Influence of Zwitterionic CAPB on Flocculation of the Aqueous Cationic Guar Gum/Glauconite Suspensions at Various pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
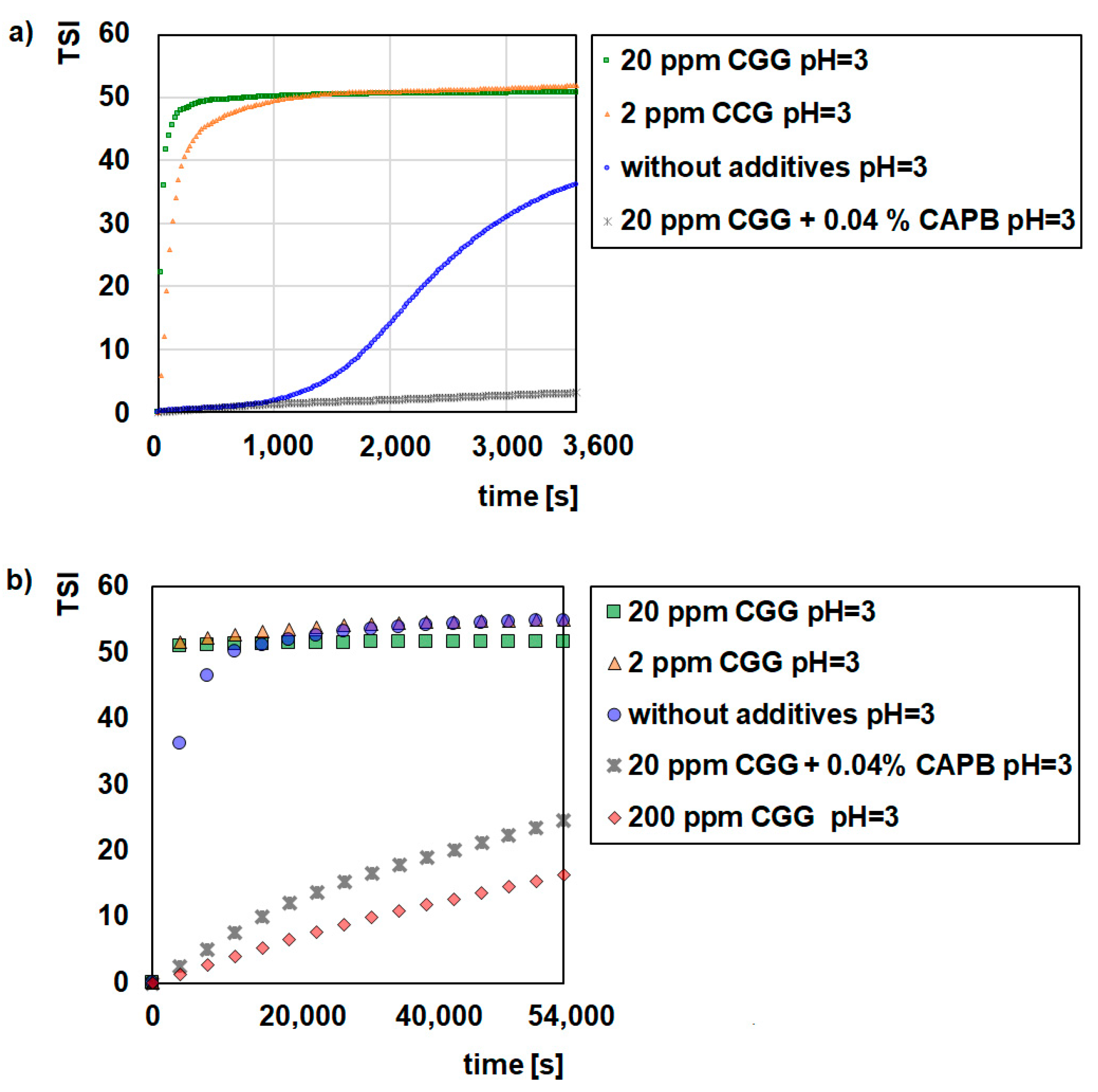
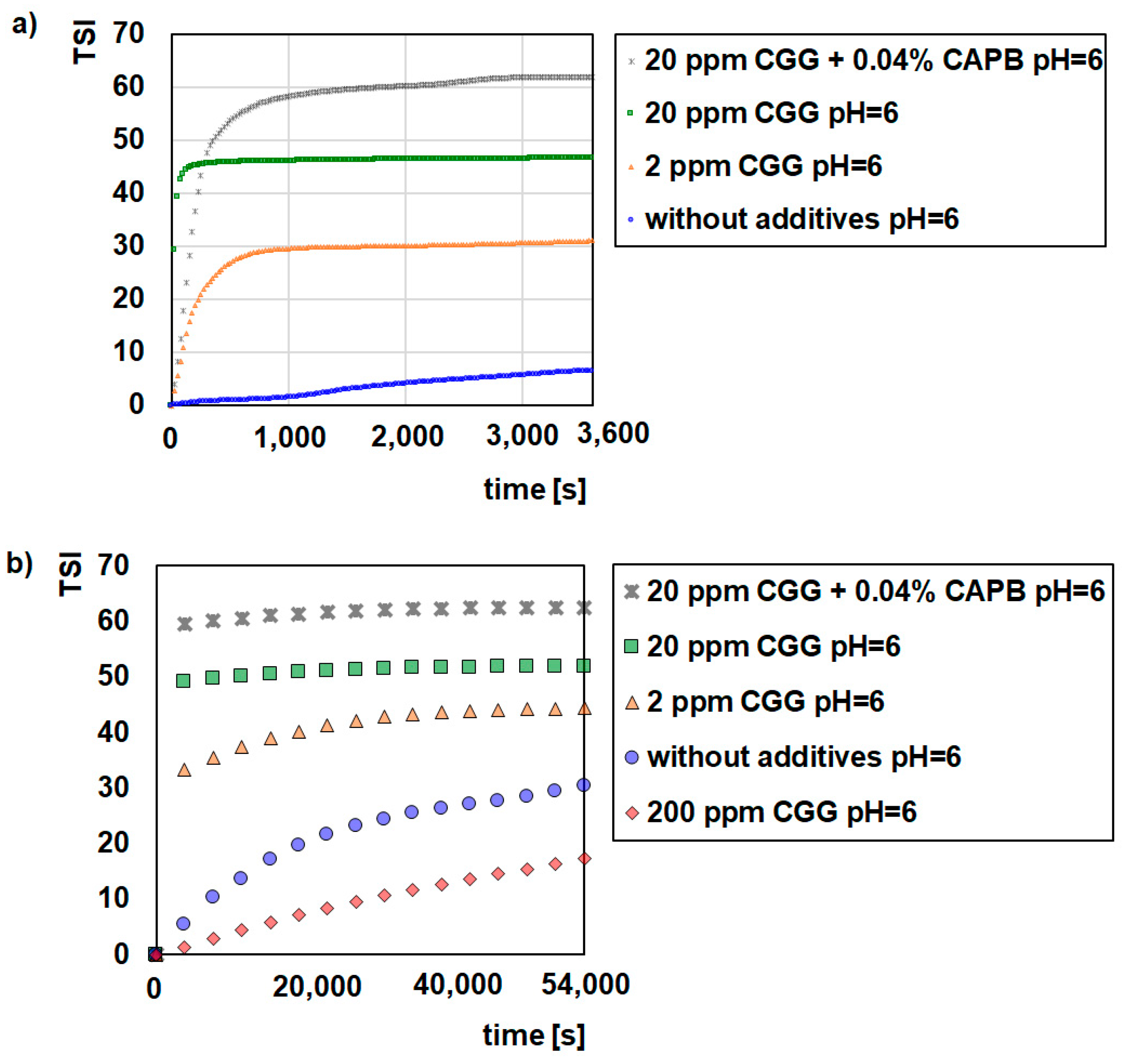
