Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State
Abstract
1. Introduction
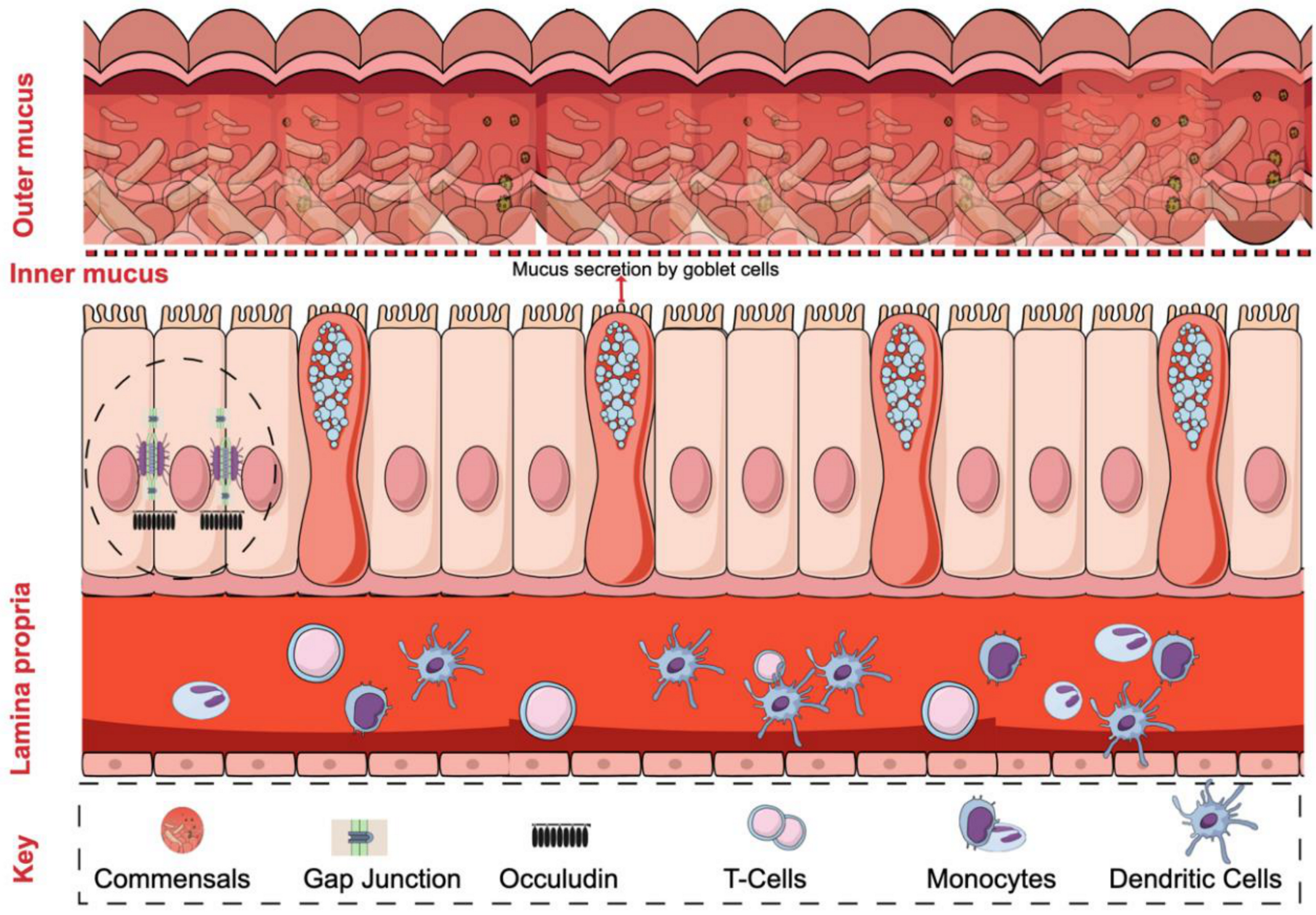
2. Intestinal Barrier Regulation
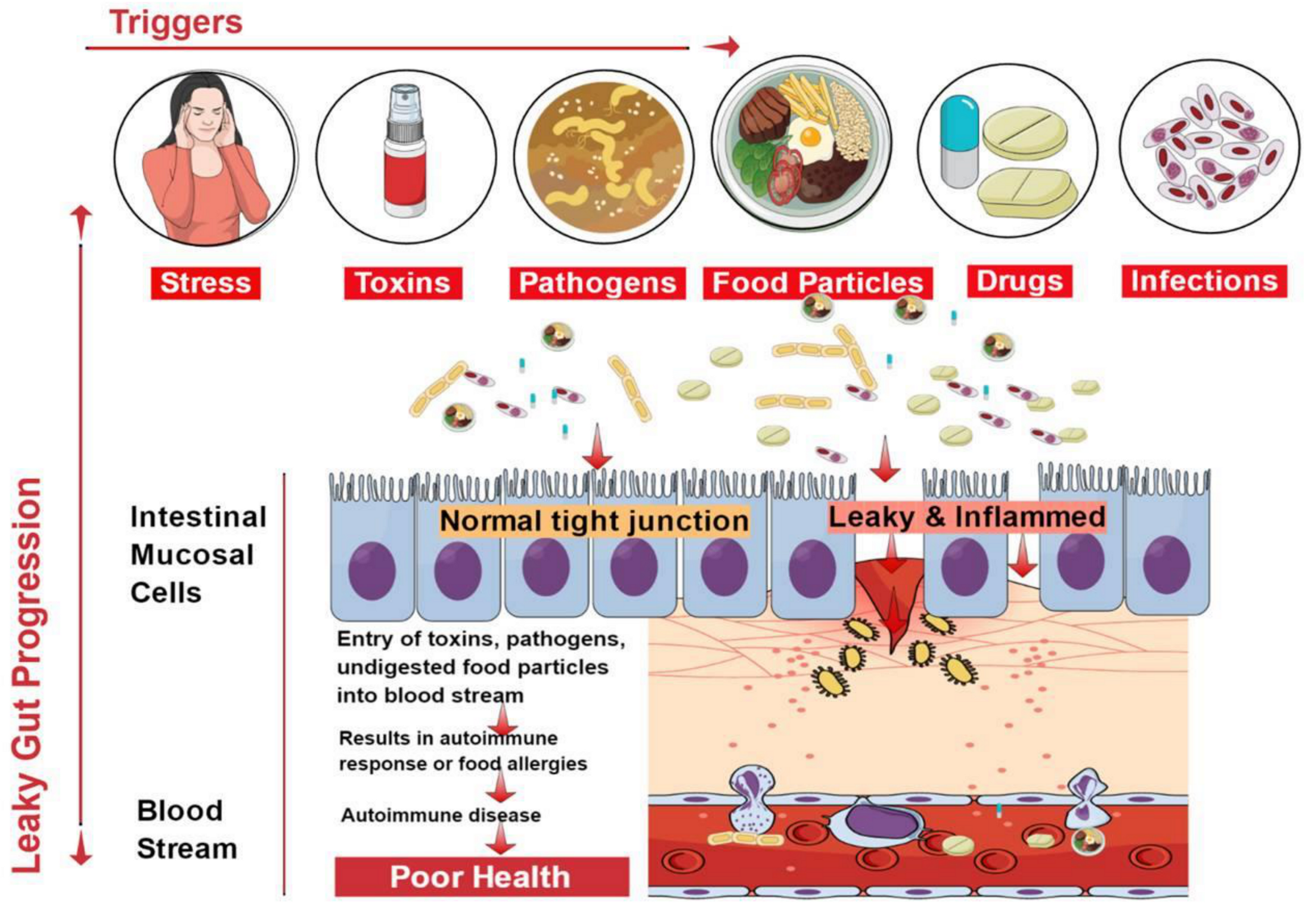
3. Causes of Leaky Gut
4. Factors Contributing to the Healing of Leaky Gut
5. Autoimmune Diseases Associated with Leaky Gut
5.1. Type 1 Diabetes
5.2. Multiple Sclerosis
5.3. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
5.4. Ankylosing Spondylitis
5.5. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
5.6. Healing the Leaky Gut
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomomasa, T.; Kuroume, T.; Arai, H.; Wakabayashi, K.; Itoh, Z. Erythromycin induces migrating motor complex in human gastrointestinal tract. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1986, 31, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, U.; von Herrath, M.G. Induction, acceleration or prevention of autoimmunity by molecular mimicry. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 40, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Lammers, K.M.; Goldblum, S.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Netzel-Arnett, S.; Buzza, M.S.; Antalis, T.M.; Vogel, S.N.; Zhao, A.; Yang, S.; et al. Identification of human zonulin, a physiological modulator of tight junctions, as prehaptoglobin-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16799–16804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Baudry, B.; Pumplin, D.W.; Wasserman, S.S.; Tall, B.D.; Ketley, J.M.; Kaper, J.B. Vibrio cholerae produces a second enterotoxin, which affects intestinal tight junctions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5242–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Kirby, J.; Reilly, C.M.; Luo, X.M. Leaky gut as a danger signal for autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Zonulin and its regulation of intestinal barrier function: The biological door to inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.M.; Van Itallie, C.M. Physiology and function of the tight junction. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2009, 1, a002584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltin, D.; Perets, T.T.; Vilkin, A.; Niv, Y. Mucin function in inflammatory bowel disease: An update. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Fiorentini, C.; Donelli, G.; Uzzau, S.; Kaper, J.B.; Margaretten, K.; Ding, X.; Guandalini, S.; Comstock, L.; Goldblum, S.E. Zonula occludens toxin modulates tight junctions through protein kinase c-dependent actin reorganization, in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Asmar, R.; Panigrahi, P.; Bamford, P.; Berti, I.; Not, T.; Coppa, G.V.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Host-dependent zonulin secretion causes the impairment of the small intestine barrier function after bacterial exposure. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.C.; Schirmer, M.; Weiss, H.; Haderlein, S.B. Microbial degradation of methyl tert-butyl ether and tert-butyl alcohol in the subsurface. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 70, 173–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Intestinal zonulin: Open sesame! Gut 2001, 49, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meddings, J.B.; Jarand, J.; Urbanski, S.J.; Hardin, J.; Gall, D.G. Increased gastrointestinal permeability is an early lesion in the spontaneously diabetic bb rat. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, G951–G957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, F.; Shoenfeld, Y. The microbiome in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 195, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitakis, N.G.; Papaioannou, W.; Sakkas, L.I.; Kousvelari, E. The autoimmunity-oral microbiome connection. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yang, C.; Tang, J. Disruption of the intestinal mucosal barrier in candida albicans infections. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishehsari, F.; Magno, E.; Swanson, G.; Desai, V.; Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Alcohol and gut-derived inflammation. Alcohol Res. 2017, 38, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. Physiological, pathological, and therapeutic implications of zonulin-mediated intestinal barrier modulation: Living life on the edge of the wall. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritscher-Ravens, A.; Schuppan, D.; Ellrichmann, M.; Schoch, S.; Rocken, C.; Brasch, J.; Bethge, J.; Bottner, M.; Klose, J.; Milla, P.J. Confocal endomicroscopy shows food-associated changes in the intestinal mucosa of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1012–1020.e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Roque, M.I.; Camilleri, M.; Smyrk, T.; Murray, J.A.; Marietta, E.; O’Neill, J.; Carlson, P.; Lamsam, J.; Janzow, D.; Eckert, D.; et al. A controlled trial of gluten-free diet in patients with irritable bowel syndrome-diarrhea: Effects on bowel frequency and intestinal function. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 903–911.e903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.P.; Huang, J.C.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, H.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, Y.T.; Yang, W.; Sun, K.H. Interactions of surface-expressed tlr-4 and endosomal tlr-9 accelerate lupus progression in anti-dsdna antibody transgenic mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.P.; Tang, S.J.; Wu, M.F.; Song, Y.C.; Yu, C.L.; Sun, K.H. Transgenic overexpression of anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody and activation of toll-like receptor 4 in mice induce severe systemic lupus erythematosus syndromes. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 35, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, M.T. Toll-like receptor signalling in the intestinal epithelium: How bacterial recognition shapes intestinal function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.M.; Sarvetnick, N.E. Current understanding of the role of gut dysbiosis in type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes 2019, 11, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereijido, M.; Anderson, J. Evolution of ideas on the tight junction. In Tight Junctions; Cereijido, M., Anderson, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Uzzau, S.; Goldblum, S.E.; Fasano, A. Human zonulin, a potential modulator of intestinal tight junctions. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 24, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, V.T.; Seifert, N.; Richard, N.; Raederstorff, D.; Steinert, R.E.; Prudence, K.; Mohajeri, M.H. The effects of fermentation products of prebiotic fibres on gut barrier and immune functions in vitro. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariadason, J.M.; Barkla, D.H.; Gibson, P.R. Effect of short-chain fatty acids on paracellular permeability in caco-2 intestinal epithelium model. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, G705–G712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, K.M.; Rast, J.P. An organismal model for gene regulatory networks in the gut-associated immune response. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.K.; Verma, S.; Jain, V.; Surapaneni, B.K.; Vinayek, R.; Phillips, L.; Nair, P.P. Parkinson’s disease: The emerging role of gut dysbiosis, antibiotics, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakansson, A.; Molin, G. Gut microbiota and inflammation. Nutrients 2011, 3, 637–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branski, D.; Fasano, A.; Troncone, R. Latest developments in the pathogenesis and treatment of celiac disease. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabri, B.; Sollid, L.M. Tissue-mediated control of immunopathology in coeliac disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, L.; Luo, X.M. Retinoic acid, leaky gut, and autoimmune diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdenakker, G.; Proost, P.; Van Damme, J. Microbiomic and posttranslational modifications as preludes to autoimmune diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Luo, X.M. Sle: Another autoimmune disorder influenced by microbes and diet? Front. Immunol. 2016, 6, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Shea-Donohue, T. Mechanisms of disease: The role of intestinal barrier function in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal autoimmune diseases. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 2, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghi, S.; Ju, J.M.; Lamba, A.; Murray, J.A. The potential utility of tight junction regulation in celiac disease: Focus on larazotide acetate. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Abnormal intestinal permeability and microbiota in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5153–5160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van der Waals, M.J.; Pijls, C.; Sinke, A.J.C.; Langenhoff, A.A.M.; Smidt, H.; Gerritse, J. Anaerobic degradation of a mixture of MtBE, EtBE, TBA, and Benzene under different redox condition. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3387–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H.; Stepankova, R.; Kozakova, H.; Hudcovic, T.; Vannucci, L.; Tuckova, L.; Rossmann, P.; Hrncir, T.; Kverka, M.; Zakostelska, Z.; et al. The role of gut microbiota (commensal bacteria) and the mucosal barrier in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and cancer: Contribution of germ-free and gnotobiotic animal models of human diseases. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Leaky gut and autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 42, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.W. Autoimmunity and the Gut. Autoimmune Dis. 2014, 2014, 152428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.M.; Kenny, D.J.; Xavier, R.J. Gut microbiota regulation of t cells during inflammation and autoimmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 599–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carratu, R.; Secondulfo, M.; de Magistris, L.; Iafusco, D.; Urio, A.; Carbone, M.G.; Pontoni, G.; Carteni, M.; Prisco, F. Altered intestinal permeability to mannitol in diabetes mellitus type I. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999, 28, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Atkinson, M.A. The role for gut permeability in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes—a solid or leaky concept? Pediatr. Diabetes 2015, 16, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacyshyn, V.J.; Thatipelli, M.R.; Lennon, R.J.; Bailey, K.R.; Stanson, A.W.; Holmes, D.R., Jr.; Gloviczki, P. Predictors of failure of endovascular therapy for peripheral arterial disease. Angiology 2006, 57, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Wekerle, H. Autoimmune diabetes mellitus and the leaky gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14788–14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, P.; Salmi, J.; Hallstrom, O.; Oksa, H.; Oksala, H.; Maki, M.; Reunala, T. High frequency of coeliac disease in adult patients with type-i diabetes. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1989, 24, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damci, T.; Nuhoglu, I.; Devranoglu, G.; Osar, Z.; Demir, M.; Ilkova, H. Increased intestinal permeability as a cause of fluctuating postprandial blood glucose levels in type 1 diabetic patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 33, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paruk, I.M.; Naidoo, V.G.; Pirie, F.J.; Maharaj, S.; Nkwanyana, N.M.; Dinnematin, H.L.; Ganie, Y.; Ramdial, P.K.; Motala, A.A. Prevalence and characteristics of celiac disease in south african patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Results from the durban diabetes and celiac disease study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secondulfo, M.; Iafusco, D.; Carratu, R.; de Magistris, L.; Sapone, A.; Generoso, M.; Mezzogiomo, A.; Sasso, F.C.; Carteni, M.; De Rosa, R.; et al. Ultrastructural mucosal alterations and increased intestinal permeability in non-celiac, type I diabetic patients. Dig. Liver Dis. 2004, 36, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, T.; Berti, I.; Sapone, A.; Gerarduzzi, T.; Not, T.; Zielke, R.; Fasano, A. Role of the intestinal tight junction modulator zonulin in the pathogenesis of type I diabetes in bb diabetic-prone rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2916–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auricchio, R.; Paparo, F.; Maglio, M.; Franzese, A.; Lombardi, F.; Valerio, G.; Nardone, G.; Percopo, S.; Greco, L.; Troncone, R. In vitro-deranged intestinal immune response to gliadin in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, F.W. Food-induced type 1 diabetes in the bb rat. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 1996, 12, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.K.; Ling, F.; Kaas, A.; Funda, D.P.; Farlov, H.; Buschard, K. Diabetes preventive gluten-free diet decreases the number of caecal bacteria in non-obese diabetic mice. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2006, 22, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Selmi, C.; Tang, R.; Gershwin, M.E.; Ma, X. The microbiome and autoimmunity: A paradigm from the gut-liver axis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, X.; He, D.; You, Q.; Zhang, T.; Dong, W.; Fei, J.; Xing, Y.; Wu, J. Ameliorating gut microenvironment through staphylococcal nuclease-mediated intestinal nets degradation for prevention of type 1 diabetes in nod mice. Life Sci. 2019, 221, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westall, F.C. Abnormal hormonal control of gut hydrolytic enzymes causes autoimmune attack on the cns by production of immune-mimic and adjuvant molecules: A comprehensive explanation for the induction of multiple sclerosis. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 68, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokote, H.; Miyake, S.; Croxford, J.L.; Oki, S.; Mizusawa, H.; Yamamura, T. Nkt cell-dependent amelioration of a mouse model of multiple sclerosis by altering gut flora. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Littman, D.R.; Macpherson, A.J. Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science 2012, 336, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Menezes, J.S.; Umesaki, Y.; Mazmanian, S.K. Proinflammatory t-cell responses to gut microbiota promote experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4615–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Shi, M.; Lang, Y.; Shen, D.; Jin, T.; Zhu, J.; Cui, L. Gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Current applications and future perspectives. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 8168717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.R. Increased gut permeability in crohn’s disease: Is tnf the link? Gut 2004, 53, 1724–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, G.; Strober, W. The immunological and genetic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, R.J.; Podolsky, D.K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2007, 448, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.R.; Turner, J.R. Inflammatory bowel disease: Is it really just another break in the wall? Gut 2007, 56, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Elamin, E.; Elizalde, M.; Bours, P.P.H.A.; Pierik, M.J.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E. Modulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by plasma from patients with crohn’s disease in a three-dimensional cell culture model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Schwarz, B.T.; Graham, W.V.; Wang, Y.; Su, L.; Clayburgh, D.R.; Abraham, C.; Turner, J.R. Ifn-gamma-induced tnfr2 expression is required for tnf-dependent intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajeri, M.H.; La Fata, G.; Steinert, R.E.; Weber, P. Relationship between the gut microbiome and brain function. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henson, M.A.; Phalak, P. Microbiota dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel diseases: In silico investigation of the oxygen hypothesis. BMC Syst. Biol. 2017, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, A.; Porta, J.; Fries, J.F.; Schurman, D.J. Clinical history as a screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. JAMA 1977, 237, 2613–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, O.; Cantero-Hinojosa, J.; Paule-Sastre, P.; Gomez-Magan, J.C.; Salvatierra-Rios, D. Intestinal permeability in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and their healthy relatives. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 33, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Alessandro, R.; Luchetti, M.M.; Milling, S.; Saieva, L.; Cypers, H.; Stampone, T.; Di Benedetto, P.; et al. Dysbiosis and zonulin upregulation alter gut epithelial and vascular barriers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.M.; Edwards, M.R.; Mu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Vieson, M.D.; Reilly, C.