Assessment of Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Inflammation In Vivo Using NF-κB Reporter Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
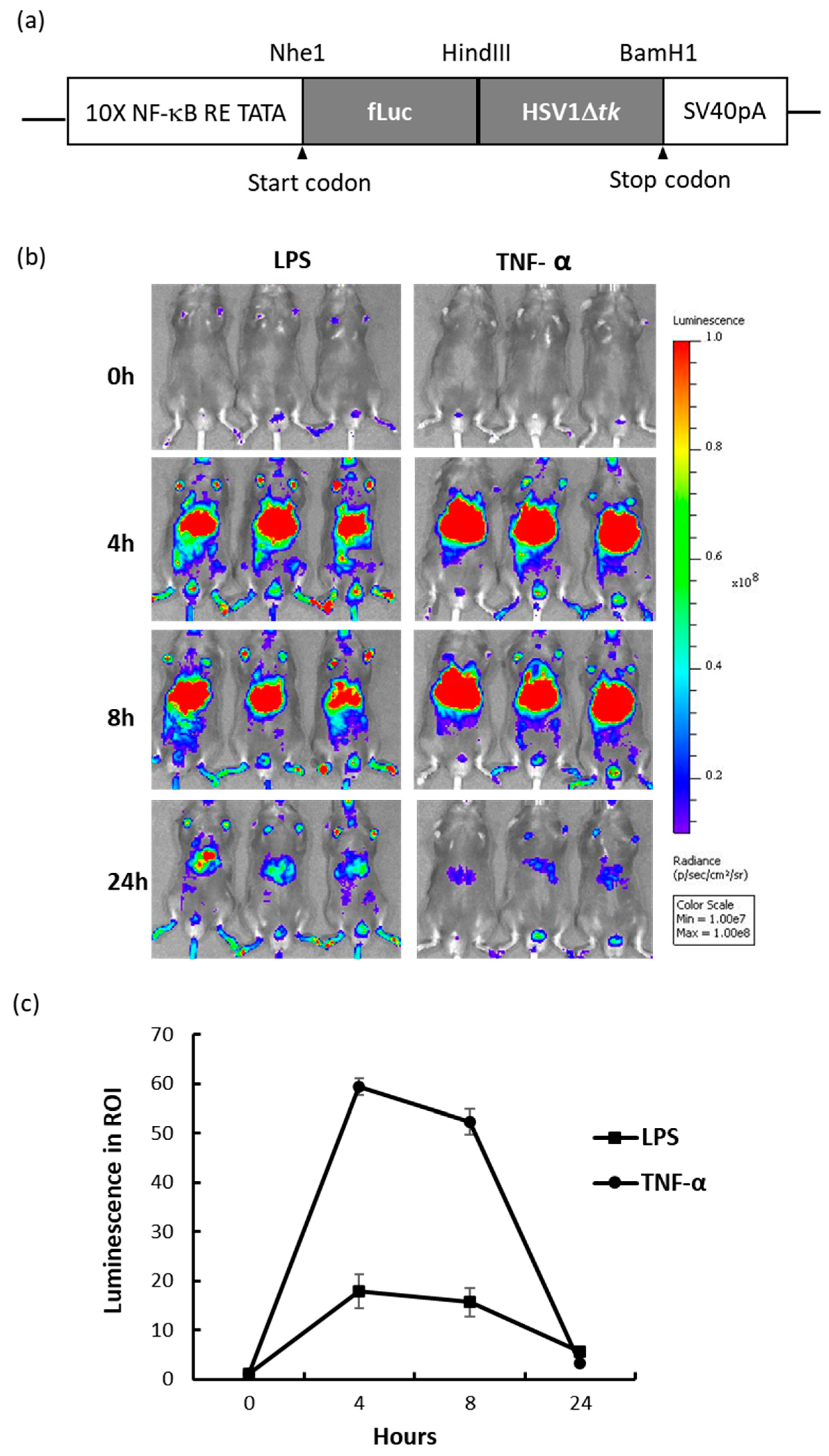
2.1. NF-κB Reporter Mouse and In Vivo Response to Inflammation-Inducing Agents
2.2. mPEG- and cPEG-AuNPs
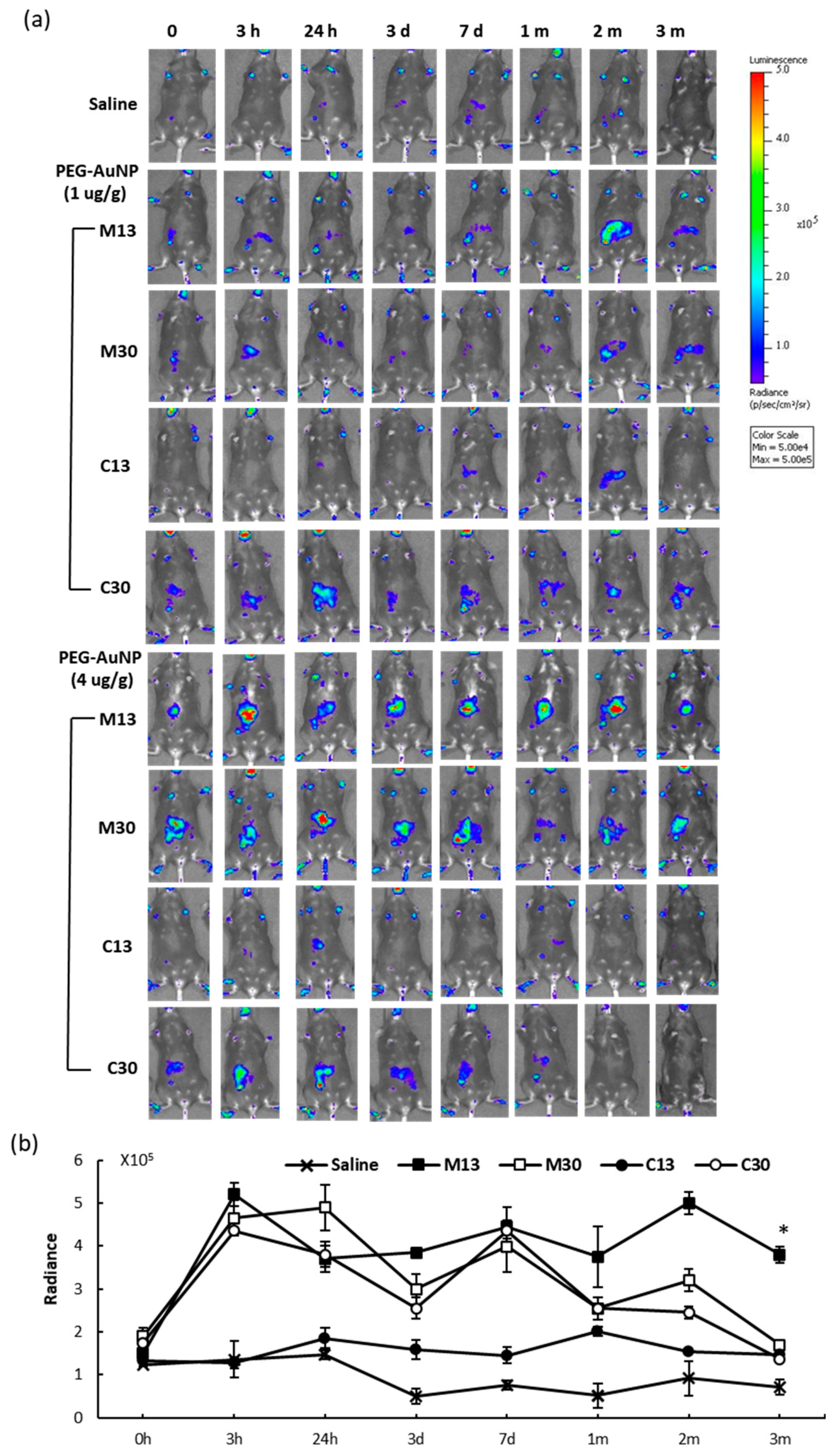
2.3. In Vivo Reporter Induction by PEG-AuNPs
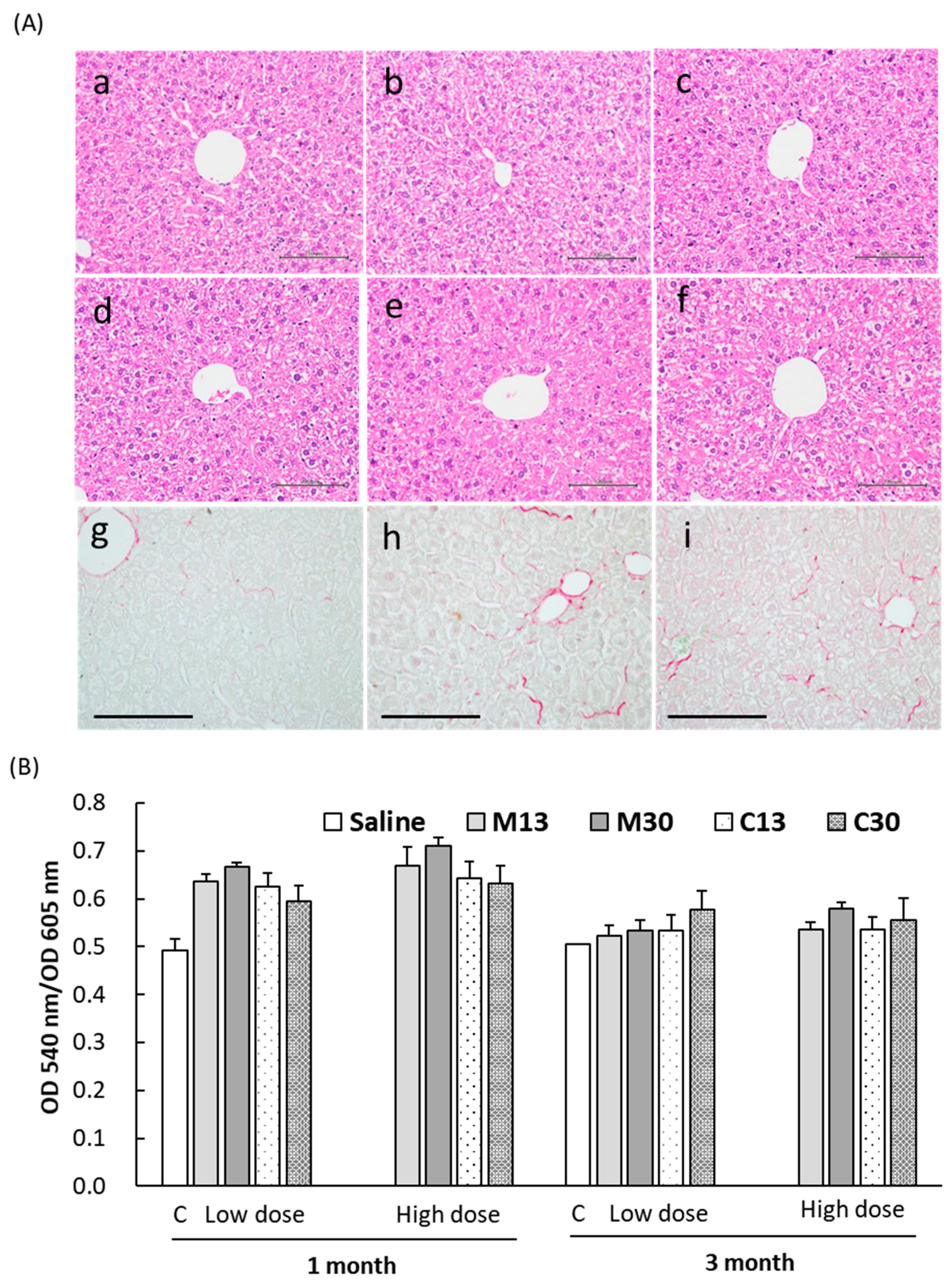
2.4. Liver Toxicity and Inflammation in Mice 3 Months after Exposure to PEGylated AuNPs
2.5. Enhanced Collagen Deposition in Liver Tissues after PEG-AuNP Injection
3. Discussion
3.1. PEGylation Reduces Acute Toxicity of AuNPs
3.2. Reporter Mice for Monitoring Liver Inflammation
3.3. Chronic Low-Grade Hepatic Inflammation Induced by PEG-AuNPs
3.4. Study Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. PEG-AuNP Preparation and Characterization
4.3. Generation of the NF-κB Reporter Tg Mouse
4.4. PEG-AuNP Injection and In Vivo Optical Imaging
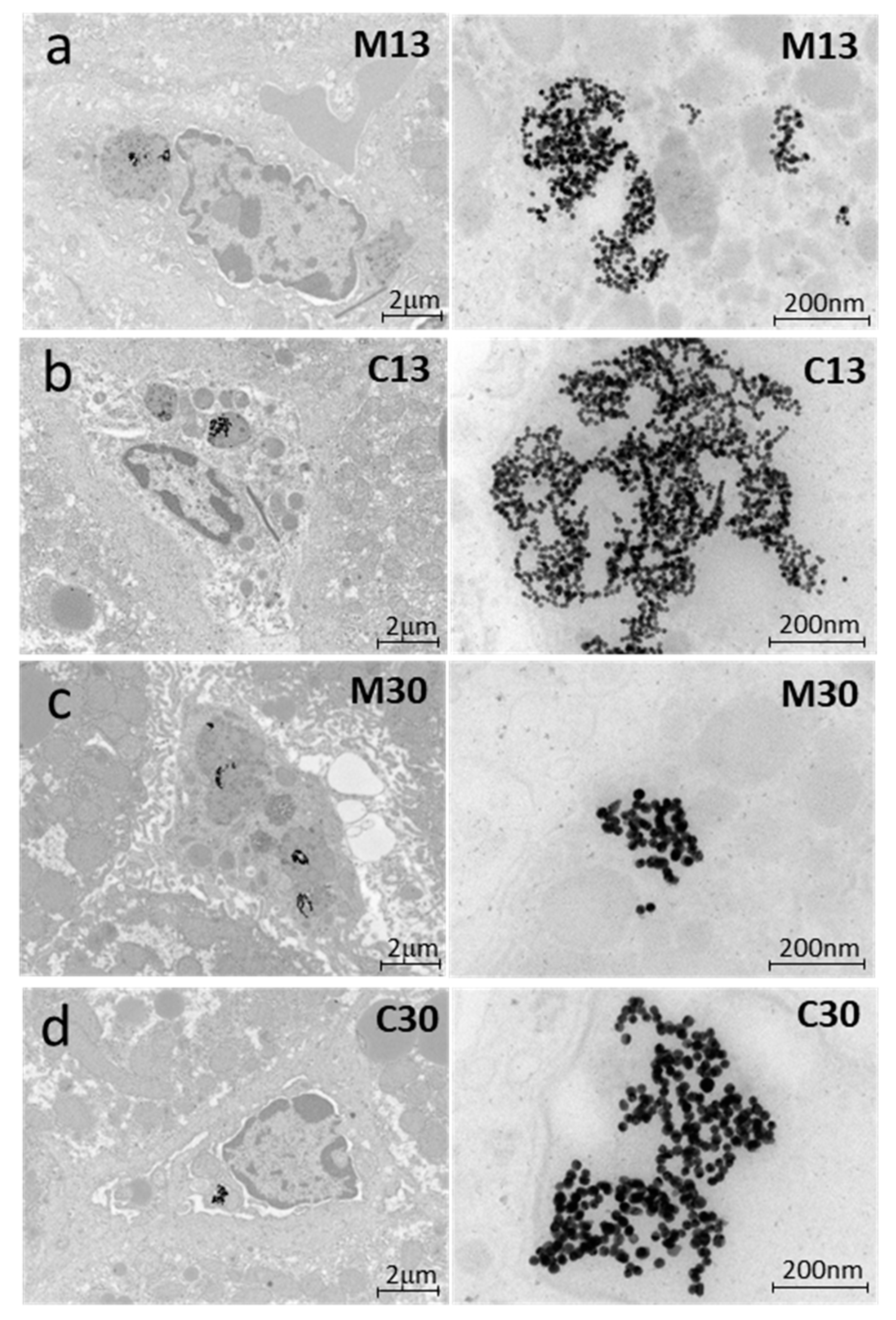
4.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.6. Histological and Blood Chemistry Analyses
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| DLS | Dynamic Laser Light Scattering |
| AuNP | Gold Nanoparticles |
| HSV1tk | Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 Thymidine Kinase |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| SPECT | Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography |
| MPS | Mononuclear Phagocyte System |
| RES | Reticuloendothelial System |
| mPEG | Methoxyl-poly(ethylene glycol)-thiol |
| cPEG | Carboxymethyl-poly(ethylene glycol)-thiol |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscope |
| ICH | International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use |
References