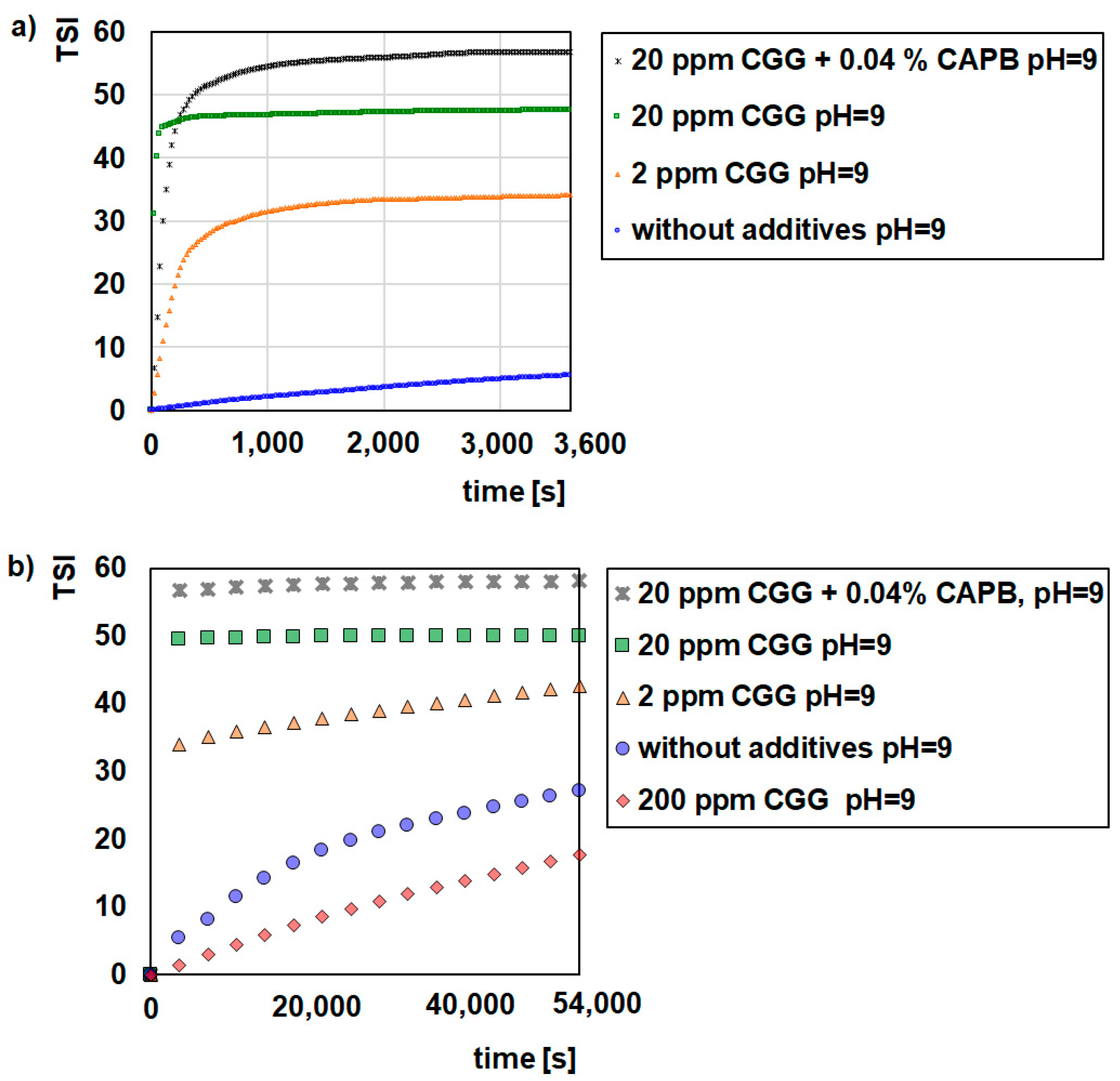
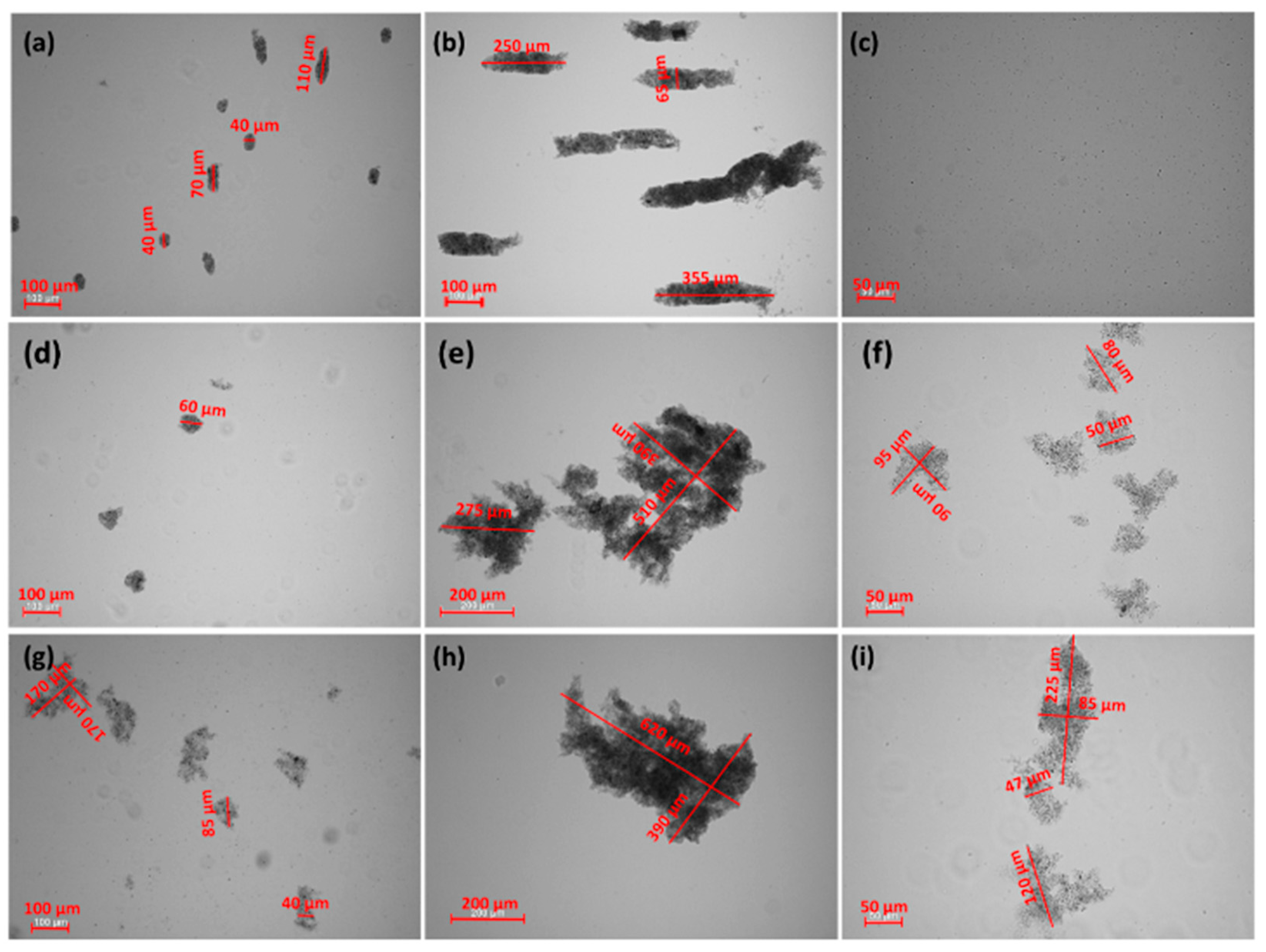
2.1. Stability Measurement
2.2. Formation of the CGG/CAPB Complexes
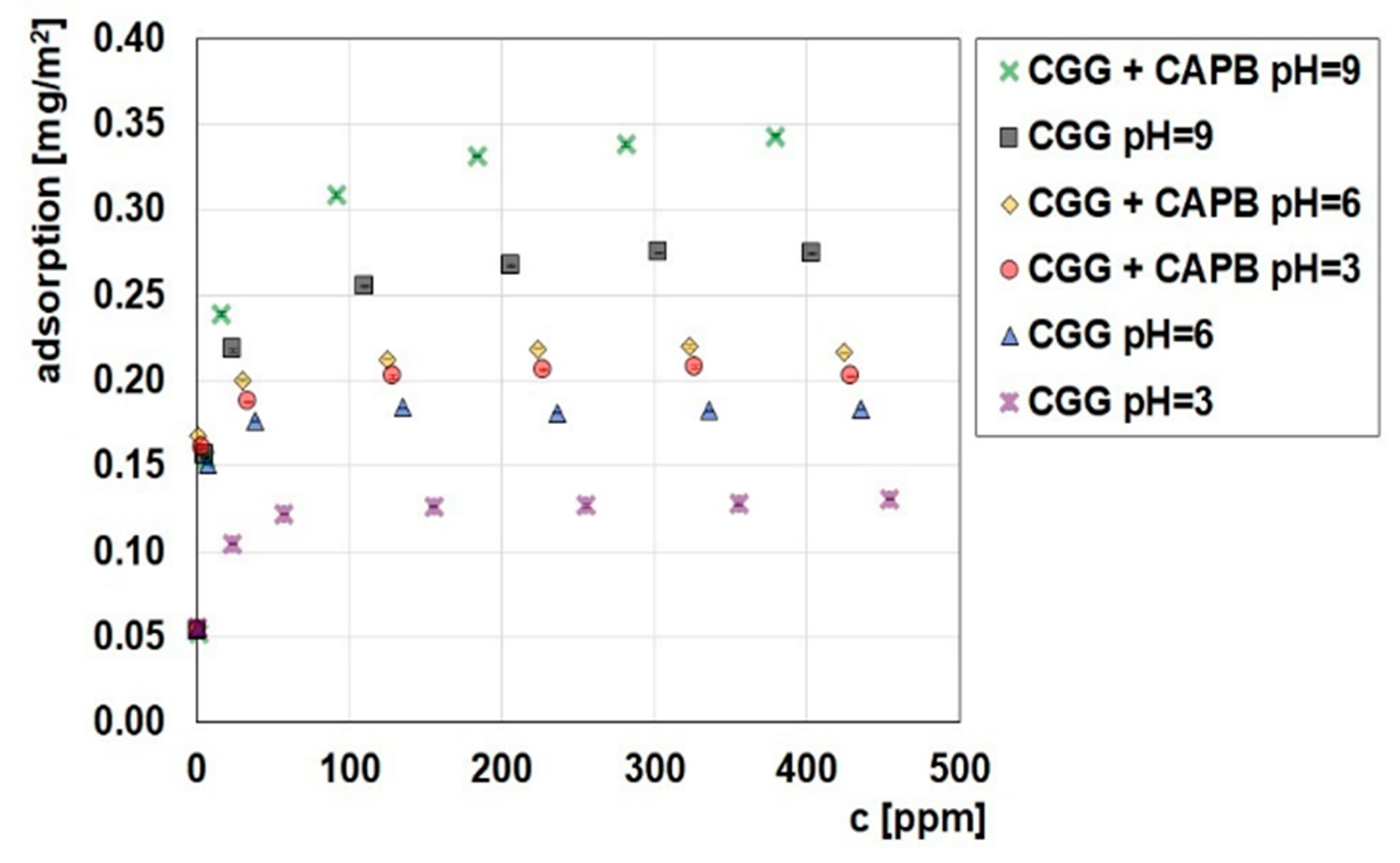
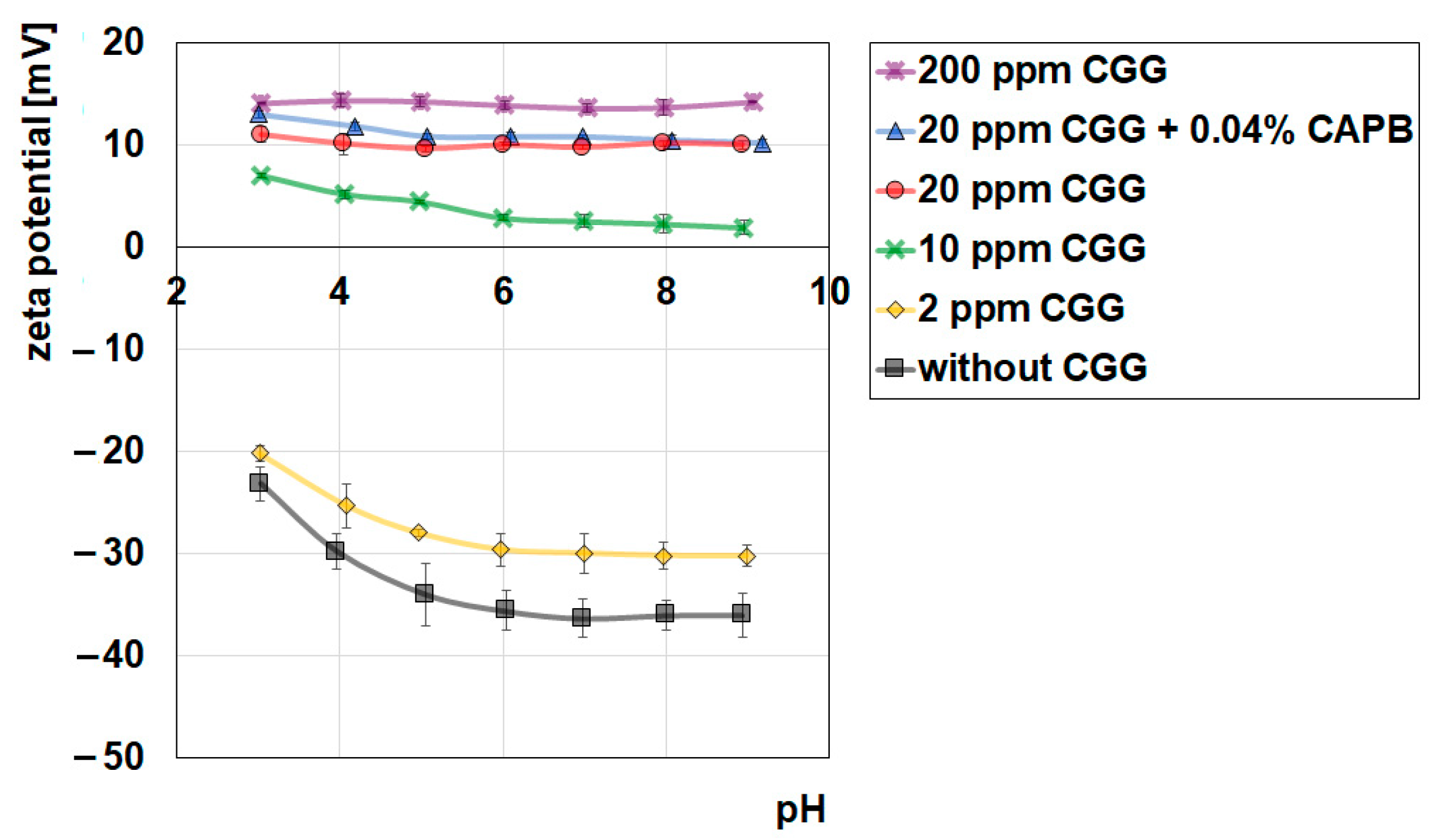
2.3. Adsorption and Electrokinetic Measurements
