An Attenuated Targeted-TNF Localizes to Tumors In Vivo and Regains Activity at the Site of Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
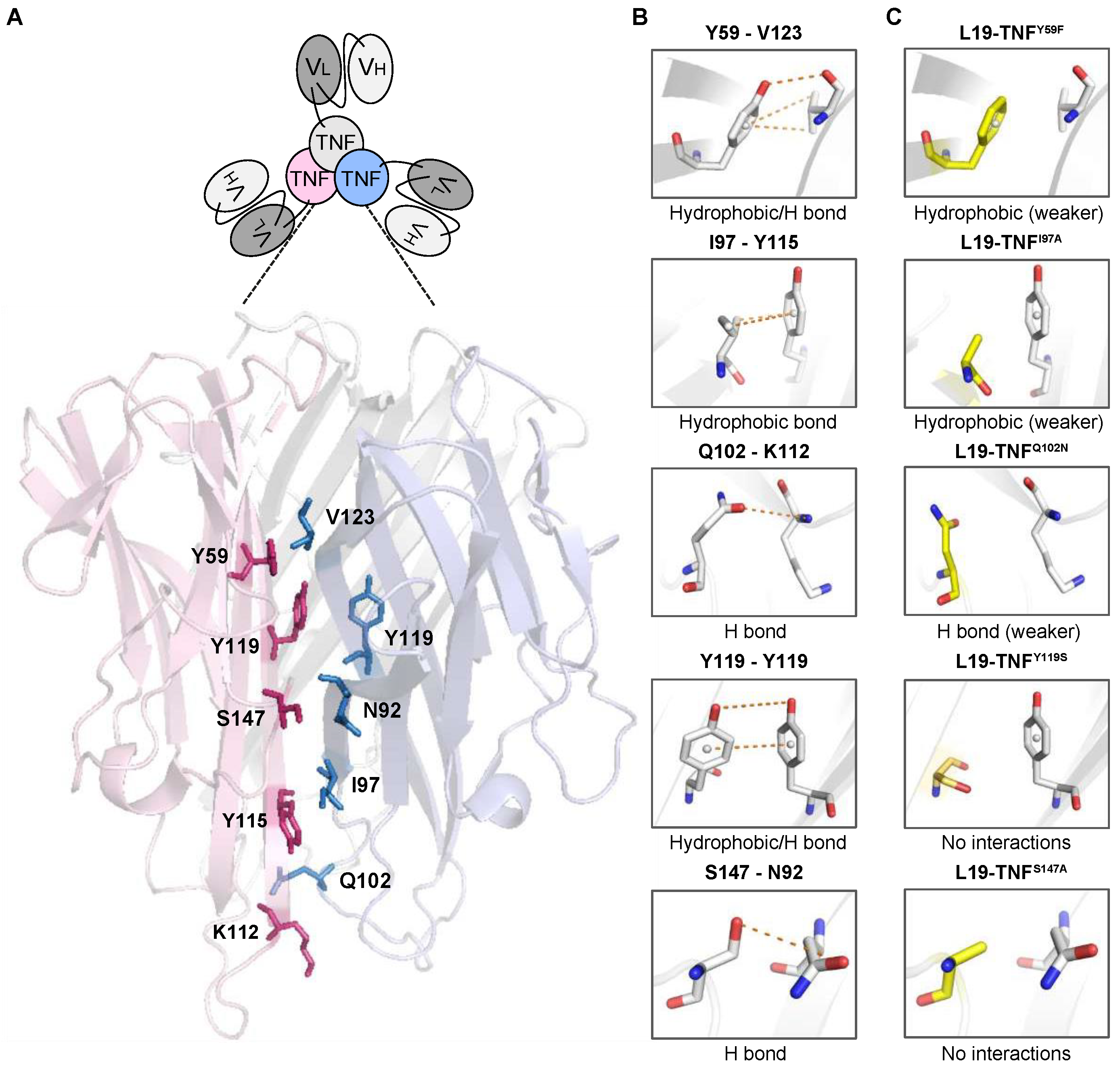
2.1. 3D-Structure Analysis of the Trimeric TNF Reveals Potential Mutations for Depotentiated Versions of the Molecule
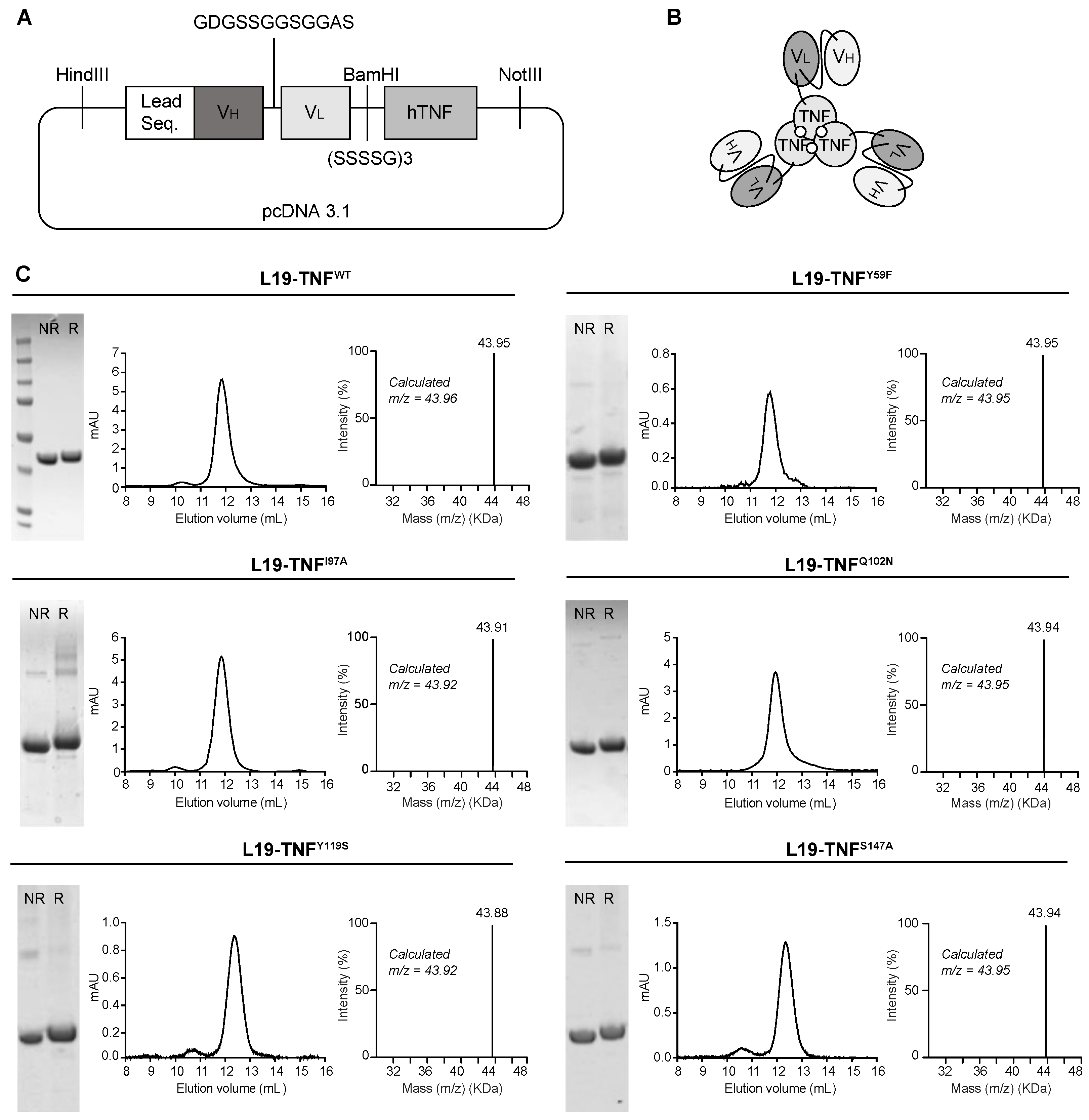
2.2. Production and Characterization of L19-TNF Mutant Fusion Proteins
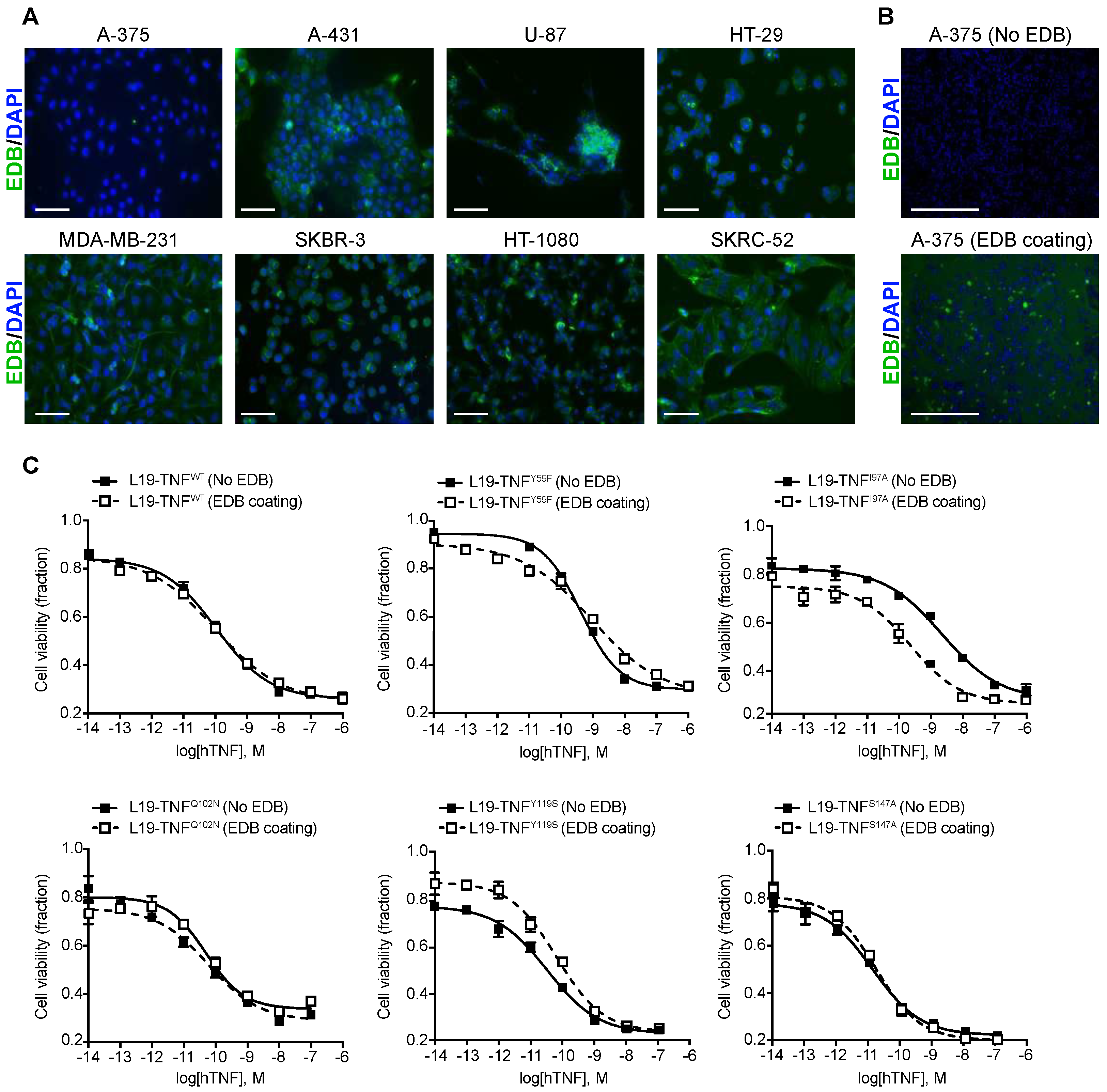
2.3. Conditional In Vitro Cytotoxicity Effect of L19-TNF Mutants upon EDB Concentration
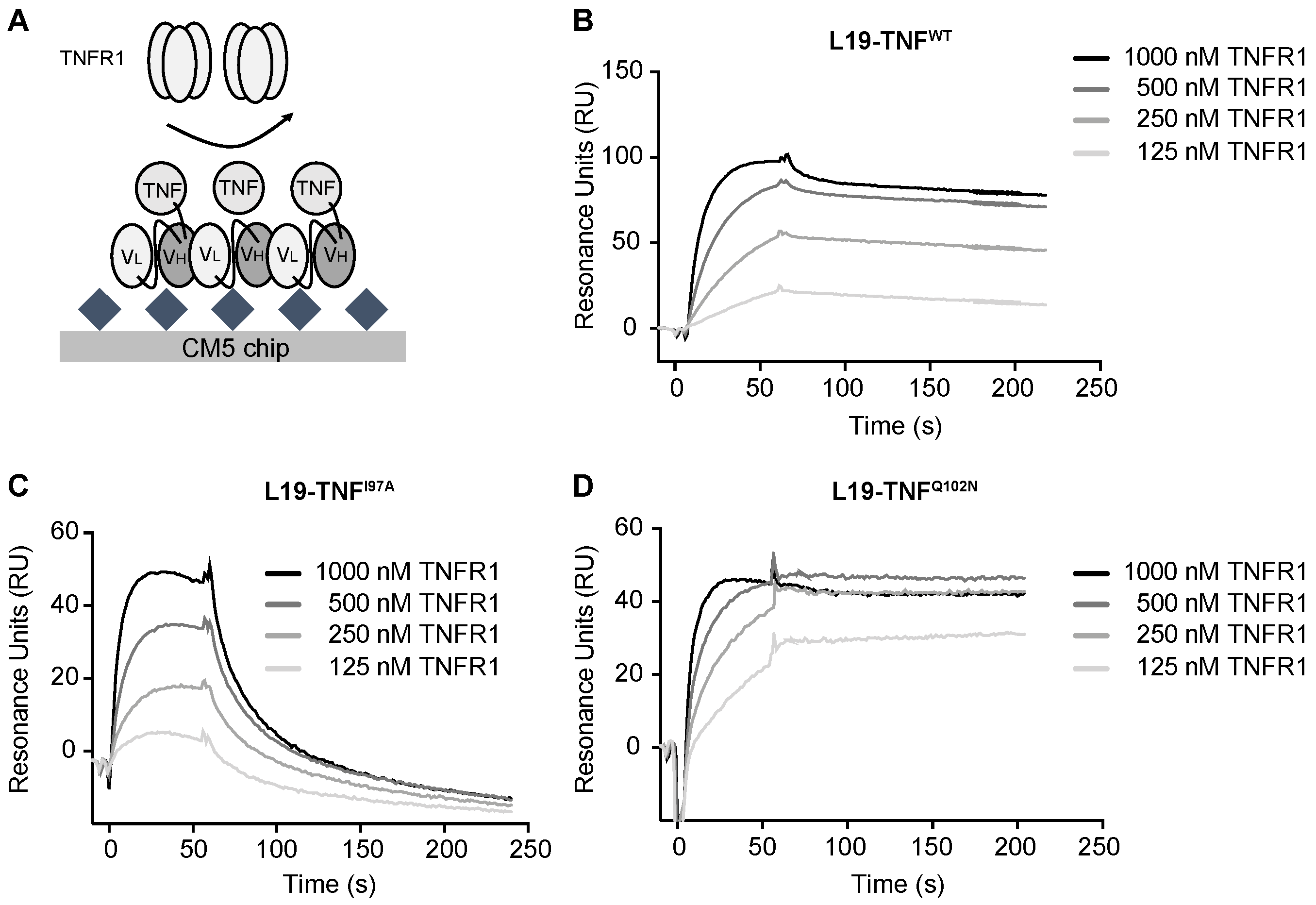
2.4. The Mutant I97A Has Reduced Binding Affinity towards TNFR1
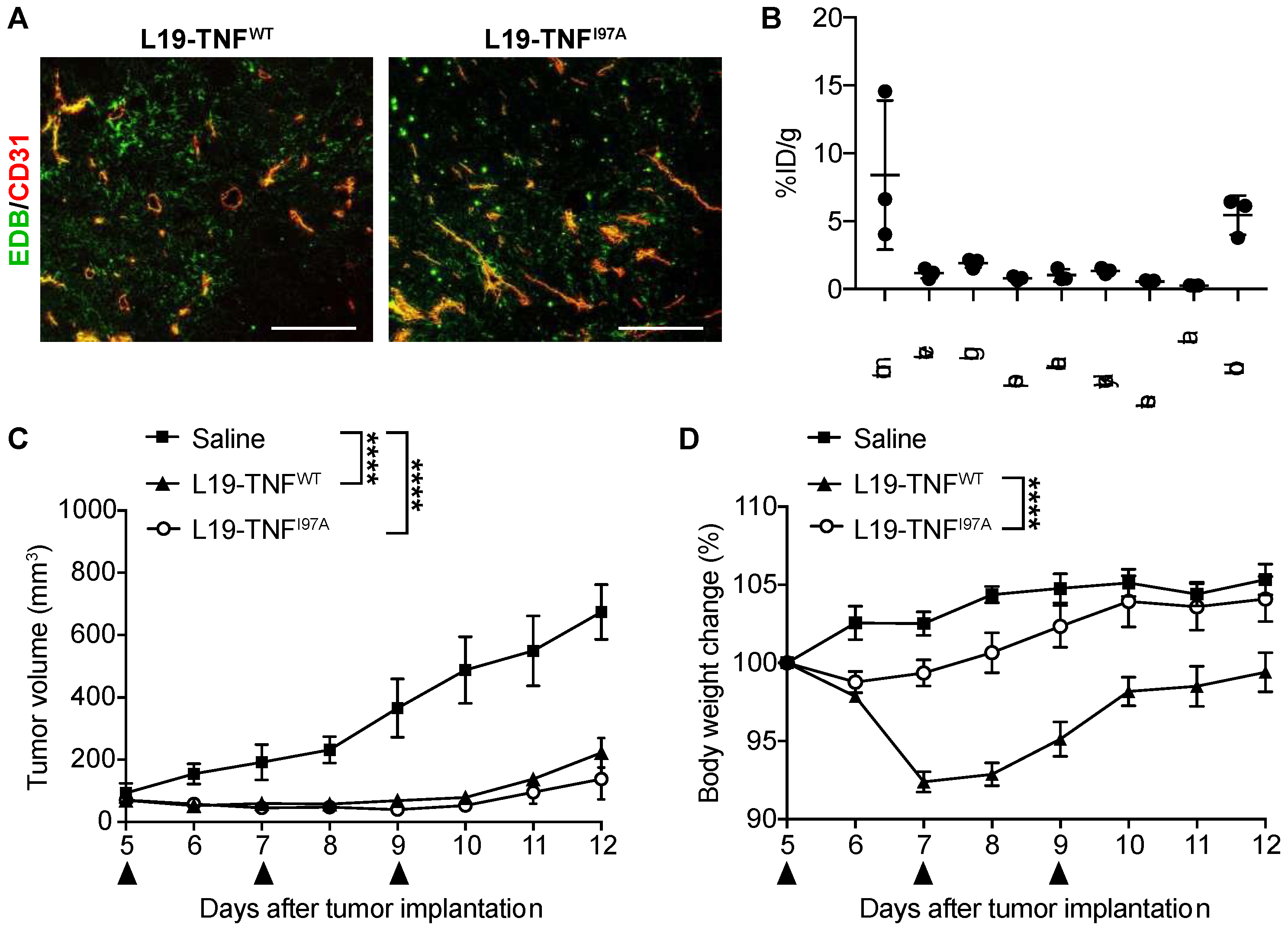
2.5. The I97A Mutant Accumulates at the Tumor Site and Shows High Levels in Blood
2.6. I97A Mutein Retains Anti-Tumor Efficacy While Decreasing Toxicity in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Animals
4.3. Structural Analysis of Human TNF and Design of Mutants
4.4. Cloning, Expression and Biochemical Characterization of Proteins
4.5. Immunofluorescence Experiments on Tumor Cell Lines
4.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assays
4.7. Affinity Measurements
4.8. Biodistribution Studies
4.9. Immunofluorescence Studies on Tissue
4.10. Therapy Experiments
4.11. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.; Margolin, K. Cytokines in cancer immunotherapy. Cancers 2011, 3, 3856–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranoff, G. Cytokines in cancer pathogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudgil, K.D.; Choubey, D. Cytokines in autoimmunity: Role in induction, regulation, and treatment. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, G.; Fisher, R.I.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Sznol, M.; Parkinson, D.R.; Louie, A.C. Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golomb, H.M.; Jacobs, A.; Fefer, A.; Ozer, H.; Thompson, J.; Portlock, C.; Ratain, M.; Golde, D.; Vardiman, J.; Burke, J.S. Alpha-2 interferon therapy of hairy-cell leukemia: A multicenter study of 64 patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 1986, 4, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, A.M.M.; Koops, H.S.; Klausner, J.M.; Kroon, B.B.R.; Schlag, P.M.; Liénard, D.; Van Geel, A.N.; Hoekstra, H.J.; Meller, I.; Nieweg, O.E.; et al. Isolated limb perfusion with tumor necrosis factor and melphalan for limb salvage in 186 patients with locally advanced soft tissue extremity sarcomas: The cumulative multicenter European experience. Ann. Surg. 1996, 224, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutcher, J.P.; Schwartzentruber, D.J.; Kaufman, H.L.; Agarwala, S.S.; Tarhini, A.A.; Lowder, J.N.; Atkins, M.B. High dose interleukin-2 (Aldesleukin)—Expert consensus on best management practices-2014. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quesada, J.R.; Talpaz, M.; Rios, A.; Kurzrock, R.; Gutterman, J.U. Clinical toxicity of interferons in cancer patients: A review. J. Clin. Oncol. 1986, 4, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, M.R.; Merlino, G. The two faces of interferon-γ in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6118–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasek, W.; Zagożdżon, R.; Jakobisiak, M. Interleukin 12: Still a promising candidate for tumor immunotherapy? Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnemolla, B.; Borsi, L.; Balza, E.; Castellani, P.; Meazza, R.; Berndt, A.; Ferrini, S.; Kosmehl, H.; Neri, D.; Zardi, L. Enhancement of the antitumor properties of interleukin-2 by its targeted delivery to the tumor blood vessel extracellular matrix. Blood 2002, 99, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borsi, L.; Balza, E.; Carnemolla, B.; Sassi, F.; Castellani, P.