- Cho, W.-S.; Cho, M.; Jeong, J.; Choi, M.; Cho, H.-Y.; Han, B.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.O.; Lim, Y.T.; Chung, B.H.; et al. Acute toxicity and pharmacokinetics of 13 nm-sized PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 236, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nie, X.; Ji, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, C.; Fang, X. Quantitative biokinetics and systemic translocation of various gold nanostructures are highly dependent on their size and shape. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 4124–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Hagens, W.I.; Krystek, P.; Burger, M.C.; Sips, A.J.; Geertsma, R.E. Particle size-dependent organ distribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lane, L.A. Probing the biological obstacles of nanomedicine with gold nanoparticles. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Lee, G.Y.; Lane, L.A.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Nie, S. Functionalized, long-circulating, and ultrasmall gold nanocarriers for overcoming the barriers of low nanoparticle delivery efficiency and poor tumor penetration. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvizo, R.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Gold nanoparticles: Opportunities and challenges in nanomedicine. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pino, P.; Yang, F.; Pelaz, B.; Zhang, Q.; Kantner, K.; Hartmann, R.; Martinez de Baroja, N.; Gallego, M.; Möller, M.; Manshian, B.B.; et al. Basic physicochemical properties of polyethylene glycol coated gold nanoparticles that determine their interaction with cells. Angew. Chem. 2016, 55, 5483–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkey, C.D.; Olsen, J.B.; Guo, H.; Emili, A.; Chan, W.C. Nanoparticle size and surface chemistry determine serum protein adsorption and macrophage uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boey, A.; Ho, H.K. All roads lead to the liver: Metal nanoparticles and their implications for liver health. Small 2020, 16, 