Shear Stress-Induced Activation of von Willebrand Factor and Cardiovascular Pathology
Abstract
1. Introduction
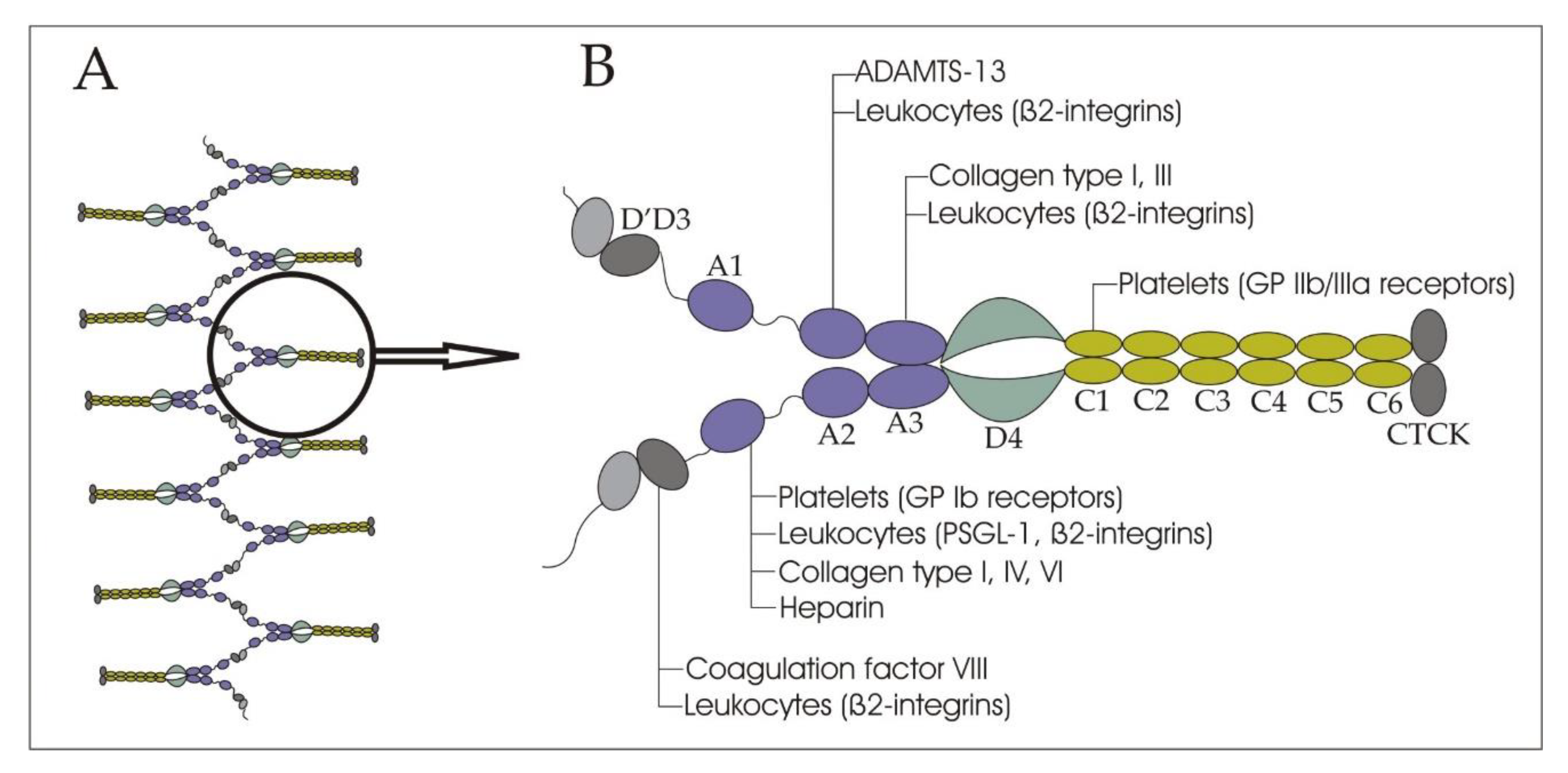
2. Structure and Functions of VWF in Bloodstream
3. Diagnostic Tests for the von Willebrand Factor Deficiency and Dysfunction
4. Diseases, Associated with von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS-13 Dysfunction
5. Acquired von Willebrand Syndrome in Heart Valve Disease and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
6. von Willebrand Factor and Coronary Artery Disease
7. Inflammatory and Stress Stimuli as a Possible Cause of Elevation in Plasma von Willebrand Factor in Coronary Artery Disease
8. The Potential for New Treatment, Targeting von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS-13 in Cardiovascular Diseases
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terraube, V.; O’Donnell, J.S.; Jenkins, P.V. Factor VIII and von Willebrand factor interaction: Biological, clinical and therapeutic importance. Haemophilia 2010, 16, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chung, D.W. Inflammation, von Willebrand factor, and ADAMTS13. Blood 2018, 132, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawecki, C.; Lenting, P.J.; Denis, C.V. von Willebrand factor and inflammation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendu, R.; Terraube, V.; Christophe, O.D.; Gahmberg, C.G.; de Groot, P.G.; Lenting, P.J.; Denis, C.V. P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 and β2-integrins cooperate in the adhesion of leukocytes to von Willebrand factor. Blood 2006, 108, 3746–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Feng, S.; Zhao, J.; Liao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Liu, J. Prognostic value of plasma von Willebrand factor levels in major adverse cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Mayer, F.J.; Jilma, B.; Buchtele, N.; Obermayer, G.; Binder, C.J.; Blann, A.D.; Minar, E.; Schillinger, M.; Hoke, M. Von Willebrand factor antigen levels predict major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with carotid stenosis of the ICARAS study. Atherosclerosis 2019, 290, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.-X.; Kong, Q.; Ma, X. Current advances in circulating inflammatory biomarkers in atherosclerosis and related cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, E.; Vincent, F.; Rauch, A.; Casari, C.; Jeanpierre, E.; Loobuyck, V.; Rosa, M.; Delhaye, C.; Spillemaeker, H.; Paris, C.; et al. von Willebrand Factor and Management of Heart Valve Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, T.A. von Willebrand factor, Jedi knight of the bloodstream. Blood 2014, 124, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, U.; Pieconka, A.; Will, K.; Schneppenheim, R. Laboratory Testing for von Willebrand Disease: Contribution of Multimer Analysis to Diagnosis and Classification. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2006, 32, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockschlaeder, M.; Schneppenheim, R.; Budde, U. Update on von Willebrand factor multimers: Focus on high-molecular-weight multimers and their role in hemostasis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2014, 25, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Springer, T.A. Structural specializations of A2, a force-sensing domain in the ultralarge vascular protein von Willebrand factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9226–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, J.E. Biochemistry and Genetics of von willebrand factor. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 395–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denorme, F.