Endothelial Lipase Modulates Paraoxonase 1 Content and Arylesterase Activity of HDL
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
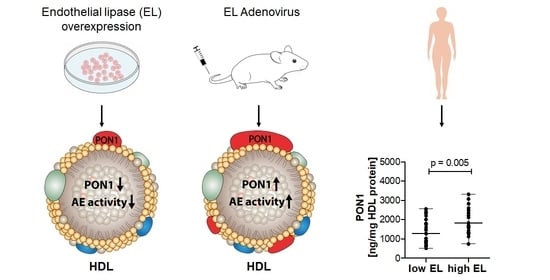
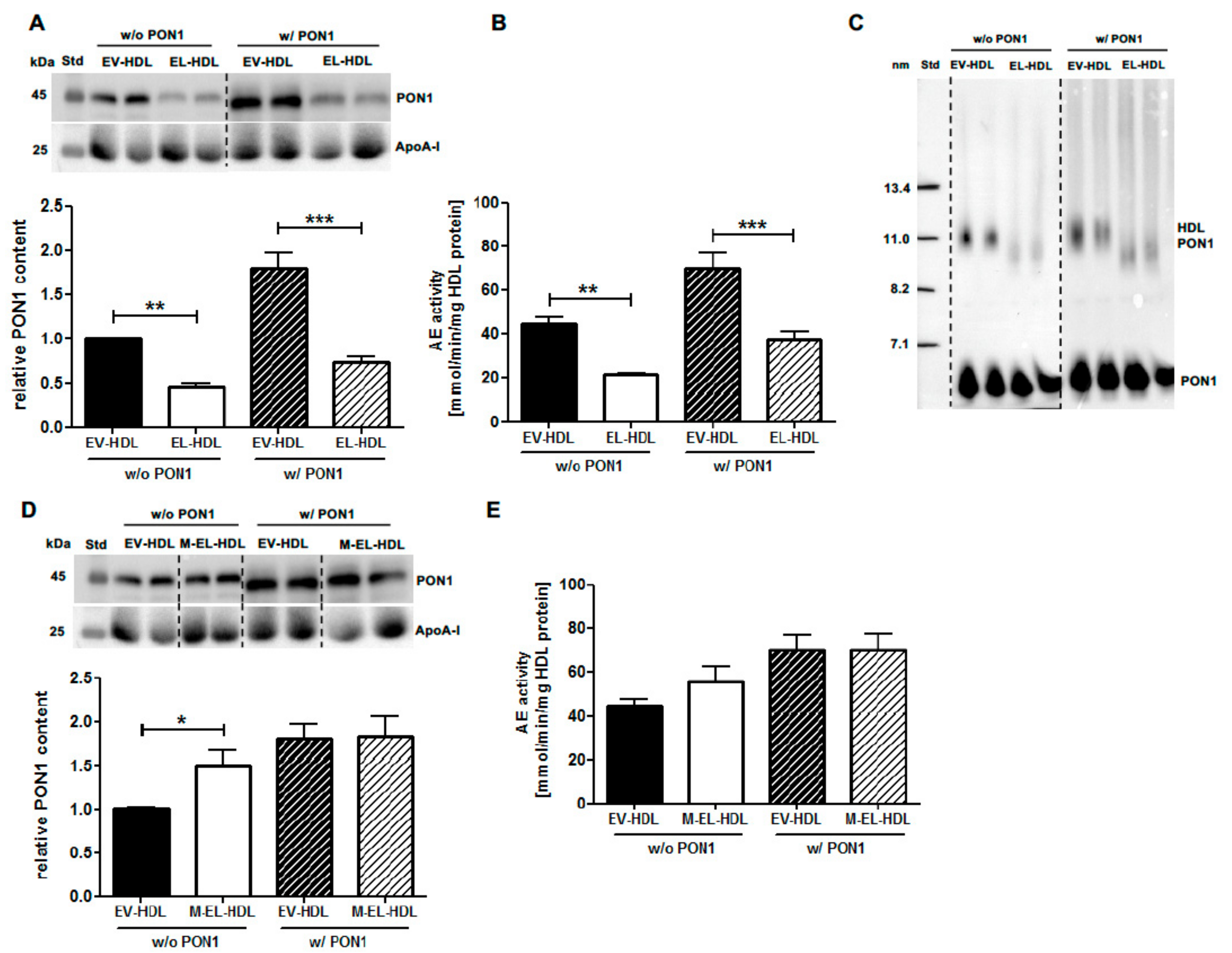
2.1. EL Decreases HDL-Associated PON1 Content and AE Activity In Vitro
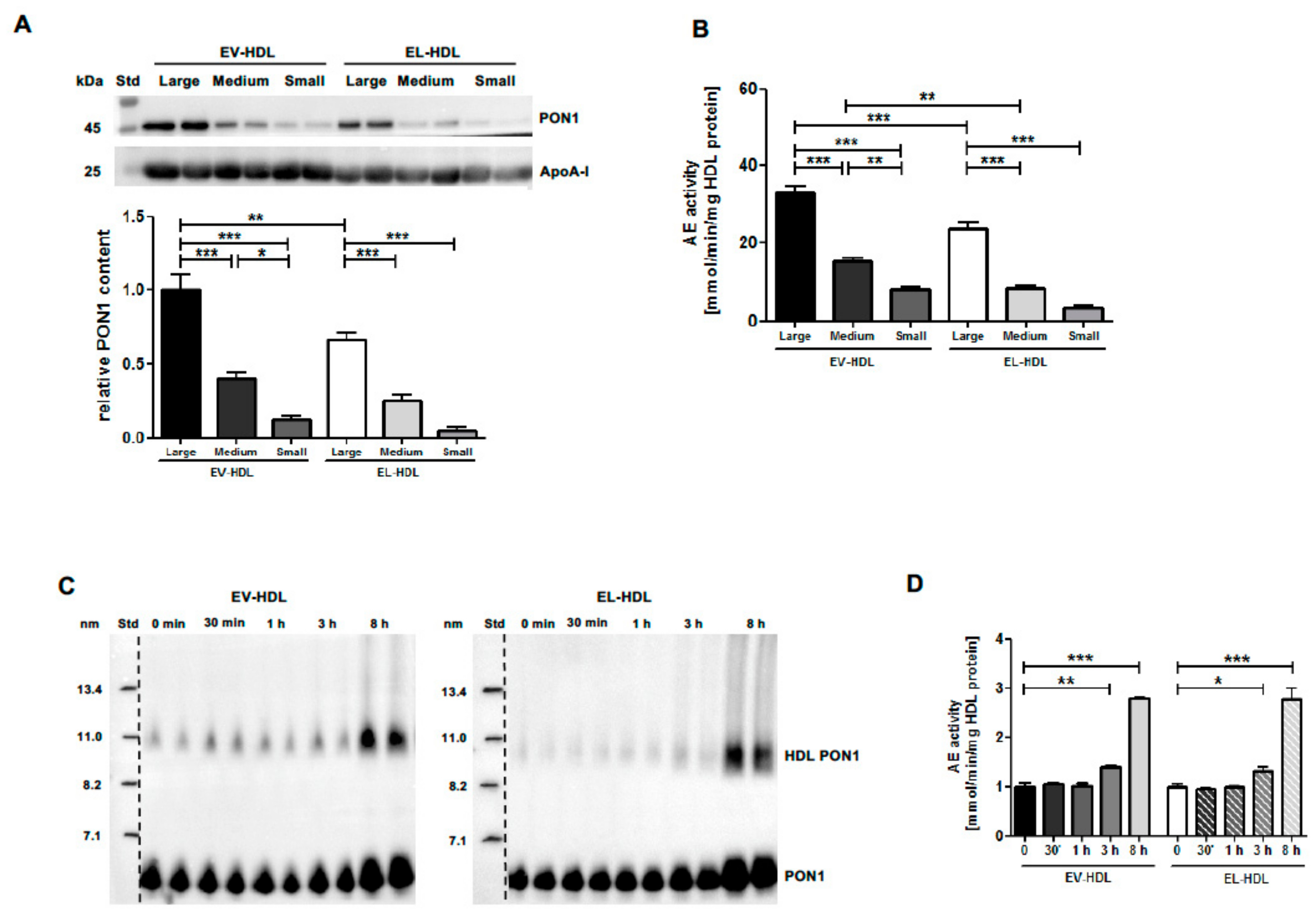
2.2. EL Decreases HDL Size and PON1 Content without Diminishing the Capacity of HDL to Associate with PON1
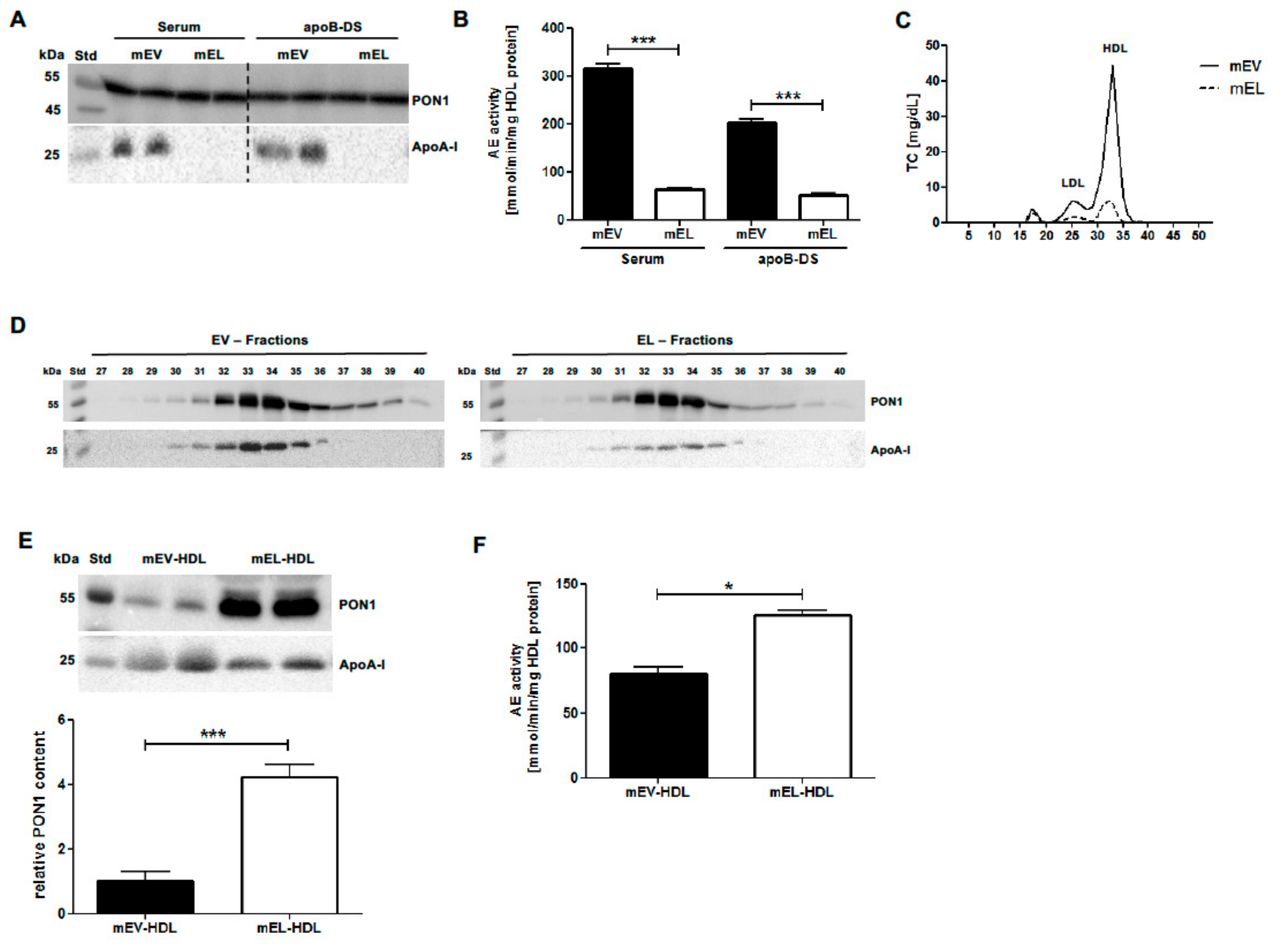
2.3. EL Overexpression in Mice Increases HDL PON1 Content and AE Activity
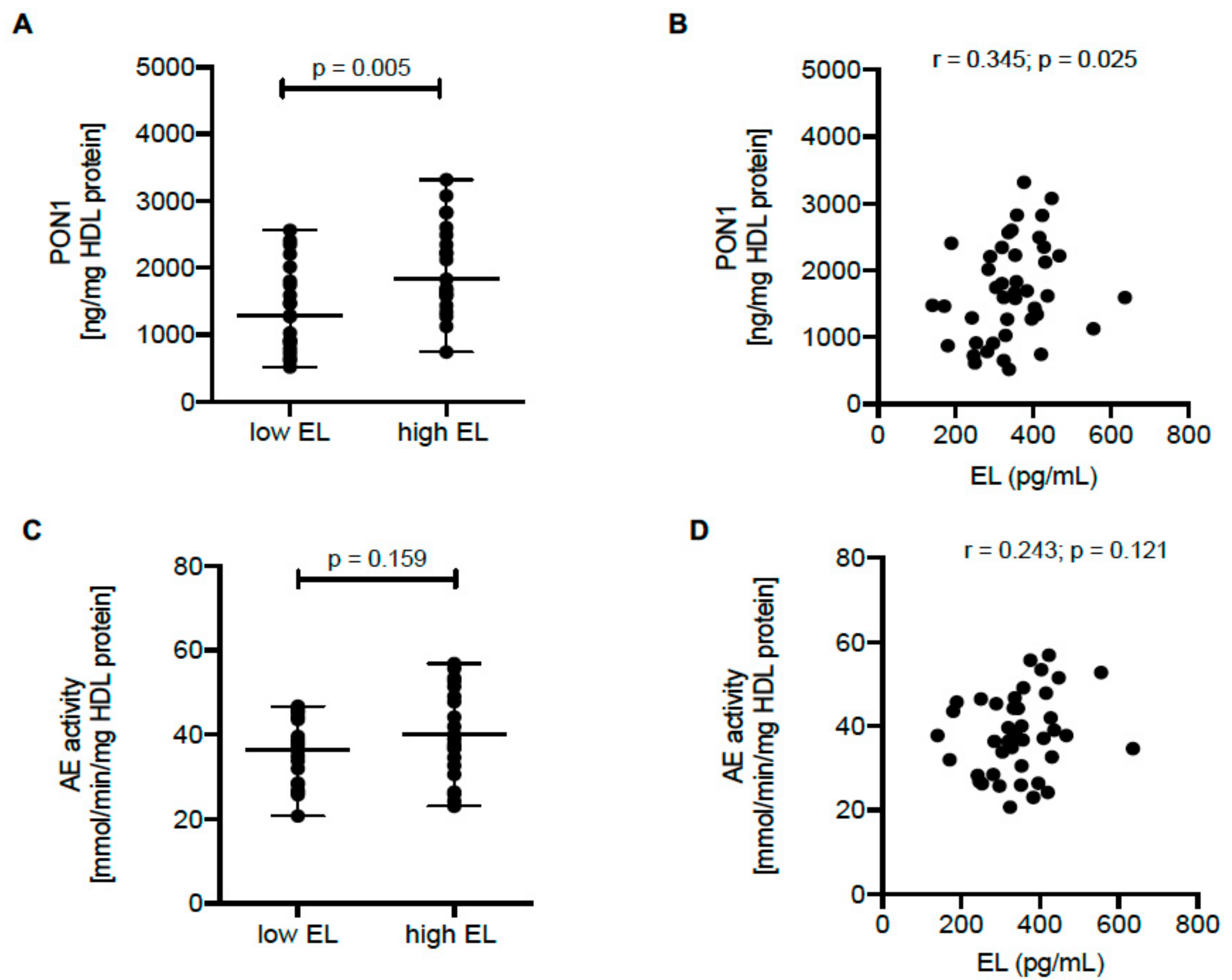
2.4. HDL PON1 Content Is Positively Associated with EL Serum Levels in Humans
2.5. EL-Induced Alterations of HDL Lipidome and HDL Serum Levels Are Not Linked to HDL PON1 Content
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Human Plasma
4.3. Blood Collection from Healthy Volunteers
4.4. Isolation of HDL
4.5. Modification of HDL and Plasma
4.6. Preparation of In Vivo EL-Modified Serum and Control EV Serum
4.7. Fractionation of HDL by FPLC
4.8. FPLC of Mouse Serum
4.9. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.10. Non-Denaturing Gradient-Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blotting
4.11. AE Activity
4.12. Cholesterol Efflux Capacity
4.13. Association of EV-HDL and EL-HDL with PON1
4.14. PON1 ELISA
4.15. EL ELISA
4.16. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.17. Lipid and (Apo)Lipoprotein Profiling by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
4.18. HDL-Lipidome Analysis by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
4.19. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| Apo A-I | apolipoprotein A-I |
| PON1 | paraoxonase 1 |
| EL | endothelial lipase |
| FCS | fetal calf serum |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| FPLC | fast protein liquid chromatography |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| PC | phosphatidylcholine |
| PE | phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PI | phosphatidylinositol |
| TAG | triacylglycerols |
| LPC | lysophosphatidylcholine |
| LPE | lysophosphatidylethanolamine |
| FC | free cholesterol |
| CE | cholesteryl ester |
| Cer | ceramide |
| SM | sphingomyelin |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| Ad | adenovirus |
