Abstract
Oxylipins are diatom-derived secondary metabolites, deriving from the oxidation of polyunsatured fatty acids that are released from cell membranes after cell damage or senescence of these single-celled algae. Previous results revealed harmful toxic effects of polyunsaturated aldehydes (PUAs) and hydroxyacids (HEPEs) on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus embryonic development by testing individual compounds and mixtures of the same chemical group. Here, we investigated the combined effects of these compounds on sea urchin development at the morphological and molecular level for the first time. Our results demonstrated that oxylipin mixtures had stronger effects on sea urchin embryos compared with individual compounds, confirming that PUAs induce malformations and HEPEs cause developmental delay. This harmful effect was also confirmed by molecular analysis. Twelve new genes, involved in stress response and embryonic developmental processes, were isolated from the sea urchin P. lividus; these genes were found to be functionally interconnected with 11 genes already identified as a stress response of P. lividus embryos to single oxylipins. The expression levels of most of the analyzed genes targeted by oxylipin mixtures were involved in stress, skeletogenesis, development/differentiation, and detoxification processes. This work has important ecological implications, considering that PUAs and HEPEs represent the most abundant oxylipins in bloom-forming diatoms, opening new perspectives in understanding the molecular pathways activated by sea urchins exposed to diatom oxylipins.
1. Introduction
Marine organisms are continuously subjected to environmental stressors deriving from human activities [1,2,3,4], climate change [5,6,7,8,9], and toxic metabolites [10,11,12,13,14]. Previous toxicological studies have focused on the exposure of single stress agents but, recently, there is growing interest on the effects of multiple stressors, such as chemical and physical xenobiotics [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. However, very few studies are available on natural toxins and on the possible effects of mixtures of these toxins on marine organisms. Oxylipins are a well-known class of diatom secondary metabolites that have been studied for their capability to induce reproductive failure in several marine invertebrates [10,24,25,26,27], including sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus [28,29,30,31,32]. Oxylipins represent a group of diverse compounds deriving from the oxidation of polyunsatured fatty acids that are released after cell damage or senescence [11,12,14]. These secondary metabolites include polyunsatured aldehydes (PUAs) and other fatty acid derivatives with hydroperoxy-, hydroxy-, keto-, oxo-, and hydroxy-epoxy functionalities [11,12]. Type and quantity of oxylipins are species-specific [33,34] due to a variety of precursor PUFAs and enzymes [11,12,35,36]. Miralto et al. [10] first isolated and identified PUAs from the bloom-forming diatoms Thalassiosira rotula, Skeletonema marinoi, and Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima but others were successively identified by Pohnert [35,37,38,39,40,41,42]. Despite PUAs being the first oxylipins identified, almost all diatoms possess LOX pathways for the synthesis of other oxylipins, generically named as non-volatile oxylipins [11,12,43,44]. Oxylipins have multiple biological and biochemical effects inducing the disruption of gametogenesis, gamete functionality, fertilization, embryonic mitosis, and larval fitness and competence in both planktonic and benthic grazers [45]. Previous studies by our group have demonstrated toxigenic effects on sea urchin P. lividus embryos exposed to individual polyunsaturated aldehydes (PUAs) and hydroxyacids (HEPEs) [30,31,32] or mixtures of these compounds belonging to the same chemical group [46,47].
In the present work we further explored the toxicity of these natural compounds on P. lividus embryonic development by testing PUA and HEPE mixtures. Sea urchin eggs were treated before and after fertilization with PUA and HEPE mixtures at different concentrations, and embryonic development was followed until the pluteus stage to detect possible negative effects at the morphological level. Moreover, we isolated 12 new genes, involved in stress response and embryonic developmental processes, from the sea urchin P. lividus. These genes were subjected to interactomic analysis, demonstrating that they were functionally interconnected with 11 genes already described in previous studies investigating the response of P. lividus embryos to single oxylipins [30,48,49]. Finally, the expression levels of these 23 genes were followed by real-time qPCR to identify possible gene targets affected by oxylipin mixtures.
2. Results
2.1. Morphological Effects of PUA/HEPE Mixtures
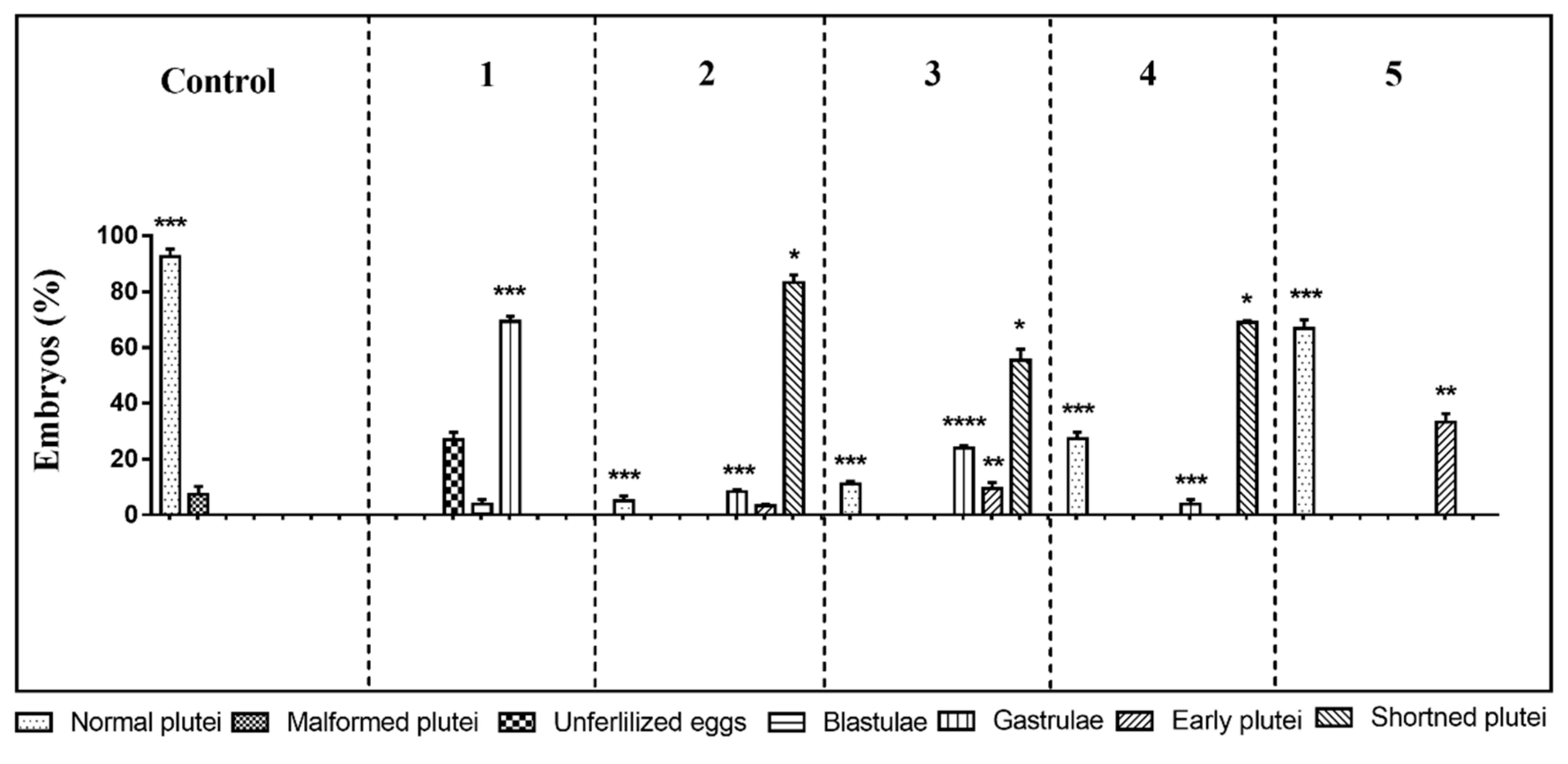
The first experiment was performed at the following concentrations: decadienal 0.5 µM, heptadienal 1.0 µM, and octadienal 1.5 µM and 2.8 µM for the four HEPEs (see also Table 1). At these concentrations, the three PUAs in mixtures produced about 60% malformed embryos [47] and the four HEPEs in mixtures about 40% malformed/delayed embryos [47]. The results showed only 73% of fertilization success; all other eggs underwent first mitotic division, but after 48 h post-fertilization (hpf) all embryos were delayed, with about 3.8% still at the blastula and 69.2% at the gastrula stages (Figure 1; p-value < 0.001; see also Table S1). Moreover, embryonic development appeared severely compromised, with embryos showing evident apoptotic processes—mitotic divisions occurred in the blastula, but their phenotypes were irregular and darker inside (see Figure S1D); gastrulae were also abnormal with some cells that were flattened at the vegetal plate but without the invagination of the archenteron (see Figure S1E).

