Complement Factor D (adipsin) Levels Are Elevated in Acquired Partial Lipodystrophy (Barraquer–Simons syndrome)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
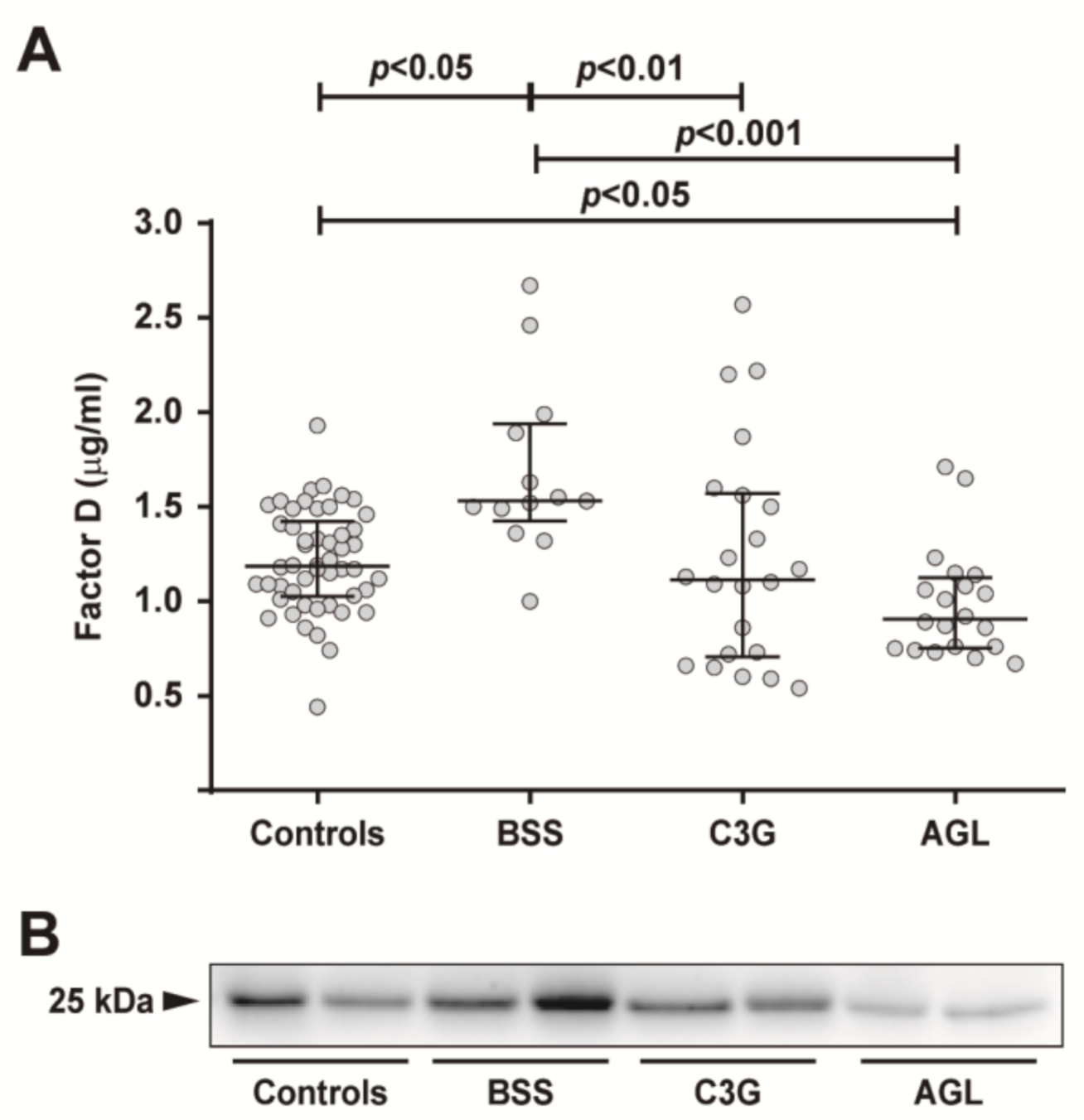
2.1. Circulating FD Levels Are Increased in Patients with BSS
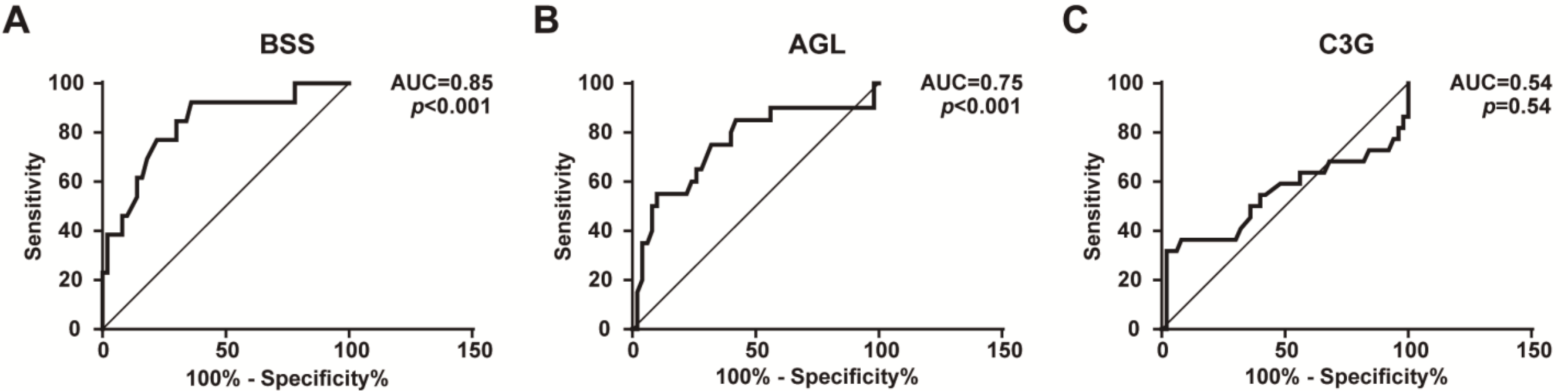
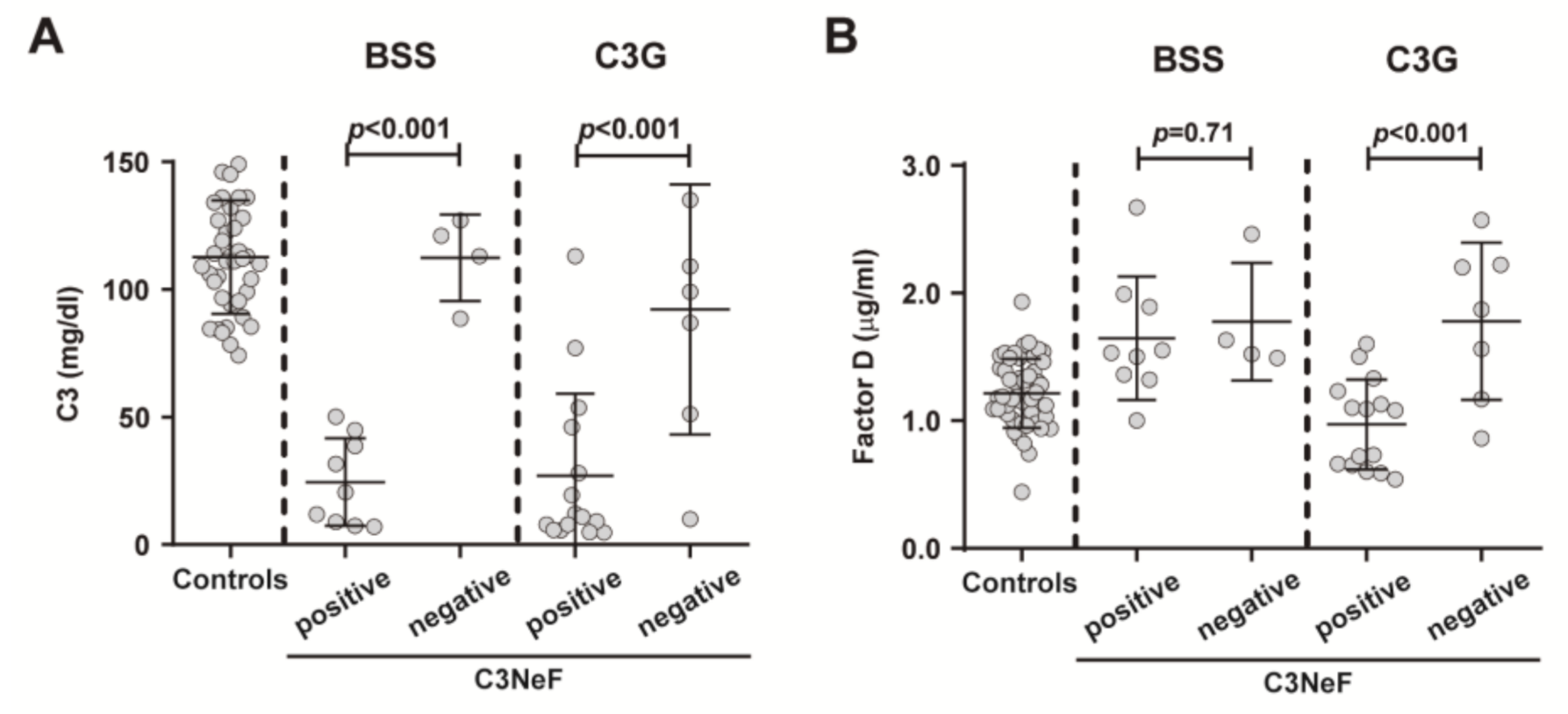
2.2. FD Levels Are a Potentially Reliable Biomarker for the Diagnosis of BSS
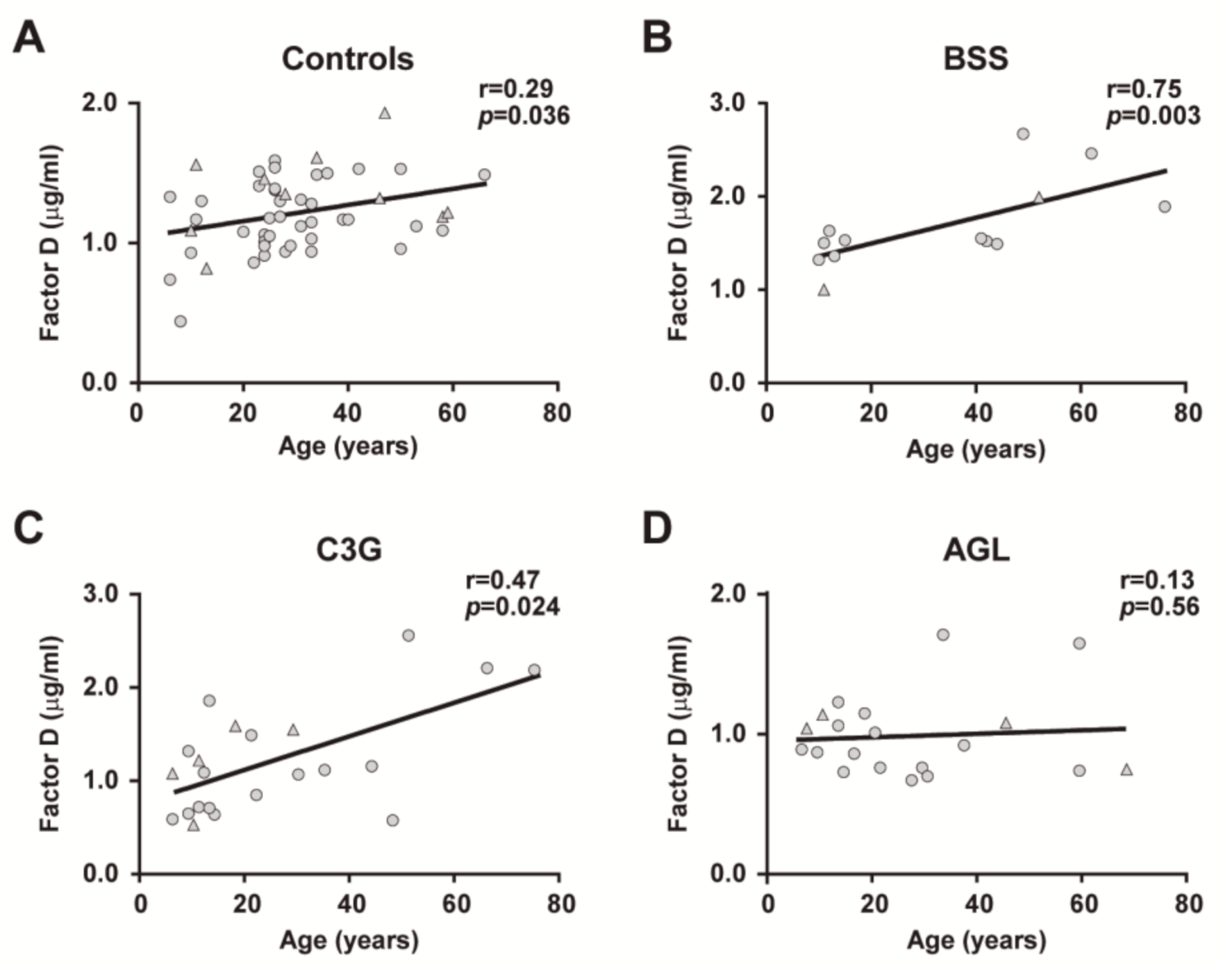
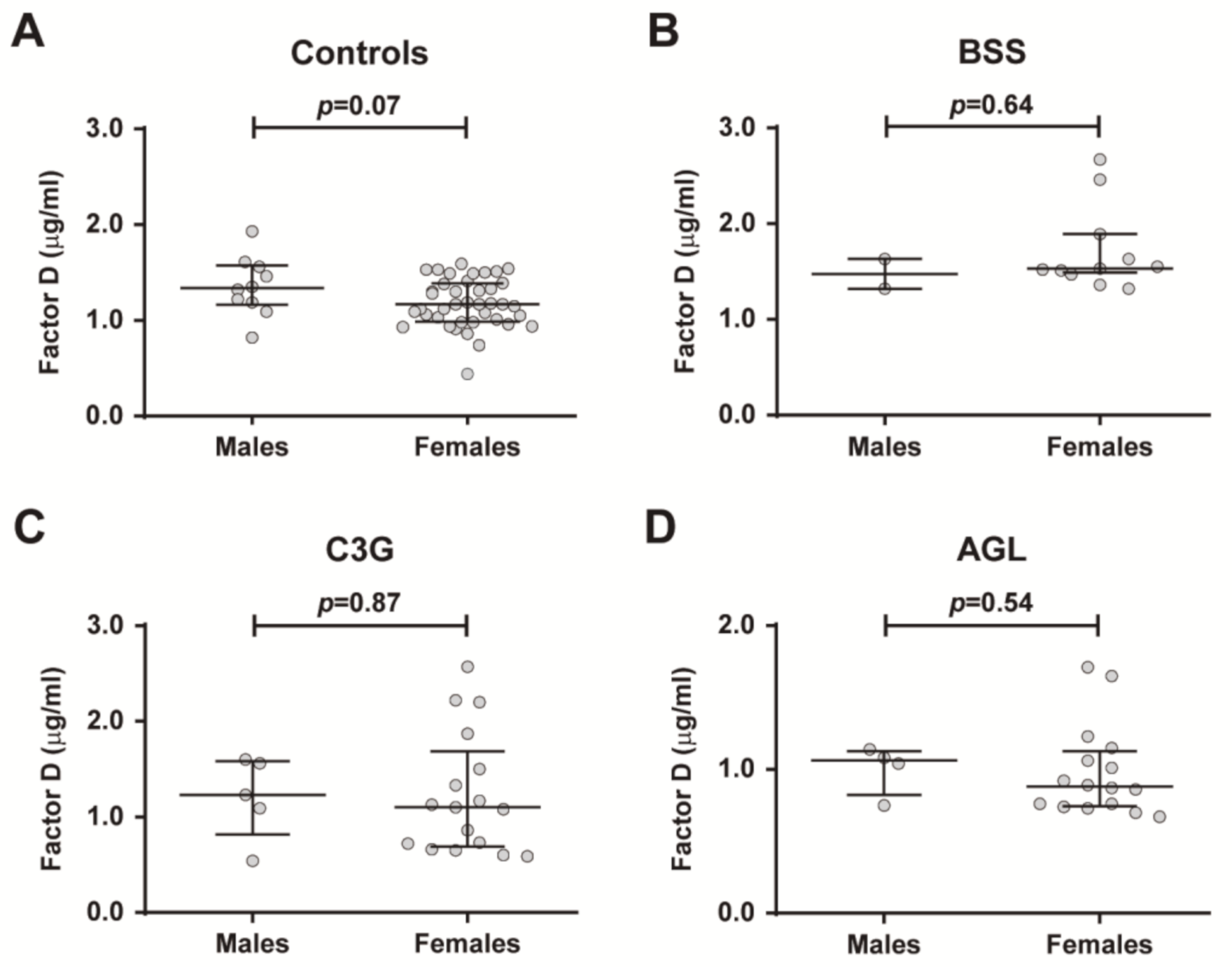
2.3. Age- and Sex-Related Differences in FD Levels
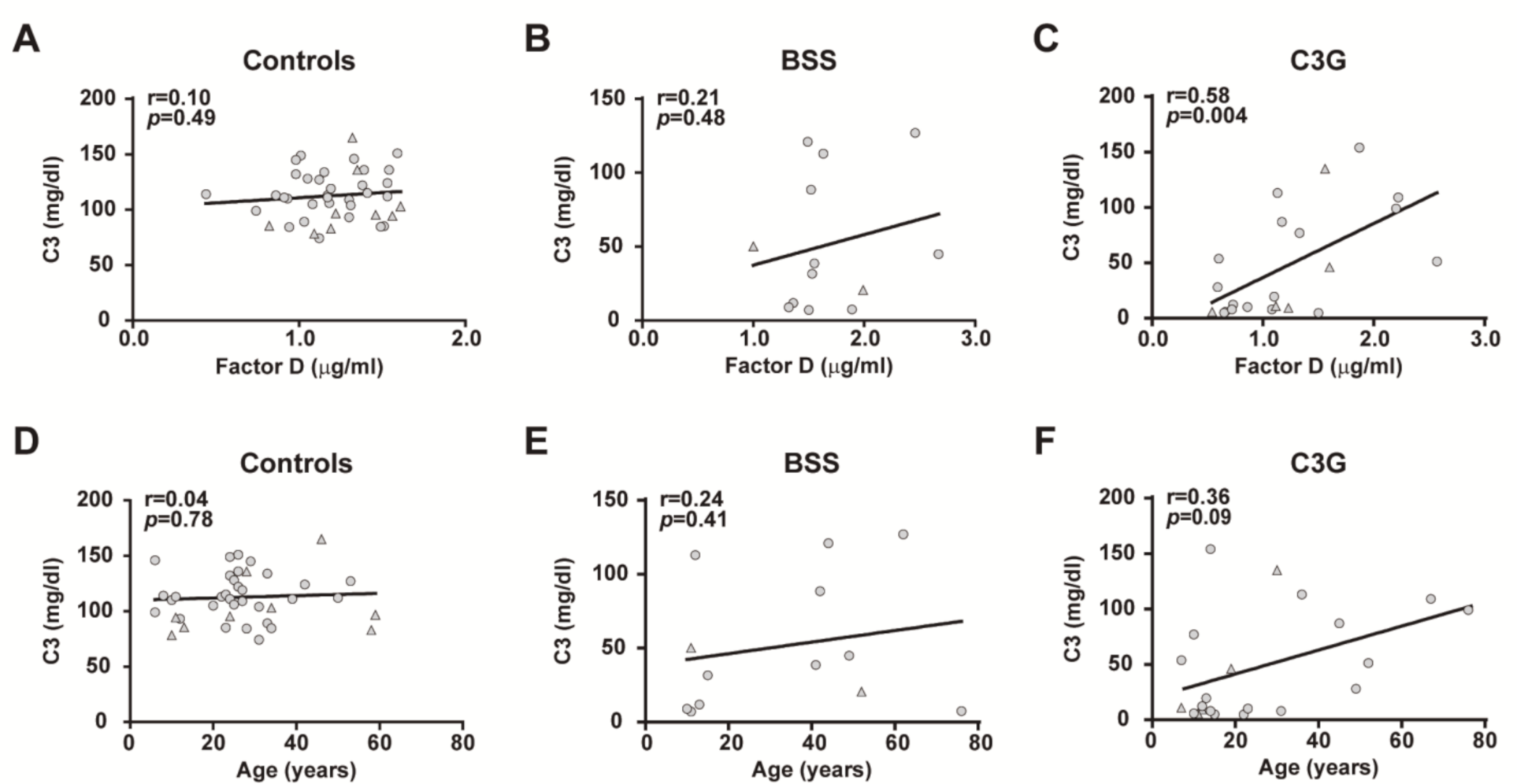
2.4. Effects of Complement System Activation on Plasma FD Levels
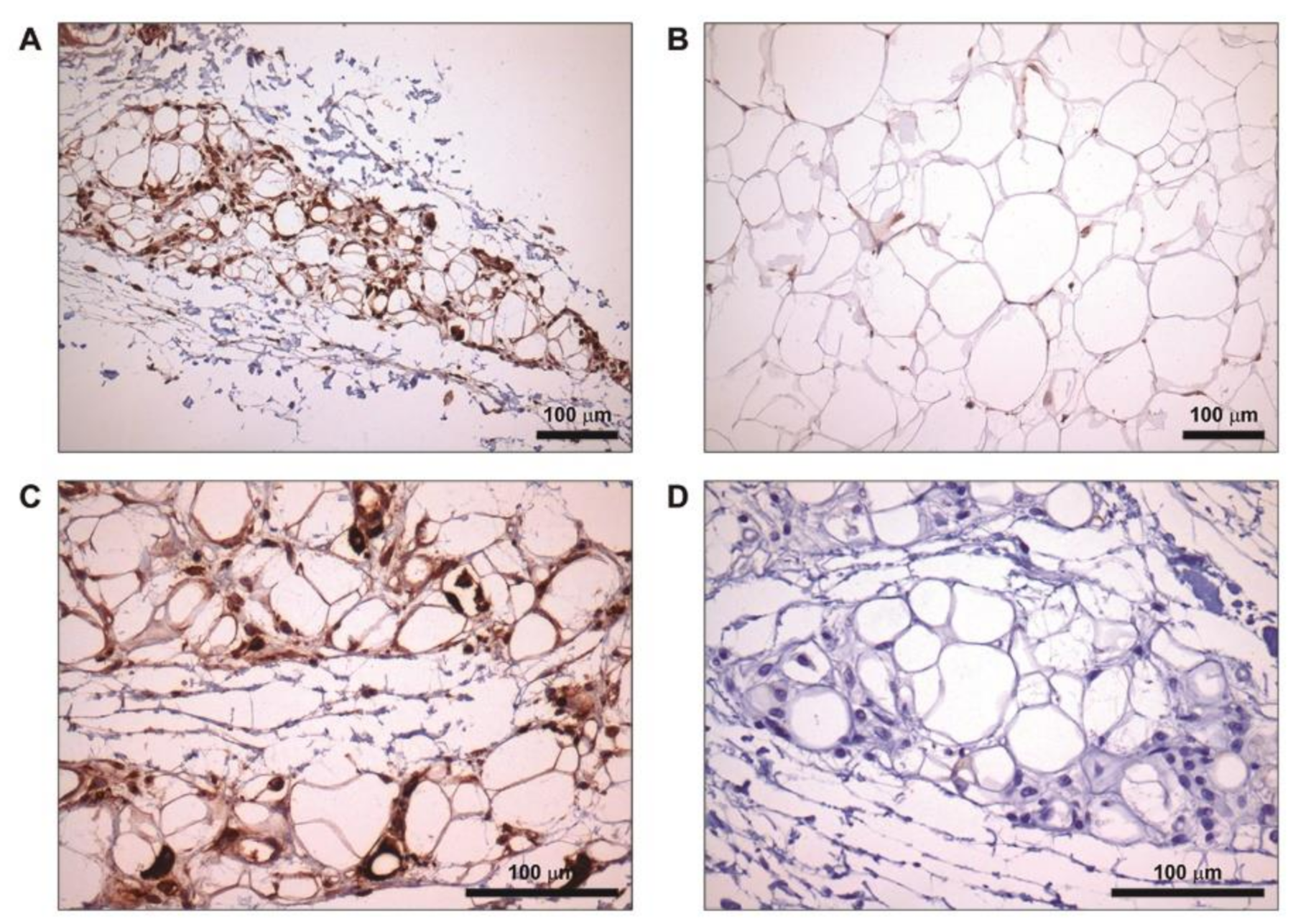
2.5. Increased FD Labelling at Lipoatrophic Areas
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Cohorts
4.2. Biological Samples
4.3. Complement System Determinations
4.4. Measurement of FD in Plasma by ELISA
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
4.7. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Brown, R.J.; Araujo-Vilar, D.; Cheung, P.T.; Dunger, D.; Garg, A.; Jack, M.; Mungai, L.; Oral, E.A.; Patni, N.; Rother, K.I.; et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Lipodystrophy Syndromes: A Multi-Society Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4500–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvillo, F.; Ceccarini, G.; Nozal, P.; Magno, S.; Pelosini, C.; Garrido, S.; López-Lera, A.; Moraru, M.; Vilches, C.; Fornaciari, S.; et al. Immunological Features of Patients Affected by Barraquer-Simons Syndrome. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvillo, F.; Okrój, M.; Nozal, P.; Melgosa, M.; Sánchez-Corral, P.; López-Trascasa, M. Nephritic Factors: An Overview of Classification, Diagnostic Tools and Clinical Associations. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Peethambaram, A.; Garg, A. Clinical Features and Metabolic and Autoimmune Derangements in Acquired Partial Lipodystrophy: Report of 35 Cases and Review of the Literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2004, 83, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieson, P.W.; Würzner, R.; Oliveria, D.B.; Lachmann, P.J.; Peters, D.K. Complement-Mediated Adipocyte Lysis by Nephritic Factor Sera. