Protease Substrate-Independent Universal Assay for Monitoring Digestion of Native Unmodified Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Instrumentation, and Assay Buffers
2.2. Potease Activity and Inhibition Monitoring Utilizing the Protein-Probe Technique
2.3. Universal, Substrate Independent Protease Activity Monitoring with the Protein-Probe
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
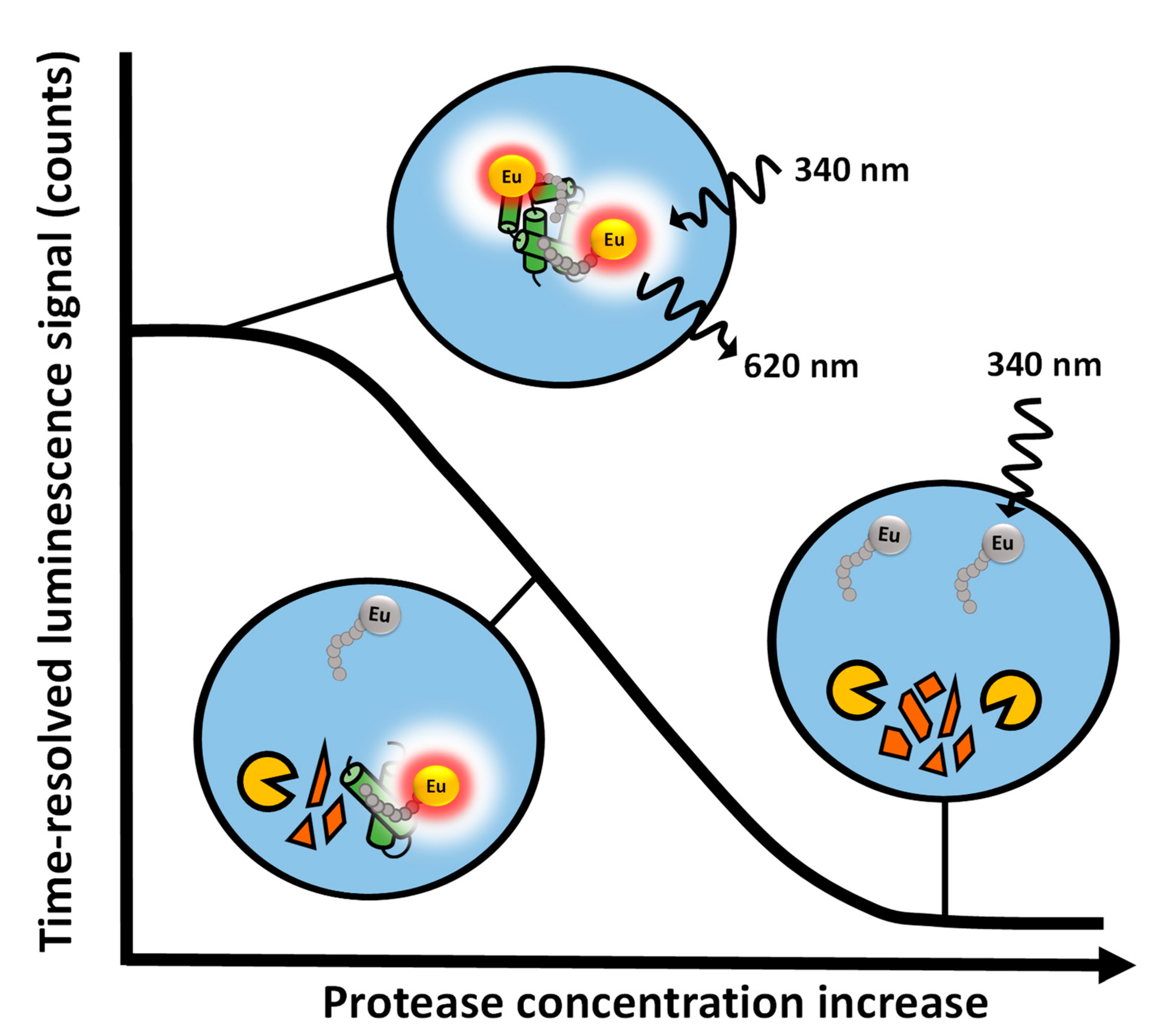
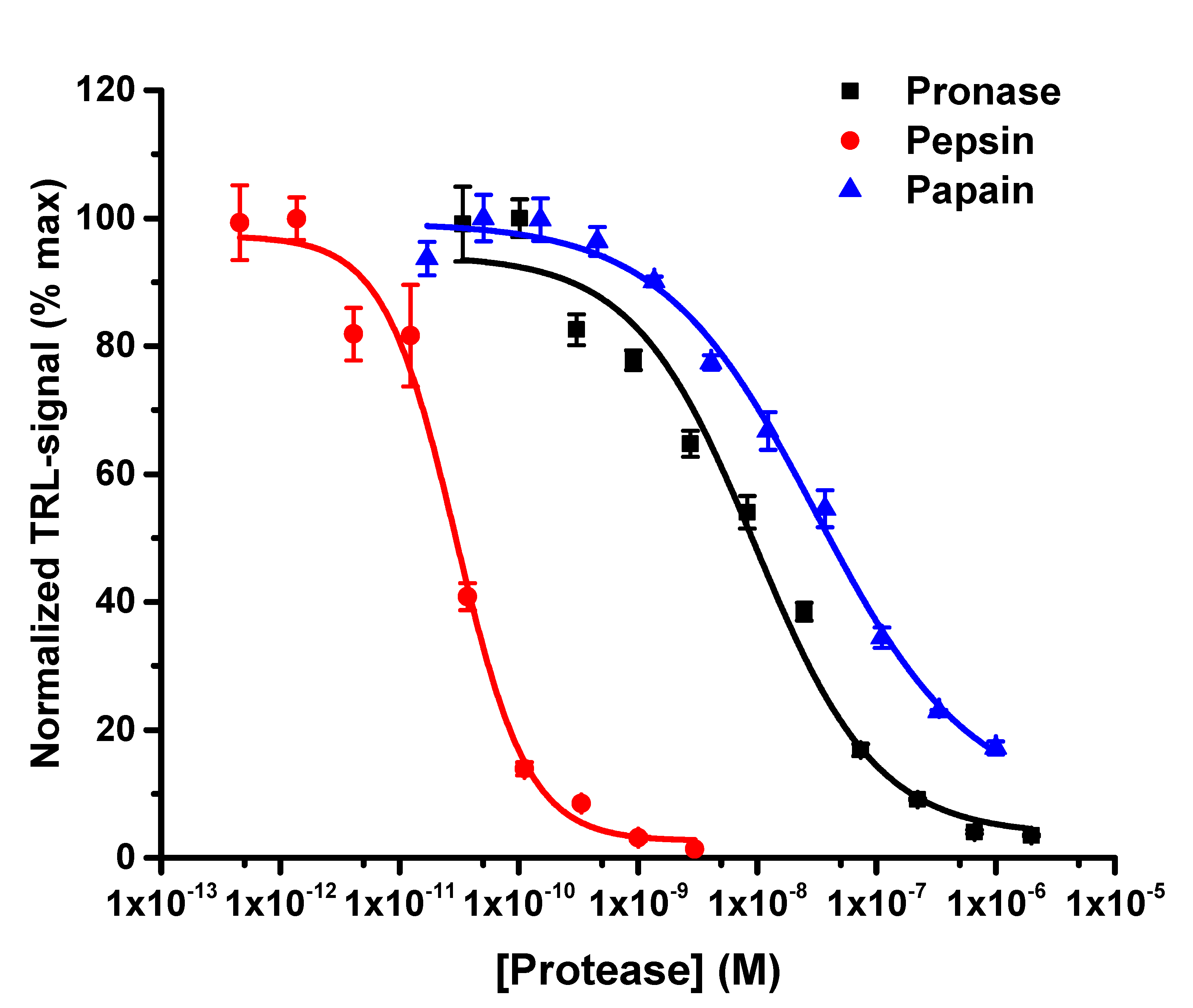
3.1. The Protein-Probe Monitors Protease Activity with High Sensitivity
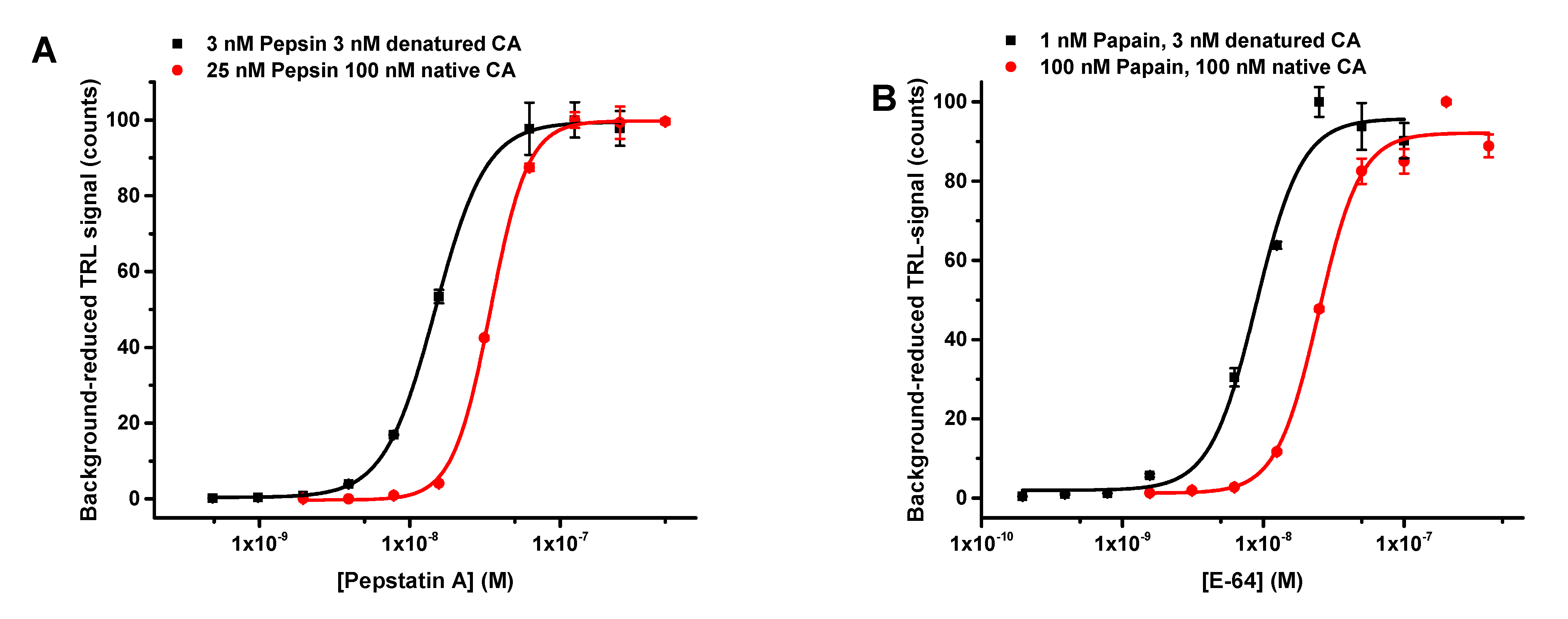
3.2. The Protein-Probe Method Enables Efficient Protease Concentration and Inhibition Dependend Activity Monitoring
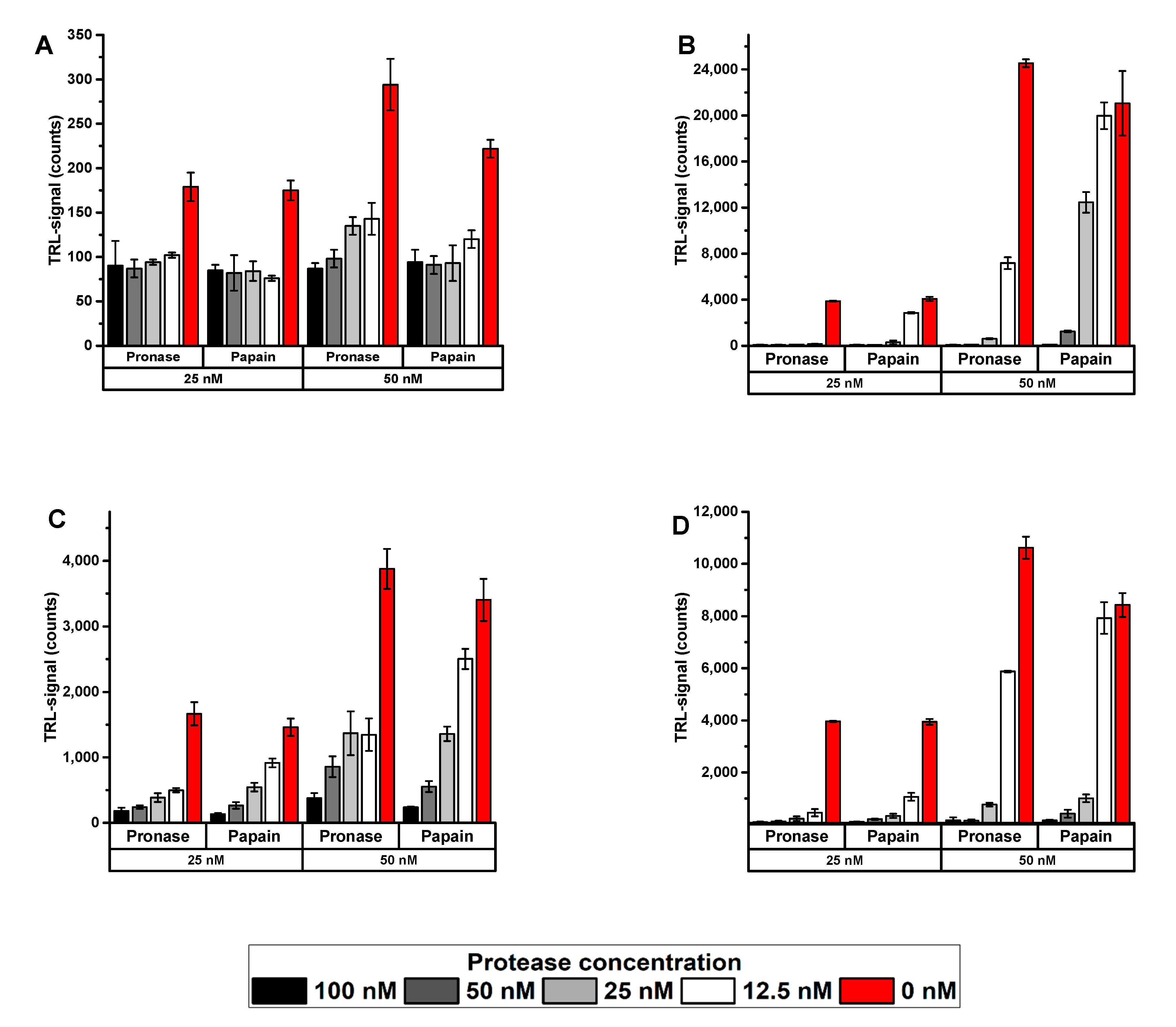
3.3. The Protein-Probe Enables Universal, Substrate-Independent Protease Activity Monitoring
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | peptidyl dipeptidase A |
| BRET | Bioluminescence energy transfer |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CA | Carbonic anhydrase |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| EC50 | Half-maximal effectivity concentration |
| eIF4A1 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A1 |
| FP | Fluorescence polarization |
| FRET | Förster resonance energy transfer |
| Gαi | G protein alpha I subunit |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| HTS | High-throughput screening |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| KRAS | Kirsten RAt Sarcoma virus |
| MDH | Malate dehydrogenase |
| PTX | Pertussis toxin |
| p120GAP | Human Ras GTPase-activating protein 1 |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SOScat | Son of sevenless catalytic domain |
| S/B | Signal to background |
| Tm | Denaturation temperature |
| TRL | Time-resolved luminescence |
References
- Rawlings, N.D.; Salvesen, G. Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes; Elsevier Ltd: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volumes 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmeade, S.R.; Lou, W.; Lövgren, J.; Malm, J.; Lilja, H.; Isaacs, J.T. Specific and Efficient Peptide Substrates for Assaying the Proteolytic Activity of Prostate-Specific Antigen. