Concepts in Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Four Main Concepts for Conditionally Replicating Adenoviruses Used in Actual Clinical Trials
2.1. Specific Cellular Promoters Control E1A and Adenoviral Replication
2.2. Modifications in E1A Control Specificity of Replication
2.2.1. E1A Deletions: Delta 24
2.2.2. E1A 13S Deletion: Dl520, Ad-Delo3-RGD (XVir-N-31)
2.2.3. E1B55K Deletion: Dl1520 (ONYX-015), Oncorine (H101)
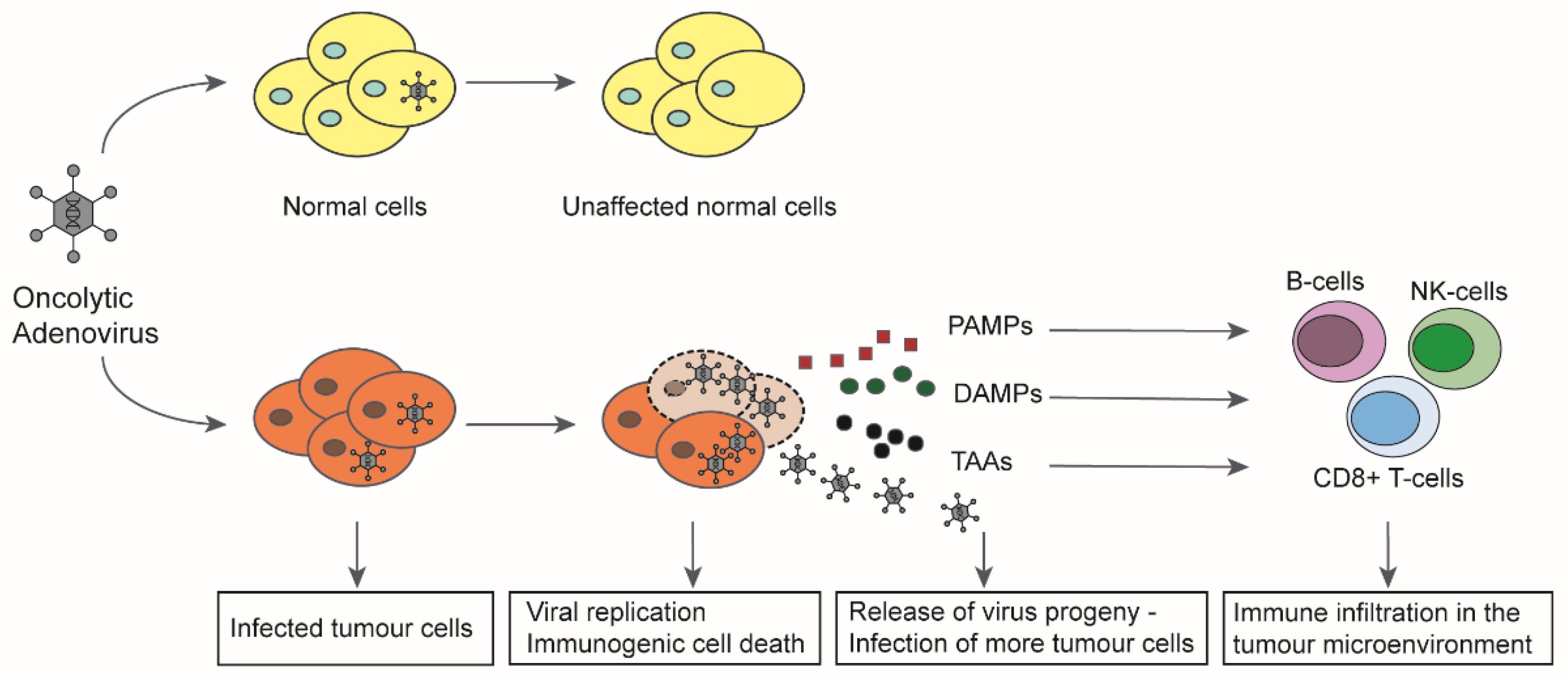
3. Oncolytic Adenoviruses and the Immune System
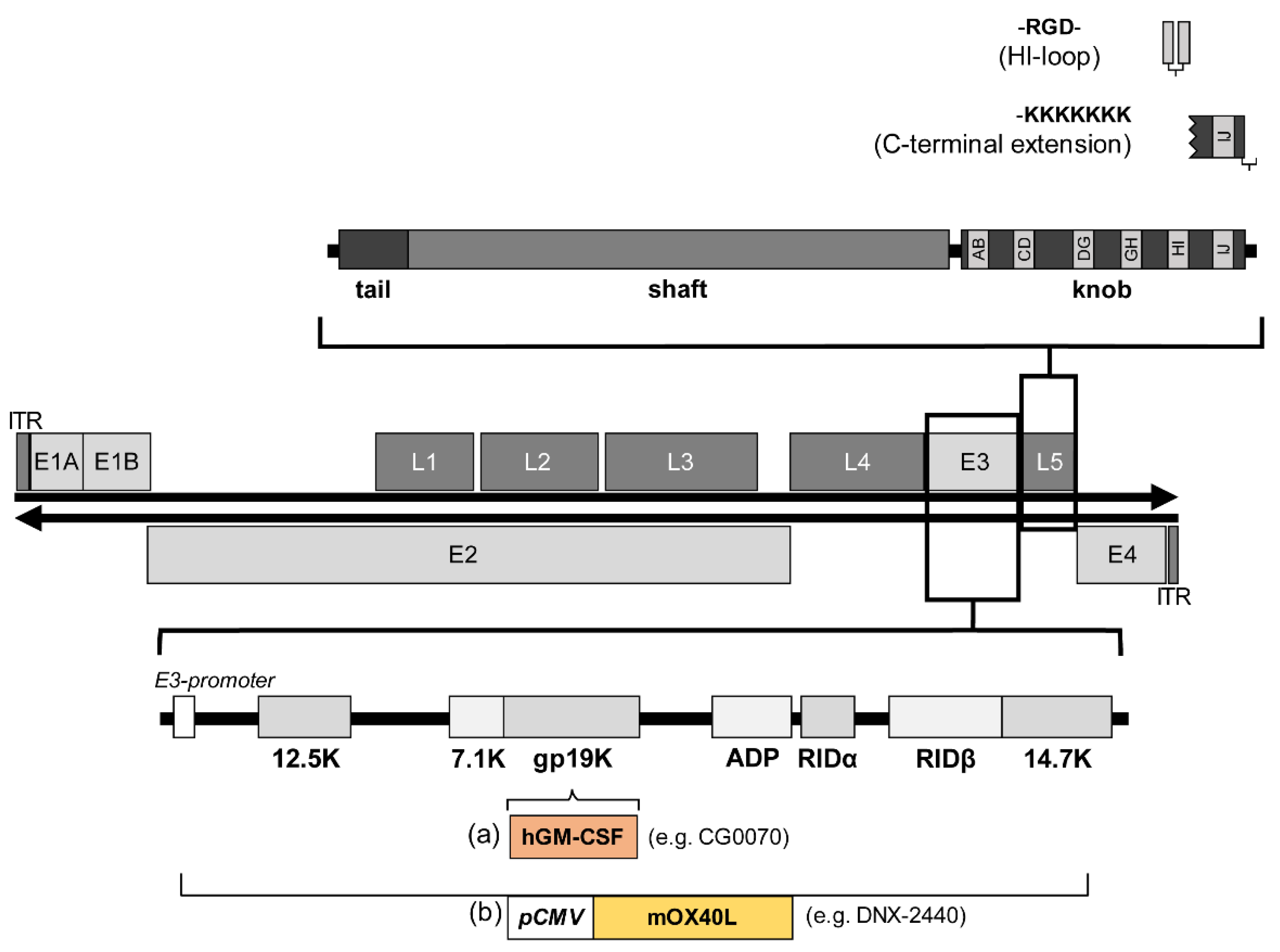
4. Arming of Adenoviral Vectors to Improve Their Therapeutic Effect
4.1. Strategies to Include Transgenes in Adenoviral Vectors
4.2. Transgenes That Confer Improved Therapeutic Effect
5. Delivery and Tropism of Oncolytic Adenoviruses
5.1. Genetic Modifications to Alter the Tropism of Adenoviruses for Clinical Use
5.2. Modification of Natural Tropism
5.3. Delivery Strategies
6. Clinical Trials with Oncolytic Adenoviruses
6.1. Clinical Vectors with Specific Cellular Promoters That Control E1A
6.2. Clinical Vectors with E1A Deletion: Ad5-Delta-24
6.3. Clinical Vectors with Specific Cellular Promoters That Control E1A-Delta-24
6.4. Clinical Vectors with E1B55K Deletions
6.5. Clinical Vectors Based on Direct Evolution
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow, L.T.; Gelinas, R.E.; Broker, T.R.; Roberts, R.J. An amazing sequence arrangement at the 5′ ends of adenovirus 2 messenger RNA. Cell 1977, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdi, I.; Reichel, R.; Nevins, J.R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell 1986, 45, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, J.; Perez-Illana, M.; Martin-Gonzalez, N.; San Martin, C. Adenovirus Structure: What Is New? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelvink, P.W.; Kovesdi, I.; Wickham, T.J. Comparative analysis of adenovirus fiber-cell interaction: Adenovirus type 2 (Ad2) and Ad9 utilize the same cellular fiber receptor but use different binding strategies for attachment. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7614–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, I.; Murray, S.M.; Reynolds, C.J.; Altmann, D.M.; Boyton, R.J. Comparative systematic review and meta-analysis of reactogenicity, immunogenicity and efficacy of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, A.; Haase, R.; Schepers, A.; Deutsch, M.J.; Lipps, H.J.; Baiker, A. Episomal vectors for gene therapy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2008, 8, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.M.; Singh, G.; Lee, J.Y.; Dehghan, S.; Rajaiya, J.; Liu, E.B.; Yousuf, M.A.; Betensky, R.A.; Jones, M.S.; Dyer, D.W.; et al. Molecular evolution of human adenoviruses. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.S., 2nd; Harrach, B.; Ganac, R.D.; Gozum, M.M.; Dela Cruz, W.P.; Riedel, B.; Pan, C.; Delwart, E.L.; Schnurr, D.P. New adenovirus species found in a patient presenting with gastroenteritis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5978–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantwill, K.; Naumann, U.; Seznec, J.; Girbinger, V.; Lage, H.; Surowiak, P.; Beier, D.; Mittelbronn, M.; Schlegel, J.; Holm, P.S. YB-1 dependent oncolytic adenovirus efficiently inhibits tumor growth of glioma cancer stem like cells. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bett, A.J.; Haddara, W.; Prevec, L.; Graham, F.L. An efficient and flexible system for construction of adenovirus vectors with insertions or deletions in early regions 1 and 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8802–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Mese, K.; Bunz, O.; Ehrhardt, A. State-of-the-art human adenovirus vectorology for therapeutic approaches. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 3609–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, F.L.; Smiley, J.; Russell, W.C.; Nairn, R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 36, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, C.; Harlow, E. Differential splicing yields novel adenovirus 5 E1A mRNAs that encode 30 kd and 35 kd proteins. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perricaudet, M.; Akusjarvi, G.; Virtanen, A.; Pettersson, U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature 1979, 281, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.R.; Zhang, A.; Tessier, T.M.; Gameiro, S.F.; Mymryk, J.S. Hacking the Cell: Network Intrusion and Exploitation by Adenovirus E1A. mBio 2018, 9, e00390-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Fueyo, J.; Krasnykh, V.; Reynolds, P.N.; Curiel, D.T.; Alemany, R. A conditionally replicative adenovirus with enhanced infectivity shows improved oncolytic potency. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.B.; Makhija, S.K.; Lu, B.; Wang, M.; Rivera, A.A.; Kim-Park, S.; Ulasov, I.V.; Zhou, F.; Alvarez, R.D.; Siegal, G.P.; et al. Incorporating the survivin promoter in an infectivity enhanced CRAd-analysis of oncolysis and anti-tumor effects in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Shen, A.; Boyle, L.; Kunich, J.; Pandey, K.; Lemmon, M.; Hermiston, T.; Giedlin, M.; McCormick, F.; Fattaey, A. Selectively replicating adenoviruses targeting deregulated E2F activity are potent, systemic antitumor agents. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Banerjee, N.S.; Rivera, A.A.; Wang, M.; Chow, L.T.; Broker, T.R.; Curiel, D.T.; Nettelbeck, D.M. Analyses of melanoma-targeted oncolytic adenoviruses with tyrosinase enhancer/promoter-driven E1A, E4, or both in submerged cells and organotypic cultures. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 437–449. [Google Scholar]
