Electrostatic Forces Mediate the Specificity of RHO GTPase-GDI Interactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
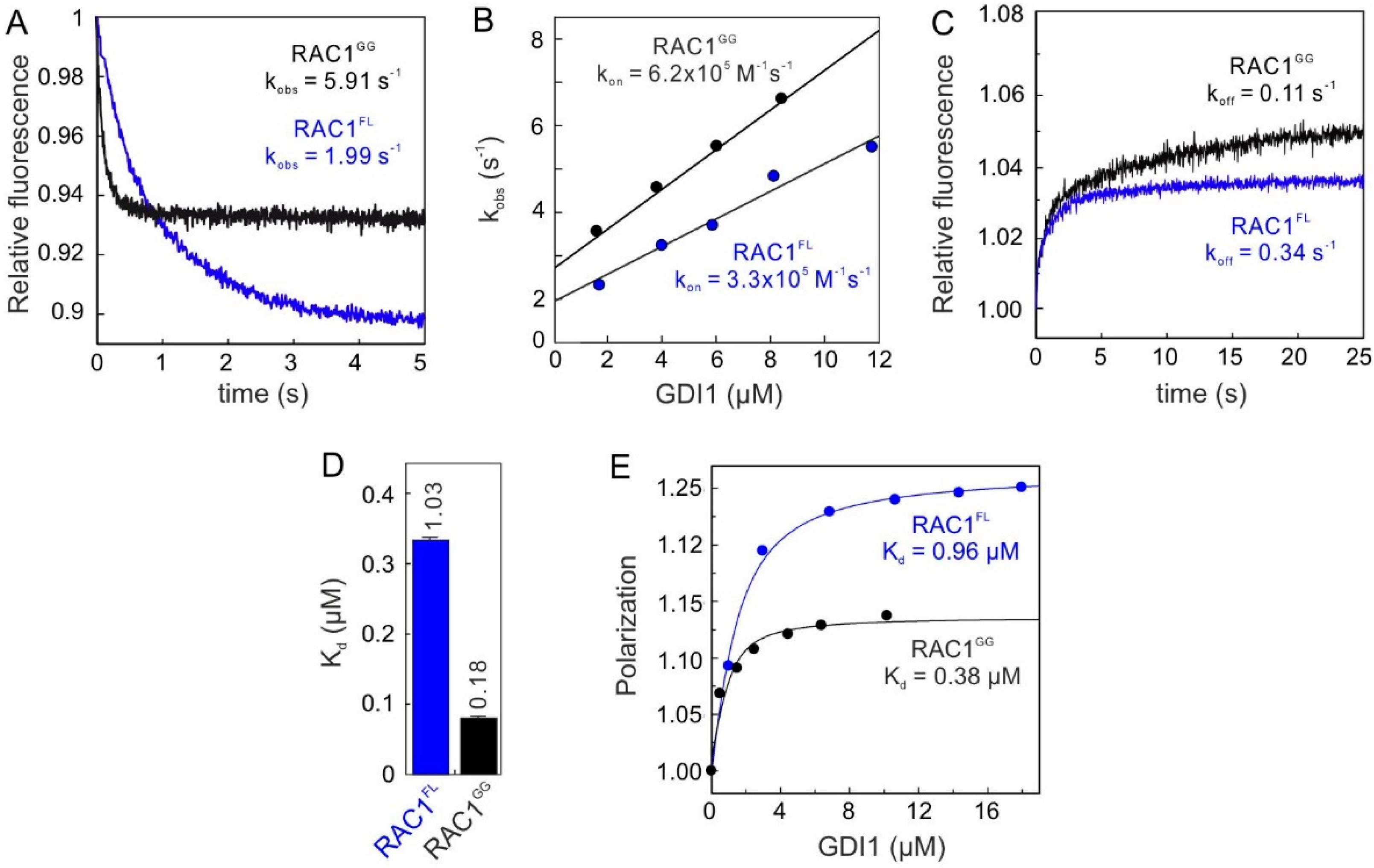
2.1. Geranylgeranyl Moiety Is Dispensable for RAC1-GDI1 Interaction
2.2. Conserved G Domain Is Not Rate-Limiting for the GDI1 Binding
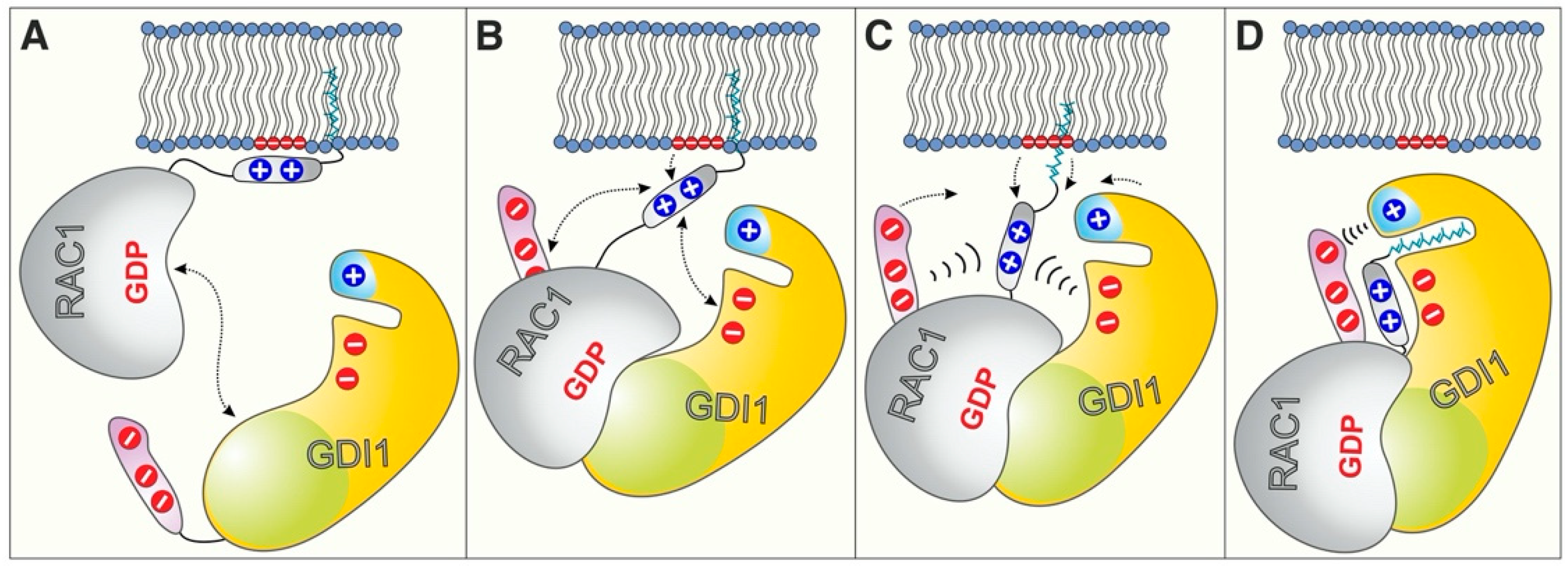
2.3. RAC1 Polybasic Motif Dictates GDI1 Binding
2.4. Electrostatic Pincer Residues of GDI1 Grasp RAC1 HVR
2.5. GDI1 Buckles RAC1 into Its Site
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Constructs
4.2. Proteins
4.3. Liposome Assays
4.4. Fluorescence Measurements
4.5. Sequence and Structural Analysis
4.6. Nucleofection and Immunofluorescence Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wennerberg, K.; Der, C.J. Rho-family GTPases: It’s not only Rac and Rho (and I like it). J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, P.J.; Mitin, N.; Keller, P.J.; Chenette, E.J.; Madigan, J.P.; Currin, R.O.; Cox, A.D.; Wilson, O.; Kirschmeier, P.; Der, C.J. Rho family GTPase modification and dependence on CAAX motif-signaled posttranslational modification. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25150–25163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmadian, M.R.; Jaiswal, M.; Fansa, E.K.; Dvorsky, R. New insight into the molecular switch mechanism of human Rho family proteins: Shifting a paradigm. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Always look on the bright site of Rho: Structural implications for a conserved intermolecular interface. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherfils, J.; Zeghouf, M. Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 269–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bishop, A.L.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem. J. 2000, 348, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.D.; Erdemir, H.H.; Sacks, D.B. IQGAP1 and its binding proteins control diverse biological functions. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.; Wang, S.; Kaibuchi, K. IQGAPs as Key Regulators of Actin-cytoskeleton Dynamics Mini-review and Review. Cell Struct. Funct. 2015, 40, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abel, A.M.; Schuldt, K.M.; Rajasekaran, K.; Hwang, D.; Riese, M.J.; Rao, S.; Thakar, M.S.; Malarkannan, S. IQGAP1: Insights into the function of a molecular puppeteer. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 65, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heasman, S.J.; Ridley, A.J. Mammalian Rho GTPases: New insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, A.C.; Smith, J.M.; Sacks, D.B. The biology of IQGAP proteins: Beyond the cytoskeleton. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, A. Rho family GTPases. In Biochemical Society Transactions; Portland Press: South Portland, ME, USA, 2012; Volume 40, pp. 1378–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Mata, R.; Boulter, E.; Burridge, K. The “invisible hand”: Regulation of RHO GTPases by RHOGDIs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, M.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Deciphering the molecular and functional basis of Dbl family proteins: A novel systematic approach toward classification of selective activation of the Rho family proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 4486–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, E.; Jaiswal, M.; Derewenda, U.; Reis, K.; Nouri, K.; Koessmeier, K.T.; Aspenström, P.; Somlyo, A.V.