Elastic and Ultradeformable Liposomes for Transdermal Delivery of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Liposomes for Transdermal Administration of APIs
2.1. Classification of Liposomes
2.2. Classic Liposomes vs. Elastic/Ultra-Deformable Liposomes
2.3. Composition of Ultra-Deformable Liposomes
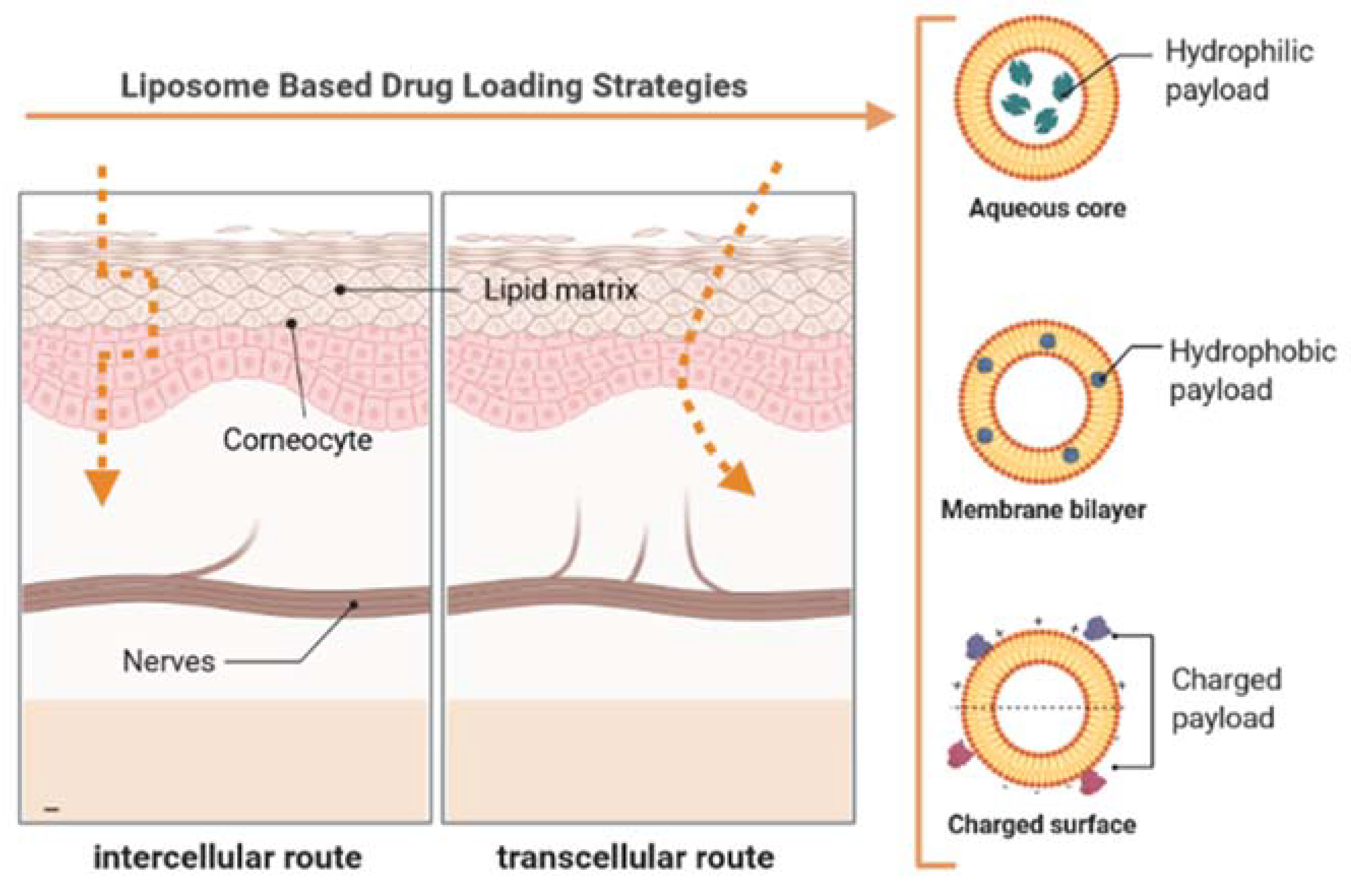
3. Preparation and Analysis of Ultra-Deformable Liposomes
4. Permeation Mechanisms of Conventional vs. Ultra-Deformable Liposomes
5. Influence of Physicochemical Characteristics on Transdermal Administration
6. Applications of Ultra-Deformable Liposomes
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dias-Ferreira, J.; Fernandes, A.R.; Soriano, J.L.; Naveros, B.C.; Severino, P.; da Silva, C.F.; Souto, E.B. Chapter 13—Skin rejuvenation: Biopolymers applied to UV sunscreens and sheet masks. In Biopolymer Membranes and Films; De Moraes, M.A., Da Silva, C.F., Vieira, R.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Fernandes, A.R.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Coutinho, T.E.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, S.B.; Silva, A.M.; Santini, A. Nanomaterials for Skin Delivery of Cosmeceuticals and Pharmaceuticals. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.D.; Verma, S.; Blume, G.; Fahr, A. Particle size of liposomes influences dermal delivery of substances into skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 258, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prow, T.W.; Grice, J.E.; Lin, L.L.; Faye, R.; Butler, M.; Becker, W.; Wurm, E.M.T.; Yoong, C.; Robertson, T.A.; Soyer, H.P.; et al. Nanoparticles and microparticles for skin drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 470–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappinen, S.; Pryazhnikov, E.; Khiroug, L.; Ericson, M.B.; Yliperttula, M.; Urtti, A. Organotypic cell cultures and two-photon imaging: Tools for in vitro and in vivo assessment of percutaneous drug delivery and skin toxicity. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Barry, B.W.; Williams, A.C. Liposomes and skin: From drug delivery to model membranes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.M. Stratum Corneum Defensive Functions: An Integrated View. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashirova, T.N.; Sapunova, A.S.; Lukashenko, S.S.; Burilova, E.A.; Lubina, A.P.; Shaihutdinova, Z.M.; Gerasimova, T.P.; Kovalenko, V.I.; Voloshina, A.D.; Souto, E.B.; et al. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship and biological evaluation of tetracationic gemini Dabco-surfactants for transdermal liposomal formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 575, 118953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Jing, Q.; Hu, H.; He, Z.; Wu, T.; Guo, T.; Feng, N. Sodium dodecyl sulfate improved stability and transdermal delivery of salidroside-encapsulated niosomes via effects on zeta potential. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourasia, M.K.; Kang, L.; Chan, S.Y. Nanosized ethosomes bearing ketoprofen for improved transdermal delivery. Results Pharma Sci. 2011, 1, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Warner, K.S.; Zhang, J.; Sharma, S.; Gale, B.K. Evaluation needle length and density of microneedle arrays in the pretreatment of skin for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Choi, S.-O.; Seo, S.; Bin Choy, Y.; Prausnitz, M.R. A microneedle roller for transdermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, V.; Siddoju, S.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Kim, H.D.; Friden, P.M.; Banga, A.K. Transdermal iontophoretic delivery of terbinafine hydrochloride: Quantitation of drug levels in stratum corneum and underlying skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, E.A.; Bonner, M.C.; Barry, B.W. Electroporation and ultradeformable liposomes; human skin barrier repair by phospholipid. J. Control. Release 2003, 92, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Ryu, H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Choi, K.