Dexamethasone Suppresses Palatal Cell Proliferation through miR-130a-3p
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
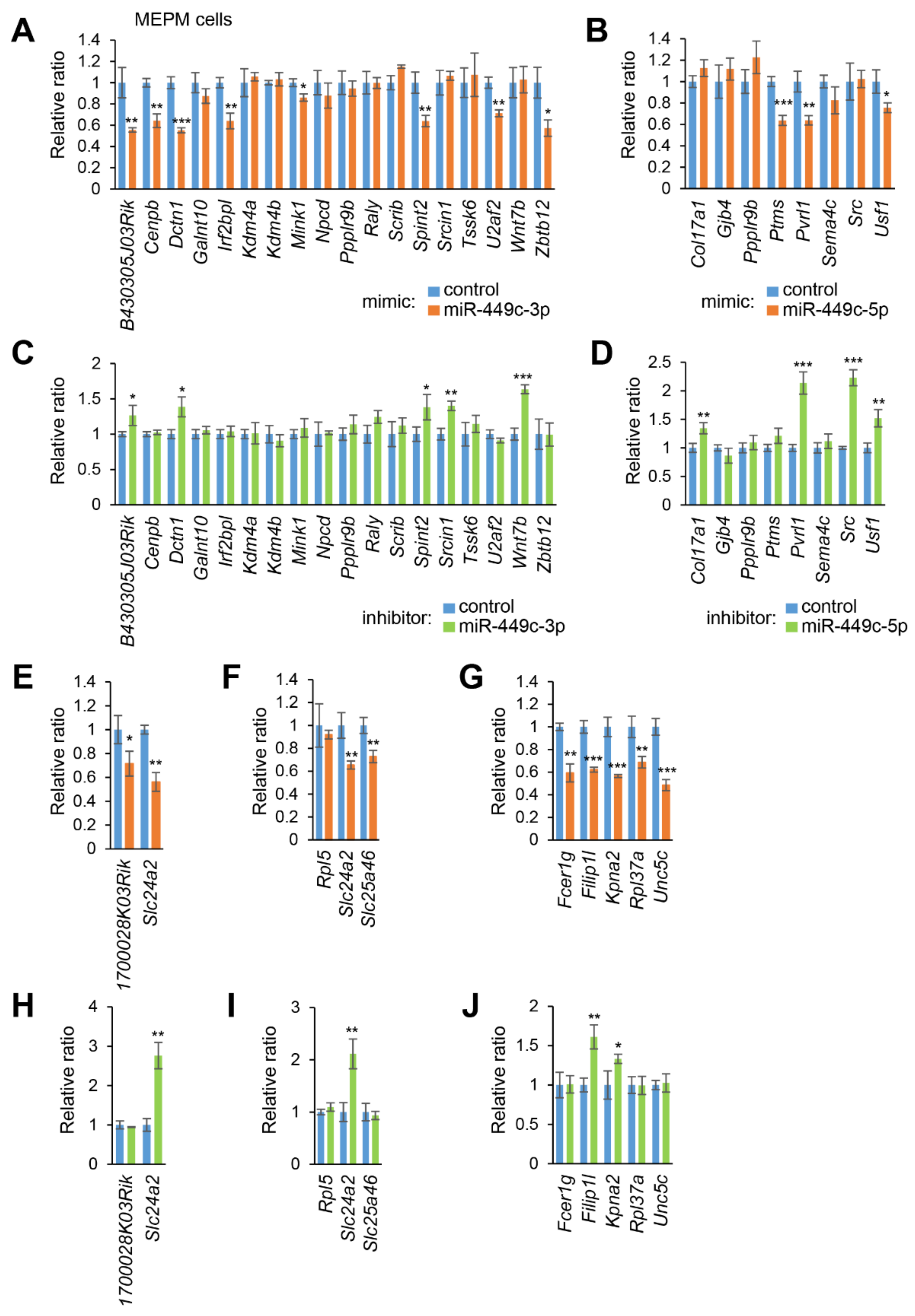
2.1. Genes and miRNAs Potentially Involved in Palate Development
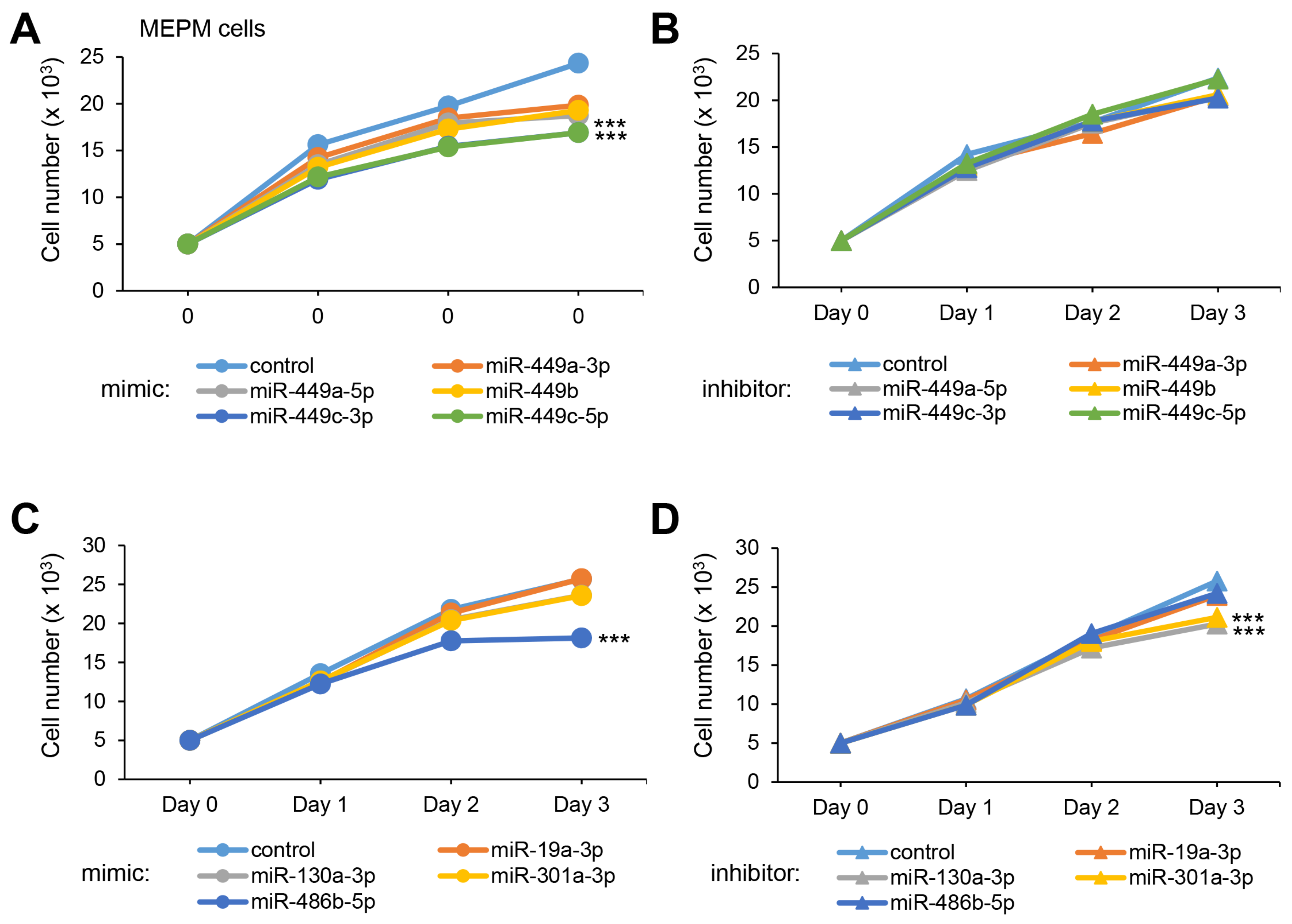
2.2. miRNAs Involved in Cell Growth in MEPM and O9-1 Cells
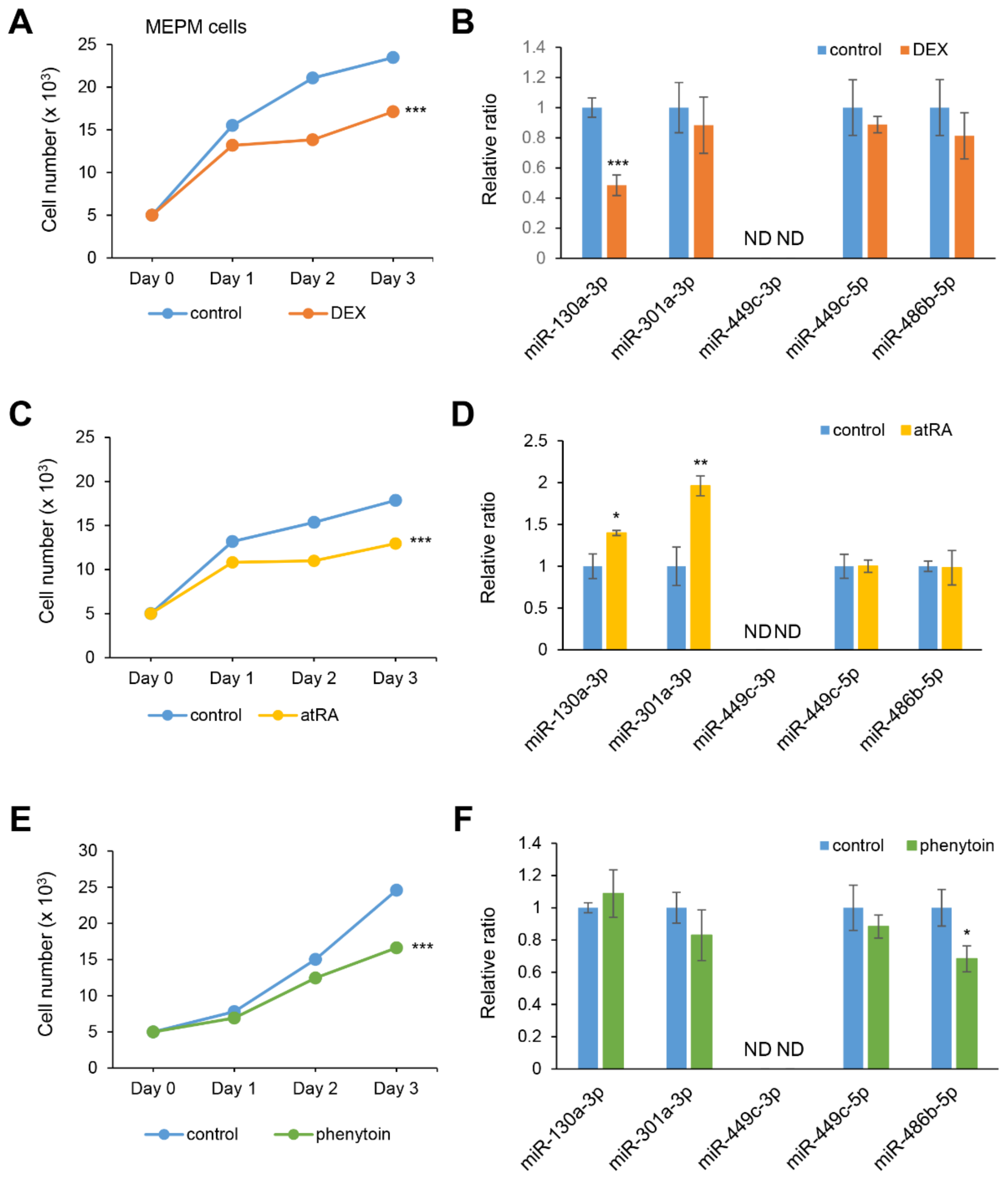
2.3. DEX Suppresses miR-130a-3p Expression in MEPM and O9-1 Cells
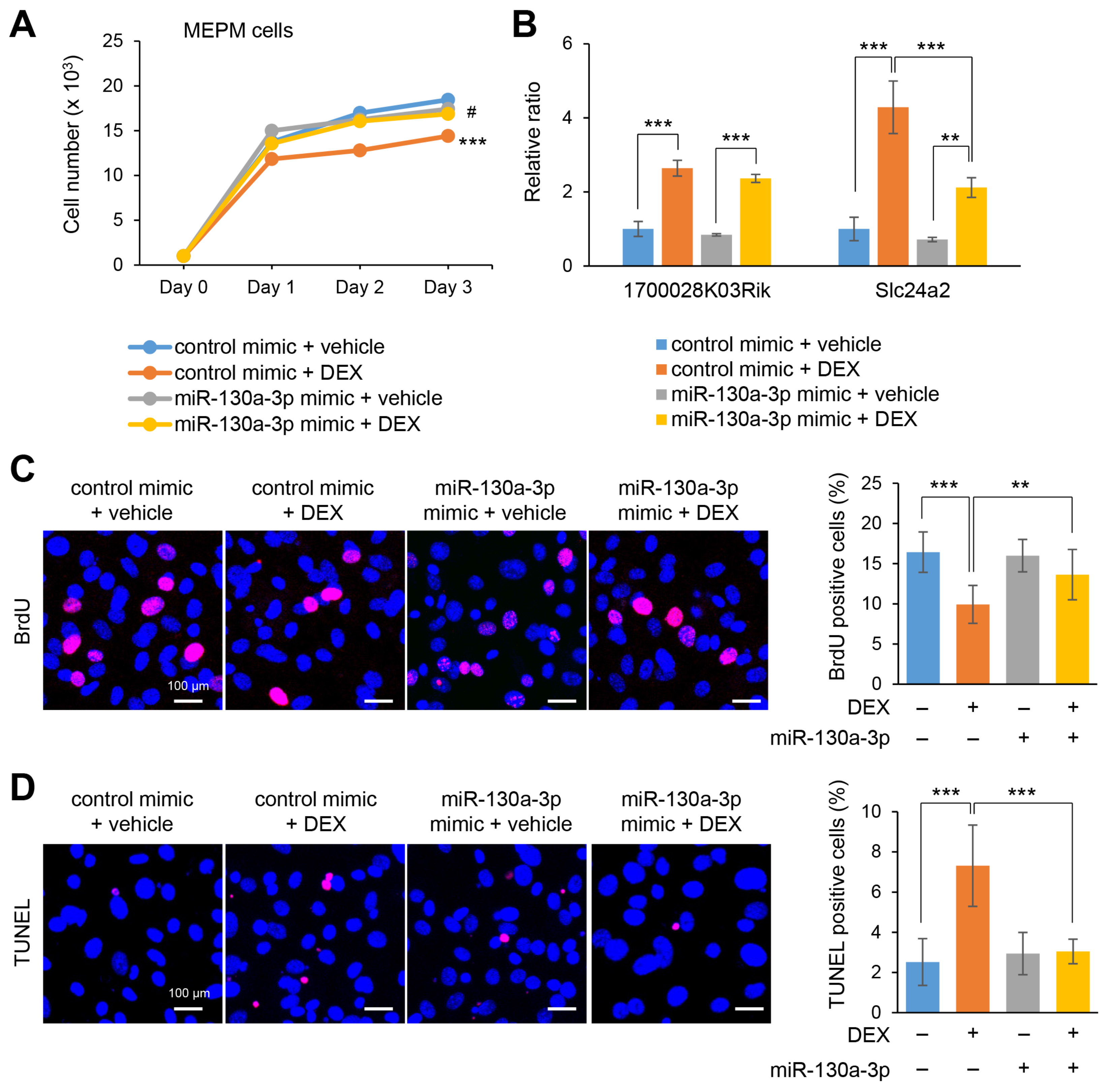
2.4. Overexpression of miR-130a-3p Restores Cell Proliferation under Treatment with DEX
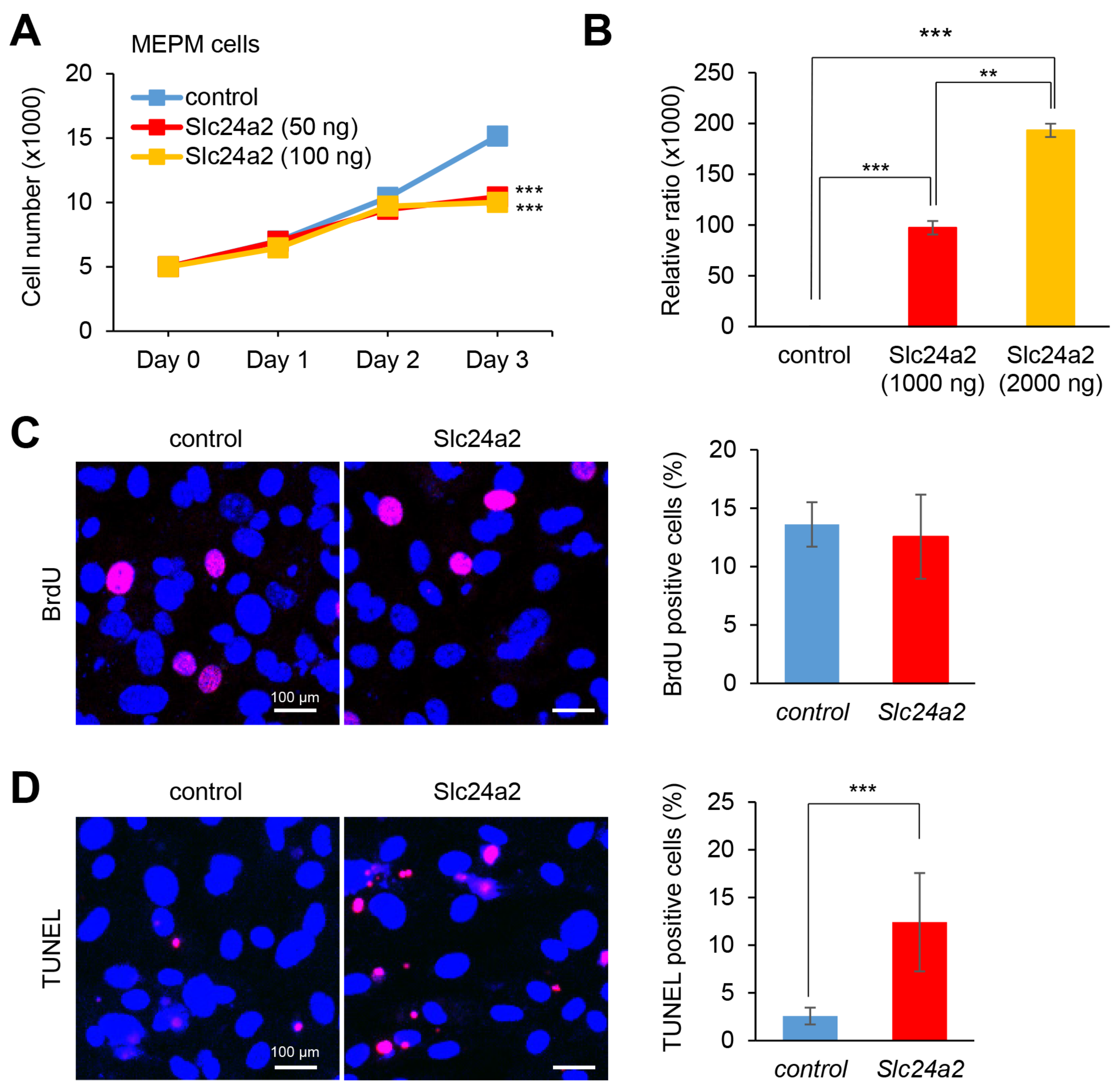
2.5. Slc24a2 Induces Apoptosis in MEPM and O9-1 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.5. BrdU Incorporation and TUNEL Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis in Experiments
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPDTOC Working Group. Prevalence at birth of cleft lip with or without cleft palate: Data from the International Perinatal Database of Typical Oral Clefts (IPDTOC). Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. Off. Publ. Am. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. Assoc. 2011, 48, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Fermin, C.; Chen, Y. Rescue of cleft palate in Msx1-deficient mice by transgenic Bmp4 reveals a network of BMP and Shh signaling in the regulation of mammalian palatogenesis. Development 2002, 129, 4135–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Abdallah, N.; Gajera, M.; Jun, G.; Jia, P.; Zhao, Z.; Iwata, J. Genes and microRNAs associated with mouse cleft palate: A systematic review and bioinformatics analysis. Mech. Dev. 2018, 150, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, M.C.; Pohl, H.R. Windows of Sensitivity to Toxic Chemicals in the Development of Cleft Palates. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2015, 18, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, J.C. Gene/environment causes of cleft lip and/or palate. Clin. Genet. 2002, 61, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, S.; Izaurralde, E. Towards a molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelan, R.S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Warner, D.R.; Appana, S.N.; Brock, G.N.; Pisano, M.M.; Greene, R.M. Methylated microRNA genes of the developing murine palate. MicroRNA 2014, 3, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.O.; Lee, J.M.; Cho, K.W.; Kwak, S.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, M.J.; Cho, S.W.; Kim, K.S.; Jung, H.S. MiR-200b is involved in Tgf-beta signaling to regulate mammalian palate development. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 137, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Li, A.; Gajera, M.; Abdallah, N.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Iwata, J. MicroRNA-374a, -4680, and -133b suppress cell proliferation through the regulation of genes associated with human cleft palate in cultured human palate cells. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Z.; Xing, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhong, X.; Shi, L.; Wan, X.; Zhou, J.; et al. MiR-106a-5p modulates apoptosis and metabonomics changes by TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway in cleft palate. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 386, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, H.; Mikami, Y.; Ramakrishnan, S.S.; Suzuki, A.; Iwata, J. MicroRNA-124-3p Plays a Crucial Role in Cleft Palate Induced by Retinoic Acid. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 621045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, T.H.; Berg, R.S.; Paludan, S.R.; Ostergaard, L. Mechanisms of dexamethasone-mediated inhibition of Toll-like receptor signaling induced by Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Corticosteroids: Mechanisms of Action in Health and Disease. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheschowitsch, K.; Leite, J.A.; Assreuy, J. New Insights in Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling-More Than Just a Ligand-Binding Receptor. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A.S.; Sharpior, B.H.; Katsumata, M. Human foetal palatal corticoid receptors and teratogens for cleft palate. Nature 1978, 272, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandoli, G.; Palmsten, K.; Forbess Smith, C.J.; Chambers, C.D. A Review of Systemic Corticosteroid Use in Pregnancy and the Risk of Select Pregnancy and Birth Outcomes. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 43, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorn, A.M.; Ehrenstein, V.; Nohr, E.A.; Norgaard, M. Use of inhaled and oral corticosteroids in pregnancy and the risk of malformations or miscarriage. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 116, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, R.S. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 41, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.H.; Lin, W.Y.; Yeh, K.T.; Chen, I.H.; Wu, W.T.; Lin, M.D. The molecular etiology and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2021, 33, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.M.; Kochhar, D.M. Some aspects of corticosteroid-induced cleft palate: A review. Teratology 1975, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, J.F. A glucocorticoid receptor in fetal mouse: Its relationship to cleft palate formation. Teratology 1980, 21, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillegass, J.M.; Villano, C.M.; Cooper, K.R.; White, L.A. Matrix metalloproteinase-13 is required for zebra fish (Danio rerio) development and is a target for glucocorticoids. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2007, 100, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillegass, J.M.; Villano, C.M.; Cooper, K.R.; White, L.A. Glucocorticoids alter craniofacial development and increase expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinases in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2008, 102, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azarbayjani, F.; Danielsson, B.R. Phenytoin-induced cleft palate: Evidence for embryonic cardiac bradyarrhythmia due to inhibition of delayed rectifier K+ channels resulting in hypoxia-reoxygenation damage. Teratology 2001, 63, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.S. Protein kinase C and chemical-induced abnormal palate development. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2005, 24, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.D.; Jiang, L.H.; Sun, D.W.; Li, J.; Ji, Z.L. The role of miR-130a in cancer. Breast Cancer 2017, 24, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Takwi, A.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Conklin, D.J.; Young, K.H.; Martin, R.; Li, Y. miR-301a as an NF-kappaB activator in pancreatic cancer cells. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, W. MicroRNA130a3p promotes the proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of cervical cancer cells via negative regulation of RUNX3. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2990–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, H.; Qu, Y.; Deng, T.; Huang, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Bai, M.; Zhou, L.; Ying, G.; et al. Onco-miR-130 promotes cell proliferation and migration by targeting TGFbetaR2 in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 44522–44533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Cui, C.; Xiao, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Shi, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Yang, X.; et al. miR-486 regulates metastasis and chemosensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CLDN10 and CITRON. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2015, 45, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Geng, S.; Hu, Y. miR-486-5p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion through repressing GAB2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3525–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ni, Z.; Shi, L.; Ma, L.; Zhao, J. MiR-486-5p inhibits the proliferation of leukemia cells and induces apoptosis through targeting FOXO1. Mol. Cell. Probes 2019, 44, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. MicroRNA-486-5p targeting PIM-1 suppresses cell proliferation in breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 11137–11145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, G.; Ntounia-Fousara, S.; Granda, B.; Rathjen, T.; Dalmay, T. Identification of new central nervous system specific mouse microRNAs. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2195–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lin, Y.W.; Mao, Y.Q.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.F.; Zheng, X.Y.; Xie, L.P. MicroRNA-449a acts as a tumor suppressor in human bladder cancer through the regulation of pocket proteins. Cancer Lett. 2012, 320, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, Z.; Xiang, J.; Chen, Z. miR-449b inhibits the proliferation of SW1116 colon cancer stem cells through downregulation of CCND1 and E2F3 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.J.; Huang, S.F.; Sun, Z.T.; Gao, Z.Y.; Zhang, R.X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. MiR-449c targets c-Myc and inhibits NSCLC cell progression. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.F.; Kiedrowski, L.; Tremblay, F.; Fernandez, F.R.; Perizzolo, M.; Winkfein, R.J.; Turner, R.W.; Bains, J.S.; Rancourt, D.E.; Lytton, J. Importance of K+-dependent Na+/Ca2+-exchanger 2, NCKX2, in motor learning and memory. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 6273–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Gao, J.; Liao, Y.; Tang, S.; Lu, F. Retinoic acid alters the proliferation and survival of the epithelium and mesenchyme and suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in developing cleft palate. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Gao, J.H.; Liao, Y.J.; Tang, S.J.; Lu, F. Dexamethasone alters epithelium proliferation and survival and suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in developing cleft palate. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2013, 56, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshdary, V.; Atlas, E. Dexamethasone induced miR-155 up-regulation in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes does not affect adipogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, S.; Cui, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, T.; Xing, H. MicroRNA-130b attenuates dexamethasone-induced increase of lipid accumulation in porcine preadipocytes by suppressing PPAR-gamma expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 87928–87943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abukiwan, A.; Nwaeburu, C.C.; Bauer, N.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, L.; Gladkich, J.; Gross, W.; Benner, A.; Strobel, O.; Fellenberg, J.; et al. Dexamethasone-induced inhibition of miR-132 via methylation promotes TGF-beta-driven progression of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwata, J.; Parada, C.; Chai, Y. The mechanism of TGF-beta signaling during palate development. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rueda, A.; Barturen, G.; Lebrón, R.; Gómez-Martín, C.; Alganza, Á.; Oliver, J.L.; Hackenberg, M. sRNAtoolbox: An integrated collection of small RNA research tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W467–W473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Smyth, G.K. Differential expression analysis of multifactor RNA-Seq experiments with respect to biological variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4288–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishii, M.; Arias, A.C.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.B.; Bronner, M.E.; Maxson, R.E. A stable cranial neural crest cell line from mouse. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 3069–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshioka, H.; Ramakrishnan, S.S.; Shim, J.; Suzuki, A.; Iwata, J. Excessive All-Trans Retinoic Acid Inhibits Cell Proliferation Through Upregulated MicroRNA-4680-3p in Cultured Human Palate Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 618876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshioka, H.; Jun, G.; Suzuki, A.; Iwata, J. Dexamethasone Suppresses Palatal Cell Proliferation through miR-130a-3p. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212453
Yoshioka H, Jun G, Suzuki A, Iwata J. Dexamethasone Suppresses Palatal Cell Proliferation through miR-130a-3p. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212453
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshioka, Hiroki, Goo Jun, Akiko Suzuki, and Junichi Iwata. 2021. "Dexamethasone Suppresses Palatal Cell Proliferation through miR-130a-3p" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212453
APA StyleYoshioka, H., Jun, G., Suzuki, A., & Iwata, J. (2021). Dexamethasone Suppresses Palatal Cell Proliferation through miR-130a-3p. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212453







