Regulation of Kv11.1 Isoform Expression by Polyadenylate Binding Protein Nuclear 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
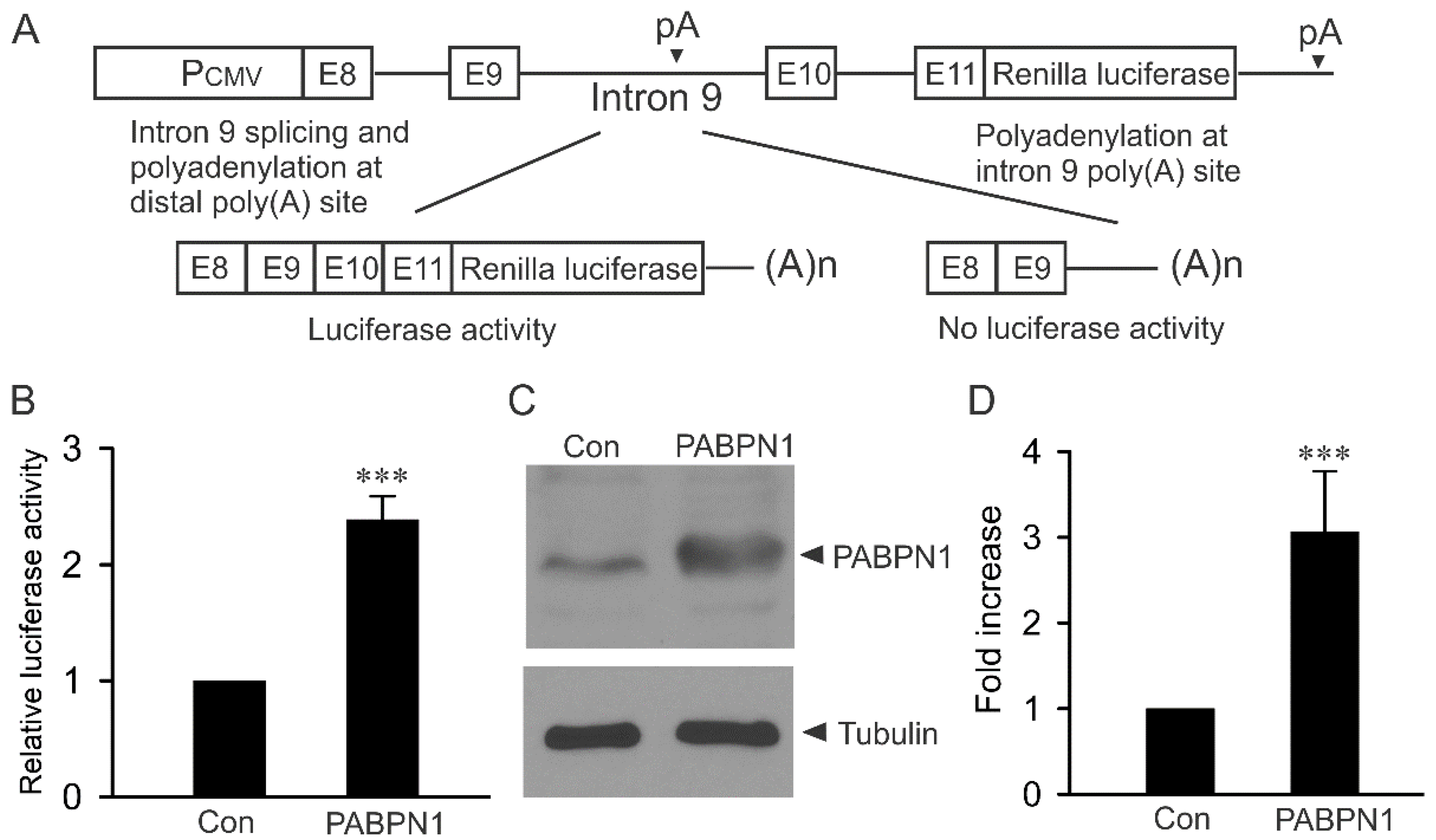
2.1. Modulation of KCNH2 Intron 9 Alternative Processing by PABPN1 Using a Luciferase Reporter Construct
2.2. PABPN1 Suppresses Noncanonical KCNH2 Intron 9 Poly(A) Signal Activity
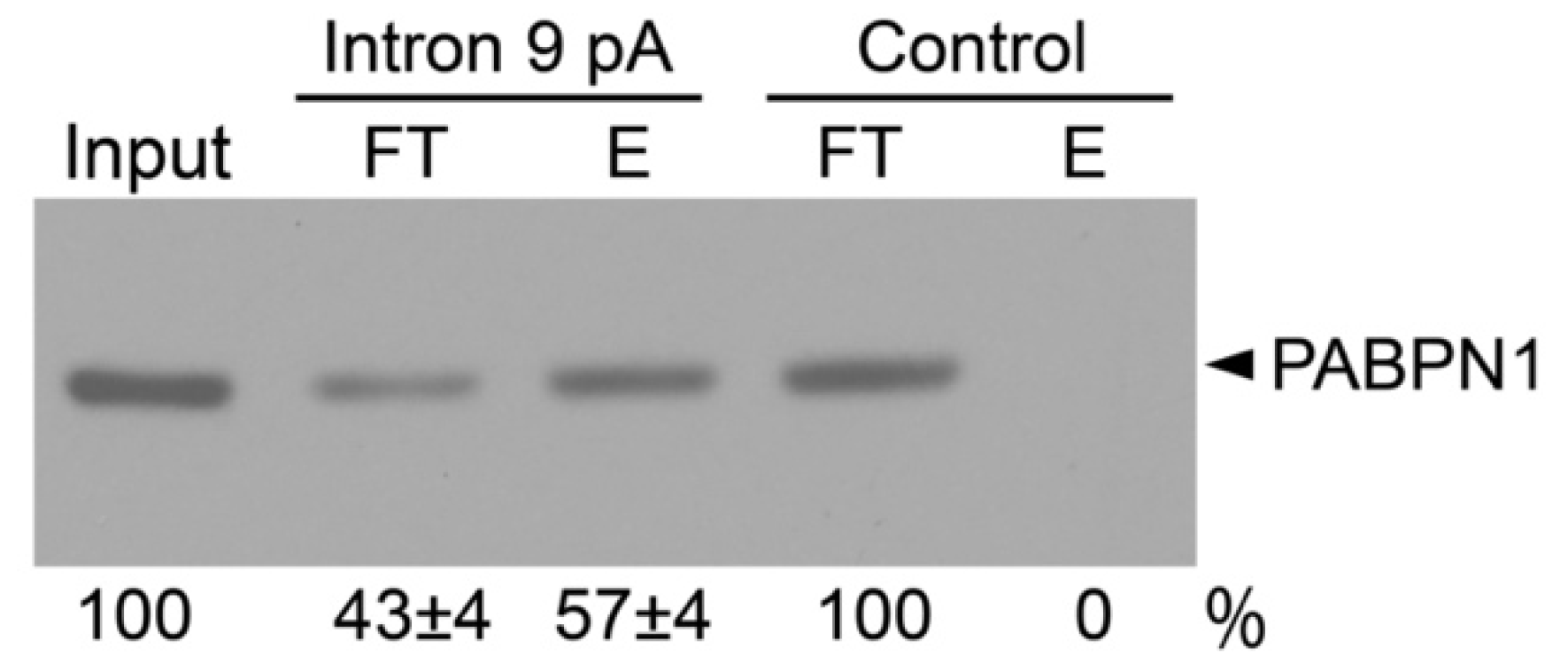
2.3. Interaction between PABPN1 and KCNH2 Intron 9 Poly(A) Signal and Polyadenosine Stretch
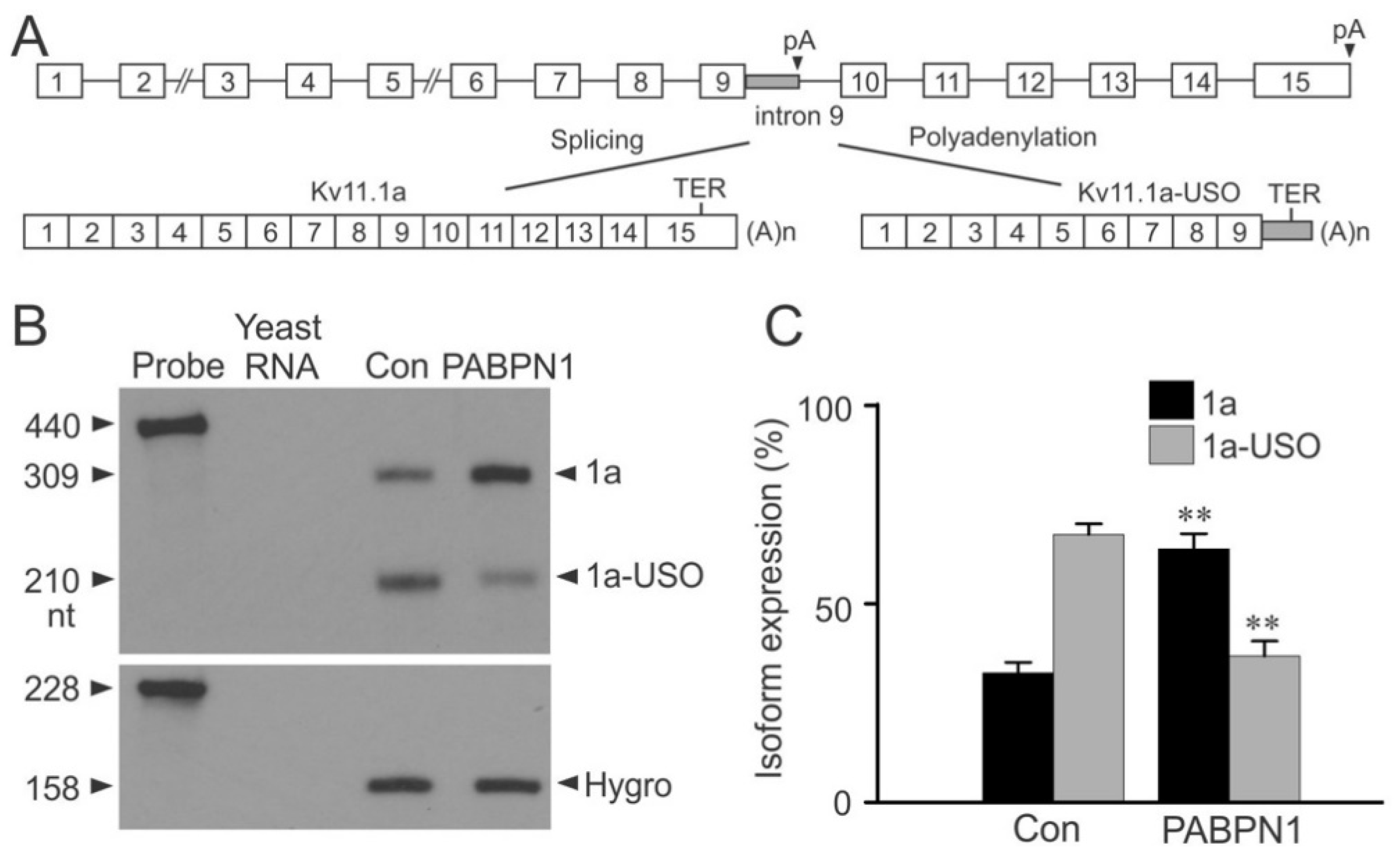
2.4. Regulation of Kv11.1 Isoform Expression by PABPN1
2.5. Upregulation of Kv11.1a Isoform Protein Expression by PABPN1
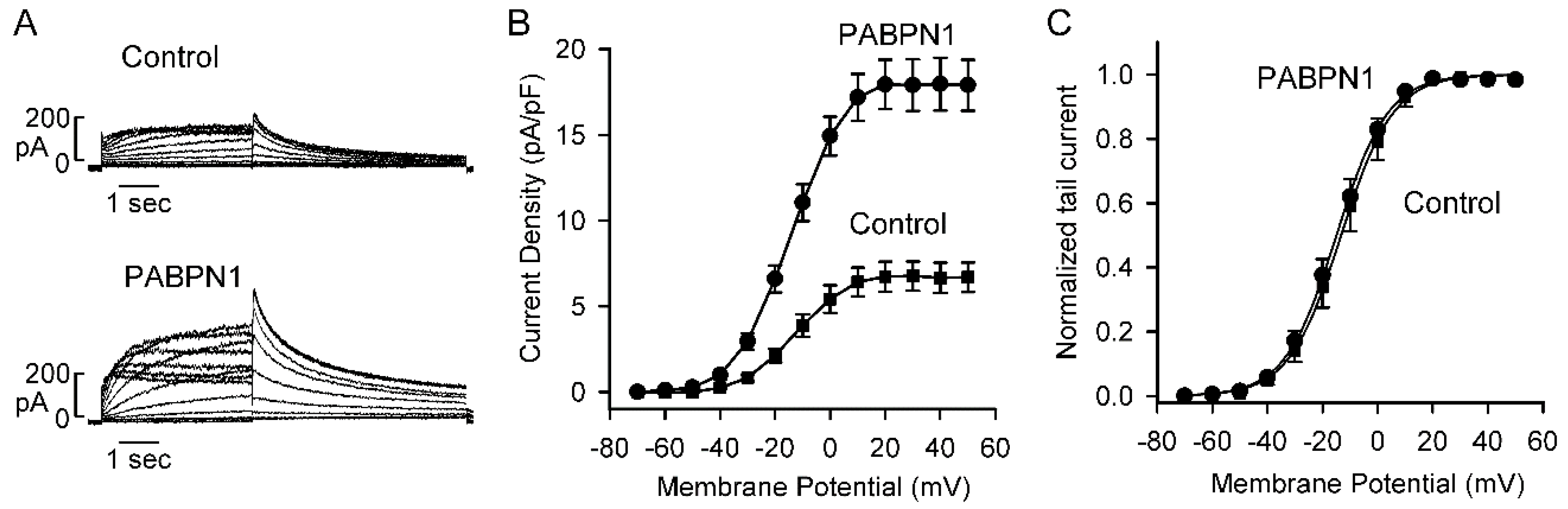
2.6. PABPN1 Increases Kv11.1 Channel Current
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmid Constructs and Transfections
4.2. Biotinylated RNA Pulldown Assay
4.3. RNase Protection Assay
4.4. Immunoblot Analysis
4.5. Patch Clamp Recordings
4.6. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KCNH2 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 2 |
| PABPN1 | Polyadenylate binding protein nuclear 1 |
| LQT2 | Long QT syndrome type 2 |
| nt | Nucleotide |
| RPA | RNase protection assay |
| DSE | Downstream sequence elements |
| HPT | Hygromycin B phosphotransferase |
| Hygro | Hygromycin B resistance gene |
References
- Sanguinetti, M.C.; Jiang, C.; Curran, M.E.; Keating, M.T. A Mechanistic Link between an Inherited and an Acquired Cardiac Arrhythmia: HERG Encodes the IKr Potassium Channel. Cell 1995, 81, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, M.C.; Warmke, J.W.; Ganetzky, B.; Robertson, G.A. HERG, a human inward rectifier in the voltage-gated potassium channel family. Science 1995, 269, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Gong, Q.; Ye, B.; Fan, Z.; Makielski, J.C.; Robertson, G.A.; January, C.T. Properties of HERG Channels Stably Expressed in HEK 293 Cells Studied at Physiological Temperature. Biophys. J. 1998, 74, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmke, J.W.; Ganetzky, B. A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3438–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, M.E.; Splawski, I.; Timothy, K.W.; Vincen, G.; Green, E.D.; Keating, M.T. A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell 1995, 80, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, M.C. HERG1 channelopathies. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2009, 460, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Stump, M.R.; Dunn, A.R.; Deng, V.; Zhou, Z. Alternative Splicing and Polyadenylation Contribute to the Generation of hERG1 C-terminal Isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 32233–32241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupershmidt, S.; Snyders, D.J.; Raes, A.; Roden, D.M. A K+ Channel Splice Variant Common in Human Heart Lacks a C-terminal Domain Required for Expression of Rapidly Activating Delayed Rectifier Current. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27231–27235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stump, M.R.; Gong, Q.; Zhou, Z. Isoform-Specific Dominant-Negative Effects Associated with hERG1 G628S Mutation in Long QT Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Stump, M.R.; Zhou, Z. Regulation of Kv11.1 potassium channel C-terminal isoform expression by the RNA-binding proteins HuR and HuD. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 19624–19632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Stump, M.R.; Deng, V.