Alternative Splicing Regulation of an Alzheimer’s Risk Variant in CLU
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
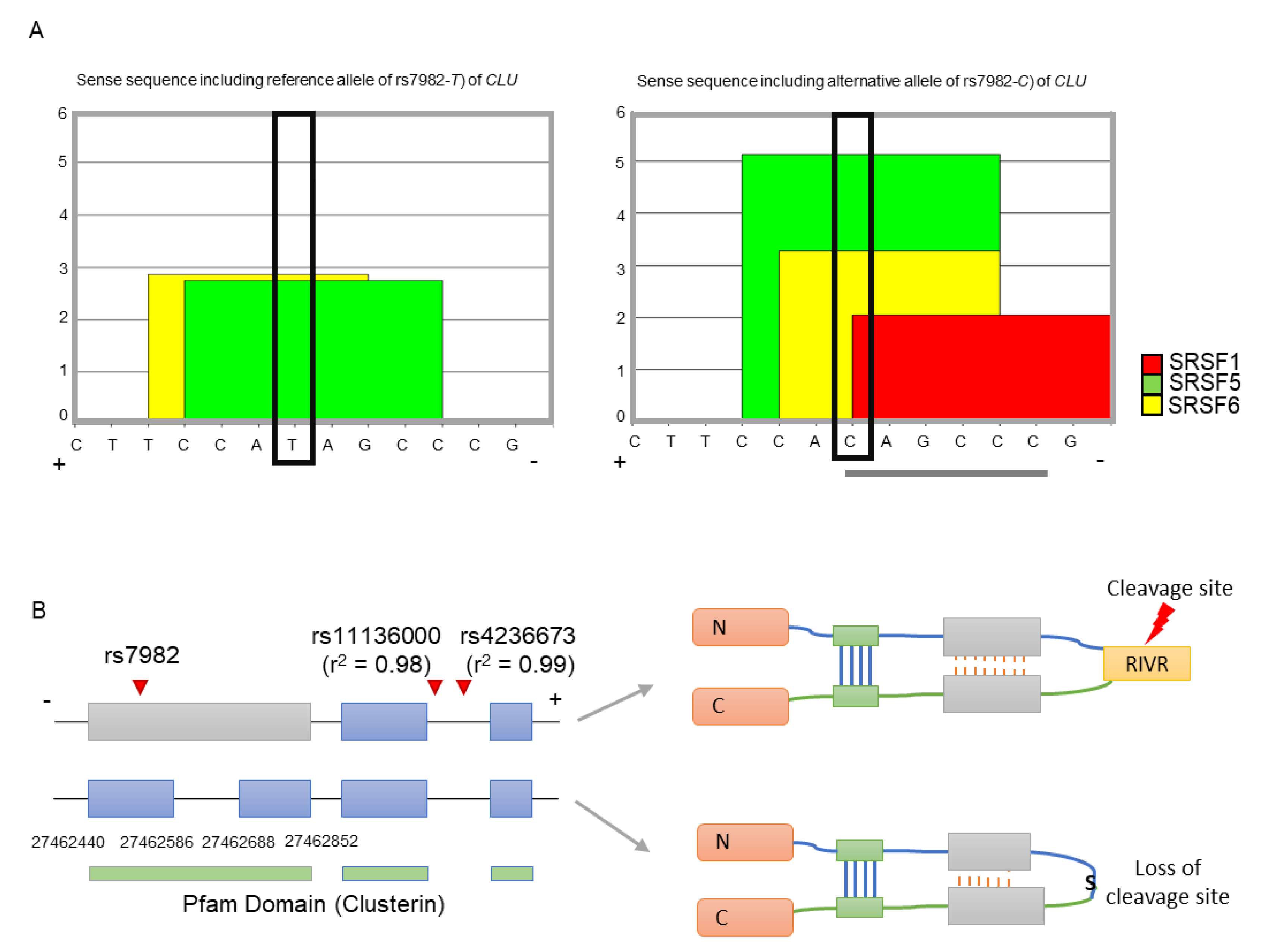
2.1. Regulatory Function of rs7982 in Splicing
2.2. Association of Intron Retention (IR) with rs7982
2.3. Sex-Dependent Association of IR with rs7982
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. RNA-Seq and WGS Analysis
4.2. Implication of rs7982 in Splicing Regulation
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCX | Temporal cortex |
| ST | Superior temporal gyrus |
| PH | Parahippocampal gyrus |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AMP-AD | Accelerating Medicines Partnership–Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ESE | Exon skipping enhancer |
| IR | Intron retention |
| AS | Alternative splicing |
| sQTLs | Splicing quantitative trait loci |
References
- Buee, L.; Bussiere, T.; Buee-Scherrer, V.; Delacourte, A.; Hof, P.R. Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 33, 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockenstein, E.M.; McConlogue, L.; Tan, H.; Power, M.; Masliah, E.; Mucke, L. Levels and alternative splicing of amyloid beta protein precursor (APP) transcripts in brains of APP transgenic mice and humans with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28257–28267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koch, L. Altered splicing in Alzheimer transcriptomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 738–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.S.; Cooper, T.A. Splicing in disease: Disruption of the splicing code and the decoding machinery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, T.; Li, Y.I.; Wong, G.; Humphrey, J.; Wang, M.; Ramdhani, S.; Wang, Y.C.; Ng, B.; Gupta, I.; Haroutunian, V.; et al. Integrative transcriptome analyses of the aging brain implicate altered splicing in Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harold, D.; Abraham, R.; Hollingworth, P.; Sims, R.; Gerrish, A.; Hamshere, M.L.; Pahwa, J.S.; Moskvina, V.; Dowzell, K.; Williams, A.; et al. Genome-Wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. The role of clusterin in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathways, pathogenesis, and therapy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, M.; Wang, R.; Bassett, S.S.; Avramopoulos, D. Alzheimer’s risk variants in the clusterin gene are associated with alternative splicing. Transl. Psychiatry 2011, 1, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mao, Z.; Woody, S.K.; Brinton, R.D. Sex differences in metabolic aging of the brain: Insights into female susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 42, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohne, P.; Prochnow, H.; Wolf, S.; Renner, B.; Koch-Brandt, C. The chaperone activity of clusterin is dependent on glycosylation and redox environment. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1626–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettens, K.; Vermeulen, S.; Van Cauwenberghe, C.; Heeman, B.; Asselbergh, B.; Robberecht, C.; Engelborghs, S.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Vandenberghe, R.; De Deyn, P.P.; et al. Reduced secreted clusterin as a mechanism for Alzheimer-associated CLU mutations. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Yamamoto, M. Modification of the alternative splicing process of testosterone-repressed prostate message-2 (TRPM-2) gene by protein synthesis inhibitors and heat shock treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1307, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hayashi, I.; Wong, J.; Tugusheva, K.; Renger, J.J.; Zerbinatti, C. Intracellular clusterin interacts with brain isoforms of the bridging integrator 1 and with the microtubule-associated protein Tau in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyn-Vanhentenryck, S.M.; Feng, H.; Ustianenko, D.; Duffie, R.; Yan, Q.; Jacko, M.; Martinez, J.C.; Goodwin, M.; Zhang, X.; Hengst, U.; et al. Precise temporal regulation of alternative splicing during neural development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.H.; Tarn, W.Y. Alternative Splicing in Neurogenesis and Brain Development. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, J.M.E.; Kim, Y.; von Jonquieres, G.; Housley, G.D. Human Brain Region-Specific Alternative Splicing of TRPC3, the Type 3 Canonical Transient Receptor Potential Non-Selective Cation Channel. Cerebellum 2019, 18, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, B.; Blencowe, B.J. Alternative Splicing in the Mammalian Nervous System: Recent Insights into Mechanisms and Functional Roles. Neuron 2015, 87, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, I.; Savage, J.; Watanabe, K.; Bryois, J.; Williams, D.; Steinberg, S.; Sealock, J.; Karlsson, I.; Hagg, S.; Athanasiu, L.; et al. Genetic meta-analysis identifies 10 novel loci and functional pathways for Alzheimer’s disease risk. bioRxiv 2018, 258533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wang, H.F.; Tan, M.S.; Tan, C.C.; Zhu, X.C.; Miao, D.; Yu, W.J.; Jiang, T.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T.; et al. Effect of CLU genetic variants on cerebrospinal fluid and neuroimaging markers in healthy, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease cohorts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralovicova, J.; Houngninou-Molango, S.; Kramer, A.; Vorechovsky, I. Branch site haplotypes that control alternative splicing. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 3189–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, Y.; Wang, E.T.; Airoldi, E.M.; Burge, C.B. Analysis and design of RNA sequencing experiments for identifying isoform regulation. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Funk, C.; Heavner, B.D.; Zou, F.; Younkin, C.S.; Burgess, J.D.; Chai, H.S.; Crook, J.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. Human whole genome genotype and transcriptome data for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Beckmann, N.D.; Roussos, P.; Wang, E.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Ming, C.; Neff, R.; Ma, W.; Fullard, J.F.; et al. The Mount Sinai cohort of large-scale genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic data in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Park, J.W.; Lu, Z.X.; Lin, L.; Henry, M.D.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhou, Q.; Xing, Y. rMATS: Robust and flexible detection of differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5593–E5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Gamazon, E.R.; Rebman, E.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Dolan, M.E.; Cox, N.J.; Lussier, Y.A. Variants affecting exon skipping contribute to complex traits. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Chew, S.L.; Zhang, M.Q.; Krainer, A.R. An increased specificity score matrix for the prediction of SF2/ASF-specific exonic splicing enhancers. Hum. Mol Genet. 2006, 15, 2490–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.; Nho, K.; Lee, Y. Alternative Splicing Regulation of an Alzheimer’s Risk Variant in CLU. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197079
Han S, Nho K, Lee Y. Alternative Splicing Regulation of an Alzheimer’s Risk Variant in CLU. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197079
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Seonggyun, Kwangsik Nho, and Younghee Lee. 2020. "Alternative Splicing Regulation of an Alzheimer’s Risk Variant in CLU" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197079
APA StyleHan, S., Nho, K., & Lee, Y. (2020). Alternative Splicing Regulation of an Alzheimer’s Risk Variant in CLU. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197079





