Genomic and Non-Genomic Actions of Glucocorticoids on Adipose Tissue Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Adipose Tissue Biology
3. Genomic Effects of GCs on AT Lipolysis in WAT
4. Additional Genomic Effects of GCs on Lipolysis
5. GC Availability and 11-β Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1
6. Loss of 11β-HSD1 Activity and Glucocorticoid Receptor in WAT
7. Effects of GCs on BAT Lipid Metabolism
8. Non-Genomic Effects of GCs on Lipolysis in AT
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhen, T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, R.C.; Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whirledge, S.; DeFranco, D.B. Glucocorticoid Signaling in Health and Disease: Insights From Tissue-Specific GR Knockout Mice. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busada, J.T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid Action During Development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 125, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.C.; Abrahamsen, C.T.; French, K.L.; Paterson, J.M.; Mullins, J.J.; Seckl, J.R. The mother or the fetus? 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 null mice provide evidence for direct fetal programming of behavior by endogenous glucocorticoids. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3840–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyrwoll, C.S.; Seckl, J.R.; Holmes, M.C. Altered placental function of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 knockout mice. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijers, R.; Jansen, J.; Riksen-Walraven, M.; de Weerth, C. Maternal prenatal anxiety and stress predict infant illnesses and health complaints. Pediatrics 2010, 126, e401–e409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madalena, K.M.; Lerch, J.K. The Effect of Glucocorticoid and Glucocorticoid Receptor Interactions on Brain, Spinal Cord, and Glial Cell Plasticity. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 8640970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovsky, A.N.; Arvikar, S.; Stern, T.A.; Axelrod, L. The neuropsychiatric complications of glucocorticoid use: Steroid psychosis revisited. Psychosomatics 2012, 53, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandi, C.; Merino, J.J.; Cordero, M.I.; Touyarot, K.; Venero, C. Effects of chronic stress on contextual fear conditioning and the hippocampal expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule, its polysialylation, and L1. Neuroscience 2001, 102, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallman, M.F.; la Fleur, S.E.; Pecoraro, N.C.; Gomez, F.; Houshyar, H.; Akana, S.F. Minireview: Glucocorticoids--food intake, abdominal obesity, and wealthy nations in 2004. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2633–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weikum, E.R.; Knuesel, M.T.; Ortlund, E.A.; Yamamoto, K.R. Glucocorticoid receptor control of transcription: Precision and plasticity via allostery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Mayba, O.; Lee, J.V.; Tran, J.; Harris, C.; Speed, T.P.; Wang, J.C. Genome-wide analysis of glucocorticoid receptor binding regions in adipocytes reveal gene network involved in triglyceride homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriza, J.L.; Weinberger, C.; Cerelli, G.; Glaser, T.M.; Handelin, B.L.; Housman, D.E.; Evans, R.M. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: Structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science 1987, 237, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanet, R.; Nguyen Dinh Cat, A.; Feraco, A.; Venteclef, N.; El Mogrhabi, S.; Sierra-Ramos, C.; Alvarez de la Rosa, D.; Adler, G.K.; Quilliot, D.; Rossignol, P.; et al. Adipocyte Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activation Leads to Metabolic Syndrome and Induction of Prostaglandin D2 Synthase. Hypertension 2015, 66, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, C.; Friederich-Persson, M.; Foufelle, F.; Nguyen Dinh Cat, A.; Jaisser, F. Adipocyte-Mineralocorticoid Receptor Alters Mitochondrial Quality Control Leading to Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Senescence of Visceral Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.; Hutson, I.; Tycksen, E.; Pietka, T.A.; Bauerle, K.; Harris, C.A. Role of Mineralocorticoid Receptor in Adipogenesis and Obesity in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqz010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Magueresse-Battistoni, B. Adipose Tissue and Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: Does Sex Matter? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.R.; Stewart, P.M.; Burt, D.; Brett, L.; McIntyre, M.A.; Sutanto, W.S.; de Kloet, E.R.; Monder, C. Localisation of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase--tissue specific protector of the mineralocorticoid receptor. Lancet 1988, 2, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuffat, A.G.; Tam, S.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Baker, M.E.; Frey, B.M.; Frey, F.J.; Odermatt, A. The 11-ketosteroid 11-ketodexamethasone is a glucocorticoid receptor agonist. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2004, 214, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viengchareun, S.; Le Menuet, D.; Martinerie, L.; Munier, M.; Pascual-Le Tallec, L.; Lombes, M. The mineralocorticoid receptor: Insights into its molecular and (patho)physiological biology. Nucl. Recept Signal. 2007, 5, e012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, J.; Mikics, E.; Makara, G.B. The effects of non-genomic glucocorticoid mechanisms on bodily functions and the central neural system. A critical evaluation of findings. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panettieri, R.A.; Schaafsma, D.; Amrani, Y.; Koziol-White, C.; Ostrom, R.; Tliba, O. Non-genomic Effects of Glucocorticoids: An Updated View. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, W.M.; Honeycutt, J.L.; Deck, C.A.; Borski, R.J. Nongenomic glucocorticoid effects and their mechanisms of action in vertebrates. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 346, 51–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusminski, C.M.; Bickel, P.E.; Scherer, P.E. Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clore, J.N.; Thurby-Hay, L. Glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia. Endocr. Pract. 2009, 15, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Pramyothin, P.; Karastergiou, K.; Fried, S.K. Deconstructing the roles of glucocorticoids in adipose tissue biology and the development of central obesity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1842, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallman, M.F.; Pecoraro, N.C.; La Fleur, S.E. Chronic stress and comfort foods: Self-medication and abdominal obesity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2005, 19, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, L.K. Cushing’s syndrome: Update on signs, symptoms and biochemical screening. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, M33–M38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saely, C.H.; Geiger, K.; Drexel, H. Brown versus white adipose tissue: A mini-review. Gerontology 2012, 58, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.S.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Pou, K.M.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Liu, C.Y.; Vasan, R.S.; Murabito, J.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Cupples, L.A.; et al. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: Association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2007, 116, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.H.; Byeon, J.S.; Myung, S.J.; Yang, S.K.; Choi, K.S.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, B.; Lee, D.; Byun, J.H.; Jang, S.J.; et al. Visceral obesity as a risk factor for colorectal neoplasm. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, D.V.; Clark, R.A.; Wolff, P.A.; Jarrett, A.R.; Kumar, N.B.; Aziz, N.M. Visceral obesity and breast cancer risk. Cancer 1994, 74, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontan, M. Advances in adipose tissue metabolism. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2008, 32 (Suppl. 7), S39–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckett, A.J.; Wright, D.C.; Riddell, M.C. The effects of glucocorticoids on adipose tissue lipid metabolism. Metabolism 2011, 60, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.; Chen, T.C.; Lee, R.A.; Nguyen, N.H.T.; Broughton, A.E.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.C. Pik3r1 Is Required for Glucocorticoid-Induced Perilipin 1 Phosphorylation in Lipid Droplet for Adipocyte Lipolysis. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, T.; Palanisamy, S.; Kramer, D.J.; Eljalby, M.; Marx, S.J.; Wibmer, A.G.; Butler, S.D.; Jiang, C.S.; Vaughan, R.; Schoder, H.; et al. Brown adipose tissue is associated with cardiometabolic health. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strack, A.M.; Bradbury, M.J.; Dallman, M.F. Corticosterone decreases nonshivering thermogenesis and increases lipid storage in brown adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, R183–R191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, E.; Church, C.D.; Holtrup, B.; Colman, L.; Rodeheffer, M.S. Rapid depot-specific activation of adipocyte precursor cells at the onset of obesity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altshuler-Keylin, S.; Shinoda, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Hong, H.; Kang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Perera, R.M.; Debnath, J.; Kajimura, S. Beige Adipocyte Maintenance Is Regulated by Autophagy-Induced Mitochondrial Clearance. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouchani, E.T.; Kajimura, S. Metabolic adaptation and maladaptation in adipose tissue. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djurhuus, C.B.; Gravholt, C.H.; Nielsen, S.; Mengel, A.; Christiansen, J.S.; Schmitz, O.E.; Moller, N. Effects of cortisol on lipolysis and regional interstitial glycerol levels in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 283, E172–E177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divertie, G.D.; Jensen, M.D.; Miles, J.M. Stimulation of lipolysis in humans by physiological hypercortisolemia. Diabetes 1991, 40, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberge, C.; Carpentier, A.C.; Langlois, M.-F.; Baillargeon, J.-P.; Ardilouze, J.-L.; Maheux, P.; Gallo-Payet, N. Adrenocortical dysregulation as a major player in insulin resistance and onset of obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1465–E1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Peckett, A.J.; D’Souza, A.M.; Hawke, T.J.; Riddell, M.C. Adipogenic and lipolytic effects of chronic glucocorticoid exposure. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C198–C209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, H.; Meuth, M. An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell 1974, 3, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Ruperez, A.I.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A.; Aguilera, C.M. Cell Models and Their Application for Studying Adipogenic Differentiation in Relation to Obesity: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoire, F.M.; Smas, C.M.; Sul, H.S. Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 783–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseti, D.; Regassa, A.; Kim, W.K. Molecular Regulation of Adipogenesis and Potential Anti-Adipogenic Bioactive Molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhan, N.; Jakovleva, T.; Feofanova, N.; Denisova, E.; Dubinina, A.; Sitnikova, N.; Makarova, E. Sex Differences in Liver, Adipose Tissue, and Muscle Transcriptional Response to Fasting and Refeeding in Mice. Cells 2019, 8, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, V.; Bloch, M.; Wardat, S.; Bohm, C.; Maurer, L.; Mahmoodzadeh, S.; Wiedmer, P.; Spranger, J.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Kintscher, U. Sexual dimorphic regulation of body weight dynamics and adipose tissue lipolysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahn, C.; Buttgereit, F. Genomic and nongenomic effects of glucocorticoids. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2008, 4, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.U.; Ohmori, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Kamitori, K.; Yamaguchi, F.; Rahman, A.; Tokuda, M.; Kobori, H. PPARgamma activation mitigates glucocorticoid receptor-induced excessive lipolysis in adipocytes via homeostatic crosstalk. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 4627–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, B.G.; Ong, J.M.; Kern, P.A. Hormonal regulation of hormone-sensitive lipase activity and mRNA levels in isolated rat adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 1994, 35, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; He, J.; Jiang, H.; Zu, L.; Zhai, W.; Pu, S.; Xu, G. Direct effect of glucocorticoids on lipolysis in adipocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, I.; Stephenson, E.J.; Redd, J.R.; Tran, Q.T.; Hochberg, I.; Qi, N.; Bridges, D. Glucocorticoid-Induced Metabolic Disturbances Are Exacerbated in Obese Male Mice. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz-Aydogan, H.; Kurnaz, O.; Kurt, O.; Akadam-Teker, B.; Kucukhuseyin, O.; Tekeli, A.; Isbir, T. Effects of the PPARG P12A and C161T gene variants on serum lipids in coronary heart disease patients with and without Type 2 diabetes. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2011, 358, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, W.H.; Tsai, H.D.; Chen, Y.C.; Wu, J.S.; Lin, T.N. Anti-apoptotic actions of PPAR-gamma against ischemic stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richelsen, B.; Pedersen, S.B.; Moller-Pedersen, T.; Bak, J.F. Regional differences in triglyceride breakdown in human adipose tissue: Effects of catecholamines, insulin, and prostaglandin E2. Metabolism 1991, 40, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnroth, P.; Smith, U. The antilipolytic effect of insulin in human adipocytes requires activation of the phosphodiesterase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 141, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimson, R.H.; Anderson, A.J.; Ramage, L.E.; Macfarlane, D.P.; de Beaux, A.C.; Mole, D.J.; Andrew, R.; Walker, B.R. Acute physiological effects of glucocorticoids on fuel metabolism in humans are permissive but not direct. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallman, M.F.; Strack, A.M.; Akana, S.F.; Bradbury, M.J.; Hanson, E.S.; Scribner, K.A.; Smith, M. Feast and famine: Critical role of glucocorticoids with insulin in daily energy flow. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1993, 14, 303–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathercole, L.L.; Morgan, S.A.; Bujalska, I.J.; Hauton, D.; Stewart, P.M.; Tomlinson, J.W. Regulation of lipogenesis by glucocorticoids and insulin in human adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jones Voy, B.; Urs, S.; Kim, S.; Soltani-Bejnood, M.; Quigley, N.; Heo, Y.R.; Standridge, M.; Andersen, B.; Dhar, M.; et al. The human fatty acid synthase gene and de novo lipogenesis are coordinately regulated in human adipose tissue. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, N.; Jorgensen, J.O. Effects of growth hormone on glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism in human subjects. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 152–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fain, J.N.; Cheema, P.; Tichansky, D.S.; Madan, A.K. Stimulation of human omental adipose tissue lipolysis by growth hormone plus dexamethasone. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2008, 295, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopchick, J.J.; Berryman, D.E.; Puri, V.; Lee, K.Y.; Jorgensen, J.O.L. The effects of growth hormone on adipose tissue: Old observations, new mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosson, M.; Lonnroth, P.; Bjorntorp, P.; Eden, S. Effects of cortisol and growth hormone on lipolysis in human adipose tissue. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurhuus, C.B.; Gravholt, C.H.; Nielsen, S.; Pedersen, S.B.; Moller, N.; Schmitz, O. Additive effects of cortisol and growth hormone on regional and systemic lipolysis in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 286, E488–E494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.S.; Betts, D.; Fain, J.N.; Bahouth, S.W.; Myers, L.K. Chronic exposure of rat fat cells to insulin enhances lipolysis and activation of partially purified hormone-sensitive lipase. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.C.; Mune, T.; Agarwal, A.K. 11 beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and the syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Masuzaki, H.; Paterson, J.; Shinyama, H.; Morton, N.M.; Mullins, J.J.; Seckl, J.R.; Flier, J.S. A transgenic model of visceral obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Science 2001, 294, 2166–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Fediuc, S.; Hawke, T.J.; Riddell, M.C. Endurance exercise training increases adipose tissue glucocorticoid exposure: Adaptations that facilitate lipolysis. Metabolism 2009, 58, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, J.N.; Cheema, P.; Madan, A.K.; Tichansky, D.S. Dexamethasone and the inflammatory response in explants of human omental adipose tissue. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 315, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Du, H.; Fan, W.; Lutfy, K.; Jiang, M.; Friedman, T.C.; Liu, Y. 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 shRNA ameliorates glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance and lipolysis in mouse abdominal adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E84–E95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viguerie, N.; Picard, F.; Hul, G.; Roussel, B.; Barbe, P.; Iacovoni, J.S.; Valle, C.; Langin, D.; Saris, W.H. Multiple effects of a short-term dexamethasone treatment in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Physiol. Genomics 2012, 44, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Grasa, M.; Casamitjana, R.; Pugeat, M.; Barret, C.; Ricart, W. Plasma total and glycosylated corticosteroid-binding globulin levels are associated with insulin secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 3192–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, H.H.; Andreassen, T.K.; Breiderhoff, T.; Brasen, J.H.; Schulz, H.; Gross, V.; Grone, H.J.; Nykjaer, A.; Willnow, T.E. Hyporesponsiveness to glucocorticoids in mice genetically deficient for the corticosteroid binding globulin. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 7236–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulfo, J.; Castel, R.; Ledda, A.; Romero, M.D.M.; Esteve, M.; Grasa, M. Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin is expressed in the adrenal gland and its absence impairs corticosterone synthesis and secretion in a sex-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Shen, W.J.; Muliro, K.; Patel, S.; Souza, S.C.; Roth, R.A.; Kraemer, F.B. Stimulation of lipolysis and hormone-sensitive lipase via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45456–45461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londos, C.; Brasaemle, D.L.; Schultz, C.J.; Adler-Wailes, D.C.; Levin, D.M.; Kimmel, A.R.; Rondinone, C.M. On the control of lipolysis in adipocytes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 892, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, S.A.; McCabe, E.L.; Gathercole, L.L.; Hassan-Smith, Z.K.; Larner, D.P.; Bujalska, I.J.; Stewart, P.M.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Lavery, G.G. 11beta-HSD1 is the major regulator of the tissue-specific effects of circulating glucocorticoid excess. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2482–E2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Blendy, J.A.; Monaghan, A.P.; Krieglstein, K.; Schmid, W.; Aguzzi, A.; Fantuzzi, G.; Hummler, E.; Unsicker, K.; Schutz, G. Targeted disruption of the glucocorticoid receptor gene blocks adrenergic chromaffin cell development and severely retards lung maturation. Genes. Dev. 1995, 9, 1608–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, K.M.; Hartmann, K.; Kaltenecker, D.; Vettorazzi, S.; Bauer, M.; Mauser, L.; Amann, S.; Jall, S.; Fischer, K.; Esterbauer, H.; et al. Adipocyte Glucocorticoid Receptor Deficiency Attenuates Aging- and HFD-Induced Obesity and Impairs the Feeding-Fasting Transition. Diabetes 2017, 66, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Roh, H.C.; Kumari, M.; Rosen, E.D. Adipocyte glucocorticoid receptor is important in lipolysis and insulin resistance due to exogenous steroids, but not insulin resistance caused by high fat feeding. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, R.; Okuno, Y.; Mukai, K.; Kitamura, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Onodera, T.; Murata, M.; Fukuhara, A.; Imamura, R.; Miyagawa, Y.; et al. Adipocyte GR Inhibits Healthy Adipose Expansion Through Multiple Mechanisms in Cushing Syndrome. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousovich-Neto, F.; Matos, M.S.; Costa, A.C.R.; de Melo Reis, R.A.; Atella, G.C.; Miranda-Alves, L.; Carvalho, D.P.; Ketzer, L.A.; Correa da Costa, V.M. Brown adipose tissue remodelling induced by corticosterone in male Wistar rats. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, F.; Chen, S.; Yin, H.; Jiang, X.; Jiao, F.; Wang, F.; Ji, H.; Hu, G.; et al. Autophagy inhibition prevents glucocorticoid-increased adiposity via suppressing BAT whitening. Autophagy 2020, 16, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glantschnig, C.; Mattijssen, F.; Vogl, E.S.; Ali Khan, A.; Rios Garcia, M.; Fischer, K.; Muller, T.; Uhlenhaut, H.; Nawroth, P.; Scheideler, M.; et al. The glucocorticoid receptor in brown adipocytes is dispensable for control of energy homeostasis. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e48552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggioli, R.; Ueta, C.B.; Drigo, R.A.; Castillo, M.; Fonseca, T.L.; Bianco, A.C. Dexamethasone reduces energy expenditure and increases susceptibility to diet-induced obesity in mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2013, 21, E415–E420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Wang, L.; Qi, H.; Di, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Zha, J.; et al. Essential roles of 11beta-HSD1 in regulating brown adipocyte function. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 50, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doig, C.L.; Fletcher, R.S.; Morgan, S.A.; McCabe, E.L.; Larner, D.P.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Stewart, P.M.; Philp, A.; Lavery, G.G. 11beta-HSD1 Modulates the Set Point of Brown Adipose Tissue Response to Glucocorticoids in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1964–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Ma, Y.; Chanturiya, T.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Kadegowda, A.K.G.; Jackson, R.; Rumore, D.; Xue, B.; Shi, H.; et al. Lipolysis in Brown Adipocytes Is Not Essential for Cold-Induced Thermogenesis in Mice. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 764–777.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, R.; Diwoky, C.; Schoiswohl, G.; Feiler, U.; Wongsiriroj, N.; Abdellatif, M.; Kolb, D.; Hoeks, J.; Kershaw, E.E.; Sedej, S.; et al. Cold-Induced Thermogenesis Depends on ATGL-Mediated Lipolysis in Cardiac Muscle, but Not Brown Adipose Tissue. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 753–763.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitraju, C.; Fischer, A.W.; Farese, R.V., Jr.; Walther, T.C. Lipid Droplets in Brown Adipose Tissue Are Dispensable for Cold-Induced Thermogenesis. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijten, I.H.N.; Brooks, K.; Boulet, N.; Shabalina, I.G.; Jaiprakash, A.; Carlsson, B.; Fischer, A.W.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Glucocorticoid-Induced Obesity Develops Independently of UCP1. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1686–1698.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijten, I.H.N.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Glucocorticoids and Brown Adipose Tissue: Do glucocorticoids really inhibit thermogenesis? Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 68, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, J.L.; Agada, H.; Jang, C.; Ward, M.; Wetzig, N.; Ho, K.K. Effects of glucocorticoids on human brown adipocytes. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 224, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, L.E.; Akyol, M.; Fletcher, A.M.; Forsythe, J.; Nixon, M.; Carter, R.N.; van Beek, E.J.; Morton, N.M.; Walker, B.R.; Stimson, R.H. Glucocorticoids Acutely Increase Brown Adipose Tissue Activity in Humans, Revealing Species-Specific Differences in UCP-1 Regulation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, V.; Verriere, V.; Grumbach, Y.; Bousquet, J.; Harvey, B.J. Rapid anti-secretory effects of glucocorticoids in human airway epithelium. Steroids 2006, 71, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttgereit, F.; Krauss, S.; Brand, M.D. Methylprednisolone inhibits uptake of Ca2+ and Na+ ions into concanavalin A-stimulated thymocytes. Biochem. J. 1997, 326 Pt 2, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Z.; Lin, W.; Chen, Y.Z. Inhibition of ATP-induced calcium influx in HT4 cells by glucocorticoids: Involvement of protein kinase A. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, A.; Vogt, E.; Locher, R.; Vetter. Stimulation of the phosphoinositide signalling system as a possible mechanism for glucocorticoid action in blood pressure control. J. Hypertension. Suppl. Off. J. Int. Soc. Hypertens. 