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Bankole, A.A. Gut microbiota in human systemic lupus erythematosus and a mouse model of lupus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02288-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsokos, G.C. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2110–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockher, W.A.; Wigand, R.; Schoeppe, W.; Scherberich, J.E. Elevated levels of soluble cd14 in serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 96, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.L.V.; Leite, A.Z.; Higuchi, B.S.; Gonzaga, M.I.; Mariano, V.S. Intestinal dysbiosis and probiotic applications in autoimmune diseases. Immunology 2017, 152, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, S.A.; Mahmoudi, M.; Momtazi, A.A.; Sahebkar, A.; Doulabi, H.; Rastin, M. Tolerogenic probiotics: Potential immunoregulators in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 1994–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Pathological and Therapeutical Implications of Macromolecule Passage through the Tight Junction. In Tight Junctions; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 715–740. [Google Scholar]
- Tio, T.L.; Tytgat, G.N. Endoscopic ultrasonography of normal and pathologic upper gastrointestinal wall structure. Comparison of studies in vivo and in vitro with histology. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1986, 123, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, P.; Viti, M.G.; Montuori, M.; La Vecchia, A.; Cipolletta, E.; Calvani, L.; Bonamico, M. The gluten-free diet: A nutritional risk factor for adolescents with celiac disease? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1998, 27, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. Surprises from celiac disease. Sci. Am. 2009, 301, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Ohno, H. Gut microbiome and metabolic diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, A.M.; Karpa, K.D. Clinical utility of probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2011, 17, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, A.C.; Bueno, A.A.; de Souza, R.G.; Mota, J.F. Gut microbiota, probiotics and diabetes. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Daubioul, C.A.; Reusens, B.; Remacle, C.; Catillon, G.; Delzenne, N.M. Involvement of endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36) amide on glycaemia-lowering effect of oligofructose in streptozotocin-treated rats. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 185, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C.; Iglesias, M.A.; Drucker, D.J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Improvement of glucose tolerance and hepatic insulin sensitivity by oligofructose requires a functional glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paray, B.A.; Albeshr, M.F.; Jan, A.T.; Rather, I.A. Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249770
Paray BA, Albeshr MF, Jan AT, Rather IA. Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(24):9770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249770
Chicago/Turabian StyleParay, Bilal Ahmad, Mohammed Fahad Albeshr, Arif Tasleem Jan, and Irfan A. Rather. 2020. "Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 24: 9770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249770
APA StyleParay, B. A., Albeshr, M. F., Jan, A. T., & Rather, I. A. (2020). Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(24), 9770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249770