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; De Meyer, S.F. von Willebrand Factor and Platelet Glycoprotein Ib: A Thromboinflammatory Axis in Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.W.; Nuschele, S.; Wixforth, A.; Gorzelanny, C.; Alexander-Katz, A.; Netz, R.R.; Schneider, M.F. Shear-induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von Willebrand factor fibers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7899–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.T.B.; de Groot, R.; Xiang, Y.; Luken, B.M.; Lane, D.A. Unraveling the scissile bond: How ADAMTS13 recognizes and cleaves von Willebrand factor. Blood 2011, 118, 3212–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sing, C.E.; Alexander-Katz, A. Elongational Flow Induces the Unfolding of von Willebrand Factor at Physiological Flow Rates. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, L35–L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westein, E.; van der Meer, A.D.; Kuijpers, M.J.E.; Frimat, J.-P.; van den Berg, A.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. Atherosclerotic geometries exacerbate pathological thrombus formation poststenosis in a von Willebrand factor-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; López, J.A. Flow-driven assembly of VWF fibres and webs in in vitro microvessels. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kelkar, A.; Neelamegham, S. von Willebrand factor self-association is regulated by the shear-dependent unfolding of the A2 domain. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaji, S.; Fahs, S.A.; Shi, Q.; Haberichter, S.L.; Montgomery, R.R. Contribution of platelet vs. endothelial VWF to platelet adhesion and hemostasis: Hemostatic effect of platelet VWF in murine VWD. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhenne, S.; Denorme, F.; Libbrecht, S.; Vandenbulcke, A.; Pareyn, I.; Deckmyn, H.; Lambrecht, A.; Nieswandt, B.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; et al. Platelet-derived VWF is not essential for normal thrombosis and hemostasis but fosters ischemic stroke injury in mice. Blood 2015, 126, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, K.; Suzuki, H.; McMullen, B.; Chung, D. Purification of human von Willebrand factor–cleaving protease and its identification as a new member of the metalloproteinase family. Blood 2001, 98, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsuyama, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Iwamoto, T.; Mori, T.; Wanaka, A.; Fukui, H.; et al. Localization of ADAMTS13 to the stellate cells of human liver. Blood 2005, 106, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, P.M.; Capoferri, C.; Canciani, M.T. Plasma levels of von Willebrand factor regulate ADAMTS-13, its major cleaving protease. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 126, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; de Groot, R.; Crawley, J.T.B.; Lane, D.A. Mechanism of von Willebrand factor scissile bond cleavage by a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13 (ADAMTS13). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11602–11607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragnano, F.; Sperlongano, S.; Golia, E.; Natale, F.; Bianchi, R.; Crisci, M.; Fimiani, F.; Pariggiano, I.; Diana, V.; Carbone, A.; et al. The Role of von Willebrand Factor in Vascular Inflammation: From Pathogenesis to Targeted Therapy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5620314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, B.; Broermann, A.; Li, H.; Khandoga, A.G.; Zarbock, A.; Krombach, F.; Goerge, T.; Schneider, S.W.; Jones, C.; Nieswandt, B.; et al. von Willebrand factor promotes leukocyte extravasation. Blood 2010, 116, 4712–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillgruber, C.; Steingräber, A.K.; Pöppelmann, B.; Denis, C.V.; Ware, J.; Vestweber, D.; Nieswandt, B.; Schneider, S.W.; Goerge, T. Blocking von Willebrand Factor for Treatment of Cutaneous Inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aymé, G.; Adam, F.; Legendre, P.; Bazaa, A.; Proulle, V.; Denis, C.V.; Christophe, O.D.; Lenting, P.J. A Novel Single-Domain Antibody against von Willebrand Factor A1 Domain Resolves Leukocyte Recruitment and Vascular Leakage during Inflammation—Brief Report. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Motto, D.G.; Lentz, S.R.; Chauhan, A.K. ADAMTS13 reduces VWF-mediated acute inflammation following focal cerebral ischemia in mice: Role of ADAMTS13 and VWF in inflammatory brain injury. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, S.F.; Savchenko, A.S.; Haas, M.S.; Schatzberg, D.; Carroll, M.C.; Schiviz, A.; Dietrich, B.; Rottensteiner, H.; Scheiflinger, F.; Wagner, D.D. Protective anti-inflammatory effect of ADAMTS13 on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Blood 2012, 120, 5217–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincentelli, A.; Susen, S.; Le Tourneau, T.; Six, I.; Fabre, O.; Juthier, F.; Bauters, A.; Decoene, C.; Goudemand, J.; Prat, A.; et al. Acquired von Willebrand Syndrome in Aortic Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, N.C.; Anicchino-Bizzacchi, J.M.; Locatelli, M.F.; Castro, V.; Barjas-Castro, M.L. The relationship between ABO groups and subgroups, factor VIII and von Willebrand factor. Haematologica 2007, 92, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budde, U.; Schneppenheim, R. von Willebrand Factor and von Willebrand disease. Rev. Clin. Exp. Hematol. 2001, 5, 335–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M.; Capra, F.; Targher, G.; Montagnana, M.; Lippi, G. Relationship between ABO blood group and von Willebrand factor levels: From biology to clinical implications. Thromb. J. 2007, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.C.; Endres-Brooks, J.; Bauer, P.J.; Marks, W.J.; Montgomery, R.R. The effect of ABO blood group on the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease. Blood 1987, 69, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.J. Laboratory Diagnosis of von Willebrand Disease. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2017, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, U.; Schneppenheim, R. Interactions of von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 in von Willebrand disease and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Hamostaseologie 2014, 34, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roberts, J.C.; Flood, V.H. Laboratory diagnosis of von Willebrand disease. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2015, 37, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J. The Platelet Function Analyser (PFA)-100 and von Willebrand disease: A story well over 16 years in the making. Haemophilia 2015, 21, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P. The role of PFA-100R testing in the investigation and management of haemostatic defects in children and adults. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 130, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeman, R.M.; Lehmann, M.; Neeves, K.B. Flow chamber and microfluidic approaches for measuring thrombus formation in genetic bleeding disorders. Platelets 2017, 28, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, A.B. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome: Is it an extremely rare disorder or do we see only the tip of the iceberg? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, C.; Rizzo, S. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: A review of the literature in the light of our experience with plasma exchange. Blood Transfus. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöbl, P. Inherited and Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) in Adults. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2014, 40, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Cataland, S.R.; Peyvandi, F.; Coppo, P.; Knöbl, P.