Blood-Based Biomarkers in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Including the Viral Genome and Glycosylated Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
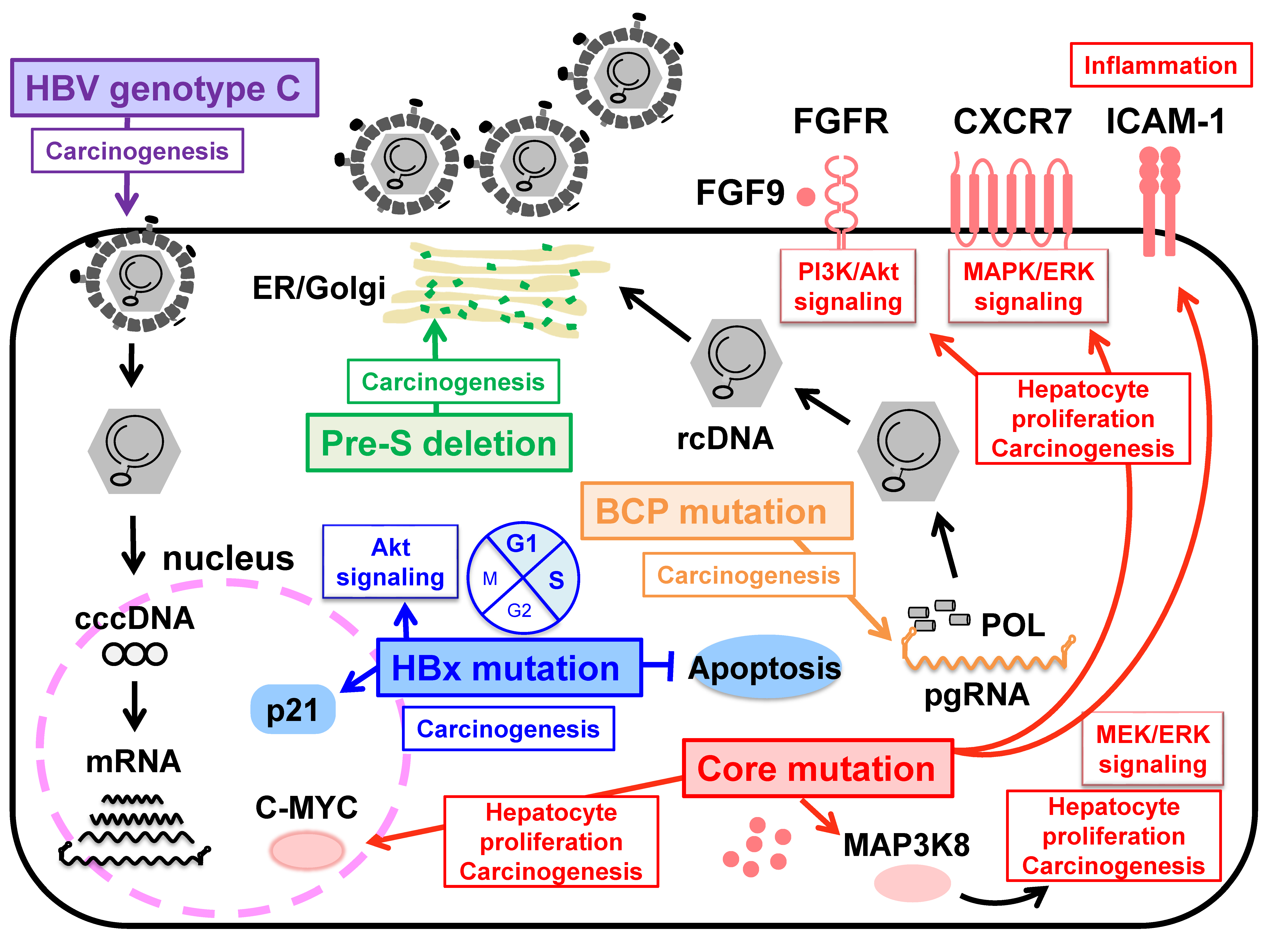
2. Carcinogenesis of Hepatocytes Infected with HBV
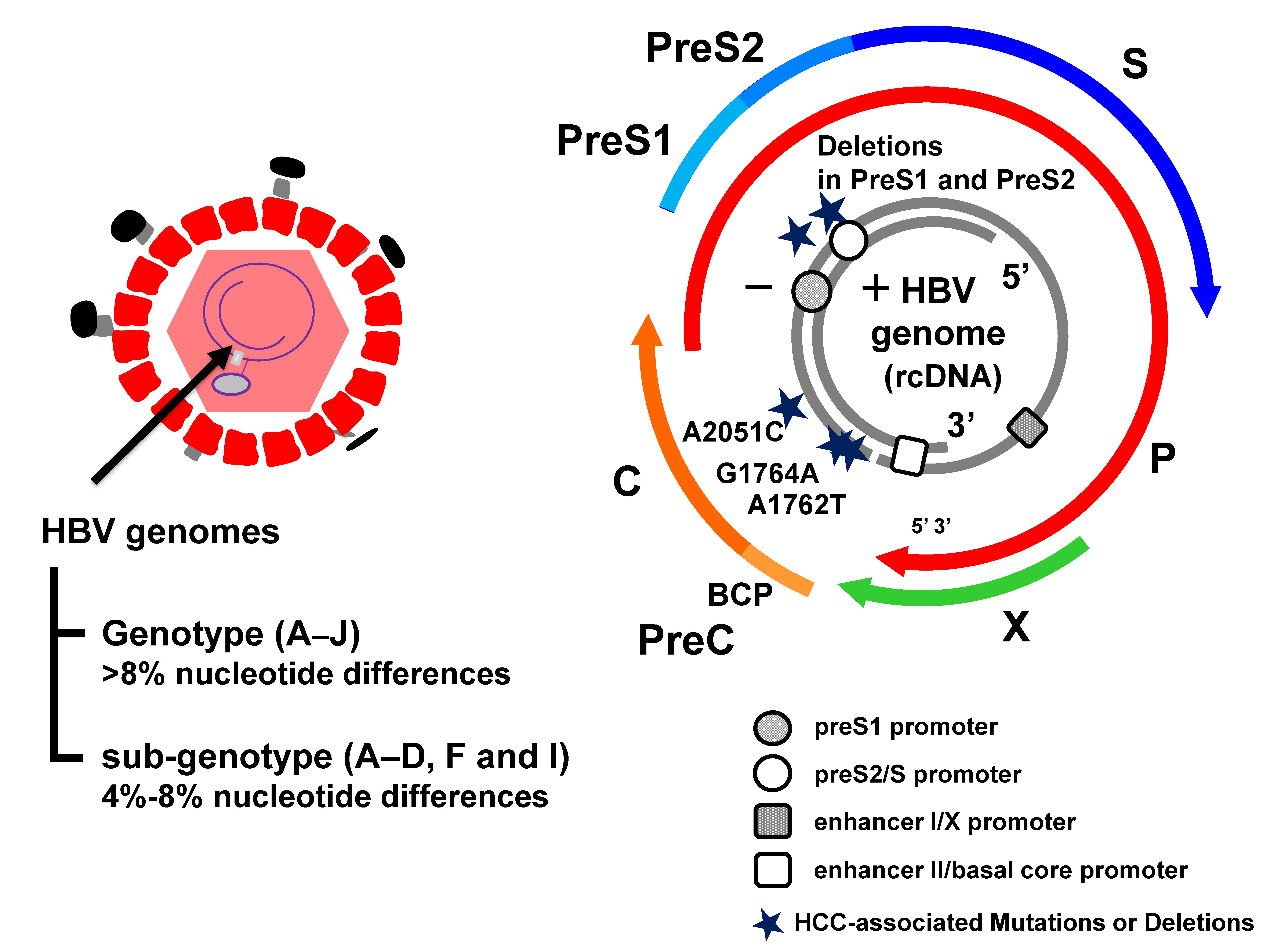
3. HBV Genotypes
4. Mutations to the HBV Protein Coding Regions and Pathogenesis
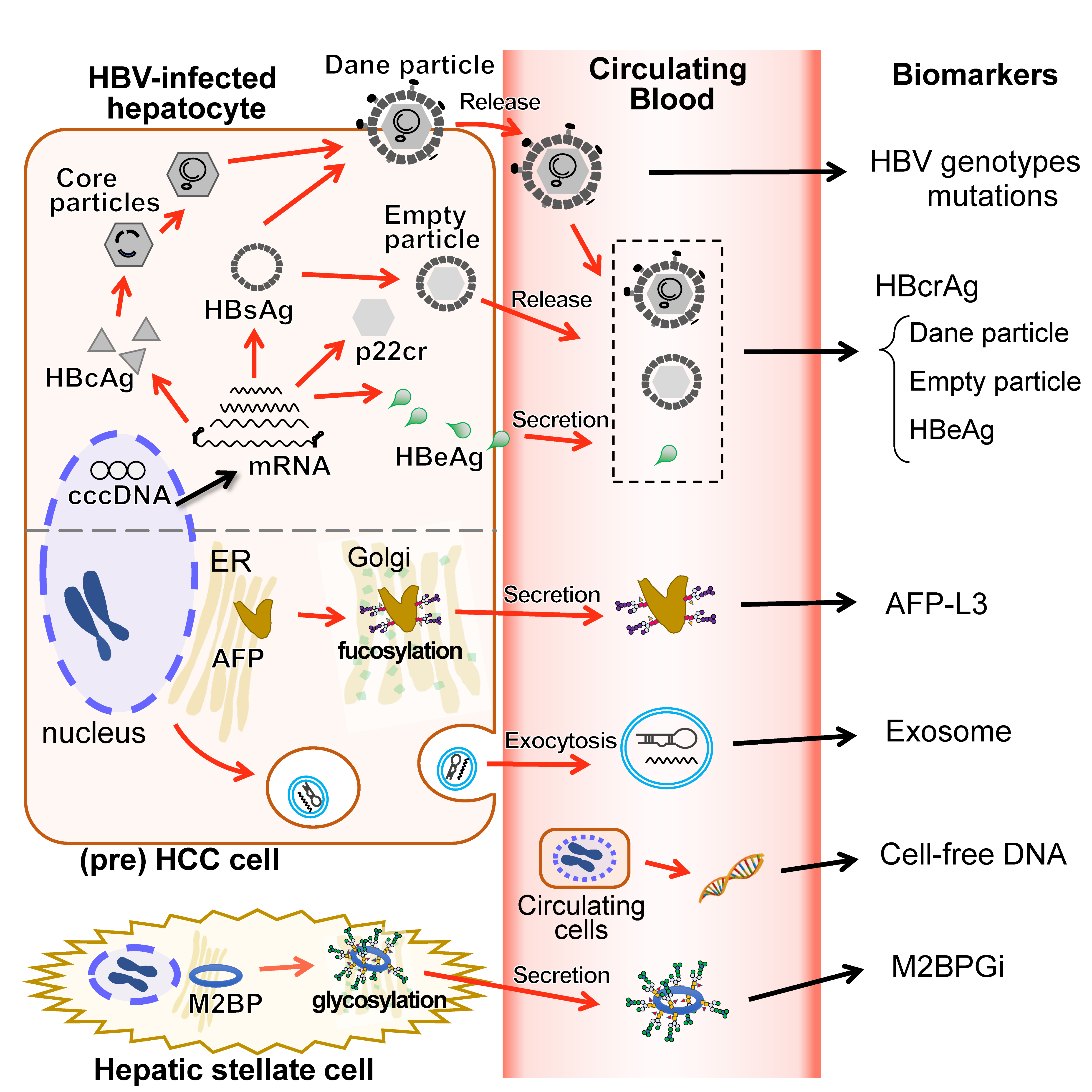
5. HBcrAg
6. AFP-L3
7. M2BPGi
8. Other Biomarkers
8.1. WFA+-CSF1R
8.2. Extracellular Vesicles
8.3. Cell-Free DNA/Circulating Tumor DNA
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zapatka, M.; Borozan, I.; Brewer, D.S.; Iskar, M.; Grundhoff, A.; Alawi, M.; Desai, N.; Sültmann, H.; Moch, H.; Cooper, C.S.; et al. The landscape of viral associations in human cancers. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, M.; de Martel, C.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F.; Franceschi, S. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2012: A synthetic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e609–e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Verma, M. Cancer biomarkers: Are we ready for the prime time? Cancers 2010, 2, 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, H.; Nagoshi, S.; Akahane, T.; Asaoka, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kurosaki, M.; Sakaida, I.; Shimizu, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis 2020. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachon, A.; Osiowy, C. Novel Biomarkers of Hepatitis B Virus and Their Use in Chronic Hepatitis B Patient Management. Viruses 2021, 13, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, N.; Qian, T.; Koneru, B.; Hoshida, Y. Omics-derived hepatocellular carcinoma risk biomarkers for precision care of chronic liver diseases. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Tanaka, Y. Novel biomarkers for the management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trépo, C.; Chan, H.L.; Lok, A. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2014, 384, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouissou, S.; Nault, J.C. Advances in molecular classification and precision oncology in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Seki, E. Inflammation and Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. In Seminars in Liver Disease; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 26–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nault, J.C.; Ningarhari, M.; Rebouissou, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J. The role of telomeres and telomerase in cirrhosis and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, Y.; Mizokami, M. Classifying hepatitis B virus genotypes. Intervirology 2003, 46, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, J.H.; Chen, P.J.; Lai, M.Y.; Chen, D.S. Basal core promoter mutations of hepatitis B virus increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B carriers. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Yang, H.I.; Su, J.; Jen, C.L.; You, S.L.; Lu, S.N.; Huang, G.T.; Iloeje, U.H.; Group, R.-H.S. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 2006, 295, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, H.C.; Su, T.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Kuo, S.F.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; et al. High levels of hepatitis B surface antigen increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low HBV load. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1140–1149.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Koike, K.; Saito, I.; Miyamura, T.; Jay, G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 1991, 351, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafritz, D.A.; Shouval, D.; Sherman, H.I.; Hadziyannis, S.J.; Kew, M.C. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the genome of liver cells in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies in percutaneous liver biopsies and post-mortem tissue specimens. N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 305, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, W.K.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, N.P.; Lee, W.H.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Tennakoon, C.; et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Tsuda, F.; Sakugawa, H.; Sastrosoewignjo, R.I.; Imai, M.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: Comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J. Gen. Virol. 1988, 69, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramvis, A.; Kew, M.; Francois, G. Hepatitis B virus genotypes. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2409–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ling, C.; Zheng, W.; Zhu, C.; Carr, M.J.; Higgins, D.G. Hepatitis B virus subgenotyping: History, effects of recombination, misclassifications, and corrections. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 16, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunbul, M. Hepatitis B virus genotypes: Global distribution and clinical importance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5427–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, M.C.; Kramvis, A.; Yu, M.C.; Arakawa, K.; Hodkinson, J. Increased hepatocarcinogenic potential of hepatitis B virus genotype A in Bantu-speaking sub-saharan Africans. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 75, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Hige, S.; Yamada, G.; Murawaki, Y.; Komatsu, M.; Kuramitsu, T.; Kawata, S.; Tanaka, E.; Izumi, N.; et al. Distribution of hepatitis B virus genotypes among patients with chronic infection in Japan shifting toward an increase of genotype A. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Kao, J.H. Hepatitis B virus genotypes and variants. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugauchi, F.; Orito, E.; Ichida, T.; Kato, H.; Sakugawa, H.; Kakumu, S.; Ishida, T.; Chutaputti, A.; Lai, C.L.; Ueda, R.; et al. Hepatitis B virus of genotype B with or without recombination with genotype Cover the precore region plus the core gene. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5985–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.J.; Hussain, M.; Lok, A.S. Hepatitis B virus genotype B is associated with earlier HBeAg seroconversion compared with hepatitis B virus genotype C. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.H.; Chang, M.H.; Wang, K.J.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Kao, J.H.; Yeh, S.H.; Jeng, Y.M.; Tsai, K.S.; Chen, D.S. Clinical relevance of hepatitis B virus genotype in children with chronic infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, H.; Yokosuka, O.; Seki, N.; Arai, M.; Imazeki, F.; Kurihara, T.; Kanda, T.; Fukai, K.; Kato, M.; Saisho, H. Influence of hepatitis B virus genotypes on the progression of chronic type B liver disease. Hepatology 2003, 37, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyanto; Pancawardani, P.; Depamede, S.N.; Wahyono, A.; Jirintai, S.; Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. Identification of four novel subgenotypes (C13-C16) and two inter-genotypic recombinants (C12/G and C13/B3) of hepatitis B virus in Papua province, Indonesia. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, W.; Ling, C.; Carr, M.J.; Higgins, D.G.; Zhang, Z. Subgenotyping of genotype C hepatitis B virus: Correcting misclassifications and identifying a novel subgenotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, S.; Eilard, A.; Larsson, S.B.; Hannoun, C.; Norkrans, G.; Lindh, M. Genotype impact on long-term virological outcome of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 54, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kurbanov, F.; Maruyama, I.; Shimada, T.; Takahashi, S.; Shirai, T.; Hino, K.; Sakaida, I.; Mizokami, M. Direct cytopathic effects of particular hepatitis B virus genotypes in severe combined immunodeficiency transgenic with urokinase-type plasminogen activator mouse with human hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, T.; Orito, E.; Ito, K.; Acharya, S.K.; Gish, R.G.; Kramvis, A.; Shimada, T.; Izumi, N.; et al. Influence of hepatitis B virus genotypes on the intra- and extracellular expression of viral DNA and antigens. Hepatology 2006, 44, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Revill, P. Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64 (Suppl. S1), S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, S.E.; Simonetti, J.P.; McMahon, B.J.; Bulkow, L.R.; Hurlburt, K.J.; Homan, C.E.; Snowball, M.M.; Cagle, H.H.; Williams, J.L.; Chulanov, V.P. Hepatitis B virus genotypes in Alaska Native people with hepatocellular carcinoma: Preponderance of genotype F. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Maruyama, I.; Shimada, T.; Takahashi, S.; Shirai, T.; Kato, H.; Nagao, M.; Miyakawa, Y.; et al. Early dynamics of hepatitis B virus in chimeric mice carrying human hepatocytes monoinfected or coinfected with genotype G. Hepatology 2007, 45, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Kani, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Murakami, S.; Matsuura, K.; Kusakabe, A.; Shinkai, N.; et al. Mechanism of the dependence of hepatitis B virus genotype G on co-infection with other genotypes for viral replication. J. Viral. Hepat. 