Interpenetrating Hydrogel Networks Enhance Mechanical Stability, Rheological Properties, Release Behavior and Adhesiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma
Abstract
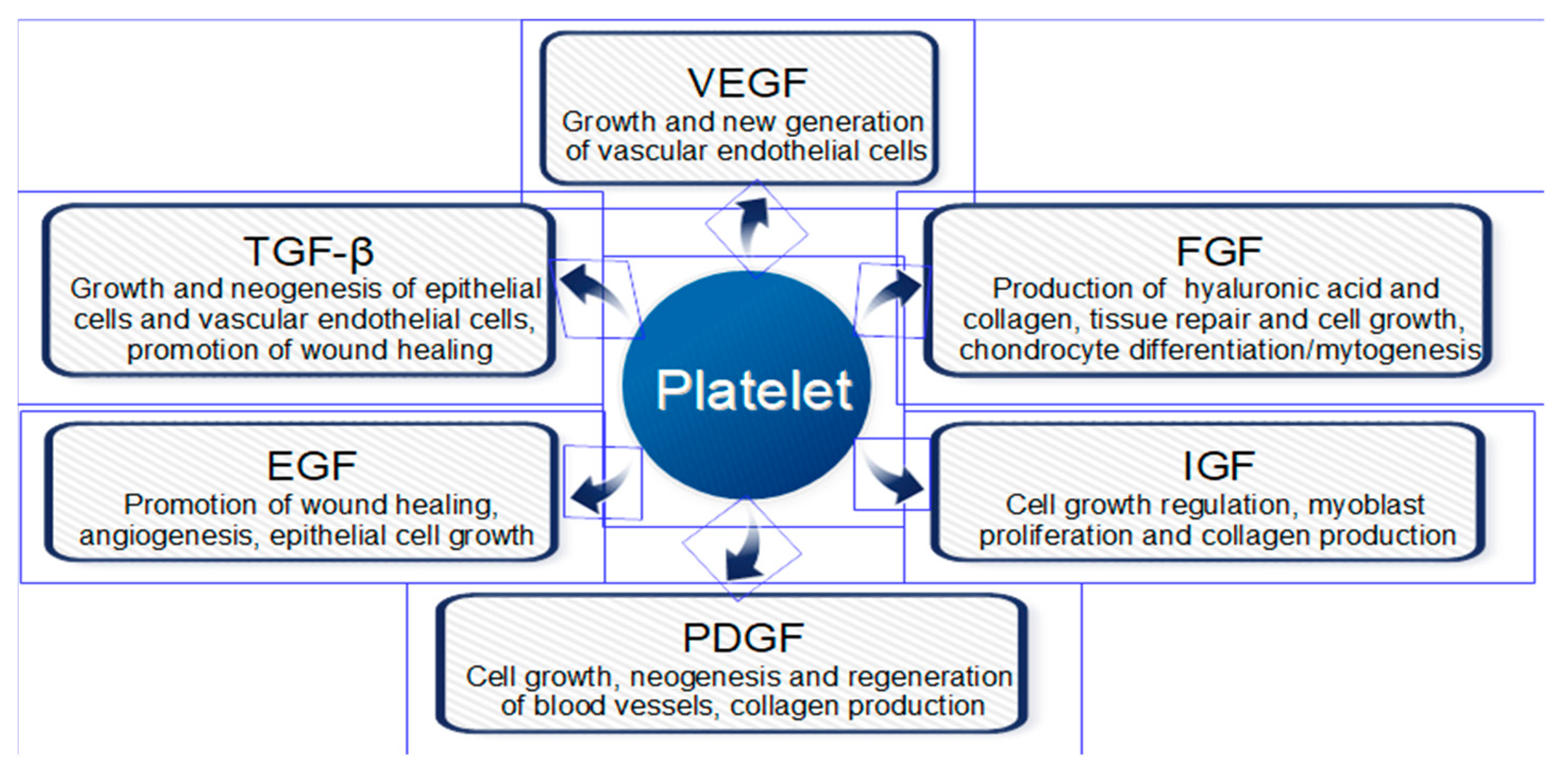
1. Introduction
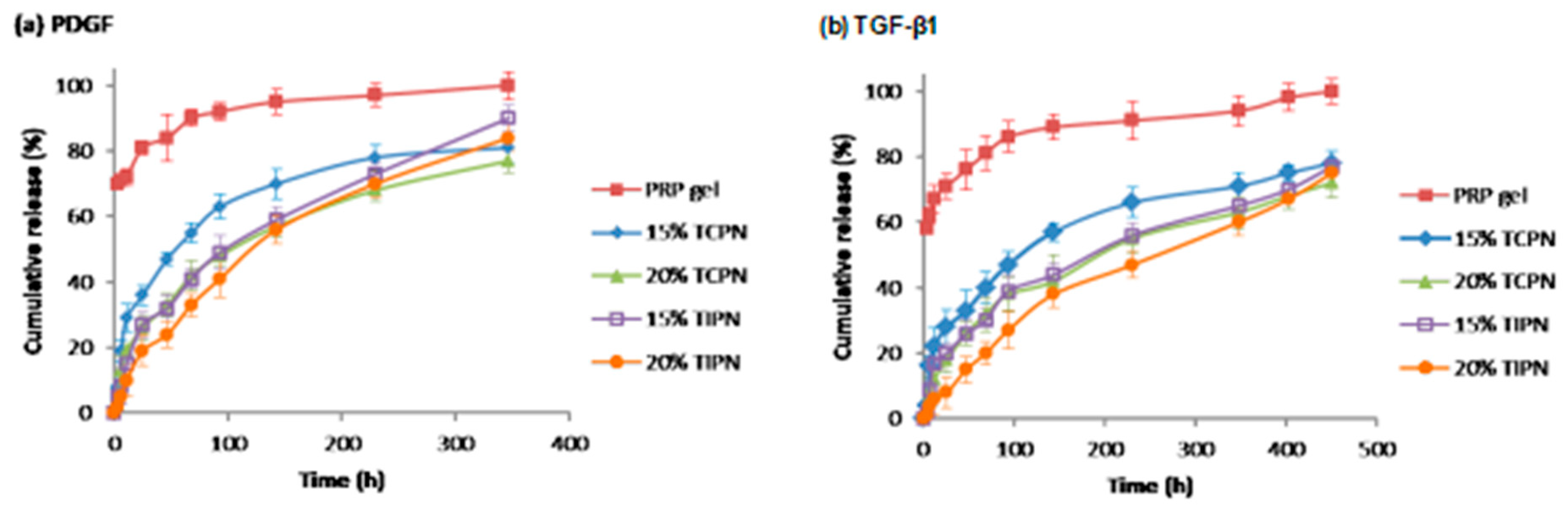
2. Results
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Polymers for the Preparation of Rapidly In-Situ Gelling Hydrogels
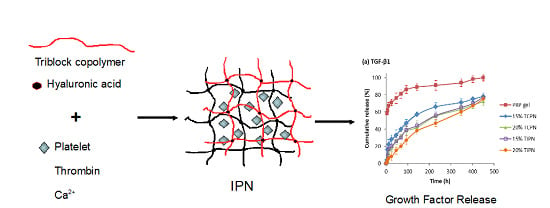
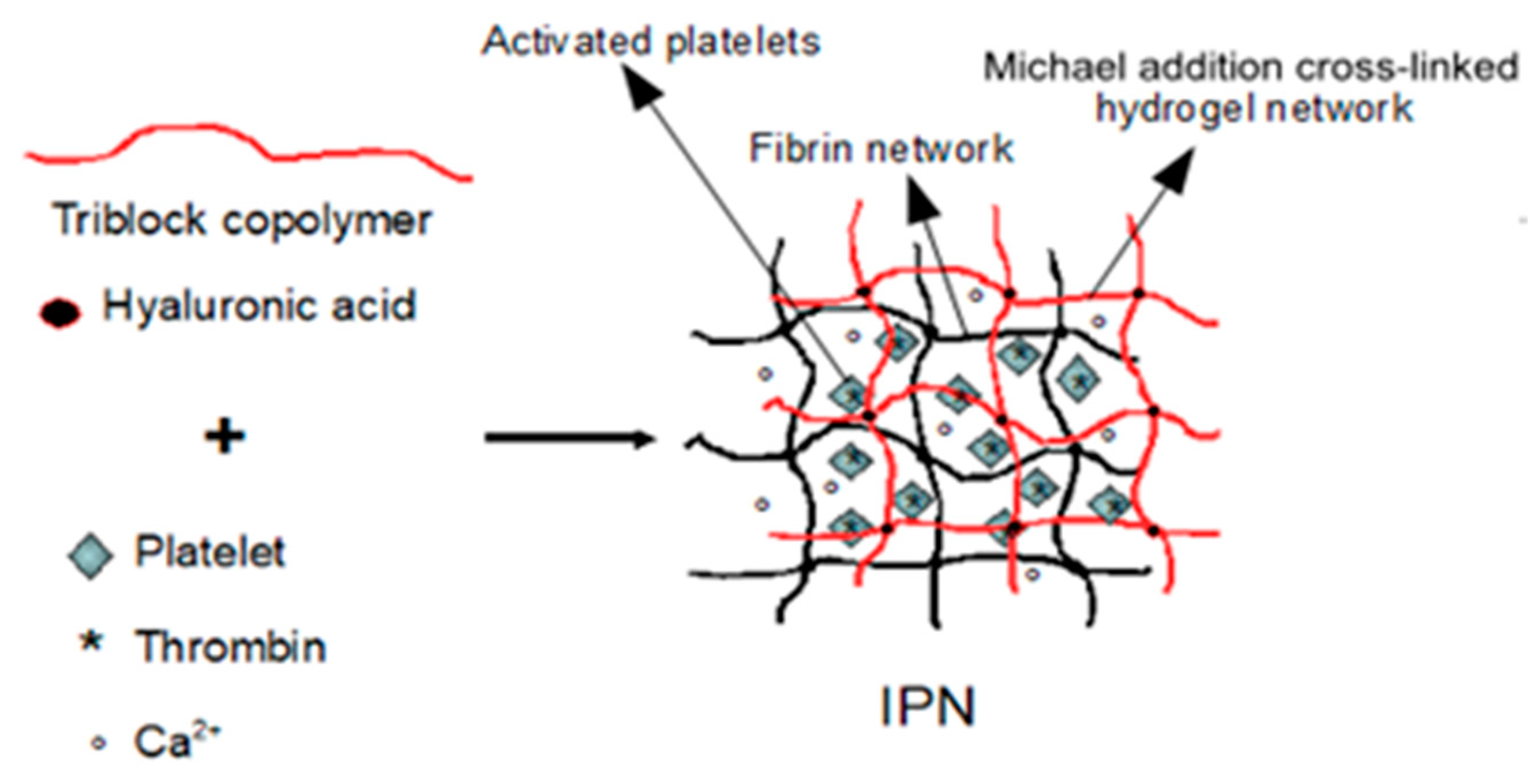
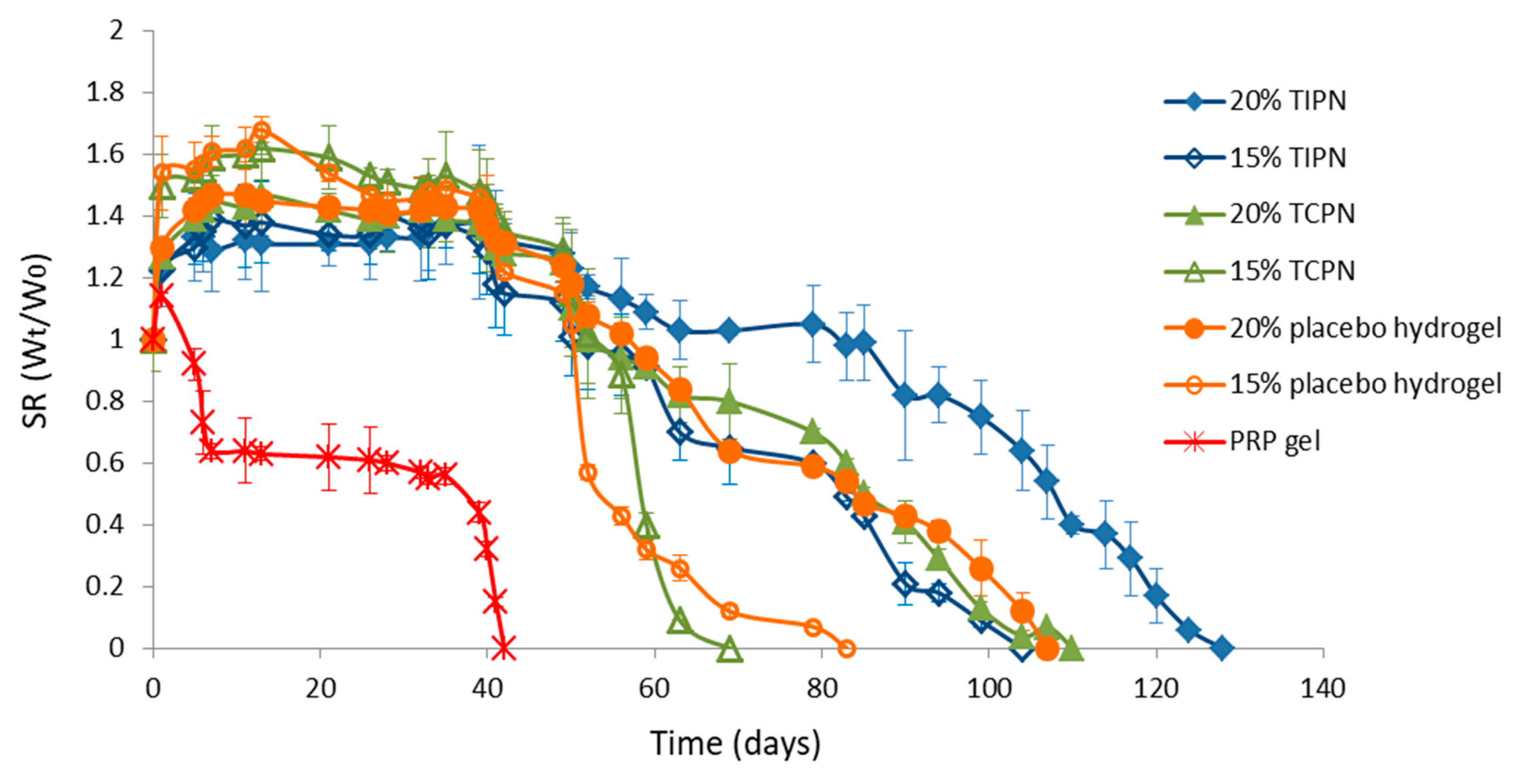
2.2. Design and Formulation of the Interpenetrating Polymer Networks
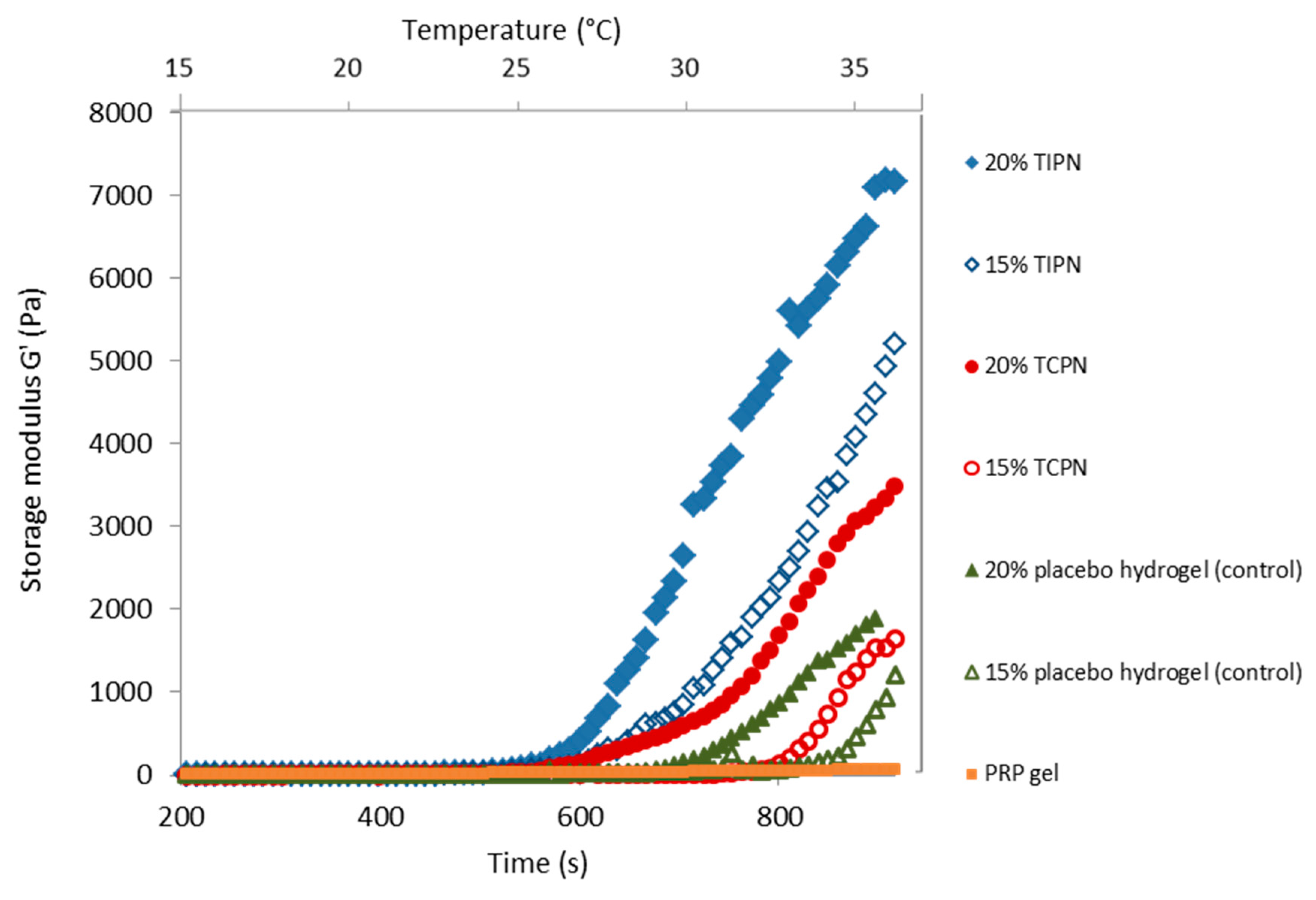
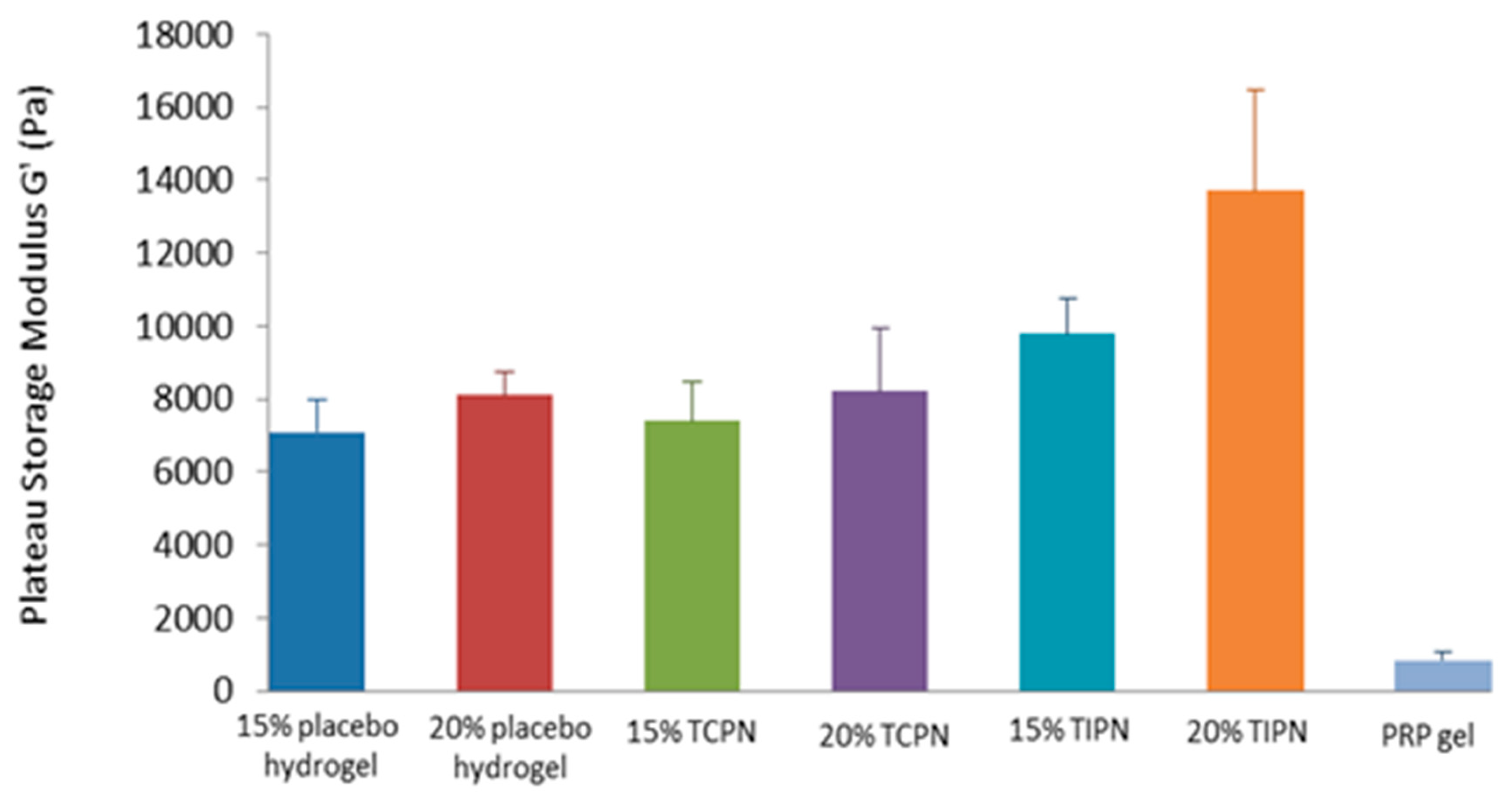
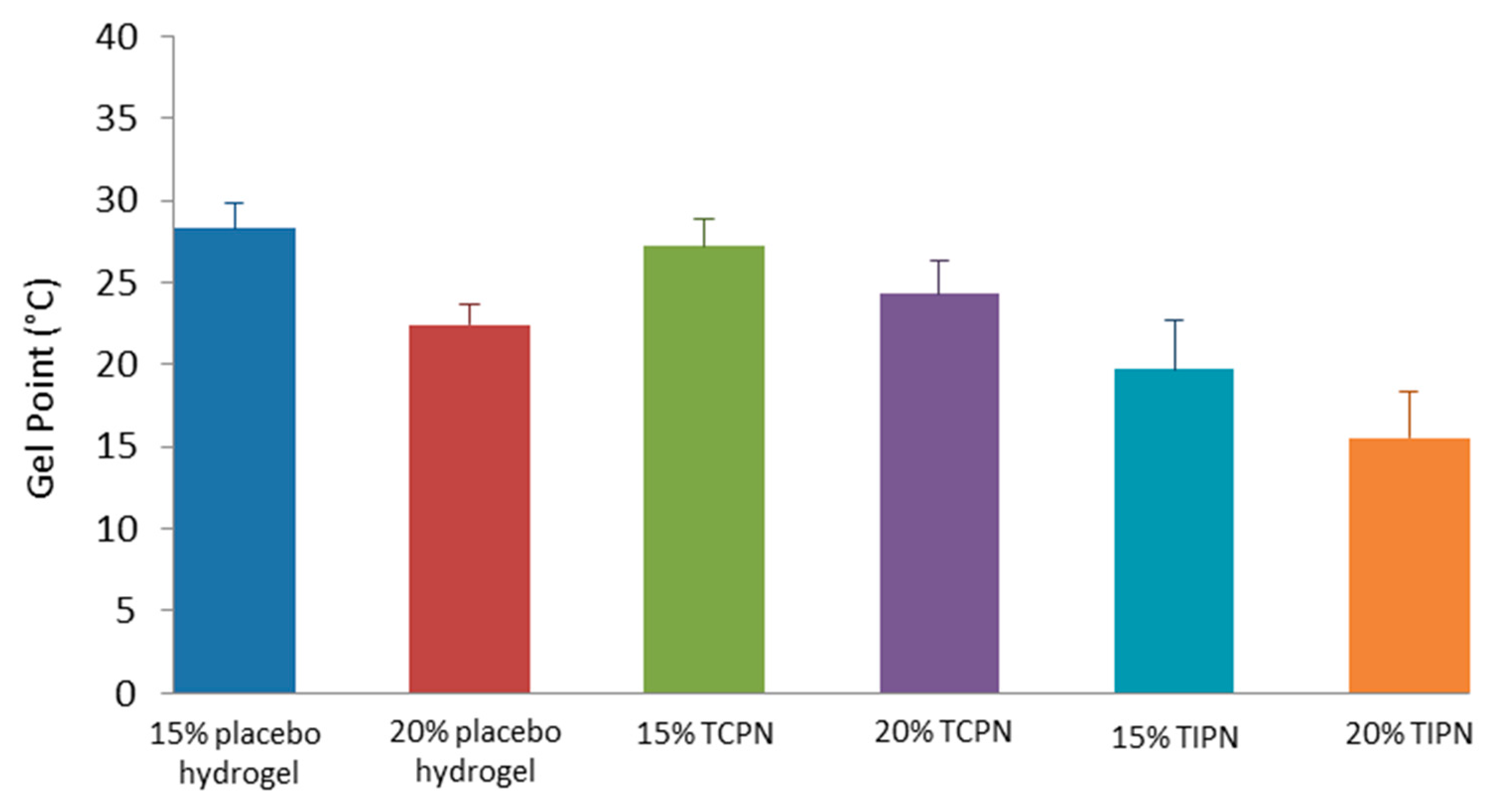
2.3. Rheology
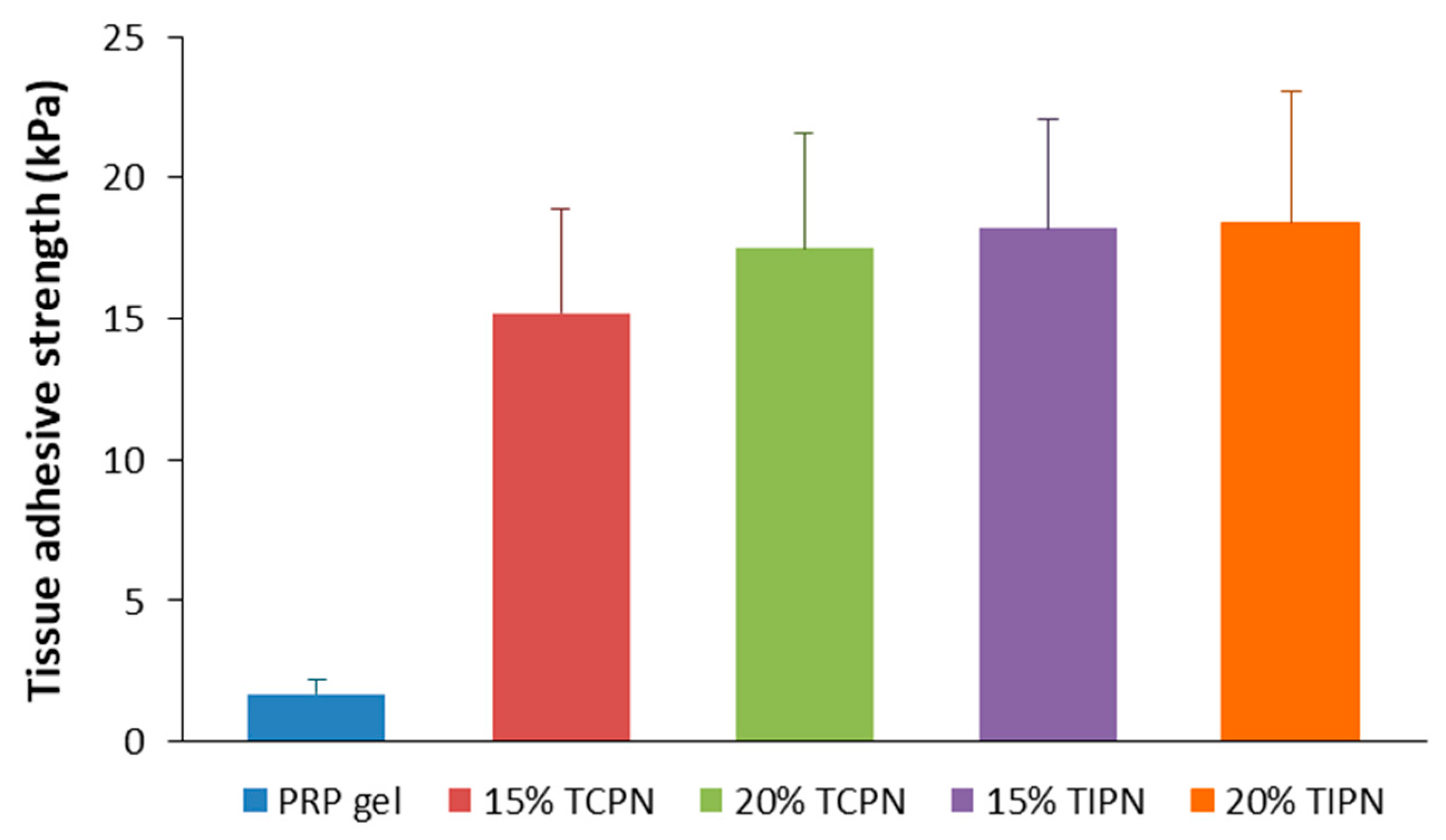
2.4. Tissue Adhesive Strength
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of (Vinyl Sulfonate) Triblock Copolymer
4.3. Synthesis of Thiolated Hyaluronic Acid (HA-SH)
4.4. H-NMR Spectroscopy
4.5. Gel Permeation Chromatography
4.6. Determination of the Cloud Point
4.7. Preparation of PC
4.8. Formulation of PRP Loaded Hydrogels
4.9. Swelling Test
4.10. Rheology
4.11. Growth Factors Release Kinetics
4.12. Tissue Adhesive Strength of PRP Loaded Hydrogels
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giannoudis, P.V.; Dinopoulos, H.; Tsiridis, E. Bone substitutes: An update. Injury 2005, 36, S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortinau, S.; Schmich, J.; Block, S.; Liedmann, A.; Ludwig, J.; Weiss, D.G.; Helm, C.A.; Rolfs, A.; Frech, M.J. Effect of 3D-scaffold formation on differentiation and survival in human neural progenitor cells. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Furuya, H.; Tabata, Y. Enhancement of bone regeneration by dual release of a macrophage recruitment agent and platelet-rich plasma from gelatin hydrogels. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censi, R.; Di Martino, P.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels for protein delivery in tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censi, R.; Fieten, P.J.; Di Martino, P.; Hennink, W.E.; Vermonden, T. In Situ Forming Hydrogels by Tandem Thermal Gelling and Michael Addition Reaction between Thermosensitive Triblock Copolymers and Thiolated Hyaluronan. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 5771–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbieti, M.G.; Dubbini, A.; Laus, F.; Paggi, E.; Marchegiani, A.; Capitani, M.; Marchetti, L.; Dini, F.; Vermonden, T.; Di Martino, P.; et al. In vivo biocompatibility of p(HPMAm-lac)-PEG hydrogels hybridized with hyaluronan. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 3056–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadidio, C.; Butini, M.E.; Trampuz, A.; Di Luca, M.; Censi, R.; Di Martino, P. Daptomycin-loaded biodegradable thermosensitive hydrogels enhance drug stability and foster bactericidal activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 130, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, R.; Casadidio, C.; Dubbini, A.; Cortese, M.; Scuri, S.; Grappasonni, I.; Golob, S.; Vojnovic, D.; Sabbieti, M.G.; Agas, D.; et al. Thermosensitive hybrid hydrogels for the controlled release of bioactive vancomycin in the treatment of orthopaedic implant infections. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agas, D.; Laus, F.; Lacava, G.; Marchegiani, A.; Deng, S.; Magnoni, F.; Silva, G.G.; Di Martino, P.; Sabbieti, M.G.; Censi, R. Thermosensitive hybrid hyaluronan/p(HPMAm-lac)-PEG hydrogels enhance cartilage regeneration in a mouse model of osteoarthritis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 20013–20027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, L.A.; Barker, J.U.; Strauss, E.J.; McCarrel, T.; Cole, B.J. The Role of Growth Factors in Cartilage Repair. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2706–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.S.M.; Leijten, J.; Wennink, J.W.; Chatterjea, A.G.; Feijen, J.; Van Blitterswijk, C.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Karperien, M. The effect of platelet lysate supplementation of a dextran-based hydrogel on cartilage formation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3651–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutlu, B.; Tiğlı Aydın, R.S.; Akman, A.C.; Gümüşderelioglu, M.; Nohutcu, R.M. Platelet-rich plasma-loaded chitosan scaffolds: Preparation and growth factor release kinetics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101B, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xing, L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ding, P.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Gui, J. Platelet-rich plasma combined with agarose as a bioactive scaffold to enhance cartilage repair: An in vitro study. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 28, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, J.; Miyamoto, M.; Ishii, Y.; Aoyama, J.; Takagi, G.; Naito, Z.; Tabata, Y.; Ochi, M.; Shimizu, K. Enhanced Vascularization by Controlled Release of Platelet-Rich Plasma Impregnated in Biodegradable Gelatin Hydrogel. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Morimoto, N.; Ikada, Y. Gelatin gel as a carrier of platelet-derived growth factors. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 28, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Tabata, Y. Enhanced angiogenesis by multiple release of platelet-rich plasma contents and basic fibroblast growth factor from gelatin hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokugo, A.; Ozeki, M.; Kawakami, O.; Sugimoto, K.; Mushimoto, K.; Morita, S.; Tabata, Y. Augmented Bone Regeneration Activity of Platelet-Rich Plasma by Biodegradable Gelatin Hydrogel. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhundov, K.; Pietramaggiori, G.; Waselle, L.; Darwiche, S.; Guerid, S.; Scaletta, C.; Hirt-Burri, N.; Applegate, L.A.; Raffoul, W. Development of a cost-effective method for platelet-rich plasma (PRP) preparation for topical wound healing. Ann. Burn. Fire Disasters 2012, 25, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Censi, R.; Vermonden, T.; Deschout, H.; Braeckmans, K.; Di Martino, P.; De Smedt, S.; Van Nostrum, C.F.; Hennink, W.E. Photopolymerized Thermosensitive Poly(HPMAlactate)-PEG-Based Hydrogels: Effect of Network Design on Mechanical Properties, Degradation, and Release Behavior. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, R.; Vermonden, T.; Van Steenbergen, M.; Deschout, H.; Braeckmans, K.; De Smedt, S.; Van Nostrum, C.; Di Martino, P.; Hennink, W.E. Photopolymerized thermosensitive hydrogels for tailorable diffusion-controlled protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolberg, A.S. Plasma and cellular contributions to fibrin network formation, structure and stability. Haemophilia 2010, 16, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevallier, N.; Anagnostou, F.; Zilber, S.; Bodivit, G.; Maurin, S.; Barrault, A.; Bierling, P.; Hernigou, P.; Layrolle, P.; Rouard, H. Osteoblastic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells with platelet lysate. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, R.A.; Sheridan, P.J.; Kupp, L.I. Is Platelet-rich Plasma the Perfect Enhancement Factor? A Current Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2003, 18, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, C.A.; Jolly, D.G.; Worden, C.E.; Hendren, D.G.; Kane, C.J.M. Platelet-rich plasma gel promotes differentiation and regeneration during equine wound healing. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 74, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, S.; Wetterö, J.; Tengvall, P.; Kratz, G. Human articular chondrocytes on macroporous gelatin microcarriers form structurally stable constructs with blood-derived biological glues in vitro. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2009, 3, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-R.; Sarkar, S.K.; Linh, N.-T.B.; Padalhin, A.R.; Kim, B.R.; Jung, H.I.; Lee, B.T. Platelet-rich plasma encapsulation in hyaluronic acid/gelatin-BCP hydrogel for growth factor delivery in BCP sponge scaffold for bone regeneration. J. Biomater. Appl. 2015, 29, 988–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, M.R.; Augat, P.; Shefelbine, S.J.; Schorlemmer, S.; Huber-Lang, M.; Claes, L.; Kinzl, L.; Ignatius, A. Bone formation in a long bone defect model using a platelet-rich plasma-loaded collagen scaffold. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Kuroda, R.; Miwa, M.; Tabata, Y.; Hokugo, A.; Kawamoto, T.; Sasaki, K.; Doita, M.; Kurosaka, M. The Regenerative Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Meniscal Cells In Vitro and Its In Vivo Application with Biodegradable Gelatin Hydrogel. Tissue Eng. 2007, 3, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Cheng, W.; Fan, H.; Pei, G. Reconstruction of goat tibial defects using an