(De)stabilization of Alpha-Synuclein Fibrillary Aggregation by Charged and Uncharged Surfactants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
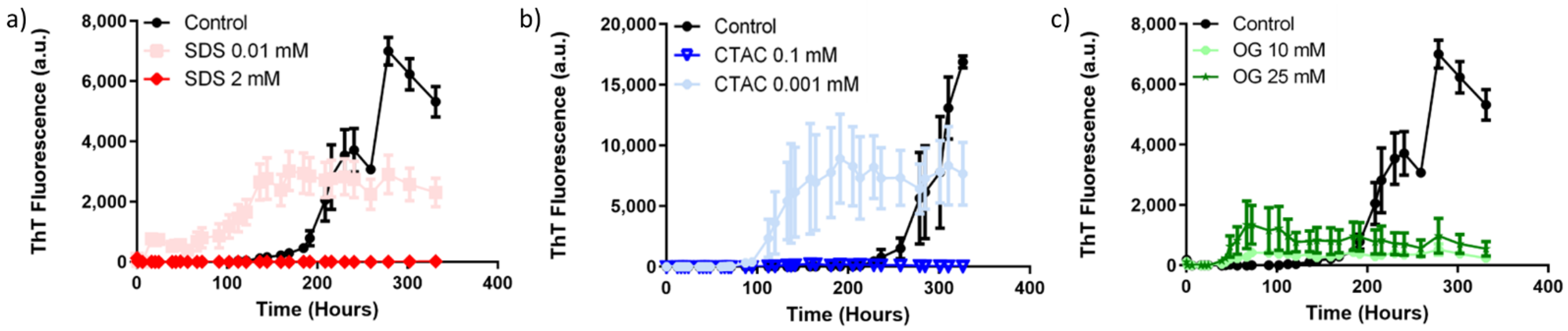
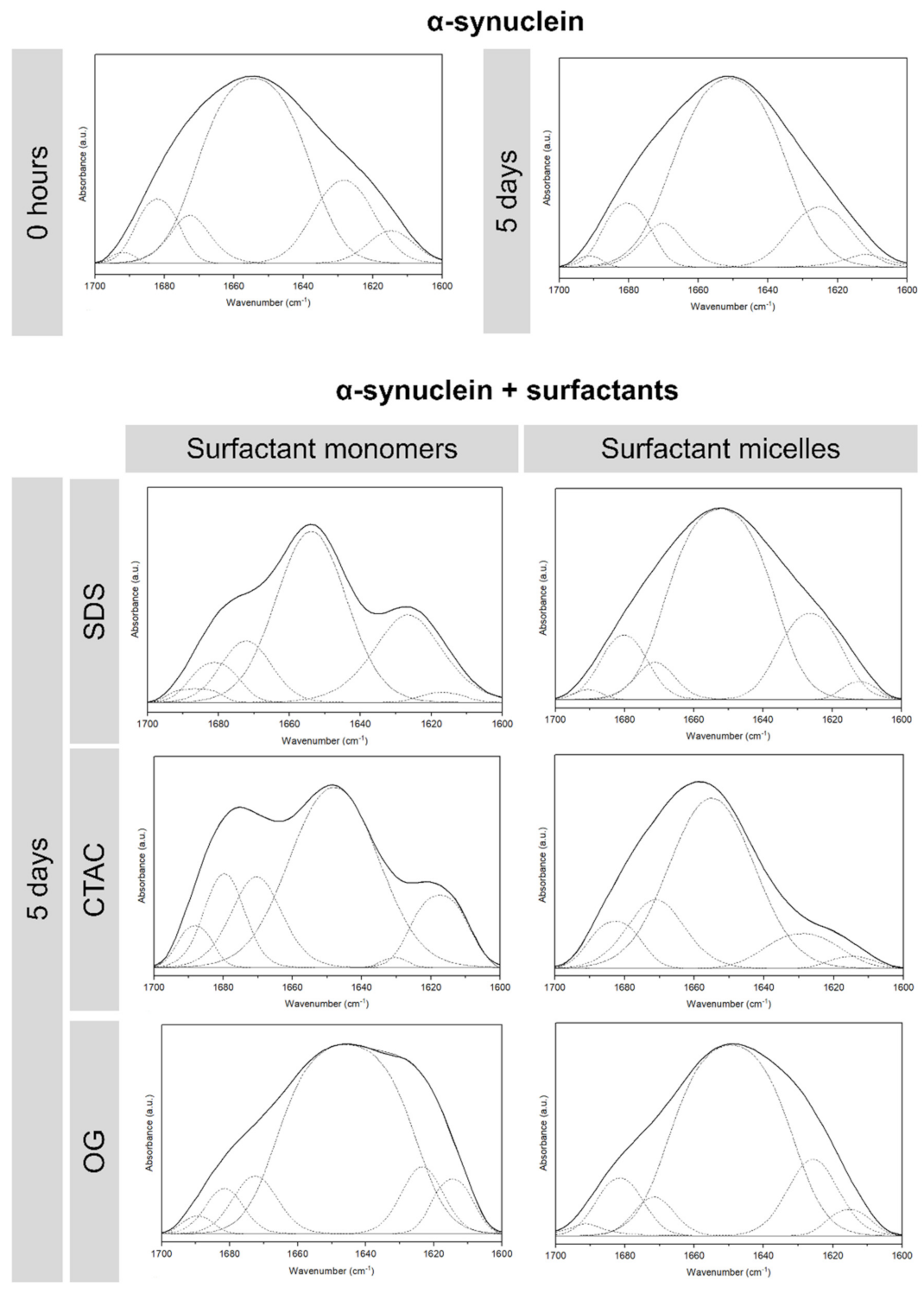
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material
3.2. Measurement of the Critical Micelle Concentration
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.4. Thioflavin T Binding Assay
3.5. α-Synuclein Aggregation Assay
3.6. Attenuated Total Reflectance–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Recchia, A.; Debetto, P.; Negro, A.; Guidolin, D.; Skaper, S.D.; Giusti, P. Alpha-synuclein and Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawkes, C.H.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. A timeline for Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahn, S.; Sulzer, D. Neurodegeneration and neuroprotection in Parkinson disease. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.A.; Poirier, M.A. Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S10–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglieri, V.; Calabrese, V.; Calabresi, P. Alpha-synuclein: From early synaptic dysfunction to neurodegeneration. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uversky, V.N. Neuropathology, biochemistry, and biophysics of alpha-synuclein aggregation. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashuel, H.A.; Overk, C.R.; Oueslati, A.; Masliah, E. The many faces of alpha-synuclein: From structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breydo, L.; Wu, J.W.; Uversky, V.N. Alpha-synuclein misfolding and Parkinson’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Patel, S.; Lee, S.J. Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of alpha-synuclein and its aggregates. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6016–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necula, M.; Chirita, C.N.; Kuret, J. Rapid anionic micelle-mediated alpha-synuclein fibrillization in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46674–46680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamiola, K.; Mulder, F.A.A. Using NMR chemical shifts to calculate the propensity for structural order and disorder in proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, J.T.; Heegaard, N.H.H. Analysis of protein aggregation in neurodegenerative disease. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4215–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; McCormack, A.A.; Nicholson, J.M.; Fabarius, A.; Hehlmann, R.; Sachs, R.K.; Duesberg, P.H. Cancer-causing karyotypes: Chromosomal equilibria between destabilizing aneuploidy and stabilizing selection for oncogenic function. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2009, 188, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otzen, D.E. Amyloid Formation in surfactants and alcohols: Membrane mimetics or structural switchers? Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2010, 11, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otzen, D. Protein-surfactant interactions: A tale of many states. BBA Proteins Proteom. 