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Metjian, A.; de la Rubia, J.; Pavenski, K.; Callewaert, F.; et al. Caplacizumab Treatment for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyde, E.C. Gastrointestinal Bleeding in Aortic Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1958, 259, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.; Morgan, D.G.; Moore, J.C. Aortic stenosis and bleeding gastrointestinal angiodysplasia: Is acquired von Willebrand’s disease the link? Lancet 1992, 340, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Moore, J.C.; Morgan, D.G. Gastrointestinal Angiodysplasia and Aortic Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 858–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.D.; Lanzmich, R.; Haager, P.K.; Budde, U. Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis: Sustained Cure of Acquired von Willebrand Syndrome after Surgical Valve Replacement. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2017, 23, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzer, S.; Eslam, R.B.; Schneller, A.; Kaider, A.; Koren, D.; Eichelberger, B.; Rosenhek, R.; Budde, U.; Lang, I. Loss of high-molecular-weight von Willebrand factor multimers mainly affects platelet aggregation in patients with aortic stenosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 103, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasar, S.J.; Abdullah, O.; Fay, W.; Balla, S. Von Willebrand factor revisited. J. Interven. Cardiol. 2018, 31, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Belle, E.; Rauch, A.; Vincent, F.; Robin, E.; Kibler, M.; Labreuche, J.; Jeanpierre, E.; Levade, M.; Hurt, C.; Rousse, N.; et al. Von Willebrand Factor Multimers during Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, C.; Budde, U.; Schneppenheim, S.; Czaja, E.; Hagl, C.; Schoechl, H.; von Depka, M.; Rahe-Meyer, N. Acquired type 2A von Willebrand syndrome caused by aortic valve disease corrects during valve surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 106, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackshear, J.L.; Wysokinska, E.M.; Safford, R.E.; Thomas, C.S.; Shapiro, B.P.; Ung, S.; Stark, M.E.; Parikh, P.; Johns, G.S.; Chen, D. Shear stress-associated acquired von Willebrand syndrome in patients with mitral regurgitation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susen, S.; Vincentelli, A.; Le Tourneau, T.; Caron, C.; Zawadzki, C.; Prat, A.; Goudemand, J.; Jude, B. Severe Aortic and Mitral Valve Regurgitation Are Associated with von Willebrand Factor Defect. Blood 2005, 106, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackshear, J.L.; Schaff, H.V.; Ommen, S.R.; Chen, D.; Nichols, W.L. Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy, Bleeding History, and Acquired von Willebrand Syndrome: Response to Septal Myectomy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tourneau, T.; Susen, S.; Caron, C.; Millaire, A.; Maréchaux, S.; Polge, A.-S.; Vincentelli, A.; Mouquet, F.; Ennezat, P.-V.; Lamblin, N.; et al. Functional Impairment of von Willebrand Factor in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Relation to Rest and Exercise Obstruction. Circulation 2008, 118, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimbene, A.; Neelamegham, S.; Frazier, O.H.; Moake, J.L.; Dong, J. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome associated with left ventricular assist device. Blood 2016, 127, 3133–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, T.C.; Bellinger, D.A.; Tate, D.A.; Reddick, R.L.; Read, M.S.; Koch, G.G.; Brinkhous, K.M.; Griggs, T.R. von Willebrand factor and occlusive arterial thrombosis. A study in normal and von Willebrand’s disease pigs with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 1990, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, C.; Motto, D.G.; Jensen, M.; Lentz, S.R.; Chauhan, A.K. ADAMTS13 deficiency exacerbates VWF-dependent acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Blood 2012, 120, 5224–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaman, C.D.; Yabes, J.; Comer, D.M.; Ragni, M.V. Does deficiency of von Willebrand factor protect against cardiovascular disease? Analysis of a national discharge register. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.-G.; Xu, R.-M.; Lu, C.-Q.; Yao, M.-Y.; Zhao, W.; Fu, X.; Guo, J.; Xu, Q.-F.; Li, D.