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Birò, A.; Siri, A.; Orecchia, P.; et al. Selective targeted delivery of TNFα to tumor blood vessels. Blood 2003, 102, 4384–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, P.; Stringhini, M.; Ritz, D.; Fugmann, T.; Neri, D. Antibody-based Delivery of TNF to the Tumor Neovasculature Potentiates the Therapeutic Activity of a Peptide Anticancer Vaccine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemmerle, T.; Probst, P.; Giovannoni, L.; Green, A.J.; Meyer, T.; Neri, D. The antibody-based targeted delivery of TNF in combination with doxorubicin eradicates sarcomas in mice and confers protective immunity. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliemann, C.; Palumbo, A.; Zuberbühler, K.; Villa, A.; Kaspar, M.; Trachsel, E.; Klapper, W.; Menssen, H.D.; Neri, D. Complete eradication of human B-cell lymphoma xenografts using rituximab in combination with the immunocytokine L19-IL2. Blood 2009, 113, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van den Heuvel, M.M.; Verheij, M.; Boshuizen, R.; Belderbos, J.; Dingemans, A.M.C.; De Ruysscher, D.; Laurent, J.; Tighe, R.; Haanen, J.; Quaratino, S. NHS-IL2 combined with radiotherapy: Preclinical rationale and phase Ib trial results in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer following first-line chemotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zappasodi, R.; Merghoub, T.; Wolchok, J.D. Emerging Concepts for Immune Checkpoint Blockade-Based Combination Therapies. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillies, S.D.; Lan, Y.; Williams, S.; Carr, F.; Forman, S.; Raubitschek, A.; Lo, K.M. An anti-CD20-IL-2 immunocytokine is highly efficacious in a SCID mouse model of established human B lymphoma. Blood 2005, 105, 3972–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwager, K.; Hemmerle, T.; Aebischer, D.; Neri, D. The immunocytokine L19-IL2 eradicates cancer when used in combination with CTLA-4 blockade or with L19-TNF. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiers, W. Tumor necrosis factor Characterization at the molecular, cellular and in vivo level. FEBS Lett. 1991, 285, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcinotto, A.; Grioni, M.; Jachetti, E.; Curnis, F.; Mondino, A.; Parmiani, G.; Corti, A.; Bellone, M. Targeting TNF-α to Neoangiogenic Vessels Enhances Lymphocyte Infiltration in Tumors and Increases the Therapeutic Potential of Immunotherapy. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2687–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elia, A.R.; Grioni, M.; Basso, V.; Curnis, F.; Freschi, M.; Corti, A.; Mondino, A.; Bellone, M. Targeting tumor vasculature with TNF leads effector t cells to the tumor and enhances therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint blockers in combination with adoptive cell therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2171–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lejeune, F.J.; Liénard, D.; Matter, M.; Rüegg, C. Efficiency of recombinant human TNF in human cancer therapy. Cancer Immun. 2006, 6, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Carswell, E.A.; Old, L.J.; Kassel, R.L.; Green, S.; Fiore, N.; Williamson, B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors (activated macrophage). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creaven, P.J.; Brenner, D.E.; Cowens, J.W.; Huben, R.P.; Wolf, R.M.; Takita, H.; Arbuck, S.G.; Razack, M.S.; Proefrock, A.D. A phase I clinical trial of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor given daily for five days. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1989, 23, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitaleri, G.; Berardi, R.; Pierantoni, C.; De Pas, T.; Noberasco, C.; Libbra, C.; González-Iglesias, R.; Giovannoni, L.; Tasciotti, A.; Neri, D.; et al. Phase I/II study of the tumour-targeting human monoclonal antibody-cytokine fusion protein L19-TNF in patients with advanced solid tumours. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadia, F.; Basso, V.; Patuzzo, R.; Maurichi, A.; Di Florio, A.; Zardi, L.; Ventura, E.; González-Iglesias, R.; Lovato, V.; Giovannoni, L.; et al. Isolated limb perfusion with the tumor-targeting human monoclonal antibody-cytokine fusion protein L19-TNF plus melphalan and mild hyperthermia in patients with locally advanced extremity melanoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, D. Antibody–Cytokine Fusions: Versatile Products for the Modulation of Anticancer Immunity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, S.D. A new platform for constructing antibody-cytokine fusion proteins (immunocytokines) with improved biological properties and adaptable cytokine activity. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2013, 26, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcin, G.; Paul, F.; Staufenbiel, M.; Bordat, Y.; Van der Heyden, J.; Wilmes, S.; Cartron, G.; Apparailly, F.; De Koker, S.; Piehler, J.; et al. High efficiency cell-specific targeting of cytokine activity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mock, J.; Stringhini, M.; Villa, A.; Weller, M.; Weiss, T.; Neri, D. An engineered 4-1BBL fusion protein with “activity on demand”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 31780–31788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetz, D.; Koovely, D.; Weder, B.; Neri, D. Targeted reconstitution of cytokine activity upon antigen binding using split cytokine antibody fusion proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 18139–18147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pogue, S.L.; Taura, T.; Bi, M.; Yun, Y.; Sho, A.; Mikesell, G.; Behrens, C.; Sokolovsky, M.; Hallak, H.; Rosenstock, M.; et al. Targeting attenuated interferon-α to myeloma cells with a CD38 antibody induces potent tumor regression with reduced off-target activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyghe, L.; Van Parys, A.; Cauwels, A.; Van Lint, S.; De Munter, S.; Bultinck, J.; Zabeau, L.; Hostens, J.; Goethals, A.; Vanderroost, N.; et al. Safe eradication of large established tumors using neovasculature-targeted tumor necrosis factor-based therapies. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.K.M.; Chun, H.J.; Zheng, L.; Siegel, R.M.; Bui, K.L.; Lenardo, M.J. A domain in TNF receptors that mediates ligand-independent receptor assembty and signaling. Science 2000, 288, 2351–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, J.L.; Schneider, P.; Tschopp, J. The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoogenboom, H.R.; Marks, J.D.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G. Building antibodies from their genes. Rev. Fr. Transfus. d’Hemobiol. 1993, 36, 19–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halin, C.; Rondini, S.; Nilsson, F.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Enhancement of the antitumor activity of interleukin-12 by targeted delivery to neovasculature. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, T.; Puca, E.; Silginer, M.; Hemmerle, T.; Pazahr, S.; Bink, A.; Weller, M.; Neri, D.; Roth, P. Immunocytokines are a promising immunotherapeutic approach against glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabb2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakhel, S.; Ongaro, T.; Gouyou, B.; Matasci, M.; Villa, A.; Neri, D.; Cazzamalli, S. Targeted enhancement of the therapeutic window of L19-TNF by transient and selective inhibition of RIPK1-signaling cascade. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 6678–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggermont, A.M.; Schraffordt Koops, H.; Liénard, D.; Kroon, B.B.; van Geel, A.N.; Hoekstra, H.J.; Lejeune, F.J. Isolated limb perfusion with high-dose tumor necrosis factor-α in combination with interferon-γ and melphalan for nonresectable extremity soft tissue sarcomas: A multicenter trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 2653–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, N.J.; Zhou, S.; Diaz, L.A.; Holdhoff, M. Systemic use of tumor necrosis factor alpha as an anticancer agent. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schliemann, C.; Hemmerle, T.; Berdel, A.F.; Angenendt, L.; Kerkhoff, A.; Hering, J.P.; Heindel, W.; Hartmann, W.; Wardelmann, E.; Chawla, S.P.; et al. Dose escalation and expansion phase I studies with the tumour-targeting antibody-tumour necrosis factor fusion protein L19TNF plus doxorubicin in patients with advanced tumours, including sarcomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 150, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauwels, A.; Van Lint, S.; Garcin, G.; Bultinck, J.; Paul, F.; Gerlo, S.; Van der Heyden, J.; Bordat, Y.; Catteeuw, D.; De Cauwer, L.; et al. A safe and highly efficient tumor-targeted type I interferon immunotherapy depends on the tumor microenvironment. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1398876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouckaert, P.G.G.; Leroux-Roels, G.G.; Guisez, Y.; Tavernier, J.; Fiers, W. In vivo anti-tumour activity of recombinant human and murine TNF, alone and in combination with murine IFN-γ, on a syngeneic murine melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 1986, 38, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossen, C.; Ingold, K.; Tardivel, A.; Bodmer, J.L.; Gaide, O.; Hertig, S.; Ambrose, C.; Tschopp, J.; Schneider, P. Interactions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and TNF receptor family members in the mouse and human. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13964–13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ongaro, T.; Matasci, M.; Cazzamalli, S.; Gouyou, B.; De Luca, R.; Neri, D.; Villa, A. A novel anti-cancer L19-interleukin-12 fusion protein with an optimized peptide linker efficiently localizes in vivo at the site of tumors. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 291, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, K.; Zivanovic, A.; Schwager, K.; Neri, D. Antibody-based targeting of interferon-alpha to the tumor neovasculature: A critical evaluation. Integr. Biol. 2011, 3, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasche, N.; Woytschak, J.; Wulhfard, S.; Villa, A.; Frey, K.; Neri, D. Cloning and characterization of novel tumor-targeting immunocytokines based on murine IL7. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 154, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No EDB Coating (M) | 100 nM EDB Coating (M) | |
|---|---|---|
| L19-TNFWT | 1.076 × 10−10 | 1.033 × 10−10 |
| L19-TNFY59F | 4.172 × 10−10 | 9.501 × 10−10 |
| L19-TNFI97A | 2.273 × 10−9 | 2.254 × 10−10 |
| L19-TNFQ102N | 5.012 × 10−11 | 5.986 × 10−11 |
| L19-TNFY119S | 3.245 × 10−11 | 6.417 × 10−11 |
| L19-TNFS147A | 1.261 × 10−11 | 1.58 × 10−11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dakhel, S.; Lizak, C.; Matasci, M.; Mock, J.; Villa, A.; Neri, D.; Cazzamalli, S. An Attenuated Targeted-TNF Localizes to Tumors In Vivo and Regains Activity at the Site of Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810020
Dakhel S, Lizak C, Matasci M, Mock J, Villa A, Neri D, Cazzamalli S. An Attenuated Targeted-TNF Localizes to Tumors In Vivo and Regains Activity at the Site of Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):10020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810020
Chicago/Turabian StyleDakhel, Sheila, Christian Lizak, Mattia Matasci, Jacqueline Mock, Alessandra Villa, Dario Neri, and Samuele Cazzamalli. 2021. "An Attenuated Targeted-TNF Localizes to Tumors In Vivo and Regains Activity at the Site of Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 10020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810020
APA StyleDakhel, S., Lizak, C., Matasci, M., Mock, J., Villa, A., Neri, D., & Cazzamalli, S. (2021). An Attenuated Targeted-TNF Localizes to Tumors In Vivo and Regains Activity at the Site of Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 10020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810020






