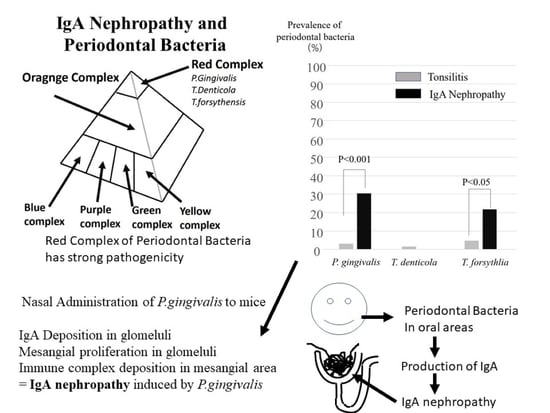
Relationship between IgA Nephropathy and Porphyromonas gingivalis; Red Complex of Periodontopathic Bacterial Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Subjects
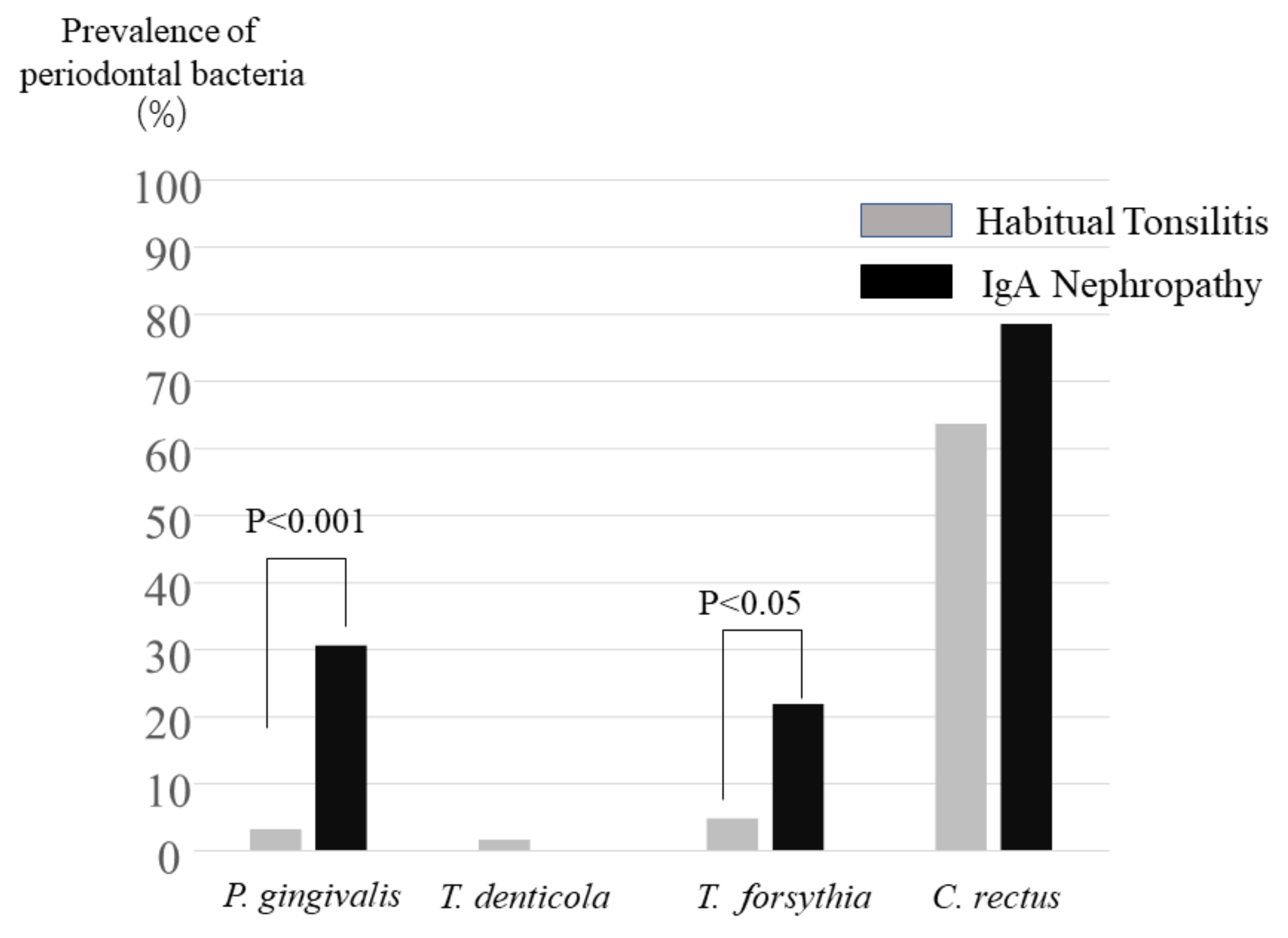
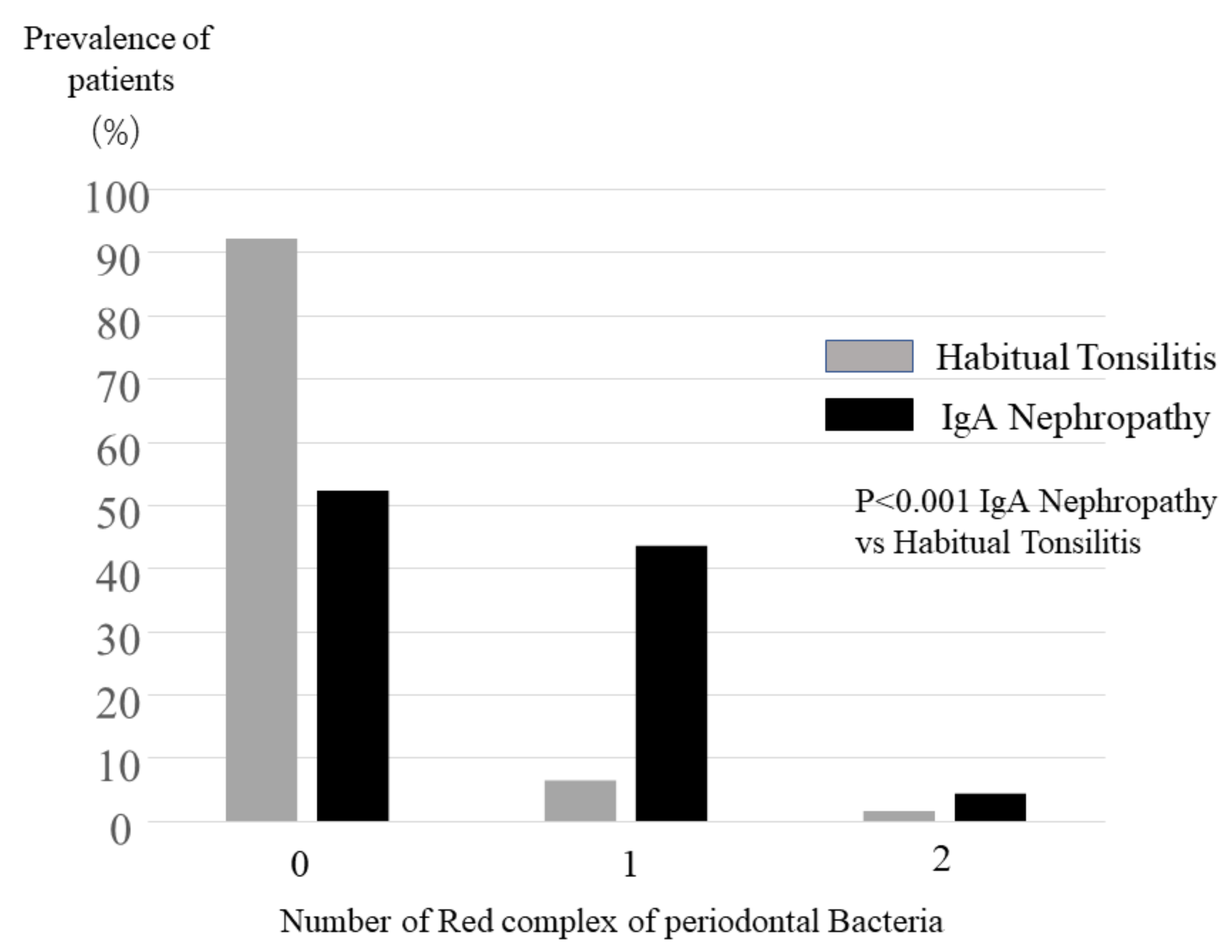
2.2. Detection of Periodontopathic Bacterial Species in Tonsil Specimens
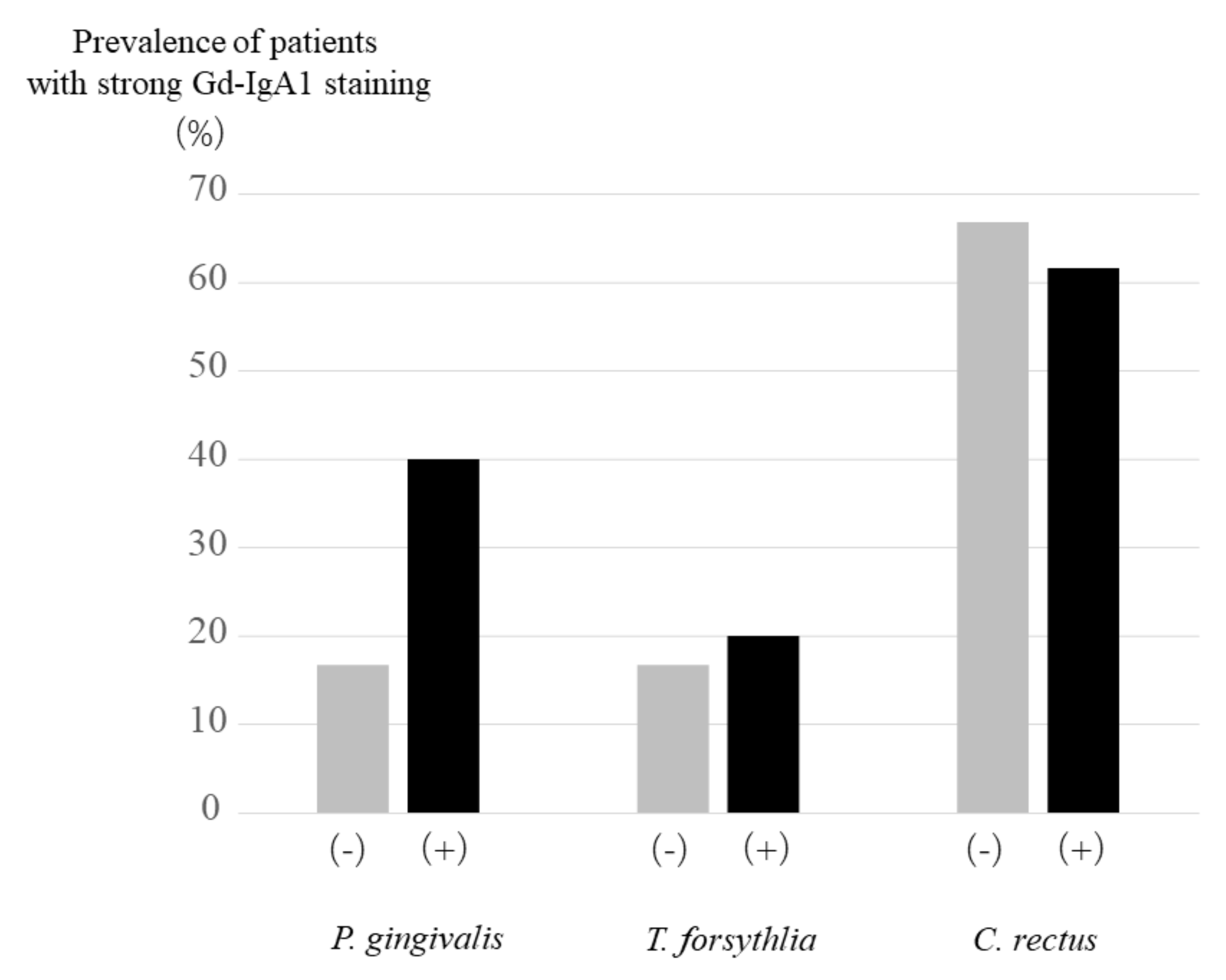
2.3. Gd-IgA1 Staining in IgA Patients with or without P. gingivalis, T. forsythia and C. rectus
2.4. IgAN Model Mice Induced by Nasal Administration of P. gingivalis
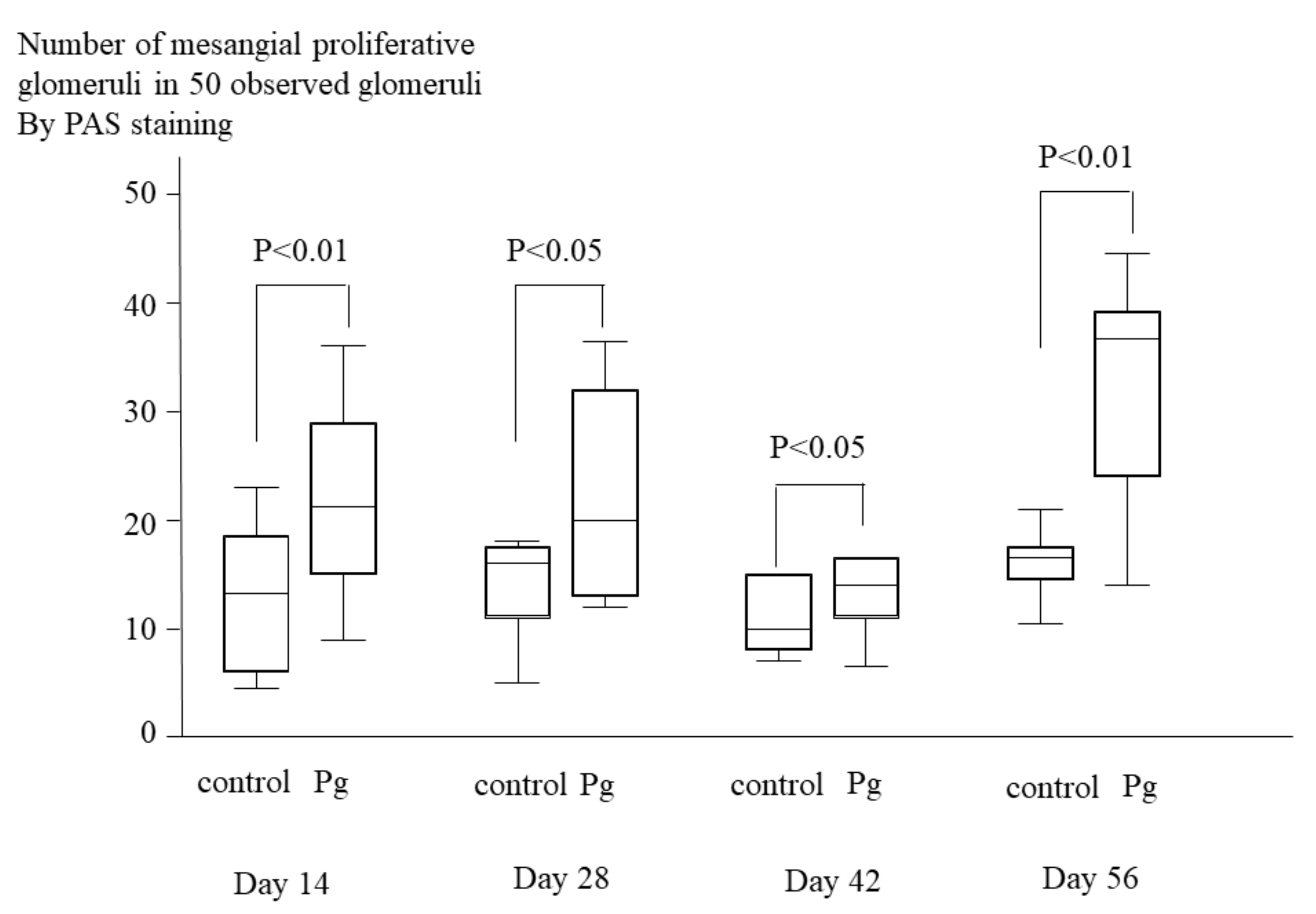
2.5. Histopathological Analyses of Kidney Tissue of IgAN Model Mice
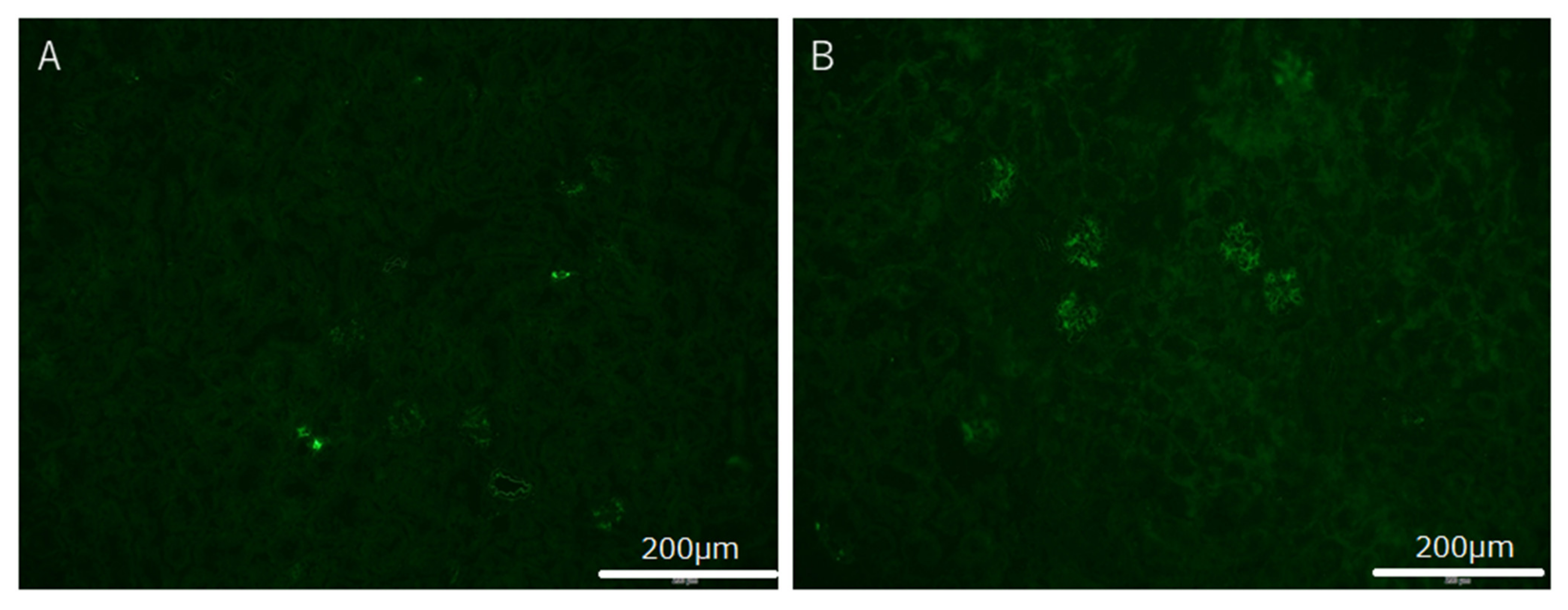
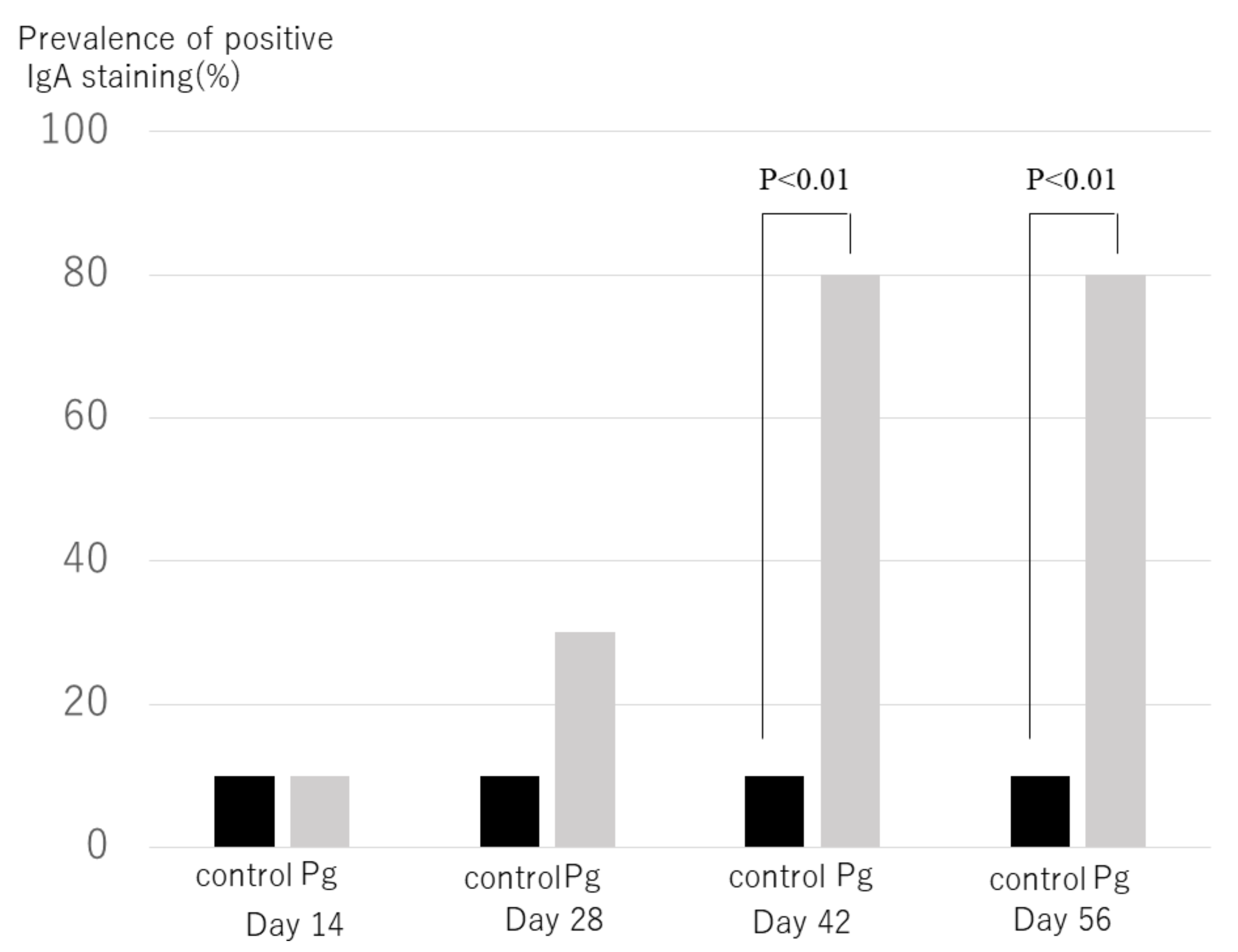
2.6. Immunohistochemical Analyses of Kidney Tissues of IgAN Model Mice
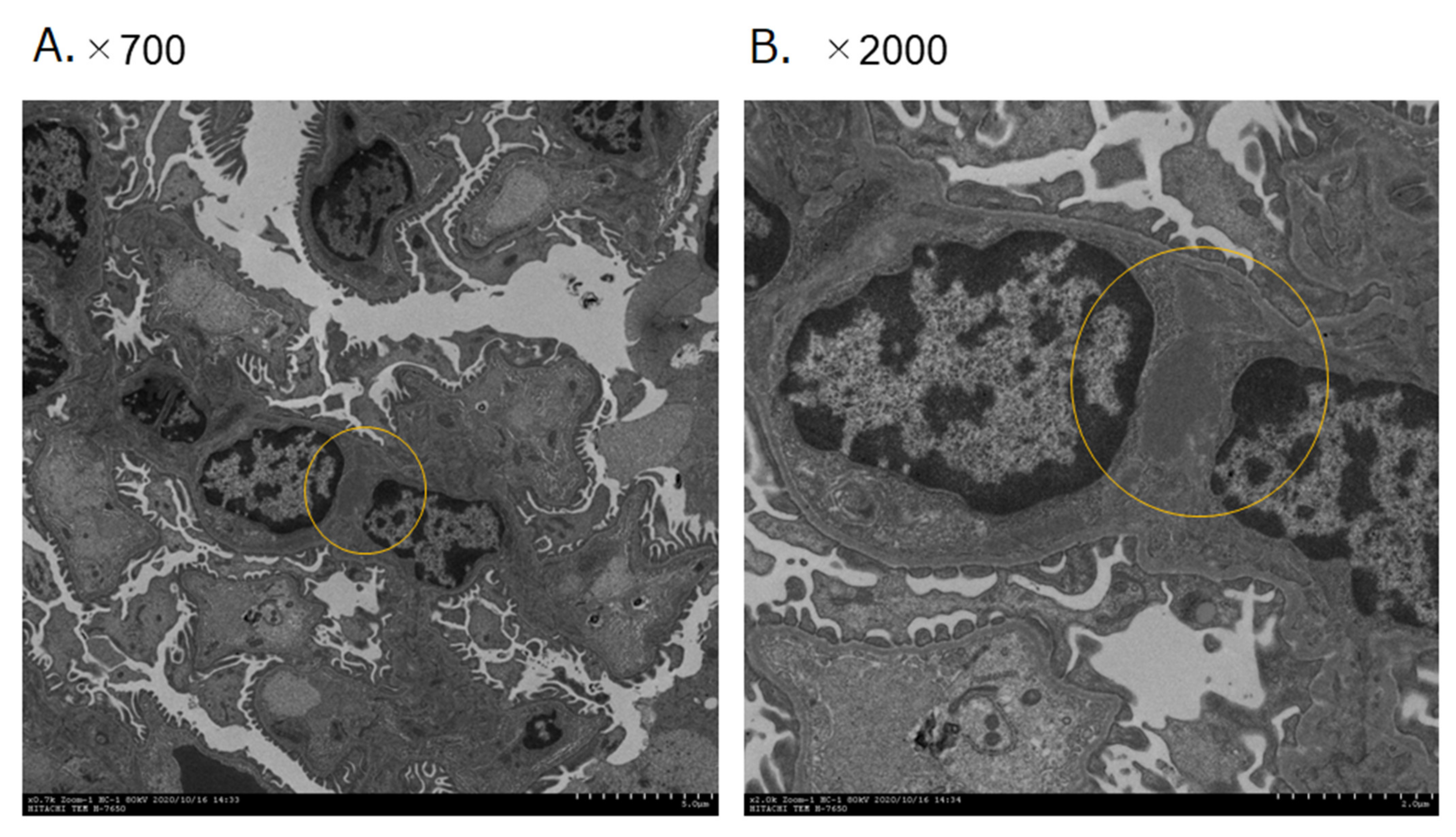
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopic of Immune Complex
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Subjects and Specimens
4.3. DNA Extraction
4.4. PCR Detection of the Periodontopathic Bacterial Species
4.5. Gd-IgA1 Staining for Kidney Biopsy Samples in IgAN Patients
4.6. P. gingivalis Strains and Culture Medium
4.7. IgA Model Mice Induced by Nasal Administration of P. gingivalis
4.8. Analysis of Urinary and Serum Components
4.9. Histological Evaluation of the Kidney
4.10. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nair, R.; Walker, P.D. Is IgA nephropathy the commonest primary glomerulopathy among young adults in the USA? Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, R.J.; Julian, B.A. IgA Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2402–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Nagasawa, Y.; Shoji, T.; Inoue, K.; Uehata, T.; Kaneko, T.; Okada, T.; Yamauchi, A.