injectable tricalcium phosphate/chitosan in combination with autologous platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3201–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Takahashi, K.; Arai, Y.; Inoue, A.; Sakao, K.; Tonomura, H.; Honjo, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Inoue, H.; Tabata, Y.; et al. Intraarticular administration of platelet-rich plasma with biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres prevents osteoarthritis progression in the rabbit knee. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Niu, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L. An in situ photocrosslinkable platelet rich plasma – Complexed hydrogel glue with growth factor controlled release ability to promote cartilage defect repair. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, B.A.G.; França, C.G.; Dávila, J.L.; Batista, N.A.; Caliari-Oliveira, C.; D’ávila, M.A.; Luzo, Â.C.M.; Lana, J.F.S.D.; Santana, M.H. Hyaluronic acid and fibrin from L-PRP form semi-IPNs with tunable properties suitable for use in regenerative medicine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Growney, E.A.; Linder, H.R.; Garg, K.; Bledsoe, J.G.; Sell, S. Bio-conjugation of platelet-rich plasma and alginate through carbodiimide chemistry for injectable hydrogel therapies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. B Appl. Biomater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fu, S.C.; Cheuk, Y.C.; Ong, T.-Y.; Feng, H.; Yung, S.-H. The effect of thermosensitive hydrogel platelet–rich–plasma complex in the treatment of partial tear of anterior cruciate ligament in rat model. J. Orthop. Transl. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iio, K.; Furukawa, K.