2013, 20, e27–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locarnini, S.; McMillan, J.; Bartholomeusz, A. The hepatitis B virus and common mutants. In Seminars in Liver Disease; Thieme Medical Publichers: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Buckwold, V.E.; Xu, Z.; Chen, M.; Yen, T.S.; Ou, J.H. Effects of a naturally occurring mutation in the hepatitis B virus basal core promoter on precore gene expression and viral replication. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5845–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Tong, S.P.; Wen, Y.M.; Vitvitski, L.; Zhang, Q.; Trepo, C. Hepatitis B virus genotype A rarely circulates as an HBe-minus mutant: Possible contribution of a single nucleotide in the precore region. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 5402–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.T.; Faruqi, A.; Shih, J.W.; Shih, C. The mechanism of natural occurrence of two closely linked HBV precore predominant mutations. Virology 1995, 211, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, J.W.; Zhao, L.G.; Bray, F.; Xiang, Y.B. Quantitative evaluation of hepatitis B virus mutations and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 27, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Bi, S.; Yan, H.; Shi, Y.; Sheng, J. Associations between hepatitis B virus basal core promoter/pre-core region mutations and the risk of acute-on-chronic liver failure: A meta-analysis. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ozasa, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Orito, E.; Sugiyama, M.; Kang, J.H.; Hige, S.; Kuramitsu, T.; Suzuki, K.; Tanaka, E.; Okada, S.; et al. Influence of genotypes and precore mutations on fulminant or chronic outcome of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2006, 44, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, D.T.Y.; Ganova-Raeva, L.; Wang, J.; Mogul, D.; Chung, R.T.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Chang, K.M.; Shaikh, O.S.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Wahed, A.S.; et al. Precore and Basal Core Promoter Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Variants Are Present from a Young Age and Differ Across HBV Genotypes. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1637–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Tang, B.; Chen, X. Naturally occurring basal core promoter A1762T/G1764A dual mutations increase the risk of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12525–12536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, K.; Okamoto, H.; Tsuda, F.; Mayumi, M. Reduced Precore Transcription and Enhanced Core-Pregenome Transcription of Hepatitis B Virus DNA after Replacement of the Precore-Core Promoter with Sequences Associated with e Antigen-Seronegative Persistent Infections. Virology 1996, 226, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, S.; Zoulim, F.; Ahn, S.H.; Tsai, A.; Li, J.; Kawai, S.; Khan, N.; Trepo, C.; Wands, J.; Tong, S. Genome Replication, Virion Secretion, and e Antigen Expression of Naturally Occurring Hepatitis B Virus Core Promoter Mutants. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6601–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammeh, S.; Tavner, F.; Watson, R.; Thomas, H.C.; Karayiannis, P. Effect of basal core promoter and pre-core mutations on hepatitis B virus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Khan, A.; Simons, B.C.; Homan, C.; Matsui, T.; Ogawa, K.; Kawashima, K.; Murakami, S.; Takahashi, S.; Isogawa, M. An Association Between Core Mutations in Hepatitis B Virus Genotype F1b and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Alaskan Native People. Hepatology 2019, 69, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Wang, Y.; Ye, L.H. Hepatitis B virus X protein accelerates the development of hepatoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2014, 11, 182–190. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Han, K.H.; Lee, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Impact of hepatitis B virus (HBV) x gene mutations on hepatocellular carcinoma development in chronic HBV infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chiu, A.P.; Tschida, B.R.; Sham, T.T.; Lo, L.H.; Moriarity, B.S.; Li, X.X.; Lo, R.C.; Hinton, D.E.; Rowlands, D.K.; Chan, C.O.; et al. HBx-K130M/V131I Promotes Liver Cancer in Transgenic Mice via AKT/FOXO1 Signaling Pathway and Arachidonic Acid Metabolism. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Al-Ananzi, M.R.; Nazir, N.; Ghai, R.; Abdo, A.A.; Sanai, F.M.; Al-Hamoudi, W.K.; Alswat, K.A.; Al-Ashgar, H.I.; Khan, M.Q. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) X gene mutations and their association with liver disease progression in HBV-infected patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 105115–105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, A.; Guo, H.; Wei, F.; Mehta, S.R.; Espitia, S.; Smith, D.M.; Liu, L.; et al. A novel mutant 10Ala/Arg together with mutant 144Ser/Arg of hepatitis B virus X protein involved in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocarcinogenesis in HepG2 cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollicino, T.; Cacciola, I.; Saffioti, F.; Raimondo, G. Hepatitis B virus PreS/S gene variants: Pathobiology and clinical implications. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichai, P.; Samuel, D. Management of Fulminant Hepatitis B. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2019, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, X.; Yan, T.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shao, Q.; Liao, H.; Huang, P.; Li, J.; et al. The preS deletion of hepatitis B virus (HBV) is associated with liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic HBV infection. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Chen, B.F. A putative hepatitis B virus splice variant associated with chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. Virology 2017, 510, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.F. Different pre-S deletion patterns and their association with hepatitis B virus genotypes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8041–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Huang, F.Y.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Wong, D.K.; Yuen, M.F. Evolutionary Changes of Hepatitis B Virus Pre-S Mutations Prior to Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bock, C.T.; Tillmann, H.L.; Manns, M.P.; Trautwein, C. The pre-S region determines the intracellular localization and appearance of hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 1999, 30, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, C.T.; Tillmann, H.L.; Maschek, H.J.; Manns, M.P.; Trautwein, C. A preS mutation isolated from a patient with chronic hepatitis B infection leads to virus retention and misassembly. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Su, I.J.; Wang, H.C.; Chang, W.W.; Lei, H.Y.; Lai, M.D.; Chang, W.T.; Huang, W. Pre-S mutant surface antigens in chronic hepatitis B virus infection induce oxidative stress and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bility, M.T.; Li, F.; Cheng, L.; Su, L. Liver immune-pathogenesis and therapy of human liver tropic virus infection in humanized mouse models. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28 (Suppl. S1), 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Yuen, L.; Littlejohn, M.; Sozzi, V.; Jackson, K.; Suri, V.; Tan, S.; Feierbach, B.; Gaggar, A.; Marcellin, P.; et al. Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus Haplotype Diversity Detects Striking Sequence Conservation Across Genotypes and Chronic Disease Phase. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1652–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Hill, A.M.; Boehme, R.; Thomas, H.C.; McDade, H. Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4398–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.Y.; Wong, D.K.; Cheung, K.S.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Review article: Hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg): An emerging marker for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Rokuhara, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yagi, S.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K.; Maki, N. Sensitive enzyme immunoassay for hepatitis B virus core-related antigens and their correlation to virus load. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.K.; Seto, W.K.; Cheung, K.S.; Chong, C.K.; Huang, F.Y.; Fung, J.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigen as a surrogate marker for covalently closed circular DNA. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, J.; Garcia, G.; Canales, E.; Silva, J.A.; Leon, Y.; Gell, O.; Estrada, R.; Moran-Bertot, I.; Muzio, V.; Guillen, G.; et al. High Functional Stability of a Low-cost HBV DNA qPCR Primer Pair and Plasmid Standard. Euroasian J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2016, 6, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Desbiolles, A.; Feldman, S.F.; Ahn, S.H.; Alidjinou, E.K.; Atsukawa, M.; Bocket, L.; Brunetto, M.R.; Buti, M.; Carey, I.; et al. Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen to Indicate High Viral Load: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 10,397 Individual Participants. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 46–60.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testoni, B.; Lebosse, F.; Scholtes, C.; Berby, F.; Miaglia, C.; Subic, M.; Loglio, A.; Facchetti, F.; Lampertico, P.; Levrero, M.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) correlates with covalently closed circular DNA transcriptional activity in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Q.; Feng, S.; Wang, M.L.; Liang, L.B.; Zhou, L.Y.; Du, L.Y.; Yan, L.B.; Tao, C.M.; Tang, H. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen is a satisfactory surrogate marker of intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA in chronic hepatitis B. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Deng, J.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, H. Correlation of HBcrAg with Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus Total DNA and Covalently Closed Circular DNA in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01303-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Q.; Wang, M.L.; Tao, Y.C.; Wu, D.B.; Liao, J.; He, M.; Tang, H. Serum HBcrAg is better than HBV RNA and HBsAg in reflecting intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA. J. Viral. Hepatol. 2019, 26, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Deng, R.; Chen, E.Q.; Tao, C.M.; Liao, J.; Zhou, T.Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, H. Performance of serum HBcrAg in chronic hepatitis B patients with 8-year nucleos(t)ide analogs therapy. Clin. Res. Hepatol. 2019, 43, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Abate, M.L.; Noviello, D.; Olivero, A.; Rosso, C.; Troshina, G.; Ciancio, A.; Rizzetto, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Smedile, A. Hepatitis B core-related antigen kinetics in chronic hepatitis B virus genotype D-infected patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues or pegylated-interferon-α. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.K.; Tanaka, Y.; Lai, C.L.; Mizokami, M.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.F. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigens as markers for monitoring chronic hepatitis B infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3942–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.S.; Park, J.Y.; Chon, Y.E.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, W.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, d.Y.; Han, K.H.; Ahn, S.H. Clinical outcomes and predictors for relapse after cessation of oral antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, A.; Tanaka, E.; Minami, M.; Okanoue, T.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Nagaoka, S.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Chayama, K.; Imamura, M.; et al. Low serum level of hepatitis B core-related antigen indicates unlikely reactivation of hepatitis after cessation of lamivudine therapy. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drafting Committee for Hepatitis Management Guidelines. Japan Society of Hepatology Guidelines for the Management of Hepatitis B Virus Infection: 2019 Update. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 892–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaypen, N.; Posuwan, N.; Payungporn, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Shinkai, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen as a treatment predictor of pegylated interferon in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Yang, R.-F.; Li, X.-H.; Jin, Q.; Wei, L. HBcrAg Identifies Patients Failing to Achieve HBeAg Seroconversion Treated with Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2b. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Niinomi, T.; Yasuda, S.; Andou, Y.; et al. Effect of nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy on hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B patients: A propensity score analysis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Kitabatake, S.; Yama, T.; Tanaka, J. HBcrAg predicts hepatocellular carcinoma development: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosaka, T.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Fujiyama, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; et al. Impact of hepatitis B core-related antigen on the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, M.; Shirasaki, T.; Terashima, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Oishi, N.; Wang, X.; Shimakami, T.; Okada, H.; Arai, K.