- Leja, J.; Dzojic, H.; Gustafson, E.; Oberg, K.; Giandomenico, V.; Essand, M. A novel chromogranin-A promoter-driven oncolytic adenovirus for midgut carcinoid therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.C.; Chen, Y.; Seng, M.; Dilley, J.; Henderson, D.R. The addition of adenovirus type 5 region E3 enables calydon virus 787 to eliminate distant prostate tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4200–4203. [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck, P.L.; Chang, Y.N.; Hay, C.; Golightly, D.; Stewart, D.; Lin, J.; Phipps, S.; Chiang, Y.L. A novel tumor-specific replication-restricted adenoviral vector for gene therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, S.J.; Prater, C.A.; Dean, D.C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature 1992, 358, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, E.S.; Nambiar, R.; Rosario, S.R.; Smiraglia, D.J.; Goodrich, D.W.; Witkiewicz, A.K. Pan-cancer molecular analysis of the RB tumor suppressor pathway. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattaey, A.R.; Harlow, E.; Helin, K. Independent regions of adenovirus E1A are required for binding to and dissociation of E2F-protein complexes. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 7267–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nevins, J.R. Transcriptional regulation. A closer look at E2F. Nature 1992, 358, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, P.; Ruley, H.E.; Harlow, E. Two regions of the adenovirus early region 1A proteins are required for transformation. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fueyo, J.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Alemany, R.; Lee, P.S.; McDonnell, T.J.; Mitlianga, P.; Shi, Y.X.; Levin, V.A.; Yung, W.K.; Kyritsis, A.P. A mutant oncolytic adenovirus targeting the Rb pathway produces anti-glioma effect in vivo. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cai, R.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Q.; Wei, X.; Zhang, H.; Qian, C. The oncolytic adenovirus targeting to TERT and RB pathway induced specific and potent anti-tumor efficacy in vitro and in vivo for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, E.; Milenova, I.; Wenthe, J.; Stahle, M.; Leja-Jarblad, J.; Ullenhag, G.; Dimberg, A.; Moreno, R.; Alemany, R.; Loskog, A. Shaping the Tumor Stroma and Sparking Immune Activation by CD40 and 4-1BB Signaling Induced by an Armed Oncolytic Virus. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5846–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascallo, M.; Alonso, M.M.; Rojas, J.J.; Perez-Gimenez, A.; Fueyo, J.; Alemany, R. Systemic toxicity-efficacy profile of ICOVIR-5, a potent and selective oncolytic adenovirus based on the pRB pathway. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.J.; Cascallo, M.; Guedan, S.; Gros, A.; Martinez-Quintanilla, J.; Hemminki, A.; Alemany, R. A modified E2F-1 promoter improves the efficacy to toxicity ratio of oncolytic adenoviruses. Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, A.; Gimenez-Alejandre, M.; Rojas, J.J.; Moreno, R.; Bazan-Peregrino, M.; Cascallo, M.; Alemany, R. Safety and efficacy of VCN-01, an oncolytic adenovirus combining fiber HSG-binding domain replacement with RGD and hyaluronidase expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, G.; SivaRaman, L.; Murthy, S.; Domer, P.; Thimmappaya, B. In vivo identification of multiple promoter domains of adenovirus EIIA-late promoter. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, P.S.; Bergmann, S.; Jurchott, K.; Lage, H.; Brand, K.; Ladhoff, A.; Mantwill, K.; Curiel, D.T.; Dobbelstein, M.; Dietel, M.; et al. YB-1 relocates to the nucleus in adenovirus-infected cells and facilitates viral replication by inducing E2 gene expression through the E2 late promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10427–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasham, A.; Print, C.G.; Woolley, A.G.; Dunn, S.E.; Braithwaite, A.W. YB-1: Oncoprotein, prognostic marker and therapeutic target? Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargou, R.C.; Jurchott, K.; Wagener, C.; Bergmann, S.; Metzner, S.; Bommert, K.; Mapara, M.Y.; Winzer, K.J.; Dietel, M.; Dorken, B.; et al. Nuclear localization and increased levels of transcription factor YB-1 in primary human breast cancers are associated with intrinsic MDR1 gene expression. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, E.; En-Nia, A.; Wiesmann, F.; Krings, R.; Djudjaj, S.; Breuer, E.; Fuchs, T.; Wild, P.J.; Hartmann, A.; Dunn, S.E.; et al. Nuclear detection of Y-box protein-1 (YB-1) closely associates with progesterone receptor negativity and is a strong adverse survival factor in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heumann, A.; Kaya, O.; Burdelski, C.; Hube-Magg, C.; Kluth, M.; Lang, D.S.; Simon, R.; Beyer, B.; Thederan, I.; Sauter, G.; et al. Up regulation and nuclear translocation of Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) is linked to poor prognosis in ERG-negative prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieler, A.; Mantwill, K.; Dravits, T.; Bernshausen, A.; Glockzin, G.; Kohler-Vargas, N.; Lage, H.; Gansbacher, B.; Holm, P.S. Novel three-pronged strategy to enhance cancer cell killing in glioblastoma cell lines: Histone deacetylase inhibitor, chemotherapy, and oncolytic adenovirus dl520. Hum. Gene Ther. 2006, 17, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, K.P.; Overhauser, J.; Babiss, L.E.; Ginsberg, H.S.; Jones, N.C. Transformation properties of type 5 adenovirus mutants that differentially express the E1A gene products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5734–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognoni, E.; Widmaier, M.; Haczek, C.; Mantwill, K.; Holzmuller, R.; Gansbacher, B.; Kolk, A.; Schuster, T.; Schmid, R.M.; Saur, D.; et al. Adenovirus-based virotherapy enabled by cellular YB-1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czolk, R.; Schwarz, N.; Koch, H.; Schotterl, S.; Wuttke, T.V.; Holm, P.S.; Huber, S.M.; Naumann, U. Irradiation enhances the therapeutic effect of the oncolytic adenovirus XVir-N-31 in brain tumor initiating cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbas, M.; White, E. Wild-type p53 mediates apoptosis by E1A, which is inhibited by E1B. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.D.; Berk, A.J. Adenovirus proteins from both E1B reading frames are required for transformation of rodent cells by viral infection and DNA transfection. Virology 1987, 156, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, J.R.; Kirn, D.H.; Williams, A.; Heise, C.; Horn, S.; Muna, M.; Ng, L.; Nye, J.A.; Sampson-Johannes, A.; Fattaey, A.; et al. An adenovirus mutant that replicates selectively in p53-deficient human tumor cells. Science 1996, 274, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, J.N.; Berk, A.J. p53-Independent and -dependent requirements for E1B-55K in adenovirus type 5 replication. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5333–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, C.C.; Johnson, L.; Bagus, B.; Choi, S.; Nicholas, C.; Shen, A.; Boyle, L.; Pandey, K.; Soria, C.; Kunich, J.; et al. Late viral RNA export, rather than p53 inactivation, determines ONYX-015 tumor selectivity. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Fang, H. Clinical trials with oncolytic adenovirus in China. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2007, 7, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestwich, R.J.; Errington, F.; Diaz, R.M.; Pandha, H.S.; Harrington, K.J.; Melcher, A.A.; Vile, R.G. The case of oncolytic viruses versus the immune system: Waiting on the judgment of Solomon. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervera-Carrascon, V.; Havunen, R.; Hemminki, A. Oncolytic adenoviruses: A game changer approach in the battle between cancer and the immune system. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunliffe, T.G.; Bates, E.A.; Parker, A.L. Hitting the Target but Missing the Point: Recent Progress towards Adenovirus-Based Precision Virotherapies. Cancers 2020, 12, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Bruni, D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davola, M.E.; Mossman, K.L. Oncolytic viruses: How “lytic” must they be for therapeutic efficacy? Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1581528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.C.; Hallden, G.; Wang, Y.; Brooks, G.; Francis, J.; Lemoine, N.; Kirn, D. An E1B-19 kDa gene deletion mutant adenovirus demonstrates tumor necrosis factor-enhanced cancer selectivity and enhanced oncolytic potency. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 786–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauthoff, H.; Heitner, S.; Rom, W.N.; Hay, J.G. Deletion of the adenoviral E1b-19kD gene enhances tumor cell killing of a replicating adenoviral vector. Hum. Gene Ther. 2000, 11, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, R.V.; Galoforo, S.S.; Corry, P.M.; Lee, Y.J. Adenoviral-mediated transfer of a heat-inducible double suicide gene into prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, J.; Sonenberg, N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature 1988, 334, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.D.; King, A.M.; Thomas, G.P. Cleavage of foot-and-mouth disease virus polyprotein is mediated by residues located within a 19 amino acid sequence. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 2727–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, L.K.; Hermiston, T. Gene delivery from the E3 region of replicating human adenovirus: Evaluation of the E3B region. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Alemany, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Curiel, D.T. The presence of the adenovirus E3 region improves the oncolytic potency of conditionally replicative adenoviruses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 3348–3359. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.; Ge, Y.; Ko, D.; Yendluri, S.; Laflamme, G.; Hawkins, L.; Jooss, K. Comparison of the E3 and L3 regions for arming oncolytic adenoviruses to achieve a high level of tumor-specific transgene expression. Cancer Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauthoff, H.; Pipiya, T.; Heitner, S.; Chen, S.; Norman, R.G.; Rom, W.N.; Hay, J.G. Late expression of p53 from a replicating adenovirus improves tumor cell killing and is more tumor cell specific than expression of the adenoviral death protein. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kale, V.; Chen, M. Gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freytag, S.O.; Stricker, H.; Pegg, J.; Paielli, D.; Pradhan, D.G.; Peabody, J.; DePeralta-Venturina, M.; Xia, X.; Brown, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Phase I study of replication-competent adenovirus-mediated double-suicide gene therapy in combination with conventional-dose three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed, intermediate- to high-risk prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7497–7506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brachtlova, T.; van Ginkel, J.-W.; Luinenburg, M.J.; de Menezes, R.X.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Pegtel, D.M.; Dong, W.; de Gruijl, T.D.; van Beusechem, V.W. Expression of Oncolytic Adenovirus-encoded RNAi Molecules is most effective in a pri-miRNA precursor format. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 19, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedan, S.; Gros, A.; Cascallo, M.; Vile, R.; Mercade, E.; Alemany, R. Syncytia formation affects the yield and cytotoxicity of an adenovirus expressing a fusogenic glycoprotein at a late stage of replication. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, A.; Martinez-Quintanilla, J.; Puig, C.; Guedan, S.; Mollevi, D.G.; Alemany, R.; Cascallo, M. Bioselection of a gain of function mutation that enhances adenovirus 5 release and improves its antitumoral potency. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8928–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Rivera-Molina, Y.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Clise-Dwyer, K.; Bover, L.; Vence, L.M.; Yuan, Y.; Lang, F.F.; Toniatti, C.; Hossain, M.B.; et al. Oncolytic Adenovirus and Tumor-Targeting Immune Modulatory Therapy Improve Autologous Cancer Vaccination. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3894–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristol, J.A.; Zhu, M.; Ji, H.; Mina, M.; Xie, Y.; Clarke, L.; Forry-Schaudies, S.; Ennist, D.L. In vitro and in vivo activities of an oncolytic adenoviral vector designed to express GM-CSF. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.H. The promise of 4-1BB (CD137)-mediated immunomodulation and the immunotherapy of cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 222, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liikanen, I.; Tahtinen, S.; Guse, K.; Gutmann, T.; Savola, P.; Oksanen, M.; Kanerva, A.; Hemminki, A. Oncolytic Adenovirus Expressing Monoclonal Antibody Trastuzumab for Treatment of HER2-Positive Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.D.; Hemminki, O.; Diaconu, I.; Hirvinen, M.; Bonetti, A.; Guse, K.; Escutenaire, S.; Kanerva, A.; Pesonen, S.; Loskog, A.; et al. Targeted cancer immunotherapy with oncolytic adenovirus coding for a fully human monoclonal antibody specific for CTLA-4. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanoue, K.; Rosewell Shaw, A.; Watanabe, N.; Porter, C.; Rana, B.; Gottschalk, S.; Brenner, M.; Suzuki, M. Armed Oncolytic Adenovirus-Expressing PD-L1 Mini-Body Enhances Antitumor Effects of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Solid Tumors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Singh, R.; Moore, M.A.; Song, W.R.; Crystal, R.G. Similarity of strain- and route-dependent murine responses to an adenovirus vector using the homologous thrombopoietin cDNA as the reporter genes. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worgall, S.; Wolff, G.; Falck-Pedersen, E.; Crystal, R.G. Innate immune mechanisms dominate elimination of adenoviral vectors following in vivo administration. Hum. Gene Ther. 1997, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, N.; Gao, G.P.; Parr, M.; Johnston, J.; Baradet, T.; Wilson, J.M.; Barsoum, J.; Fawell, S.E. Sequestration of adenoviral vector by Kupffer cells leads to a nonlinear dose response of transduction in liver. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemany, R.; Suzuki, K.; Curiel, D.T. Blood clearance rates of adenovirus type 5 in mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2605–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, M.; Perrotte, P.; Onishi, E.; Harper, M.E.; Dinney, C.; Pagliaro, L.; Wilson, D.R. Biodistribution of an adenoviral vector carrying the luciferase reporter gene following intravesical or intravenous administration to a mouse. Cancer Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Nunes, F.A.; Berencsi, K.; Furth, E.E.; Gonczol, E.; Wilson, J.M. Cellular immunity to viral antigens limits E1-deleted adenoviruses for gene therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4407–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomko, R.P.; Xu, R.; Philipson, L. HCAR and MCAR: The human and mouse cellular receptors for subgroup C adenoviruses and group B coxsackieviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3352–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, T.J.; Mathias, P.; Cheresh, D.A.; Nemerow, G.R. Integrins alpha v beta 3 and alpha v beta 5 promote adenovirus internalization but not virus attachment. Cell 1993, 73, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Kauwe, L.K. Endocytosis of adenovirus and adenovirus capsid proteins. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechner, H.; Haack, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Eizema, K.; Pauschinger, M.; Schoemaker, R.; Veghel, R.; Houtsmuller, A.; Schultheiss, H.P.; et al. Expression of coxsackie adenovirus receptor and alphav-integrin does not correlate with adenovector targeting in vivo indicating anatomical vector barriers. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, A.A.; Davydova, J.; Schierer, S.; Wang, M.; Krasnykh, V.; Yamamoto, M.; Curiel, D.T.; Nettelbeck, D.M. Combining high selectivity of replication with fiber chimerism for effective adenoviral oncolysis of CAR-negative melanoma cells. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, I.; Krasnykh, V.; Miller, C.R.; Wang, M.; Kashentseva, E.; Mikheeva, G.; Belousova, N.; Curiel, D.T. An adenovirus vector with genetically modified fibers demonstrates expanded tropism via utilization of a coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor-independent cell entry mechanism. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9706–9713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnykh, V.; Dmitriev, I.; Mikheeva, G.; Miller, C.R.; Belousova, N.; Curiel, D.T. Characterization of an adenovirus vector containing a heterologous peptide epitope in the HI loop of the fiber knob. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackhall, F.H.; Merry, C.L.; Davies, E.J.; Jayson, G.C. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einfeld, D.A.; Schroeder, R.; Roelvink, P.W.; Lizonova, A.; King, C.R.; Kovesdi, I.; Wickham, T.J. Reducing the native tropism of adenovirus vectors requires removal of both CAR and integrin interactions. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11284–11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, N.; Mizuguchi, H.; Sakurai, F.; Yamaguchi, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Hayakawa, T. Reduction of natural adenovirus tropism to mouse liver by fiber-shaft exchange in combination with both CAR- and alphav integrin-binding ablation. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13062–13072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnykh, V.N.; Mikheeva, G.V.; Douglas, J.T.; Curiel, D.T. Generation of recombinant adenovirus vectors with modified fibers for altering viral tropism. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6839–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirena, D.; Lilienfeld, B.; Eisenhut, M.; Kalin, S.; Boucke, K.; Beerli, R.R.; Vogt, L.; Ruedl, C.; Bachmann, M.F.; Greber, U.F.; et al. The human membrane cofactor CD46 is a receptor for species B adenovirus serotype 3. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4454–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.T.; Rogers, B.E.; Rosenfeld, M.E.; Michael, S.I.; Feng, M.; Curiel, D.T. Targeted gene delivery by tropism-modified adenoviral vectors. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haisma, H.J.; Grill, J.; Curiel, D.T.; Hoogeland, S.; van Beusechem, V.W.; Pinedo, H.M.; Gerritsen, W.R. Targeting of adenoviral vectors through a bispecific single-chain antibody. Cancer Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettelbeck, D.M.; Rivera, A.A.; Kupsch, J.; Dieckmann, D.; Douglas, J.T.; Kontermann, R.E.; Alemany, R.; Curiel, D.T. Retargeting of adenoviral infection to melanoma: Combining genetic ablation of native tropism with a recombinant bispecific single-chain diabody (scDb) adapter that binds to fiber knob and HMWMAA. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliger, P.; Prospero, T.; Winter, G. “Diabodies”: Small bivalent and bispecific antibody fragments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6444–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nord, K.; Gunneriusson, E.; Ringdahl, J.; Stahl, S.; Uhlen, M.; Nygren, P.A. Binding proteins selected from combinatorial libraries of an alpha-helical bacterial receptor domain. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, P.; Magnusson, M.K.; Gunneriusson, E.; Hong, S.S.; Boulanger, P.; Nygren, P.A.; Lindholm, L. Genetic modification of adenovirus 5 tropism by a novel class of ligands based on a three-helix bundle scaffold derived from staphylococcal protein A. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.U.; Thaci, B.; Tobias, A.L.; Auffinger, B.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Kim, C.K.; Yunis, C.; Han, Y.; Alexiades, N.G.; et al. A preclinical evaluation of neural stem cell-based cell carrier for targeted antiglioma oncolytic virotherapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, A.R.; Hong, J.; Li, Y.; Shin, H.C.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.S.; Yun, C.O. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Delivery of an Oncolytic Adenovirus Enhances Antitumor Efficacy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4503–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.U.; Thaci, B.; Alexiades, N.G.; Han, Y.; Qian, S.; Liu, F.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Ulasov, I.Y.; Aboody, K.S.; Lesniak, M.S. Neural stem cell-based cell carriers enhance therapeutic efficacy of an oncolytic adenovirus in an orthotopic mouse model of human glioblastoma. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goradel, N.H.; Mohajel, N.; Malekshahi, Z.V.; Jahangiri, S.; Najafi, M.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K.; Negahdari, B.; Arashkia, A. Oncolytic adenovirus: A tool for cancer therapy in combination with other therapeutic approaches. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8636–8646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, T.; Kagawa, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Shirakiya, Y.; Umeoka, T.; Teraishi, F.; Taki, M.; Kyo, S.; Tanaka, N.; Fujiwara, T. Telomerase-specific replication-selective virotherapy for human cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemunaitis, J.; Tong, A.W.; Nemunaitis, M.; Senzer, N.; Phadke, A.P.; Bedell, C.; Adams, N.; Zhang, Y.A.; Maples, P.B.; Chen, S.; et al. A phase I study of telomerase-specific replication competent oncolytic adenovirus (telomelysin) for various solid tumors. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubczak, J.L.; Ryan, P.; Gorziglia, M.; Clarke, L.; Hawkins, L.K.; Hay, C.; Huang, Y.; Kaloss, M.; Marinov, A.; Phipps, S.; et al. An oncolytic adenovirus selective for retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein pathway-defective tumors: Dependence on E1A, the E2F-1 promoter, and viral replication for selectivity and efficacy. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Packiam, V.T.; Lamm, D.L.; Barocas, D.A.; Trainer, A.; Fand, B.; Davis, R.L., III; Clark, W.; Kroeger, M.; Dumbadze, I.; Chamie, K. An open label, single-arm, phase II multicenter study of the safety and efficacy of CG0070 oncolytic vector regimen in patients with BCG-unresponsive non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Interim results. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2018, 36, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.F.; Conrad, C.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Yung, W.K.A.; Sawaya, R.; Weinberg, J.S.; Prabhu, S.S.; Rao, G.; Fuller, G.N.; Aldape, K.D.; et al. Phase I Study of DNX-2401 (Delta-24-RGD) Oncolytic Adenovirus: Replication and Immunotherapeutic Effects in Recurrent Malignant Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranki, T.; Pesonen, S.; Hemminki, A.; Partanen, K.; Kairemo, K.; Alanko, T.; Lundin, J.; Linder, N.; Turkki, R.; Ristimaki, A.; et al. Phase I study with ONCOS-102 for the treatment of solid tumors—An evaluation of clinical response and exploratory analyses of immune markers. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Moreno, R.; Gil-Martin, M.; Cascallo, M.; de Olza, M.O.; Cuadra, C.; Piulats, J.M.; Navarro, V.; Domenech, M.; Alemany, R.; et al. A Phase 1 Trial of Oncolytic Adenovirus ICOVIR-5 Administered Intravenously to Cutaneous and Uveal Melanoma Patients. Hum. Gene Ther. 2019, 30, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Pasto, G.; Bazan-Peregrino, M.; Olaciregui, N.G.; Restrepo-Perdomo, C.A.; Mato-Berciano, A.; Ottaviani, D.; Weber, K.; Correa, G.; Paco, S.; Vila-Ubach, M.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the RB1 pathway in retinoblastoma with the oncolytic adenovirus VCN-01. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaat9321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganly, I.; Kirn, D.; Eckhardt, G.; Rodriguez, G.I.; Soutar, D.S.; Otto, R.; Robertson, A.G.; Park, O.; Gulley, M.L.; Heise, C.; et al. A phase I study of Onyx-015, an E1B attenuated adenovirus, administered intratumorally to patients with recurrent head and neck cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, M. Oncorine, the World First Oncolytic Virus Medicine and its Update in China. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, I.; Harden, P.; Bauzon, M.; Chartier, C.; Nye, J.; Thorne, S.; Reid, T.; Ni, S.; Lieber, A.; Fisher, K.; et al. Directed evolution generates a novel oncolytic virus for the treatment of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, C.; Sampson-Johannes, A.; Williams, A.; McCormick, F.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Kirn, D.H. ONYX-015, an E1B gene-attenuated adenovirus, causes tumor-specific cytolysis and antitumoral efficacy that can be augmented by standard chemotherapeutic agents. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindupur, S.V.; Schmid, S.C.; Koch, J.A.; Youssef, A.; Baur, E.M.; Wang, D.; Horn, T.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Gschwend, J.E.; Holm, P.S.; et al. STAT3/5 Inhibitors Suppress Proliferation in Bladder Cancer and Enhance Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Ulasov, I.V.; Tyler, M.A.; Sugihara, A.Q.; Molinero, L.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Z.B.; Lesniak, M.S. Low-dose radiation enhances survivin-mediated virotherapy against malignant glioma stem cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5778–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Gao, L.; Yeagy, B.; Reid, T. Virus combinations and chemotherapy for the treatment of human cancers. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2008, 10, 371–379. [Google Scholar]

| Concept: Promoter | Indication | Clinical Trials.gov No. | Vector Name | Construct | Additional Features | Pre-Clinical | I | II | III | Combination | Application of AdV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2F1- promoter | Bladder Cancer | NCT00109655 | CG0070 | Ad5-E2F-E1A-GMCSF | GM-CSF | 2005 | Intravesical | |||||
| NCT02365818 | 2015 completed | Intravesical | ||||||||||
| NCT04452591 | 2020 recruiting | Intravesical | ||||||||||
| NCT04610671 | 2020 recruiting | Nivolumab | Intravesical | |||||||||
| NCT04387461 | 2020 recruiting | Pembrolizumab | Intravesical | |||||||||
| hTERT- promoter | Hepatocellular Carcinoma | NCT02293850 | OBP-301 | Ad5-hTERT-E1A-IRES-E1B | 2014 unknown | Intratumoural | ||||||
| Melanoma | NCT03190824 | 2017 active | Intratumoural | |||||||||
| Solid Tumours | NCT03172819 | 2017 active | Pembrolizumab | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Esophageal Cancer | NCT03213054 | 2017 recruiting | Radiation | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Esophagogastric Adenocarcinoma | NCT03921021 | 2019 recruiting | Pembrolizumab | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | NCT04685499 | 2020 recruiting | Pembrolizumab | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Esophageal and Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma | NCT04391049 | 2020 not recruiting | Paclitaxel, Carboplatin, Radiation | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Survivin- promoter | Glioma | NCT03072134 | CRAd-S-pk7 | NSC-CRAd-Survivin-pk7 | pk7 | 2017 active | Intratumoural | |||||
| CgA- promoter | Neuroendocrine Tumours | NCT02749331 | AdVince | CgA -PTD-miR122 | PTD-peptide, miRNA 122 | 2016 recruiting | Intraarterial | |||||
| Concept: Promoter & Δ24 | Indication | Clinical Trials.gov No. | Vector Name | Construct | Additional Features | Preclinical | I | II | III | Combination | Application of AdV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFP promoter | Hepatocellular Carcinoma | NCT04612504 | SynOV1.1 | Ad5-AFP-delta24-RGD | GM-CSF | 2020 recruiting | Atezolizumab | Intratumoural | ||||
| E2F1 promoter | Melanoma | NCT01864759 | ICOVIR-5 | Ad5-E2F-delta24-RGD | 2013 completed | Intravenous | ||||||
| Solid Tumours | NCT01844661 | Mesenchymal allogenic cells | 2013 completed | Intravenous | ||||||||
| Glioma | NCT04758533 | 2021 not recruiting | Intravenous | |||||||||
| Advanced Solid Tumours Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | NCT02045602 | VCN-01 | Ad5-E2F-delta24-RGD -PH20 | Hyaluronidase (PH20) | 2014 completed | Gemcitabine, Abraxane | Intravenous | |||||
| Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | NCT02045589 | 2014 completed | Gemcitabine, Abraxane | Intravenous | ||||||||
| Refractory Retinoblastoma | NCT03284268 | 2017 recruiting | Intravitreal | |||||||||
| Squamous cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck | NCT03799744 | 2019 recruiting | Durvalumab | Intravenous | ||||||||
| Pancreatic Cancer | NCT02705196 | LOAd-703 | Ad5/35-E2F-delta24 | CD40L, 4-1BBL | 2016 recruiting | Gemcitabine, Nab-Paclitaxel, Atezolizumab | Intratumoural | |||||
| Pancreatic Cancer/Ovarian, biliary, colorectal Cancer | NCT03225989 | 2017 completed | Standard chemotherapy or Gemcitabine | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Colorectal Cancer | NCT03555149 | 2018 recruiting | Standard chemotherapy | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Melanoma | NCT04123470 | 2019 recruiting | Atezolizumab | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Concept: | Indication | Clinical Trials.gov No | Vector Name | Construct | Additional Features | Preclinical | I | II | III | Combination | Application of AdV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ24 | Ovarian Cancer, Primary Peritoneal Cancer | NCT00562003 | Ad5-Delta 24RGD | 2017 completed | Intraperitoneal | |||||||
| Brain Cancer | NCT00805376 | DNX-2401 | Ad5-Delta 24RGD | 2018 completed | Intratumoural | |||||||
| Glioblastoma | NCT01582516 | 2012 completed | Intratumoural | |||||||||