Table 1.
Concentrations in micromolar (μM) of the seven oxylipins in the five experiments.
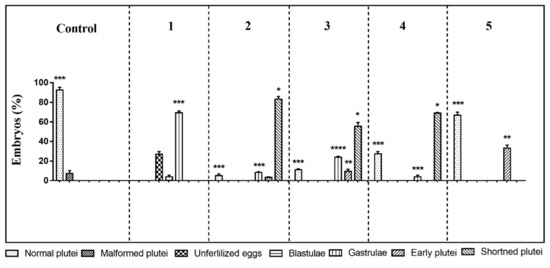
Figure 1.
Sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus exposed before fertilization to different concentrations of mixtures of polyunsaturated aldehydes (PUA) + hydroxyacids (HEPE). Percentage of normal, malformed, early, delayed, and shortened plutei and gastrulae in controls (embryos grown in the absence of PUA/HEPE mixtures) and treated samples are reported. Five experiments are numbered on the top of the histogram. For the numerical data of the five experiments see also Supplementary Table S1. The statistical significance between different groups is reported as follows: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.
In the second experiment, the oxylipin concentrations were decreased to 0.4, 0.8, and 1.3 µM for decadienal, heptadienal, and octadienal, respectively, and 2.1 μM for HEPEs. This mixture produced no effect on fertilization success and first mitotic division, with a slower delay in development of embryos at 48 hpf. In fact, 83.2% of the embryos reached the pluteus stage but these embryos were shorter than the plutei in control conditions (circulating sea-water without oxylipins; Figure 1 and Figure S1H; p-value < 0.05); 8.4% of the gastrulae (Figure S1B; p-value < 0.001) and 3.3% of early plutei (Figure 1 and Figure S1F) were non-apoptotic.
In the third experiment, we further decreased the concentrations in the oxylipin mixture to 0.3 µM decadienal, 0.7 µM heptadienal, 1.0 µM octadienal, and 1.8 μM HEPEs. After 48 hpf, about 55.3% of embryos appeared as shortened plutei (Figure 1 and Figure S1H; p-value < 0.05) with a low number of delayed embryos at the early pluteus (9.6%; p-value < 0.01; Figure S1H) and gastrula stages (24%; p-value < 0.0001; Figure S1B).
In the fourth experiment, we only lowered the concentration of the four HEPEs to 1.6 µM and the obtained results were similar to the third experiment, with 60.3% shortened plutei (p-value < 0.05) and 5.6% gastrulae (p-value < 0.001; Figure 1).
In the last experiment, we tested concentrations of 0.25, 0.5, and 0.75 µM for PUAs (decadienal, heptadienal, and octadienal, respectively) and 1.4 µM for HEPEs (fifth experiment); after 48 hpf, only 33.2% of embryos were delayed at the early pluteus stage (p-value < 0.01) and the other embryos (66.8%) were normal plutei, as in the controls (Figure 1 and Figure S1C).
We then extended the exposure time of PUA + HEPE mixtures to 1 week post-fertilization (wpf) to follow the fate of delayed embryos in the mixture with 0.3 µM decadienal, 0.7 µM heptadienal, and 1.0 µM octadienal for PUAs and 1.8 μM for HEPEs. Observations under the light microscope indicated that embryos had reached the pluteus stage but were malformed (degraded arms and apex) because they did not display the characteristic ampoule-like shape, as observed in the controls (Figure S2) [31].
The five experiments were also performed treating sea urchin eggs soon after fertilization at the same mixture concentrations reported above. In these post-fertilization experiments, the results were almost the same, with only a lower percentage of delayed embryos with respect to incubations with oxylipin mixtures added before fertilization (Figure S3 and Table S2).