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Imai, E.; et al. A candidate gene approach to genetic prognostic factors of IgA nephropathy—A result of Polymorphism REsearch to DIstinguish genetic factors Contributing To progression of IgA Nephropathy (PREDICT-IgAN). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3686–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yamamoto, R.; Nagasawa, Y.; Shoji, T.; Katakami, N.; Ohtoshi, K.; Hayaishi-Okano, R.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamauchi, A.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Imai, E.; et al. A candidate gene approach to genetic contributors to the development of IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 27, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J. The genetics and immunobiology of IgA nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharavi, A.G.; Kiryluk, K.; Choi, M.; Li, Y.; Hou, P.; Xie, J.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Men, C.J.; Julian, B.A.; Wyatt, R.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Nagasawa, Y.; Shoji, T.; Iwatani, H.; Hamano, T.; Kawada, N.; Inoue, K.; Uehata, T.; Kaneko, T.; Okada, N.; et al. Cigarette Smoking and Progression of IgA Nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Rakugi, H.; Isaka, Y. Cigarette smoking and chronic kidney diseases. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 35, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Shoji, T.; Shinzawa, M.; Hasuike, Y.; Nagatoya, K.; Yamauchi, A.; Hayashi, T.; Kuragano, T.; Moriyama, T.; et al. Serum Uric Acid Level Predicts Progression of IgA Nephropathy in Females but Not in Males. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollino, C.; Vischini, G.; Coppo, R. IgA nephropathy and infections. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Nishi, S.; Ueno, M.; Imai, N.; Sakatsume, M.; Narita, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Akazawa, K.; Shimada, H.; Arakawa, M.; et al. The efficacy of tonsillectomy on long-term renal survival in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Yasuda, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Koike, K.; Maruyama, S.; Yokoo, T.; Matsuo, S.; Kawamura, T.; et al. Association Between Tonsillectomy and Outcomes in Patients with Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e194772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Miyazaki, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Kimura, K.; Hirano, K.; Matsushima, M.; Utsunomiya, Y.; Ogura, M.; Yokoo, T.; et al. A multicenter randomized controlled trial of tonsillectomy combined with steroid pulse therapy in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaki, T.; Naka, S.; Kuroda, K.; Nomura, R.; Shiooka, T.; Naito, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Isozaki, T.; Nakano, K. Distribution of Streptococcus mutans strains with collagen-binding proteins in the oral cavity of IgA nephropathy patients. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2014, 19, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misaki, T.; Naka, S.; Hatakeyama, R.; Fukunaga, A.; Nomura, R.; Isozaki, T.; Nakano, K. Presence of Streptococcus mutans strains harbouring the cnm gene correlates with dental caries status and IgA nephropathy conditions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misaki, T.; Naka, S.; Wato, K.; Hatakeyama, R.; Nagasawa, Y.; Ito, S.; Inaba, H.; Nomura, R.; Matsumoto-Nakano, M.; Nakano, K. Campylobacter rectus in the Oral Cavity Correlates with Proteinuria in Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy Patients. Nephron 2018, 139, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, S.; Wato, K.; Misaki, T.; Ito, S.; Nagasawa, Y.; Nomura, R.; Matsumoto-Nakano, M.; Nakano, K. Intravenous administration of Streptococcus mutans induces IgA nephropathy-like lesions. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naka, S.; Wato, K.; Misaki, T.; Ito, S.; Matsuoka, D.; Nagasawa, Y.; Nomura, R.; Matsumoto-Nakano, M.; Nakano, K. Streptococcus mutans induces IgA nephropathy-like glomerulonephritis in rats with severe dental caries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinane, D.F.; Stathopoulou, P.G.; Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, nrdp201738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, V.; Alqallaf, H.; De Bedout, T. Periodontal Disease and Systemic Diseases: An Update for the Clinician. J. Indiana Dent. Assoc. 2016, 95, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Iio, K.; Fukuda, S.; Date, Y.; Iwatani, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Horii, A.; Inohara, H.; Imai, E.; Nakanishi, T.; et al. Periodontal Disease Bacteria Specific to Tonsil in IgA Nephropathy Patients Predicts the Remission by the Treatment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e81636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; Brinkhoff, T.; Nübel, U.; Santegoeds, C.; Schäfer, H.; Wawer, C. Denaturant Gradient Gel Electrophoresis in Microbial Ecology. In Molecular Microbial Ecology Manual; Akkermans, A., van Elsas, J.D., de Bruijin, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mysak, J.; Podzimek, S.; Sommerova, P.; Lyuya-Mi, Y.; Bartova, J.; Janatova, T.; Prochazkova, J.; Duskova, J. Porphyromonas gingivalis: Major Periodontopathic Pathogen Overview. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 476068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lamont, R. Beyond the red complex and into more complexity: The polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis (PSD) model of periodontal disease etiology. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2012, 27, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, A.; Iwase, H.; Takatani, T.; Nakamura, I.; Hayashi, M.; Oba, K.; Hiki, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Okamoto, M. Tonsillar IgA1 as a possible source of hypoglycosylated IgA1 in the serum of