-D. Correlation of von Willebrand factor gene polymorphism and coronary heart disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thompson, S.G.; Kienast, J.; Pyke, S.D.M.; Haverkate, F.; van de Loo, J.C.W. Hemostatic Factors and the Risk of Myocardial Infarction or Sudden Death in Patients with Angina Pectoris. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeit, P.; Thompson, A.; Aspelund, T.; Rumley, A.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Lowe, G.; Gudnason, V.; Di Angelantonio, E. Hemostatic Factors and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in General Populations: New Prospective Study and Updated Meta-Analyses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.K.; Morrow, D.A.; Gibson, C.M.; Murphy, S.; Antman, E.M.; Braunwald, E. Predictors of the rise in vWF after ST elevation myocardial infarction: Implications for treatment strategies and clinical outcome. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, J.H.; Nilsson, T.K.; Johnson, O. von Willebrand factor in plasma: A novel risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction and death. Heart 1991, 66, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, B.; Maseri, A.; Cianflone, D.; Laricchia, A.; Cristell, N.; Durante, A.; Spartera, M.; Ancona, F.; Limite, L.; Hu, D.; et al. Plasma levels of active von Willebrand factor are increased in patients with first ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: A multicenter and multiethnic study. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2015, 4, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikita, K.; Soejima, K.; Matsukawa, M.; Nakagaki, T.; Ogawa, H. Reduced von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) activity in acute myocardial infarction. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2490–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.T.B.; Lane, D.A.; Woodward, M.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.O. Evidence that high von Willebrand factor and low ADAMTS-13 levels independently increase the risk of a non-fatal heart attack. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chion, C.K.N.K.; Doggen, C.J.M.; Crawley, J.T.B.; Lane, D.A.; Rosendaal, F.R. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor and the risk of myocardial infarction in men. Blood 2007, 109, 1998–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morange, P.E.; Simon, C.; Alessi, M.C.; Luc, G.; Arveiler, D.; Ferrieres, J.; Amouyel, P.; Evans, A.; Ducimetiere, P.; Juhan-Vague, I. Endothelial Cell Markers and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: The Prospective Epidemiological Study of Myocardial Infarction (PRIME) Study. Circulation 2004, 109, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Dong, F.; Guo, L.; Hou, Y.; Hu, H.; Yan, S.; Zhou, X.; Liao, L.; Allen, T.D.; et al. Plasma von Willebrand factor level is transiently elevated in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J. Relationship between smoking and cardiovascular risk factors in the development of peripheral arterial disease and coronary artery disease; Edinburgh Artery Study Edinburgh Artery Study. Eur. Heart J. 1999, 20, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesh, J.; Wheeler, J.G.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Eda, S.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.O.; Pepys, M.B.; Gudnason, V. C-Reactive Protein and Other Circulating Markers of Inflammation in the Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Blann, A.; Lip, G. High pulse pressure and nondipping circadian blood pressure in patients with coronary artery disease: Relationship to thrombogenesis and endothelial damage/dysfunction. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Blann, A.D.; Jones, A.F.; Lip, P.L.; Beevers, D.G. Relation of Endothelium, Thrombogenesis, and Hemorheology in Systemic Hypertension to Ethnicity and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997, 80, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, A.