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4924–4930. [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín, C.; Bond, J.S. Proteases: Multifunctional Enzymes in Life and Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30433–30437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, I.L.H.; Yang, K.L. Recent Developments in Protease Activity Assays and Sensors. Analyst 2017, 142, 1867–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, X.S.; Sánchez, L.M.; Overall, C.M.; López-Otín, C. Human and Mouse Proteases: A Comparative Genomic Approach. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davie, E.W.; Fujikawa, K.; Kisiel, W. The Coagulation Cascade: Initiation, Maintenance, and Regulation. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 10363–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haim, H.; Salas, I.; Sodroski, J. Proteolytic Processing of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Envelope Glycoprotein Precursor Decreases Conformational Flexibility. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1884–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Nair, S. Proteases in Cardiometabolic Diseases: Pathophysiology, Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Basis of Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saftig, P.; Hunziker, E.; Wehmeyer, O.; Jones, S.; Boyde, A.; Rommerskirch, W.; Moritz, J.D.; Schu, P.; Von Figura, K. Impaired Osteoclastic Bone Resorption Leads to Osteopetrosis in Cathepsin-K-Deficient Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13453–13458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelb, B.D.; Shi, G.-P.; Chapman, H.A.; Desnick, R.J. Pycnodysostosis, a Lysosomal Disease Caused by Cathepsin K Deficiency. Science 1996, 273, 1236–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Yankner, B.A. Apoptosis in the Nervous System. Nature 2000, 407, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberds, S.L. BACE Knockout Mice Are Healthy despite Lacking the Primary Beta-Secretase Activity in Brain: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havale, S.H.; Pal, M. Medicinal Chemistry Approaches to the Inhibition