IgA nephropathy patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Makita, Y.; Fukao, Y.; Suzuki, Y. Nasal-associated lymphoid tissue is the major induction site for nephritogenic IgA in murine IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, R.; Nagasawa, Y.; Misaki, T.; Ito, S.; Naka, S.; Wato, K.; Okunaka, M.; Watabe, M.; Tsuzuki, K.; Matsumoto-Nakano, M.; et al. Relationship of distribution of periodontopathic bacterial species between saliva and tonsils. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y. Murine Models of Human IgA Nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Z.; Brown, R.; Hall, S.; Julian, B.A.; Chatham, W.W.; Suzuki, Y.; Wyatt, R.J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; et al. Aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 in IgA nephropathy patients is recognized by IgG antibodies with restricted heterogeneity. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H. Biomarkers for IgA nephropathy on the basis of multi-hit pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Misaki, T.; Naka, S.; Wato, K.; Nagasawa, Y.; Nomura, R.; Otsugu, M.; Matsumoto-Nakano, M.; Nakano, K.; Kumagai, H.; et al. Specific strains of Streptococcus mutans, a pathogen of dental caries, in the tonsils, are associated with IgA nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Hirose, S.; Nishimura, H.; Toei, J.; Horikoshi, S.; Tomino, Y. Genome-Wide Scan in a Novel IgA Nephropathy Model Identifies a Susceptibility Locus on Murine Chromosome 10, in a Region Syntenic to HumanIGAN1on Chromosome 6q22–23. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.M.; Caugant, D.A.; Eribe, E.R.; Aas, J.A.; Lingaas, P.S.; Geiran, O.; Tronstad, L.; Olsen, I. Bacterial diversity in aortic aneurysms determined by 16S ribosomal RNA gene analysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2006, 44, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Shirai, M.; Murakami, M.; Mizusawa, T.; Hagimoto, A.; Wada, K.; Nomura, R.; Nakano, K.; Ooshima, T.; Asai, F. Molecular Detection of Human Periodontal Pathogens in Oral Swab Specimens from Dogs in Japan. J. Veter-Dent. 2011, 28, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Frommel, T.O. Porphyromonas gingivaiis, Actinobacillus actinomycetemeomitans and Treponema denticola detection in oral plaque samples using the polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1996, 23, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashimoto, A.; Chen, C.; Bakker, I.; Slots, J. Polymerase chain reaction detection of 8 putative periodontal pathogens in subgingival plaque of gingivitis and advanced periodontitis lesions. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1996, 11, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Suzuki, T.; Saito, T.; Kanazawa, N.; Tachibana, S.; Iseri, K.; Sugiyama, M.; Iyoda, M.; Shibata, T. Clinical significance of serum and mesangial galactose-deficient IgA1 in patients with IgA nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Yasutake, J.; Makita, Y.; Tanbo, Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Sofue, T.; Kano, T.; Suzuki, Y. IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis with nephritis have a shared feature involving galactose-deficient IgA1-oriented pathogenesis. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, A.; Nakagawa, I.; Okahashi, N.; Hamada, N. Variations of Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae in relation to microbial pathogenesis. J. Periodontal Res. 2004, 39, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Kuboniwa, M.; Bainbridge, B.; Yilmaz, Ö.; Katz, J.; Shiverick, K.T.; Amano, A.; Lamont, R.J. Porphyromonas gingivalisinvades human trophoblasts and inhibits proliferation by inducing G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schaart, G.; Hesselink, R.P.; Keizer, H.H.