Chromene-Containing Aromatic Sulfonamides with Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitory Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Evaluation of CA Inhibitory Activity
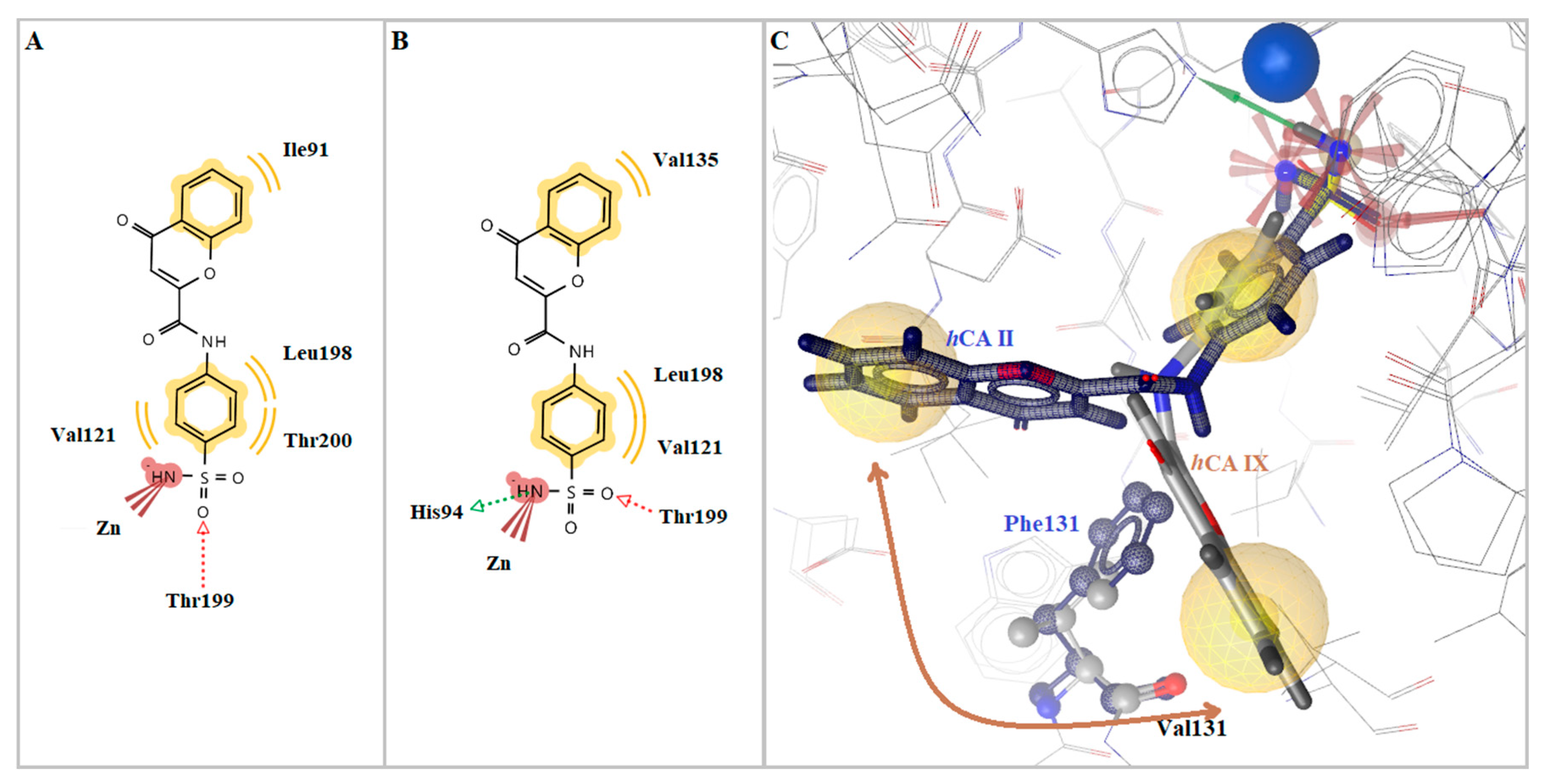
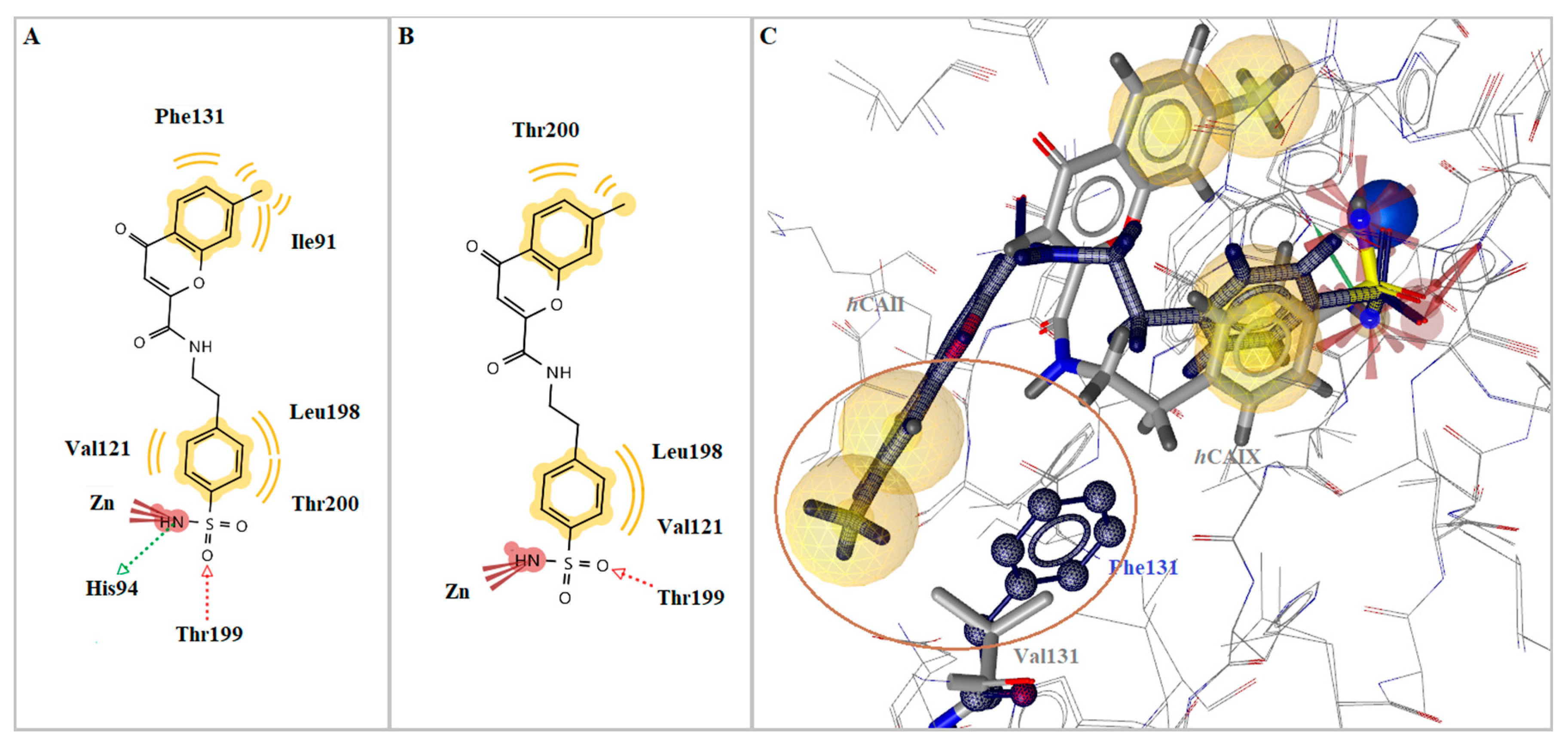
2.3. Molecular Modeling Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Procedure for Synthesis of Compounds (2a–j)
3.1.2. 7,8-Dimethyl-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylic Acid (2f)
3.1.3. 5,7-Dimethyl-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylic Acid (2g)
3.1.4. General Procedure for Synthesis of Compounds 5a–j
3.1.5. 4-Oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5a)
3.1.6. 6-Methyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5b)
3.1.7. 7-Methyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5c)
3.1.8. 6-Ethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5d)
3.1.9. 6,7-Dimethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5e)
3.1.10. 7,8-Dimethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5f)
3.1.11. 5,7-Dimethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5g)
3.1.12. 6,8-Dimethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5h)
3.1.13. 6-Chloro-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5i)
3.1.14. 6-Chloro-7-methyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (5j)
3.1.15. General Procedure for Synthesis of Compounds 6a–k
3.1.16. 4-Oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylbenzyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6a)
3.1.17. 6-Methyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylbenzyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6b)
3.1.18. 6-Chloro-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylbenzyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6c)
3.1.19. 4-Oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenethyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6d)
3.1.20. 6-Methyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenethyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6e)
3.1.21. 7-Methyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenethyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6f)
3.1.22. 6-Ethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenethyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6g)
3.1.23. 6,7-Dimethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenethyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6h)
3.1.24. 7,8-Dimethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenethyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6i)
3.1.25. 6,8-Dimethyl-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenethyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6j)
3.1.26. 6-Chloro-4-oxo-N-(4-sulfamoylphenethyl)-4H-chromene-2-carboxamide (6k)
3.2. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition
3.3. Molecular Modeling Studies (Experimental Part)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | Carbonic Anhydrase |
| CAI | Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors |
| SAR | Structure Activity Relationships |
| SI | Selectivity Index |
References
- Neri, D.; Supuran, C.T. Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A. Carbonic anhydrases as targets for medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 4336–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and activators for novel therapeutic applications. Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, V.; Di Fiore, A.; D’Ambrosio, K.; Supuran, C.T.; De Simone, G. Multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic an-hydrases: How to design specific drugs targeting 15 different isoforms? Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4421–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thiry, A.; Dogné, J.-M.; Masereel, B.; Supuran, C.T. Targeting tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase IX in cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccinardi, T.; Ortore, G.; Rossello, A.; Supuran, A.C.T.; Martinelli, A. Homology Modeling and Receptor-Based 3D-QSAR Study of Carbonic Anhydrase IX. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullo, D.; Innocenti, A.; Nishimori, I.; Pastorek, J.; Scozzafava, A.; Pastorekova, S.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition of the transmembrane isozyme XII with sulfonamides—A new target for the design of antitumor and an-tiglaucoma drugs? Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, E.; Carta, F.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Antiglaucoma carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, S.A.; Hessein, S.A.; Abbas, S.Y.; Farrag, A.M.; Ammar, Y.A. Synthesis of Chromen-2-one, Pyrano[3,4-c]chromene and Pyridino[3,4-c]chromene Derivatives as Potent Antimicrobial Agents. Croat. Chem. Acta 2018, 91, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadinezhad, M.; Mamaghani, M.; Rassa, M.; Shirini, F. A Facile Green Synthesis of Chromene Derivatives as Antioxidant and Antibacterial Agents through a Modified Natural Soil. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 4920–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasha, R.M.; Alblewi, F.F.; Afifi, T.H.; Naqvi, A.; Fouda, A.M.; Al-Dies, A.M.; El-Agrody, A.M. Design of New Ben-zo[h]chromene Derivatives: Antitumor Activities and Structure-Activity Relationships of the 2,3-Positions and Fused Rings at the 2,3-Positions. Molecules 2017, 22, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agrody, A.M.; Fouda, A.M.; Assiri, M.A.; Mora, A.; Ali, T.E.; Alam, M.M.; Alfaifi, M.Y. In vitro anticancer activity of py-rano[3, 2-c]chromene derivativeswith both cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshibl, H.M.; Al-Abdullah, E.S.; Haiba, M.E.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Awad, G.E.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Ibrahim, B.M.; Bari, A.; Villinger, A. Synthesis and Evaluation of New Coumarin Derivatives as Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-T.; Huang, W.-H.; Huang, C.-K.; Liu, F.-C.; Huang, R.