Novel Molecular Markers in Glioblastoma—Benefits of Liquid Biopsy
Abstract
1. Glioblastoma—Background
2. Molecular Markers in Glioblastoma
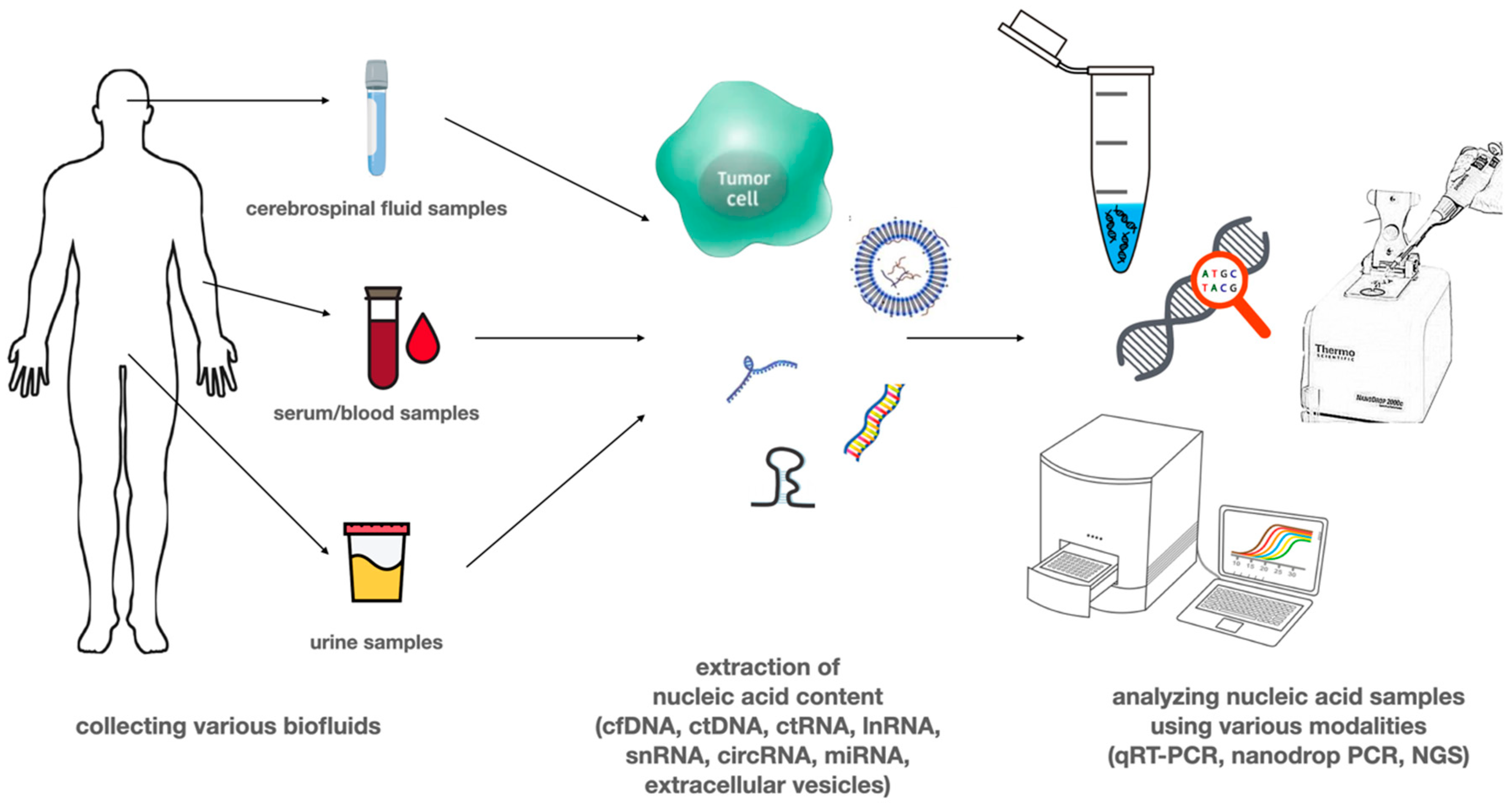
3. Circulating Tumor Nucleic Acids
4. Circulating DNA
5. Circulating RNA
6. Extracellular Vesicles
| miRNA | Expression in GBM | Effect of Altered Expression | Source of Samples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | Upregulation | high levels are associated with poor prognosis, levels drop after chemoirradiation | EVs | [50] |
| miR-128 | Downregulation | downregulated in glioma, levels increase after surgery and chemoirradiation | plasma and tissue | [52] |
| miR-342 | Downregulation | downregulated in glioma, levels increase after surgery and chemoirradiation | plasma and tissue | [52] |
| miR-221 | Upregulation | increased levels are associated with tumor prognosis and low survival rates | serum | [53] |
| miR-210 | Upregulation | increased levels are associated with tumor prognosis and low survival rates | serum | [53] |
| miR-182 | Upregulation | increased levels are associated with tumor prognosis and low survival rates | serum | [53] |
| miR-454 | Upregulation | increased levels are associated with tumor prognosis and low survival rates | serum | [53] |
| lncRNA | ||||
| HOTAIR | Upregulation | elevated levels are associated with poor prognosis, early tumor recurrence | serum | [57], [58] |
| GAS5 | Upregulation | elevated levels are associated with better prognosis and decreased chance of recurrence | serum | [59] |
| SBF2-AS1 lncRNA | EVs | associated with TMZ resistance | EVs | [77] |
| circRNA | ||||
| circ_0001649 | Downregulation | associated with larger tumor size and advanced WHO grade | tissue | [68] |
| circ_BRAF | Upregulation | associated with better progression free and overall survival | tissue | [68] |
| circ_0034642 | Upregulation | associated with poor prognosis | tissue | [70] |
| circ_0074362 | Upregulation | associated with poor prognosis | tissue | [70] |
| circ_ ITCH | Upregulation | associated with poor prognosis | tissue | [70] |
| circHIPK3 | Upregulation | associated with poor prognosis | tissue | [70] |
| circCPA4 | Upregulation | associated with poor prognosis | tissue | [70] |
| ATP8B4 circRNA | Upregulation | associated with insensitivity to radiotherapy | EVs | [78] |
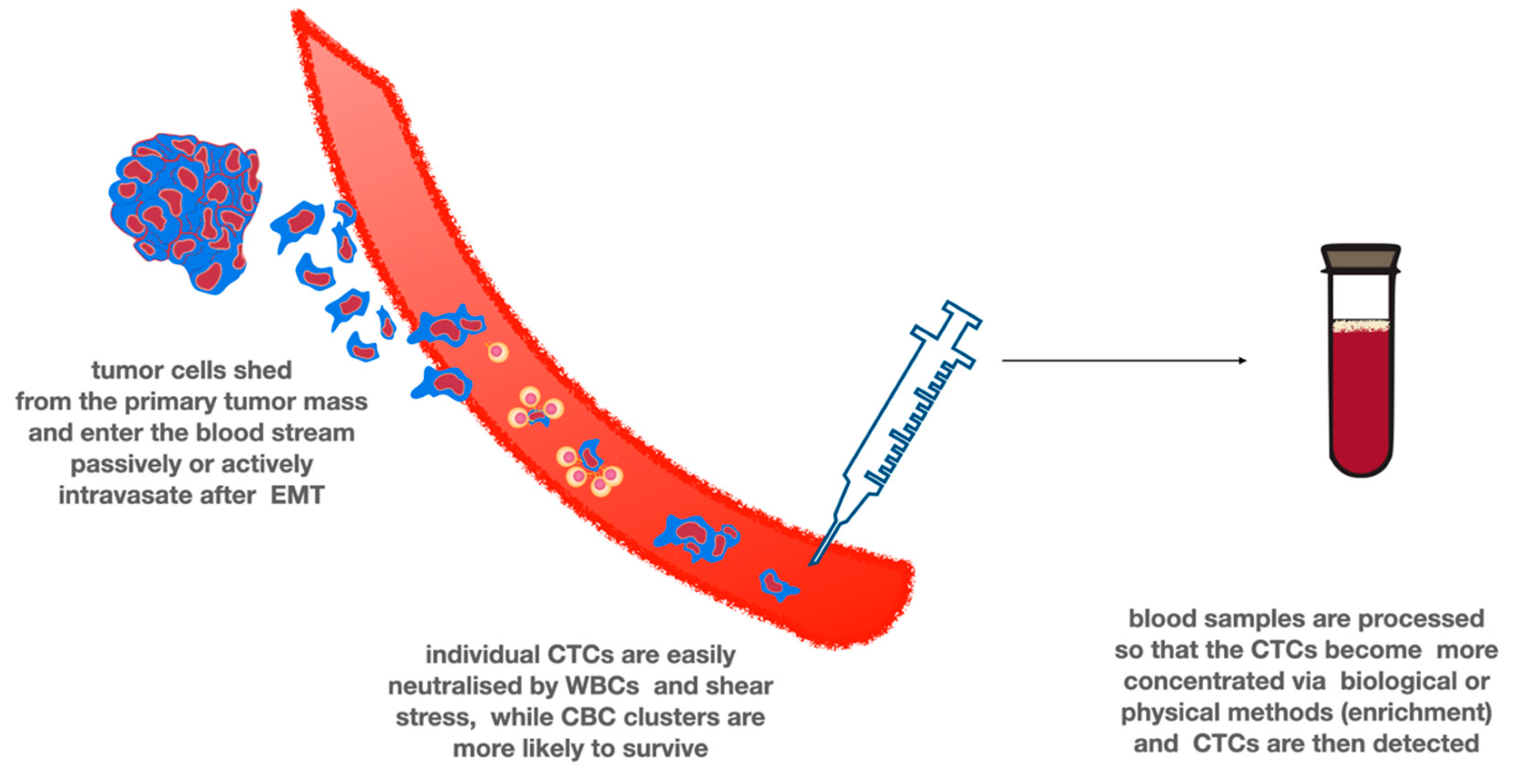
7. Circulating Tumor Cells
8. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grossman, S.A.; Ye, X.; Piantadosi, S.; Desideri, S.; Nabors, L.B.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Fisher, J. NABTT CNS Consortium Survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with radiation and temozolomide in research studies in the United States. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2443–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Mawrin, C.; Scherlach, C.; Skalej, M.; Firsching, R. Gliomas in Adults. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2010, 107, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinot, O.L.; Wick, W.; Mason, W.; Henriksson, R.; Saran, F.; Nishikawa, R.; Carpentier, A.F.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Kavan, P.; Cernea, D.; et al. Bevacizumab plus Radiotherapy–Temozolomide for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbańska, K.; Sokołowska, J.; Szmidt, M.; Sysa, P. Glioblastoma multiforme—An overview. Contemp. Oncol. 2014, 18, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, A.; Idema, A.J.; Wesseling, P. Diffuse glioma growth: A guerilla war. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, V.; Papaleo, A.; Castrichino, A.; Banelli, E.; Giangaspero, F.; Salvati, M.; Delfini, R. Prognostic implication of clinical and pathologic features in patients with glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide. Tumori J. 2007, 93, 248–256. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17679459 (accessed on 3 April 2016). [CrossRef]
