Contribution of K2P Potassium Channels to Cardiac Physiology and Pathophysiology
Abstract
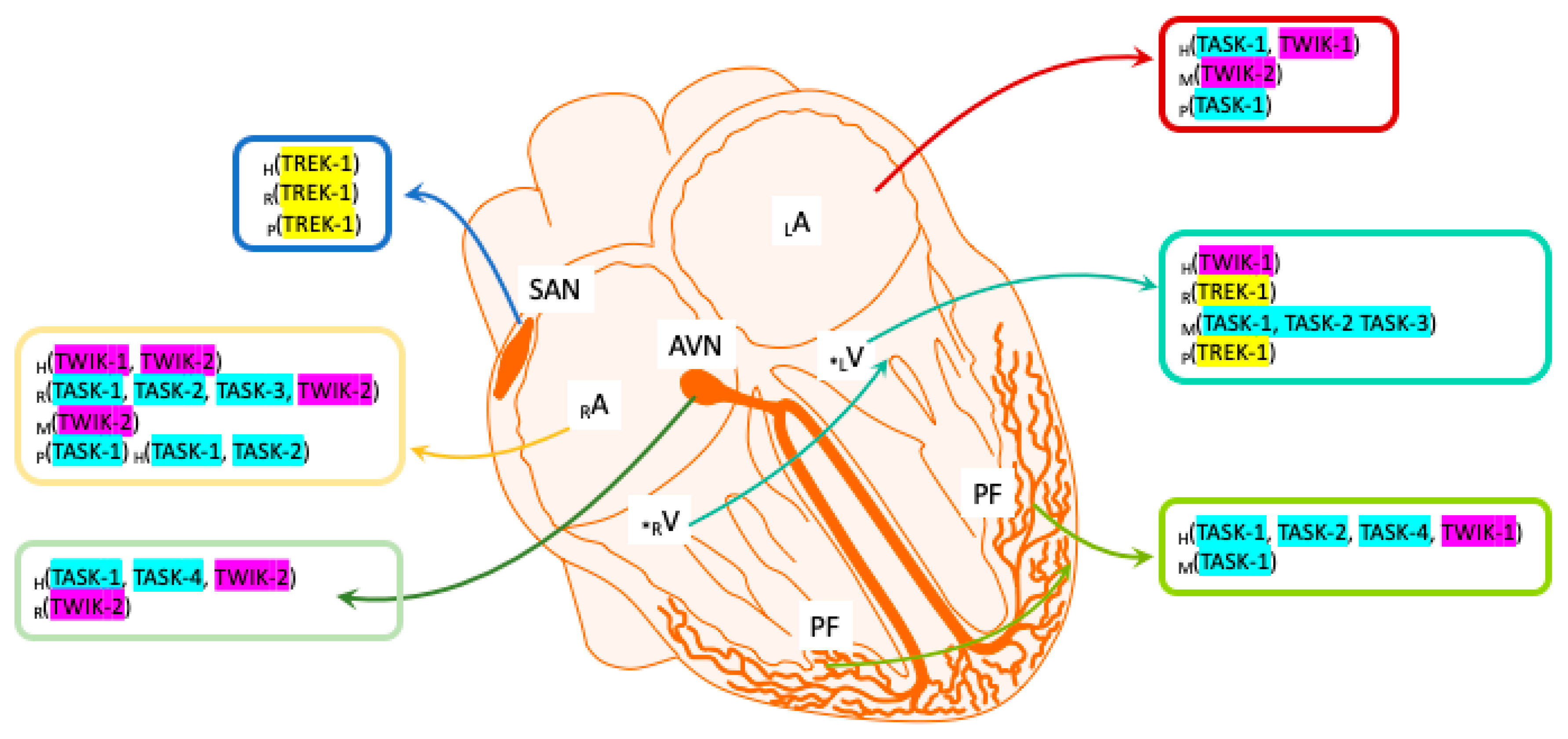
1. Introduction
2. Two-Pore Domain in a Weak Inward Rectifying K+ Channel (TWIK)
3. TWIK-Related Acid-Sensitive K+ Channels (TASK)
4. TWIK-Related K+ Channels (TREK)
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lesage, F.; Guillemare, E.; Fink, M.; Duprat, F.; Lazdunski, M.; Romey, G.; Barhanin, J. TWIK-1, a ubiquitous human weakly inward rectifying K+ channel with a novel structure. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyedi, P.; Czirják, G. Molecular Background of Leak K+ Currents: Two-Pore Domain Potassium Channels. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 559–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Kim, D. Single-channel properties and pH sensitivity of two-pore domain K+ channels of the TALK family. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 315, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyedi, P.; Czirjak, G. Properties, regulation, pharmacology, and functions of the K2P channel, TRESK. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 467, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechotta, P.L.; Rapedius, M.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Bollepalli, M.K.; Erhlich, G.; Andres-Enguix, I.; Fritzenschaft, H.; Decher, N.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Tucker, S.J.; et al. The pore structure and gating mechanism of K2P channels. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3607–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciangeli, S.; Chatelain, F.C.; Bichet, D.; Lesage, F. The family of K2Pchannels: Salient structural and functional properties. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 2587–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talley, E.M.; Solórzano, G.; Lei, Q.; Kim, D.; Bayliss, D.A. CNS Distribution of Members of the Two-Pore-Domain (KCNK) Potassium Channel Family. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7491–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, E.M.; Sirois, J.E.; Lei, Q.; Bayliss, D.A. Two-Pore-Domain (Kcnk) Potassium Channels: Dynamic Roles in Neuronal Function. Neuroscientist 2003, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuth, S.G.; Budde, T.; Kanyshkova, T.; Broicher, T.; Munsch, T.; Pape, H.-C. Contribution of TWIK-Related Acid-Sensitive K+Channel 1 (TASK1) and TASK3 Channels to the Control of Activity Modes in Thalamocortical Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 6460–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.; Abdallah, M.; Yost, C.S.; Winegar, B.D.; Kindler, C.H. Localization of the tandem pore domain K+ channel KCNK5 (TASK-2) in the rat central nervous system. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 98, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.; Wischmeyer, E.; Karschin, C.; Preisig-Müller, R.; Grzeschik, K.-H.; Daut, J.; Karschin, A.; Derst, C. THIK-1 and THIK-2, a Novel Subfamily of Tandem Pore Domain K+ Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7302–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushell, T.; Clarke, C.; Mathie, A.; Robertson, B. Pharmacological characterization of a non-inactivating outward current observed in mouse cerebellar Purkinje neurones. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, P.; Cerina, M.; Ehling, P.; Leist, M.; Pape, H.-C.; Meuth, S.G.; Budde, T. The role of two-pore-domain background K+ (K2P) channels in the thalamus. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 467, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Bang, H.; Gnatenco, C.; Kim, D. Synergistic interaction and the role of C-terminus in the activation of TRAAK K+ channels by pressure, free fatty acids and alkali. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2001, 442, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Gnatenco, C.; Sladek, C.D.; Kim, D. Background and tandem-pore potassium channels in magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the rat supraoptic nucleus. J. Physiol. 