of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1783–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koblinski, J.E.; Ahram, M.; Sloane, B.F. Unraveling the Role of Proteases in Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 291, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, G.; Rittenhouse, H.G.; Mikolajczyk, S.D.; Blair Shamel, L.; Semjonow, A. Twenty Years of PSA: From Prostate Antigen to Tumor Marker. Rev. Urol. 2007, 9, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Y. HIV Protease Inhibitors: A Review of Molecular Selectivity and Toxicity. HIV/AIDS Res. Palliat. Care 2015, 7, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leuw, P.; Stephan, C. Protease Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. GMS Infect. Dis. 2017, 5, Doc08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E. Antiviral Drugs in Current Clinical Use. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 30, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhanisamy, S.; Stuver, C.M.; Livingston, D.J. Automation of a High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Based Enzyme Assay: Evaluation of Inhibition Constants for Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Protease Inhibitors. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 229, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schebb, N.H.; Vielhaber, T.; Jousset, A.; Karst, U. Development of a Liquid Chromatography-Based Screening Methodology for Proteolytic Enzyme Activity. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4407–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittampalam, G.S.; Coussens, N.P.; Editor, A.S.; Arkin, M.; Auld, D.; Austin, C.; Bejcek, B.; Glicksman, M.; Inglese, J.; Iversen, P.W.; et al. Assay Guidance Manual; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Charney, J.; Tomarelli, R.M. A Colorimetric Method for the Determination of the Proteolytic Activity of Duodenal Juice. J. Biol. Chem. 1947, 171, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupp-Enyard, C. Sigma’s Non-Specific Protease Activity Assay—Casein as a Substrate. J. Vis. Exp. 2008, 19, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twining, S.S. Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-Labeled Casein Assay for Proteolytic Enzymes. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 143, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kim, C.; Cho, J.; Ahn, K.; Kim, K. Measurement of Protease Activity of Live Uronema Marinum (Ciliata: Scuticociliatida) by Fluorescence Polarization. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2003, 54, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zauner, T.; Berger-Hoffmann, R.; Müller, K.; Hoffmann, R.; Zuchner, T. Highly Adaptable and Sensitive Protease Assay Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7356–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettritz, R. Neutral Serine Proteases of Neutrophils. Immunological Reviews; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacres, H.; Dumancic, M.M.; Horne, I.; Trowell, S.C. Direct Comparison of Fluorescence- and Bioluminescence-Based Resonance Energy Transfer Methods for Real-Time Monitoring of Thrombin-Catalysed Proteolytic Cleavage. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Dacres, H.; Anderson, A.; Trowell, S.C.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of Static and Microfluidic Protease Assays Using Modified Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer Chemistry. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H. Assay of Proteolytic Enzymes by the Fluorescence Polarization Technique. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 92, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, L.; Nurnberg, J.; Vacari, B.M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y. Cleavage of Pro-Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha by ADAM Metallopeptidase Domain 17: A Fluorescence-Based Protease Assay Cleaves Its Natural Protein Substrate. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 445, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côlho, D.F.; Saturnino, T.P.; Fernandes, F.F.; Mazzola, P.G.; Silveira, E.; Tambourgi, E.B. Azocasein Substrate for Determination of Proteolytic Activity: Reexamining a Traditional Method Using Bromelain Samples. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorinen, E.; Valtonen, S.; Eskonen, V.; Kariniemi, T.; Jakovleva, J.; Kopra, K.; Härmä, H. Sensitive Label-Free Thermal Stability Assay for Protein Denaturation and Protein–Ligand Interaction Studies. Anal. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, S.; Vuorinen, E.; Kariniemi, T.; Eskonen, V.; Le Quesne, J.; Bushell, M.; Härmä, H.; Kopra, K. Nanomolar Protein–Protein Interaction Monitoring with a Label-Free Protein-Probe Technique. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, Y.; Miettinen, M.; de Oliveira, D.K.H.; Tamirat, M.Z.; Näreoja, K.; Tiwari, A.; Hottiger, M.O.; Johnson, M.S.; Lehtiö, L.; Pulliainen, A.T. Discovery of Compounds Inhibiting the ADP-Ribosyltransferase Activity of Pertussis Toxin. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, A.; Veltel, S.; Pellinen, T.; Padzik, A.; Coffey, E.; Marjomäki, V.; Ivaska, J. Competitive Binding of Rab21 and P120RasGAP to Integrins Regulates Receptor Traffic and Migration. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopra, K.; Vuorinen, E.; Abreu-Blanco, M.; Wang, Q.; Eskonen, V.; Gillette, W.; Pulliainen, A.T.; Holderfield, M.; Härmä, H. Homogeneous Dual-Parametric Coupled Assay for Simultaneous Nucleotide Exchange and KRAS/RAF-RBD Interaction Monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezawa, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Morishima, H.; Matsuzaki, M.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T. Pepstatin, A New Pepsin Inhibitor Produced by Actinomygetes. J. Antibiot. 1970, 23, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, N.B.; Taylor, W.H. Comparative Pepstatin Inhibition Studies on Individual Human Pepsins and Pepsinogens 1, 3 and 5(Gastricsin) and Pig Pepsin A. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2003, 18, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Mizoue, K.; Kitamura, K.; Tse, W.C.; Huber, C.P.; Ishida, T. Structural Basis of Inhibition of Cysteine Proteases by E-64 and Its Derivatives. Biopolym. Pept. Sci. Sect. 1999, 51, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Substrate Protein | Tm (°C) | Temperature for Substrate Screening |
|---|---|---|
| p120GAP | 53.6 ± 0.6 | 60 °C |
| PTX | 54.1 ± 0.6 | 60 °C |
| KRAS | 62.7 ± 0.3 | 70 °C |
| MDH | 44.6 ± 0.5 | 60 °C |
| Gαi | 56.9 ± 0.6 | 60 °C |