- Idbaih, A.; Omuro, A.; Ducray, F.; Hoang-Xuan, K. Molecular genetic markers as predictors of response to chemotherapy in gliomas. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2007, 19, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemée, J.-M.; Clavreul, A.; Menei, P. Intratumoral heterogeneity in glioblastoma: Don’t forget the peritumoral brain zone. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuss, D.E.; Mamatjan, Y.; Schrimpf, D.; Capper, D.; Hovestadt, V.; Kratz, A.; Sahm, F.; Koelsche, C.; Korshunov, A.; Olar, A.; et al. IDH mutant diffuse and anaplastic astrocytomas have similar age at presentation and little difference in survival: A grading problem for WHO. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, A.; Van De Bergh, J.; Hedderich, J.; Mehdorn, H.M.; Nabavi, A. Glioblastoma: Clinical characteristics, prognostic factors and survival in 492 patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2012, 114, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.L.; Holmen, S.L.; Colman, H. IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations in Gliomas. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelot, A.; De Cremoux, P.; Quillien, V.; Polivka, M.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Françoise, L.; Carpentier, A.F.; George, B.; Mandonnet, E.; et al. IDH-Mutation Is a Weak Predictor of Long-Term Survival in Glioblastoma Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.-F.; De Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMTGene Silencing and Benefit from Temozolomide in Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, W.; Meisner, C.; Hentschel, B.; Platten, M.; Schilling, A.; Wiestler, B.; Sabel, M.; Koeppen, S.; Ketter, R.; Weiler, M.; et al. Prognostic or predictive value of MGMT promoter methylation in gliomas depends on IDH1 mutation. Neurology 2013, 81, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldape, K.D.; Ballman, K.; Furth, A.; Buckner, J.C.; Giannini, C.; Burger, P.C.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Jenkins, R.B.; James, C.D. Immunohistochemical detection of EGFRvIII in high malignancy grade astrocytomas and evaluation of prognostic significance. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinghoff, I.K.; Wang, M.Y.; Vivanco, I.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; Zhu, S.; Dia, E.Q.; Lu, K.V.; Yoshimoto, K.; Huang, J.H.; Chute, D.J.; et al. Molecular Determinants of the Response of Glioblastomas to EGFR Kinase Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krex, D.; Klink, B.; Hartmann, C.; Von Deimling, A.; Pietsch, T.; Simon, M.; Sabel, M.; Steinbach, J.P.; Heese, O.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. Long-term survival with glioblastoma multiforme. Brain 2007, 130, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, M.C. Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Recurrent Glioblastoma. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2011, 5, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduin, M.; Compter, I.; Steijvers, D.; Postma, A.A.; Eekers, D.B.P.; Anten, M.M.; Ackermans, L.; Ter Laan, M.