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, H.T. C3 Glomerulopathy. F1000Research 2017, 6, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corvillo, F.; Nozal, P.; López-Lera, A.; De Miguel, M.P.; Piñero-Fernández, J.A.; De Lucas, R.; García-Concepción, M.D.; Beato, M.J.; Araújo-Vilar, D.; López-Trascasa, M. Evidence of Ongoing Complement Activation on Adipose Tissue from an 11-Year-Old Girl with Barraquer-Simons Syndrome. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.S.; Min, H.Y.; Johnson, D.; Chaplinsky, R.J.; Flier, J.S.; Hunt, C.R.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipsin: A Circulating Serine Protease Homolog Secreted by Adipose Tissue and Sciatic Nerve. Science 1987, 237, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.T.; Damm, D.; Hancock, N.; Rosen, B.S.; Lowell, B.B.; Usher, P.; Flier, J.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Human Adipsin Is Identical to Complement Factor D and Is Expressed at High Levels in Adipose Tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9210–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaley, K. Biosynthesis of the Complement Components and the Regulatory Proteins of the Alternative Complement Pathway by Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1980, 151, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Freitas, P.; Lau, E.; Carvalho, D. Barraquer-Simons Syndrome: A Rare Form of Acquired Lipodystrophy. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Hutson, I.; Akk, A.M.; Mascharak, S.; Pham, C.T.N.; Hourcade, D.E.; Brown, R.; Atkinson, J.P.; Harris, C.A. Contribution of Adipose-Derived Factor D/Adipsin to Complement Alternative Pathway Activation: Lessons from Lipodystrophy. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A Key System for Immune Surveillance and Homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleh, J.; Al-Maqbali, M.; Abdel-Hadi, D. Role of Complement and Complement-Related Adipokines in Regulation of Energy Metabolism and Fat Storage. Compr. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1411–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Fernández-Real, J.M. The Complement System Is Dysfunctional in Metabolic Disease: Evidences in Plasma and Adipose Tissue from Obese and Insulin Resistant Subjects. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 85, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phieler, J.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Lambris, J.D.; Chavakis, T. The Role of the Complement System in Metabolic Organs and Metabolic Diseases. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauvreau, D.; Roy, C.; Tom, F.-Q.; Lu, H.; Miegueu, P.; Richard, D.; Song, W.-C.; Stover, C.; Cianflone, K. A New Effector of Lipid Metabolism: Complement Factor Properdin. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 51, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, H.; Iwashita, M.; Shinjo, T.; Yamashita, A.; Tsuruta, M.; Nagasaka, S.; Taniguchi, A.; Fukushima, M.; Watanabe, N.; Nishimura, F. Adipose Tissue Complement Factor B Promotes Adipocyte Maturation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaicu, S.I.; Tatomir, A.; Boodhoo, D.; Vesa, S.; Mircea, P.A.; Rus, H. The Role of Complement System in Adipose Tissue-Related Inflammation. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, S.; Lokki, A.I.; Hanttu, A.; Nissilä, E.; Heinonen, S.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lundbom, J.; Lundbom, N.; Saarinen, L.; Tynninen, O.; et al. Upregulation of Early and Downregulation of Terminal Pathway Complement Genes in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue and Adipocytes in Acquired Obesity. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, N.-J.; Kim, S.; Jang, B.-H.; Chang, S.-H.; Yun, U.J.; Park, K.