-S.; Park, H.; Seo, J. Sonophoresis Using Ultrasound Contrast Agents for Transdermal Drug Delivery: An In Vivo Experimental Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geusens, B.; Lambert, J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Buyens, K.; Sanders, N.N.; Van Gele, M. Ultradeformable cationic liposomes for delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) into human primary melanocytes. J. Control. Release 2009, 133, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepps, O.G.; Dancik, Y.; Anissimov, Y.G.; Roberts, M.S. Modeling the human skin barrier—Towards a better understanding of dermal absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimisiaris, S.G.; Marazioti, A.; Kannavou, M.; Natsaridis, E.; Gkartziou, F.; Kogkos, G.; Mourtas, S. Overcoming barriers by local drug delivery with liposomes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 53–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, A.D.; Standish, M.M.; Watkins, J.C.; Weissmann, G. The Diffusion of Ions from a Phospholipid Model Membrane System. In Symposium on Biophysics and Physiology of Biological Transport; Bolis, L., Capraro, V., Porter, K.R., Robertson, J.D., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1967; pp. 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, M.B.R.; Costa, I.D.S.M. Liposomal systems as drug delivery vehicles for dermal and transdermal applications. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Dorotkiewicz-Jach, A. Liposomes as delivery systems for antibiotics. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, R.R.; Torchilin, V.P. Challenges in Development of Targeted Liposomal Therapeutics. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šegota, S.; Heimer, S.; Težak, Đ. New catanionic mixtures of dodecyldimethylammonium bromide/sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate/water: I. Surface properties of dispersed particles. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 274, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firooz, A.; Nafisi, S.; Maibach, H.I. Novel drug delivery strategies for improving econazole antifungal action. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Földvari, M.; Gesztes, A.; Mezei, M. Dermal drug delivery by liposome encapsulation: Clinical and electron microscopic studies. J. Microencapsul. 1990, 7, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, M.M.A.; Abdallah, O.Y.; Naggar, V.F.; Khalafallah, N.M. Lipid vesicles for skin delivery of drugs: Reviewing three decades of research. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 332, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kuijk-Meuwissen, M.E.M.J.; Junginger, H.E.; Bouwstra, J.A. Interactions between liposomes and human skin in vitro, a confocal laser scanning microscopy study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1998, 1371, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, R.; Jose, S.; Mukund, V.P.B.; Vasudevan, D.T. Transferosomes—A vesicular transdermal delivery system for enhanced drug permeation. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, K.R.; Kumar, M.S.; Anbazhagan, S.; Sandhya, S.; Saikumar, P.; Rohit, R.T.; Banji, D. Critical issues related to transfersomes—Novel vesicular system. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2012, 11, 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Godin, B.; Touitou, E. Transdermal skin delivery: Predictions for humans from in vivo, ex vivo and animal models. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.J.; Maibach, H.I. Elastic vesicles as topical/transdermal drug delivery systems. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 27, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, B.A.V.D.; Vroom, J.; Gerritsen, H.; Junginger, H.E.; Bouwstra, J.A. Interactions of elastic and rigid vesicles with human skin in vitro: Electron microscopy and two-photon excitation microscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1999, 1461, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G.; Blume, G. Lipid vesicles penetrate into intact skin owing to the transdermal osmotic gradients and hydration force. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1992, 1104, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Pathak, K. Therapeutic and cosmeceutical potential of ethosomes: An overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.G.S.; Tekade, R.K.; Sharma, P.A.; Darwhekar, G.; Tyagi, A.; Patel, R.P.; Jain, D.K. Ethosomes and ultradeformable liposomes for transdermal delivery of clotrimazole: A comparative assessment. Saudi Pharm. J. 2012, 20, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.K.; Jin, S.-E.; Kim, J.-K.; Park, J.-S.; Park, Y.; Kim, C.