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Van De Weijer, T.; et al. Noninvasive Glioblastoma Testing: Multimodal Approach to Monitoring and Predicting Treatment Response. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 2908609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanilles, M.; Durán-Peña, A.; Idbaih, A. Liquid Biopsy in Primary Brain Tumors: Looking for Stardust! Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, C.; Adnani, L.; Choi, D.-S.; Rak, J. Extracellular Vesicles as Conduits of Non-Coding RNA Emission and Intercellular Transfer in Brain Tumors. Non Coding RNA 2018, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids—the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Alix-Panabières, C.; Müller, I.; Letang, N.; Vendrell, J.-P.; Rebillard, X.; Pantel, K. Cell-free Tumor DNA in Blood Plasma As a Marker for Circulating Tumor Cells in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Vaart, M.; Pretorius, P.J. Circulating DNA. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-J.; Reich, C.F.; Pisetsky, D.S. The role of macrophages in the in vitro generation of extracellular DNA from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Immunology 2005, 115, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Choti, A.M.; Romans, K.; Goodman, S.; Li, M.; Thornton, K.; Agrawal, N.; Sokoll, L.; Szabo, A.S.; et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA in Early- and Late-Stage Human Malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, G.M.; Balaj, L.; Stott, S.L.; Nahed, B.; Carter, B.S. Liquid biopsy for brain tumors. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Lee, M.; Jeffrey, S.S. Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA: Challenges and Opportunities on the Path to Clinical Utility. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4786–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.; Siravegna, G.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Corti, G.; Crisafulli, G.; Ahronian, L.G.; Mussolin, B.; Kwak, E.L.; Buscarino, M.; Lazzari, L.; et al. Tumor Heterogeneity and Lesion-Specific Response to Targeted Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015, 6, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Bettegowda, C. Applications of DNA-Based Liquid Biopsy for Central Nervous System Neoplasms. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postel, M.; Roosen, A.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Taly, V.; Wang-Renault, S.-F. Droplet-based digital PCR and next generation sequencing for monitoring circulating tumor DNA: A cancer diagnostic perspective. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 18, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlin-Neumann, G. Improved liquid biopsies with combined digital PCR and next-generation sequencing. Am. Lab. Mag. 2016, 48, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Komatsubara, K.M.; Sacher, A.G. Circulating Tumor DNA as a Liquid Biopsy: Current Clinical Applications and Future Directions. Oncol. (Williston Park. NY) 2017, 31, 618–627. [Google Scholar]