2000153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.S.; Cho, M.; Jeong, J.; Choi, M.; Han, B.S.; Shin, H.S.; Hong, J.; Chung, B.H.; Jeong, J.; Cho, M.H.; et al. Size-dependent tissue kinetics of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 245, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlolla, A.K.; Kumari, S.A.; Tchounwou, P.B. A comparison of poly-ethylene-glycol-coated and uncoated gold nanoparticle-mediated hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in Sprague Dawley rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.S.; Hung, Y.C.; Liau, I.; Huang, G.S. Assessment of the in vivo toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauck, T.S.; Anderson, R.E.; Fischer, H.C.; Newbigging, S.; Chan, W.C. In vivo quantum-dot toxicity assessment. Small 2010, 6, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.J.; Jansen, E.D.; Powers, A.C.; Wang, T.G. A novel method of monitoring response to islet transplantation: Bioluminescent imaging of an NF-kB transgenic mouse model. Transplantation 2006, 81, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contag, P.R.; Olomu, I.N.; Stevenson, D.K.; Contag, C.H. Bioluminescent indicators in living mammals. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikot, R.T.; Blackwell, T.S. Bioluminescence imaging. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2005, 2, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, H.; Moskaug, J.; Fromm, S.H.; Blomhoff, R. In vivo imaging of NF-kappa B activity. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, T.S.; Yull, F.E.; Chen, C.L.; Venkatakrishnan, A.; Blackwell, T.R.; Hicks, D.J.; Lancaster, L.H.; Christman, J.W.; Kerr, L.D. Multiorgan nuclear factor kappa B activation in a transgenic mouse model of systemic inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, M.R.; Chiu, I.M.; Lin, K.M. A Tri-fusion reporter mouse reveals tissue-specific FGF1B promoter activity in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, F.S.; Liao, W.N.; Liang, S.L.; Chen, M.