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Deciphering the molecular and functional basis of RHOGAP family proteins: A systematic approach toward selective inactivation of RHO family proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 20353–20371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dovas, A.; Couchman, J.R. RhoGDI: Multiple functions in the regulation of Rho family GTPase activities. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Shao, S.; Aziz, A.U.R.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, B. Role of Rho-specific guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor α regulation in cell migration. Acta Histochem. 2017, 119, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griner, E.M.; Theodorescu, D. The faces and friends of RhoGDI2. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De León-Bautista, M.P.; del Carmen Cardenas-Aguayo, M.; Casique-Aguirre, D.; Almaraz-Salinas, M.; Parraguirre-Martinez, S.; Olivo-Diaz, A.; del Rocío Thompson-Bonilla, M.; Vargas, M. Immunological and functional characterization of RhoGDI3 and its molecular targets RhoG and RhoB in human pancreatic cancerous and normal cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, N.; Morin, A.; Olofsson, B. RhoGDI-3 regulates RhoG and targets this protein to the Golgi complex through its unique N-terminal domain. Traffic 2002, 3, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Mokhtar, A.M.B.; Ahmed, S.B.M.; Darling, N.J.; Harris, M.; Mott, H.R.; Owen, D. A Complete Survey of RhoGDI Targets Reveals Novel Interactions with Atypical Small GTPases. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 1533–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, T.; Son, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Hamada, T.; Nakamura, T.; Sakaguchi, H.; Shirafuji, T.; Saito, N. Negative Charges in the Flexible N-Terminal Domain of Rho GDP-Dissociation Inhibitors (RhoGDIs) Regulate the Targeting of the RhoGDI–Rac1 Complex to Membranes. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 2560–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Lin, V.Y.; Ke, S.; Lin, G.E.; Lin, F.-T.; Lin, W.-C. 14-3-3 Promotes Breast Cancer Invasion and Metastasis by Inhibiting RhoGDI. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 2635–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harding, M.A.; Theodorescu, D. RhoGDI signaling provides targets for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moissoglu, K.; Schwartz, M.A. Spatial and temporal control of Rho GTPase functions. Cell. Logist. 2014, 4, e943618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hodge, R.G.; Ridley, A.J. Regulating Rho GTPases and their regulators. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerMardirossian, C.; Bokoch, G.M. GDIs: Central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaiah, S.; Bindu, L.; Tran, T.H.; Gillette, W.K.; Frank, P.H.; Ghirlando, R.; Nissley, D.V.; Esposito, D.; McCormick, F.; Stephen, A.G.; et al. Structural basis of recognition of farnesylated and methylated KRAS4b by PDEd. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6766–E6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weise, K.; Kapoor, S.; Werkmüller, A.; Möbitz, S.; Zimmermann, G.; Triola, G.; Waldmann, H.; Winter, R. Dissociation of the K-Ras4B/PDEδ complex upon contact with lipid membranes: Membrane delivery instead of extraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11503–11510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, S.A.; Chen, Y.X.; Rusinova, A.; Chandra, A.; Bierbaum, M.; Gremer, L.; Triola, G.; Waldmann, H.; Bastiaens, P.I.H.; Wittinghofer, A. Arl2-GTP and Arl3-GTP regulate a GDI-like transport system for farnesylated cargo. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Grecco, H.E.; Pisupati, V.; Perera, D.; Cassidy, L.; Skoulidis, F.; Ismail, S.A.; Hedberg, C.; Hanzal-Bayer, M.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; et al. The GDI-like solubilizing factor PDEδ sustains the spatial organization and signalling of Ras family proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tnimov, Z.; Abankwa, D.; Alexandrov, K. RhoGDI facilitates geranylgeranyltransferase-I-mediated RhoA prenylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 452, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbe, K.; Otto-Bruc, A.; Chardin, P.; Antonny, B. Dissociation of GDP dissociation inhibitor and membrane translocation are required for efficient activation of Rac by the Dbl homology-pleckstrin homology region of Tiam. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4756–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.C.; Gremer, L.; Heise, H.; Janning, P.; Shymanets, A.; Cirstea, I.C.; Krause, E.; Nürnberg, B.; Ahmadian, M.R. Liposome reconstitution and modulation of recombinant prenylated human Rac1 by GEFs, GDI1 and Pak1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grizot, S.; Fauré, J.; Fieschi, F.; Vignais, P.V.; Dagher, M.C.; Pebay-Peyroula, E. Crystal structure of the Rac1—RhoGDI complex involved in NADPH oxidase activation. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 10007–10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffzek, K.; Stephan, I.; Jensen, O.N.; Illenberger, D.; Gierschik, P. The Rac-RhoGDI complex and the structural basis for the regulation of Rho proteins by RhoGDI. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dransart, E.; Olofsson, B.; Cherfils, J. RhoGDIs revisited: Novel roles in Rho regulation. Traffic 2005, 6, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, G.R.; Nassar, N.; Cerione, R.A. Structure of the Rho family GTP-binding protein Cdc42 in complex with the multifunctional regulator RhoGDI. Cell 2000, 100, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longenecker, K.; Read, P.; Derewenda, U.; Dauter, Z.; Liu, X.; Garrard, S.; Walker, L.; Somlyo, A.V.; Nakamoto, R.K.; Somlyo, A.P.; et al. How RhoGDI binds Rho. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1999, 55, 1503–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.L.; Erickson, J.W.; Cerione, R.A. New insights into how the Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor regulates the interaction of Cdc42 with membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23860–23871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newcombe, A.R.; Stockley, R.W.; Hunter, J.L.; Webb, M.R. The Interaction between Rac1 and Its Guanine Nucleotide Dissociation Inhibitor (GDI), Monitored by a Single Fluorescent Coumarin Attached to GDI. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 6879–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tnimov, Z.; Guo, Z.; Gambin, Y.; Nguyen, U.T.T.; Wu, Y.W.; Abankwa, D.; Stigter, A.; Collins, B.M.; Waldmann, H.; Goody, R.S.; et al. Quantitative analysis of prenylated RhoA interaction with its chaperone, RhoGDI. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26549–26562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haeusler, L.C.; Hemsath, L.; Fiegen, D.; Blumenstein, L.; Herbrand, U.; Stege, P.