- Piccioni, D.E.; Achrol, A.S.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Banks, K.C.; Boucher, N.; Barkhoudarian, G.; Kelly, D.F.; Juarez, T.; Lanman, R.B.; Raymond, V.M.; et al. Analysis of cell-free circulating tumor DNA in 419 patients with glioblastoma and other primary brain tumors. CNS Oncol. 2019, 8, CNS34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiegl, H.; Millinger, S.; Mueller-Holzner, E.; Marth, C.; Ensinger, C.; Berger, A.; Klocker, H.; Göbel, G.; Widschwendter, M. Circulating Tumor-Specific DNA: A Marker for Monitoring Efficacy of Adjuvant Therapy in Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavon, I.; Refael, M.; Zelikovitch, B.; Shalom, E.; Siegal, T. Serum DNA can define tumor-specific genetic and epigenetic markers in gliomas of various grades. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cong, Z.; Du, F. MGMT promoter methylation in serum and; cerebrospinal fluid as a tumor-specific biomarker of glioma. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huan, W.; Zuo, H.; Zhao, L.; Huang, C.; Liu, X.; Hou, S.; Qi, J.; Shi, W. Alu methylation serves as a biomarker for non-invasive diagnosis of glioma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 26099–26106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M. Generation, function and diagnostic value of mitochondrial DNA copy number alterations in human cancers. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormio, A.; Guerra, F.; Cormio, G.; Pesce, V.; Fracasso, F.; Loizzi, V.; Resta, L.; Putignano, G.; Cantatore, P.; Selvaggi, L.E.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA content and mass increase in progression from normal to hyperplastic to cancer endometrium. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Qu, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, H.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Xing, J. Association of leukocyte mitochondrial DNA content with glioma risk: Evidence from a Chinese case-control study. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, X.; Hu, J.; Li, G.; He, S.; Xing, J. High leukocyte mitochondrial DNA content contributes to poor prognosis in glioma patients through its immunosuppressive effect. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mair, R.; Mouliere, F.; Smith, C.G.; Chandrananda, D.; Gale, D.; Marass, F.; Tsui, D.W.Y.; Massie, C.L.E.; Wright, A.J.; Watts, C.; et al. Measurement of Plasma Cell-Free Mitochondrial Tumor DNA Improves Detection of Glioblastoma in Patient-Derived Orthotopic Xenograft Models. Cancer Res. 2018, 79, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Mercado, M.; Manterola, L.; Larrea, E.; Goicoechea, I.; Arestin, M.; Armesto, M.; Otaegui, D.; Lawrie, C.H. The circulating transcriptome as a source of non-invasive cancer biomarkers: Concepts and controversies of non-coding and coding RNA in body fluids. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2307–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Hoon, D.S.B.; Pantel, K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montani, F.; Bianchi, F. Circulating Cancer Biomarkers: The Macro-revolution of the Micro-RNA. EBio Med. 2016, 5, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Guan, J.; Liu, Y. Identification of microRNAs as novel biomarkers for glioma detection: A meta-analysis based on 11 articles. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 348, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, G.; Feng, D.; Qin, H.; Gong, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, G.-D. MicroRNA-21 expression is associated with overall survival in patients with glioma. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Li, A.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, K. Plasma specific miRNAs as predictive biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz-Antoñanzas, A.; Auzmendi-Iriarte, J.; Carrasco-Garcia, E.; Moreno-Cugnon, L.; Ruiz, I.; Villanua, J.; Egaña, L.; Otaegui, D.; Samprón, N.; Matheu, A. Liquid Biopsy in Glioblastoma: Opportunities, Applications and Challenges. Cancers 2019, 11, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, J.; Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Santoyo-Lopez, J.