Interactions of Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Platelet Factor 4: New Insights in the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
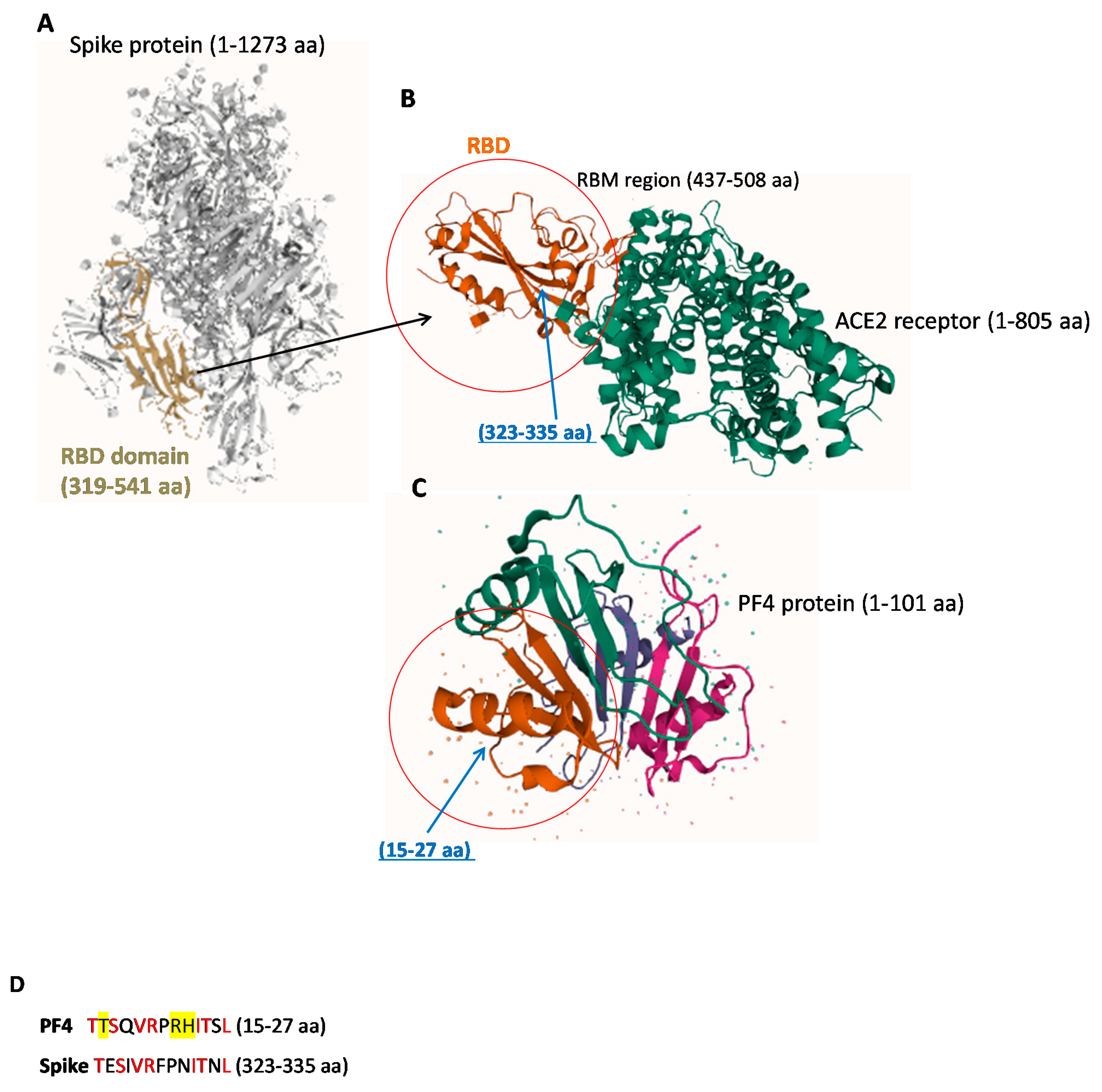
2.1. Structural Similarity between Spike-RBD and PF4 Proteins
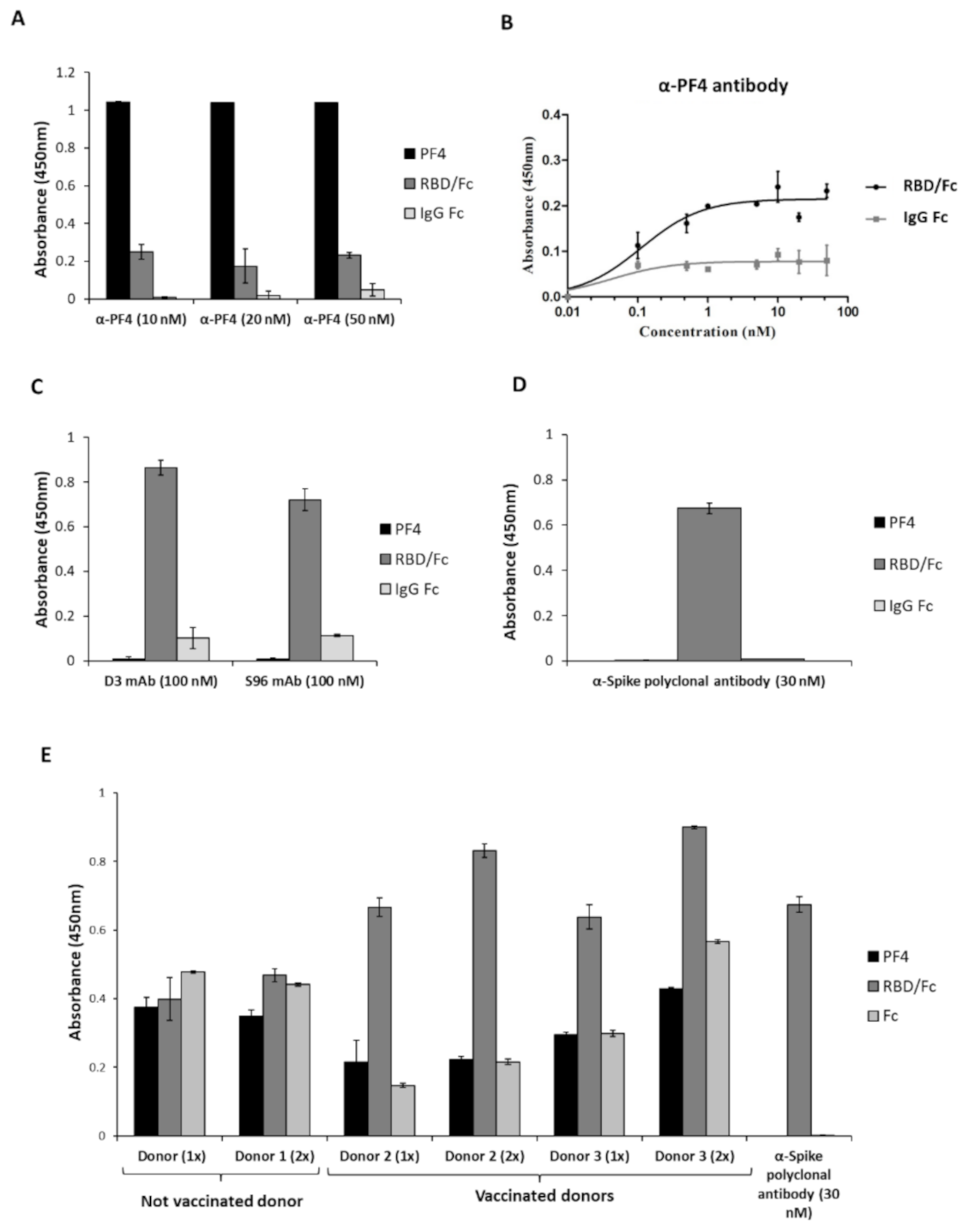
2.2. Analysis of the Cross-Reactivity of the Anti-PF4 or the Anti-Spike-RBD Antibodies for the Two Proteins
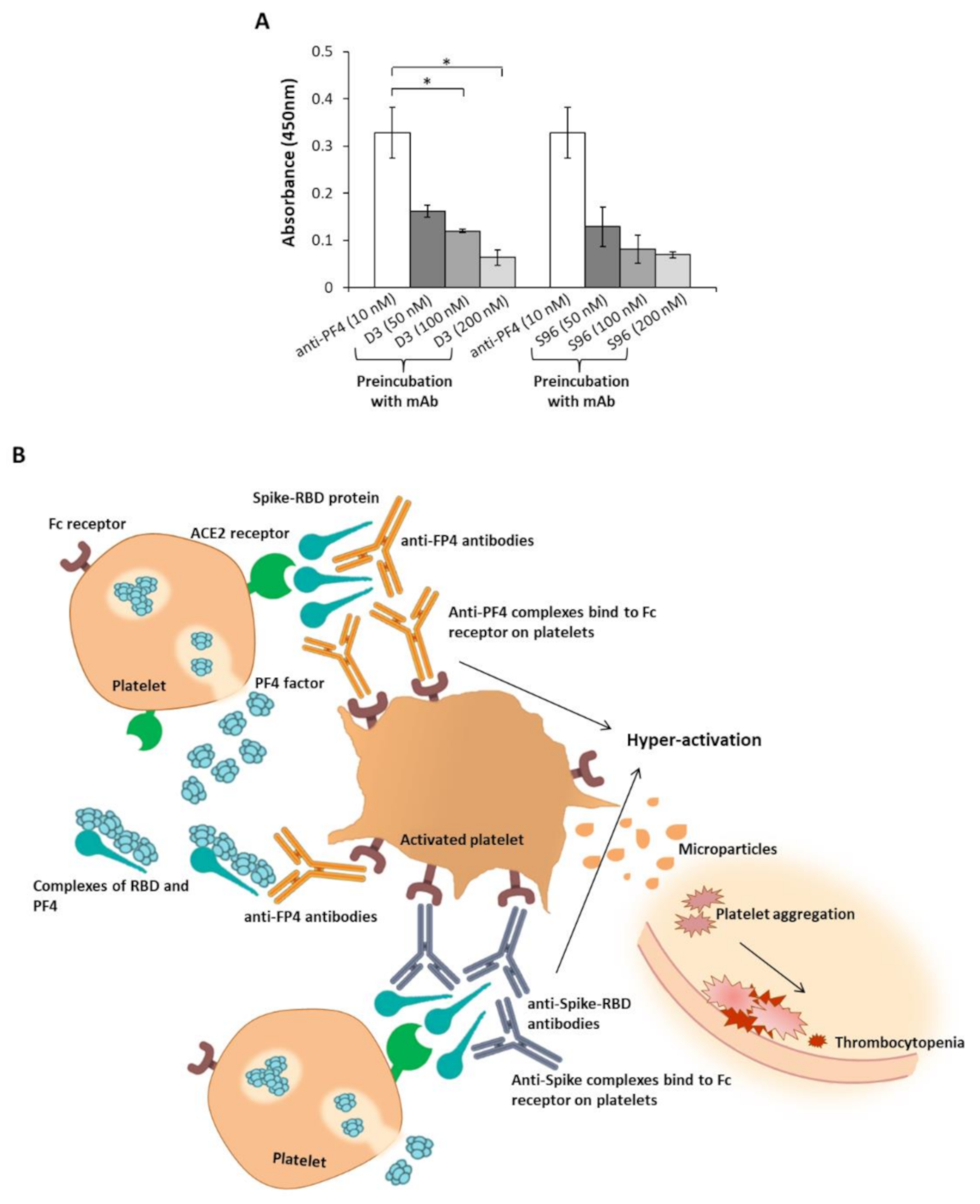
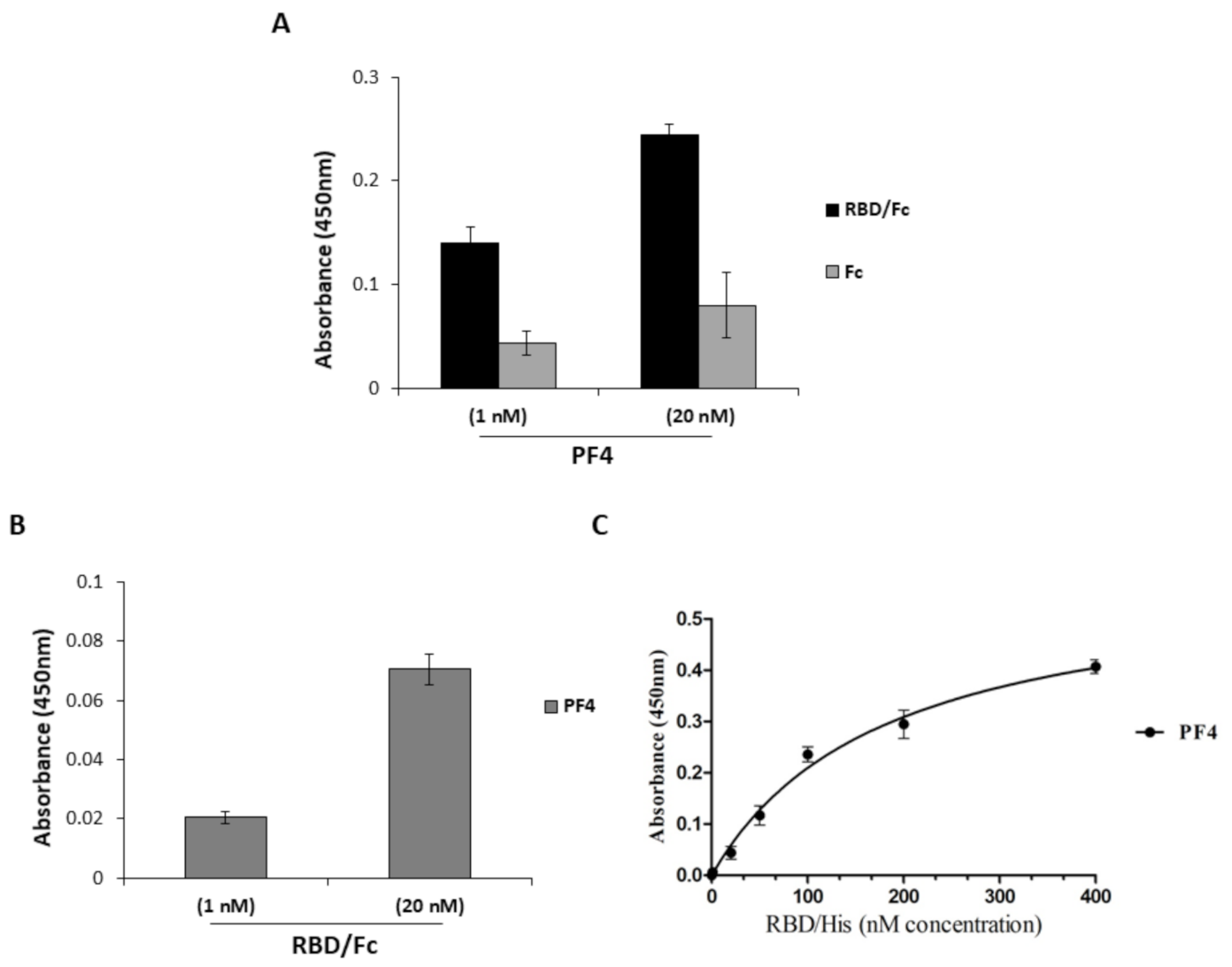
2.3. Interaction of PF4 and Spike-RBD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies and Human Recombinant Proteins
4.2. Identification of Homologies between Human PF4 and SARS-CoV-2 Spike-RBD Protein and Comparison of Their 3D Structures
4.3. ELISA Assays
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greinacher, A.; Selleng, K.; Mayerle, J.; Palankar, R.; Wesche, J.; Reiche, S.; Aebischer, A.; Warkentin, E.T.; Muenchhoffet, M.; Hellmuth, C.J.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Anti-Platelet Factor 4 Antibody Responses Induced by COVID-19 Disease and ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccination. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, N.H.; Sørvoll, I.H.; Michelsen, A.E.; Munthe, L.A.; Lund, J.F.; Ahlen, M.T.; Wiedmann, M.; Aamodt, A.H.; Skattør, T.H.