Establishment and Characterization of a Cell Line (S-RMS1) Derived from an Infantile Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma with SRF-NCOA2 Fusion Transcript
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
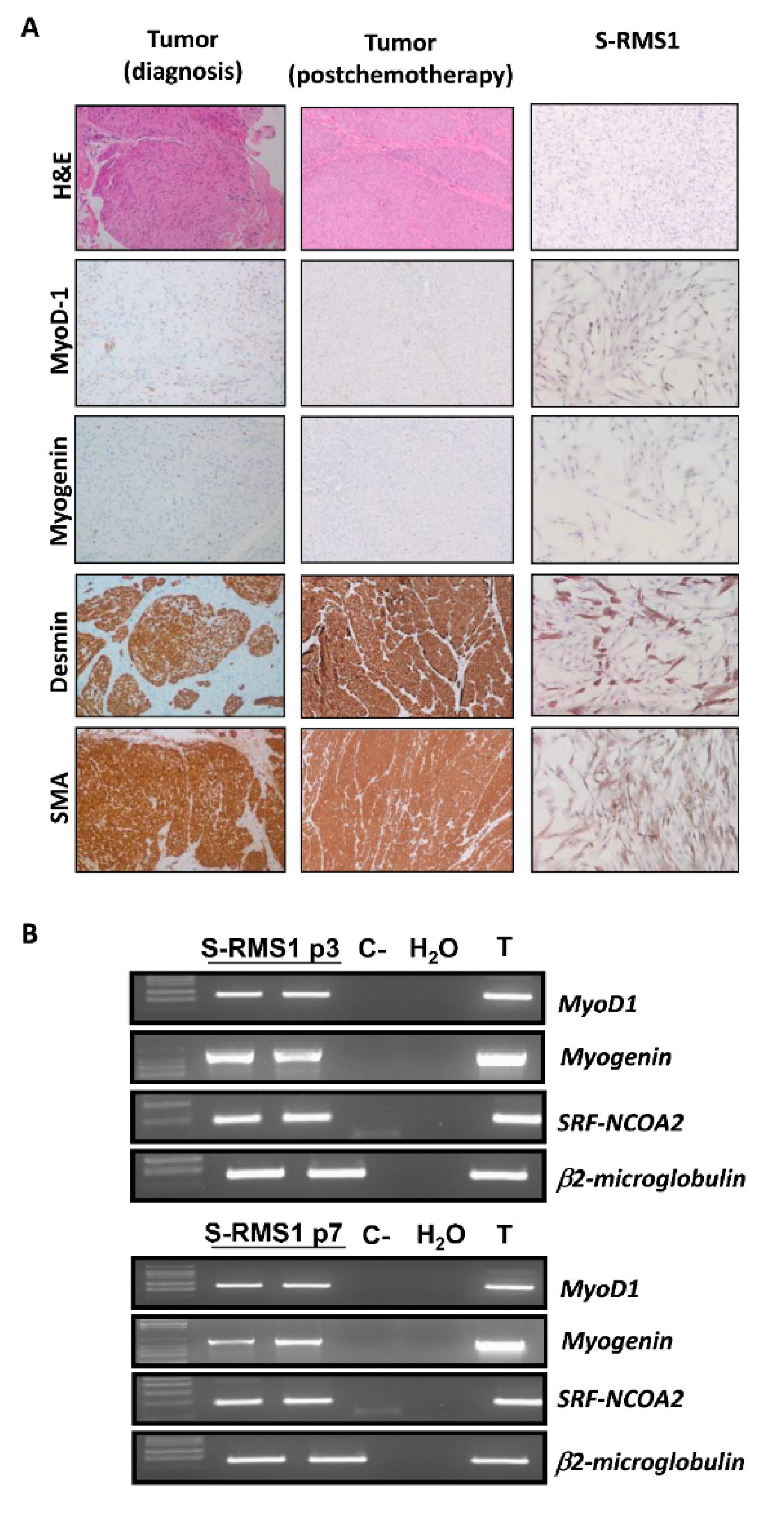
2.1. Establishment of S-RMS1 Cell Line
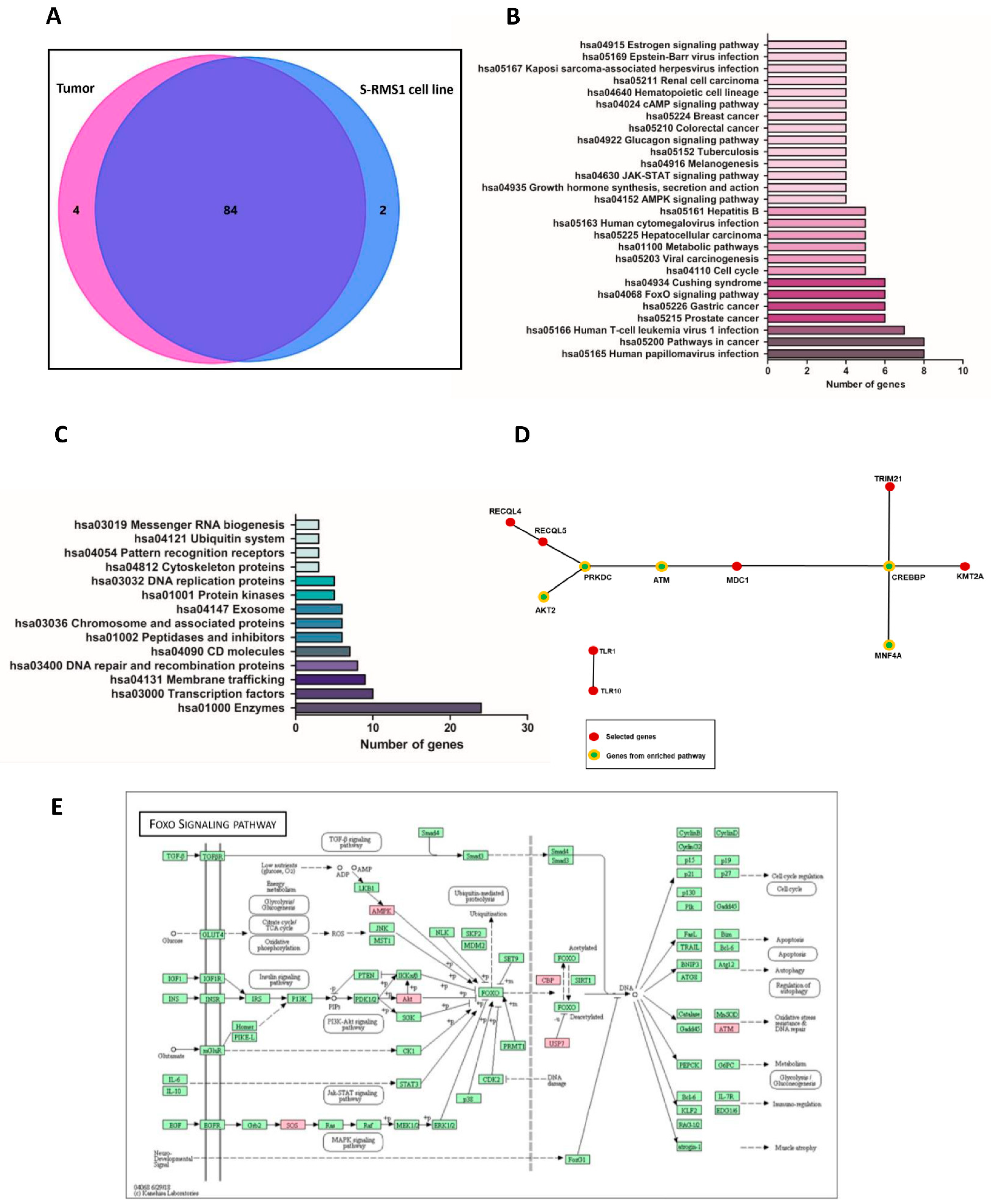
2.2. Whole Genome Resequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis of the S-RMS1 Cell Line
2.3. Clinical Exome Sequencing of Genomic DNA and Germline Variant Identification
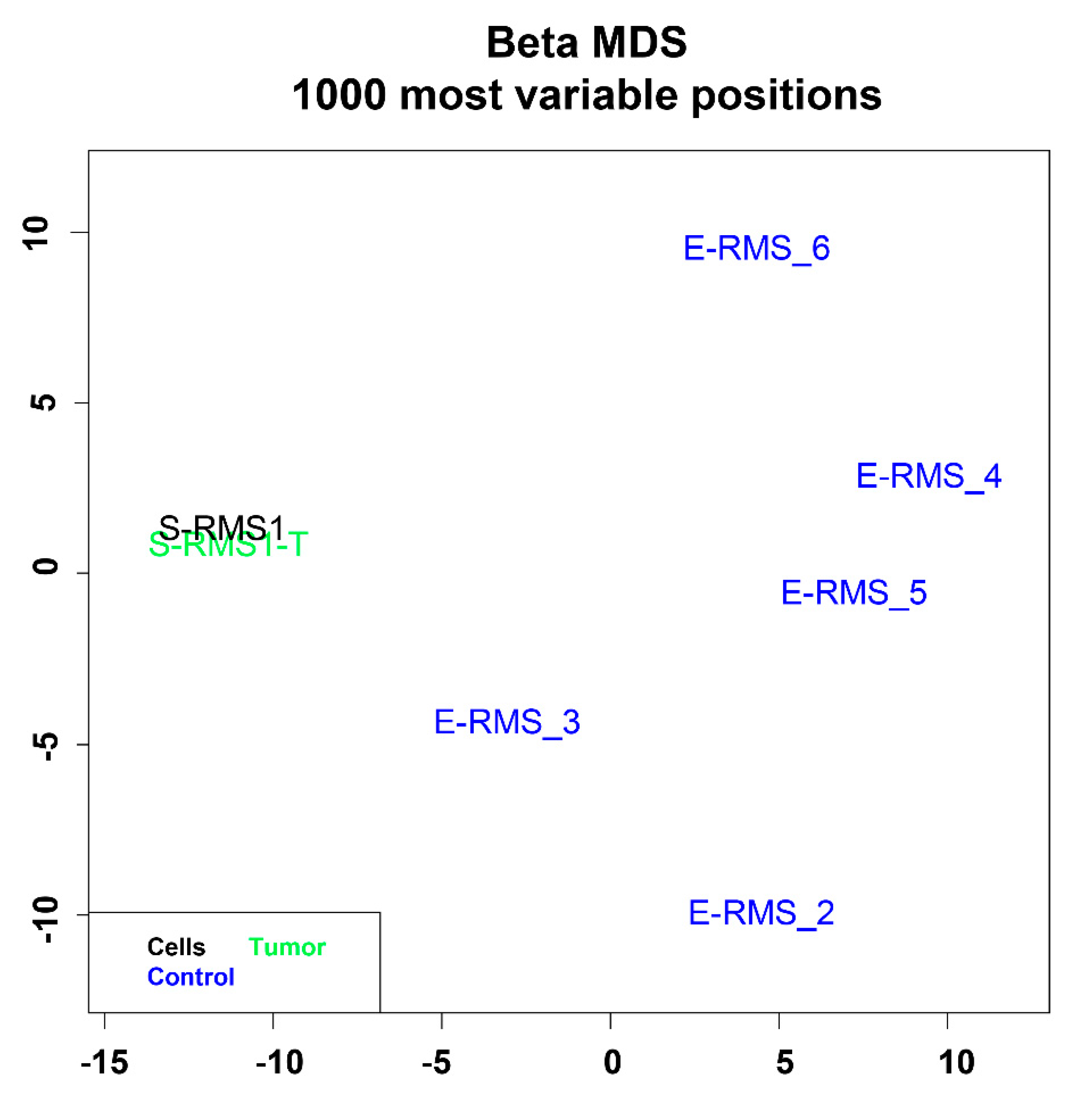
2.4. DNA Methylation Profiling of S-RMS1 Cell Line
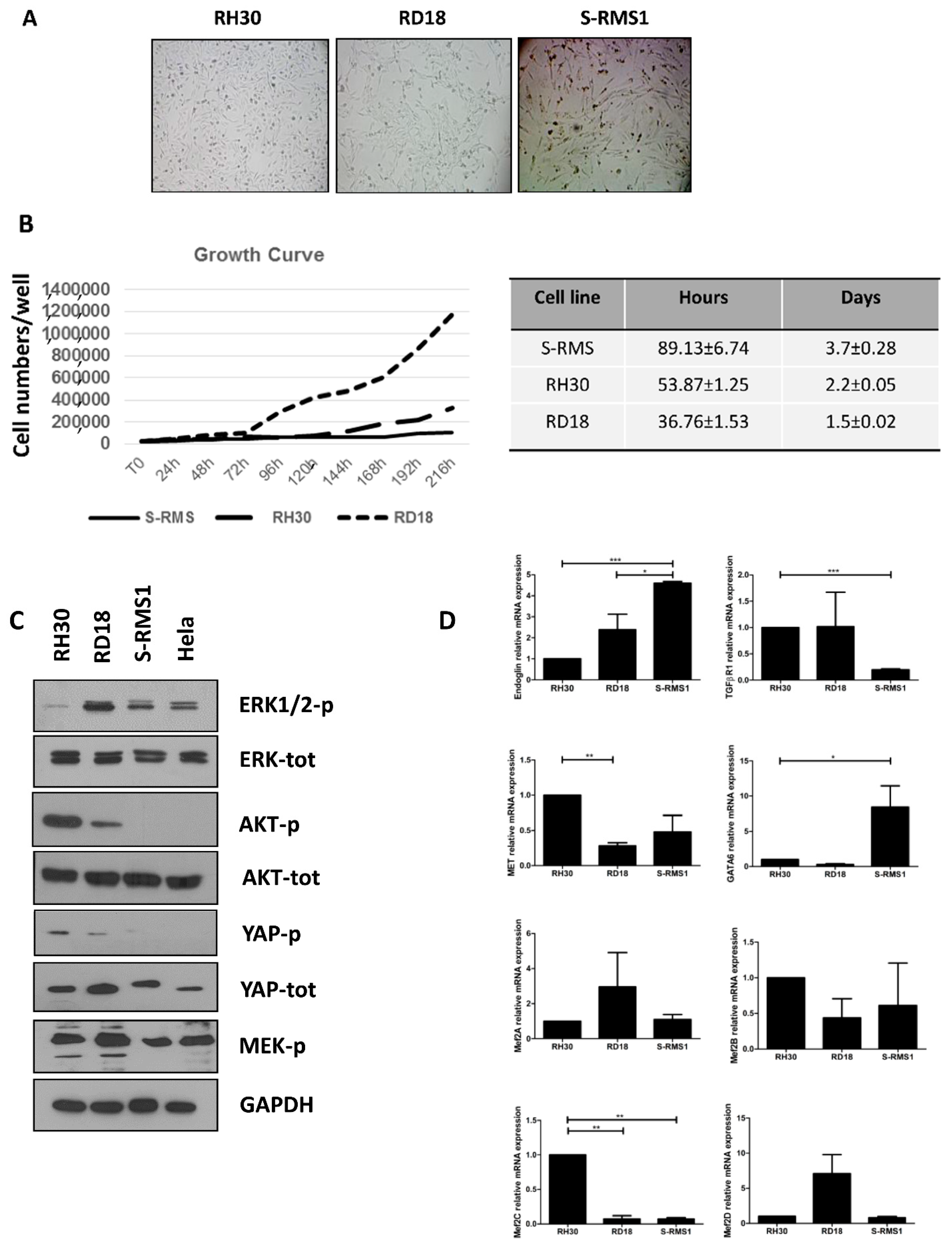
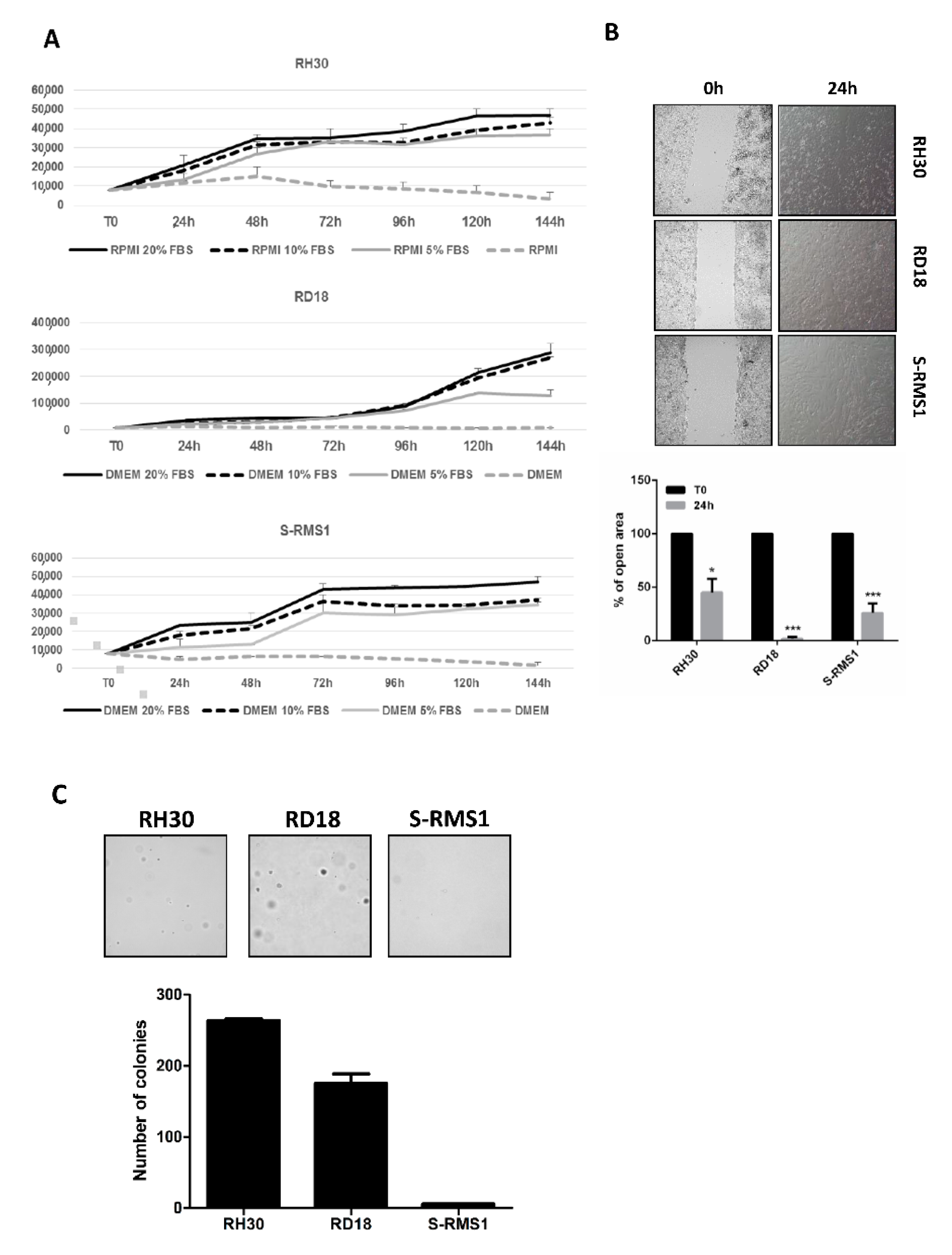
2.5. Morphology, Growth, and Molecular Characterization of S-RMS1 Cell Line
2.6. Tumorigenic Properties of S-RMS1 Cell Line
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient and Tumor Characteristics
4.2. Cell Line Establishment
4.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.4. Whole Genome Resequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.5. Clinical Exome Sequencing of Genomic DNA and Germline Variant Identification
4.6. DNA Methylation Profiling
4.7. RNA-Extraction, RT-PCR, and RT-qPCR
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Growth Characteristics
4.10. Serum Independent Growth
4.11. Wound Healing Assay
4.12. Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russo, I.; Di Paolo, V.; Gurnari, C.; Mastronuzzi, A.; Del Bufalo, F.; Di Paolo, P.L.; Di Giannatale, A.; Boldrini, R.; Milano, G.M. Congenital Rhabdomyosarcoma: A different clinical presentation in two cases. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missiaglia, E.; Williamson, D.; Chisholm, J.; Wirapati, P.; Pierron, G.; Petel, F.; Concordet, J.P.; Thway, K.; Oberlin, O.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; et al. PAX3/FOXO1 fusion gene status is the key prognostic molecular marker in rhabdomyosarcoma and significantly improves current risk stratification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzana, A.O.; Schmidt, D.; Ninfo, V.; Harms, D.; Tollot, M.; Carli, M.; Treuner, J.; Betto, R.; Salviati, G. Spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma. A prognostically favorable variant of rhabdomyosarcoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1992, 16, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschner, I.; Newton, W.A., Jr.; Schmidt, D.; Sachs, N.; Asmar, L.; Hamoudi, A.; Harms, D.; Maurer, H.M. Spindle cell variants of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma in the paratesticular region. A report of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1993, 17, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentzel, T.; Kuhnen, C. Spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma in adults: Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of seven new cases. Virchows Arch. 2006, 449, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, A.F.; Fletcher, C.D. Spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma in adults. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentzel, T.; Katenkamp, D. Sclerosing, pseudovascular rhabdomyosarcoma in adults. Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of three cases. Virchows Arch. 2000, 436, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.D.M.; Bridge, J.A.; Hogendoorn, P.C.W. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone; IARC: Lyon, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren, L.; Angervall, L.; Stenman, G.; Kindblom, L.G. Infantile rhabdomyofibrosarcoma: A high-grade sarcoma distinguishable from infantile fibrosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. Hum. Pathol. 1993, 24, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.M.; Sboner, A.; Zhang, L.; Kitabayashi, N.; Chen, C.L.; Sung, Y.S.; Wexler, L.H.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Edelman, M.; Sreekantaiah, C.; et al. Recurrent NCOA2 gene rearrangements in congenital/infantile spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013, 52, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Zhang, L.; Sung, Y.S.; Huang, S.C.; Chen, C.L.; Bisogno, G.; Zin, A.; Agaram, N.P.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Wexler, L.H.; et al. A Molecular Study of Pediatric Spindle and Sclerosing Rhabdomyosarcoma: Identification of Novel and Recurrent VGLL2-related Fusions in Infantile Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimatsu, Y.; Noguchi, R.; Tsuchiya, R.; Sei, A.; Sugaya, J.; Iwata, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Yoshida, A.; Kawai, A.; Kondo, T. Establishment and characterization of NCC-ssRMS1-C1: A novel patient-derived spindle-cell/sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma cell line. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleicher, S.; Grote, S.; Malenke, E.; Chan, K.C.; Schaller, M.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Riester, R.; Kluba, T.; Frauenfeld, L.; Boesmueller, H.; et al. Establishment and Characterization of a Sclerosing Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma Cell Line with a Complex Genomic Profile. Cells 2020, 9, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Yoshimatsu, Y.; Noguchi, R.; Ono, T.; Sei, A.; Takeshita, F.; Sugaya, J.; Fukushima, S.; Yoshida, A.; Ohtori, S.; et al. Establishment and characterization of NCC-DDLPS3-C1: A novel patient-derived cell line of dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vita, A.; Recine, F.; Mercatali, L.; Miserocchi, G.; Liverani, C.; Spadazzi, C.; Casadei, R.; Bongiovanni, A.; Pieri, F.; Riva, N.; et al. Myxofibrosarcoma primary cultures: Molecular and pharmacological profile. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2017, 9, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserocchi, G.; Mercatali, L.; Liverani, C.; De Vita, A.; Spadazzi, C.; Pieri, F.; Bongiovanni, A.; Recine, F.; Amadori, D.; Ibrahim, T. Management and potentialities of primary cancer cultures in preclinical and translational studies. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, D.; Brenca, M.; Baldazzi, D.; Goeman, F.; Casini, B.; De Angelis, B.; Guercio, M.; Milano, G.M.; Tamborini, E.; Busico, A.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Approaches for the Identification of Pathognomonic Fusion Transcripts in Sarcomas: The Experience of the Italian ACC Sarcoma Working Group. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; O’Malley, B.W. Molecular mechanisms and cellular biology of the steroid receptor coactivator (SRC) family in steroid receptor function. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2002, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipes, G.C.; Creemers, E.E.; Olson, E.N. The myocardin family of transcriptional coactivators: Versatile regulators of cell growth, migration and myogenesis. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaousis, G.N.; Papadopoulou, E.; Apessos, A.; Agiannitopoulos, K.; Pepe, G.; Kampouri, S.; Diamantopoulos, N.; Floros, T.; Iosifidou, R.; Katopodi, O.; et al. Analysis of hereditary cancer syndromes by using a panel of genes: Novel and multiple pathogenic mutations. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelsche, C.; Schrimpf, D.; Stichel, D.; Sill, M.; Sahm, F.; Reuss, D.; Blattner, M.; Worst, B.; Heilig, C.E.; Bec, K.; et al. Sarcoma classification by DNA methylation profiling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, V.; Russo, I.; Boldrini, R.; Ravà, L.; Pezzullo, M.; Benedetti, M.C.; Galardi, A.; Colletti, M.; Rota, R.; Orlando, D.; et al. Evaluation of Endoglin (CD105) expression in pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, V.Y.; Fletcher, C.D.M. WHO classification of soft tissue tumours: An update based on the 2013 (4th) edition. Pathology 2014, 46, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butel, T.; Marie Karanian, M.; Pierron, G.; Orbach, D.; Ranchere, D.; Cozic, N.; Louise Galmiche, L.; Coulomb, A.; Corradini, N.; Lacour, B.; et al. Integrative clinical and biopathology analyses to understand the clinical heterogeneity of infantile rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the French MMT committee. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 2698–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanian, M.; Kelsey, A.; Paindavoine, S.; Duc, A.; Vanacker, H.; Hook, L.; Weinbreck, N.; Delfour, C.; Minard, V.; Baillard, P.; et al. SRF Fusions Other Than With RELA Expand the Molecular Definition of SRF-fused Perivascular Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cen, L.; Hsieh, F.C.; Lin, H.J.; Chen, C.S.; Qualman, S.J.; Lin, J. PDK-1/AKT pathway as a novel therapeutic target in rhabdomyosarcoma cells using OSU-03012 compound. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfleger, C.M. The Hippo pathway: A master regulatory network important in development and dysregulated in disease. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 123, 181–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.D.; Tremblay, A.M.; Murray, G.I.; Wackerhage, H. The Hippo signal transduction pathway in soft tissue sarcomas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1856, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Habeebu, S.S.; Sherman, A.K.; Ye, S.Q.; Wood, N.; Chastain, K.M.; Tsokos, M.G. Potential Value of YAP Staining in Rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2018, 66, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, A.M.; Missiaglia, E.; Galli, G.G.; Hettmer, S.; Urcia, R.; Carrara, M.; Judson, R.N.; Thway, K.; Nadal, G.; Selfe, J.L.; et al. The Hippo transducer YAP1 transforms activated satellite cells and is a potent effector of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma formation. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, N.; Kattih, B.; Breitbart, A.; Grund, A.; Geffers, R.; Molkentin, J.D.; Kispert, A.; Wollert, K.C.; Drexler, H.; Heineke, J. GATA6 promotes angiogenic function and survival in endothelial cells by suppression of autocrine transforming growth factor beta/activin receptor-like kinase 5 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5680–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.D.; Funkhouser, J.D.; Tuck-Muller, C.M.; Gatti, R.A. Cancer susceptibility in ataxia-telangiectasia. Leukemia 1992, 6 (Suppl. 1), 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Reiman, A.; Srinivasan, V.; Barone, G.; Last, J.I.; Wootton, L.L.; Davies, E.G.; Verhagen, M.M.; Willemsen, M.A.; Weemaes, C.M.; Byrd, P.J.; et al. Lymphoid tumours and breast cancer in ataxia telangiectasia; substantial protective effect of residual ATM kinase activity against childhood tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Bhakta, K.S.; Puri, P.L.; Newbury, R.O.; Feramisco, J.R.; Wang, J.Y. Association of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) gene mutation/deletion with rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2003, 2, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. Tracking telomerase. Cell 2004, 116, S83–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blasco, M.A. Telomeres and human disease: Ageing, cancer and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojesen, S.E.; Pooley, K.A.; Johnatty, S.E.; Beesley, J.; Michailidou, K.; Tyrer, J.P.; Edwards, S.L.; Pickett, H.A.; Shen, H.C.; Smart, C.E.; et al. Multiple independent variants at the TERT locus are associated with telomere length and risks of breast and ovarian cancer. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, V.; Nelson, C.P.; Albrecht, E.; Mangino, M.; Deelen, J.; Buxton, J.L.; Hottenga, J.J.; Fischer, K.; Esko, T.; Surakka, I.; et al. Identification of seven loci affecting mean telomere length and their association with disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafnar, T.; Sulem, P.; Stacey, S.N.; Geller, F.; Gudmundsson, J.; Sigurdsson, A.; Jakobsdottir, M.; Helgadottir, H.; Thorlacius, S.; Aben, K.K.; et al. Sequence variants at the TERT-CLPTM1L locus associate with many cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borriello, A.; Caldarelli, I.; Bencivenga, D.; Criscuolo, M.; Cucciolla, V.; Tramontano, A.; Oliva, A.; Perrotta, S.; Della Ragione, F. p57(Kip2) and cancer: Time for a critical appraisal. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 10, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Karuturi, R.K.M.; Sun, F.; Aau, M.; Yu, K.; Shao, R.; Miller, L.D.; Tan, P.B.O.; Yu, Q. CDKN1C (p57) is a direct target of EZH2 and suppressed by multiple epigenetic mechanisms in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, I.; Giordano, A.; Bagella, L. Roles of enhancer of zeste homolog 2: From skeletal muscle differentiation to rhabdomyosarcoma carcinogenesis. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.M.; La Thangue, N.B. p300/CBP proteins: HATs for transcriptional bridges and scaffolds. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, D.E.; Berger, S.L. Acetylation of histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 435–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.C.; Choi, J.E.; Lombardo, S.R.; Carey, M. A mechanism for coordinating chromatin modification and preinitiation complex assembly. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, W.; Anderson, J.R.; Gehan, E.A.; Maurer, H. Pretreatment TNM staging of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A report of the intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study group. Children’s cancer study group. Pediatric oncology group. Cancer 1997, 80, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczy, C.; Petrovski, R.; Saunders, C.T.; Chorny, I.; Kruglyak, S.; Margulies, E.H.; Chuang, H.Y.; Kallberg, M.; Kumar, S.A.; Liao, A.; et al. Isaac: Ultra-fast whole-genome secondary analysis on Illumina sequencing platforms. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2041–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.C.; Berg, J.S.; Grody, W.W.; Kalia, S.S.; Korf, B.R.; Martin, C.L.; McGuire, A.L.; Nussbaum, R.L.; O’Daniel, J.M.; Ormond, K.E.; et al. ACMG recommendations for reporting of incidental findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing. American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet. Med. 2013, 15, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine JHUB, MD. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM® 2016 [cited 2016]. Available online: http://omim.org/ (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Fokkema, I.F.; Taschner, P.E.; Schaafsma, G.C.; Celli, J.; Laros, J.F.; den Dunnen, J.T. LOVD v.2.0: The next generation in gene variant databases. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, E.; De Vito, R.; Ciolfi, A.; Pedace, L.; Russo, I.; De Pasquale, M.D.; Di Giannatale, A.; Crocoli, A.; De Angelis, B.; Tartaglia, M.; et al. DNA Methylation Profiling for Diagnosing Undifferentiated Sarcoma with Capicua Transcriptional Receptor (CIC) Alterations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, C.; Anderle, M.; Gianesello, M.; Lago, C.; Miele, E.; Cardano, M.; Aiello, G.; Piazza, S.; Caron, D.; Gianno, F.; et al. Modeling medulloblastoma in vivo and with human cerebellar organoids. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, R.; Holmkvist, J.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Wang, J.; Nielsen, R. Design of association studies with pooled or un-pooled next-generation sequencing data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2010, 34, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Variation Type | Chr | dbSNP | AA Change | Zygosity | Region | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBP | Indel | chr6 | rs1478666781 | p.Gln73_Gln78del | het | Exonic | Nonframeshift |
| CASQ2 | Indel | chr1 | rs1491387135 | het | Splice Region | ||
| IL23R | Indel | chr1 | rs779016240 | hom | Splice Region | ||
| FCGR2A | SNP | chr1 | rs382627 | p.Leu273Pro | het | Exonic | Missense |
| Gene | Variation Type | Chr | dbSNP | AA Change | Zygosity | Region | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRRC37B | SNP | chr17 | rs471887 | p.Gln621His | het | Exonic | Missense |
| TPTE2 | SNP | chr13 | rs78472618 | p.Lys39Glu | het | Exonic | Missense |
| Gene | Variation Type AA Change | Location | dbSNP | ACMG | Segregation | MAX AF (%) | SIFT–PolyPhen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POLE | c.5221C>T p.Gln1741* | 12:133218390 | rs781481160 | LP | Mat | 0.00082 | |
| CDKN1C | c.392_394delAGG p.Glu131del | 11:2906325 | VUS | Pat | 0 | ||
| TERT | c.922C>A p.Pro308Thr | 5:1294079 | VUS | Mat | 0 | ||
| ATM | c.8428A>C p.Lys2810Gln | 11:108216479 | rs730881325 | VUS | Mat | 0.004 | 0.05–0.04 |
| CREBBP | c.5800T>C p.Ser1934Pro | 16:3779248 | rs587783504 | VUS | Mat | 0.035 | 0.035 |