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Tapanari, E.; Mudge, J.M.; Steward, C.A.; Wilming, L.; Tanzer, A.; Howald, C.; et al. Extension of human lncRNA transcripts by RACE coupled with long-read high-throughput sequencing (RACE-Seq). Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dong, B.; Cao, J.; Mao, Y.; Guan, W.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S. Long non-coding RNA in glioma: Signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27582–27592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Han, L.; Kong, L.; Wei, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; et al. HOTAIR is a therapeutic target in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8353–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Q.; Sun, S.; Lam, K.F.; Kiang, K.M.-Y.; Pu, J.K.-S.; Ho, A.S.-W.; Lui, W.-M.; Fung, C.-F.; Wong, T.-S.; Leung, G.K.K. A long non-coding RNA signature in glioblastoma multiforme predicts survival. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 58, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Hodges, T.R.; Song, R.; Gong, Y.; Calin, G.A.; Heimberger, A.B.; Zhao, H. Serum HOTAIR and GAS5 levels as predictors of survival in patients with glioblastoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 57, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Kats, L.M.; Salmena, L.; Weiss, D.; Tan, S.M.; Ala, U.; Karreth, F.; Poliseno, L.; Provero, P.; Di Cunto, F.; et al. Coding-Independent Regulation of the Tumor Suppressor PTEN by Competing Endogenous mRNAs. Cell 2011, 147, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, P.; Chen, M. CircPro: An integrated tool for the identification of circRNAs with protein-coding potential. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3314–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasda, E.; Parker, R. Circular RNAs: Diversity of form and function. RNA 2014, 20, 1829–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotorynski, E. Circular RNAs promote transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, S.; Müller, S. RNA circularization strategies in vivo and in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence andmortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Schuman, E.M. Circular RNAs in Brain and Other Tissues: A Functional Enigma. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ye, J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, L.; Hu, H.; Jiang, H.; Wan, Z.; Sheng, F.; Ma, Y.; Li, W.; et al. Differential expression of circular RNAs in Glioblastoma Multiforme and its correlation with prognosis. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sui, X.; Zhao, H.; Cong, L.; Li, Y.; Xin, T.; Guo, M.; Hao, W. Decreased circular RNA hsa_circ_0001649 predicts unfavorable prognosis in glioma and exerts oncogenic properties in vitro and in vivo. Gene 2018, 676, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, B.; Shu, C.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J. Functions and clinical significance of circular RNAs in glioma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, J. Exosomes: Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Delivery Vehicles for Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3333–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osti, D.; Del Bene, M.; Rappa, G.; Santos, M.; Matafora, V.; Richichi, C.; Faletti, S.