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Lee, A.-R. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activities of 4H-chromene and chromeno[2,3-b]pyridine derivatives. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 1195–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadallah, F.M.; El-Waei, T.A.; Hanna, M.M.; Abbas, S.E.; Ceruso, M.; Oz, B.E.; Guler, O.O.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis, carbonic anhydrase inhibition and cytotoxic activity of novel chromone-based sulfonamide derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 96, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelino, C.L.; Supuran, C.T.; McKenna, R. Non-Classical Inhibition of Carbonic Anhydrase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esirden, I.; Tanç, M.; Supuran, C.T.; Kaya, M. Microwave assisted synthesis of novel tetrazole/sulfonamide derivatives based on octahydroacridine, xanthene and chromene skeletons as inhibitors of the carbonic anhydrases isoforms I, II, IV and VII. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clima, L.; Craciun, B.F.; Angeli, A.; Petreni, A.; Bonardi, A.; Nocentini, A.; Carta, F.; Gratteri, P.; Pinteala, M.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis, Computational Studies and Assessment of in Vitro Activity of Squalene Derivatives as Carbonic Anhydrase Inhib-itors. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.S.; Abd El-Karim, S.S.; Abdelwahed, N. Synthesis and biological evaluation of sulfonamide derivatives as antimi-crobial agents. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2017, 74, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azzam, R.A.; Elsayed, R.E.; Elgemeie, G.H. Design, Synthesis, and Antimicrobial Evaluation of a New Series ofN Sulfonamide 2 Pyridones as Dual Inhibitors of DHPS and DHFR Enzymes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10401–10414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakesh, K.P.; Wang, S.-M.; Leng, J.; Ravindar, L.; Asiri, A.M.; Marwani, H.M.; Qin, H.-L. Recent Development of Sulfonyl or Sulfonamide Hybrids as Potential Anticancer Agents: A Key Review. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachaeva, M.V.; Hodyna, D.M.; Semenyuta, I.V.; Pilyo, S.G.; Prokopenko, V.M.; Kovalishyn, V.V.; Metelytsia, L.O.; Brovarets, V.S. Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel sulfonamides as potential anticancer agents. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2018, 74, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.-D.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; Gao, F. Sulfonamide-1,3,5-triazine–thiazoles: Discovery of a novel class of antidiabetic agents via inhibition of DPP-4. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83438–83447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, A.; Rubab, L.; Rehman, M.U.; Anjum, R.; Ullah, S.; Marjana, M.; Qadeer, S.; Sana, S. Coumarin sulfonamide derivatives: An emerging class of therapeutic agents. Heterocycl. Commun. 