2011, 1814, 562–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, J.A.; Rocha, S.; Pereira, M.D. Charged surfactants induce a non-fibrillar aggregation pathway of amyloid-beta peptide. J. Pept. Sci. 2013, 19, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, S.; Loureiro, J.A.; Brezesinski, G.; Pereira, M.D. Peptide-surfactant interactions: Consequences for the amyloid-beta structure. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otzen, D.E.; Sehgal, P.; Westh, P. alpha-Lactalbumin is unfolded by all classes of surfactants but by different mechanisms. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 329, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaliauskas, T.; Mickevicius, M.; Budvytyte, R.; Niaura, G.; Carbonnier, B.; Valincius, G. Adsorption of beta-amyloid oligomers on octadecanethiol monolayers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 425, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikiy, I.; Eliezer, D. N-terminal acetylation stabilizes N-terminal helicity in lipid- and micelle-bound alpha-synuclein and increases its affinity for physiological membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3652–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giehm, L.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Christiansen, G.; Pedersen, J.S.; Otzen, D.E. SDS-Induced Fibrillation of alpha-Synuclein: An Alternative Fibrillation Pathway. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 401, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giehm, L.; Lorenzen, N.; Otzen, D.E. Assays for alpha-synuclein aggregation. Methods 2011, 53, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wietek, J.; Haralampiev, I.; Amoussouvi, A.; Herrmann, A.; Stockl, M. Membrane bound alpha-synuclein is fully embedded in the lipid bilayer while segments with higher flexibility remain. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 2572–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baquerizo, I.; Ruiz, M.A.; Holgado, J.A.; Cabrerizo, M.A.; Gallardo, V. Measurement of dynamic surface tension to determine critical micellar concentration in lipophilic silicons surfactants. Il Farm. 2000, 55, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClendon, S.; Rospigliosi, C.C.; Eliezer, D. Charge neutralization and collapse of the C-terminal tail of alpha-synuclein at low pH. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dedmon, M.M.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Christodoulou, J.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. Mapping long-range interactions in alpha-synuclein using spin-label NMR and ensemble molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, S.; Pacheco, C.; Peters, C.; Opazo, C.M.; Aguayo, L.G. Features of alpha-synuclein that could explain the progression and irreversibility of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giasson, B.I.; Murray, I.V.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhmud, B.V.; Tiberg, F.; Kizling, J. Dynamic surface tension in concentrated solutions of CnEm surfactants: A comparison between the theory and experiment. Langmuir 2000, 16, 2557–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azum, N.; Naqvi, A.Z.; Akram, M. Studies of mixed micelle formation between cationic gemini and cationic conventional surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Horta, A.; Hernandez, B.G.; Chavez-Montes, A. Fluorescence as a tool to study lipid-protein interactions: The case of α-synuclein. Open J. Biophys. 