| Sample | Sex | Age (Months) | Histology | Specimen | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-RMS1 | Male | 2 | SS-RMS | Tumor_cells | Right dorsal muscle |
| S-RMS1-T | Male | 2 | SS-RMS | Tumor_FF | Right dorsal muscle |
| E-RMS_2 | Female | 14 | E-RMS | Tumor_FFPE | Right psoas muscle |
| E-RMS_3 | Male | 5 | E-RMS | Tumor_FFPE | abdomen |
| E-RMS_4 | Male | 240 | E-RMS | Tumor_FFPE | Left paratesticular |
| E-RMS_5 | Female | 29 | E-RMS botryoid variant | Tumor_FFPE | Bladder |
| E-RMS_6 | Male | 84 | E-RMS | Tumor_FFPE | Prostate |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colletti, M.; Galardi, A.; Miele, E.; Di Paolo, V.; Russo, I.; De Stefanis, C.; De Vito, R.; Rinelli, M.; Ciolfi, A.; De Angelis, B.; et al. Establishment and Characterization of a Cell Line (S-RMS1) Derived from an Infantile Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma with SRF-NCOA2 Fusion Transcript. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115484
Colletti M, Galardi A, Miele E, Di Paolo V, Russo I, De Stefanis C, De Vito R, Rinelli M, Ciolfi A, De Angelis B, et al. Establishment and Characterization of a Cell Line (S-RMS1) Derived from an Infantile Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma with SRF-NCOA2 Fusion Transcript. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(11):5484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115484
Chicago/Turabian StyleColletti, Marta, Angela Galardi, Evelina Miele, Virginia Di Paolo, Ida Russo, Cristiano De Stefanis, Rita De Vito, Martina Rinelli, Andrea Ciolfi, Biagio De Angelis, and et al. 2021. "Establishment and Characterization of a Cell Line (S-RMS1) Derived from an Infantile Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma with SRF-NCOA2 Fusion Transcript" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 11: 5484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115484
APA StyleColletti, M., Galardi, A., Miele, E., Di Paolo, V., Russo, I., De Stefanis, C., De Vito, R., Rinelli, M., Ciolfi, A., De Angelis, B., Zin, A., Guffanti, A., Digilio, M. C., Novelli, A., Alaggio, R., Milano, G. M., & Di Giannatale, A. (2021). Establishment and Characterization of a Cell Line (S-RMS1) Derived from an Infantile Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma with SRF-NCOA2 Fusion Transcript. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115484