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Lin, W.Y.; Hsu, M.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Peir, J.J.; et al. Establishment of a trimodality analytical platform for tracing, imaging and quantification of gold nanoparticles in animals by radiotracer techniques. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Yang, Y.-T.; Lin, C.-T.; Yu, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-K.; Chu, L.-K. Monitoring the transient thermal infrared emission of gold nanoparticles upon photoexcitation with a step-scan fourier-transform spectrometer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, A.M.; Peters, D.; Rouse, R.; Stewart, S.; Rosen, E.T.; Tyner, K.M. Tissue and cellular distribution of gold nanoparticles varies based on aggregation/agglomeration status. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, J.L.; Tobin, G.A.; Ingle, T.; Bancos, S.; Stevens, D.; Rouse, R.; Howard, K.E.; Goodwin, D.; Knapton, A.; Li, X.; et al. Evaluating the potential of gold, silver, and silica nanoparticles to saturate mononuclear phagocytic system tissues under repeat dosing conditions. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, H.; Baldrick, P.; Beken, S.; Booler, H.; Bower, N.; Brooker, P.; Brown, P.; Burlinson, B.; Burns-Naas, L.A.; Casey, W.; et al. Opportunities for use of one species for longer-term toxicology testing during drug development: A cross-industry evaluation. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 113, 104624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH M3 (R2) Non-Clinical Safety Studies for the Conduct of Human Clinical Trials for Pharmaceuticals. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-m3-r2-non-clinical-safety-studies-conduct-human-clinical-trials-pharmaceuticals (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Semmler-Behnke, M.; Kreyling, W.; Lipka, J.; Fertsch, S.; Wenk, A.; Takenaka, S.; Brandau, W. Biodistribution of 1.4-and 18-nm gold particles in rats. Small 2008, 4, 2108–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirn, S.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Schleh, C.; Wenk, A.; Lipka, J.; Schaffler, M.; Takenaka, S.; Moller, W.; Schmid, G.; Simon, U.; et al. Particle size-dependent and surface charge-dependent biodistribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, L.; Hart, J. The pathology of alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoutene, A.; Rautou, P.E. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, D.A.; Shepherd, E.L.; Weston, C.J.; Shetty, S. Novel targets in the immune microenvironment of the hepatic sinusoids for treating liver diseases. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.J.; Kang, S.W.S.; Lockwood, G.P.; Le Couteur, D.G.; Cogger, V.C. Hallmarks of aging in the liver. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Noh, J.-R.; Gang, G.-T.; Chung, B.H.; Song, N.W.; Lee, C.-H. Susceptibility to gold nanoparticle-induced hepatotoxicity is enhanced in a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Toxicology 2012, 294, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Li, F.; Zhou, H.; Bai, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Yan, B. Oral exposure to silver nanoparticles or silver ions may aggravate fatty liver disease in overweight mice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9334–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ng, J.P.M.; Tan, Y.; McGrath, K.; Bishop, D.P.; Oliver, B.; Chan, Y.L.; Cortie, M.B.; Milthorpe, B.K.; Valenzuela, S.M.; et al. Gold nanoparticles improve metabolic profile of mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ng, J.P.M.; Bishop, D.P.; Milthorpe, B.K.; Valenzuela, S.M. Gold nanoparticles as cell regulators: Beneficial effects of gold nanoparticles