2.2. Network Analysis
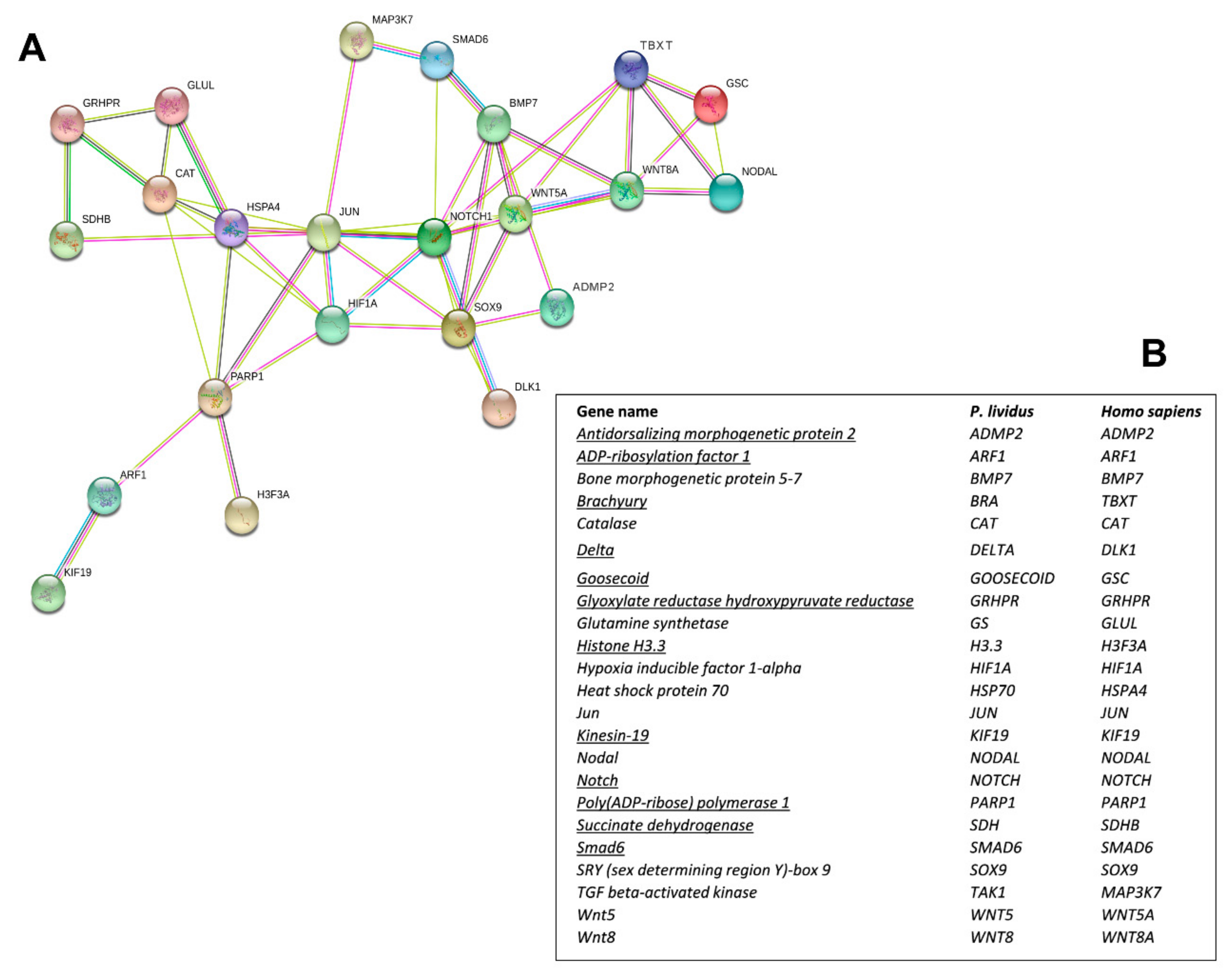
Interactomic analysis showed that the 12 new genes identified are connected to the following 11 genes, previously analyzed in response to single PUAs and HEPEs treatments: bone morphogenetic protein 5-7 (BMP5-7), catalase (CAT), glutamine synthetase (GS), hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A), heat shock protein 70 (hsp70), Jun (Jun), sex-determining region Y (SRY)-box9 (Sox9), TGF beta-activated kinase (TAK1), Wnt5 (Wnt5), and Wnt8 (Wnt8) [30,48,49]. As shown in the network reported in Figure 2A, the genes are correlated as follows:
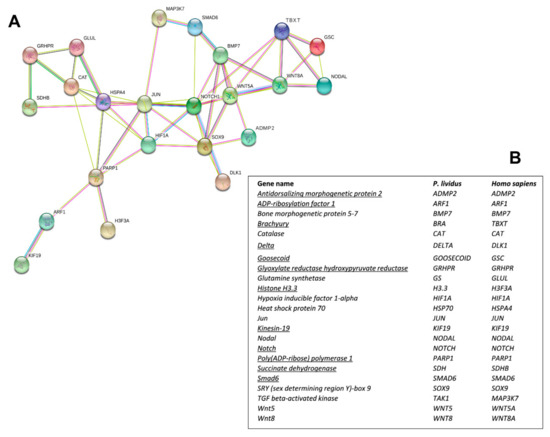
Figure 2.
(A) Interactomic analysis by STRING (https://string-db.org/). The network graphically displays the relationship between genes. The biological relationships between genes are indicated by different colors. Known interactions: reported by database = light blue and determined experimentally = pink. Expected interactions: gene proximity = green; gene fusion = red; genes with similar pattern = light blue. (B) Homo sapiens gene names and the corresponding P. lividus orthologous genes. The new genes isolated in the present work are underlined.
(1) ADMP2 with BMP5-7 and Sox9; (2) Notch with BMP5-7, Delta, HIF1A, Jun, Smad6, Sox9, and Wnt5; (3) Goosecoid with Brachyury, Nodal, and Wnt8; (4) Brachyury with Goosecoid, Nodal, Notch, Wnt5, and Wnt8; (5) Smad6 with BMP5-7, Notch, and MAPK3/7; (6) GRHPR with CAT, Glut, and SDH; (7) PARP1 with ARF1, CAT, hsp70, Jun, H3.3, and HIF1A; (8) ARF1 with KIF19 and PARP1; (9) SDH with GRHPR and hsp70. The corresponding human orthologous genes are reported in Figure 2B.
2.3. Molecular Analyses by Real-Time qPCR
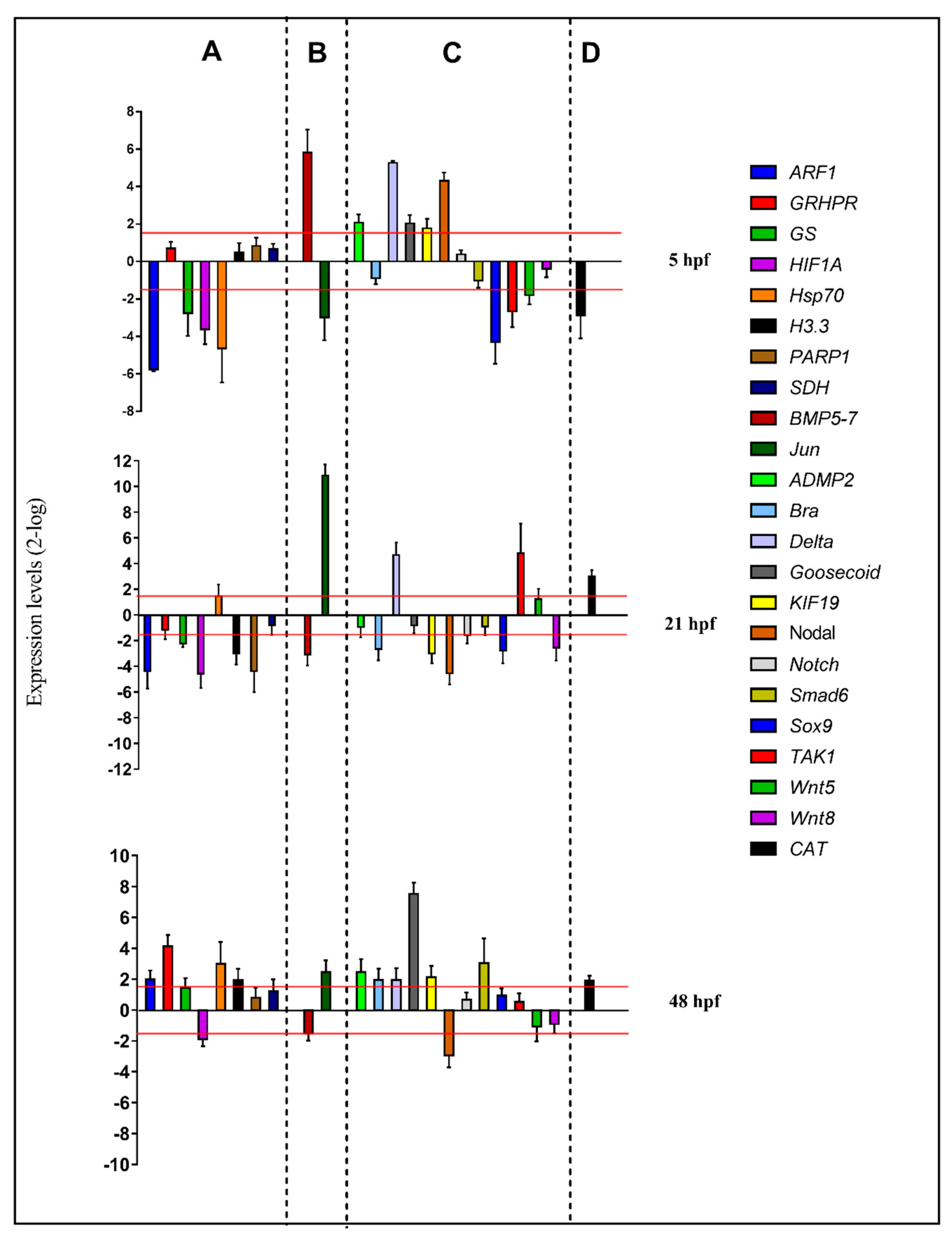
For molecular experiments, the expression levels of the 23 functionally interconnected genes were followed by real-time qPCR. Gene expression was detected at the blastula (5 hpf), gastrula (21 hpf), and pluteus (48 hpf) stages, as reported in the histograms in Figure 3 (see also Table S3):
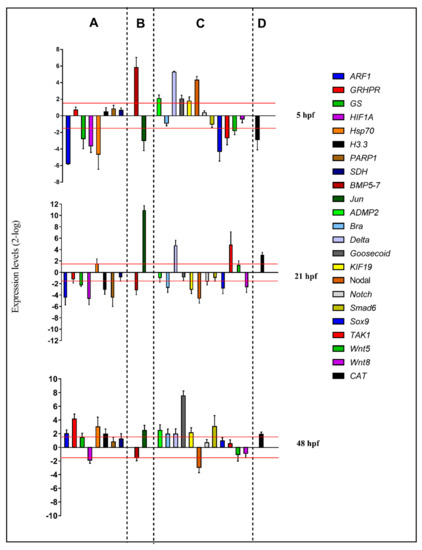
Figure 3.
Real-time qPCR at the blastula (5 hpf), gastrula (21 hpf), and pluteus (48 hpf) stages of the sea urchin P. lividus. Histograms show the fold-changes of 23 genes involved in different functional processes: stress (A), skeletogenesis (B), development/differentiation (C), and detoxification (D). Fold differences greater than ± 1.5 (see red dotted horizontal guidelines at values of +1.5 and −1.5) were considered significant.
2.3.1. Stress Response Genes
At the blastula stage, four genes were down-regulated with respect to the control: ARF (5.8), GS (2.8), HIF1A (3.6), and hsp70 (4.6). At the gastrula stage, five genes were targeted by the PUA + HEPE mixture: ARF (4.4), GS (2.2), HIF1A (4.6-), H3.3 (3.0-), and PARP1 (4.4), all of which were down-regulated. At the pluteus stage, four genes were up-regulated by the PUA + HEPE mixture: ARF1 (2.0), GRHPR (4.1-), Hsp70 (3.0), and H3.3 (2.0). Only the HIF1A gene was down-regulated (2.0).
2.3.2. Skeletogenic Genes
At 5 hpf, Jun (2.3) was down-regulated and BMP5-7 (5.8) was up-regulated by the PUA + HEPE mixture. At the gastrula stage, Jun was strongly up-regulated (10.9) and BMP5-7 (3.1-fold) was down-regulated; then, at the pluteus stage, Jun was targeted by PUA + HEPE mixture with an expression level higher than 2.5-fold compared to the control.
2.3.3. Development/Differentiation Genes
