.K.; Winkler, A.; Lilienthal, G.-M.; et al. Sialylated Autoantigen-Reactive IgG Antibodies Attenuate Disease Development in Autoimmune Mouse Models of Lupus Nephritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potier, M.; Mameli, L.; Bélisle, M.; Dallaire, L.; Melançon, S. Fluorometric Assay of Neuraminidase with a Sodium (4-methylumbelliferyl-α-d-N-acetylneuraminate) Substrate. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 94, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-L.; Wang, P.-H. Aberrant Sialylation of Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Bäcklund, J.; Vestberg, M.; Holmdahl, R. Collagen type II (CII)-specific Antibodies Induce Arthritis in the Absence of T or B Cells but the Arthritis Progression Is Enhanced by CII-Reactive T Cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, R544–R550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörner, T.; Radbruch, A.; Burmester, G.R. B-Cell-Directed Therapies for Autoimmune Disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2009, 5, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, L.; Jirholt, J.; Holmdahl, R.; Jansson, L. B Cell-Deficient Mice Do Not Develop Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 111, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanaba, K.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Venturi, G.M.; Steeber, D.A.; St Clair, E.W.; Tedder, T.F. B Cell Depletion Delays Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice: Arthritis Induction Requires Synergy between Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahdah, A.; Habir, K.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Saxena, A.; Xu, B.; Holmdahl, R.; Malin, S.G. Germinal Center B Cells Are Essential for Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnrot, C.E.; Prokopec, K.; Råsbo, K.; Karlsson, M.C.; Kleinau, S. Marginal Zone B Cells Are Naturally Reactive to Collagen Type II and Are Involved in the Initiation of the Immune Response in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monach, P.; Hattori, K.; Huang, H.; Hyatt, E.; Morse, J.; Nguyen, L.; Ortiz-Lopez, A.; Wu, H.-J.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. The K/BxN Mouse Model of Inflammatory Arthritis: Theory and Practice. Methods Mol. Med. 2007, 136, 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Sakarya, S.; Rifat, S.; Zhou, J.; Bannerman, U.D.; Stamatos, N.M.; Cross, A.S.; Goldblum, S.E. Mobilization of Neutrophil Sialidase Activity Desialylates the Pulmonary Vascular Endothelial Surface and Increases Resting Neutrophil Adhesion to and Migration across the Endothelium. Glycobiology 2004, 14, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, L.; Almulki, L.; Faez, S.; Whitford, M.; Hafezi-Moghadam, A.; Cross, A.S. Endogenous PMN Sialidase Activity Exposes Activation Epitope On CD11b/CD18 Which Enhances Its Binding Interaction with ICAM-1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifat, S.; Kang, T.J.; Mann, D.; Zhang, L.; Puche, A.C.; Stamatos, N.M.; Goldblum, S.E.; Brossmer, R.; Cross, A.S. Expression of Sialyltransferase Activity on Intact Human Neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizov, V.; Dietel, K.; Steffen, F.; Dürholz, K.; Meidenbauer, J.; Lucas, S.; Frech, M.; Omata, Y.; Tajik, N.; Knipfer, L.; et al. Ethanol Consumption Inhibits TFH Cell Responses and the Development of Autoimmune Arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, I.; Nimmerjahn, F. Role of Sialylation in the Anti-inflammatory Activity of Intravenous Immunoglobulin—F(ab′)2 versus Fc Sialylation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 178, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Ding, J. Sialylation Is Involved in Cell Fate Decision during Development, Reprogramming and Cancer Progression. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, X.; Carubelli, I.; Stamatos, N.M. Sialidase Expression in Activated Human T Lymphocytes Influences Production of IFN-Gamma. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Bian, H.; Wu, P.; Kuvelkar, R.; Kung, T.T.; Crawley, Y.; Egan, R.W.; Billah, M.M. Induction of Lysosomal and Plasma Membrane-Bound Sialidases in Human T-Cells via T-Cell Receptor. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatos, N.M.; Liang, F.; Nan, X.; Landry, K.; Cross, A.S.; Wang, L.X.; Pshezhetsky, A.V. Differential Expression of en-Dogenous Sialidases of Human Monocytes during Cellular Differentiation into Macrophages. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehnert, B.; Burkhardt, H.; Wessels, J.T.; Schroder, A.; May, M.J.; Vestweber, D.; Zwerina, J.; Warnatz, K.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Schett, G.; et al. NF-kappaB Inhibitor Targeted to Activated Endothelium Demonstrates a Critical Role of Endo-Thelial NF-kappaB in Immune-Mediated Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16556–16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehnert, B.; Burkhardt, H.; May, M.J.; Zwerina, J.; Voll, R.E. Sneaking-Ligand Fusion Proteins Attenuate Serum Transfer Arthritis by Endothelium-Targeted NF-kappaB Inhibition. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1280, 579–591. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sehnert, B.; Mietz, J.; Rzepka, R.; Buchholz, S.; Maul-Pavicic, A.; Schaffer, S.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Voll, R.E. Neuraminidase Inhibitor Zanamivir Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031428
Sehnert B, Mietz J, Rzepka R, Buchholz S, Maul-Pavicic A, Schaffer S, Nimmerjahn F, Voll RE. Neuraminidase Inhibitor Zanamivir Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031428
Chicago/Turabian StyleSehnert, Bettina, Juliane Mietz, Rita Rzepka, Stefanie Buchholz, Andrea Maul-Pavicic, Sandra Schaffer, Falk Nimmerjahn, and Reinhard E. Voll. 2021. "Neuraminidase Inhibitor Zanamivir Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031428
APA StyleSehnert, B., Mietz, J., Rzepka, R., Buchholz, S., Maul-Pavicic, A., Schaffer, S., Nimmerjahn, F., & Voll, R. E. (2021). Neuraminidase Inhibitor Zanamivir Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031428