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Core-Related Antigen During Nucleos(t)ide Analog Therapy Is Related to Intra-hepatic HBV Replication and Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Komatsu, N.; Sato, M.; Tatsumi, A.; Miura, M.; Matsuda, S.; Muraoka, M.; Nakakuki, N.; Shindo, H.; et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected patients with low hepatitis B surface antigen and high hepatitis B core-related antigen titers have a high risk of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jia, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Fang, M.; Feng, H.; Guan, W.; Ji, J.; Gao, Z.; Gao, C. Clinical evaluation of hepatitis B core-related antigen in chronic hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 486, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Inoue, T.; Tanaka, Y. Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen and New Therapies for Hepatitis, B. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghany, M.G.; King, W.C.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Lok, A.S.F.; Terrault, N.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Khalili, M.; Chung, R.T.; Lee, W.M.; Lau, D.T.Y.; et al. Comparison of HBV RNA and Hepatitis B Core Related Antigen with Conventional HBV Markers Among Untreated Adults with Chronic Hepatitis B in North America. Hepatology 2021. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, I.; Gersch, J.; Wang, B.; Moigboi, C.; Kuhns, M.; Cloherty, G.; Dusheiko, G.; Agarwal, K. Pregenomic HBV RNA and Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen Predict Outcomes in Hepatitis Be Antigen-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Suppressed on Nucleos(T)ide Analogue Therapy. Hepatology 2020, 72, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgand, B.; Desterke, C.; Rivière, L.; Fallot, G.; Sebagh, M.; Calderaro, J.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Neuveut, C.; Buendia, M.A.; Samuel, D.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Pregenomic RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nosological and Prognostic Determinant. Hepatology 2018, 67, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Veeraraghavan, V.; Pinkerton, M.; Fu, J.; Douglas, M.W.; George, J.; Tu, T. Viral Biomarkers for Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Occurrence and Recurrence. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 665201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Iio, E.; Ogawa, S.; Suzuki, T.; Yagi, S.; Kaneko, A.; Matsuura, K.; Aoyagi, K.; Tanaka, Y. Clinical efficacy of a novel, high-sensitivity HBcrAg assay in the management of chronic hepatitis B and HBV reactivation. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Matsui, T.; Tanaka, Y. Novel strategies for the early diagnosis of hepatitis B virus reactivation. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, F.; Hosaka, T.; Imaizumi, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Ohue, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Fujiyama, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Akuta, N.; et al. Potential of ultra-highly sensitive immunoassays for hepatitis B surface and core-related antigens in patients with or without development of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisani, F.; Garuti, F.; Neri, A. Alpha-fetoprotein for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Transplant Selection. In Seminars in Liver Disease; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 163–177. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, E.; Kamada, Y.; Suzuki, T. Functional glycomics: Application to medical science and hepatology. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Nakao, S.; Sumiyoshi, H.; Mikami, K.; Tanno, Y.; Sueoka, M.; Kasahara, D.; Kimura, H.; Moro, T.; Kamiya, A.; et al. Identification of a novel alpha-fetoprotein-expressing cell population induced by the Jagged1/Notch2 signal in murine fibrotic liver. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varki, A.; Cummings, R.D.; Esko, J.D.; Stanley, P.; Hart, G.W.; Aebi, M.; Darvill, A.G.; Kinoshita, T.; Packer, N.H.; Prestegard, J.H.; et al. Essentials of Glycobiology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Breborowicz, J.; Mackiewicz, A.; Breborowicz, D. Microheterogeneity of alpha-fetoprotein in patient serum as demonstrated by lectin affino-electrophoresis. Scand. J. Immunol. 1981, 14, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketa, K.; Sekiya, C.; Namiki, M.; Akamatsu, K.; Ohta, Y.; Endo, Y.; Kosaka, K. Lectin-reactive profiles of alpha-fetoprotein characterizing hepatocellular carcinoma and related conditions. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, F.; Tanaka, M.; Satomura, S.; Tanikawa, K. Prognostic significance of Lens culinaris agglutinin A-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in small hepatocellular carcinomas. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Tada, T.; Sone, Y.; Kaneoka, Y.; Maeda, A. Tumor Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Simple and Significant Predictors of Outcome in Patients with HCC. Liver Cancer 2015, 4, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, S.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Schweitzer, N.; Vogel, A.; Manns, M.P.; Benckert, J.; et al. Role of the GALAD and BALAD-2 Serologic Models in Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Prediction of Survival in Patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 875–886.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.X.; Mehta, N. Does Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Increase Survival in At-Risk Populations? Patient Selection, Biomarkers, and Barriers. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 3456–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.L.; Mo, F.; Johnson, P.; Li, L.; Tang, N.; Loong, H.; Chan, A.W.; Koh, J.; Chan, A.T.; Yeo, W. Applicability of BALAD score in prognostication of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuno, A.; Ikehara, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Ito, K.; Matsuda, A.; Sekiya, S.; Hige, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Kage, M.; Mizokami, M.; et al. A serum “sweet-doughnut” protein facilitates fibrosis evaluation and therapy assessment in patients with viral hepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, Y.; Morishita, K.; Koseki, M.; Nishida, M.; Asuka, T.; Naito, Y.; Yamada, M.; Takamatsu, S.; Sakata, Y.; Takehara, T.; et al. Serum Mac-2 Binding Protein Levels Associate with Metabolic Parameters and Predict Liver Fibrosis Progression in Subjects with Fatty Liver Disease: A 7-Year Longitudinal Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Joshita, S.; Umemura, T.; Shobugawa, Y.; Usami, Y.; Shibata, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Fujimori, N.; Komatsu, M.; Matsumoto, A.; et al. Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein may predict liver fibrosis and progression to hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Brakebusch, C.; Engel, J.; Timpl, R. Mac-2 binding protein is a cell-adhesive protein of the extracellular matrix which self-assembles into ring-like structures and binds beta1 integrins, collagens and fibronectin. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekki, Y.; Yoshizumi, T.; Shimoda, S.; Itoh, S.; Harimoto, N.; Ikegami, T.; Kuno, A.; Narimatsu, H.; Shirabe, K.; Maehara, Y. Hepatic stellate cells secreting WFA+-M2BP: Its role in biological interactions with Kupffer cells. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirabe, K.; Bekki, Y.; Gantumur, D.; Araki, K.; Ishii, N.; Kuno, A.; Narimatsu, H.; Mizokami, M. Mac-2 binding protein glycan isomer (M2BPGi) is a new serum biomarker for assessing liver fibrosis: More than a biomarker of liver fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantumur, D.; Harimoto, N.; Muranushi, R.; Hoshino, K.; Batbayar, C.; Hagiwara, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Ishii, N.; Tsukagoshi, M.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Hepatic stellate cell as a Mac-2-binding protein-producing cell in patients with liver fibrosis. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, K.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, Y. Mac-2 binding protein and its glycan isomer: Where does it come from? Where is it going? Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Tateyama, M.; Abiru, S.; Komori, A.; Nagaoka, S.; Saeki, A.; Hashimoto, S.; Sasaki, R.; Bekki, S.; Kugiyama, Y.; et al. Elevated serum levels of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein predict the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C patients. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.U.; Heo, J.Y.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, K.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein predicts the risk of HBV-related liver cancer development. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Honda, M.; Ohta, H.; Terashima, T.; Shimakami, T.; Arai, K.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; Mizukoshi, E.; Komura, T.; et al. Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein predicts hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and recurrence in nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy for chronic hepatitis B. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, T.; Hsu, Y.C.; Ogawa, S.; Huang, Y.T.; Yeh, M.L.; Tseng, C.H.; Huang, C.F.; Tai, C.M.; Dai, C.Y.; Huang, J.F.; et al. Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer as a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marker in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B or C Infection. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Jun, T.; Huang, Y.T.; Yeh, M.L.; Lee, C.L.; Ogawa, S.; Cho, S.H.; Lin, J.T.; Yu, M.L.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Serum M2BPGi level and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after oral anti-viral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.S.; Seto, W.K.; Wong, D.K.; Mak, L.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein predicts liver cancer development in chronic hepatitis B patients under antiviral treatment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47507–47517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocho, M.; Togayachi, A.; Iio, E.; Kaji, H.; Kuno, A.; Sogabe, M.; Korenaga, M.; Gotoh, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Ikehara, Y.; et al. Application of a glycoproteomics-based biomarker development method: Alteration in glycan structure on colony stimulating factor 1 receptor as a possible glycobiomarker candidate for evaluation of liver cirrhosis. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iio, E.; Ocho, M.; Togayachi, A.; Nojima, M.; Kuno, A.; Ikehara, Y.; Hasegawa, I.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Shimada, N.; et al. A novel glycobiomarker, Wisteria floribunda agglutinin macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor, for predicting carcinogenesis of liver cirrhosis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, X. Tumorigenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic potential of exosomes in liver cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, K.; De Giorgi, V.; Schechterly, C.; Wang, R.Y.; Farci, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Alter, H.J. Circulating let-7 levels in plasma and extracellular vesicles correlate with hepatic fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2016, 64, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, J.; Jan Poortmans, P.; Verhulst, S.; Reynaert, H.; Mannaerts, I.; van Grunsven, L.A. Circulating ECV-Associated miRNAs as Potential Clinical Biomarkers in Early Stage HBV and HCV Induced Liver Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hou, L.; Li, A.; Duan, Y.; Gao, H.; Song, X. Expression of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 864894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjelle, R.; Dima, S.O.; Bacalbasa, N.; Chawla, K.; Sorop, A.; Cucu, D.; Herlea, V.; Sætrom, P.; Popescu, I. Comprehensive transcriptomic analyses of tissue, serum, and serum exosomes from hepatocellular carcinoma patients. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, W.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.H.; Yang, S.R.; Cho, J.Y.; Cho, H.C.; Shim, S.G.; Paik, Y.H. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Serum exosomal hnRNPH1 mRNA as a novel marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, K.; Wang, M.; Zeng, H.; Lu, J.; Song, Q.; Diplas, B.H.; Tan, D.; et al. Detection of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in asymptomatic HBsAg-seropositive individuals by liquid biopsy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6308–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Hu, X.; Long, G.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, L.D. The clinical value of total plasma cell-free DNA in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayashi, S.; Nagaoka, K.; Tanaka, Y. Blood-Based Biomarkers in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Including the Viral Genome and Glycosylated Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011051
Hayashi S, Nagaoka K, Tanaka Y. Blood-Based Biomarkers in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Including the Viral Genome and Glycosylated Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(20):11051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011051
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayashi, Sanae, Katsuya Nagaoka, and Yasuhito Tanaka. 2021. "Blood-Based Biomarkers in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Including the Viral Genome and Glycosylated Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 20: 11051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011051
APA StyleHayashi, S., Nagaoka, K., & Tanaka, Y. (2021). Blood-Based Biomarkers in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Including the Viral Genome and Glycosylated Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(20), 11051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011051