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Purification and biochemical properties of Rac1, 2, 3 and the splice variant Rac1b. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 406, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Haeusler, L.C.; Blumenstein, L.; Stege, P.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Comparative functional analysis of the Rac GTPases. FEBS Lett. 2003, 555, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovanov, A.P.; Hawkins, D.; Barsukov, I.; Badii, R.; Bokoch, G.M.; Lian, L.-Y.; Roberts, G.C.K. Structural consequences of site-directed mutagenesis in flexible protein domains. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, B.D.; Hordijk, P.L. The Rac1 hyper variable region in targeting and signaling-a tail of many stories. Small GTPases 2013, 4, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joseph, G.; Gorzalczany, Y.; Koshkin, V.; Pick, E. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation by synthetic peptides mapping within the carboxyl-terminal domain of small GTP-binding proteins. Lack of amino acid sequence specificity and importance of polybasic motif. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29024–29031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, K.N.; Zhou, Y.; Hancock, J.F. Rac1 Nanoscale Organization on the Plasma Membrane Is Driven by Lipid Binding Specificity Encoded in the Membrane Anchor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 38, e00186-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gosser, Y.Q.; Nomanbhoy, T.K.; Aghazadeh, B.; Manor, D.; Combs, C.; Cerione, R.A.; Rosen, M.K. C-terminal binding domain of Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor directs N-terminal inhibitory peptide to GTPases. Nature 1997, 387, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, M.A.; Desrosiers, R.R.; Gingras, D.; Béliveau, R. Phosphorylation states of Cdc42 and RhoA regulate their interactions with Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor and their extraction from biological membranes. Biochem. J. 2002, 361, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovanov, A.P.; Chuang, T.H.; DerMardirossian, C.; Barsukov, I.; Hawkins, D.; Badii, R.; Bokoch, G.M.; Lian, L.Y.; Roberts, G.C.K. Structure-activity relationships in flexible protein domains: Regulation of rho GTPases by RhoGDI and D4 GDI. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.T.; Coppola, S.; Krumbach, O.H.F.; Prencipe, G.; Insalaco, A.; Cifaldi, C.; Brigida, I.; Zara, E.; Scala, S.; di Cesare, S.; et al. A novel disorder involving dyshematopoiesis, inflammation, and HLH due to aberrant CDC42 function. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2778–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keep, N.H.; Barnes, M.; Barsukov, I.; Badii, R.; Lian, L.Y.; Segal, A.W.; Moody, P.C.E.; Roberts, G.C.K. A modulator of rho family G proteins, rhoGDI, binds these G proteins via an immunoglobulin-like domain and a flexible N-terminal arm. Structure 1997, 5, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemsath, L.; Dvorsky, R.; Fiegen, D.; Carlier, M.F.; Ahmadian, M.R. An electrostatic steering mechanism of Cdc42 recognition by Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome proteins. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetley, G.J.N.; Szeto, A.; Fountain, A.J.; Mott, H.R.; Owen, D. Bond swapping from a charge cloud allows flexible coordination of upstream signals through WASP: Multiple regulatory roles for the WASP basic region. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15136–15151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Fu, H.; Springer, T.A.; Wong, W.P. Electrostatic Steering Enables Flow-Activated Von Willebrand Factor to Bind Platelet Glycoprotein, Revealed by Single-Molecule Stretching and Imaging. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 1380–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didsbury, J.; Weber, R.F.; Bokoch, G.M.; Evans, T.; Snyderman, R. Rac, a Novel Ras-Related Family of Proteins That Are Botulinum Toxin Substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 16378–16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherle, P.; Behrens, T.; Staudt, L.M. Ly-GDI, a GDP-dissociation inhibitor of the RhoA GTP-binding protein, is expressed preferentially in lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7568–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majolée, J.; Podieh, F.; Hordijk, P.L.; Kovačević, I. The interplay of Rac1 activity, ubiquitination and GDI binding and its consequences for endothelial cell spreading. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelson, D.; Silletti, J.; Murphy, G.; D’Eustachio, P.; Rush, M.; Philips, M.R. Differential localization of Rho GTPases in live cells: Regulation by hypervariable regions and RhoGDI binding. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ten Klooster, J.P.; Jaffer, Z.M.; Chernoff, J.; Hordijk, P.L. Targeting and activation of Rac1 are mediated by the exchange factor β-Pix. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kreuk, B.J.; Nethe, M.; Fernandez-Borja, M.; Anthony, E.C.; Hensbergen, P.J.; Deelder, A.M.; Plomann, M.; Hordijk, P.L. The F-BAR domain protein PACSIN2 associates with Rac1 and regulates cell spreading and migration. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2375–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoughlami, Y.; van Stalborgh, A.M.; van Hennik, P.B.; Hordijk, P.L. Nucleophosmin1 Is a Negative Regulator of the Small GTPase Rac1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanning, C.C.; Ruiz-Velasco, R.; Williams, C.L. Novel mechanism of the co-regulation of nuclear transport of SmgGDS and Rac1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12495–12506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Chelikani, P.; Bhullar, R.P. Characterization and Functional Analysis of the Calmodulin-Binding Domain of Rac1 GTPase. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Tohyama, M. The p75 receptor acts as a displacement factor that releases Rho from Rho-GDI. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Tann, J.Y.; Goh, E.T.; Kelly, C.; Lim, K.B.; Gao, J.F.; Ibanez, C.F. Structural basis of death domain signaling in the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Elife 2015, 4, e11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Huang, A.; Zhou, J.; He, C. TROY interacts with Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor α (RhoGDIα) to mediate Nogo-induced inhibition of neurite outgrowth. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34276–34286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scoles, D.R. The merlin interacting proteins reveal multiple targets for NF2 therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1785, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Sasaki, T.; Mammoto, A.; Takaishi, K.; Kameyama, T.