1988, 6, S336–S338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, R.L.; Owen, M.; Fagan-Murphy, A.; Intabli, H.; Healy, D.; Patel, A.; Allen, M.C.; Patel, B.A.; Flint, M.S. Glucocorticoids induce production of reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species and DNA damage through an iNOS mediated pathway in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degerman, E.; Ahmad, F.; Chung, Y.W.; Guirguis, E.; Omar, B.; Stenson, L.; Manganiello, V. From PDE3B to the regulation of energy homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Hino, Y.; Ando, M.; Kotani, K.; Konishi, H.; Matsuzaki, H.; Kikkawa, U.; Ogawa, W.; et al. Insulin-induced phosphorylation and activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3B by the serine-threonine kinase Akt. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 6286–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degerman, E.; Landstrom, T.R.; Wijkander, J.; Holst, L.S.; Ahmad, F.; Belfrage, P.; Manganiello, V. Phosphorylation and activation of hormone-sensitive adipocyte phosphodiesterase type 3B. Methods 1998, 14, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztalryd, C.; Xu, G.; Dorward, H.; Tansey, J.T.; Contreras, J.A.; Kimmel, A.R.; Londos, C. Perilipin A is essential for the translocation of hormone-sensitive lipase during lipolytic activation. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Dalen, K.; Dorward, H.; Marcinkiewicz, A.; Russell, D.; Gong, D.; Londos, C.; Yamaguchi, T.; Holm, C.; et al. Activation of hormone-sensitive lipase requires two steps, protein phosphorylation and binding to the PAT-1 domain of lipid droplet coat proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32116–32125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.E.; Ahmadian, M.; Jaworski, K.; Sarkadi-Nagy, E.; Sul, H.S. Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi-Moghadam, A.; Simoncini, T.; Yang, Z.; Limbourg, F.P.; Plumier, J.C.; Rebsamen, M.C.; Hsieh, C.M.; Chui, D.S.; Thomas, K.L.; Prorock, A.J.; et al. Acute cardiovascular protective effects of corticosteroids are mediated by non-transcriptional activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, N.E.; Lam, L.N.; Yang, K.; Zhou, A.Y.; Koliwad, S.; Wang, J.C. Angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4) protein is a physiological mediator of intracellular lipolysis in murine adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Aryal, B.; Chaube, B.; Rotllan, N.; Varela, L.; Horvath, T.L.; Suarez, Y.; Fernandez-Hernando, C. Brown adipose tissue derived ANGPTL4 controls glucose and lipid metabolism and regulates thermogenesis. Mol. Metab. 2018, 11, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiper-Bergeron, N.; Wu, D.; Pope, L.; Schild-Poulter, C.; Hache, R.J. Stimulation of preadipocyte differentiation by steroid through targeting of an HDAC1 complex. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; Daniel Lane, M. Sequential gene promoter interactions by C/EBPbeta, C/EBPalpha, and PPARgamma during adipogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroud, M.; Tsokanos, F.F.; Caratti, G.; Kotschi, S.; Khani, S.; Jouffe, C.; Vogl, E.S.; Irmler, M.; Glantschnig, C.; Gil-Lozano, M.; et al. HAND2 is a novel obesity-linked adipogenic transcription factor regulated by glucocorticoid signalling. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1850–1865.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
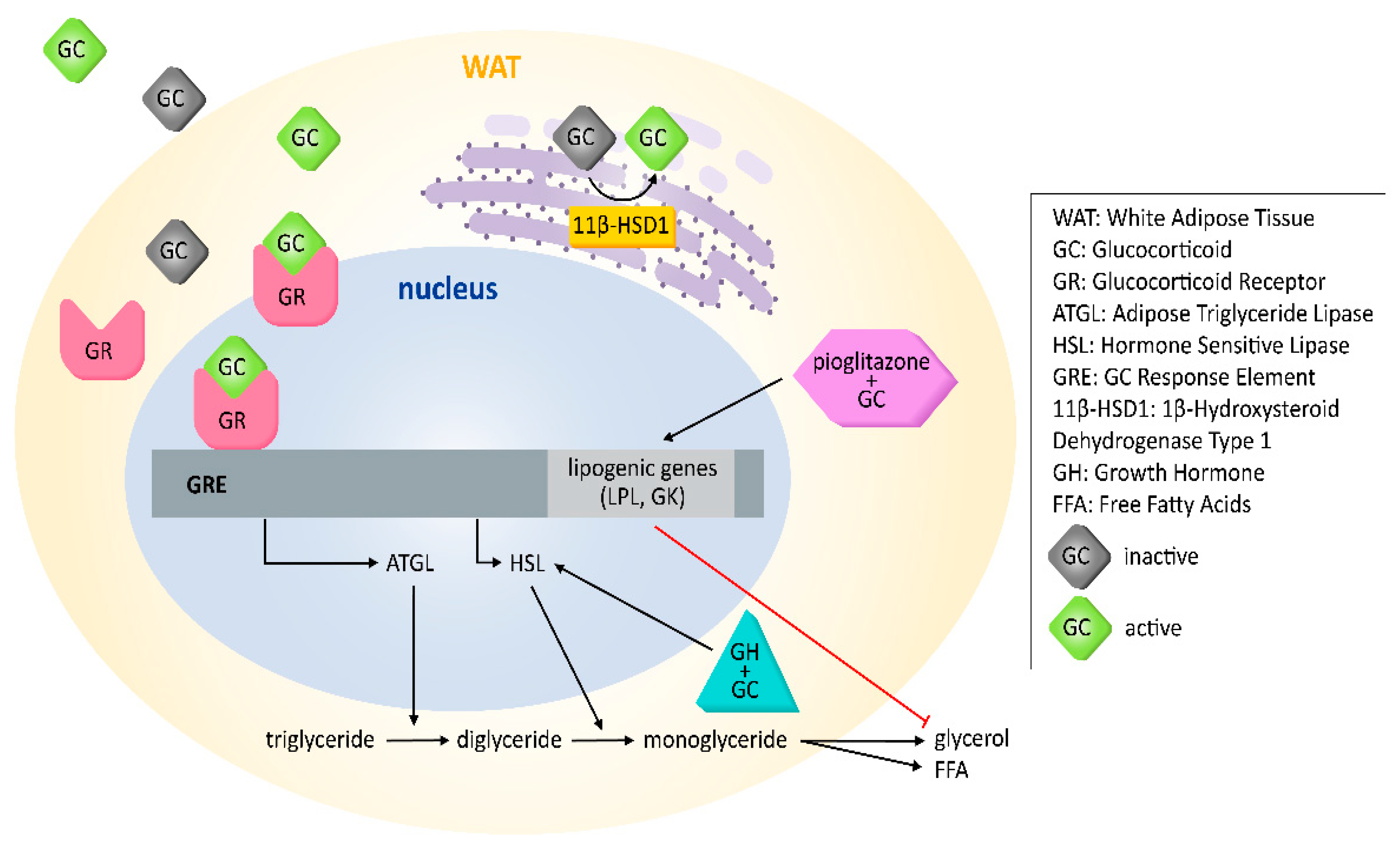

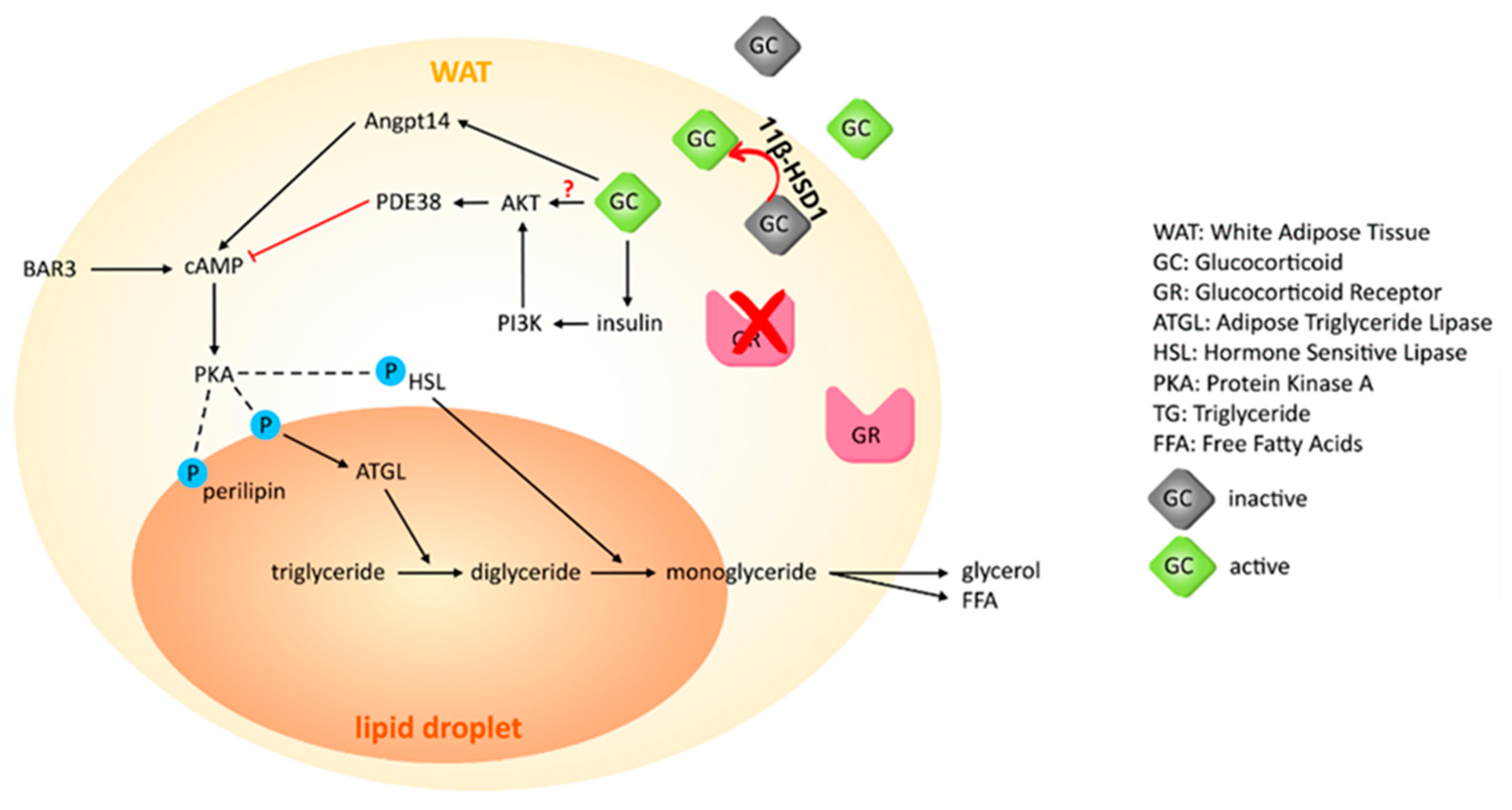
| Molecule Inhibited | Effects of Lipolysis | Effects on ATGL | Effects on HSL | Effects on Other Molecules |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11β-HSD1 in epididymal fat of mice [77] (shRNA injection) | Decrease | Decrease | Decrease | Decreased CORT in CORT-treated mice compared to WT |
| 11β-HSD1 in AT [84] (Adipocyte-Cre crossed with floxed 11β-hsd1, C57BL/6J mice) | Decrease compared to CORT-treated WT mice | Decrease | Decrease | |
| Epididymal adipocyte GR KO in mice [86] (Adipoq-Cre crossed with Nr3c1 floxed, C57BL/6J mice) | Decrease | Decrease | None | |
| Adipocyte GR KO in mice [87] Adipoq-Cre crossed with Nr3c1 floxed, C57BL/6J mice | Decrease in isoproterenol-stimulated glycerol release | Decrease | None |
| Cell/Tissue/Species | Type of Manipulation | GC Concentration | Duration of Exposure | Effects on UCP1 | Effects on Lipolysis | Effects on Thermogenesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male Wistar rat [89] | CORT | 0.1–0.5 mg/mL | 21 days | Decrease | Decrease | N/A |