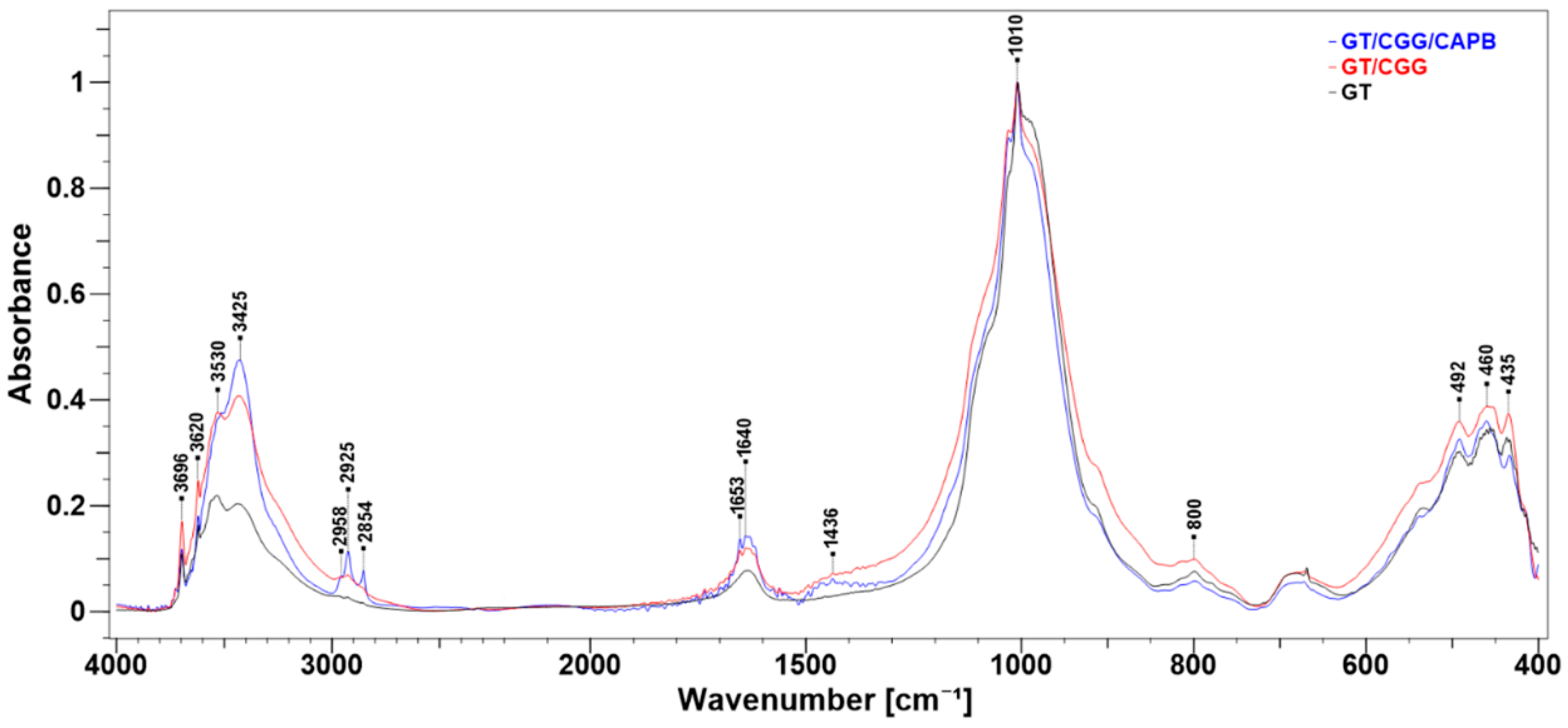
2.4. FT-IR Measurements
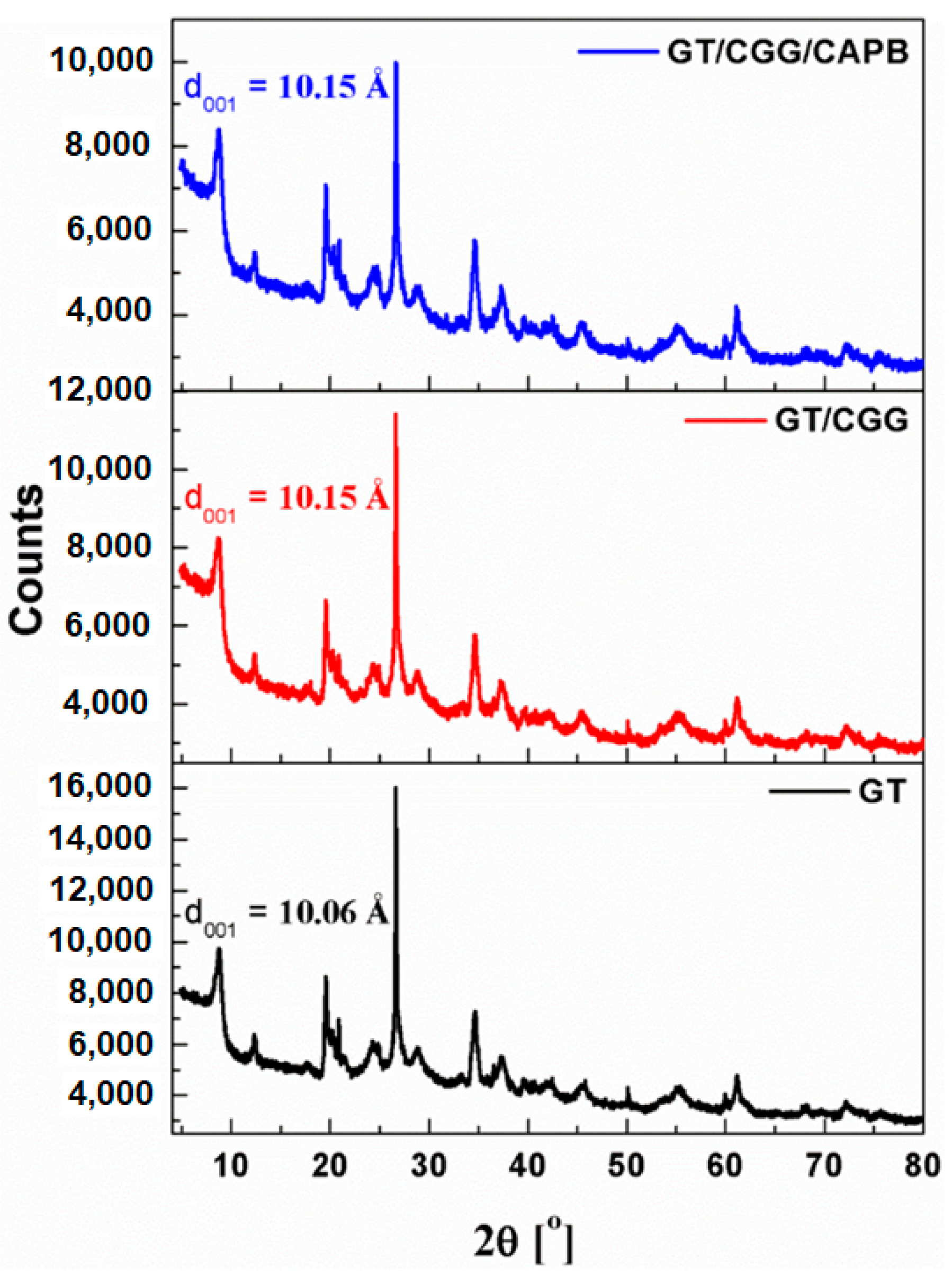
2.5. Powder X-ray Diffraction Measurements
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Stability Measurement
3.2.2. Formation of the CGG/CAPB Complexes
3.2.3. Adsorption Measurements
3.2.4. Electrokinetic Measurements
3.2.5. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.2.6. Powder X-ray Diffraction Study
4. Conclusions
- Glauconite (GT) can be used as water purifying material.
- CGG is an effective flocculant for glauconite suspensions.
- CAPB increased the CGG adsorption on the glauconite surface but deteriorated flocculation.
- Intermolecular polymer–surfactant complexes between CGG and CAPB were formed.