on the metabolic profile of mice with pre-existing obesity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dorrigan, A.; Saad, S.; Hare, D.J.; Cortie, M.B.; Valenzuela, S.M. In vivo study of spherical gold nanoparticles: Inflammatory effects and distribution in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solana, R.; Pawelec, G.; Tarazona, R. Aging and innate immunity. Immunity 2006, 24, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chondrex, Sirius Red/Fast Green Collagen Staining Kit. Available online: https://www.chondrex.com/products/sirius-red-fast-green-collagen-staining-kit (accessed on 23 October 2020).


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, M.-R.; Liu, S.-W.; Lin, J.-Y.; Yang, Y.-T.; Huang, H.-Y.; Chen, J.-K.; Yang, C.-S.; Lin, K.M.-C. Assessment of Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Inflammation In Vivo Using NF-κB Reporter Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218158
Chen T-Y, Chen M-R, Liu S-W, Lin J-Y, Yang Y-T, Huang H-Y, Chen J-K, Yang C-S, Lin KM-C. Assessment of Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Inflammation In Vivo Using NF-κB Reporter Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218158
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tzu-Yin, Mei-Ru Chen, Shan-Wen Liu, Jin-Yan Lin, Ya-Ting Yang, Hsin-Ying Huang, Jen-Kun Chen, Chung-Shi Yang, and Kurt Ming-Chao Lin. 2020. "Assessment of Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Inflammation In Vivo Using NF-κB Reporter Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 8158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218158
APA StyleChen, T.-Y., Chen, M.-R., Liu, S.-W., Lin, J.-Y., Yang, Y.-T., Huang, H.-Y., Chen, J.-K., Yang, C.-S., & Lin, K. M.-C. (2020). Assessment of Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Inflammation In Vivo Using NF-κB Reporter Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218158