-J.; Van Kranenburg, G.; Drost, M.R.; Hesselink, M.K.C. A modified PAS stain combined with immunofluorescence for quantitative analyses of glycogen in muscle sections. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 122, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katafuchi, R.; Kiyoshi, Y.; Oh, Y.; Uesugi, N.; Ikeda, K.; Yanase, T.; Fujimi, S. Glomerular score as a prognosticator in IgA nephropathy: Its usefulness and limitation. Clin. Nephrol. 1998, 49, 878–891. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Narita, I.; Aizawa, M.; Kihara, M.; Yamanaka, T.; Kanou, T.; Tsukaguchi, H.; Novak, J.; Horikoshi, S.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 9 Affects Severity of IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 2384–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| IgAnephropathy | Habitual Tonsilitis | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 33 ± 14 | 27 ± 7 | <0.01 | ||
| Sex | 9 Male | 14 Female | 26 Male | 37 Female | NS |
| Height (cm) | 160 ± 10 | 162 ± 20 | NS | ||
| Weight (Kg) | 54 ± 11 | 62 ± 15 | <0.05 | ||
| Proteinuria (g/gCre) | 0.9 ± 1.1 | N/A | N/A | ||
| Purpose | Sequence (5′-3′) | Size (bp) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Universal primer | |||
| (positive control) | |||
| PA | AGA GTT TGA TCC TGG CTC AG | 315 | [25] |
| PD | GTA TTA CCG CGG CTG CTG | ||
| Detection of periodontitis-related species | |||
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | CCG CAT ACA CTT GTA TTA TTG CAT GAT A | 267 | [26] |
| AAG AAG TTT ACA ATC CTT AGG ACT GTC T | |||
| Treponema denticola | AAG GCG GTA GAG CCG CTC A | 311 | [27] |
| AGC CGC TGT CGA AAA GCC CA | |||
| Tannerella forsythia | GCG TAT GTA ACC TGC CCG CA | 641 | [28] |
| TGC TTC AGT GTC AGT TAT ACC T | |||
| Campylobacter rectus | TTT CGG AGC GTA AAC TCC TTT TC | 598 | [28] |
| TTT CTG CAA GCA GAC ACT CTT |
| P. gingivaris | |||
| (−) (N = 16) | (+) (N = 7) | p | |
| Protenuria (g/acre) | 1.1 ± 0.8 | 1.1+1.4 | NS |