2020, 26, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuva, N.H.; Talpara, P.K.; Singala, P.M.; Gothaliya, V.K.; Shah, V.H. Synthesis and biological evaluation of pyrimidinyl sulphonamide derivatives as promising class of antitubercular agents. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cagide, F.; Oliveira, C.; Reis, J.; Borges, F. Optimizing the Synthetic Route of Chromone-2-carboxylic Acids: A Step forward to Speed-Up the Discovery of Chromone-Based Multitarget-Directed Ligands. Molecules 2019, 24, 4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanamori, K.; Roberts, J.D. Nitrogen-15 nuclear magnetic resonance study of benzenesulfonamide and cyanate binding to carbonic anhydrase. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 2658–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, V.; Hilvo, M.; Di Fiore, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Pan, P.; Parkkila, S.; Scaloni, A.; Pastorek, J.; Pastorekova, S.; Pedone, C.; et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the tumor-associated human carbonic anhydrase IX. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16233–16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Fiore, A.; Truppo, E.; Supuran, C.T.; Alterio, V.; Dathan, N.; Bootorabi, F.; Parkkila, S.; Monti, S.M.; De Simone, G. Crystal structure of the C183S/C217S mutant of human CA VII in complex with acetazolamide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5023–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, D.A.; Waheed, A.; Ulmasov, B.; Shah, G.N.; Grubb, J.H.; Sly, W.S.; Christianson, D.W. Crystal structure of the dimeric extracellular domain of human carbonic anhydrase XII, a bitopic membrane protein overexpressed in certain cancer tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9545–9550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jiuhui, L.; Hongfeng, S.; Jiagao, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, X. Synthesis, nematicidal activity and docking study of novel chromone derivatives containing substituted pyrazole. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 911–914. [Google Scholar]
- Sami, S.M.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Abdel-Halim, A.M.; Aly, Y.L. Synthesis and Reactions of Some 4-Oxo-4H-1-benzopyran-2-carboxaldehydes. Indian J. Chem. Sec. B Org. Med. Chem. 1986, 25, 384–389. [Google Scholar]
- Helguera, A.M.; Pérez-Garrido, A.; Gaspar, A.; Reis, J.; Cagide, F.; Vina, D.; Cordeiro, M.D.; Borges, F. Combining QSAR classification models for predictive modeling of human monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 59, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, G.P.; Shaw, D. Benzopyrones. 7. Synthesis and antiallergic activity of some 2-(5-tetrazolyl)chromones. J. Med. Chem. 1972, 15, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifah, R.G. The Carbon Dioxide Hydration Activity of Carbonic Anhydrase. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocentini, A.; Angeli, A.; Carta, F.; Winum, J.Y.; Zalubovskis, R.; Carradori, S.; Capasso, C.; Donald, W.A.; Supuran, C.T. Reconsidering anion inhibitors in the general context of drug design studies of modulators of activity of the classical enzyme carbonic anhydrase. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, E.; Buemi, M.R.; Di Fiore, A.; De Luca, L.; Ferro, S.; Angeli, A.; Cirilli, R.; Sadutto, D.; Alterio, V.; Monti, S.M.; et al. Probing Molecular Interactions between Human Carbonic Anhydrases (hCAs) and a Novel Class of Benzenesulfonamides. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4316–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, A.; Carta, F.; Bartolucci, G.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis of novel acyl selenoureido benzensulfonamides as carbonic an-hydrase I, II, VII and IX inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 3567–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vats, L.; Sharma, V.; Angeli, A.; Kumar, R.; Supuran, C.T.; Sharma, P.K. Synthesis of novel 4-functionalized 1,5-diaryl-1,2,3-triazoles containing benzenesulfonamide moiety as carbonic anhydrase I, II, IV and IX inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S. and Olson, A.J. Autodock4 and Auto-DockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexiblity. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 16, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- RCSB, PDB. A Structural View of Biology. Available online: http://www.rcsb.org/ (accessed on 21 March 2021).
| Ki (nM) * | Ki (nM) * | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | hCA I | hCA II | hCA IX | hCA XII | N | hCA I | hCA II | hCA IX | hCA XII |
| 5a | 525.2 ± 44.4 | 35.1 ± 3.3 | 16.6 ± 1.5 | 20.1 ± 1.7 | 6b | 612.3 ± 49.5 | 81.7 ± 4.2 | 2039 ± 189.0 | 320.4 ± 23.2 |
| 5b | 5314 ± 272 | 95.9 ± 8.0 | 77 ± 6.5 | 64.8 ± 6.1 | 6c | 2646 ± 227 | 678.8 ± 45.0 | 3285 ± 302 | 59.4 ± 5.0 |
| 5c | 3563 ± 228 | 39.5 ± 3.2 | 63.4 ± 6.3 | 50.8 ± 4.3 | 6d | 321.9 ± 27.9 | 16.6 ± 1.2 | 81.0 ± 7.7 | 211.6 ± 13.7 |
| 5e | 2891 ± 161 | 311.4 ± 28.3 | 298.6 ± 18.4 | 619.1 ± 36.7 | 6e | 246.7 ± 24.3 | 36.4 ± 2.1 | 72.7 ± 4.3 | 439.3 ± 32.2 |
| 5f | 341.1 ± 29.6 | 9.3 ± 0.5 | 19.5 ± 1.6 | 76.3 ± 6.0 | 6f | 333.5 ± 17.5 | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 64.8 ± 3.4 | 337.3 ± 27.4 |
| 5g | 681.5 ± 40.6 | 61.4 ± 4.4 | 54.7 ± 5.0 | 46.4 ± 4.4 | 6g | 971.0 ± 82.4 | 279.9 ± 15.5 | 182.6 ± 16.1 | 147.9 ± 8.1 |
| 5h | 504.8 ± 27.0 | 46.6 ± 2.9 | 22.5 ± 1.9 | 26.8 ± 1.4 | 6h | 547.3 ± 39.2 | 51.2 ± 3.6 | 51.4 ± 4.5 | 22.6 ± 1.5 |
| 5i | 2698 ± 265 | 66.2 ± 5.8 | 51.0 ± 4.8 | 424.7 ± 41.0 | 6i | 213.6 ± 15.9 | 39.2 ± 3.7 | 84.5 ± 4.3 | 132.2 ± 11.0 |
| 5j | 580.3 ± 50.5 | 900.7 ± 75.4 | 515.5 ± 37.2 | 155.3 ± 10.1 | 6j | 4412 ± 347 | 143.0 ± 12.8 | 91.1 ± 8.9 | 31.4 ± 2.6 |
| 6a | 627.7 ± 35.5 | 219.3 ± 11.8 | 855.2 ± 49.2 | 34.0 ± 2.2 | 6k | 926.9 ± 68.9 | 91.6 ± 7.0 | 1917 ± 146 | 41.4 ± 3.4 |
| AAZ | 250 ± 13.0 | 12.1 ± 0.6 | 25.7 ± 2.1 | 5.7 ± 0.4 | AAZ | 250 ± 13.0 | 12.1 ± 0.6 | 25.7 ± 2.1 | 5.7 ± 0.4 |
