Biodegradable Amphoteric Surfactants in Titration-Ultrasound Formulation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions: Rational Design, Development, and Kinetic Stability
Abstract
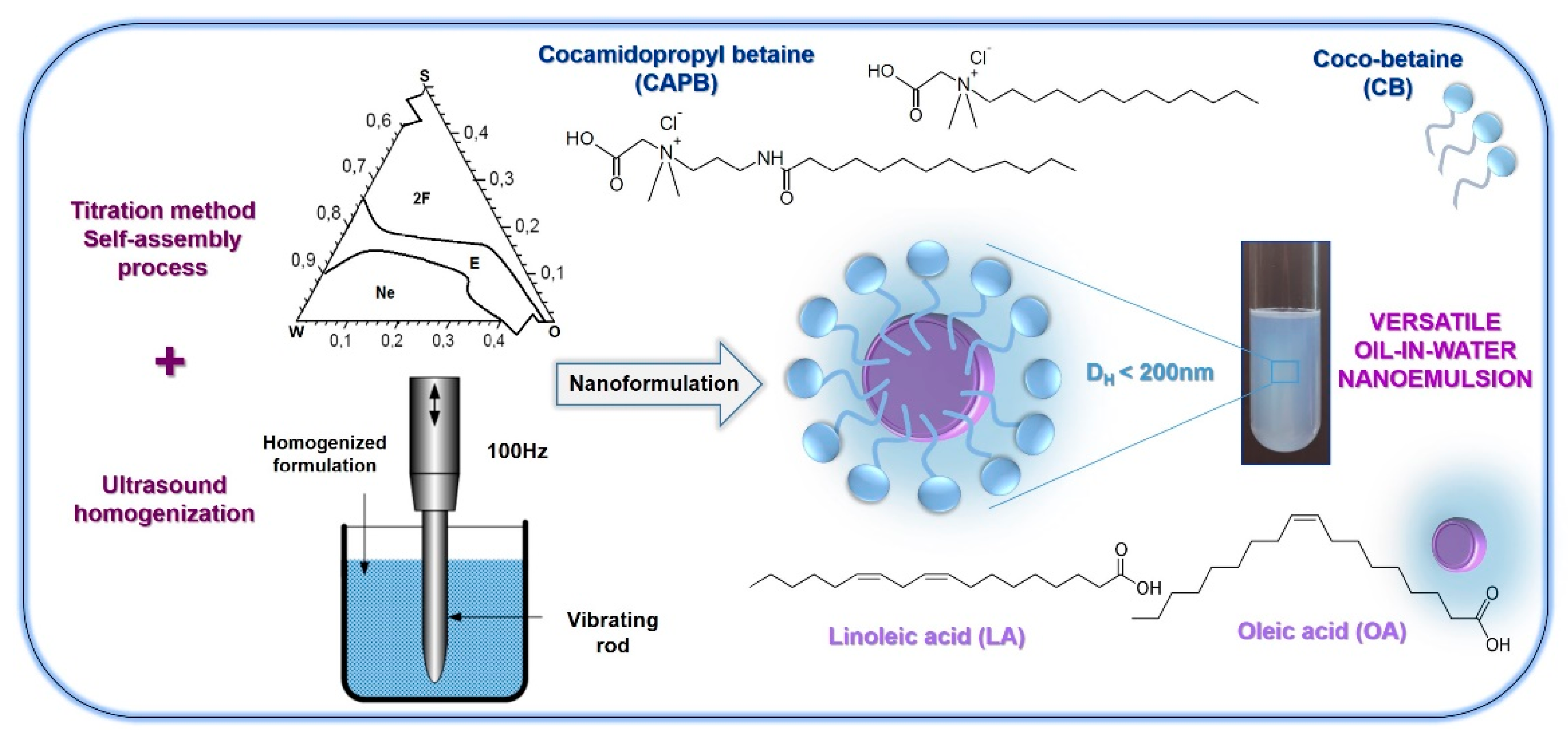
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of Phase Diagrams
2.2. Estimation of the Droplet Size, Surface Charge, and Morphology
2.3. Kinetic Stability Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions by Titration-Ultrasound Approach
3.3. Physicochemical Characteristics of the Obtained Nanoformulations
3.3.1. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index by Dynamic Light Scattering
3.3.2. Zeta Potential by Electrophoretic Light Scattering
3.3.3. Shape and Morphology by Transmission Electron and Atomic Force Microscopies
3.3.4. Dispersion Stability Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pucek, A.; Tokarek, B.; Waglewska, E.; Bazylińska, U. Recent advances in the structural design of photosensitive agent formulations using “soft” colloidal nanocarriers. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrot, K.C.; Zaręba, J.K.; Toporkiewicz, M.; Chodaczek, G.; Wawrzyńczyk, D.; Kulbacka, J.; Bazylińska, U.; Nyk, M. Polymeric nanocarriers with luminescent colloidal nanoplatelets as hydrophilic and non-toxic two- photon bioimaging agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3649–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucek-Kaczmarek, A. Influence of process design on the preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles by an ultrasonic-nanoemulsification method. Processes 2021, 9, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewińska, A.; Domżał-Kędzia, M.; Jaromin, A.; Łukaszewicz, M. Nanoemulsion stabilized by safe surfactin rom Bacillus subtilis as a multifunctional, custom-designed smart delivery system. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waglewska, E.; Pucek-Kaczmarek, A.; Bazylińska, U. Novel surface-modified bilosomes as functional and biocompatible nanocarriers of hybrid compounds. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, S.; Prévot, G.; Mornet, S.; Jacobin-Valat, M.J.; Mousli, Y.; Hemadou, A.; Duttine, M.; Trotier, A.; Sanchez, S.; Duonor-Cérutti, M.; et al. A nano-emulsion platform functionalized with a fully human scfv-fc antibody for atheroma targeting: Towards a theranostic approach to atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Fernandes, A.R.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Coutinho, T.E.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, S.B.; Silva, A.M.; Santini, A. Nanomaterials for skin delivery of cosmeceuticals and pharmaceuticals. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazylińska, U.; Kulbacka, J.; Chodaczek, G. Nanoemulsion structural design in co-encapsulation of hybrid multifunctional agents: Influence of the smart PLGA polymers on the nanosystem-enhanced delivery and lectro-photodynamic treatment. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar Gupta, P.; Bhandari, N.; Shah, H.N.; Khanchandani, V.; Keerthana, R.; Nagarajan, V.; Hiremath, L. An update on nanoemulsions using nanosized liquid in liquid colloidal systems. Nanoemulsions-Prop. Fabr. Appl. 2019, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Eral, H.B.; Hatton, T.A.; Doyle, P.S. Nanoemulsions: Formation, properties and applications. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2826–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinshaw, I.J.; Ahmad, N.; Salim, N.; Leo, B.F. Nanoemulsions: A review on the conceptualization of treatment for psoriasis using a “green“ surfactant with low-energy emulsification method. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaya, M.; Rotliwala, Y.C. Nanoemulsions: A review on low energy formulation methods, characterization, applications and optimization technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Mandal, A. Surfactant stabilized oil-in-water nanoemulsion: Stability, interfacial tension, and rheology study for enhanced oil recovery application. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 6452–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Jafari, S.M. General aspects of nanoemulsions and their formulation. In Nanoemulsions: Formulation, Applications, and Characterization, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 3–20. ISBN 9780128118399. [Google Scholar]
- Banasaz, S.; Morozova, K.; Ferrentino, G.; Scampicchio, M. Encapsulation of lipid-soluble bioactives by nanoemulsions. Molecules 2020, 25, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswathanarayan, J.B.; Vittal, R.R. Nanoemulsions and their potential applications in food industry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashaolu, T.J. Nanoemulsions for health, food, and cosmetics: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3381–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J. Advances in fabrication of emulsions with enhanced functionality using structural design principles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Pal, A.; Rakshit, A.; Saha, B. Properties and applications of amphoteric surfactant: A concise review. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2021, 24, 517–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clendennen, S.K.; Boaz, N.W. Betaine amphoteric surfactants—Synthesis, properties, and applications. In Biobased Surfactants, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldes, A.B.; Rodríguez-López, L.; Rincón-Fontán, M.; López-Prieto, A.; Vecino, X.; Cruz, J.M. Synthetic and bio-derived surfactants versus microbial biosurfactants in the cosmetic industry: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Janakiraman, A.K.; Khan, A.; Naeem, A.; Badshah, S.F. Surfactants and their role in pharmaceutical product development: An overview. J. Pharm. Pharm. 2019, 6, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanno, A.; Guzmán, E.; Fernández-Peña, L.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Surfactant-like behavior for the adsorption of mixtures of a polycation and two different zwitterionic surfactants at the water/vapor interface. Molecules 2019, 24, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozaini, M.Z.H. Phase behavior of pseudo-ternary gemini surfactant + 1-hexanol/oil/water systems. J. Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2012, 2012, 839074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewińska, A. Optimizing the process design of oil-in-water nanoemulsion for delivering poorly soluble cannabidiol oil. Processes 2021, 9, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas, S.; Guzman, E.