Human Epidermal Zinc Concentrations after Topical Application of ZnO Nanoparticles in Sunscreens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterisation of 67ZnO-PEG NPs
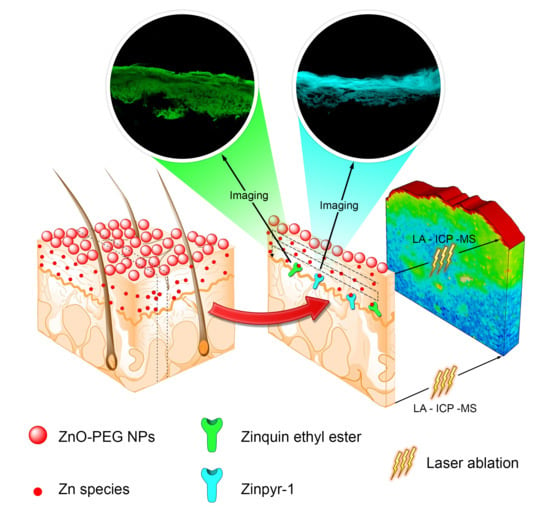
2.2. Multiphoton Microscopy Imaging
2.3. Quantitative Measurement of Absorbed 67Zn in Skin Layers by LA-ICP-MS and ICP-MS
2.4. Cytotoxicity of 67ZnO-PEG NPs in HaCaT Cells
2.5. Discussion
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of 67ZnO-PEG NPs via a Co-Precipitation Method
3.2. Characterisation of 67ZnO-PEG NPs
3.3. Preparation of Heat-Separated Human Epidermis Samples
3.4. Skin Penetration Assay
3.5. Sample Preparation for Microscopy
3.6. Multiphoton Laser-Scanning Microscopy
3.7. LA-ICP-MS Analysis
3.8. Sample Preparation for Solution Nebulisation ICP-MS
3.9. Solution Nebulisation ICP-MS
3.10. Cell Culture and MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
3.11. Determination of Labile Zinc Species in Cell-Mediated Culture Media
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raj, S.; Jose, S.; Sumod, U.; Sabitha, M. Nanotechnology in cosmetics: Opportunities and challenges. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhri, N.; Soni, G.C.; Prajapati, S. Nanotechnology: An advance tool for nano-cosmetics preparation. Int. J. Pharma Res. Rev. 2015, 4, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, U.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, A.A.; Akhtar, J.; Singh, S.P.; Ahmad, F.J. Strategies in development and delivery of nanotechnology based cosmetic products. Drug Res. 2018, 68, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.S.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Pastore, M.; Namjoshi, S.; Yousef, S.; Alinaghi, A.; Haridass, I.N.; Abd, E.; Leite-Silva, V.R.; Benson, H.A.E.; et al. Topical and cutaneous delivery using nanosystems. J. Control. Release 2017, 247, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prow, T.W.; Grice, J.E.; Lin, L.L.; Faye, R.; Butler, M.; Becker, W.; Wurm, E.M.; Yoong, C.; Robertson, T.A.; Soyer, H.P.; et al. Nanoparticles and microparticles for skin drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 470–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, F.; Chan, J.; Wang, A.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O. Nanoparticles in medicine: Therapeutic applications and developments. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, T.O.; Siccardi, M.; Moss, D.; Liptrott, N.; Giardiello, M.; Rannard, S.; Owen, A. The application of nanotechnology to drug delivery in medicine. Chapter 2015, 2, 173–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kargozar, S.; Mozafari, M.M. Nanotechnology and Nanomedicine: Start small, think big. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 15492–15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, M.R.; Lowry, G.V.; Alvarez, P.; Dionysiou, D.; Biswas, P. Assessing the Risks of Manufactured Nanomaterials; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Colvin, V.L. The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, M.; Bowman, D. Nanotechnology Environmental Health and Safety: Risks, Regulation, and Management; William Andrew: Norwich, New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karahalil, B. Challenges, Recommendations, and Strategies for Nanotoxicology Evaluation and Its Management. In Nanotoxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, USA, 2018; pp. 649–655. [Google Scholar]
- Piccinno, F.; Gottschalk, F.; Seeger, S.; Nowack, B. Industrial production quantities and uses of ten engineered nanomaterials in Europe and the world. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nohynek, G.J.; Lademann, J.; Ribaud, C.; Roberts, M.S. Grey goo on the skin? Nanotechnology, cosmetic and sunscreen safety. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 251–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smijs, T.G.; Pavel, S. Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in sunscreens: Focus on their safety and effectiveness. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2011, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berube, D.M. Rhetorical gamesmanship in the nano debates over sunscreens and nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, M.; Mohammed, Y.; Prow, T.W. Advances and controversies in studying sunscreen delivery and toxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 135, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Singh, S.K.; Anderson, D.; Tobin, D.J.; Dhawan, A. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced genotoxicity in primary human epidermal keratinocytes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 3782–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Pie, J.-E.; Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, H.R.; Son, S.W.; Kim, M.-K. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on gene expression profile in human keratinocytes. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Shukla, R.K.; Saxena, N.; Parmar, D.; Das, M.; Dhawan, A. DNA damaging potential of zinc oxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 185, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, H.; Archana, G.; Rakshit, M.; Ng, K.W.; Tay, C.Y.J.N. Human keratinocytes adapt to ZnO nanoparticles induced toxicity via complex paracrine crosstalk and Nrf2-proteasomal signal transduction. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuilleabhain, S.N.; Mothersill, C.; Sheehan, D.; O’Brien, N.; O’Halloran, J.; Van Pelt, F.; Davoren, M. In vitro cytotoxicity testing of three zinc metal salts using established fish cell lines. Toxicol. Vitr. 2004, 18, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, F.; Li, L.; Sun, Z. Role of the dissolved zinc ion and reactive oxygen species in cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 199, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momose, A.; Shiraiwa, Y.; Narita, S.; Kusumi, T.; Goto, S.; Sera, K.J.N. Total Calcium and Albumin Are Decreased in the Deeper Epidermis of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Pruritus. Nephron 2017, 136, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelsson, G.; Ljunghall, K.; Danielson, B.J. Zinc in epidermis and dermis in healthy subjects. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1980, 60, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gamer, A.; Leibold, E.v.; Van Ravenzwaay, B. The in vitro absorption of microfine zinc oxide and titanium dioxide through porcine skin. Toxicol. Vitr. 2006, 20, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, S.E.; Innes, B.; Roberts, M.S.; Tsuzuki, T.; Robertson, T.A.; McCormick, P. Human skin penetration of sunscreen nanoparticles: In-vitro assessment of a novel micronized zinc oxide formulation. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 20, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvyagin, A.V.; Zhao, X.; Gierden, A.; Sanchez, W.; Ross, J.A.; Roberts, M.S. Imaging of zinc oxide nanoparticle penetration in human skin in vitro and in vivo. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 064031–064039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, M.S.; Roberts, M.J.; Robertson, T.A.; Sanchez, W.; Thörling, C.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Becker, W.; Zvyagin, A.V. In vitro and in vivo imaging of xenobiotic transport in human skin and in the rat liver. J. Biophotonics 2008, 1, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.M.; Song, Z.; Moghimi, H.R.; Roberts, M.S. Relative penetration of zinc oxide and zinc ions into human skin after application of different zinc oxide formulations. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.C.; Bunge, A.L.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Nanoparticles do not penetrate human skin—A theoretical perspective. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1943–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite-Silva, V.R.; Sanchez, W.Y.; Studier, H.; Liu, D.C.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Holmes, A.M.; Ryan, E.M.; Haridass, I.N.; Chandrasekaran, N.C.; Becker, W.; et al. Human skin penetration and local effects of topical nano zinc oxide after occlusion and barrier impairment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 104, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filipe, P.; Silva, J.; Silva, R.; De Castro, J.C.; Gomes, M.M.; Alves, L.; Santus, R.; Pinheiro, T. Stratum corneum is an effective barrier to TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticle percutaneous absorption. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 22, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite-Silva, V.R.; Liu, D.C.; Sanchez, W.Y.; Studier, H.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Holmes, A.; Becker, W.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.; Roberts, M.S. Effect of flexing and massage on in vivo human skin penetration and toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GoodsAdmnistration, Therapeutic. Literature review on the safety of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide on nanoparticles in sunscreens. Dep. Health Ageing 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ohman, H.; Vahlquist, A. In vivo studies concerning a pH gradient in human stratum corneum and upper epidermis. Acta Derm. Venereol. Stockh. 1994, 74, 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Ågren, M.S. Percutaneous absorption of zinc from zinc oxide applied topically to intact skin in man. Dermatology 1990, 180, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirot, F.; Millet, J.; Kalia, Y.; Humbert, P. In vitro study of percutaneous absorption, cutaneous bioavailability and bioequivalence of zinc and copper from five topical formulations. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1996, 9, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.M.; Kempson, I.; Turnbull, T.; Paterson, D.; Roberts, M.S. Penetration of zinc into human skin after topical application of nano zinc oxide used in commercial sunscreen formulations. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 3640–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.M.; Mackenzie, L.; Roberts, M.S. Disposition and measured toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles and zinc ions against keratinocytes in cell culture and viable human epidermis. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, Y.H.; Holmes, A.; Haridass, I.N.; Sanchez, W.Y.; Studier, H.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.; Roberts, M.S. Support for the safe use of zinc oxide nanoparticle sunscreens: Lack of skin penetration or cellular toxicity after repeated application in volunteers. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, Y.H.; Haridass, I.N.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.; Roberts, M.S. Bathing Does Not Facilitate Human Skin Penetration or Adverse Cellular Effects of Nanoparticulate Zinc Oxide Sunscreens after Topical Application. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, Y.H.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Holmes, A.; Grice, J.; Roberts, M.S. Noninvasive in vivo human multiphoton microscopy: A key method in proving nanoparticulate zinc oxide sunscreen safety. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 014509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cotton, A.F.; Wilkinson, G.; Bochmann, M.; Murillo, C.A. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gulson, B.; McCall, M.; Korsch, M.; Gomez, L.; Casey, P.; Oytam, Y.; Taylor, A.; McCulloch, M.; Trotter, J.; Kinsley, L. Small amounts of zinc from zinc oxide particles in sunscreens applied outdoors are absorbed through human skin. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 118, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gulson, B.; Wong, H.; Korsch, M.; Gomez, L.; Casey, P.; McCall, M.; McCulloch, M.; Trotter, J.; Stauber, J.; Greenoak, G. Comparison of dermal absorption of zinc from different sunscreen formulations and differing UV exposure based on stable isotope tracing. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 420, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulson, B.; Wong, H. Stable isotopic tracing—a way forward for nanotechnology. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darvin, M.; König, K.; Kellner-Hoefer, M.; Breunig, H.; Werncke, W.; Meinke, M.; Patzelt, A.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Safety assessment by multiphoton fluorescence/second harmonic generation/hyper-Rayleigh scattering tomography of ZnO nanoparticles used in cosmetic products. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2012, 25, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joulaud, C.; Mugnier, Y.; Djanta, G.; Dubled, M.; Marty, J.-C.; Galez, C.; Wolf, J.-P.; Bonacina, L.; Le Dantec, R. Characterization of the nonlinear optical properties of nanocrystals by Hyper Rayleigh Scattering. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 11, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keller, A.A.; Wang, H.; Zhou, D.; Lenihan, H.S.; Cherr, G.; Cardinale, B.J.; Miller, R.; Ji, Z. Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, C.-P.; Zhung, C.-M.; Shih, Y.-H.; Tseng, Y.-M.; Wu, S.-C.; Doong, R.-A. Stability of metal oxide nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reed, R.B.; Ladner, D.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Westerhoff, P.; Ranville, J.F. Solubility of nano-zinc oxide in environmentally and biologically important matrices. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Wang, P.; Miao, L.; Lv, B.; Yang, Y.; You, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.J.E.S.; et al. Aggregation, sedimentation, and dissolution of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles in five waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31240–31249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ebraheem, A.; Dao, E.; Desouza, E.; Li, C.; Wainman, B.; McNeill, F.; Farquharson, M. Effect of sample preparation techniques on the concentrations and distributions of elements in biological tissues using µSRXRF: A comparative study. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, N51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.A.L.; Vignesh, K.S.; Deepe, G.S.; Caruso, J. Selectivity and specificity of small molecule fluorescent dyes/probes used for the detection of Zn2+ and Ca2+ in cells. Metallomics 2014, 6, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowakowski, A.B.; Petering, D.H. Reactions of the fluorescent sensor, Zinquin, with the zinc-proteome: Adduct formation and ligand substitution. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 10124–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karim, M.R. The Role of Proteome in Cellular Zn2+ Trafficking and in the Ability of Fluorescent Zinc Sensors to Image Intracellular Zn2+. Doctoral Dissertation, The University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Meija, J.; Coplen, T.B.; Berglund, M.; Brand, W.A.; De Bièvre, P.; Gröning, M.; Holden, N.E.; Irrgeher, J.; Loss, R.D.; Walczyk, T. Isotopic compositions of the elements 2013 (IUPAC technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorodetsky, R.; Sheskin, J.; Weinreb, A. Iron, copper, and zinc concentrations in normal skin and in various nonmalignant and malignant lesions. Int. J. Dermatol. 1986, 25, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.; Priezzhev, A.; Lademann, J.; Myllylä, R. TiO2 nanoparticles as an effective UV-B radiation skin-protective compound in sunscreens. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Taneda, A.; Kanaoka, Y.; Sekine, T. The histochemical distribution of protein bound sulfhydryl groups in human epidermis by the new staining method. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1979, 27, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Haase, H. The essential toxin: Impact of zinc on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bielfeldt, S.; Schoder, V.; Ely, U.; Van Der Pol, A.; De Sterke, J.; Wilhelm, K.P. Assessment of human stratum corneum thickness and its barrier properties by in-vivo confocal Raman spectroscopy. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlica, S.; Gaunitz, F.; Gebhardt, R. Comparative in vitro toxicity of seven zinc-salts towards neuronal PC12 cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinardell, M.P.; Llanas, H.; Marics, L.; Mitjans, M. In Vitro Comparative Skin Irritation Induced by Nano and Non-Nano Zinc Oxide. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Ryu, H.J.; Ryu, W.I.; Park, Y.-H.; Bae, H.C.; Jang, Y.S.; Son, S.W. ZnO nanoparticles induce TNF-α expression via ROS-ERK-Egr-1 pathway in human keratinocytes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 72, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, H.; Hebel, S.; Engelhardt, G.; Rink, L. The biochemical effects of extracellular Zn2+ and other metal ions are severely affected by their speciation in cell culture media. Metallomics 2015, 7, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, H.L.; Cronholm, P.; Hedberg, Y.; Tornberg, M.; De Battice, L.; Svedhem, S.; Wallinder, I.O. Cell membrane damage and protein interaction induced by copper containing nanoparticles—Importance of the metal release process. Toxicology 2013, 313, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Shen, C.; Feltis, B.N.; Martin, L.L.; Hughes, A.E.; Wright, P.F.; Turney, T.W. Reducing ZnO nanoparticle cytotoxicity by surface modification. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5791–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lademann, J.; Jacobi, U.; Surber, C.; Weigmann, H.-J.; Fluhr, J. The tape stripping procedure–evaluation of some critical parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šala, M.; Šelih, V.S.; van Elteren, J.T.J.A. Gelatin gels as multi-element calibration standards in LA-ICP-MS bioimaging: Fabrication of homogeneous standards and microhomogeneity testing. Analyst 2017, 142, 3356–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Care, A.; Ortega, T.A.; Deyev, S.M.; Qian, Y.; Zvyaginacd, A.V. Upconversion nanoparticles mediated deep-penetrating photodynamic therapy of KillerRed. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodroofe, C.C.; Masalha, R.; Barnes, K.R.; Frederickson, C.J.; Lippard, S.J. Membrane-permeable and-impermeable sensors of the Zinpyr family and their application to imaging of hippocampal zinc in vivo. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, M.S.; Cheruvu, H.S.; Mangion, S.E.; Alinaghi, A.; Benson, H.A.E.; Mohammed, Y.; Holmes, A.; van der Hoek, J.; Pastore, M.; Grice, J.E. Topical drug delivery: History, percutaneous absorption, and product development. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021, 177, 113929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA Advances new proposed regulation to make sure that sunscreens are safe and effective. Fed. Regist. 84FR6204 2019, 3019, 2019. [Google Scholar]






μg/g | μg/g | μg/g | μg/mL | μg/mL | IC50 *, μg Zn/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 235 ± 49 | 360 ± 70 | 39 ± 5 | 120 ± 23 | 13 ± 2 | - |
| VE | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.8 | 13 ± 2 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 4.3 ± 0.7 | - |
| Dermis | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 16 ± 7 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 5 ± 2 | - |
| HaCaT cells | - | - | - | - | - | 26 ± 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khabir, Z.; Holmes, A.M.; Lai, Y.-J.; Liang, L.; Deva, A.; Polikarpov, M.A.; Roberts, M.S.; Zvyagin, A.V. Human Epidermal Zinc Concentrations after Topical Application of ZnO Nanoparticles in Sunscreens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212372
Khabir Z, Holmes AM, Lai Y-J, Liang L, Deva A, Polikarpov MA, Roberts MS, Zvyagin AV. Human Epidermal Zinc Concentrations after Topical Application of ZnO Nanoparticles in Sunscreens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212372
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhabir, Zahra, Amy M. Holmes, Yi-Jen Lai, Liuen Liang, Anand Deva, Michael A. Polikarpov, Michael S. Roberts, and Andrei V. Zvyagin. 2021. "Human Epidermal Zinc Concentrations after Topical Application of ZnO Nanoparticles in Sunscreens" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212372
APA StyleKhabir, Z., Holmes, A. M., Lai, Y.-J., Liang, L., Deva, A., Polikarpov, M. A., Roberts, M. S., & Zvyagin, A. V. (2021). Human Epidermal Zinc Concentrations after Topical Application of ZnO Nanoparticles in Sunscreens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212372