| C3 (mg/dL) | 98.5 ± 4.5 | 100.7 ± 8.4 | NS |
| C4 (mg/dL) | 25.2 ± 1.6 | 22.7 ± 3.0 | NS |
| IgA (mg/dL) | 368 ± 49 | 398 ± 36 | NS |
| T. forsythia | |||
| (−) (N = 18) | (+) (N = 5) | p | |
| Protenuria (g/gcre) | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | NS |
| C3 (mg/dL) | 98.5 ± 4.5 | 99.5 ± 4.7 | NS |
| C4 (mg/dL) | 23.4 ± 1.6 | 30.0 ± 6.0 | NS |
| IgA (mg/dL) | 380 ± 33 | 384 ± 148 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagasawa, Y.; Nomura, R.; Misaki, T.; Ito, S.; Naka, S.; Wato, K.; Okunaka, M.; Watabe, M.; Fushimi, K.; Tsuzuki, K.; et al. Relationship between IgA Nephropathy and Porphyromonas gingivalis; Red Complex of Periodontopathic Bacterial Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313022
Nagasawa Y, Nomura R, Misaki T, Ito S, Naka S, Wato K, Okunaka M, Watabe M, Fushimi K, Tsuzuki K, et al. Relationship between IgA Nephropathy and Porphyromonas gingivalis; Red Complex of Periodontopathic Bacterial Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):13022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313022
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagasawa, Yasuyuki, Ryota Nomura, Taro Misaki, Seigo Ito, Shuhei Naka, Kaoruko Wato, Mieko Okunaka, Maiko Watabe, Katsuya Fushimi, Kenzo Tsuzuki, and et al. 2021. "Relationship between IgA Nephropathy and Porphyromonas gingivalis; Red Complex of Periodontopathic Bacterial Species" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 13022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313022
APA StyleNagasawa, Y., Nomura, R., Misaki, T., Ito, S., Naka, S., Wato, K., Okunaka, M., Watabe, M., Fushimi, K., Tsuzuki, K., Matsumoto-Nakano, M., & Nakano, K. (2021). Relationship between IgA Nephropathy and Porphyromonas gingivalis; Red Complex of Periodontopathic Bacterial Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 13022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313022