| Glioblastoma or Gliosarcoma | NCT01956734 | 2013 completed | Temozolomide | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Brain Cancer | NCT02798406 | 2016 completed | Pembrolizumab | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Glioblastoma or Gliosarcoma | NCT02197169 | 2014 completed | Interferon-gamma | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Gliomas | NCT03178032 | 2017 active, not recruiting | Radiotherapy, chemotherapy | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Gliomas | NCT03896568 | Ad5-Delta 24RGD | Mesenchymal stem cells as carriers | 2019 recruiting | Intraarterial | |||||||
| Gliomas | NCT03714334 | DNX-2440 | Ad5-delta24-RGD-OX40L | CMV-OX40L-BGHpA repl. E3 | 2018 recruiting | Intratumoural | ||||||
| Glioblastoma and multiple Solid Tumours | NCT04714983 | 2021 recruiting | Intratumoural | |||||||||
| Solid Tumours | NCT01598129 | ONCOS-102 | Ad5/3-delta24-GMCSF | GM-CSF | 2012 completed | Cyclophosphamide | Intratumoural and intravenous | |||||
| Melanoma | NCT03003676 | 2016 active, not recruiting | Cyclophosphamide, Pembrolizumab | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Colorectal, Ovarian, Appendiceal Cancer | NCT02963831 | 2017 active, not recruiting | Durvalumab | Intraperitoneal | ||||||||
| Colorectal, Ovarian, Appendiceal Cancer | NCT03514836 | 2018 active, not recruiting | Durvalumab | Intratumoural | ||||||||
| Prostate Cancer | NCT04097002 | ORCA-010 | Ad5-delta24-RGD | E3/19K-T1 protein | 2019 recruiting | Intratumoural | ||||||
| Melanoma | NCT04217473 | TILT 123 | Ad5/3-delta24-TNFα-IRES-IL2 | TNFα-IRES-IL2 in E3 | 2020 recruiting | Intratumoural | ||||||
| Melanoma, Solid Tumours | NCT04695327 | 2021 recruiting | Intratumoural | |||||||||
| Diverse HER2 positive Solid Tumours | NCT03740256 | CAdVec | Ad5-Delta 24 | HER2-specific autol. CAR T cells | 2018 recruiting | Helper dependent Ad expressing PD-1 minibody | Intratumoural | |||||
| Concept: | Indication | Clinical Trials.gov No. | Vector Name | Construct | Additional Features | Preclinical | I | II | III | Combination | Application of AdV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔE1A 13S | Glioblastoma | 2016-000292-25 (EudraCT no.) | XVir-N-31 | Ad5 E1A13S/E1B19K/E3 deletions, Fibre RGD | 2021 active, not recruiting | Intratumoural | |||||
| ΔE1B 55K | Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma | no number | Ad5 E1B55K/E3 deletions | 2005 approved by the State Food and Drug Administration of China | Cisplatin, 5-Fluorouracil, Adriamycin | Intratumoural | |||||
| Refractory Malignant Ascites | NCT04771676 | Oncorine (H101) | 2021 recruiting | Intraperitoneal | |||||||
| Lung Cancer | NCT02579564 | 2015 active, not recruiting | Gemcitabine, Vinorelbine, Paclitaxel, Pemetrexed, Endostar, Cisplatin | Intrathoracic | |||||||
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | NCT03780049 | 2018 recruiting | Oxaliplatin, 5-Fluorouracil, Leucovorin | Intraarterial | |||||||
| Prostate Cancer | NCT02555397 | Ad5-yCD/ mutTKSR39rep-hIL12 | E1B55K deletion | yCD, mutTk, IL-12 * | 2015 unknown | Intraprostatic | |||||
| Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer | NCT03281382 | 2017 unknown | 5-Fluorocytosine (5-FC), chemotherapy | Intratumoural | |||||||
| Other Approaches | Indication | Clinical Trials.gov No. | Vector Name | Construct | Additional Features | Preclinical | I | II | III | Combination | Application of AdV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evolution | Solid Tumours | NCT02053220 | Enadenotucirev (Colo-Ad1) | Ad3/11 Chimera | 2014 completed | Intravenous | ||||||
| Solid Tumours of Epithelial Origin | NCT02028442 | 2014 completed | Intravenous | |||||||||
| Ovarian Cancer | NCT02028117 | 2014 completed | Intravenous | |||||||||
| Colorectal Cancer, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, Epithelial Tumours | NCT02636036 | 2015, active not recruiting | Nivolumab | Intravenous | ||||||||
| Rectal Cancer | NCT03916510 | 2019 recruiting | Capecitabine, radiation | Intravenous | ||||||||
| Epithelial Tumours | NCT03852511 | NG-350A | Anti-CD40 Ab | 2019 recruiting | Intratumoural, intravenous | |||||||
| Epithelial Tumours | NCT04053283 | NG-641 | FAP/CD3, CXCL9, CXCL10, IFNa | 2019 recruiting | chemotherapy, checkpoint inhibitors | Intratumoural, intravenous | ||||||
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck | NCT04830592 | NG-641 | 2021 active, not recruiting | Pembrolizumab | Intravenous | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mantwill, K.; Klein, F.G.; Wang, D.; Hindupur, S.V.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Holm, P.S.; Nawroth, R. Concepts in Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910522
Mantwill K, Klein FG, Wang D, Hindupur SV, Ehrenfeld M, Holm PS, Nawroth R. Concepts in Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910522
Chicago/Turabian StyleMantwill, Klaus, Florian Gerhard Klein, Dongbiao Wang, Sruthi Vasantamadhava Hindupur, Maximilian Ehrenfeld, Per Sonne Holm, and Roman Nawroth. 2021. "Concepts in Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910522
APA StyleMantwill, K., Klein, F. G., Wang, D., Hindupur, S. V., Ehrenfeld, M., Holm, P. S., & Nawroth, R. (2021). Concepts in Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910522