-M.; Waki, H.; Li, D.Y.; Tontonoz, P.; Park, K.W. Small Molecule-Induced Complement Factor D (Adipsin) Promotes Lipid Accumulation and Adipocyte Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, A.; Lowell, B.B.; Damm, D.; Leibel, R.L.; Ravussin, E.; Jimerson, D.C.; Lesem, M.D.; Van Dyke, D.C.; Daly, P.A.; Chatis, P. Concentrations of Adipsin in Blood and Rates of Adipsin Secretion by Adipose Tissue in Humans with Normal, Elevated and Diminished Adipose Tissue Mass. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1994, 18, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Maslowska, M.; Vu, H.; Phelis, S.; Sniderman, A.D.; Rhode, B.M.; Blank, D.; Cianflone, K. Plasma Acylation Stimulating Protein, Adipsin and Lipids in Non-Obese and Obese Populations. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 29, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, G.; Fogari, E.; D’Angelo, A.; Bianchi, L.; Bonaventura, A.; Romano, D.; Maffioli, P. Adipocytokine Levels in Obese and Non-Obese Subjects: An Observational Study. Inflammation 2013, 36, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, C.M.; Yates, J.R.W.; den Hollander, A.I.; Seddon, J.M.; Swaroop, A.; Stambolian, D.; Fauser, S.; Hoyng, C.; Yu, Y.; Atsuhiro, K.; et al. Complement Factor D in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 8828–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, T.; Satoh, K.; Shimizu, T.; Ikeda, S.; Kikuchi, N.; Satoh, T.; Kurosawa, R.; Nogi, M.; Sunamura, S.; Yaoita, N.; et al. Identification of Adipsin as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e013716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Franco, G.; Tardif, G.; Mineau, F.; Paré, F.; Lussier, B.; Fahmi, H.; Pelletier, J.-P.; Martel-Pelletier, J. High in Vivo Levels of Adipsin Lead to Increased Knee Tissue Degradation in Osteoarthritis: Data from Humans and Animal Models. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2018, 57, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, S.-F.; Yu, C.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, R.; Pei, L.; Huang, Y.-L.; Pang, N.-Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ling, W.; et al. Association of Circulating Adipsin, Visfatin, and Adiponectin with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adults: A Case-Control Study. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursoy Calan, O.; Calan, M.; Yesil Senses, P.; Unal Kocabas, G.; Ozden, E.; Sari, K.R.; Kocar, M.; Imamoglu, C.; Senses, Y.M.; Bozkaya, G.; et al. Increased Adipsin Is Associated with Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Metabolic Disturbances in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2016, 85, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilenko, M.A.; Kirienkova, E.V.; Skuratovskaia, D.A.; Zatolokin, P.A.; Mironyuk, N.I.; Litvinova, L.S. The Role of Production of Adipsin and Leptin in the Development of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Abdominal Obesity. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 475, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ge, Q.; Ding, Y.; Qu, H.; Wei, H.; Wu, R.; Yao, L.; Wei, Q.; Feng, Z.; Long, J.; et al. Relationship between Serum Adipsin and the First Phase of Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Individuals with Different Glucose Tolerance. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-S.; Lee, W.-J.; Lee, I.-T.; Lin, S.-Y.; Lee, W.-L.; Liang, K.-W.; Sheu, W.H.-H. Association Between Serum Adipsin Levels and Insulin Resistance in Subjects With Various Degrees of Glucose Intolerance. J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 3, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.C.; Ljubicic, S.; Leibiger, B.; Kern, M.; Leibiger, I.B.; Moede, T.; Kelly, M.E.; Bhowmick, D.C.; Murano, I.; Cohen, P.; et al. Adipsin Is an Adipokine That Improves β Cell Function in Diabetes. Cell 2014, 158, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volanakis, J.E.; Narayana, S.V. Complement Factor D, a Novel Serine Protease. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pascual, M.; Steiger, G.; Estreicher, J.; Macon, K.; Volanakis, J.E.; Schifferli, J.A. Metabolism of Complement Factor D in Renal Failure. Kidney Int. 1988, 34, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volanakis, J.E.; Barnum, S.R.; Giddens, M.; Galla, J.H. Renal Filtration and Catabolism of Complement Protein D. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 312, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, M.; Paccaud, J.P.; Macon, K.; Volanakis, J.E.; Schifferli, J.A. Complement Activation by the Alternative Pathway Is Modified in Renal Failure: The Role of Factor D. Clin. Nephrol. 1989, 32, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaya da Costa, M.; Poppelaars, F.; van Kooten, C.; Mollnes, T.E.; Tedesco, F.; Würzner, R.; Trouw, L.A.; Truedsson, L.; Daha, M.R.; Roos, A.; et al. Age and Sex-Associated Changes of Complement Activity and Complement Levels in a Healthy Caucasian Population. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnum, S.R.; Niemann, M.A.; Kearney, J.F.; Volanakis, J.E. Quantitation of Complement Factor D in Human Serum by a Solid-Phase Radioimmunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1984, 67, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-P.; Li, H.-M.; Leng, R.-X.; Li, X.-P.; Li, X.-M.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Plasma Levels of Adipokines in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Cytokine 2016, 86, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomback, A.S.; Santoriello, D.; Avasare, R.S.; Regunathan-Shenk, R.; Canetta, P.A.; Ahn, W.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Marasa, M.; Rosenstiel, P.E.; Herlitz, L.C.; et al. C3 Glomerulonephritis and Dense Deposit Disease Share a Similar Disease Course in a Large United States Cohort of Patients with C3 Glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigouroux, C.; Caron-Debarle, M.; Le Dour, C.; Magré, J.; Capeau, J. Molecular Mechanisms of Human Lipodystrophies: From Adipocyte Lipid Droplet to Oxidative Stress and Lipotoxicity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, K.-Y.; Jeon, E.J.; Leem, J.; Park, J.-H.; Cho, H. Regulation of Adipsin Expression by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Adipocytes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mogilenko, D.A.; Kudriavtsev, I.V.; Shavva, V.S.; Dizhe, E.B.; Vilenskaya, E.G.; Efremov, A.M.; Perevozchikov, A.P.; Orlov, S.V. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α Positively Regulates Complement C3 Expression but Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor α-Mediated Activation of C3 Gene in Mammalian Hepatic-Derived Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araújo-Vilar, D.; Santini, F. Diagnosis and Treatment of Lipodystrophy: A Step-by-Step Approach. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caravaca-Fontán, F.; Lucientes, L.; Cavero, T.; Praga, M. Update on C3 Glomerulopathy: A Complement-Mediated Disease. Nephron 2020, 144, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Haas, M.; Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D.; Rennke, H.G.; Jennette, J.C.; Bajema, I.M.; Alpers, C.E.; Chang, A.; Cornell, L.D.; et al. Mayo Clinic/Renal Pathology Society Consensus Report on Pathologic Classification, Diagnosis, and Reporting of GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cereijo, R.; Quesada-López, T.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Tarascó, J.; Pellitero, S.; Reyes, M.; Puig-Domingo, M.; Giralt, M.; Sánchez-Infantes, D.; Villarroya, F. The Chemokine CXCL14 Is Negatively Associated with Obesity and Concomitant Type-2 Diabetes in Humans. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 2021, 45, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, A.M.; Corvillo, F.; Magda, M.; Stasiłojć, G.; Nozal, P.; Pérez-Valdivia, M.Á.; Cabello-Chaves, V.; Rodríguez de Córdoba, S.; López-Trascasa, M.; Okrój, M. Testing the Activity of Complement Convertases in Serum/Plasma for Diagnosis of C4NeF-Mediated C3 Glomerulonephritis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Female Sex (%) | Mean Age (Range) | C3 (mg/dL) * | C3 Low (%) | C3NeF Positive (%) | Glomerulopathy (%) | Location of Lipodystrophy | Lipodystrophy Related Mutations ¥ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls (n = 50) | 80% | 29.88 (6–66) | 112.65 | None | None | NA | NA | NA |
| BSS (n = 13) | 85% | 33.69 (11–76) | 63.75 | 69.23 | 69.23 | 23.07 | Upper body | None |