-I.; Tsuda, E.; Yamamoto, Y.; Maeda, S.; Naraoka, T.; Kimura, Y.; Ishibashi, Y. Hyaluronic acid induces the release of growth factors from platelet-rich plasma. Asia-Pacific J. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rehabilitation Technol. 2016, 4, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Lo, W.-C.; Hsu, W.-C.; Wei, H.-J.; Liu, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.T.; Shieh, Y.-H.; Williams, D.F.; Deng, W.-P. Synergistic anabolic actions of hyaluronic acid and platelet-rich plasma on cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9599–9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, O.; Van Nostrum, C.F.; Ramzi, A.; Visser, T.; Soulimani, F.; Frederik, P.M.; Bomans, P.H.H.; Hennink, W.E. Physicochemical Characterization of Degradable Thermosensitive Polymeric Micelles. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9388–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermonden, T.; Besseling, N.A.M.; Van Steenbergen, M.; Hennink, W.E. Rheological Studies of Thermosensitive Triblock Copolymer Hydrogels. Langmuir 2006, 22, 10180–10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.P.; Marecak, D.M.; Marecek, J.F.; Prestwich, G.D. Synthesis and in vitro degradation of new polyvalent hydrazide cross-linked hydrogels of hyaluronic acid. Bioconjugate Chem. 1997, 8, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Roberts, M.C.; Prestwich, G.D. Disulfide Cross-Linked Hyaluronan Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, C.E.; Messersmith, P. Enzymatically Degradable Mussel-Inspired Adhesive Hydrogel. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4326–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Mn † (kDa) | Mn ‡ (kDa) | Mw ‡ (kDa) | PDI ‡ | Cloud Point * (°C) | Feed Molar Ratio 3-MPA/OH | Obtained DS † (%) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VinylSulTC_0 | 47 | 25.7 | 52.5 | 2.04 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 60 |