At the blastula stage, six genes were targeted: sox9 and TAK1 genes were down-regulated (4.3 and 2.7-fold, respectively), whereas ADMP2, Delta, Goosecoid, and Nodal genes were up-regulated (2.1-, 5.3-, 2.0-, and 4.3-fold, respectively). At 21 hpf, Brachyury, KIF19, Nodal, Sox9, and Wnt8 were down-regulated (2.7-, 3.0-, 4.5-, 2.8-, and 2.6-fold, respectively), whereas TAK1 and Delta were up-regulated (4.8- and 4.7-fold, respectively). At 48 hpf, the PUA + HEPE mixture targeted the expression of six genes: ADMP2, Brachyury, Delta, Goosecoid, KIF19, and Smad6 were up-regulated (2.5-, 2.0-, 2.0-, 7.5-, 2.1-, and 3.0-fold, respectively). On the contrary, only the Nodal gene was down-regulated (3.0-fold).
2.3.4. Detoxification Genes
The only gene followed by real-time qPCR, CAT, was targeted by PUA + HEPE mixture at all stages under analysis; in particular, at 5 hpf, this gene showed an increase in its expression level (2.9-fold), whereas at 21 hpf and 48 hpf it was down-regulated (2.0- and 3.0-fold, respectively).
3. Discussion
This is the first study describing the negative impact of diatom-derived PUA + HEPE mixtures on sea urchins, considered as model organisms among marine invertebrates. The negative effects of these two classes of oxylipins have been widely studied on the embryonic development of the sea urchin P. lividus. Initial studies were performed using single PUAs at low concentrations, demonstrating that decadienal, heptadienal, and octadienal exerted toxigenic effects on embryo development [30]. The strongest effect was induced by decadienal, with heptadienal and octadienal requiring higher concentrations to reach the same effects as decadienal [32]. By contrast, HEPEs induced developmental malformations at much higher concentrations when compared to PUAs. Interestingly, HEPEs also induced a marked developmental delay in sea urchin embryos, which is also evident at higher concentrations, and has not hitherto been reported for PUAs [31]. Our current results indicate that mixtures of these compounds induce a synergistic effect, confirming that PUAs induce malformations and HEPE developmental delay but with a stronger effect with respect to individual compounds [46,47]. The harmful effects of these compounds were also confirmed by molecular analysis, indicating that sea urchins place in motion functionally intercorrelated genes to counteract negative effects against these natural toxins [48,49,50].
Our morphological results demonstrate a synergistic effect of the seven oxylipins in mixtures. More specifically, PUA and HEPE mixtures induce a dose-dependent delay in sea urchin development. Even if PUAs in individual tests seem to be stronger than HEPEs, when in mixtures the effects of HEPEs seem to dilute those of PUAs. In fact, in the first 48 hpf, oxylipin mixtures only induced delay of sea urchin embryos and no malformed embryos were detected. Malformations of P. lividus embryos (usually induced by individual PUAs or in mixtures of PUAs) were visible only after one-week post-fertilization. These results indicate that PUAs + HEPEs induce delay but not arrest of embryonic development. These findings can be explained in light of previous results demonstrating a reversible effect for individual PUAs and irreversible effects for HEPEs. P. lividus embryos can recover after exposure to PUAs [30] but not HEPEs [31]. Our morphological results are also linked to the molecular response of sea urchin embryos to PUAs that occurred later (at the pluteus stage) compared to HEPEs (at the blastula stage). Taken together, these results indicate that the delay observed in the early development of sea urchins may be due to HEPEs, which act in an irreversible way and precociously on embryos, targeting many genes involved in skeletogenesis and development/differentiation processes already at the blastula stage. PUA-induced malformations were detectable only one week post fertilization, with gene expression mainly affected later at the pluteus stage.