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; et al. Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.; Singh, D.; Lown, R.; Poles, A.; Solomon, T.; Levi, M.; Goldblatt, D.; Kotoucek, P.; Thomas, W.; Lester, W. Pathologic Antibodies to Platelet Factor 4 after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 binds platelet ACE2 to enhance thrombosis in COVID-19. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J. Laboratory testing for suspected COVID-19 vaccine-induced (immune) thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cines, D.B.; Bussel, J.B. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2254–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.R.; Zhang, D.; Oswald, B.E.; Carrim, N.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lavalle, C.; McKeown, T.; Marshall, A.H.; et al. Platelets are versatile cells: New discoveries in hemostasis, thrombosis, immune responses, tumor metastasis and beyond. Crit. Rev. Cl. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, S.; Han, J.; Liu, S. Promoting platelets is a therapeutic option to combat severe viral infection of the lung. Blood. Adv. 2020, 4, 1640–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, J.C.; Niewiarowski, S. Biochemistry of alpha granule proteins. Semin. Hematol. 1985, 22, 151–163. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Greene, M.I.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H. Structural Features and PF4 Functions that Occur in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Complicated by COVID-19. Antibodies 2020, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Yarovoi, S.V.; Zhu, Z.; Rauova, L.; Hayes, V.; Lebedeva, T.; Liu, Q.; Poncz, M.; Arepally, G.; Cines, D.B. Atomic description of the immune complex involved in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, A.; Kelton, J.G.; Arnold, D.M.; Daka, M.; Naz, I. Antibody epitopes in vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Nature 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.; Nadeem, A.J. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570605/ (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Yang, J.; Doyle, M.; Faulk, T.; Visentin, G.; Aster, R.; Edwards, B. Structure Comparison of Two Platelet Factor 4 Mutants with the Wild-Type Reveals the Epitopes for the Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Antibodies. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1F9S (accessed on 4 October 2017).