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.M.; Kostense, P.J.; Emeis, J.J.; Yudkin, J.S.; Nijpels, G.; Dekker, J.M.; Heine, R.J.; Bouter, L.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. von Willebrand Factor, C-Reactive Protein, and 5-Year Mortality in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Subjects: The Hoorn Study. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 1999, 19, 3071–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehouwer, C.A.; Zeldenrust, G.C.; den Ottolander, G.H.; Hackeng, W.H.L.; Donker, A.J.M.; Nauta, J.J.P. Urinary albumin excretion, cardiovascular disease, and endothelial dysfunction in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1992, 340, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warlo, E.M.K.; Pettersen, A.-Å.R.; Arnesen, H.; Seljeflot, I. vWF/ADAMTS13 is associated with on-aspirin residual platelet reactivity and clinical outcome in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Thromb. J. 2017, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blann, A.D.; Herrick, A.; Jayson, M.I.V. Altered levels of soluble adhesion molecules in rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis and systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 1995, 34, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nossent, J.C.; Raymond, W.D.; Eilertsen, G.Ø. Increased von Willebrand factor levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus reflect inflammation rather than increased propensity for platelet activation. Lupus Sci. Med. 2016, 3, e000162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacquemant, C.; Gaucher, C.; Delorme, C.; Chatellier, G.; Gallois, Y.; Rodier, M.; Passa, P.; Balkau, B.; Mazurier, C.; Marre, M.; et al. Association between high von Willebrand factor levels and the Thr789Ala vWF gene polymorphism but not with nephropathy in type I diabetes. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonetti, P.O.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Endothelial Dysfunction: A Marker of Atherosclerotic Risk. ATVB 2003, 23, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heper, G.; Murat, S.N.; Durmaz, T.; Kalkan, F. Prospective Evaluation of von Willebrand Factor Release after Multiple and Single Stenting. Angiology 2004, 55, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefer, J.M.; Galanti, L.M.; Desmet, S.; Deneys, V.; Hanet, C.E. Time course of release of inflammatory markers after coronary stenting: Comparison between bare metal stent and sirolimus-eluting stent. Coron. Artery Dis. 2005, 16, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottinger, B.E.; Read, R.C.; Paleolog, E.M.; Higgins, P.G.; Pearson, J.D. von Willebrand factor is an acute phase reactant in man. Thromb. Res. 1989, 53, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, A.; Ball, C.; Nolasco, L.; Choi, H.; Moake, J.L.; Dong, J.F. Platelets adhered to endothelial cell-bound ultra-large von Willebrand factor strings support leukocyte tethering and rolling under high shear stress. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, J.E.; Oksche, A.; Wollheim, C.B.; Günther, G.; Rosenthal, W.; Vischer, U.M. Vasopressin-induced von Willebrand factor secretion from endothelial cells involves V2 receptors and cAMP. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, I.; Avtaeva, Y.; Kozlov, S.; Nozadze, D.; Gabbasov, Z. P721Shear stress induced unfolding of von willebrand factor may be involved in the premature development of myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, ehz747.0326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, M.; McNeill, P.M.; Carlson, P.L.; Kermode, J.C.; Adelman, B.; Conroy, R.; Marques, D. Heparin inhibition of von Willebrand factor-dependent platelet function in vitro and in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalescot, G.; Philippe, F.; Ankri, A.; Vicaut, E.; Bearez, E.; Poulard, J.E.; Carrie, D.; Flammang, D.; Dutoit, A.; Carayon, A.; et