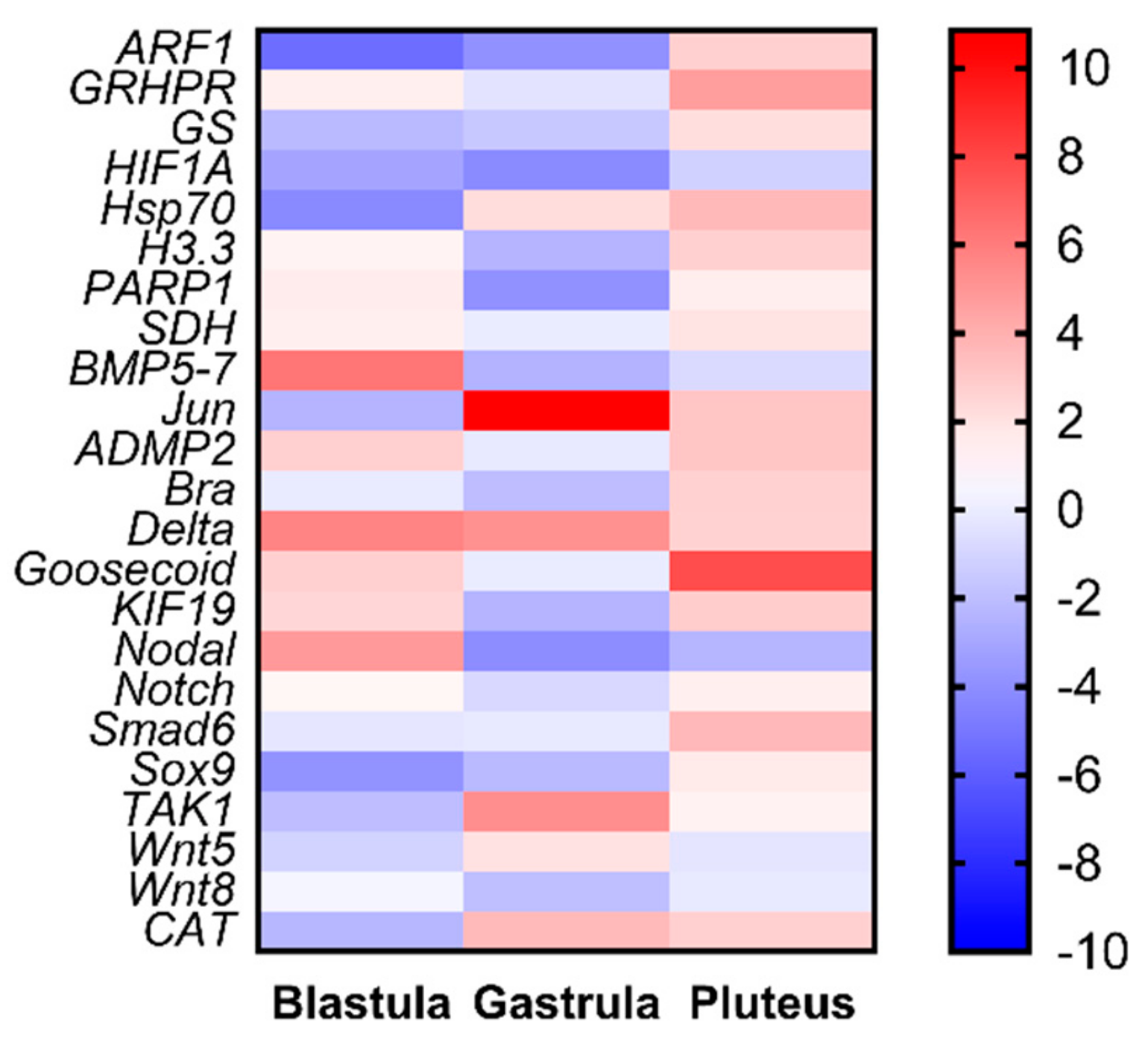
Our study also provides new information on the molecular effects of oxylipins on sea urchin embryos. Even if P. lividus represents a well-established model organism for ecotoxicological studies, its genome is still not available. Hence, the availability of 12 new genes provides a better understanding on the molecular mechanisms of response in sea urchins to toxins. An important outcome of this work consists in the fact that these new genes are not only functionally intercorrelated with one another, but also with another 11 genes previously analyzed in response to tests on individual PUAs and HEPEs. PUA + HEPE mixtures are able to affect the expression level of most of the analyzed genes, with the only exception of SDH, Notch, and Wnt5. These genes were involved in stress, skeletogenesis, development and differentiation, and detoxification processes. Furthermore, PUAs + HEPEs targeted genes in all three developmental stages analyzed (as summarized in the heat map reported in Figure 4), mainly down-regulating genes at the early gastrula stage and up-regulating these genes at the pluteus stage. It is worth noting that the new genes (mainly those involved in differentiation and developmental processes) isolated in this work have never been studied before in response to environmental stress.
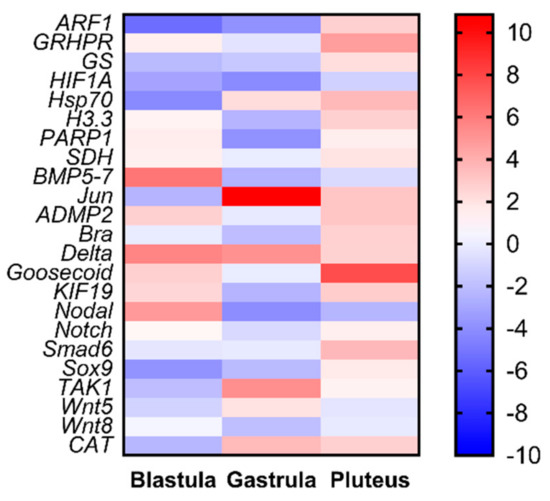
Figure 4.
Heatmaps (Heatmapper available at www.heatmapper.ca) showing the expression profiles and hierarchical clustering of 23 genes analyzed by real-time qPCR in P. lividus embryos at the three different developmental stages (blastula, gastrula, and pluteus) treated with mixtures decadienal 0.3 μM, heptadienal 0.7 μM, and octadienal 1.0 μM, and HEPEs 1.6 μM. Colour code: red, up-regulated genes respect to the control (embryos grown without PUAs + HEPEs mixtures); blue, down-regulated genes.
To date, no data were available on the combined effects of natural toxins on the sea urchin P. lividus. Several studies focused on the exposure of sea urchins to heavy metal mixtures and combinations with other stressors [15,16,17], as the anthropogenic release into the environment of these chemicals represents a serious risk for normal physiological processes of exposed biota. Moreover, many studies have also explored how ocean acidification and warming may both impact the reproductive success and larval fitness of sea urchins [18,19,20,21,22,23].
