Development of A Continuous Fluorescence-Based Assay for N-Terminal Acetyltransferase D
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NatD Protein Purification
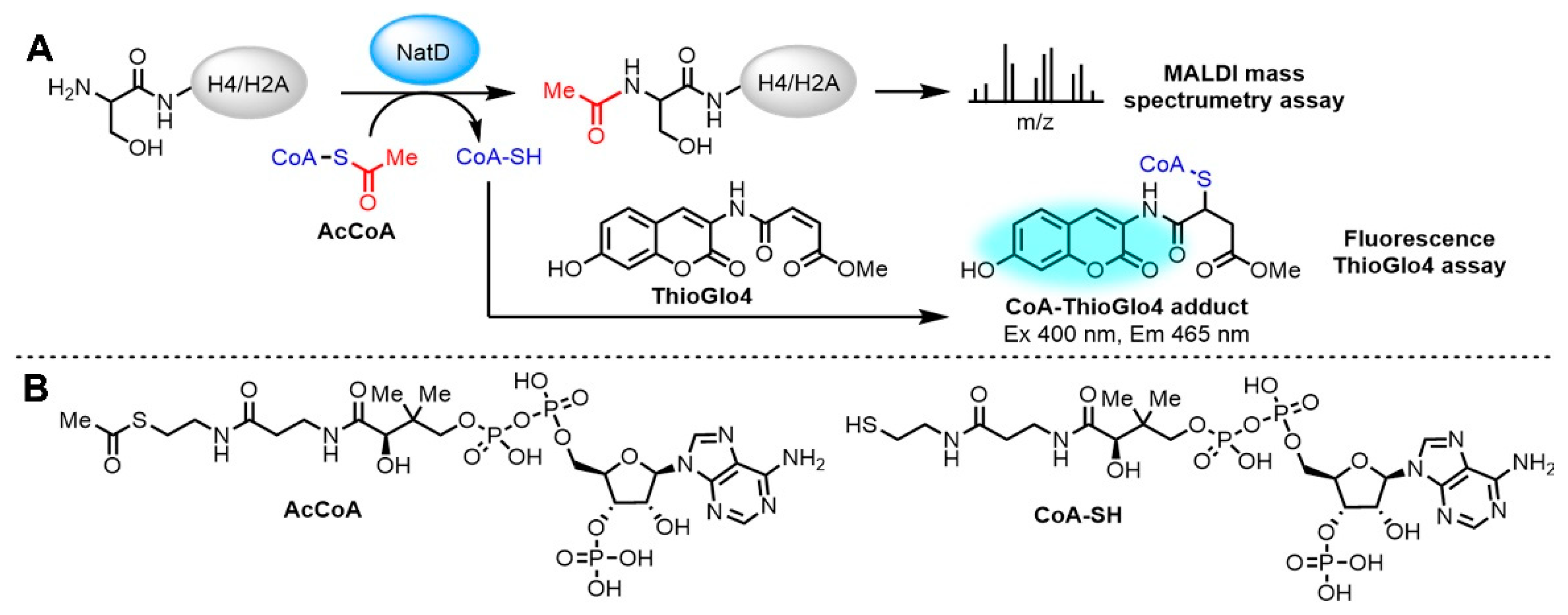
2.2. Fluorescence-Based NatD Activity Assay
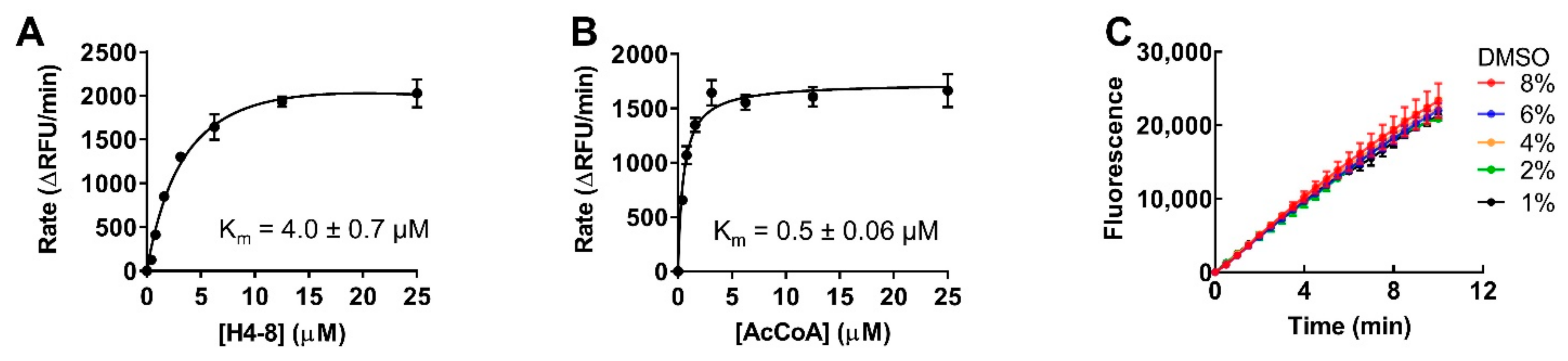
2.3. Optimization for Primary Fluorescence Assay in a 384-Well Format
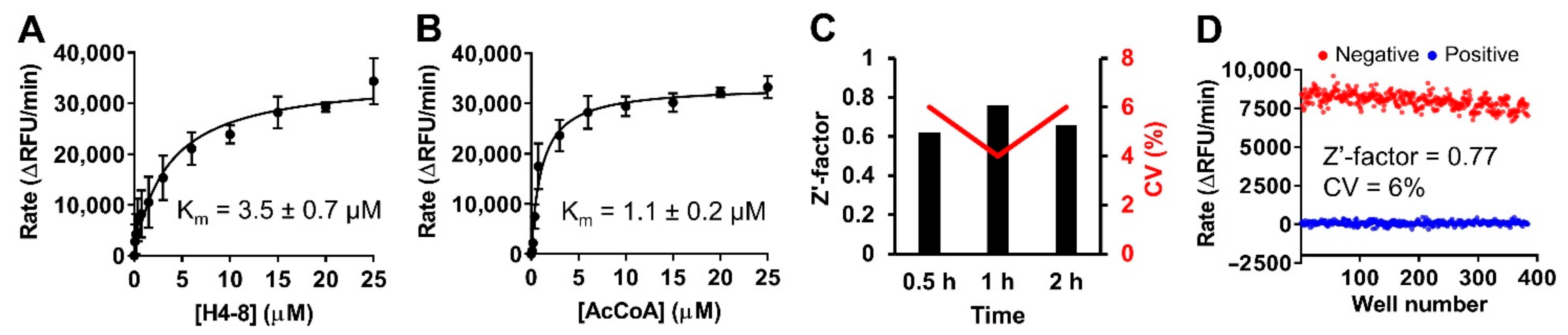
2.4. Stability of Protein and Reagent
2.5. Assay Performance
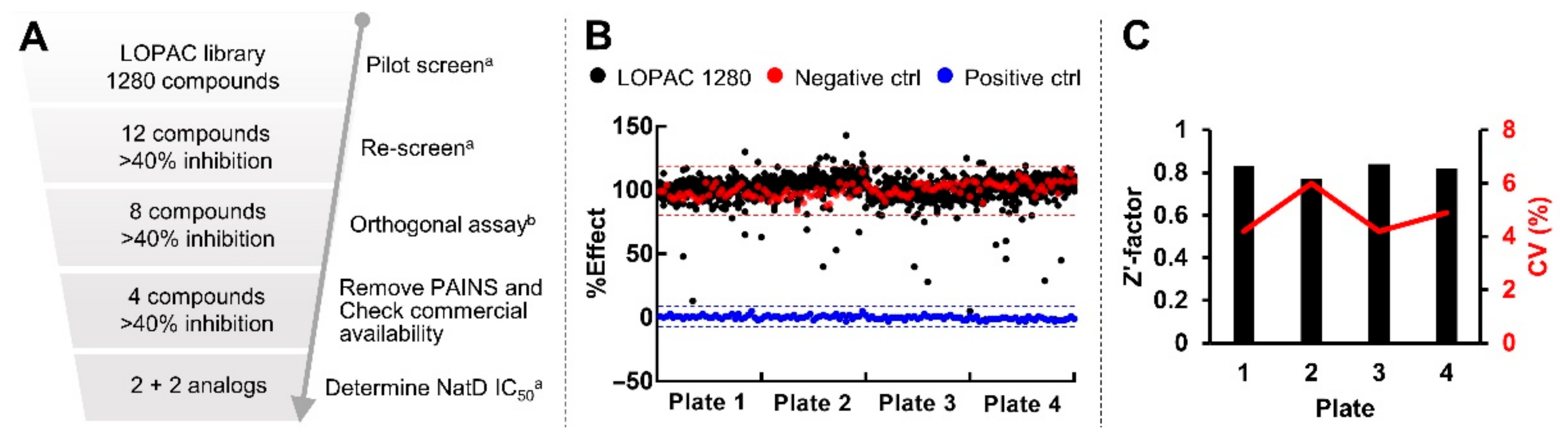
2.6. Pilot Screen with LOPAC Library
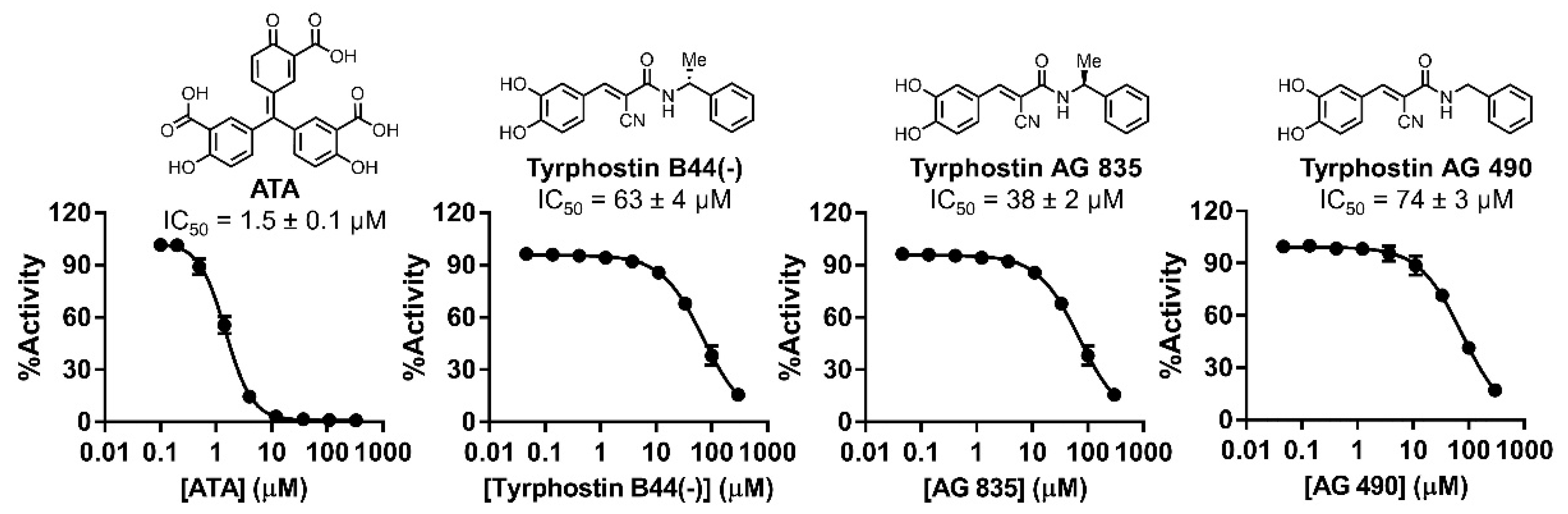
2.7. Validation Assays
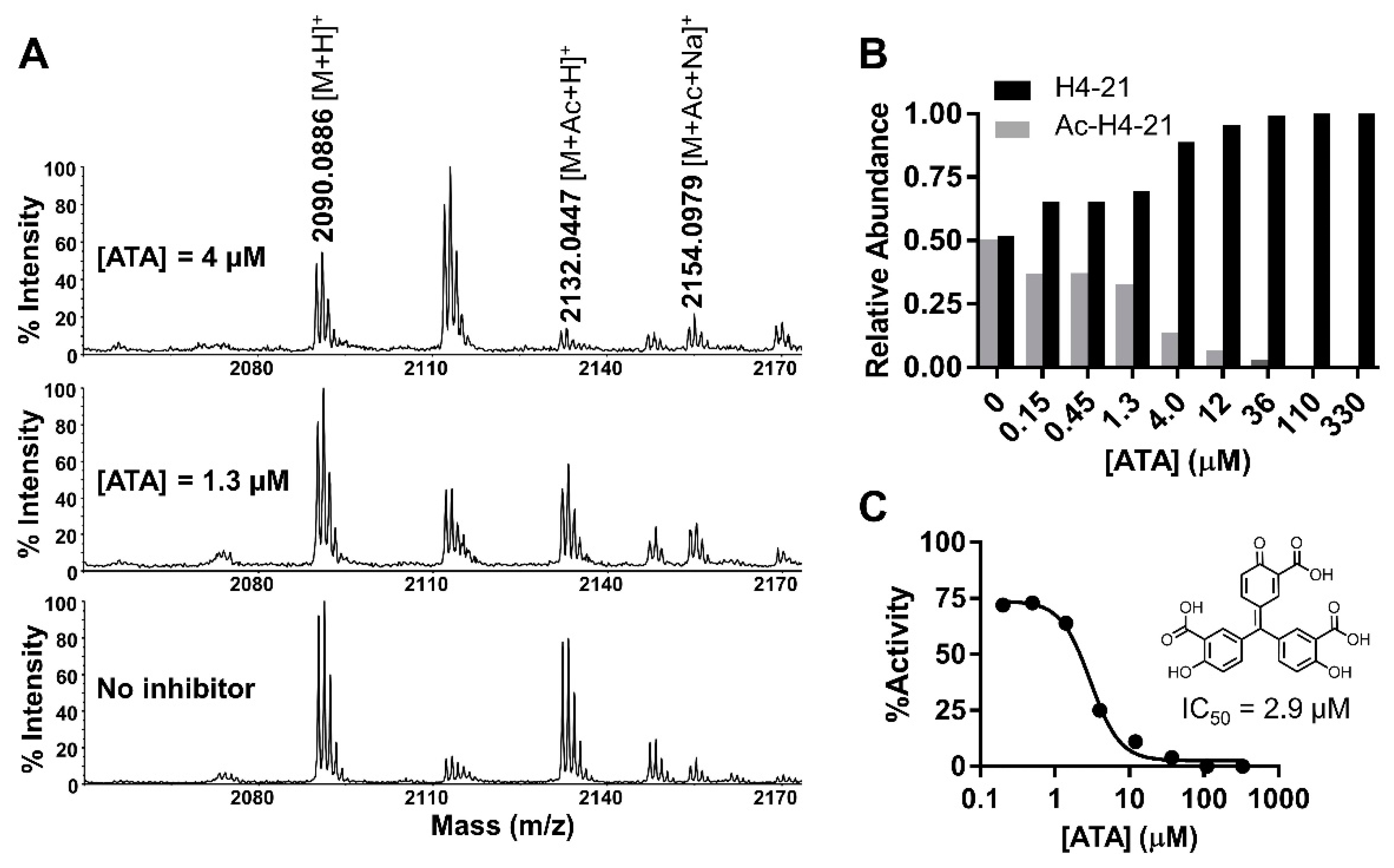
2.8. IC50 Characterization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Human NatD
4.3. Synthesis of Peptide Substrates
4.4. Standard Calibration Curve
4.5. Continuous Fluorescence-Based Acetylation Assay
4.6. Km Determination for Peptide Substrate and AcCoA
4.7. DMSO Effect Determination
4.8. Stability Evaluation of Protein and Reagent
4.9. Assay Performance
4.10. High Throughput Screening
4.11. MALDI-MS Acetylation and Inhibition Assay
4.12. IC50 Determination
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnesen, T.; Van Damme, P.; Polevoda, B.; Helsens, K.; Evjenth, R.; Colaert, N.; Varhaug, J.E.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Lillehaug, J.R.; Sherman, F.; et al. Proteomics Analyses Reveal the Evolutionary Conservation and Divergence of N-Terminal Acetyltransferases from Yeast and Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8157–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksnes, H.; Van Damme, P.; Goris, M.; Starheim, K.K.; Marie, M.; Støve, S.I.; Hoel, C.; Kalvik, T.V.; Hole, K.; Glomnes, N.; et al. An Organellar Nα-Acetyltransferase, Naa60, Acetylates Cytosolic n Termini of Transmembrane Proteins and Maintains Golgi Integrity. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksnes, H.; Drazic, A.; Marie, M.; Arnesen, T. First Things First: Vital Protein Marks by N-Terminal Acetyltransferases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnesen, T. Towards a Functional Understanding of Protein N-Terminal Acetylation. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksnes, H.; Ree, R.; Arnesen, T. Co-Translational, Post-Translational, and Non-Catalytic Roles of N-Terminal Acetyltransferases. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 1097–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polevoda, B.; Hoskins, J.; Sherman, F. Properties of Nat4, an N-Acetyltransferase of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae That Modifies N Termini of Histones H2A and H4. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 2913–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, O.; Wang, X.; Waterborg, J.H.; Sternglanz, R. An Nα-Acetyltransferase Responsible for Acetylation of the N-Terminal Residues of Histones H4 and H2A. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38109–38113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, K.; Van Damme, P.; Dalva, M.; Aksnes, H.; Glomnes, N.; Varhaug, J.E.; Lillehaug, J.R.; Gevaert, K.; Arnesen, T. The Human N-Alpha-Acetyltransferase 40 (HNaa40p/HNatD) Is Conserved from Yeast and N-Terminally Acetylates Histones H2A and H4. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magin, R.S.; Liszczak, G.P.; Marmorstein, R. The Molecular Basis for Histone H4- and H2A-Specific Amino-Terminal Acetylation by NatD. Structure 2015, 23, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, D.; Kirmizis, A. Depletion of Histone N-Terminal-Acetyltransferase Naa40 Induces P53-Independent Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells via the Mitochondrial Pathway. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriadou, C.; Pavlou, D.; Mpekris, F.; Achilleos, C.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Zaravinos, A.; Papageorgis, P.; Kirmizis, A. NAA40 Contributes to Colorectal Cancer Growth by Controlling PRMT5 Expression. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Chen, A.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Nie, M.; Wang, C.; Ding, H.; Yao, B.; et al. NatD Promotes Lung Cancer Progression by Preventing Histone H4 Serine Phosphorylation to Activate Slug Expression. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evjenth, R.; Hole, K.; Ziegler, M.; Lillehaug, J.R. Application of Reverse-Phase HPLC to Quantify Oligopeptide Acetylation Eliminates Interference from Unspecific Acetyl CoA Hydrolysis. BMC Proc. 2009, 3, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evjenth, R.H.; Van