| VinylSulTC_10 | 54 | 25.7 | 54.2 | 2.1 | 29 | 0.20 † | 10.7 | 98 |
| Name | DTP Feed Ratio (%) | Obtained DS ‡ (%) | Obtained DS * (%) | Conversion % | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA-SH_56 | 75 | 59 | 53 ± 4 | 37 | 82 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Censi, R.; Casadidio, C.; Deng, S.; Gigliobianco, M.R.; Sabbieti, M.G.; Agas, D.; Laus, F.; Di Martino, P. Interpenetrating Hydrogel Networks Enhance Mechanical Stability, Rheological Properties, Release Behavior and Adhesiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041399
Censi R, Casadidio C, Deng S, Gigliobianco MR, Sabbieti MG, Agas D, Laus F, Di Martino P. Interpenetrating Hydrogel Networks Enhance Mechanical Stability, Rheological Properties, Release Behavior and Adhesiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(4):1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041399
Chicago/Turabian StyleCensi, Roberta, Cristina Casadidio, Siyuan Deng, Maria Rosa Gigliobianco, Maria Giovanna Sabbieti, Dimitrios Agas, Fulvio Laus, and Piera Di Martino. 2020. "Interpenetrating Hydrogel Networks Enhance Mechanical Stability, Rheological Properties, Release Behavior and Adhesiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 4: 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041399
APA StyleCensi, R., Casadidio, C., Deng, S., Gigliobianco, M. R., Sabbieti, M. G., Agas, D., Laus, F., & Di Martino, P. (2020). Interpenetrating Hydrogel Networks Enhance Mechanical Stability, Rheological Properties, Release Behavior and Adhesiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(4), 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041399