2003, 546, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhurst, A.D.; Rennie, G.; Chapman, C.G.; Meadows, H.; Duckworth, M.D.; Kelsell, R.E.; Gloger, I.I.; Pangalos, M.N. Distribution analysis of human two pore domain potassium channels in tissues of the central nervous system and periphery. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 86, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, B.; Acosta, C.; Djouhri, L.; Lawson, S.N. Leak K+ channel mRNAs in dorsal root ganglia: Relation to inflammation and spontaneous pain behaviour. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 49, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Kim, G.-T.; Kim, E.-J.; La, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, E.-S.; Park, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-G.; Han, J. Lamotrigine inhibits TRESK regulated by G-protein coupled receptor agonists. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Kim, D. TREK-2 (K2P10.1) and TRESK (K2P18.1) are major background K+ channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C138–C146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengyel, M.; Czirják, G.; Enyedi, P. Formation of Functional Heterodimers by TREK-1 and TREK-2 Two-pore Domain Potassium Channel Subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13649–13661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadaveira-Mosquera, A.; Pérez, M.; Reboreda, A.; Rivas-Ramírez, P.; Fernández-Fernández, D.; Lamas, J.A. Expression of K2P Channels in Sensory and Motor Neurons of the Autonomic Nervous System. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 48, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadaveira-Mosquera, A.; Ribeiro, S.J.; Reboreda, A.; Perez, M.; Lamas, J.A. Activation of TREK Currents by the Neuroprotective Agent Riluzole in Mouse Sympathetic Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Ramírez, P.; Cadaveira-Mosquera, A.; Lamas, J.A.; Reboreda, A. Muscarinic modulation of TREK currents in mouse sympathetic superior cervical ganglion neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 42, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Fernández, D.; Cadaveira-Mosquera, A.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Herrera-Pérez, S.; Veale, E.L.; Reboreda, A.; Mathie, A.; Lamas, J.A. Activation of TREK currents by riluzole in three subgroups of cultured mouse nodose ganglion neurons. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backx, P.H.; Marban, E. Background potassium current active during the plateau of the action potential in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Circ. Res. 1993, 72, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D. A mechanosensitive K+ channel in heart cells. Activation by arachidonic acid. J. Gen. Physiol. 1992, 100, 1021–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Clapham, D. Potassium channels in cardiac cells activated by arachidonic acid and phospholipids. Science 1989, 244, 1174–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Saint, D.A. Heterogeneous expression of tandem-pore K+ channel genes in adult and embryonic rat heart quantified by re-al-time polymerase chain reaction. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 31, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzke, C.; Wemhöner, K.; Sachse, F.; Rinné, S.; Schlichthörl, G.; Li, X.T.; Jaé, L.; Eckhardt, I.; Wischmeyer, E.; Wulf, H.; et al. The acid-sensitive potassium channel TASK-1 in rat cardiac muscle. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 75, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, N.; Wemhöner, K.; Rinné, S.; Netter, M.F.; Zuzarte, M.; Aller, M.I.; Kaufmann, S.G.; Li, X.T.; Meuth, S.G.; Daut, J.; et al. Knock-Out of the Potassium Channel TASK-1 Leads to a Prolonged QT Interval and a Disturbed QRS Complex. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, H.J.; Chapman, C.G.; Duckworth, D.M.; Kelsell, R.E.; Murdock, P.R.; Nasir, S.; Rennie, G.; Randall, A.D. The neuroprotective agent sipatrigine (BW619C89) potently inhibits the human tandem pore-domain K+ channels TREK-1 and TRAAK. Brain Res. 2001, 892, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Schlichthörl, G.; Hirsch, J.R.; Engels, H.; Karschin, C.; Karschin, A.; Derst, C.; Steinlein, O.K.; Daut, J. Expression pattern and functional characteristics of two novel splice variants of the two-pore-domain potassium channel TREK-2. J. Physiol. 2002, 539, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrenoire, C.; Lauritzen, I.; Lesage, F.; Romey, G.; Lazdunski, M. A TREK-1-like potassium channel in atrial cells inhibited by be-ta-adrenergic stimulation and activated by volatile anesthetics. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Wiedmann, F.; Voigt, N.; Zhou, X.-B.; Heijman, J.; Lang, S.; Albert, V.; Kallenberger, S.; Ruhparwar, A.; Szabó, G.; et al. Upregulation of K 2P 3.1 K + Current Causes Action Potential Shortening in Patients with Chronic Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2015, 132, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, R.A.; Gray, A.T.; Zhao, B.B.; Kindler, C.H.; Mazurek, M.J.; Mehta, Y.; Forsayeth, J.R.; Yost, C.S. TWIK-2, a New Weak Inward Rectifying Member of the Tandem Pore Domain Potassium Channel Family. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7887–7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Goldstein, S.A.N. Two-P-Domain (K2P) Potassium Channels: Leak Conductance Regulators of Excitability. In EnCyclopedia of Neuroscience; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 1207–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.J.; Maingret, F.; Magnone, V.; Fosset, M.; Lazdunski, M.; Honoré, E. TWIK-2, an Inactivating 2P Domain K+ Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28722–28730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yue, L.; White, M.; Pelletier, G.; Nattel, S. Differential Distribution of Inward Rectifier Potassium Channel Transcripts in Human Atrium Versus Ventricle. Circulation 1998, 98, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinghaus, P.; Scheubel, R.J.; Dobrev, D.; Ravens, U.; Holtz, J.; Huetter, J.; Nielsch, U.; Morawietz, H. Comparing the global mRNA expression profile of human atrial and ventricular myocardium with high-density oligonucleotide arrays. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 129, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gaborit, N.; Steenman, M.; Lamirault, G.; Le Meur, N.; Le Bouter, S.; Lande, G.; Léger, J.; Charpentier, F.; Christ, T.; Dobrev, D.; et al. Human Atrial Ion Channel and Transporter Subunit Gene-Expression Remodeling Associated with Valvular Heart Disease and Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2005, 112, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.H.; Chatelain, F.C.; Huttner, I.G.; Olesen, M.S.; Soka, M.; Feliciangeli, S.; Horvat, C.; Santiago, C.F.; Vandenberg, J.I.; Schmitt, N.; et al. The two-pore domain potassium channel, TWIK-1, has a role in the regulation of heart rate and atrial size. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 97, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaborit, N.; Le Bouter, S.; Szüts, V.; Varro, A.; Escande, D.; Nattel, S.; Demolombe, S. Regional and tissue specific transcript signatures of ion channel genes in the non-diseased human heart. J. Physiol. 2007, 582, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Fujita, A.; Horio, Y.; Kurachi, Y. Cloning and Functional Expression of a Novel Cardiac Two-Pore Background K + Channel (cTBAK-1). Circ. Res. 1998, 82, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, B.C.; Schullenberg, M.; Geduldig, N.; Hüning, A.; Mersmann, J.; Zacharowski, K.; Kovacevic, A.; Decking, U.; Aller, M.I.; Schmidt, K.G. Functional role of TASK-1 in the heart: Studies in TASK-1-deficient mice show prolonged cardiac repolarization and reduced heart rate variability. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.S.; Wilde, A.A.M. Inheritable Potassium Channel Diseases. In Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside, 7th ed.; Zipes, D.P., Jalife, J., Stevenson, W.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 494–503. [Google Scholar]