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z. Identification of Kv11.1 Isoform Switch as a Novel Pathogenic Mechanism of Long-QT Syndrome. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerwitz, Y.; Kühn, U.; Lilie, H.; Knoth, A.; Scheuermann, T.; Friedrich, H.; Schwarz, E.; Wahle, E. Stimulation of poly(A) polymerase through a direct interaction with the nuclear poly(A) binding protein allosterically regulated by RNA. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3705–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, U.; Gündel, M.; Knoth, A.; Kerwitz, Y.; Rüdel, S.; Wahle, E. Poly(A) Tail Length Is Controlled by the Nuclear Poly(A)-binding Protein Regulating the Interaction between Poly(A) Polymerase and the Cleavage and Polyadenylation Specificity Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22803–22814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, D.G.; Fomproix, N.; Soop, T.; Björkroth, B.; Masich, S.; Daneholt, B. Nuclear poly(A)-binding protein PABPN1 is associated with RNA polymerase II during transcription and accompanies the released transcript to the nuclear pore. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 286, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenal, M.; Elkon, R.; Loayza-Puch, F.; van Haaften, G.; Kühn, U.; Menzies, F.M.; Oude Vrielink, J.A.F.; Bos, A.J.; Drost, J.; Rooijers, K.; et al. The Poly(A)-Binding Protein Nuclear 1 Suppresses Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation Sites. Cell 2012, 149, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahle, E. A novel poly(A)-binding protein acts as a specificity factor in the second phase of messenger RNA polyadenylation. Cell 1991, 66, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Manley, J.L. Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation: The long and short of it. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.; Urbanke, C.; Wahle, E. Equilibrium Studies on the Association of the Nuclear Poly(A) Binding Protein with Poly(A) of Different Lengths†. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 6082–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Stump, M.R.; Zhou, Z. Upregulation of functional Kv11.1a isoform expression by modified U1 small nuclear RNA. Gene 2017, 641, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creemers, E.E.; Bawazeer, A.C.; Ugalde, A.P.; Van Deutekom, H.W.; Van Der Made, I.; De Groot, N.E.; Adriaens, M.E.; Cook, S.A.; Bezzina, C.R.; Hubner, N.; et al. Genome-Wide Polyadenylation Maps Reveal Dynamic mRNA 3′-End Formation in the Failing Human Heart. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klerk, E.; Venema, A.; Anvar, S.Y.; Goeman, J.J.; Hu, O.; Trollet, C.; Dickson, G.; den Dunnen, J.T.; van der Maarel, S.M.; Raz, V.; et al. Poly(A) Binding Protein Nuclear 1 Levels Affect Alternative Polyadenylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 9089–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonelig, M. PABPN1 shuts down alternative poly(A) sites. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brais, B.; Bouchard, J.P.; Xie, Y.G.; Rochefort, D.L.; Chrétien, N.; Tomé, F.M.; Lafrenière, R.G.; Rommens, J.M.; Uyama, E.; Nohira, O.; et al. Short GCG Expansions in the PABP2 Gene Cause Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbassi-Daloii, T.; Yousefi, S.; de Klerk, E.; Grossouw, L.; Riaz, M.; AC’t Hoen, P.; Raz, V. An Alanine Expanded PABPN1 Causes Increased Utilization of Intronic Polyadenylation Sites. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankodi, A.; Wheeler, T.M.; Shetty, R.; Salceies, K.M.; Becher, M.W.; Thornton, C.A. Progressive myopathy in an inducible mouse model of oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gong, Q.; Stump, M.R.; Zhou, Z. Upregulation of functional Kv11.1 isoform expression by inhibition of intronic polyadenylation with antisense morpholino oligonucleotides. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 76, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Gong, Q.; Epstein, M.L.; January, C.T. HERG Channel Dysfunction in Human Long QT Syndrome: Intracellular Transport and Functional Defects. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 21061–21066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, L. Patch-Clamp Techniques. In Cell Physiology Source Book; Sperelakis, N., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 369–381. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stump, M.R.; Nguyen, R.T.; Drgastin, R.H.; Search, D.; Gong, Q.; Zhou, Z. Regulation of Kv11.1 Isoform Expression by Polyadenylate Binding Protein Nuclear 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020863
Stump MR, Nguyen RT, Drgastin RH, Search D, Gong Q, Zhou Z. Regulation of Kv11.1 Isoform Expression by Polyadenylate Binding Protein Nuclear 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020863
Chicago/Turabian StyleStump, Matthew R., Rachel T. Nguyen, Rachel H. Drgastin, Delaney Search, Qiuming Gong, and Zhengfeng Zhou. 2021. "Regulation of Kv11.1 Isoform Expression by Polyadenylate Binding Protein Nuclear 1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020863
APA StyleStump, M. R., Nguyen, R. T., Drgastin, R. H., Search, D., Gong, Q., & Zhou, Z. (2021). Regulation of Kv11.1 Isoform Expression by Polyadenylate Binding Protein Nuclear 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020863