| eIF4A1 | 54.9 ± 0.2 | 60 °C |
| SOScat | 45.3 ± 0.2 | 60 °C |
| BSA | 57.0 ± 1.3 | 60 °C |
| CA | 67.9 ± 0.9 | 70 °C |
| Digestion Efficiency (%) | S/B Ratio (Sample/Buffer) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronase | Papain | Pronase | Papain | ||||||
| Substrate | Protease (nM) | Native a | Denatured b | Native | Denatured | Native | Denatured | Native | Denatured |
| p120GAP | 100 | 99 | 100 | 98 | 99 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 50 | 95 | 98 | 98 | 99 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | |
| 25 | 87 | 83 | 97 | 98 | 9 | 19 | 3 | 3 | |
| 12.5 | 78 | 68 | 97 | 100 | 14 | 35 | 3 | 1 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 58 | 106 | 71 | 121 | |
| PTX | 100 | 97 | 100 | 94 | 100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 50 | 93 | 99 | 87 | 100 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| 25 | 91 | 100 | 86 | 100 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| 12.5 | 87 | 99 | 77 | 100 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 7 | 58 | 5 | 54 | |
| KRAS | 100 | 95 | 100 | 88 | 95 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 50 | 96 | 100 | 82 | 84 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | |
| 25 | 93 | 99 | 66 | 55 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 11 | |
| 12.5 | 91 | 99 | 62 | 49 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 13 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 9 | 168 | 5 | 24 | |
| MDH | 100 | 88 | 100 | ND c | 100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 50 | 82 | 100 | ND | 95 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 16 | |
| 25 | 65 | 98 | ND | 52 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 140 | |
| 12.5 | 62 | 72 | ND | 5 | 2 | 110 | 2 | 276 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 5 | 385 | 2.9 | 291 | |
| Gαi | 100 | 82 | 73 | 82 | 71 | 10 | 25 | 7 | 29 |
| 50 | 71 | 61 | 79 | 73 | 15 | 35 | 8 | 27 | |
| 25 | 65 | 55 | 60 | 62 | 18 | 40 | 14 | 38 | |
| 12.5 | 61 | 45 | 57 | 62 | 20 | 50 | 15 | 38 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 50 | 89 | 33 | 99 | |
| eIF4A1 | 100 | 96 | 99 | 92 | 99 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| 50 | 86 | 96 | 80 | 99 | 6 | 5 | 11 | 2 | |