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; Mironov, A.; Bachi, A.; et al. Clinical Significance of Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma from Glioblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 25, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller Bark, J.; Kulasinghe, A.; Chua, B.W.; Day, B.; Punyadeera, C. Circulating biomarkers in patients with glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimkhani, S.; Vafaee, F.; Hallal, S.; Wei, H.; Lee, M.Y.T.; Young, P.E. Deep sequencing of circulating exosomal microRNA allows non-invasive glioblastoma diagnosis. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, A.; Imbrucè, P.; Gardenghi, B.; Belli, L.; Agushi, R.; Tamanini, A.; Munari, S.; Bossi, A.M.; Scambi, I.; Benati, D.; et al. A microRNA signature from serum exosomes of patients with glioma as complementary diagnostic biomarker. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 136, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Lu, C.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, A.; You, Y. Exosomal transfer of long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 enhances chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, J.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Geng, L.; Liu, H. Expression profiles and potential functions of circular RNAs in extracellular vesicles isolated from radioresistant glioma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L.; Peng, Y. Exosomal noncoding RNAs in Glioma: Biological functions and potential clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marleau, A.M.; Chen, C.-S.; Joyce, A.J.; Tullis, R.H. Exosome removal as a therapeutic adjuvant in cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Holtschmidt, J.; Auer, M.; Heitzer, E.; Lamszus, K.; Schulte, A.; Matschke, J.; Langer-Freitag, S.; Gasch, C.; Stoupiec, M.; et al. Hematogenous dissemination of glioblastoma multiforme. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 247ra10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacArthur, K.M.; Kao, G.D.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Chapman, C.; Lustig, R.A.; Wileyto, E.P.; Hahn, S.M.; Dorsey, J.F. Detection of Brain Tumor Cells in the Peripheral Blood by a Telomerase Promoter-Based Assay. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, J.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Madden, M.W.; Oliveira, S.M.; Springer, S.; Bhere, D.; Chi, A.S.; Wakimoto, H.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Sequist, L.V.; et al. Brain Tumor Cells in Circulation Are Enriched for Mesenchymal Gene Expression. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birkó, Z.; Nagy, B.; Klekner, Á.; Virga, J. Novel Molecular Markers in Glioblastoma—Benefits of Liquid Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207522
Birkó Z, Nagy B, Klekner Á, Virga J. Novel Molecular Markers in Glioblastoma—Benefits of Liquid Biopsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(20):7522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207522
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirkó, Zsuzsanna, Bálint Nagy, Álmos Klekner, and József Virga. 2020. "Novel Molecular Markers in Glioblastoma—Benefits of Liquid Biopsy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 20: 7522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207522
APA StyleBirkó, Z., Nagy, B., Klekner, Á., & Virga, J. (2020). Novel Molecular Markers in Glioblastoma—Benefits of Liquid Biopsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(20), 7522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207522