| C3G (n = 22) | 77% | 26.2 (7–76) | 47.8 | 72.72 | 68.18 | 100 | None | NA |
| AGL (n = 20) | 80% | 27 (6–68) | 104.56 | None | None | None | Whole body | None |
| C3 | C5 | CFD | PPARG | CEBPA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female Barraquer–Simons syndrome (arm, n = 1) | 56.9 | 0.95 | 99.3 | 10.1 | 10.9 |
| Female control (arm, n = 1) | 84.8 | 0.67 | 194.0 | 36.5 | 37.7 |
| Male control (arm, n = 1) | 116.0 | 0.40 | 100.3 | 51.0 | 58.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corvillo, F.; González-Sánchez, L.; López-Lera, A.; Arjona, E.; Ceccarini, G.; Santini, F.; Araújo-Vilar, D.; Brown, R.J.; Villarroya, J.; Villarroya, F.; et al. Complement Factor D (adipsin) Levels Are Elevated in Acquired Partial Lipodystrophy (Barraquer–Simons syndrome). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126608
Corvillo F, González-Sánchez L, López-Lera A, Arjona E, Ceccarini G, Santini F, Araújo-Vilar D, Brown RJ, Villarroya J, Villarroya F, et al. Complement Factor D (adipsin) Levels Are Elevated in Acquired Partial Lipodystrophy (Barraquer–Simons syndrome). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126608
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorvillo, Fernando, Laura González-Sánchez, Alberto López-Lera, Emilia Arjona, Giovanni Ceccarini, Ferruccio Santini, David Araújo-Vilar, Rebecca J Brown, Joan Villarroya, Francesc Villarroya, and et al. 2021. "Complement Factor D (adipsin) Levels Are Elevated in Acquired Partial Lipodystrophy (Barraquer–Simons syndrome)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126608
APA StyleCorvillo, F., González-Sánchez, L., López-Lera, A., Arjona, E., Ceccarini, G., Santini, F., Araújo-Vilar, D., Brown, R. J., Villarroya, J., Villarroya, F., Rodríguez de Córdoba, S., Caballero, T., Nozal, P., & López-Trascasa, M. (2021). Complement Factor D (adipsin) Levels Are Elevated in Acquired Partial Lipodystrophy (Barraquer–Simons syndrome). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6608. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126608