| 25 | 62 | 89 | 66 | 93 | 16 | 13 | 17 | 10 | |
| 12.5 | 27 | 13 | 67 | 38 | 29 | 95 | 17 | 88 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 39 | 110 | 48 | 142 | |
| SOScat | 100 | 96 | 99 | 86 | 57 | 5 | 3 | 19 | 77 |
| 50 | 92 | 99 | 77 | 35 | 8 | 4 | 31 | 117 | |
| 25 | 89 | 98 | 63 | 26 | 11 | 7 | 49 | 133 | |
| 12.5 | 75 | 96 | 49 | 12 | 23 | 14 | 66 | 157 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 90 | 327 | 130 | 180 | |
| BSA | 100 | 79 | 84 | 79 | 78 | 26 | 18 | 20 | 14 |
| 50 | 69 | 73 | 74 | 74 | 38 | 30 | 24 | 17 | |
| 25 | 52 | 59 | 65 | 68 | 59 | 44 | 31 | 21 | |
| 12.5 | 37 | 46 | 52 | 52 | 77 | 57 | 42 | 31 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 121 | 106 | 88 | 62 | |
| CA | 100 | 94 | 98 | 80 | 77 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 24 |
| 50 | 89 | 48 | 72 | 57 | 3 | 106 | 5 | 44 | |
| 25 | 79 | 4 | 60 | 31 | 4 | 192 | 6 | 70 | |
| 12.5 | 65 | 10 | 42 | 14 | 7 | 181 | 8 | 87 | |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | 17 | 200 | 14 | 101 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vuorinen, E.; Valtonen, S.; Hassan, N.; Mahran, R.; Habib, H.; Malakoutikhah, M.; Kopra, K.; Härmä, H. Protease Substrate-Independent Universal Assay for Monitoring Digestion of Native Unmodified Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126362
Vuorinen E, Valtonen S, Hassan N, Mahran R, Habib H, Malakoutikhah M, Kopra K, Härmä H. Protease Substrate-Independent Universal Assay for Monitoring Digestion of Native Unmodified Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126362
Chicago/Turabian StyleVuorinen, Emmiliisa, Salla Valtonen, Nazia Hassan, Randa Mahran, Huda Habib, Morteza Malakoutikhah, Kari Kopra, and Harri Härmä. 2021. "Protease Substrate-Independent Universal Assay for Monitoring Digestion of Native Unmodified Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126362
APA StyleVuorinen, E., Valtonen, S., Hassan, N., Mahran, R., Habib, H., Malakoutikhah, M., Kopra, K., & Härmä, H. (2021). Protease Substrate-Independent Universal Assay for Monitoring Digestion of Native Unmodified Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126362