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S.; Takai, Y. Direct interaction of the Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor with ezrin/radixin/moesin initiates the activation of the Rho small G protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 23371–23375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, M.; Matsui, T.; Imamura, M.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Expression level, subcellular distribution and Rho-GDI binding affinity of merlin in comparison with ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4788–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castro-Castro, A.; Ojeda, V.; Barreira, M.; Sauzeau, V.; Navarro-Lérida, I.; Muriel, O.; Couceiro, J.R.; Pimentel-Muíños, F.X.; del Pozo, M.A.; Bustelo, X.R. Coronin 1A promotes a cytoskeletal-based feedback loop that facilitates Rac1 translocation and activation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3913–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castro-Castro, A.; Muriel, O.; del Pozo, M.A.; Bustelo, X.R. Characterization of Novel Molecular Mechanisms Favoring Rac1 Membrane Translocation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elfenbein, A.; Rhodes, J.M.; Meller, J.; Schwartz, M.A.; Matsuda, M.; Simons, M. Suppression of RhoG activity is mediated by a syndecan 4-synectin-RhoGDI1 complex and is reversed by PKCα in a Rac1 activation pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kweon, S.-M.; Cho, Y.J.; Minoo, P.; Groffen, J.; Heisterkamp, N. Activity of the Bcr GTPase-activating domain is regulated through direct protein/protein interaction with the Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3023–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ota, T.; Maeda, M.; Okamoto, M.; Tatsuka, M. Positive regulation of Rho GTPase activity by RhoGDIs as a result of their direct interaction with GAPs. BMC Syst. Biol. 2015, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ugolev, Y.; Berdichevsky, Y.; Weinbaum, C.; Pick, E. Dissociation of Rac1(GDP).RhoGDI complexes by the cooperative action of anionic liposomes containing phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor, and GTP. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 22257–22271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Der Mardirossian, C.; Schnelzer, A.; Bokoch, G.M. Phosphorylation of RhoGDI by Pak1 mediates dissociation of Rac GTPase. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, N.; Wroblowski, S.; Knyphausen, P.; de Boor, S.; Brenig, J.; Zienert, A.Y.; Meyer-Teschendorf, K.; Praefcke, G.J.K.; Nolte, H.; Krüger, M.; et al. Structural and Mechanistic Insights into the Regulation of the Fundamental Rho Regulator RhoGDIα by Lysine Acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, X.-R.; Huang, C. RhoGDI SUMOylation at Lys-138 increases its binding activity to Rho GTPase and its inhibiting cancer cell motility. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13752–13760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Luo, W.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.-R.; et al. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) mediates cancer cell motility via Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (RhoGDI)-dependent regulation of the cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15630–15640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, L.; Lineberry, N.; Huh, Y.; Soares, L.; Fathman, C.G. A novel E3 ubiquitin ligase substrate screen identifies Rho guanine dissociation inhibitor as a substrate of gene related to anergy in lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7559–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jasemi, N.S.K.; Herrmann, C.; Estirado, E.M.; Gremer, L.; Willbold, D.; Brunsveld, L.