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Adsorption of mixtures of a pegylated lipid with anionic and zwitterionic surfactants at solid/liquid. Colloids Interfaces 2020, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posocco, P.; Perazzo, A.; Preziosi, V.; Laurini, E.; Prici, S.; Guido, S. Interfacial tension of oil/water emulsions with mixed non-ionic surfactants: Comparison between experiments and molecular simulations. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 4723–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarheed, O.; Dibi, M.; Ramesh, K.V.R.N.S. Studies on the effect of oil and surfactant on the formation of alginate- based o/w lidocaine nanocarriers using nanoemulsion template. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, F.; Ramadan, W. Transdermal delivery of anticancer drug caffeine from water-in-oil nanoemulsions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Composition | DH g (d.nm) | PdI h | ζ i (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LA a | CB c | 3% S e/1% O f | 132 ± 6 | 0.193 ± 0.02 | −12 ± 1 |
| 2 | LA | CB | 1% S/0.5% O | 70 ± 3 | 0.046 ± 0.01 | −24 ± 3 |
| 3 | LA | CB | 5% S/2% O | 295 ± 8 | 0.198 ± 0.03 | −7 ± 1 |
| 4 | LA | CAPB d | 3% S/1% O | 130 ± 6 | 0.135 ± 0.02 | −18 ± 2 |
| 5 | LA | CAPB | 1% S/0.5% O | 69 ± 3 | 0.254 ± 0.03 | −29 ± 3 |
| 6 | LA | CAPB | 5% S/2% O | 316 ± 9 | 0.290 ± 0.04 | −11 ± 2 |
| 7 | OA b | CB | 3% S/1% O | 105 ± 5 | 0.294 ± 0.04 | −17 ± 2 |
| 8 | OA | CB | 1% S/0.5% O | 65 ± 2 | 0.046 ± 0.01 | −26 ± 3 |
| 9 | OA | CB | 5% S/2% O | 272 ± 8 | 0.249 ± 0.04 | −10 ± 1 |
| 10 | OA | CAPB | 3% S/1% O | 165 ± 7 | 0.148 ± 0.03 | −21 ± 3 |
| 11 | OA | CAPB | 1% S/0.5% O | 78 ± 4 | 0.245 ± 0.03 | −27 ± 3 |
| 12 | OA | CAPB | 5% S/2% O | 183 ± 6 | 0.161 ± 0.02 | −14 ± 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waglewska, E.; Bazylińska, U. Biodegradable Amphoteric Surfactants in Titration-Ultrasound Formulation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions: Rational Design, Development, and Kinetic Stability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111776
Waglewska E, Bazylińska U. Biodegradable Amphoteric Surfactants in Titration-Ultrasound Formulation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions: Rational Design, Development, and Kinetic Stability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(21):11776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111776
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaglewska, Ewelina, and Urszula Bazylińska. 2021. "Biodegradable Amphoteric Surfactants in Titration-Ultrasound Formulation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions: Rational Design, Development, and Kinetic Stability" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 21: 11776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111776
APA StyleWaglewska, E., & Bazylińska, U. (2021). Biodegradable Amphoteric Surfactants in Titration-Ultrasound Formulation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions: Rational Design, Development, and Kinetic Stability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(21), 11776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111776