Damme, P.; Gevaert, K.; Arnesen, T. HPLC-Based Quantification of In Vitro N-Terminal Acetylation. In Protein Acetylation: Methods and Protocols; Hake, S.B., Janzen, C.J., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Drazic, A.; Arnesen, T. [14C]-Acetyl-Coenzyme A-Based In Vitro N-Terminal Acetylation Assay. In Protein Terminal Profiling: Methods and Protocols; Schilling, O., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue Sulfhydryl Groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyn, H.; Thompson, P.R.; Arnesen, T. DTNB-Based Quantification of In Vitro Enzymatic N-Terminal Acetyltransferase Activity. In Protein Terminal Profiling: Methods and Protocols; Schilling, O., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Yasgar, A.; Peterson, D.L.; Zakharov, A.; Talley, D.; Chih-Chien Cheng, K.; Jadhav, A.; Simeonov, A.; Huang, R. Optimization of High-Throughput Methyltransferase Assays for the Discovery of Small Molecule Inhibitors. ACS Comb. Sci. 2020, 22, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Xi, Z. A Highly Sensitive Fluorescence Probe for Fast Thiol-Quantification Assay of Glutathione Reductase. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4034–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yang, C.; Zheng, Y.G. Comparative Studies of Thiol-Sensitive Fluorogenic Probes for HAT Assays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagnon, A.; Corbeil, M. Use of an Organic Buffer (Hepes) in Human Lymphocytoid Cell Line