- pH strongly influences the stabilizing flocculating properties of the GT suspensions.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McRae, S.G. Glauconite. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1972, 8, 397–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, O.A.; Abd El-Wahed, A.G. Origin of the glauconite from the Middle Eocene, Qarara Formation, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 123, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bansal, U.; Pande, K.; Meena, S.S. Compositional variability of glauconites within the Upper Cretaceous Karai Shale Formation, Cauvery Basin, India: Implications for evaluation of stratigraphic condensation. Sediment. Geol. 2016, 331, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, M.A.; Ahmed, E.A.; Kurzweil, H. Genesis, maturity and weathering of some Upper Cretaceous Egyptian glauconites: Mineralogical and geochemical implications. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 124, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, J.M. Minerals: Glauconites and green clays, Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Sinha, S.; Mishra, D.; Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K.K. A sustainable process for recovery of potash fertilizer from glauconite through simultaneous production of pigment grade red oxide. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 23, e00129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.; Alex, T.C.; Kumar, R. On Mechanical Activation of Glauconite: Physicochemical Changes, Alterations in Cation Exchange Capacity and Mechanisms. Powder Technol. 2020, 360, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.N.; Elimelech, M. Colloid mobilization and transport in groundwater. Colloids Surf. A. 1996, 107, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, K.A.; El-Tawil, R.S.; Rostom, M. Utilization of surface modified phyllosilicate mineral for heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.H.; Lu, W.; Vengris, T.; Binkiene, R. Sorption of heavy metals by Lithuanian glauconite. Water Res. 2016, 30, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoa, O.J.; Tsai, C.M. The removal of metals and ammonium by natural glauconite. Environ. Int. 1987, 13, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Mal, D.; Singh, R.P. Synthesis and characterization of cationic guar gum: A high performance flocculating agent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 324–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, C.; Deb, T.K.; Moin, A.; Shivakumar, H.G. Cationic guar gum polyelectrolyte complex microparticles. J. Young Pharm. 2014, 6, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, A.; Sandewicz, R.S. Cosmetic Science and Polymer Chemistry: Perfect Together, Polymers for Personal Care and Cosmetics; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Chapter 2; pp. 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Tiwary, A.K.; Kaur, G. Investigations on inter polymer complexes of cationic guar gum and xanthan gum for formulation of bioadhesive films. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Tang, S.; Li, Q.; Hu, G.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; Cai, Z. Addition of cationic guar-gum and oleic acid improved the stability of plasma emulsions prepared with enzymatically hydrolyzed egg yolk. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Su, J. Adding cationic guar gum after collector: A novel investigation in flotation separation of galena from sphalerite. Miner. Eng. 2020, 157, 106542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Ozaki, M.; Murakami, K. Elucidation of the aggregation mechanism of bentonite with cationic guar gum as flocculant and application to filtration. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 596, 124660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daia, L.; Wanga, Y.; Lia, Z.; Wanga, X.; Duana, C.; Zhaoa, W.; Xionga, C.; Nieb, S.; Xua, Y.; Ni, Y. A multifunctional self-crosslinked chitosan/cationic guar gum composite hydrogel and its versatile uses in phosphate-containing water treatment and energy storage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 244, 116472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, J.; Xiao, C. Thermal and mechanical properties of cationic guar gum/poly (acrylic acid) hydrogel membranes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Xiao, C. pH-sensitive cationic guar gum/poly (acrylic acid) polyelectrolyte hydrogels: Swelling and in vitro drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Feng, J.; Shi, J.; He, L.; Guo, P.; Guan, S.; Fu, H.; Ao, Y. Ultra-stretchable, self-recovering, self-healing cationic guar gum/poly (stearyl methacrylate-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.; Feng, N.; An, H.; You, G.; Mo, C.; Zhong, H.; Pan, L.; Hu, D. Design and validation of antibacterial and pH response of cationic guar gum film by combining hydroxyethyl cellulose and red cabbage pigment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, J.K. (Ed.) Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition), The International Encyclopedia of Adverse Drug Reactions and Interactions; Cocamidopropyl Betaine; Newnes: London, UK, 2016; p. 543. [Google Scholar]