| No. | hCA Isoform | Estimated Free Binding Energy (Kcal/mol) | Chelating the Zn(II) Ion | Residues Involved in H-Bond Interactions | Residues Involved in Hydrophobic Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a | hCA I | −6.49 | Yes | Thr199 | Ala121, Leu198 |
| hCA II | −7.42 | Yes | Thr199 | Ile91, Val121, Leu198, Thr200 | |
| hCA IX | −9.25 | Yes | His94, Thr199 | Val121, Val195, Leu198 | |
| hCA XII | −9.61 | Yes | His94, His96, Thr199, Thr200 | Val121, Leu198 | |
| 5h | hCA I | −5.17 | No | - | Ala121, Ala135 |
| hCA II | −7.11 | Yes | Thr199 | Ile91, Leu198, Thr200 | |
| hCA IX | −8.74 | Yes | His94, Thr199 | Val121, Leu198 | |
| hCA XII | −9.02 | Yes | His94, Thr200 | Val121, Leu198 | |
| 6d | hCA I | −6.77 | Yes | Thr199 | Ala121, Ala135, Leu198 |
| hCA II | −9.14 | Yes | His94, Thr199 | Ile91, Val121, Phe131, Thr200 | |
| hCA IX | −6.44 | Yes | Thr199 | Val121, Leu198, Thr200 | |
| hCA XII | −4.81 | No | - | Val121 | |
| 6f | hCA I | −6.62 | Yes | Thr199 | Ala135, Leu198 |
| hCA II | −9.34 | Yes | His94, Thr199 | Ile91, Val121, Phe131, Leu198, Thr200 | |
| hCA IX | −6.81 | Yes | Thr199 | Val121, Leu198, Thr200 | |
| hCA XII | −4.72 | No | - | Val121, Thr200 | |
| 6h | hCA I | −5.29 | Yes | - | Ala135, Leu198 |
| hCA II | −7.87 | Yes | His94 | Val121, Phe131, Leu198 | |
| hCA IX | −6.53 | Yes | Thr199 | Val121, Thr200 | |
| hCA XII | −9.52 | Yes | Ala131, Ser132, Thr200 | Trp5, Val121, Leu198 | |
| 6i | hCA I | −8.15 | Yes | Gln92, Thr199 | Leu131, Ala135, Ala132, Thr202, Leu198 |
| hCA II | −7.14 | Yes | Thr200 | Val121, Phe131, Thr200 | |
| hCA IX | −6.27 | Yes | Thr199 | Val121, Thr200 | |
| hCA XII | −4.35 | No | - | Val121, Leu198 | |
| AAZ | hCA I | Yes | Gln92 | Leu198, Thr199, His200, Pro 201, Trp209 | |
| hCA II | Yes | Thr199, Thr200 | Val121, Phe131, Leu198, Trp209 | ||
| hCA IX | Yes | Thr199, Thr200 | Val121, Val143, Val131, Leu198, Trp209 | ||
| hCA XII | Yes | Thr199, Thr200 | Val121, Val143, Leu198, Trp209 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angeli, A.; Kartsev, V.; Petrou, A.; Pinteala, M.; Brovarets, V.; Slyvchuk, S.; Pilyo, S.; Geronikaki, A.; Supuran, C.T. Chromene-Containing Aromatic Sulfonamides with Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitory Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105082
Angeli A, Kartsev V, Petrou A, Pinteala M, Brovarets V, Slyvchuk S, Pilyo S, Geronikaki A, Supuran CT. Chromene-Containing Aromatic Sulfonamides with Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitory Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(10):5082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105082
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngeli, Andrea, Victor Kartsev, Anthi Petrou, Mariana Pinteala, Volodymyr Brovarets, Sergii Slyvchuk, Stepan Pilyo, Athina Geronikaki, and Claudiu T. Supuran. 2021. "Chromene-Containing Aromatic Sulfonamides with Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitory Properties" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 10: 5082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105082