References
- Fisher, E.A.; Feig, J.E.; Hewing, B.; Hazen, S.L.; Smith, J.D. High-density lipoprotein function, dysfunction, and reverse cholesterol transport. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besler, C.; Luscher, T.F.; Landmesser, U. Molecular mechanisms of vascular effects of High-density lipoprotein: Alterations in cardiovascular disease. Embo Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.S.; Silva, R.A.; Chantepie, S.; Lagor, W.R.; Chapman, M.J.; Kontush, A. Proteomic analysis of defined HDL subpopulations reveals particle-specific protein clusters: Relevance to antioxidative function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviram, M.; Rosenblat, M.; Bisgaier, C.L.; Newton, R.S.; Primo-Parmo, S.L.; La Du, B.N. Paraoxonase inhibits high-density lipoprotein oxidation and preserves its functions. A possible peroxidative role for paraoxonase. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblat, M.; Vaya, J.; Shih, D.; Aviram, M. Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) enhances HDL-mediated macrophage cholesterol efflux via the ABCA1 transporter in association with increased HDL binding to the cells: A possible role for lysophosphatidylcholine. Atherosclerosis 2005, 179, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, S.; Leviev, I.; Gomaraschi, M.; Calabresi, L.; Franceschini, G.; James, R.W. Enzymatically active paraoxonase-1 is located at the external membrane of producing cells and released by a high affinity, saturable, desorption mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4301–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.W.; Brulhart-Meynet, M.C.; Singh, A.K.; Riederer, B.; Seidler, U.; Out, R.; Van Berkel, T.J.; Deakin, S. The scavenger receptor class B, type I is a primary determinant of paraoxonase-1 association with high-density lipoproteins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Riwanto, M.; Gao, S.; Levison, B.S.; Gu, X.; Fu, X.; Wagner, M.A.; Besler, C.; Gerstenecker, G.; et al. Myeloperoxidase, paraoxonase-1, and HDL form a functional ternary complex. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3815–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Huang, Y.; Levison, B.S.; Gerstenecker, G.; DiDonato, A.J.; Hazen, L.B.; Lee, J.; Gogonea, V.; DiDonato, J.A.; Hazen, S.L. Identification of Critical Paraoxonase 1 Residues Involved in High Density Lipoprotein Interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1890–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, R.C.; Bisgaier, C.L.; Aviram, M.; Hsu, C.; Billecke, S.; La Du, B.N. Human serum Paraoxonase/Arylesterase’s retained hydrophobic N-terminal leader sequence associates with HDLs by binding phospholipids: Apolipoprotein A-I stabilizes activity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 2214–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, S.P.; Bioletto, S.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; James, R.W. HDL-associated paraoxonase-1 can redistribute to cell membranes and influence sensitivity to oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrat, M.; Aviram, M. Macrophage paraoxonase 1 (PON1) binding sites. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatter, M.C.; James, R.W.; Messmer, S.; Barja, F.; Pometta, D. Identification of a distinct human high-density lipoprotein subspecies defined by a lipoprotein-associated protein, K-45. Identity of K-45 with paraoxonase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 211, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliucci, A.; Menini, T. Paraoxonase 1 and HDL maturation. Clin Chim Acta 2015, 439, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontush, A. HDL-mediated mechanisms of protection in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 103, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingwell, B.A.; Chapman, M.J.; Kontush, A.; Miller, N.E. HDL-targeted therapies: Progress, failures and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moren, X.; Lhomme, M.; Bulla, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Kontush, A.; James, R.W. Proteomic and lipidomic analyses of paraoxonase defined high density lipoprotein particles: Association of paraoxonase with the anti-coagulant, protein S. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, T.; Nicholls, S.J.; Topol, E.J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Schmitt, D.; Fu, X.; Shao, M.; Brennan, D.M.; Ellis, S.G.; et al. Relationship of paraoxonase 1 (PON1) gene polymorphisms and functional activity with systemic oxidative stress and cardiovascular risk. JAMA 2008, 299, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.H.; Hartiala, J.; Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Stewart, A.F.; Erdmann, J.; Kathiresan, S.; Consortium, C.A.; Roberts, R.; McPherson, R.; et al. Clinical and genetic association of serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities with cardiovascular risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, D.M.; Gu, L.; Xia, Y.R.; Navab, M.; Li, W.F.; Hama, S.; Castellani, L.W.; Furlong, C.E.; Costa, L.G.; Fogelman, A.M.; et al. Mice lacking serum paraoxonase are susceptible to organophosphate toxicity and atherosclerosis. Nature 1998, 394, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, O.; Rosenblat, M.; Coleman, R.; Shih, D.M.; Aviram, M. Paraoxonase (PON1) deficiency is associated with increased macrophage oxidative stress: Studies in PON1-knockout mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackness, B.; Quarck, R.; Verreth, W.; Mackness, M.; Holvoet, P. Human paraoxonase-1 overexpression inhibits atherosclerosis in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaye, M.; Lynch, K.J.; Krawiec, J.; Marchadier, D.; Maugeais, C.; Doan, K.; South, V.; Amin, D.; Perrone, M.; Rader, D.J. A novel endothelial-derived lipase that modulates HDL metabolism. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, K.; Dichek, H.L.; Cioffi, J.A.; Choi, S.Y.; Leeper, N.J.; Quintana, L.; Kronmal, G.S.; Cooper, A.D.; Quertermous, T. Cloning of a unique lipase from endothelial cells extends the lipase gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 14170–14175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Choi, S.; Kundu, R.K.; Hirata, K.; Rubin, E.M.; Cooper, A.D.; Quertermous, T. Endothelial lipase is a major determinant of HDL level. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaraja, R.R.; Sivapalaratnam, S.; Hovingh, K.; Dube, M.P.; Castro-Perez, J.; Collins, H.L.; Adelman, S.J.; Riwanto, M.; Manz, J.; Hubbard, B.; et al. The impact of partial and complete loss-of-function mutations in endothelial lipase on high-density lipoprotein levels and functionality in humans. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilcher, I.; Kern, S.; Hrzenjak, A.; Eichmann, T.O.; Stojakovic, T.; Scharnagl, H.; Duta-Mare, M.; Kratky, D.; Marsche, G.; Frank, S. Impact of Endothelial Lipase on Cholesterol Efflux Capacity of Serum and High-density Lipoprotein. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauster, M.; Rechberger, G.; Sovic, A.; Horl, G.; Steyrer, E.; Sattler, W.; Frank, S. Endothelial lipase releases saturated and unsaturated fatty acids of high density lipoprotein phosphatidylcholine. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauster, M.; Oskolkova, O.V.; Innerlohinger, J.; Glatter, O.; Knipping, G.; Frank, S. Endothelial lipase-modified high-density lipoprotein exhibits diminished ability to mediate SR-BI (scavenger receptor B type I)-dependent free-cholesterol efflux. Biochem. J. 2004, 382, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schilcher, I.; Ledinski, G.; Radulovic, S.; Hallstrom, S.; Eichmann, T.; Madl, T.; Zhang, F.; Leitinger, G.; Kolb-Lenz, D.; Darnhofer, B.; et al. Endothelial lipase increases antioxidative capacity of high-density lipoprotein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovic, S.; Gottschalk, B.; Horl, G.; Zardoya-Laguardia, P.; Schilcher, I.; Hallstrom, S.; Vujic, N.; Schmidt, K.; Trieb, M.; Graier, W.F.; et al. Endothelial lipase increases eNOS activating capacity of high-density lipoprotein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.C.; Mintah, I.J.; Alexa-Braun, C.A.; Shihanian, L.M.; Lee, J.S.; Banerjee, P.; Hamon, S.C.; Kim, H.I.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H.; et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 3 governs LDL-cholesterol levels through endothelial lipase-dependent VLDL clearance. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1271–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badellino, K.O.; Wolfe, M.L.; Reilly, M.P.; Rader, D.J. Endothelial lipase concentrations are increased in metabolic syndrome and associated with coronary atherosclerosis. PloS Med. 2006, 3, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, M.E.; Badellino, K.O.; Rader, D.J.; Deshaies, Y.; Couture, P.; Archer, W.R.; Bergeron, N.; Lamarche, B. Endothelial lipase is associated with inflammation in humans. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 2808–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potocnjak, I.; Trbusic, M.; Teresak, S.D.; Radulovic, B.; Pregartner, G.; Berghold, A.; Tiran, B.; Marsche, G.; Degoricija, V.; Frank, S. Metabolic Syndrome Modulates Association between Endothelial Lipase and Lipid/Lipoprotein Plasma Levels in Acute Heart Failure Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.W.; Paul, A.; Ma, K.; Li, L.; Chan, L. Endothelial lipase modulates HDL but has no effect on atherosclerosis development in apoE-/- and LDLR-/- mice. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Choi, S.Y.; Kundu, R.K.; Spin, J.; Yamashita, T.; Hirata, K.; Kojima, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Cooper, A.D.; Quertermous, T. Endothelial lipase modulates susceptibility to atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45085–45092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Nishijima, K.; Kitajima, S.; Niimi, M.; Yan, H.; Chen, Y.; Ning, B.; Matsuhisa, F.; Liu, E.; Zhang, J.; et al. Increased Hepatic Expression of Endothelial Lipase Inhibits Cholesterol Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia and Atherosclerosis in Transgenic Rabbits. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riederer, M.; Kofeler, H.; Lechleitner, M.; Tritscher, M.; Frank, S. Impact of endothelial lipase on cellular lipid composition. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeais, C.; Tietge, U.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Marchadier, D.; Cain, W.; McCoy, M.G.; Lund-Katz, S.; Glick, J.M.; Rader, D.J. Dose-dependent acceleration of high-density lipoprotein catabolism by endothelial lipase. Circulation 2003, 108, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijstad, N.; Wiersma, H.; Gautier, T.; van der Giet, M.; Maugeais, C.; Tietge, U.J. Scavenger receptor BI-mediated selective uptake is required for the remodeling of high density lipoprotein by endothelial lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6093–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Nguyen, S.D.; Kim, M.R.; Jeong, T.S.; Sok, D.E. Differential effect of lysophospholipids on activities of human plasma paraoxonase1, either soluble or lipid-bound. Lipids 2006, 41, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Miyashita, K.; Shimizu, M.; Kinoshita, N.; Mori, K.; Sun, L.; Yasuda, T.; Imamura, S.; Nakajima, K.; Stanhope, K.L.; et al. ELISA system for human endothelial lipase. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrougui, H.; Loued, S.; Khalil, A. Purified human paraoxonase-1 interacts with plasma membrane lipid rafts and mediates cholesterol efflux from macrophages. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieb, M.; Horvath, A.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Spindelboeck, W.; Stadlbauer, V.; Taschler, U.; Curcic, S.; Stauber, R.E.; Holzer, M.; Pasterk, L.; et al. Liver disease alters high-density lipoprotein composition, metabolism and function. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schilcher, I.; Stadler, J.T.; Lechleitner, M.; Hrzenjak, A.; Berghold, A.; Pregartner, G.; Lhomme, M.; Holzer, M.; Korbelius, M.; Reichmann, F.; et al. Endothelial Lipase Modulates Paraoxonase 1 Content and Arylesterase Activity of HDL. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020719
Schilcher I, Stadler JT, Lechleitner M, Hrzenjak A, Berghold A, Pregartner G, Lhomme M, Holzer M, Korbelius M, Reichmann F, et al. Endothelial Lipase Modulates Paraoxonase 1 Content and Arylesterase Activity of HDL. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020719
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchilcher, Irene, Julia T. Stadler, Margarete Lechleitner, Andelko Hrzenjak, Andrea Berghold, Gudrun Pregartner, Marie Lhomme, Michael Holzer, Melanie Korbelius, Florian Reichmann, and et al. 2021. "Endothelial Lipase Modulates Paraoxonase 1 Content and Arylesterase Activity of HDL" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020719
APA StyleSchilcher, I., Stadler, J. T., Lechleitner, M., Hrzenjak, A., Berghold, A., Pregartner, G., Lhomme, M., Holzer, M., Korbelius, M., Reichmann, F., Springer, A., Wadsack, C., Madl, T., Kratky, D., Kontush, A., Marsche, G., & Frank, S. (2021). Endothelial Lipase Modulates Paraoxonase 1 Content and Arylesterase Activity of HDL. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020719