This study can be considered a step forward in the ecotoxicological assessment of natural toxins on these organisms. Given the importance of diatom blooms in nutrient-rich aquatic environments, our findings acquire interesting ecological implications. In fact, hydroxyacids represent one of the most common classes of oxylipins produced by some diatoms, much more common than the better-known PUAs [13,35,39,51,52]. Both PUA-producing and non-producing diatoms are able to negatively affect hatching success in copepods, with induction of apoptosis in newly hatched nauplii [12].
In a previous study, we demonstrated that the concentrations tested in this study are well within the significant range for affecting growth and performance of sea urchins during bloom conditions [31]. In their natural habitats sea urchins and their larvae may come in contact with diatom PUAs in the field at the end of a bloom [53]. In fact, in aquatic ecosystems, a considerable proportion of the primary production from phytoplankton bloom sinks to the sediment [54,55]. Because sea urchins are browsing animals that eat phytoplankton and organic matter in the sand or mud, they may accumulate oxylipins through feeding or be exposed to high local concentrations of these compounds that may affect growth performance, as already demonstrated for copepods exposed to PUAs [45]. Very recently, Russo et al. [56] reported on oxylipin production rates in natural planktonic diatom communities in the Gulf of Naples, from which sea urchins were collected in the present study. These authors provided the first piece of evidence that the oxylipins analysed from natural phytoplankton communities derive mostly from diatoms. High phytoplankton abundance was observed from April to July, whereas low values were detected in March and November. Overall, diatoms dominated phytoplankton assemblages during peaks observed in late spring, summer, and September–October, corresponding to the reproductive period of the sea urchin P. lividus. Not only planktonic diatoms, but also benthic diatoms from the Gulf of Naples have been shown to produce oxylipins [57,58,59,60], with dramatic effects on benthic grazers [24], including the sea urchin P. lividus, indicating that potentially all diatoms can negatively impact reproductive success and development in sea urchins.
More generally, this study on multiple stressors can also help predict and understand their effects through the study of the molecular pathways activated in response to stressors, allowing organisms to counteract deleterious consequences and irreversible damage.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck) were collected from a site in the Bay of Naples that is not privately owned or protected in any way, according to Italian legislation (DPR 1639/68, 19 September 1980, confirmed on 10 January 2000). Field studies did not include endangered or protected species. All experimental procedures on animals were in compliance with the guidelines of the European Union (directive 2010/63/EU).
4.2. Gamete Collection, Egg Incubation with Mixtures of PUAs and HEPEs, Embryo Cultures, and Morphological Analyses
Adult sea urchin P. lividus were collected in the Gulf of Naples during their reproductive period by scuba diving and were stored in tanks with circulating sea-water (FSW) until testing. To induce gamete emission, sea urchins were shaken or injected with 2 M KCl through the peribuccal membrane. Eggs were washed with filtered sea water and kept in FSW until use. Dry sperm was collected and kept undiluted at +4 °C until use. Experiments were performed treating eggs with the seven oxylipins: 2-trans,4-trans-decadienal (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), 2-trans,4-trans-heptadienal (Sigma-Aldrich), 2-trans,4-trans-octadienal (Sigma-Aldrich), 5-hydroxy-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z-eicosapentaenoic acid (5-HEPE; Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA; purity ≥98%), 9-hydroxy-5Z,7E,11Z,14Z,17Z-eicosapentaenoic acid (9-HEPE; Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA; purity ≥98%), 11-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,12E,14Z,17Z-eicosapentaenoic acid (11-HEPE; Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA; purity ≥98%), and 15-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,11Z,13E,17Z-eicosapentaenoic acid (15-HEPE; Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA; purity ≥98%). Five experiments were performed adding the oxylipins 10 min before and 10 min after fertilization (with the exception of the fourth and fifth experiments performed by only treating eggs before fertilization) at different concentrations, as reported in Table 1.
Eggs were fertilized using sperm-to-egg ratios of 100:1 for both controls and treatments. Experiments were conducted in triplicate, collecting eggs from three different females. A control experiment was conducted fertilizing eggs in FSW without PUA/HEPE mixtures. To evaluate the effects of mixture treatments, three different endpoints were checked: (i) fertilization success, (ii) first cleavage, and (iii) pluteus stage (48 hpf). At 48 hpf, controls and treated embryos were fixed with glutaraldehyde (1% in FSW) and observed under the light microscope (Zeiss Axiovert 135TV, Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) to assess the percentage of normal and malformed plutei.
4.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
About 5000 eggs in 12 mL of FSW were treated with mixtures of three PUAs (0.3 μM decadienal, 0.7 μM heptadienal, 1.0 μM octadienal) and four hydroxyacids (5-, 9-, 11-, 15-HEPEs 1.8 μM) for 10 min and then fertilized. Samples were then collected at blastula, early gastrula, and pluteus, corresponding to 5, 21, and 48 hpf, respectively, and centrifuged at 3500 relative centrifugal force for 15 min in a swing out rotor at 4 °C. The pellet was washed with phosphate-buffered saline and then frozen in liquid nitrogen and kept at −80 °C until use. Total RNA was extracted using Aurum Total RNA Mini Kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA), according to [61]. The amount of total RNA extracted was estimated by the absorbance at 260 nm and the purity by 260/280 and 260/230 nm ratios, using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (ND-1000 UV-VIS Spectrophotometer; NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA). The integrity of RNA was evaluated observing the rRNA subunits (28S and 18S) on agarose gel electrophoresis. For each sample, 1000 ng of total RNA was retrotranscribed with an iScript cDNA Synthesis kit (Bio-Rad, Milan, Italy), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Experiments were conducted in triplicate using different egg groups collected from four individuals.
4.4. Gene Isolation and Interactomic Analysis
The sequences of 12 new genes were retrieved from the transcriptome of the sea urchin P. lividus deposited in the SRA database (Sequence Read Archive, available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra, accession number PRJNA495004) [60] and from the Taxonomy Broswer (available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi). For each gene, specific primers were designed on the nucleotide sequences (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Gene name, acronym, accession numbers, primer names, primer sequences, primer efficiency, and amplicon lengths of PCR fragments. Accession number indicated with * derived from the transcriptome (accession number PRJNA495004)
PCR fragments were purified from agarose gel using the QIAquick Gel Extraction kit (Qiagen, Milan, Italy), and the specificity of the PCR product was checked by DNA sequencing. Five serial dilutions were set up to determine Ct values and PCR efficiencies for all primer pairs (for real-time qPCR conditions, see below). The efficiency of each primer pair was calculated by E = [10^(-1/slope)-1]*100 (Table 2). Standard curves were generated for each oligonucleotide pair using Ct values versus the logarithm of each dilution factor.
The network analysis was performed by STRING [62], an online database of known and predicted protein–protein interactions, to identify relationships on the basis of associated functions and data mining from experimental studies reported in the literature. Because sea urchin genes are not annotated in the STRING database, we used the name of the human orthologues to search for P. lividus genes (see Figure 1). The biological functions for these 12 genes are reported in Table S4.