- Bartos, D.C.; Grandi, E.; Ripplinger, C.M. Ion Channels in the Heart. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1423–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudit, G.Y.; Backx, P.H. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. In Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside, 7th ed.; Zipes, D.P., Jalife, J., Stevenson, W.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mackaay, A.J.; Op’t Hof, T.; Bleeker, W.K.; Jongsma, H.J.; Bouman, L.N. Interaction of adrenaline and acetylcholine on cardiac pace-maker function. Functional inhomogeneity of the rabbit sinus node. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1980, 214, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Métayer, P.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous Initiation of Atrial Fibrillation by Ectopic Beats Originating in the Pulmonary Veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-A.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Tai, C.-T.; Tsai, C.-F.; Prakash, V.S.; Yu, W.-C.; Hsu, T.-L.; Ding, Y.-A.; Chang, M.-S. Initiation of Atrial Fibrillation by Ectopic Beats Originating from the Pulmonary Veins. Circulation 1999, 100, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, K.; Maguy, A.; Sakabe, M.; Comtois, P.; Inoue, H.; Nattel, S. The role of pulmonary veins vs. autonomic ganglia in different experimental substrates of canine atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 89, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filgueiras-Rama, D. Sympathetic Innervation and Cardiac Arrhythmias. In Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside, 7th ed.; Douglas, P., Zipes, J.J., William, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Brack, K.E.; Winter, J.; Ng, G.A. Mechanisms underlying the autonomic modulation of ventricular fibrillation initiation—tentative prophylactic properties of vagus nerve stimulation on malignant arrhythmias in heart failure. Hear. Fail. Rev. 2012, 18, 389–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. TWIK-1 Two-Pore Domain Potassium Channels Change Ion Selectivity and Conduct Inward Leak Sodium Currents in Hypokalemia. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezhouman, A.; Singh, N.; Song, Z.; Nivala, M.; Eskandari, A.; Cao, H.; Bapat, A.; Ko, C.Y.; Nguyen, T.; Qu, Z.; et al. Molecular Basis of Hypokalemia-Induced Ventricular Fibrillation. Circulation 2015, 132, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Wiedmann, F.; Schweizer, P.A.; Becker, R.; Katus, H.A.; Thomas, D. Novel electrophysiological properties of dronedarone: Inhibition of human cardiac two-pore-domain potassium (K2P) channels. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaborit, N.; Wichter, T.; Varro, A.; Szuts, V.; Lamirault, G.; Eckardt, L.; Paul, M.; Breithardt, G.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; Escande, D.; et al. Transcrip-tional profiling of ion channel genes in Brugada syndrome and other right ventricular arrhythmogenic diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duprat, F.; Lesage, F.; Fink, M.; Reyes, R.; Heurteaux, C.; Lazdunski, M. TASK, a human background K+ channel to sense external pH variations near physiological pH. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5464–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Gnatenco, C. TASK-5, a New Member of the Tandem-Pore K+ Channel Family. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 284, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuth, S.G.