-K. Retained topical delivery of 5-aminolevulinic acid using cationic ultradeformable liposomes for photodynamic therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, M.; Caddeo, C.; Sinico, C.; Valenti, D.; Mostallino, M.C.; Biggio, G.; Fadda, A.M. Ex vivo skin delivery of diclofenac by transcutol containing liposomes and suggested mechanism of vesicle–skin interaction. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, A.; Lecomte, F.; Hubert, P.; Ducat, E.; Evrard, B.; Piel, G. Skin penetration behaviour of liposomes as a function of their composition. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-García, R.; Lalatsa, A.; Statts, L.; Bolás-Fernández, F.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Serrano, D.R. Transferosomes as nanocarriers for drugs across the skin: Quality by design from lab to industrial scale. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manconi, M.; Mura, S.; Sinico, C.; Fadda, A.M.; Vila, A.O.; Molina, F. Development and characterization of liposomes containing glycols as carriers for diclofenac. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 342, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanthi, D.; Lakshmi, P.K. Vesicles—Mechanism of transdermal permeation: A review. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2012, 5, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Srisuk, P.; Thongnopnua, P.; Raktanonchai, U.; Kanokpanont, S. Physico-chemical characteristics of methotrexate-entrapped oleic acid-containing deformable liposomes for in vitro transepidermal delivery targeting psoriasis treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 427, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zaafarany, G.M.; Awad, G.A.S.; Holayel, S.M.; Mortada, N.D. Role of edge activators and surface charge in developing ultradeformable vesicles with enhanced skin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Eum, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kang, M.H.; Park, K.H.; Choi, S.E.; Lee, M.W.; Kang, K.H.; Oh, C.H.; Choi, Y.W. Pep-1 peptide-conjugated elastic liposomal formulation of taxifolin glycoside for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 402, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, V.; Mishra, D.; Asthana, A.; Jain, N.K. Transdermal delivery of a pineal hormone: Melatonin via elastic liposomes. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3491–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, A.D.; Standish, M.M.; Watkins, J.C. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J. Mol. Biol. 1965, 13, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayen, J. Micelles, monolayers and biomembranes. M. N. Jones and D. Chapman. Wiley-Liss, New York and Chichester. xii + 252 pages, £36.75 (1995). Cell Biochem. Funct. 1996, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodle, M.C.; Papahadjopoulos, D. [9] Liposome preparation and size characterization. Methods Enzymol. 1989, 171, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šegota, S.; Težak, D. Spontaneous formation of vesicles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 121, 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, L.D.; Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1986, 858, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goñi, F.M.; Alonso, A. Membrane Fusion Induced by Phospholipase C and Sphingomyelinases. Biosci. Rep. 2000, 20, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Edwards, K.A.; Baeumner, A.J. Optimization of DNA-tagged liposomes for use in microtiter plate analyses. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Sitaru, C.; Jakus, Z.; Anderson, K.E.; Damoulakis, G.; Davidson, K.; Hirose, M.; Juss, J.; Oxley, D.; Chessa, T.A.; et al. PI3Kbeta plays a critical role in neutrophil activation by immune complexes. Sci. Signal 2011, 4, 2001617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G.; Gebauer, D. Hydration-Driven Transport of Deformable Lipid Vesicles through Fine Pores and the Skin Barrier. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, N.Ø.; Rønholt, S.; Salte, R.D.; Jorgensen, L.; Thormann, T.; Basse, L.H.; Hansen, J.; Frokjaer, S.; Foged, C. Calcipotriol delivery into the skin with PEGylated liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G.; Schatzlein, A.G.; Richardsen, H. Ultradeformable lipid vesicles can penetrate the skin and other semi-permeable barriers unfragmented. Evidence from double label CLSM experiments and direct size measurements. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2002, 1564, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruta, Y.; Hattori, Y.; Kawano, K.; Obata, Y.; Maitani, Y. Novel ultra-deformable vesicles entrapped with bleomycin and enhanced to penetrate rat skin. J. Control. Release 2006, 113, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Shamim, M.A.; Shahid, A.; Yeung, S.; Andresen, B.T.; Wang, J.; Nekkanti, V.; Meyskens, F.L., Jr.; Kelly, K.M.; Huang, Y. Topical Delivery of Carvedilol Loaded Nano-Transfersomes for Skin Cancer Chemoprevention. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevc, G.; Blume, G. Hydrocortisone and dexamethasone in very deformable drug carriers have increased biological potency, prolonged effect, and reduced therapeutic dosage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2004, 1663, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Ping, Q.; Sun, G.; Jiao, C. Lecithin vesicular carriers for transdermal delivery of cyclosporin A. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 194, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchall, J.C.; Marichal, C.; Campbell, L.; Alwan, A.; Hadgraft, J.; Gumbleton, M. Gene expression in an intact ex-vivo skin tissue model following percutaneous delivery of cationic liposome–plasmid DNA complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, K.; Li, F. Enhancement of skin permeation of docetaxel: A novel approach combining microneedle and elastic liposomes. J. Control. Release 2008, 129, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maghraby, G.M.M.; Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Oestradiol skin delivery from ultradeformable liposomes: Refinement of surfactant concentration. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 196, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosco, D.; Paolino, D.; Maiuolo, J.; Di Marzio, L.; Carafa, M.; Ventura, C.A.; Fresta, M. Ultradeformable liposomes as multidrug carrier of resveratrol and 5-fluorouracil for their topical delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 489, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.-K.; Kim, C.-K. Topical delivery of low-molecular-weight heparin with surface-charged flexible liposomes. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahor, S.; Rawat, A.; Dubey, P.K.; Gupta, P.N.; Khatri, K.; Goyal, A.K.; Vyas, S. Cationic transfersomes based topical genetic vaccine against hepatitis B. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 340, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakar, J.; Sen, S.O.; Nayak, A.K.; Sen, K.K. Formulation, optimization and evaluation of transferosomal gel for transdermal insulin delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2012, 20, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevc, G.; Vierl, U.; Mazgareanu, S. Functional characterisation of novel analgesic product based on self-regulating drug carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 360, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, D.; Khurana, B.; Nanda, S. DoE directed optimization, development and evaluation of resveratrol loaded ultradeformable vesicular cream for topical antioxidant benefits. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.N.; Mishra, V.; Rawat, A.; Dubey, P.; Mahor, S.; Jain, S.; Chatterji, D.; Vyas, S.P. Non-invasive vaccine delivery in transfersomes, niosomes and liposomes: A comparative study. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, J.; Maidana, C.; Esteva, M.I.; Salomon, C.; Morilla, M.J.; Romero, E.L. Sunlight triggered photodynamic ultradeformable liposomes against Leishmania braziliensis are also leishmanicidal in the dark. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrelli, F.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Rabasco, A.M.; Ghelardini, C.; Mura, P. New “drug-in cyclodextrin-in deformable liposomes” formulations to improve the therapeutic efficacy of local anaesthetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 395, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, A.; Aqil, M.; Kohli, K.; Sultana, Y.; Mujeeb, M.; Ali, A. Formulation and optimization of nanotransfersomes using experimental design technique for accentuated transdermal delivery of valsartan. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Dubey, V.; Asthana, A.; Saraf, D.K.; Jain, N.K. Elastic liposomes mediated transcutaneous immunization against Hepatitis B. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4847–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, G.; Piñón, E.; Mendoza, L.; Mendoza, N.; Quintanar, D.; Ganem, A. Formulation and in Vitro, ex Vivo and in Vivo Evaluation of Elastic Liposomes for Transdermal Delivery of Ketorolac Tromethamine. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashyal, S.; Seo, J.-E.; Keum, T.; Noh, G.; Lamichhane, S.; Lee, S. Development, Characterization, and Ex Vivo Assessment of Elastic Liposomes for Enhancing the Buccal Delivery of Insulin. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacha, M.; Faucon, L.; Hamon, E.; Ly, I.; Haltner-Ukomadu, E. Ex vivo transdermal absorption of a liposome formulation of diclofenac. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type | Abbreviation | Size | Other Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multilamellar Vesicles | MV | Diameter between 0.4 and 3.5 µm in diameter, with the average size being about 1 µm | Obtained by simply dispersing the phospholipids in the aqueous medium, and not subject to further processing. Each vesicle consists of several lipid lamellae (around five or more) arranged concentrically, including a fraction of the internal aqueous medium. |
| Large Unilamellar Vesicles | LUV | Diameter greater than 100 nm | Composed by a single layer. |
| Small Unilamellar Vesicles | SUV | Diameter between 25 and 50 nm | |
| Unilamellar vesicles of intermedian size | UVIS | Diameter between 50 and 100 nm | |
| Giant unilamellar vesicles | GiUV | Radius greater than 10 µm | |
| Oligovesicular vesicles | OVV | - | Structures formed by small vesicles incorporated in a larger one. |
| Drug | Therapeutic Indication | Observations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bleomycin | Anti-tumoral | Increased dermal and epidermal permeation | [57] |
| Carvedilol | Skin carcinogenesis | EGF-induced neoplastic transformation of mouse epidermal JB6 P+ cells at non-toxic concentrations | [58] |
| Clotrimazole | Fungal infections | Increased skin permeation and inhibition of fungal growth | [35] |
| Corticosteroids | Anti-inflammatory | Decrease in the dose of corticosteroids needed to suppress edema | [59] |
| Cyclosporine A | Immunosuppression | Increased transepidermal flow | [60] |
| DNA | Gene therapy | Increased cell internalization and gene expression | [61] |
| Diclofenac | Joint anti-inflammatory | Increased skin permeation | [37] |
| Docetaxel | Anti-tumoral | Increased transdermal flow | [62] |
| Estradiol | Hormonal therapy | Increased transepidermal flow | [63] |
| Fluorouracil | Non-melanoma skin cancer | Co-loaded with resveratrol arrested cell proliferation in G1/S, modifying the action of 5-fluorouracil and increasing the activity of resveratrol | [64] |
| Heparin | Antiplatelet agent | Skin permeation | [65] |
| Hepatitis B antigen (anti-HBsAg) | Hepatitis B virus | Increased immune response | [66] |
| Insulin | Diabetes mellitus type 1 | Increased transepidermal flow | [67] |
| Ketoprofen | Anti-inflammatory | Increased drug concentration in muscles | [68] |
| Methotrexate | Psoriasis | Increased permeation and accumulation in the dermis and epidermis | [42] |
| Resveratrol | Antioxidant | Resveratrol-loaded liposomes were formulated in a topical cream retained inherent antioxidant activity of the drug | [69] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souto, E.B.; Macedo, A.S.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Cano, A.; Zielińska, A.; Matos, C.M. Elastic and Ultradeformable Liposomes for Transdermal Delivery of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189743
Souto EB, Macedo AS, Dias-Ferreira J, Cano A, Zielińska A, Matos CM. Elastic and Ultradeformable Liposomes for Transdermal Delivery of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189743
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouto, Eliana B., Ana S. Macedo, João Dias-Ferreira, Amanda Cano, Aleksandra Zielińska, and Carla M. Matos. 2021. "Elastic and Ultradeformable Liposomes for Transdermal Delivery of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189743
APA StyleSouto, E. B., Macedo, A. S., Dias-Ferreira, J., Cano, A., Zielińska, A., & Matos, C. M. (2021). Elastic and Ultradeformable Liposomes for Transdermal Delivery of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189743