2013, 3, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groenning, M. Binding mode of Thioflavin T and other molecular probes in the context of amyloid fibrils-current status. J. Chem. Biol. 2010, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, H.; Singh, J.; Kumari, P.; Udgaonkar, J.B. Modulation of the extent of structural heterogeneity in alpha-synuclein fibrils by the small molecule thioflavin T. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16891–16903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, K.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, Z.; Gong, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K. Inhibition effects of tanshinone on the aggregation of alpha-synuclein. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, D.J.; Wranne, M.S.; Gilbert Gatty, M.; Westerlund, F.; Esbjorner, E.K. Steady-state and time-resolved Thioflavin-T fluorescence can report on morphological differences in amyloid fibrils formed by Abeta(1-40) and Abeta(1-42). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisaglia, M.; Tessari, I.; Pinato, L.; Bellanda, M.; Giraudo, S.; Fasano, M.; Bergantino, E.; Bubacco, L.; Mammi, S. A topological model of the interaction between alpha-synuclein and sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.P.; Weinstock, D.S.; Narayanan, C.; Levy, R.M.; Baum, J. structural reorganization of alpha-synuclein at low pH observed by NMR and REMD simulations. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 391, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sjogren, H.; Ericsson, C.A.; Evenas, J.; Ulvenlund, S. Interactions between charged polypeptides and nonionic surfactants. Biophys. J. 2005, 89, 4219–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gai, W.P.; Pountney, D.L.; Power, J.H.T.; Li, Q.X.; Culvenor, J.G.; McLean, C.A.; Jensen, P.H.; Blumbergs, P.C. alpha-synuclein fibrils constitute the central core of oligodendroglial inclusion filaments in multiple system atrophy. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 181, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrondo, J.L.; Muga, A.; Castresana, J.; Goni, F.M. Quantitative studies of the structure of proteins in solution by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1993, 59, 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Hu, D.; Han, S.; Reaney, S.H.; Di Monte, D.A.; Fink, A.L. Effect of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal modification on alpha-synuclein aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5862–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerf, E.; Sarroukh, R.; Tamamizu-Kato, S.; Breydo, L.; Derclaye, S.; Dufrene, Y.F.; Narayanaswami, V.; Goormaghtigh, E.; Ruysschaert, J.M.; Raussens, V. Antiparallel beta-sheet: A signature structure of the oligomeric amyloid beta-peptide. Biochem. J. 2009, 421, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, M.J.; Loureiro, J.A.; Coelho, M.A.N.; Pereira, M.C. Factorial design as a tool for the optimization of PLGA nanoparticles for the co-delivery of temozolomide and O6-benzylguanine. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loureiro, J.A.; Andrade, S.; Duarte, A.; Neves, A.R.; Queiroz, J.F.; Nunes, C.; Sevin, E.; Fenart, L.; Gosselet, F.; Coelho, M.A.N.; et al. Resveratrol and grape extract-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 2017, 22, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Tokuda, T.; Waragai, M.; Mendez, N.; Ishii, R.; Trenkwalder, C.; Mollenhauer, B.; Soto, C. Development of a biochemical diagnosis of Parkinson disease by detection of alpha-synuclein misfolded aggregates in cerebrospinal fluid. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Region | N-Terminal | NAC 1 | C-Terminal | α-Synuclein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of a.a. | 60 | 35 | 45 | 140 |
| Number of charged a.a. | 18 | 3 | 18 | 39 |
| % Charged | 30.0 | 8.6 | 40.0 | 27.8 |
| Total charge | +4 | −1 | −12 | −9 |
| Number of hydrophobic a.a. | 28 | 20 | 16 | 64 |
| % Hydrophobic a.a. | 46.7 | 57.1 | 35.6 | 45.7 |
| Surfactant | SDS | CTAC | OG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charge | Anionic | Cationic | Nonionic |
| Molecular weight (Da) | 288.38 | 320.01 | 292.37 |
| Structure | 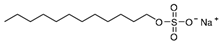 | 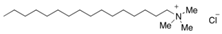 | 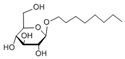 |
| Shape of the micelle | Spherical | Spherical | Cylinder |
| Size of the micelle (nm) | 4.8 | 4.8 | R:1.3 |
| L: 9.6 |
| Surfactant | CMC without α-Synuclein (mM) | CMC with α-Synuclein (mM) |
|---|---|---|
| SDS | 1.27 ± 0.04 | 0.42 ± 0.01 |
| CTAC | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.04 |
| OG | 19.9 ± 0.3 | 22.5 ± 0.9 |
| α-Synuclein in SDS Solutions | α-Synuclein in CTAC Solutions | α-Synuclein in OG Solutions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days | 1 | 5 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 9 |
| Above CMC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Below CMC | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loureiro, J.A.; Andrade, S.; Goderis, L.; Gomez-Gutierrez, R.; Soto, C.; Morales, R.; Pereira, M.C. (De)stabilization of Alpha-Synuclein Fibrillary Aggregation by Charged and Uncharged Surfactants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212509
Loureiro JA, Andrade S, Goderis L, Gomez-Gutierrez R, Soto C, Morales R, Pereira MC. (De)stabilization of Alpha-Synuclein Fibrillary Aggregation by Charged and Uncharged Surfactants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212509
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoureiro, Joana Angélica, Stéphanie Andrade, Lies Goderis, Ruben Gomez-Gutierrez, Claudio Soto, Rodrigo Morales, and Maria Carmo Pereira. 2021. "(De)stabilization of Alpha-Synuclein Fibrillary Aggregation by Charged and Uncharged Surfactants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212509
APA StyleLoureiro, J. A., Andrade, S., Goderis, L., Gomez-Gutierrez, R., Soto, C., Morales, R., & Pereira, M. C. (2021). (De)stabilization of Alpha-Synuclein Fibrillary Aggregation by Charged and Uncharged Surfactants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212509