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Broicher, T.; Austinat, M.; Braeuninger, S.; Bittner, S.; Fischer, S.; Bayliss, D.A.; Budde, T.; Stoll, G.; et al. The neuroprotective impact of the leak potassium channel TASK1 on stroke development in mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.M.; Gallagher, P.G.; Buck, M.E.; Butler, M.H.; Goldstein, S.A. Proton Block and Voltage Gating Are Potassium-dependent in the Cardiac Leak Channel Kcnk3. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 16969–16978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Bang, H.; Kim, D. TBAK-1 and TASK-1, two-pore K(+) channel subunits: Kinetic properties and expression in rat heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1999, 277, H1669–H1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonoudakis, D.; Gray, A.T.; Winegar, B.D.; Kindler, C.H.; Harada, M.; Taylor, D.M.; Chavez, R.A.; Forsayeth, J.R.; Yost, C.S. An Open Rectifier Potassium Channel with Two Pore Domains in Tandem Cloned from Rat Cerebellum. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Wiedmann, F.; Beyersdorf, C.; Zhao, Z.; El-Battrawy, I.; Lan, H.; Szabo, G.; Li, X.; Lang, S.; Korkmaz-Icöz, S.; et al. Genetic Ablation of TASK-1 (Tandem of P Domains in a Weak Inward Rectifying K + Channel–Related Acid-Sensitive K + Channel-1) (K 2P 3.1) K + Channels Suppresses Atrial Fibrillation and Prevents Electrical Remodeling. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, A.S.; Merk, S.; Arnoldi, E.; Zwermann, L.; Kloos, P.; Gebauer, M.; Steinmeyer, K.; Bleich, M.; Kääb, S.; Hinterseer, M.; et al. Reprogramming of the Human Atrial Transcriptome in Permanent Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, S.H.; Netter, M.F.; Rolfes, C.; Rinné, S.; Schlichthörl, G.; Zuzarte, M.; Vassiliou, T.; Moosdorf, R.; Wulf, H.; Daut, J.; et al. TASK-1 Channels May Modulate Action Potential Duration of Human Atrial Cardiomyocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, V.; Zhang, H.; Willis, S.; Creazzo, T.L. Expression of a two-pore domain K+ channel (TASK-1) in developing avian and mouse ventricular conduction systems. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 235, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, C.; Rinné, S.; Zumhagen, S.; Kiper, A.K.; Silbernagel, N.; Netter, M.F.; Stallmeyer, B.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; Decher, N. Gain-of-function mutation in TASK-4 channels and severe cardiac conduction disorder. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, N.; Kiper, A.K.; Rolfes, C.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; Rinne, S. The role of acid-sensitive two-pore domain potassium channels in cardiac electrophysiology: Focus on arrhythmias. Pflugers Arch 2015, 467, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Wiedmann, F.; Tristram, F.; Anand, P.; Wenzel, W.; Lugenbiel, P.; Schweizer, P.A.; Katus, H.A.; Thomas, D. Cardiac expression and atrial fibrillation-associated remodeling of K2P2.1 (TREK-1) K+ channels in a porcine model. Life Sci. 2014, 97, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Bateman, A.; O’Kelly, I. Altered Expression of Two-Pore Domain Potassium (K2P) Channels in Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmann, F.; Schmidt, C.; Lugenbiel, P.; Staudacher, I.; Rahm, A.-K.; Seyler, C.; Schweizer, P.A.; Katus, H.A.; Thomas, D. Therapeutic targeting of two-pore-domain potassium (K2P) channels in the cardiovascular system. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingret, F.; Fosset, M.; Lesage, F.; Lazdunski, M.; Honoré, E. TRAAK Is a Mammalian Neuronal Mechano-gated K+Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimond, F.; Rauzier, J.