4.5. Real-Time qPCR
Molecular analyses were performed on specimens treated with PUA/HEPE mixtures at 1.6 µM for HEPEs and 0.3 µM decadienal, 0.7 µM heptadienal, and 1 µM octadienal. Samples were then collected at different developmental stages after fertilization, corresponding to early blastula (5 hpf), late gastrula (21 hpf), and pluteus (48 hpf). Undiluted cDNA was used as a template in a reaction containing a final concentration of 0.3 mM for each primer and 1× FastStart SYBR Green master mix (total volume of 10 μL) (Applied Biosystems, Monza, Italy). PCR amplifications were performed in a ViiATM7 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Monza, Italy) thermal cycler using the following thermal profile: 95 °C for 10 min, one cycle for cDNA denaturation; 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min, 40 cycles for amplification; 72 °C for 5 min, one cycle for final elongation; one cycle for melting curve analysis (from 60 to 95 °C) to verify the presence of a single product. Each assay included a no-template control for each primer pair. To capture intra-assay variability, all real-time qPCR reactions were carried out in triplicate. Fluorescence was measured using the ViiATM7 software (Applied Biosystems, Monza, Italy). The expression of each gene was analyzed and internally normalized against ubiquitin [29] and 18S rRNA [63,64] using REST software (Relative Expression Software Tool, Weihenstephan, Germany) on the basis of the Pfaffl method [65,66]. Relative expression ratios above 1.5 were considered significant (see Table S3).
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/3/719/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C., A.I., L.M., G.L.; methodology, M.C., R.E., N.R., L.A.; validation M.C., R.E.; formal analysis, R.E., N.R., L.A.; resources, M.C., A.I.; data curation, M.C., R.E., N.R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C., R.E., N.R., L.A., G.L.; writing—review and editing, all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Roberta Esposito was supported by a PhD (PhD in Biology, University of Naples Federico II) fellowship funded by the Photosynthesis 2.0 project of the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn. Luisa Albarano was supported by a PhD (PhD in Biology, University of Naples Federico II) fellowship co-funded by the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn and University of Naples Federico II. Thanks are also due to the Fishery Service for providing sea urchins and Davide Caramiello of the Marine Resources for Research Unit of the Stazione Zoologica for his technical support for maintenance and gamete collection. We thank the Molecular Biology and Bioinformatics Units for providing primers for PCR experiments and for PCR product sequencing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Singh, B.R.; Steinnes, E. Soil and water contamination by heavy metals. In Soil Processes and Water Quality; Lal, R., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; Advances in Soil Science; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 233–271. [Google Scholar]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Lubchenco, J.; Melill, J.M. Human Domination of Earth’s Ecosystems. Science 1997, 277, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, V.L.; Buzby, M.; Hutchinson, T.; Mastrocco, F.; Parke, N.; Roden, N. Effects of human pharmaceuticals on aquatic life: Next steps. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3456–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lein, N.P.H.; Fujii, S.; Tanaka, S.; Nozoe, M.; Tanaka, H. Contamination of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in surface water of the Yodo River basin (Japan). Desalination 2008, 226, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, J.C.; Fabry, V.J.; Aumont, O.; Bopp, L.; Doney, S.C.; Feely, R.A.; Gnanadesikan, A.; Gruber, N.; Ishida, A.; Joos, F.; et al. Anthropogenic ocean acidification over the twenty-first century and its impact on calcifying organisms. Nature 2005, 437, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinotte, J.M.; Fabry, V.J. Ocean acidification and its potential effects on marine ecosystems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1134, 320–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabry, V.J.; Seibel, B.A.; Feely, R.A.; Orr, J.C. Impacts of ocean acidification on marine fauna and ecosystem processes. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 414–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeker, K.J.; Kordas, R.L.; Crim, R.; Hendriks, I.E.; Ramajo, L.; Singh, G.S.; Duarte, C.M.; Gattuso, J.P. Impacts of ocean acidification on marine organisms: Quantifying sensitivities and interaction with warming. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bruno, J.F. The Impact of Climate Change on the World’s Marine Ecosystems. Science 2010, 328, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralto, A.; Barone, G.; Romano, G.; Poulet, S.A.; Ianora, A.; Russo, G.L.; Buttino, I.; Mazzarella, G.; Laabir, M.; Cabrini, M.; et al. The insidious effect of diatoms on copepod reproduction. Nature 1999, 402, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.; d’Ippolito, G.; Cutignano, A.; Miralto, A.; Ianora, A.; Romano, G.; Cimino, G. Chemistry of oxylipin pathways in marine diatoms. Pure Appl. Chem. 2007, 79, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.; d’Ippolito, G.; Cutignano, A.; Romano, G.; Lamari, N.; Massa Gallucci, A.; Cimino, G.; Miralto, A.; Ianora, A. LOX-induced lipid peroxidation mechanism responsible for the detrimental effect of marine diatoms on zooplankton grazers. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Ippolito, G.; Lamari, N.; Montresor, M.; Romano, G.; Cutignano, A.; Gerecht, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. 15S-lipoxygenase metabolism in the marine diatom Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima. New Phytol. 2009, 183, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutignano, A.; Lamari, N.; D’ippolito, G.; Manzo, E.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. Lipoxygenase products in marine diatoms: A concise analytical method to explore the functional potential of oxylipins. J. Physiol. 2011, 47, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Assessment of toxic interactions of heavy metals in multi-component mixtures using sea urchin embryo-larval bioassay. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventura, P.; Benedetti, G.; Albarède, F.; Miossec, P. Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation. Autoimm. Rev. 2015, 14, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, M.A.; Costa, S.; Cuttitta, A.; Gianguzza, F.; Nicosia, A. Coexposure to sulfamethoxazole and cadmium impairs development and attenuates transcriptional response in sea urchin embryo. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla-Gamiño, J.L.; Kelly, M.W.; Evans, T.G.; Hofmann, G.E. Temperature and CO2 additively regulate physiology, morphology and genomic responses of larval sea urchins, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Proc. R. Soc. B 2013, 280, 20130155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorey, N.; Maboloc, E.; Chana, K.Y.K. Development of the sea urchin Heliocidaris crassispina from Hong Kong is robust to ocean acidification and copper contamination. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 205, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.K.Y.; Chan, K.K.Y. Interactive effects of temperature and salinity on early life stages of the sea urchin Heliocidaris crassispina. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feehan, C.J.; Grauman, B.C.; Strathmann, R.R.; Dethier, M.N.; Duggins, D.O. Kelp detritus provides high quality food for sea urchin larvae. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, S299–S306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glockner-Fagetti, A.; Phillips, N.E. Low salinity and sediment stress on sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus larvae has latent effects on juvenile performance. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 619, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, B.; Fogartya, N.D.; Figueiredo, J. Effects of ocean warming and acidification on fertilization success and early larval development in the green sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, G.S. The influence of bioactive oxylipins from marine diatoms on invertebrate reproduction and development. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 367–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, C.A.; Bentley, M.G.; Cadwell, G.S. 2,4-Decadienal: Exploring a novel approach for the control of polychaete pests on cultured abalone. Aquaculture 2010, 310, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, A.; Esposito, R.; Ianora, A.; Spagnuolo, A. Ciona intestinalis as a marine model system to study some key developmental genes targeted by the diatom-derived aldehyde decadienal. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, C.; Romano, G.; Roncalli, V.; Amoresano, A.; Fontanarosa, C.; Bastianini, M.; Braga, F.; Carotenuto, Y.; Ianora, A. New oxylipins produced at the end of a diatom bloom and their effects on copepod reproductive success and gene expression levels. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Miralto, A.; Ianora, A. Teratogenic effects of diatom metabolites on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus embryos. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 950–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Costantini, M.; Buttino, I.; Ianora, A.; Palumbo, A. Nitric oxide mediates the stress response induced by diatom aldehydes in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrella, S.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Ruocco, N.; Costantini, M. Molecular response to toxic diatom-derived aldehydes in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2089–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrella, S.; Romano, G.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Costantini, M. First morphological and molecular evidence of the negative impact of diatom-derived hydroxyacids on the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 151, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, N.; Varrella, S.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Somma, D.; Leonardi, A.; Mellone, S.; Zuppa, A.; Costantini, M. Diatom-derived oxylipins induce cell death in sea urchin embryos activating caspase-8 and caspase 3/7. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 176, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohnert, G.; Lumineau, O.; Cueff, A.; Adolph, S.; Cordevant, C.; Lange, M.; Poulet, S. Are volatile unsaturated aldehydes from diatoms the main line of chemical defence against copepods? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 245, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.L.; Abrahamsson, K.; Godhe, A.; Wangberg, S.A. Seasonal variability in polyunsaturated aldehyde production potential among strains of Skeletonema marinoi (bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Romano, G.; Caruso, T.; Spinella, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. Production of Octadienal in the Marine Diatom Skeletonema costatum. Org. Lett. 2003, 6, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ippolito, G.; Tucci, S.; Cutignano, A.; Romano, G.; Cimino, G.; Miralto, A.; Fontana, A. The role of complex lipids in the synthesis of bioactive aldehydes of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1686, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G. Wound-activated chemical defense in unicellular planktonic algae. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 4352–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G. Phospholipase A(2) activity triggers the wound-activated chemical defense in the diatom Thalassiosira rotula. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ippolito, G.; Iadicicco, I.; Romano, G.; Fontana, A.; Iadicicco, O. Detection of short-chain aldehydes in marine organisms: The diatom Thalassiosira rotula. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6137–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ippolito, G.; Romano, G.; Iadicicco, O.; Miralto, A.; Ianora, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. New birth-control aldehydes from the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum: Characterization and biogenesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6133–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichard, T.; Poulet, S.A.; Pohnert, G. Determination and quantification of α,β,γ,δ-unsaturated aldehydes as pentafluorobenzyl-oxime derivates in diatom cultures and natural phytoplankton populations: Application in marine field studies. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2005, 814, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichard, T.; Poulet, S.A.; Halsband-Lenk, C.; Albaina, A.; Harris, R.; Liu, D.; Pohnert, G. Survey of the chemical defense potential of diatoms: Screening of fifty species for α,β,γ,δ-unsaturated aldehydes. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiro, A.; Carotenuto, Y.; Lamari, N.; Esposito, F.; D’Ippolito, G.; Fontana, A.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A.; Miralto, A.; Guisande, C. Diatom induction of reproductive failure in copepods: The effect of PUAs versus non volatile oxylipins. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 401, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjappa, D.; D’Ippolito, G.; Gallo, C.; Zingone, A.; Fontana, A. Oxylipin diversity in the diatom family Leptocylindraceae reveals DHA derivatives in marine diatoms. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianora, A.; Miralto, A. Toxigenic effects of diatoms on grazers, phytoplankton and other microbes: A review. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarano, L.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A.; Libralato, G.; Manfra, L.; Costantini, M. Molecular and morphological toxicity of diatom-derived hydroxyacid mixtures to sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus embryos. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruocco, N.; Annunziata, C.; Ianora, A.; Libralato, G.; Manfra, L.; Costantini, S.; Costantini, M. Toxicity of diatom-derived polyunsaturated aldehyde mixtures on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus development. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrella, S.; Romano, G.; Costantini, S.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Costantini, M. Toxic diatom aldehydes affect defence gene networks in sea urchins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, N.; Fedele, A.M.; Costantini, S.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A.; Costantini, M. New inter-correlated genes targeted by diatom-derived polyunsaturated aldehydes in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2017, 142, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, V.; Piscopo, M.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A.; Palumbo, A.; Costantini, M. Defensome against toxic diatom aldehydes in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Cutignano, A.; Briante, R.; Febbraio, F.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. New C16 fatty-acid-based oxylipin pathway in the marine diatom Thalassiosira rotula. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 4065–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Cutignano, A.; Tucci, S.; Romano, G.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. Biosynthetic intermediates and stereochemical aspects of aldehyde biosynthesis in the marine diatom Thalassiosira Rotula. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaverbeke, J.; Franco, M.A.; van Oevelen, D.; Moodley, L.; Provoost, P.; Steyaert, M.; Soetaert, K.; Vincx, M. Benthic responses to sedimentation of phytoplankton on the Belgian Continental Shelf. In Current Status of Eutrophication in the Belgian Coastal Zone; Presses Universitaires de Bruxelles: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2006; pp. 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lignell, R.; Heiskanen, A.S.; Kuosa, H.; Gundersen, K.; Kuuppo-Leinikki, P.; Pajuniemi, R.; Vitto, A. Fate of a phytoplankton spring bloom: Sedimentation and carbon flow in the planktonic food web in the northern baltic. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 94, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Death, detritus and energy flow in aquatic ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 1995, 33, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Ianora, A.; Carotenuto, Y. Re-shaping marine plankton communities: Effects of diatoms oxylipins on copepods and beyond. Mar. Biol. 2019, 116, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raniello, R.; Iannicielli, M.M.; Nappo, M.; Avilla, C.; Zupo, V. Production of Cocconeis neothumensis (Bacillariophyceae) biomass in batch cultures and bioreactors for biotechnological applications: Light and nutrient requirements. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 4, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappo, M.; Berkov, S.; Codina, C.; Avila, C.; Messina, P.; Zupo, V.; Bastida, J. Metabolite profiling of the benthic diatom Cocconeis scutellum by GC-MS (2009). J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 21, 295. [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco, N.; Costantini, S.; Zupo, V.; Lauritano, C.; Caramiello, D.; Ianora, A.; Budillon, A.; Romano, G.; Nuzzo, G.; D’Ippolito, G.; et al. Toxigenic effects of two benthic diatoms upon grazing activity of the sea urchin: Morphological, metabolomic and de novo transcriptomic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruocco, N.; Cavaccini, V.; Caramiello, D.; Ianora, A.; Fontana, A.; Zupo, V.; Costantini, M. Noxious effects of the benthic diatoms Cocconeis scutellum and Diploneis sp. on sea urchin development: Morphological and de novo transcriptomic analysis. Harmful Algae 2019, 86, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruocco, N.; Costantini, S.; Zupo, V.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A.; Fontana, A.; Costantini, M. High-quality RNA extraction from the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus embryos. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, M.A.; Costa, S.; Gianguzza, M.; Roccheri, M.C.; Gianguzza, F. Effects of cadmium exposure on sea urchin development assessed by SSH and RT-qPCR: Metallothionein genes and their differential induction. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinsino, A.; Bergami, E.; Della Torre, C.; Vannuccini, M.L. Amino modified polystyrene nanoparticles affect signalling pathways of the sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) embryos. Nanotoxicology 2017, 2, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in realtime RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).