Cultures. In Vitro 1973, 8, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.D.; Cox, P. Use of a New Buffer in the Culture of Animal Cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1968, 2, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.L.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hanjra, P.; Peterson, D.L.; Huang, R. Kinetic Mechanism of Protein N-Terminal Methyltransferase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 11601–11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.L.; Hanjra, P.; Zhang, G.; Mackie, B.D.; Peterson, D.L.; Huang, R. A Direct, Ratiometric, and Quantitative MALDI–MS Assay for Protein Methyltransferases and Acetyltransferases. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, Y.G.; Nieves, E.; Angeletti, R.H.; Stanley, E.R. Removal of Detergents from Protein Digests for Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 382, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avendaño, C.; Menéndez, J.C. Chapter 14 Drugs That Modulate Resistance to Antitumor Agents. In Medicinal Chemistry of Anticancer Drugs, 2nd ed.; Avendaño, C., Menéndez, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 655–700. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Chung, T.D.Y.; Oldenburg, K.R. A Simple Statistical Parameter for Use in Evaluation and Validation of High Throughput Screening Assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ID | Structure | %Inhibition at 10 μM | ID | Structure | %Inhibition at 10 μM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorescence | MALDI-MS | Fluorescence | MALDI-MS | ||||
| P1401H06 | 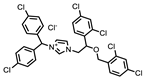 | 51%, 92% | 17% | P1403K20 (Mitoxantrone) |  | 41%, 49% | 0% |
| P1401K09 (ATA) | 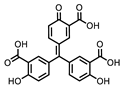 | 87%, 89% | 78% | P1404C10 (Reactive blue 2) | 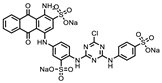 | 61%, 67% | 100% |
| P1402C17 | 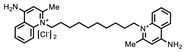 | 63%, 54% | 0% | P1404G18 (SCH-202676) | 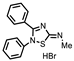 | 71%, 79% | 11% |
| P1403H18 (Cisplatin) | Pt(NH3)2Cl2 | 43%, 45% | 86% | P1404L15 (Tyrphostin B44(-)) | 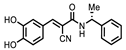 | 56%, 48% | 50% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, Y.-H.; Chen, L.; Huang, R. Development of A Continuous Fluorescence-Based Assay for N-Terminal Acetyltransferase D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020594
Ho Y-H, Chen L, Huang R. Development of A Continuous Fluorescence-Based Assay for N-Terminal Acetyltransferase D. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020594
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Yi-Hsun, Lan Chen, and Rong Huang. 2021. "Development of A Continuous Fluorescence-Based Assay for N-Terminal Acetyltransferase D" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020594
APA StyleHo, Y.-H., Chen, L., & Huang, R. (2021). Development of A Continuous Fluorescence-Based Assay for N-Terminal Acetyltransferase D. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020594