-M.; Bony, C.; Vassort, G. Simultaneous Activation of p38 MAPK and p42/44 MAPK by ATP Stimulates the K+ Current ITREK in Cardiomyocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39110–39116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesage, F.; Maingret, F.; Lazdunski, M. Cloning and expression of human TRAAK, a polyunsaturated fatty acids-activated and mecha-no-sensitive K+ channel. FEBS Lett. 2000, 471, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemin, J.; Patel, A.J.; Duprat, F.; Lauritzen, I.; Lazdunski, M.; Honoré, E. A phospholipid sensor controls mechanogating of the K+ channel TREK-1. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.J.; Honoré, E.; Maingret, F.; Lesage, F.; Fink, M.; Duprat, F.; Lazdunski, M. A mammalian two pore domain mechano-gated S-like K+ channel. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4283–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, J.A. Mechanosensitive K2P channels, TREKking through the autonomic nervous system. In Mechanically Gated Channels and Their Regulation; Kamkin, A., Lozinsky, I., Eds.; Mechanosensitivity in Cells and Tissues; Springer Science + Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 6, pp. 35–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mathie, A.; Veale, E.L. Two-pore domain potassium channels: Potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of pain. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2015, 467, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brohawn, S.G.; Campbell, E.B.; MacKinnon, R. Physical mechanism for gating and mechanosensitivity of the human TRAAK K+ channel. Nature 2014, 516, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, J.; Zimmermann, K.; Busserolles, J.; Deval, E.; Alloui, A.; Diochot, S.; Guy, N.; Borsotto, M.; Reeh, P.; Eschalier, A.; et al. The mechano-activated K+ channels TRAAK and TREK-1 control both warm and cold perception. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, J.A.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Herrera-Pérez, S. Ion Channels and Thermosensitivity: TRP, TREK, or Both? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Dyachenko, V.; Zuzarte, M.; Putzke, C.; Preisig-Müller, R.; Isenberg, G.; Daut, J. The stretch-activated potassium channel TREK-1 in rat cardiac ventricular muscle. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.; Duprat, F.; Lesage, F.; Reyes, R.; Romey, G.; Heurteaux, C.; Lazdunski, M. Cloning, functional expression and brain localiza-tion of a novel unconventional outward rectifier K+ channel. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 6854–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.H.C.; Liu, W.; Saint, D.A. Differential expression of the mechanosensitive potassium channelTREK-1in epicardial and endocardial myocytes in rat ventricle. Exp. Physiol. 2004, 89, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, P.; Yuan, H.; Feng, N.; Peng, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. An Increased TREK-1–like Potassium Current in Ventricular Myocytes During Rat Cardiac Hypertrophy. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, D.M.; Lee, T.E.; Watson, L.J.; Mao, L.; Chandok, G.; Wang, H.G.; Frangakis, S.; Pitt, G.S.; Shah, S.H.; Wolf, M.J.; et al. The two-pore domain potassium channel TREK-1 mediates cardiac fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4843–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unudurthi, S.D.; Wu, X.; Qian, L.; Amari, F.; Onal, B.; Li, N.; Makara, M.A.; Smith, S.A.; Snyder, J.; Fedorov, V.V.; et al. Two-Pore K + Channel TREK-1 Regulates Sinoatrial Node Membrane Excitability. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, N.; Kiper, A.K.; Rinné, S. Stretch-activated potassium currents in the heart: Focus on TREK-1 and arrhythmias. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2017, 130, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmann, F.; Rinné, S.; Donner, B.; Decher, N.; Katus, H.A.; Schmidt, C. Mechanosensitive TREK-1 two-pore-domain potassium (K2P) channels in the cardiovascular system. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2021, 159, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, M.; Lesage, F.; Duprat, F.; Heurteaux, C.; Reyes, R.; Fosset, M.; Lazdunski, M. A neuronal two P domain K+ channel stimulated by arachidonic acid and polyunsaturated fatty acids. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3297–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaita, A.; de Miera, E.V.S. Cloning of two transcripts, HKT4.1a and HKT4.1b, from the human two-pore K+ channel gene KCNK4: Chromosomal localization, tissue distribution and functional expression. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 102, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, P.; Bollensdorff, C.; Garny, A. Effects of mechanosensitive ion channels on ventricular electrophysiology: Experimental and theoretical models. Exp. Physiol. 2006, 91, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Peyronnet, R. Voltage-gated and stretch-activated potassium channels in the human heart. Herzschrittmachertherapie Elektrophysiologie 2018, 29, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamatham, S.; Waters, C.M.; Schwingshackl, A.; Mancarella, S. TREK-1 protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury and from adverse remodeling after myocardial infarction. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2019, 471, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyler, C.; Li, J.; Schweizer, P.A.; Katus, H.A.; Thomas, D. Inhibition of cardiac two-pore-domain K+ (K2P) channels by the antiarrhythmic drug vernakalant—Comparison with flecainide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 724, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahira, M.; Sakurai, M.; Sakurada, N.; Sugiyama, K. Fenamates and diltiazem modulate lipid-sensitive mechano-gated 2P domain K+ channels. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2005, 451, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decher, N.; Ortiz-Bonnin, B.; Friedrich, C.; Schewe, M.; Kiper, A.K.; Rinné, S.; Seemann, G.; Peyronnet, R.; Zumhagen, S.; Bustos, D.; et al. Sodium permeable and “hypersensitive” TREK-1 channels cause ventricular tachycardia. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goonetilleke, L.; Quayle, J. TREK-1 K+ Channels in the Cardiovascular System: Their Significance and Potential as a Therapeutic Target. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2012, 30, e23–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, P. Cardiac Stretch-Activated Channels and Mechano-Electric Coupling. In Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside, 7th ed.; Douglas, P., Zipes, J.J., William, G., Stevenson, Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 128–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bodnár, M.; Schlichthörl, G.; Daut, J. The potassium current carried by TREK-1 channels in rat cardiac ventricular muscle. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 467, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froese, A.; Breher, S.S.; Waldeyer, C.; Schindler, R.F.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Rinné, S.; Wischmeyer, E.; Schlueter, J.; Becher, J.; Simrick, S.; et al. Popeye domain containing proteins are essential for stress-mediated modulation of cardiac pacemaking in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbuti, A.; Ishii, S.; Shimizu, T.; Robinson, R.B.; Feinmark, S.J. Block of the background K+ channel TASK-1 contributes to arrhythmogenic effects of platelet-activating factor. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2002, 282, H2024–H2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiper, A.K.; Rinné, S.; Rolfes, C.; Ramirez, D.; Seebohm, G.; Netter, M.F.; González, W.; Decher, N. Kv1.5 blockers preferentially inhibit TASK-1 channels: TASK-1 as a target against atrial fibrillation and obstructive sleep apnea? Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 467, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiamvimonvat, N.; Chen-Izu, Y.; Clancy, C.E.; Deschenes, I.; Dobrev, D.; Heijman, J.; Izu, L.; Qu, Z.; Ripplinger, C.M.; Vandenberg, J.I.; et al. Potassium currents in the heart: Functional roles in repolarization, arrhythmia and therapeutics. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2229–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravens, U.; Odening, K.E. Atrial fibrillation: Therapeutic potential of atrial K + channel blockers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 176, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Heijman, J.; Voigt, N.; Wehrens, X.H.; Dobrev, D. The Molecular Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation. In Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside, 7th ed.; Zipes, D.P., Jalife, J., Stevenson, W.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 396–408. [Google Scholar]
- Benito, B.; Brugada, R.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, P. Brugada Syndrome. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Marmol, J.; Rietmeijer, R.; Brohawn, S.G. Studying Mechanosensitivity of Two-Pore Domain K+ Channels in Cellular and Reconstituted Proteoliposome Membranes. Breast Cancer 2017, 1684, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D. TREK-2, a New Member of the Mechanosensitive Tandem-pore K+ Channel Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17412–17419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, P. Cardiac Stretch–Activated Channels and Mechano-Electric Coupling. In Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside, 6th ed.; Zipes, D.P., Jalife, J., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Pauza, D.H.; Skripka, V.; Pauziene, N.; Stropus, R. Morphology, distribution, and variability of the epicardiac neural ganglionated subplexuses in the human heart. Anat. Rec. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2000, 259, 353–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, F.R.; Hirst, G.D.; Klemm, M.F.; Steele, P.A. Different types of ganglion cell in the cardiac plexus of guinea-pigs. J. Physiol. 1995, 486, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.C. Towards an understanding of the function of the intrinsic cardiac ganglia. J. Physiol. 2000, 528, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiallourou, S.R.; Sands, S.A.; Walker, A.M.; Horne, R.S. Maturation of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Variability during Sleep in Term-Born Infants. Sleep 2012, 35, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordan, R.; Gwathmey, J.K.; Xie, L.-H. Autonomic and endocrine control of cardiovascular function. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, G.; Zarzoso, M.; Noujaim, S.F. Pulmonary Vein Ganglia and the Neural Regulation of the Heart Rate. In Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside, 7th ed.; Douglas, P., Zipes, J.J., William, G., Stevenson, Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 370–374. [Google Scholar]
| Cardiac Condition | References | |
|---|---|---|
| TREK | AF; CH; CF; L-QT | [56,70,86,87,88,95] |
| TASK | L-QT; AF; SB | [30,34,44,64,65,66,67] |
| TWIK | AF; BS | [40,42,54,57] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Pérez, S.; Campos-Ríos, A.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Lamas, J.A. Contribution of K2P Potassium Channels to Cardiac Physiology and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126635
Herrera-Pérez S, Campos-Ríos A, Rueda-Ruzafa L, Lamas JA. Contribution of K2P Potassium Channels to Cardiac Physiology and Pathophysiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126635
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Pérez, Salvador, Ana Campos-Ríos, Lola Rueda-Ruzafa, and José Antonio Lamas. 2021. "Contribution of K2P Potassium Channels to Cardiac Physiology and Pathophysiology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126635
APA StyleHerrera-Pérez, S., Campos-Ríos, A., Rueda-Ruzafa, L., & Lamas, J. A. (2021). Contribution of K2P Potassium Channels to Cardiac Physiology and Pathophysiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126635