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passariello, M.; Gentile, C.; Ferrucci, V.; Sasso, E.; Vetrei, C.; Fusco, G.; Viscardi, M.; Brandi, S.; Cerino, P.; Zambrano, N.; et al. Novel human neutralizing mAbs specific for Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Selleng, K.; Mayerle, J.; Palankar, R.; Wesche, J.; Reiche, S.; Aebischer, A.; Warkentin, T.E.; Muenchhoff, M.; Hellmuth, J.C.; et al. Anti-Platelet Factor 4 Antibodies Causing VITT do not Cross-React with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Blood 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, E.; D’Avino, C.; Passariello, M.; D’Alise, A.M.; Siciliano, D.; Esposito, M.L.; Froechlich, G.; Cortese, R.; Scarselli, E.; Zambrano, N.; et al. Massive parallel screening of phage libraries for the generation of repertoires of human immunomodulatory monoclonal antibodies. MAbs 2018, 10, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passariello, M.; Vetrei, C.; Sasso, E.; Froechlich, G.; Gentile, C.; D’Alise, A.M.; Zambrano, N.; Scarselli, E.; Nicosia, A.; De Lorenzo, C. Isolation of Two Novel Human Anti-CTLA-4 mAbs with Intriguing Biological Properties on Tumor and NK Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passariello, M.; Camorani, S.; Vetrei, C.; Cerchia, L.; De Lorenzo, C. Novel Human Bispecific Aptamer-Antibody Conjugates for Efficient Cancer Cell Killing. Cancers 2019, 11, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passariello, M.; Camorani, S.; Vetrei, C.; Ricci, S.; Cerchia, L.; De Lorenzo, C. Ipilimumab and Its Derived EGFR Aptamer-Based Conjugate Induce Efficient NK Cell Activation against Cancer Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Passariello, M.; Vetrei, C.; Amato, F.; De Lorenzo, C. Interactions of Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Platelet Factor 4: New Insights in the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168562
Passariello M, Vetrei C, Amato F, De Lorenzo C. Interactions of Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Platelet Factor 4: New Insights in the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(16):8562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168562
Chicago/Turabian StylePassariello, Margherita, Cinzia Vetrei, Felice Amato, and Claudia De Lorenzo. 2021. "Interactions of Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Platelet Factor 4: New Insights in the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 16: 8562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168562
APA StylePassariello, M., Vetrei, C., Amato, F., & De Lorenzo, C. (2021). Interactions of Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Platelet Factor 4: New Insights in the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(16), 8562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168562