- Clendennen, S.; Boaz, N.W. Betaine Amphoteric Surfactants-Synthesis, Properties, and Applications, Biobased Surfactants, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, V.; Choudhary, N.; Chakrabarty, S.; Kumar, R. Morphology and dynamics of self-assembled structures in mixed surfactant systems (SDS + CAPB) in the context of methane hydrate growth. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, E. Using of CAPB as a surfactant to improve the surface morphology and optical features of PbS films. Superlattices Microstruct. 2019, 135, 106287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.E.; Fowler, J.F. Safety to Human Skin of Cocamidopropyl Betaine: A Mild Surfactant for Personal-Care Products. J. Surfactants Deterg. 1998, 1, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Stuart, M.C.; Adachi, Y. Dynamics of polyelectrolyte adsorption and colloidal flocculation upon mixing studied using mono-dispersed polystyrene latex particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 226, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignon, P.; Corbin, G.; Crom, S.L.; Marry, V.; Hao, J.; Daniel, I. Adsorption of nucleotides on clay surfaces: Effects of mineral composition, pH and solution salts. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, K.L.; Fairbanks, D.B.; Bull, D.S.; Stoykovich, M.P.; Bowman, C.N. Flocculation behavior and mechanisms of block copolymer architectures on silica microparticle and Chlorella vulgaris systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 567, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, S.; Habgooda, M.; Jameson, G.J.; Yan, Y. Aggregate structures formed via a bridging flocculation mechanism. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 80, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, D.H. Polymeric Stabilization of Colloidal Dispersion; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, F. Particle aggregation by coagulation and flocculation. In Solid-Liquid Separation in the Mining Industry; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinsoni, E.; Eriksson, L. Particle flocculation by adsorbing polymers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 34, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaei, R.; Kharrat, R.; Madani, M. Stability, flocculation, and rheological behavior of silica suspension-augmented polyacrylamide and the possibility to improve polymer flooding functionality. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 322, 114572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijmanand, S.G.J.; Stein, N. Electrostatic and sterical stabilization of TiO2 dispersions. Langmuir 1995, 11, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, C.; Zhao, J.; Yan, L.; Zhao, M. Adsorption behavior of cocamidopropyl betaine under conditions of high temperature and high salinity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangsakan, A.; Chinachoti, P.; McClements, D.J. Effect of Surfactant Type on Surfactant−Maltodextrin Interactions: Isothermal Titration Calorimetry, Surface Tensiometry, and Ultrasonic Velocimetry Study. Langmuir 2004, 20, 3913–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matusiak, J.; Grządka, E.; Paszkiewicz, M.; Patkowski, J. Complexes of fluorinated, silicone and hydrocarbon surfactants with carboxymethylcellulose and their influence on properties of the alumina suspension. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konduri, M.K.R.; Fatehi, P. Influence of pH and ionic strength on flocculation of clay suspensions with cationic xylan copolymer. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 530, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárány, S.; Meszaros, R.; Marcinova, L.; Skvarla, J. Effect of polyelectrolyte mixtures on the electrokinetic potential and kinetics of flocculation of clay mineral particles. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 383, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, N.; Metaxas, A.; Quinney, C.; Wickramaratne, S.; Reineke, T.M.; Dutcher, C.S. pH dependence of bentonite aggregate size and morphology on polymer clay flocculation. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 537, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusiak, J.; Grządka, E. Cationic starch as the effective flocculant of silica in the presence of different surfactants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, H.A.; Bevan, J.C.; Brown, K.M.; Johnson, L.R.; Farmer, V.C. Glauconite and celadonite: Two separate mineral species. Mineral. Mag. 1978, 42, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConchie, D.M.; Lewis, D.W. Varieties of glauconite in late Cretaceous and early Tertiary rocks of the South Island of New Zealand, and new proposals for classification. N. Z. J. Geol. Geophys. 1980, 23, 413–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J. Mineralogical characteristics and geological significance of Albian (Early Cretaceous) glauconite in Zanda, southwestern Tibet. China. Clay Miner. 2012, 47, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J.; Kečkéš, J.; Pálková, H.; Komadel, P. Identification of components in smectite/kaolinite mixtures. Clay Miner. 2002, 37, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghafar, H.H.; Radwan, E.K.; El-Wakeel, S.T. Removal of Hazardous Contaminants from Water by Natural and Zwitterionic Surfactant-modified Clay. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6834–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanić, M.; Vdović, N.; Barreto, S.D.; Bermanec, V.; Sondi, I. Mineralogy, surface properties and electrokinetic behaviour of kaolin clays from the naturally occurring pegmatite deposits. Geol. Croat. 2015, 68, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mbaye, A.; Diop, C.A.K.; Rhouta, B.; Brendle, J.M.; Senocq, F.; Maury, F.; Diallo, D.P.; Adams, J. Mineralogical and physicochemical characterizations of clay from Keur Saër (Senegal). Clay Miner. 2012, 47, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S. Montmorillonite Functionalized with Zwitterionic Surfactant as a Highly Efficient Adsorbent for Herbicides. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4947–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, X.; Huang, Q.; Lang, W. Adsorption of Cu2+ and methylene blue on dodecyl sulfobetaine surfactant-modified montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Gu, X. Synthesis of cationic guar gum-graft-polyacrylamide at low temperature and its flocculating properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3655–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Kundu, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Basu, A.; Gupta, M.; Mukherjee, A. Guar gum cinnamate ouzo nanoparticles for bacterial contact killing in water environment. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 491, 107983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolei, L.; Gutz, I.G.R. Simultaneous determination of three surfactants and water in shampoo and liquid soap by ATR-FTIR. Talanta 2005, 66, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, W.; Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Xu, B. Synthesis, Characterization, and Surface-Active Properties of Carboxylbetaine and Sulfobetaine Surfactants based on Vegetable Oil. J. Surfact. Deterg. 2018, 22, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, M.S.; Baioumy, H.M. Structural and Chemical Alteration of Glauconite under Progressive Acid Treatment. Clays Clay Miner. 2006, 54, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, M.; Fanning, D.S. Glauconite Pellets: Similar X-ray Patterns from Individual Pellets of Lobate and Vermiform Morphology. Clays Clay Miner. 1968, 16, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.S.; Shau, Y.H.; Wang, M.K.; Ku, C.T.; Chiang, P.N. Mineralogy and occurrence of glauconite in central Taiwan. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 42, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srasra, E.; Trabelsi-Ayedi, M. Textural properties of acid activated glauconite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 17, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesse, W.D. Introduction to Mineralogy; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 254–255. [Google Scholar]
- Aksu, I.; Bazilevskaya, E.; Karpyn, Z.T. Swelling of clay minerals in unconsolidated porous media and its impact on permeability. Geo. Res. J. 2015, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleam, W. Surface Chemistry and Adsorption. In Soil and Environmental Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Chapter 8; pp. 385–443. [Google Scholar]
- Meziane, O.; Bensedira, A.; Guessoum, M.; Haddaoui, N. Polypropylene-modified kaolinite composites: Effect of chemical modification on mechanical, thermal and morphological properties. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2016, 8, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, G.R.; Hower, J. The mineralogy of glauconite. Clays Clay Miner. 1975, 23, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, T.; Watanabe, T. X-ray diffraction line profile of glauconitic clay from the Minamishiraoi deposit and evaluation of its mixed-layer structure. Appl. Clay Sci. 1994, 9, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drits, V.A.; Zviagina, B.B.; McCarty, D.K.; Salyn, A.L. Factors responsible for crystal-chemical variations in the solid solutions from illite to aluminoceladonite and from glauconite to celadonite. Am. Mineral. 2010, 95, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, P.; Chen, M.; Yu, L.; Kang, C.; Zhu, N.; Dang, Z. Amphoteric modified vermiculites as adsorbents for enhancing removal of organic pollutants: Bisphenol A and Tetrabromobisphenol. A. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudzielwana, R.; Gitari, M.W.; Ndungu, P. Performance evaluation of surfactant modified kaolin clay in As(III) and As(V) adsorption from groundwater: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, X.; Jiang, M.; Du, J.; Chen, Z. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by surfactant-modified kaolinite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3025–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
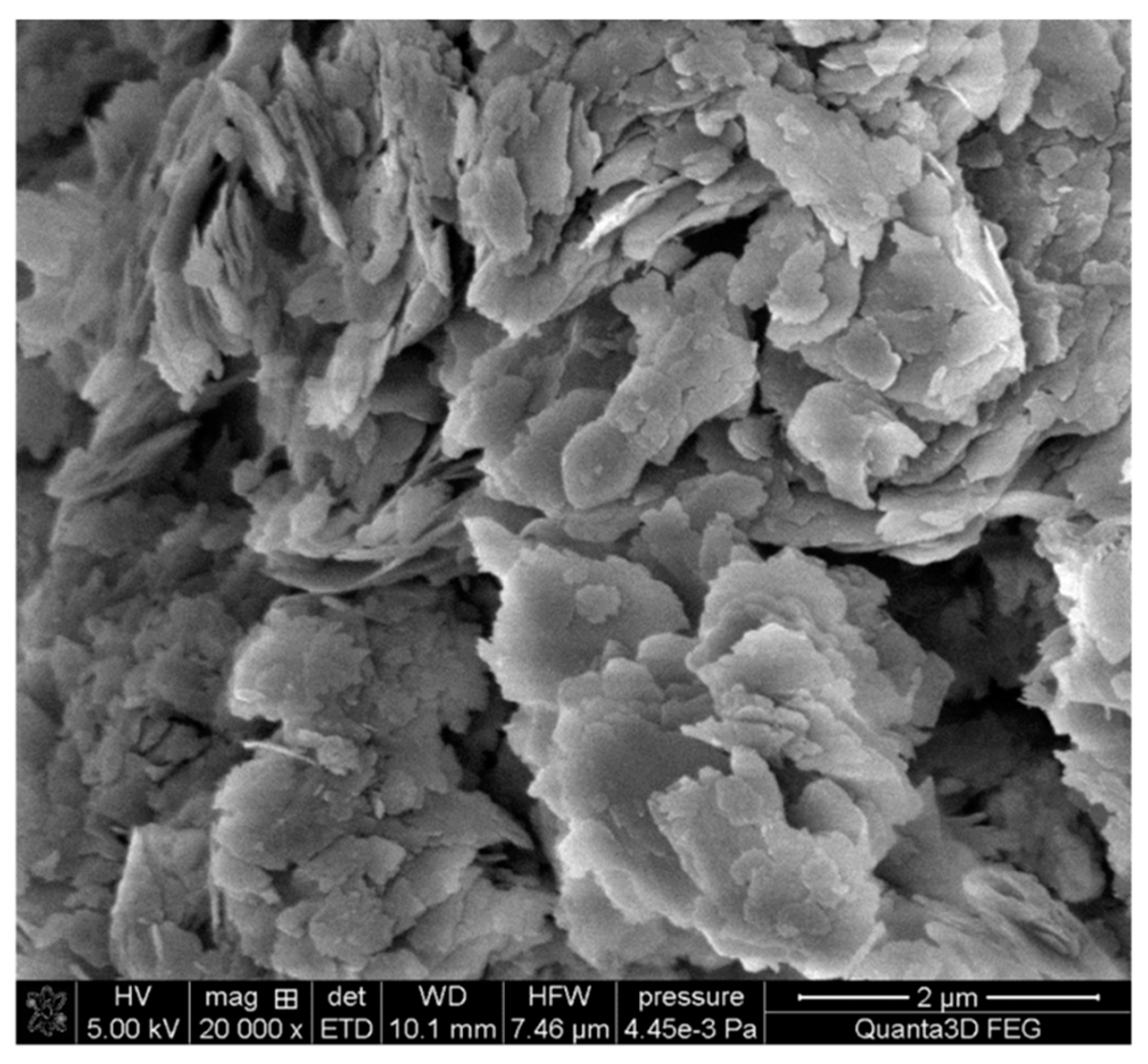





| CGG (ppm) | CAPB (%) | GT Removal (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH = 3 | pH = 6 | pH = 9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 76.2 | 34.7 | 36.0 |
| 2 | 0 | 96.5 | 68.4 | 71.9 |
| 20 | 0 | 99.9 | 97.8 | 99.6 |
| 20 | 0.04 | 9.0 | 98.5 | 99.2 |
| 200 | 0 | 10.9 | 10.6 | 10.2 |
| CGG (ppm) | CAPB (%) | Sediment Layer Thickness (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH = 3 | pH = 6 | pH = 9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 1.01 | 0.44 | 0.45 |
| 2 | 0 | 1.19 | 0.77 | 0.65 |
| 20 | 0 | 1.28 | 1.01 | 1.01 |
| 20 | 0.04 | - | 1.26 | 1.34 |
| GT | GT + CGG | GT + CGG + CAPB | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BET surface area (m2/g) | 70.73 | 56.06 | 16.53 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.1691 | 0.1519 | 0.1015 |
| GT (wt. %) | GT/CGG (wt. %) | GT/CGG/CAPB (wt. %) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 8.81 ± 0.39 | 13.27 ± 0.19 | 17.66 ± 0.79 |
| O | 44.1 ± 1.51 | 45.27 ± 0.29 | 45.60 ± 0.49 |
| Mg | 1.62 ± 0.05 | 1.45 ± 0.41 | 1.36 ± 0.24 |
| Al | 4.81 ± 0.27 | 4.37 ± 1.04 | 3.87 ± 0.69 |
| Si | 20.1 ± 0.90 | 16.66 ± 0.32 | 15.07 ± 0.87 |
| K | 5.38 ± 0.68 | 4.38 ± 0.70 | 3.37 ± 0.51 |
| Ca | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 0.42 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.05 |
| Ti | 0.2 ± 0.07 | 0.12 ± 0.09 | 0.07 ± 0.07 |
| Fe | 14.36 ± 1.72 | 11.47 ± 0.58 | 8.64 ± 0.40 |
| Na | 0.1 ± 0.04 | 0.08 ± 0.06 | 0.43 ± 0.07 |
| N | - | 1.99 ± 0.09 | 2.73 ± 0.22 |
| Cl | - | 0.95 ± 0.08 | 1.12 ± 0.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godek, E.; Grządka, E.; Maciołek, U.; Bastrzyk, A. Influence of Zwitterionic CAPB on Flocculation of the Aqueous Cationic Guar Gum/Glauconite Suspensions at Various pH. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212157
Godek E, Grządka E, Maciołek U, Bastrzyk A. Influence of Zwitterionic CAPB on Flocculation of the Aqueous Cationic Guar Gum/Glauconite Suspensions at Various pH. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212157
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodek, Ewelina, Elżbieta Grządka, Urszula Maciołek, and Anna Bastrzyk. 2021. "Influence of Zwitterionic CAPB on Flocculation of the Aqueous Cationic Guar Gum/Glauconite Suspensions at Various pH" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212157
APA StyleGodek, E., Grządka, E., Maciołek, U., & Bastrzyk, A. (2021). Influence of Zwitterionic CAPB on Flocculation of the Aqueous Cationic Guar Gum/Glauconite Suspensions at Various pH. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212157