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. The intramolecular allostery of GRB2 governing its interaction with SOS1 is modulated by phosphotyrosine ligands. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 2793–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.F. Rho GTPases, their post-translational modifications, disease-associated mutations and pharmacological inhibitors. Small GTPases 2018, 9, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, M.R.; Stege, P.; Scheffzek, K.; Wittinghofer, A. Confirmation of the arginine-finger hypothesis for the GAP-stimulated GTP-hydrolysis reaction of Ras. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemsath, L.; Ahmadian, M.R. Fluorescence approaches for monitoring interactions of Rho GTPases with nucleotides, regulators, and effectors. Methods 2005, 37, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberth, A.; Ahmadian, M.R. In vitro GEF and GAP assays. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2009, 43, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- John, J.; Sohmen, R.; Feuerstein, J.; Linke, R.; Wittinghofer, A.; Goody, R.S. Kinetics of interaction of nucleotides with nucleotide-free H-ras p21. Biochemistry 2002, 29, 6058–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95–98. References—Scientific Research Publishing. 1999. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/(S(lz5mqp453edsnp55rrgjct55))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1383440 (accessed on 22 February 2021).
- Cock, P.J.A.; Antao, T.; Chang, J.T.; Chapman, B.A.; Cox, C.J.; Dalke, A.; Friedberg, I.; Hamelryck, T.; Kauff, F.; Wilczynski, B.; et al. Biopython: Freely available Python tools for computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1422–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. Delano Scientific, San Carlos. References—Scientific Research Publishing. 2002. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/(S(vtj3fa45qm1ean45vvffcz55))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1958992 (accessed on 22 February 2021).



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosaddeghzadeh, N.; Kazemein Jasemi, N.S.; Majolée, J.; Zhang, S.-C.; Hordijk, P.L.; Dvorsky, R.; Ahmadian, M.R. Electrostatic Forces Mediate the Specificity of RHO GTPase-GDI Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212493
Mosaddeghzadeh N, Kazemein Jasemi NS, Majolée J, Zhang S-C, Hordijk PL, Dvorsky R, Ahmadian MR. Electrostatic Forces Mediate the Specificity of RHO GTPase-GDI Interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212493
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosaddeghzadeh, Niloufar, Neda S. Kazemein Jasemi, Jisca Majolée, Si-Cai Zhang, Peter L. Hordijk, Radovan Dvorsky, and Mohammad Reza Ahmadian. 2021. "Electrostatic Forces Mediate the Specificity of RHO GTPase-GDI Interactions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212493
APA StyleMosaddeghzadeh, N., Kazemein Jasemi, N. S., Majolée, J., Zhang, S.-C., Hordijk, P. L., Dvorsky, R., & Ahmadian, M. R. (2021). Electrostatic Forces Mediate the Specificity of RHO GTPase-GDI Interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212493