al. Early Increase of von Willebrand Factor Predicts Adverse Outcome in Unstable Coronary Artery Disease: Beneficial Effects of Enoxaparin. Circulation 1998, 98, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, S.; Matsushita, J.; Yamamoto, H. Effect of a humanized monoclonal antibody to von Willebrand factor in a canine model of coronary arterial thrombosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 443, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.C.; DeFeo-Fraulini, T.; Hutabarat, R.M.; Horvath, C.J.; Merlino, P.G.; Marsh, H.N.; Healy, J.M.; BouFakhreddine, S.; Holohan, T.V.; Schaub, R.G. First-in-Human Evaluation of Anti–von Willebrand Factor Therapeutic Aptamer ARC1779 in Healthy Volunteers. Circulation 2007, 116, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, H.S.; McCollum, C.; Imray, C.; Goulder, M.A.; Gilbert, J.; King, A. The von Willebrand Inhibitor ARC1779 Reduces Cerebral Embolization after Carotid Endarterectomy: A Randomized Trial. Stroke 2011, 42, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Buchtele, N.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Derhaschnig, U.; Gelbenegger, G.; Brostjan, C.; Zhu, S.; Gilbert, J.C.; Jilma, B. The aptamer BT200 effectively inhibits von Willebrand factor (VWF) dependent platelet function after stimulated VWF release by desmopressin or endotoxin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Someya, T.; Harada, K.; Yagi, H.; Matsui, T.; Matsumoto, M. Novel aptamer to von Willebrand factor A1 domain (TAGX-0004) shows total inhibition of thrombus formation superior to ARC1779 and comparable to caplacizumab. Haematologica 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, J.E.; de Jaegere, P.P.T.; van Vliet, H.H.D.M.; de Maat, M.P.M.; de Groot, P.G.; Simoons, M.L.; Leebeek, F.W.G. The in vitro effect of the new antithrombotic drug candidate ALX-0081 on blood samples of patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Thromb. Haemost 2011, 106, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartunek, J.; Barbato, E.; Vercruysse, K.; Duby, C.; Wijns, W.; Heyndrickx, G.; Holz, J.-B. Abstract 15084: Safety and Efficacy of Anti-von Willebrand Factor Nanobody® ALX-0081 in Stable Angina Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Circulation 2010, 122, A15084. [Google Scholar]
- Bartunek, J.; Barbato, E.; Heyndrickx, G.; Vanderheyden, M.; Wijns, W.; Holz, J.-B. Novel Antiplatelet Agents: ALX-0081, a Nanobody Directed towards von Willebrand Factor. J. Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 2013, 6, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witsch, T.; Martinod, K.; Sorvillo, N.; Portier, I.; De Meyer, S.F.; Wagner, D.D. Recombinant Human ADAMTS13 Treatment Improves Myocardial Remodeling and Functionality after Pressure Overload Injury in Mice. JAHA 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okhota, S.; Melnikov, I.; Avtaeva, Y.; Kozlov, S.; Gabbasov, Z. Shear Stress-Induced Activation of von Willebrand Factor and Cardiovascular Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207804
Okhota S, Melnikov I, Avtaeva Y, Kozlov S, Gabbasov Z. Shear Stress-Induced Activation of von Willebrand Factor and Cardiovascular Pathology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(20):7804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207804
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkhota, Sergey, Ivan Melnikov, Yuliya Avtaeva, Sergey Kozlov, and Zufar Gabbasov. 2020. "Shear Stress-Induced Activation of von Willebrand Factor and Cardiovascular Pathology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 20: 7804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207804
APA StyleOkhota, S., Melnikov, I., Avtaeva, Y., Kozlov, S., & Gabbasov, Z. (2020). Shear Stress-Induced Activation of von Willebrand Factor and Cardiovascular Pathology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(20), 7804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207804