| Male C57BL/6J Mice [90] | CORT | 5 mg/kg | 1 week | Decrease | Decrease | N/A |
| Male Mice [86] (Adipoq-Cre crossed with Nr3c1 floxed C57BL/6 mice) | Adipocyte-specific GR KO | N/A | N/A | None | None | Decrease |
| Male C57BL/6J Mice [98] | UCP1 KO | 50 µg/mL drinking water | 2 weeks | KO | Not changed compared to CORT-treated WT | Not changed compared to CORT-treated WT |
| Male mice [91] (Ucp1-CreERT2 crossed with Nr3c1 floxed C57BL/6 mice) | BAT-specific GR KO induced by tamoxifen | 0.1 mg/kg injected subcutaneously | 150 min | None | None | None |
| Human BAT depot [101] | Cortisol | 0–1000 nM | 24 h | Increase (peak increase at 100 nM of Cortisol) | N/A | Increase (peak increase at 100 nM) |
| Male human [101] | prednisolone | 10 mg every 12 h | 36 h | Increase | Increase (NEFAs) | Increase |
| Male human patients [101], retrospective study | oral GC therapy | unknown | >2 weeks | Decrease | N/A | Decrease |
| Cells/Tissue/Species | Stimulation | Amount of GC | Duration of GC Exposure | Effect on Lipolysis | Effect on ATGL | Effect on HSL | Effect on Other Molecules | Genomic/Non-genomic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differentiated 3T3-L1 cells [55] | DEX | 20 nM | 6 days | Increase | Increase | None | Gen | |
| Rat primary epididymal adipocytes [56] | DEX | 100–1000 nM | 24 h | Increase | N/A | Increase | Gen | |
| Rat primary epididymal adipocytes [56] | DEX | 1000 nM | 4 h | None | N/A | None | Gen | |
| Rat primary epididymal adipocytes [57] | DEX | 0–1000 | 24 h | Increase (peak at 1000 nM) | Increase | Increase | Gen | |
| Female human omental depot [68] | DEX | 50 nM | 48 h | None | Increase | Increase | Gen | |
| Male C57BL/6J Mice [58] | DEX | 1 mg/kg/d | 12 weeks | Increase | Increase | None | Gen | |
| Differentiated 3T3-L1 cells [55] | DEX + pioglitazone | 10–100 nM | 6 days | Increase compared to basal Decrease compared to DEX alone | Increase | Increase | Increase in GK and PEPK (lipogenic enzymes) | Gen |
| Female human omental depot [68] | DEX + GH | 50 nM | 48 h | Increase | Increase | Increase | Gen | |
| Subcutaneous abdominal depot [70] | Cortisol | 1000 nmol/L | 3 days | Decrease | N/A | N/A | Gen | |
| Subcutaneous abdominal depot [70] | Cortisol + GH | 1000 nmol/L | 3 days | Increase compared to cortisol alone | N/A | N/A | Gen | |
| Human male [71] | Cortisol | 2 μg/kg/min | 3 h | Increase | N/A | N/A | Gen | |
| Human male [71] | Cortisol + GH | 2 μg/kg/min | 3 h | Increase compared to placebo AND Cortisol alobe | N/A | N/A | Gen | |
| AT–specific Pik3r1-null mice (Adipoq-Cre cross with floxed Pik3r1) [38] | DEX | 10 mg/kg body | 24 h | None compared to placebo, Decreased compared to DEX-treated WT | Increase compared to placebo | Increased non-significantly compared to WT | Decrease in lipid droplet PKA | Gen and Non-Gen |
| Angptl4-null mice (Mixed background, C57BL6:129 Sv [114] | DEX | (5 mg/kg body | 24 h | Decrease compared to WT | Decrease | None | Decrease in PKA-inducedphosphorylation of HSL | Gen and Non-Gen |
| Rat primary epididymal adipocytes [57] | DEX + H89 | 0–1000 nM | 24 h | Decrease compared to DEX alone | N/A | N/A | Decrease in PKA | Non-Gen |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mir, N.; Chin, S.A.; Riddell, M.C.; Beaudry, J.L. Genomic and Non-Genomic Actions of Glucocorticoids on Adipose Tissue Lipid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168503
Mir N, Chin SA, Riddell MC, Beaudry JL. Genomic and Non-Genomic Actions of Glucocorticoids on Adipose Tissue Lipid Metabolism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(16):8503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168503
Chicago/Turabian StyleMir, Negar, Shannon A. Chin, Michael C. Riddell, and Jacqueline L. Beaudry. 2021. "Genomic and Non-Genomic Actions of Glucocorticoids on Adipose Tissue Lipid Metabolism" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 16: 8503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168503
APA StyleMir, N., Chin, S. A., Riddell, M. C., & Beaudry, J. L. (2021). Genomic and Non-Genomic Actions of Glucocorticoids on Adipose Tissue Lipid Metabolism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(16), 8503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168503






